IP地址管理方法有很多,工具也不少,但像我这种需求的应该不多,不但需要局域网IP扫描,还需要从其他的管理系统中导入数据,某些服务端管理用户设备的助手类工具,一般外部网络用不着这个,但是像我们内部网络就用得着了,包括杀毒类的企业版和安全登录网络的工具,都涉及到IP地址授权什么东西,而且不只是这样,作为运维,还要保证每台内网上的计算机都要同时确保安装了这两种软件,总不能每台每台的挨个再去查吧,只能从各个后台管理导出数据进行比对,也是麻烦。最主要的是IP地址来回变动的多,管理起来也麻烦,原来都是通过各个系统查那些地址空闲,每个系统统计的还不一样。。。。。反正是各种各样的问题,没办法,还是我亲自下手处理处理这个问题。这么啰啰嗦嗦的说,可能也没说明白,因为有些东西是不让说的,所以只要我知道这个工具适合我们的运维就好了,分享上来,如果看到和你用的环境类似,有需求就可以用了。
🔺先看看界面。
进入后界面显示的功能很简单,一看图就明白了。
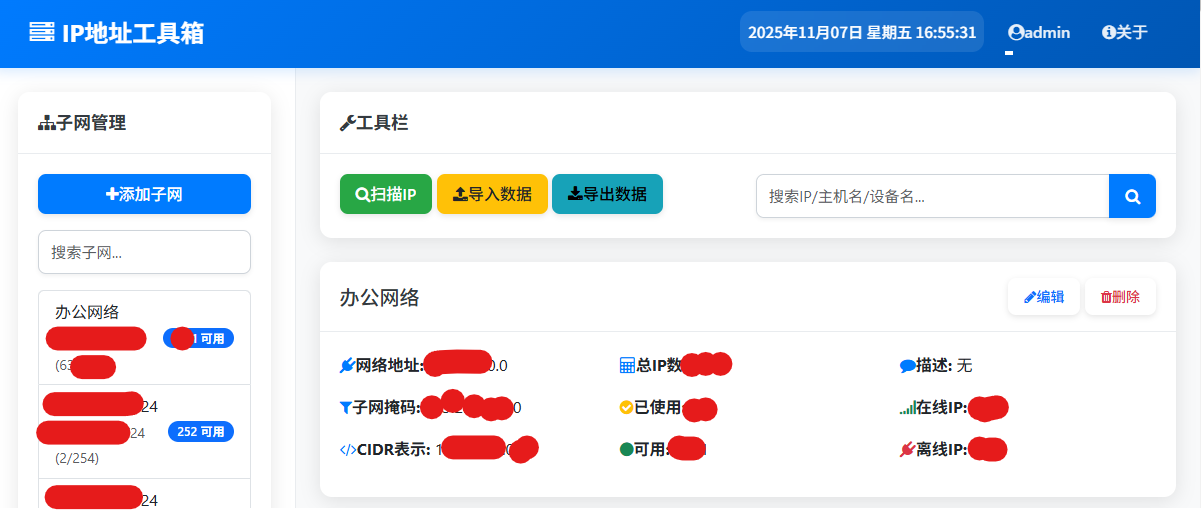

IP地址分布支持扫描后检测是否在线的功能,红色离线,绿色在线,都有图示。
▲开发背景
IP地址管理是网络运维的重要组成部分,尤其在大型网络环境中,需要清晰了解IP地址的使用情况,包括已分配、空闲、冲突等状态,以便进行有效的资源管理和问题排查。本项目旨在开发一个直观、高效的IP地址工具箱,帮助网络管理员更好地管理IP地址资源。
▲▲实现目标
-
提供直观的IP地址可视化界面,以网格形式展示IP使用情况
-
支持多种方式扫描IP地址段,实时检测IP占用状态
-
支持导入多种格式的IP地址信息表格,整合不同系统的IP数据
-
提供详细的IP信息查询和展示功能
-
实现现代化、简洁优雅的用户界面
-
确保系统的全面性、完整性、健壮性和高效性
目前这些都已经完成了,说说技术栈方面。
后端技术栈就是Python+ Flask,SQLAlchemy,数据库是 SQLite,因为运维人数不多,没有必要考虑并发的问题。
▲目录结构也就是如图这个样子。
▲主要功能
▼实现对指定IP地址段的扫描,支持多种扫描方式,包括ICMP Ping扫描、TCP端口、ARP扫描等。
-
使用多线程并发扫描以提高效率
-
动态调整线程池大小以适应系统资源
-
支持扫描任务的取消和进度监控
-
实现ARP缓存优化以提高MAC地址获取效率
▼支持导入多种格式的IP地址信息表格,包括ipscanner导出的CSV、XXXX系统导出的终端概况、XXXX导出的设备列表等。
-
使用Pandas库解析不同格式的文件
-
自动检测文件类型和编码
-
实现批量导入以提高性能
-
提供导入进度和状态监控
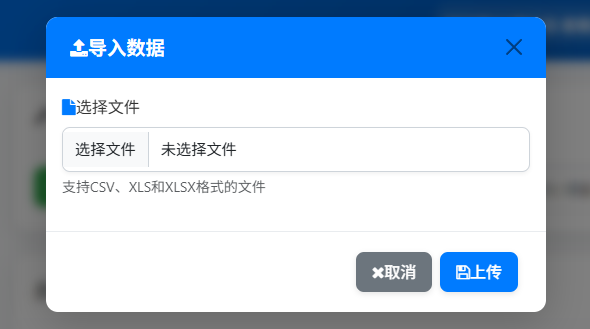
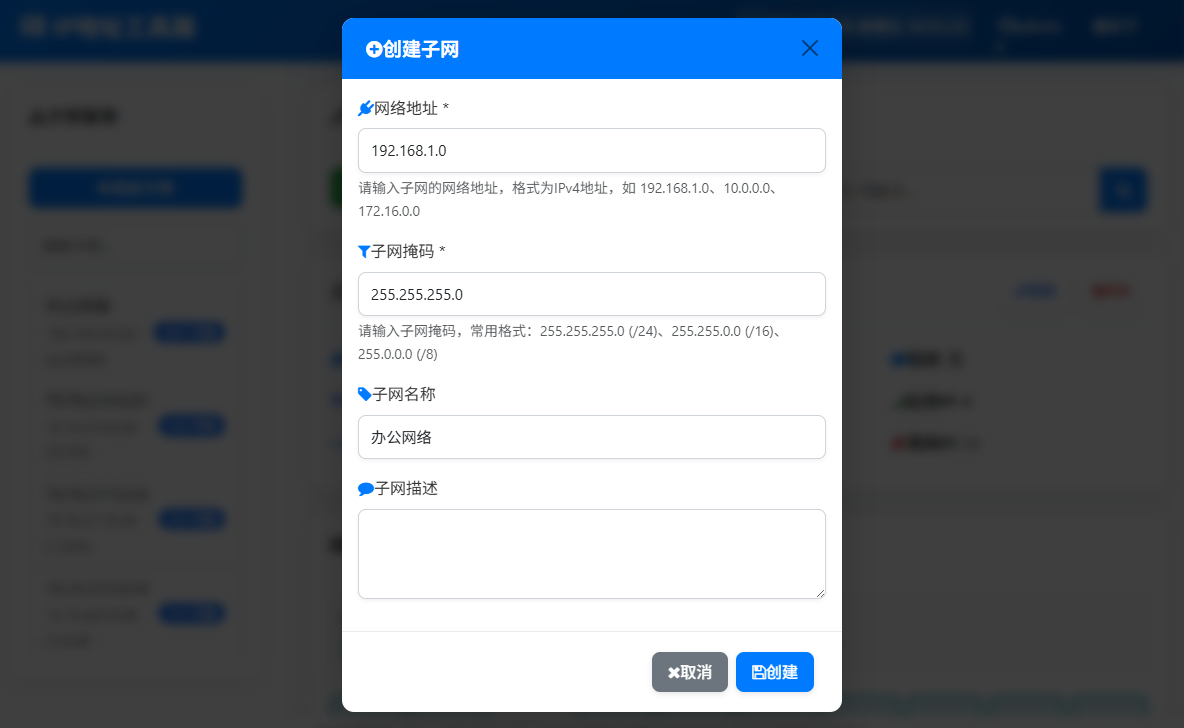
▼管理网络子网,支持创建、编辑、删除子网,并提供子网信息查询。
-
支持CIDR表示法和子网掩码两种方式
-
自动计算子网信息(网络地址、广播地址等)
-
提供子网IP地址统计
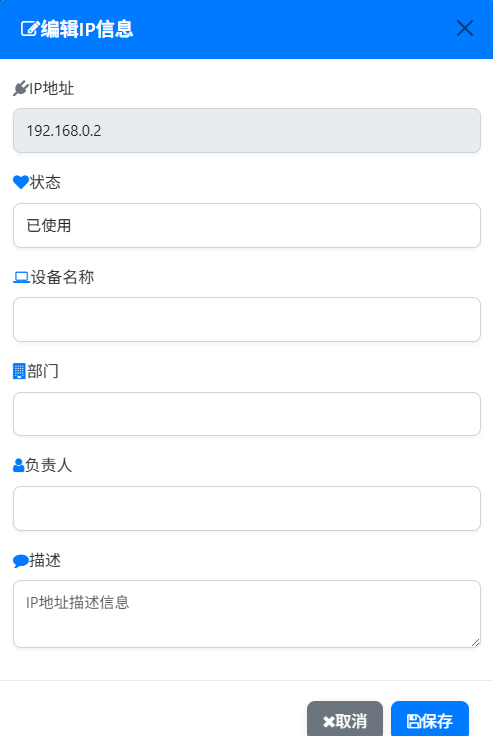
▼管理IP地址信息,支持查看、编辑、搜索IP地址。
-
维护IP地址的状态信息
-
支持多来源数据整合
-
提供IP地址搜索和筛选

▼主要类和方法
-
`ScanService`: 扫描服务的主类
-
`ping_scan()`: ICMP Ping扫描单个IP
-
`tcp_port_scan()`: TCP端口扫描
-
`start_scan_task()`: 启动扫描任务
-
`ImportService`: 导入服务的主类
-
`import_file()`: 导入文件的主函数
-
`_import_ipscanner_csv()`: 导入ipscanner格式CSV
-
`_import_360_qing()`: 导入360天擎格式文件
-
`_import_security_assistant()`: 导入安全助手格式文件
▼主要API
-
`/api/subnets`: 获取/创建子网
-
`/api/subnets/<id>`: 获取/更新/删除子网详情
-
`/api/subnets/<id>/ip-addresses`: 获取子网IP地址列表
-
`/api/ip-addresses/<ip>`: 获取/更新IP地址详情
-
`/api/ip-addresses/search`: 搜索IP地址
-
`/api/ip-addresses`: 创建IP地址记录
子网管理API
▼获取子网列表
-
URL: `/api/subnets`
-
Method: `GET`
-
Response: `[{id, network_address, subnet_mask, cidr, name, description, ip_count, used_count, available_count}]`
▼创建子网
-
URL: `/api/subnets`
-
Method: `POST`
-
Request Body: `{network_address, subnet_mask, name, description}`
-
Response: `{id, network_address, subnet_mask, cidr, name, description}`
▼获取子网详情
-
URL: `/api/subnets/:id`
-
Method: `GET`
-
Response: `{id, network_address, subnet_mask, cidr, name, description, ip_count, used_count, available_count}`
▼更新子网
-
URL: `/api/subnets/:id`
-
Method: `PUT`
-
Request Body: `{name, description}`
-
Response: `{id, network_address, subnet_mask, cidr, name, description}`
▼删除子网
-
URL: `/api/subnets/:id`
-
Method: `DELETE`
-
Response: `{success: true}`
IP地址管理API
▼获取子网IP地址列表
-
URL: `/api/subnets/:subnetId/ip-addresses`
-
Method: `GET`
-
Response: `[{id, ip_address, status, host_name, mac_address, device_name, department, responsible_person, last_seen}]`
▼获取IP地址详情
-
URL: `/api/ip-addresses/:ipAddress`
-
Method: `GET`
-
Response: `{id, ip_address, subnet_id, status, host_name, mac_address, device_name, department, responsible_person, last_seen}`
▼更新IP地址信息
-
URL: `/api/ip-addresses/:ipAddress`
-
Method: `PUT`
-
Request Body: `{status, device_name, department, responsible_person}`
-
Response: `{id, ip_address, status, device_name, department, responsible_person}`
▼搜索IP地址
-
URL: `/api/ip-addresses/search`
-
Method: `GET`
-
Query Params: `q=search_term&fields=fields_to_search`
-
Response: `[{id, ip_address, status, host_name, device_name, department}]`
扫描管理API
▼开始扫描
-
URL: `/api/scans`
-
Method: `POST`
-
Request Body: `{subnet_id, start_ip, end_ip, scan_type, options}`
-
Response: `{task_id, status: "started"}`
▼获取扫描任务状态
-
URL: `/api/scans/:taskId`
-
Method: `GET`
-
Response: `{task_id, status, progress, results}`
▼取消扫描任务
-
URL: `/api/scans/:taskId/cancel`
-
Method: `POST`
-
Response: `{task_id, status: "cancelled"}`
文件导入API
▼上传文件
-
URL: `/api/imports`
-
Method: `POST`
-
Content-Type: `multipart/form-data`
-
Form Data: `file, file_type`
-
Response: `{import_id, status: "processing"}`
▼获取导入状态
-
URL: `/api/imports/:importId`
-
Method: `GET`
-
Response: `{import_id, status, progress, total_records, success_records, failed_records, errors}`
🔺部分代码如下
数据导入服务类部分代码
python
def detect_file_type(self, file_path):
"""检测文件类型并确定导入策略"""
try:
file_name = os.path.basename(file_path).lower()
file_ext = file_path.split('.')[-1].lower()
if file_ext not in self.supported_formats:
raise ValueError(f"不支持的文件格式: {file_ext}")
# 根据文件名和内容判断导入类型
if '终端概况' in file_name:
return '360_qing'
elif '设备列表' in file_name:
return 'security_assistant'
elif file_ext == 'csv':
# 尝试根据内容判断是否为ipscanner格式
try:
df = pd.read_csv(file_path, nrows=5)
# 检查是否包含典型的ipscanner列名
common_columns = ['IP', '主机名', 'MAC地址']
if any(col in df.columns for col in common_columns):
return 'ipscanner'
except Exception:
pass
return 'generic_csv'
else:
return 'generic'
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"检测文件类型失败: {str(e)}")
return 'generic'
def import_file(self, file_path, import_id):
"""导入文件的主函数"""
# 确保在应用上下文中执行数据库操作
if self.app:
with self.app.app_context():
self._import_file_with_context(file_path, import_id)
else:
# 如果没有提供应用实例,尝试直接执行
logger.warning("未提供Flask应用实例,可能导致上下文问题")
self._import_file_with_context(file_path, import_id)
def start_import_task(self, file_path, file_name, subnet_id=None, source=None):
"""启动导入任务"""
# 确保在应用上下文中执行数据库操作
if self.app:
with self.app.app_context():
return self._start_import_task_with_context(file_path, file_name, subnet_id, source)
else:
# 如果没有提供应用实例,尝试直接执行
logger.warning("未提供Flask应用实例,可能导致上下文问题")
return self._start_import_task_with_context(file_path, file_name, subnet_id, source)
def get_recent_import_tasks(self, limit=10):
"""获取最近的导入任务"""
try:
tasks = ImportLog.query.order_by(ImportLog.import_time.desc()).limit(limit).all()
return [task.to_dict() for task in tasks]
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"获取最近导入任务失败: {str(e)}")
return []
def cancel_import_task(self, import_id):
"""取消导入任务"""
try:
import_log = ImportLog.query.get(import_id)
if not import_log or import_log.status in ['completed', 'failed']:
return False
import_log.status = 'cancelled'
import_log.end_time = TimeUtils.get_beijing_time()
db.session.commit()
logger.info(f"导入任务已取消: {import_id}")
return True
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"取消导入任务失败: {str(e)}")
db.session.rollback()
return False
def _update_import_progress(self, import_id, progress, success_count=None, failed_count=None, new_count=None, updated_count=None):
"""更新导入进度,使用独立的数据库会话确保事务隔离"""
try:
# 创建新的数据库会话,避免与主导入流程的会话冲突
with db.session.no_autoflush:
# 使用SQLAlchemy的with_lockmode来确保正确的锁定
import_log = db.session.query(ImportLog).filter_by(id=import_id).with_for_update().first()
if not import_log:
logger.error(f"无法找到导入记录 {import_id}")
return
# 更新进度
import_log.progress = min(progress, 100)
# 更新统计数据,确保数值的有效性
if success_count is not None and success_count >= 0:
import_log.success_records = success_count
logger.info(f"更新导入进度 {import_id}: 成功记录数={success_count}")
if failed_count is not None and failed_count >= 0:
import_log.failed_records = failed_count
logger.info(f"更新导入进度 {import_id}: 失败记录数={failed_count}")
if new_count is not None and new_count >= 0:
import_log.new_records = new_count
logger.info(f"更新导入进度 {import_id}: 新增记录数={new_count}")
if updated_count is not None and updated_count >= 0:
import_log.updated_records = updated_count
logger.info(f"更新导入进度 {import_id}: 更新记录数={updated_count}")
# 立即提交确保前端能获取到最新数据
db.session.commit()
logger.info(f"导入进度已成功提交: ID={import_id}, 进度={progress}%, 成功={import_log.success_records}, 失败={import_log.failed_records}")
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"更新导入进度失败: {str(e)}")
db.session.rollback()
# 尝试使用备用方法更新进度
try:
db.session.close()
db.session.remove()
# 创建全新的会话
new_session = db.create_scoped_session()
import_log = new_session.query(ImportLog).filter_by(id=import_id).first()
if import_log:
import_log.progress = min(progress, 100)
new_session.commit()
new_session.close()
logger.info(f"备用方法更新进度成功: ID={import_id}, 进度={progress}%")
except Exception as backup_error:
logger.error(f"备用更新方法也失败: {str(backup_error)}")扫描服务类部分代码
python
class ScanService:
"""IP扫描服务类 - 简洁高效的实现,只包含ping、tcp和ARP扫描功能"""
def __init__(self):
# 基础配置
self.min_threads = 4 # 最小线程数
self.base_max_threads = min(100, psutil.cpu_count(logical=False) * 10) # 基于CPU核心数的基础最大线程数
self.max_threads = self._calculate_optimal_threads() # 初始动态计算线程数
# 资源监控配置
self.last_resource_check = time.time()
self.resource_check_interval = 10 # 每10秒检查一次系统资源
# 常用端口映射
self.common_ports = {
21: 'ftp', 22: 'ssh', 23: 'telnet', 25: 'smtp', 53: 'dns',
80: 'http', 110: 'pop3', 143: 'imap', 443: 'https', 465: 'smtps',
587: 'smtp', 993: 'imaps', 995: 'pop3s', 1723: 'pptp', 3306: 'mysql',
3389: 'rdp', 5432: 'postgresql', 8080: 'http-alt', 8443: 'https-alt',
8888: 'http-alt', 9000: 'http-alt'
}
# 初始化回调管理器
self.callback_manager = CallbackManager()
# 初始化任务管理器
self.task_manager = TaskManager()
# ARP缓存相关
self._arp_cache = None
self._arp_cache_time = 0
self._arp_cache_lock = threading.Lock()
self._arp_cache_ttl = 60 # 优化:缓存有效期从5秒增加到60秒
self._arp_cache_hits = 0 # 缓存命中次数统计
self._arp_cache_misses = 0 # 缓存未命中次数统计
self._arp_cache_refreshes = 0 # 缓存刷新次数统计
# 执行ARP缓存预热
self._warm_up_arp_cache()
logger.info(f"初始化扫描服务,动态线程数配置:最小={self.min_threads},初始最大={self.max_threads}")
def _calculate_optimal_threads(self):
"""
基于系统资源动态计算最佳线程数
考虑因素:CPU使用率、内存使用、系统负载
"""
try:
# 获取CPU使用率
cpu_percent = psutil.cpu_percent(interval=0.1)
# 获取可用内存百分比
memory = psutil.virtual_memory()
available_memory_percent = memory.available * 100 / memory.total
# 基础线程数
base_threads = self.base_max_threads
# CPU负载调整因子 (CPU使用率越低,可使用的线程数越多)
if cpu_percent > 80:
cpu_factor = 0.3 # 高负载时减少到30%
elif cpu_percent > 60:
cpu_factor = 0.6 # 中等负载时减少到60%
elif cpu_percent > 40:
cpu_factor = 0.8 # 低负载时减少到80%
else:
cpu_factor = 1.0 # 正常负载
# 内存调整因子 (可用内存越少,线程数越少)
if available_memory_percent < 10:
memory_factor = 0.4 # 内存紧张时减少到40%
elif available_memory_percent < 20:
memory_factor = 0.7 # 内存较小时减少到70%
else:
memory_factor = 1.0 # 内存充足
# 计算最终线程数
adjusted_threads = int(base_threads * cpu_factor * memory_factor)
# 确保在合理范围内
optimal_threads = max(self.min_threads, min(adjusted_threads, self.base_max_threads))
logger.debug(f"动态线程计算:CPU={cpu_percent}%,内存可用={available_memory_percent:.1f}%,调整后={optimal_threads}")
return optimal_threads
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"计算最佳线程数失败: {e}")
# 出错时返回基础配置
return max(self.min_threads, self.base_max_threads // 2)
def get_current_threads(self):
"""
获取当前可用的线程数,定期检查系统资源并动态调整
"""
current_time = time.time()
# 定期检查系统资源并调整线程数
if current_time - self.last_resource_check > self.resource_check_interval:
new_threads = self._calculate_optimal_threads()
# 避免频繁调整,只在变化超过20%时更新
if abs(new_threads - self.max_threads) / max(1, self.max_threads) > 0.2:
self.max_threads = new_threads
logger.info(f"动态调整线程池大小为: {self.max_threads}")
self.last_resource_check = current_time
return self.max_threads
def ping_scan(self, ip_address, timeout=1):
"""使用ICMP Ping扫描单个IP"""
try:
# 根据操作系统选择正确的ping参数
param = '-n' if platform.system().lower() == 'windows' else '-c'
command = ['ping', param, '1', '-w' if platform.system().lower() == 'windows' else '-W',
str(timeout * 1000) if platform.system().lower() == 'windows' else str(timeout), ip_address]
# 执行ping命令,设置超时保护
process = subprocess.Popen(
command,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
shell=False # 安全起见,不使用shell
)
stdout, stderr = process.communicate(timeout=timeout + 2)
# 检查返回码和输出
if process.returncode == 0:
# 尝试解析响应时间
output = stdout.decode('utf-8', errors='ignore').lower()
response_time = 0
if 'time=' in output:
match = re.search(r'time=(\d+\.?\d*)', output)
if match:
response_time = float(match.group(1))
# 尝试获取主机名
hostname = None
try:
# 优先通过socket.gethostbyaddr获取主机名
hostname = socket.gethostbyaddr(ip_address)[0]
except (socket.herror, socket.gaierror):
# 如果socket.gethostbyaddr失败,尝试从ping输出中解析主机名
# Windows系统的ping命令如果成功解析主机名,会在输出中显示
# 例如:Pinging example.com [192.168.1.1] with 32 bytes of data:
if platform.system().lower() == 'windows':
hostname_match = re.search(r'Pinging\s+([^\[\]]+)\s*\[', output)
if hostname_match:
hostname = hostname_match.group(1)
else:
# Linux/macOS系统的ping输出格式可能不同,也尝试解析
hostname_match = re.search(r'PING\s+([^\(\)]+)\s*\(', output)
if hostname_match:
hostname = hostname_match.group(1)
return {
'ip_address': ip_address,
'status': 'up',
'host_name': hostname,
'response_time': response_time,
'scan_time': TimeUtils.get_beijing_time()
}
else:
return {
'ip_address': ip_address,
'status': 'down',
'scan_time': TimeUtils.get_beijing_time()
}
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired:
# 处理ping命令超时的情况
process.kill()
process.communicate() # 清理资源
logger.warning(f"Ping scan timeout for {ip_address}")
return {
'ip_address': ip_address,
'status': 'timeout',
'scan_time': TimeUtils.get_beijing_time()
}
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"Ping scan error for {ip_address}: {e}")
return {
'ip_address': ip_address,
'status': 'error',
'error': str(e),
'scan_time': TimeUtils.get_beijing_time()
}
def _tcp_scan_single_port(self, ip_address, port, timeout=1):
"""扫描单个TCP端口"""
try:
sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sock.settimeout(timeout)
result = sock.connect_ex((ip_address, port))
sock.close()
if result == 0:
# 尝试获取服务名称
service = self.common_ports.get(port, 'unknown')
try:
service = socket.getservbyport(port) or service
except:
pass
return {
'port': port,
'service': service
}
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"TCP scan error for {ip_address}:{port}: {e}")
return None
def tcp_scan(self, ip_address, ports=None, timeout=1):
"""TCP端口扫描(并行扫描端口)"""
# 默认扫描的端口
if ports is None:
ports = [22, 80, 443]
open_ports = []
# 根据端口数量动态调整线程数,最多20个线程
max_workers = min(len(ports), 20)
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=max_workers) as executor:
# 提交所有端口扫描任务
future_to_port = {executor.submit(self._tcp_scan_single_port, ip_address, port, timeout): port for port in ports}
# 处理完成的任务
for future in as_completed(future_to_port):
try:
result = future.result()
if result:
open_ports.append(result)
except Exception as e:
port = future_to_port[future]
logger.error(f"Error processing TCP scan result for {ip_address}:{port}: {e}")
# 按端口号排序
open_ports.sort(key=lambda x: x['port'])
status = 'up' if open_ports else 'down'
return {
'ip_address': ip_address,
'status': status,
'open_ports': open_ports,
'scan_time': TimeUtils.get_beijing_time()
}
def _get_arp_table(self, timeout=2):
"""获取ARP表,带缓存机制"""
current_time = time.time()
# 检查缓存是否有效
with self._arp_cache_lock:
if self._arp_cache and current_time - self._arp_cache_time < self._arp_cache_ttl:
self._arp_cache_hits += 1
return self._arp_cache
# 缓存过期或不存在,重新获取
self._arp_cache_misses += 1
self._arp_cache_refreshes += 1
arp_table = {}
try:
if platform.system().lower() == 'windows':
# Windows系统获取ARP表
command = ['arp', '-a']
else:
# Linux/Mac系统获取ARP表
command = ['arp', '-n']
process = subprocess.Popen(
command,
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
shell=False
)
stdout, stderr = process.communicate(timeout=timeout)
if process.returncode == 0:
# 解析ARP表输出
output = stdout.decode('utf-8', errors='ignore')
lines = output.splitlines()
for line in lines:
# Windows格式: " 192.168.1.1 00-11-22-33-44-55 dynamic "
# Linux格式: "? (192.168.1.1) at 00:11:22:33:44:55 [ether] on eth0"
if platform.system().lower() == 'windows':
# 匹配Windows格式的ARP条目
match = re.search(r'(\d+\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+)\s+([0-9a-fA-F-:]+)', line)
else:
# 匹配Linux格式的ARP条目
match = re.search(r'\(?([0-9.]+)\)?\s+at\s+([0-9a-fA-F:]+)', line)
if match:
ip = match.group(1)
mac = match.group(2)
# 标准化MAC地址格式
mac = mac.replace('-', ':').lower()
arp_table[ip] = mac
except Exception as e:
logger.error(f"获取ARP表失败: {e}")
# 更新缓存
self._arp_cache = arp_table
self._arp_cache_time = current_time
logger.info(f"ARP缓存刷新完成,共 {len(arp_table)} 条记录,缓存命中率: {self.get_arp_cache_hit_rate():.2%}")
return arp_tableIP地址工具类部分代码
python
class IPUtils:
"""IP地址工具类"""
@staticmethod
def validate_ip(ip: str) -> bool:
"""验证IP地址格式是否正确"""
try:
IPAddress(ip)
return True
except AddrFormatError:
return False
@staticmethod
def validate_cidr(cidr: str) -> bool:
"""验证CIDR格式是否正确"""
try:
IPNetwork(cidr)
return True
except AddrFormatError:
return False
@staticmethod
def validate_subnet_mask(mask: str) -> bool:
"""验证子网掩码格式是否正确"""
try:
ip = IPAddress(mask)
# 检查是否是有效的子网掩码
binary = bin(int(ip))[2:].zfill(32)
# 允许/32子网掩码(全1),其他子网掩码需要有至少一个0且没有01模式
return binary == '11111111111111111111111111111111' or (binary.count('0') >= 1 and '01' not in binary)
except AddrFormatError:
return False
@staticmethod
def ip_to_int(ip_address: str) -> Optional[int]:
"""将IP地址转换为整数"""
try:
return int(IPAddress(ip_address))
except AddrFormatError:
return None
@staticmethod
def int_to_ip(ip_int: int) -> Optional[str]:
"""将整数转换为IP地址"""
try:
return str(IPAddress(ip_int))
except (AddrFormatError, TypeError):
return None
@staticmethod
def mask_to_cidr(subnet_mask: str) -> Optional[int]:
"""将子网掩码转换为CIDR前缀长度"""
try:
# 首先验证子网掩码是否有效
if not IPUtils.validate_subnet_mask(subnet_mask):
return None
# 使用netaddr库正确计算CIDR前缀长度
ip = IPAddress(subnet_mask)
binary = bin(int(ip))[2:].zfill(32)
# 计算连续的1的位数
prefix_length = 0
for bit in binary:
if bit == '1':
prefix_length += 1
else:
break
return prefix_length
except (ValueError, AttributeError):
return None就先这些吧。
感觉怎么样?欢迎来评论。