著有《React 源码》《React 用到的一些算法》《javascript地月星》等多个专栏。欢迎关注。
文章不好写,要是有帮助别忘了点赞,收藏~ 你的鼓励是我继续挖干货的的动力🔥。
另外,本文为原创内容,商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载需注明出处,感谢理解~
第一部分
之前写过一篇React SSR 设计原理阅读量不高,感觉写的还可以,所以重新整理和增加了一些内容,再发一遍。末尾的"总结"非常值得看一下,感觉没有人把SSR解读的这么彻底。记得点赞哦~👍。
SSR搭建 四个角色
server服务器(server.js) + server ssr返回纯html首页(entry-server.jsx) + client hydrateRoot注水给html,把 Fiber 树挂接到现有 DOM 上(对应client.jsx),给 DOM 节点加上 React 的事件绑定、内部状态,使 DOM 变"活"。
流程:请求server服务器(server.js),返回首页内容(entry-server.jsx) ----> 首页下载脚本client.jsx,client.jsx执行hydrateRoot水合,React接管。
所以能看到四个角色:【server.js】【entry-server.jsx】【client.jsx】【App.jsx LazyComp.jsx】。
其中【App.jsx LazyComp.jsx】这两个属于公共的,服务端和客户端都用到。
sql
my-react-app
├── dist/
│ ├── server/
│ │ └── server.js ← 这个在 Node 跑,不会发给客户端 打包前是entry-server.jsx
│ └── client/
│ └── client.js ← 这个才会发给浏览器
├── server.js 和上面的server.js不同同一个,node server.js启动的是这个
在提供的例子中还有App.jsx LazyComp.jsx的打包没有在上方体现,简化逻辑,主要就是这3方。
App LazyComp在服务的和客户端都被使用属于公共的。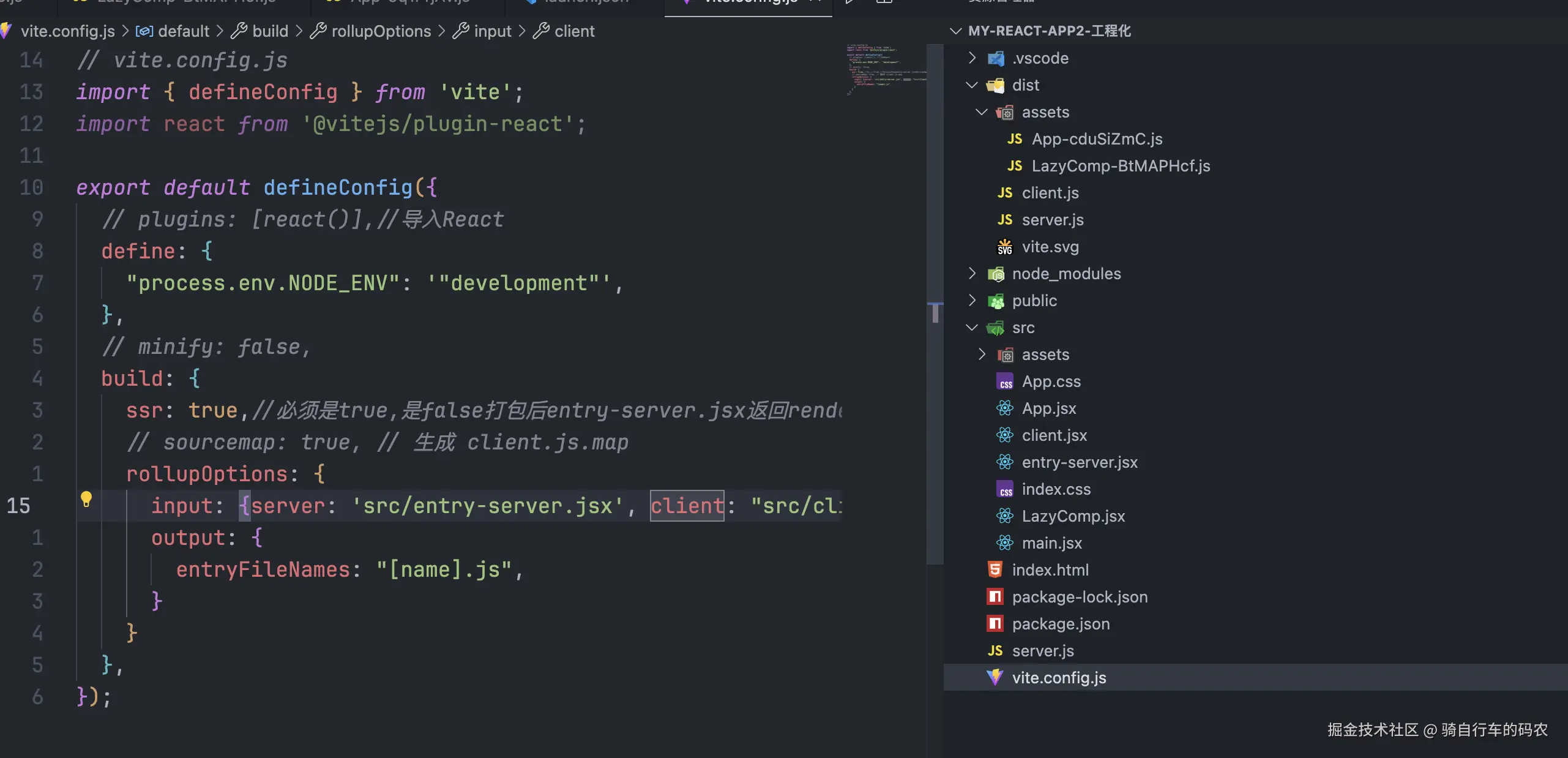
我改了打包目录部分的配置,打包后的目录不一样了,不影响阅读
运行两遍React组件
在服务器端执行一遍React组件,生成html后返回纯html给客户端,完成首次渲染。
在客户端执行client.js进行水合,再次执行一遍React组件,创建Fiber、挂接到DOM、绑定事件等。
jsx
entry-server.jsx
const { pipe } = renderToPipeableStream(<App />, {...pipe(res)...})
注意这里的<App/>经过打包后是,
const { pipe } = renderToPipeableStream(/* @__PURE__ */ React.createElement(App, null), {...pipe(res)...})
服务端运行React.createElement得到App的html。
明显已经运行了一遍React.createElement(App, null),纯App的html。
下面在客户端还会运行一遍。返回App的纯html,通过pipe能获取,在option中注入。
客户端会再运行一遍。
js
hydrateRoot(document.getElementById("root"), <App />);
打包后:
hydrateRoot(document.getElementById("root"), /* @__PURE__ */ React.createElement(App, null));这一遍叫水合。没有水合前是纯html的页面。水合后被React接管。
例如在后面的实践例子中,第8秒在vscode打印一次,第16秒在浏览器打印一次。
HTML的水合
水合就是给服务端的返回的HTML的DOM添加internalInstanceKey,能找到它的Fiber。
变量internalInstanceKey,值类似于__reactFiberchytmrjmd38,__reactFiber+随机数。
每个真实DOM都有__reactFiber$...属性,指向真实DOM对应的Fiber Node。
如果真实DOM没有__reactFiber$...表示这个DOM没有受到React的管理,例如SSR时服务端返回的HTML。
我简单的把"给DOM添加__reactFiber$..属性"一起归到hydrateRoot()。(实际hydrateRoot没有做这件事。添加属性是触发任意事件的时候做的),有对应的Fiber Node,这个DOM就被React接管了。
| 水合前 只是简单的html 没有__reactFiber$...属性 | 水合后 多了__reactFiber$...属性 |
|---|---|
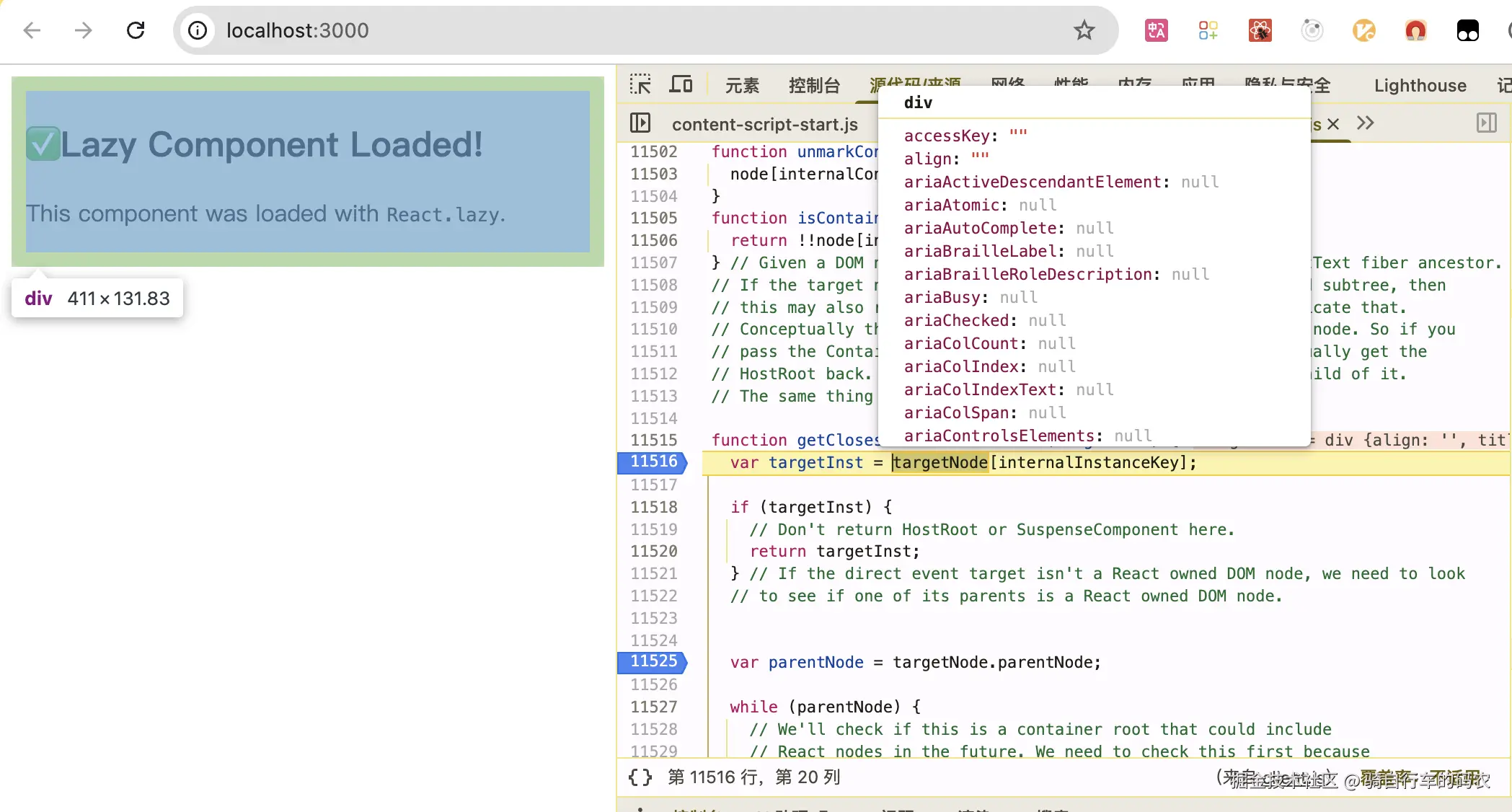 |
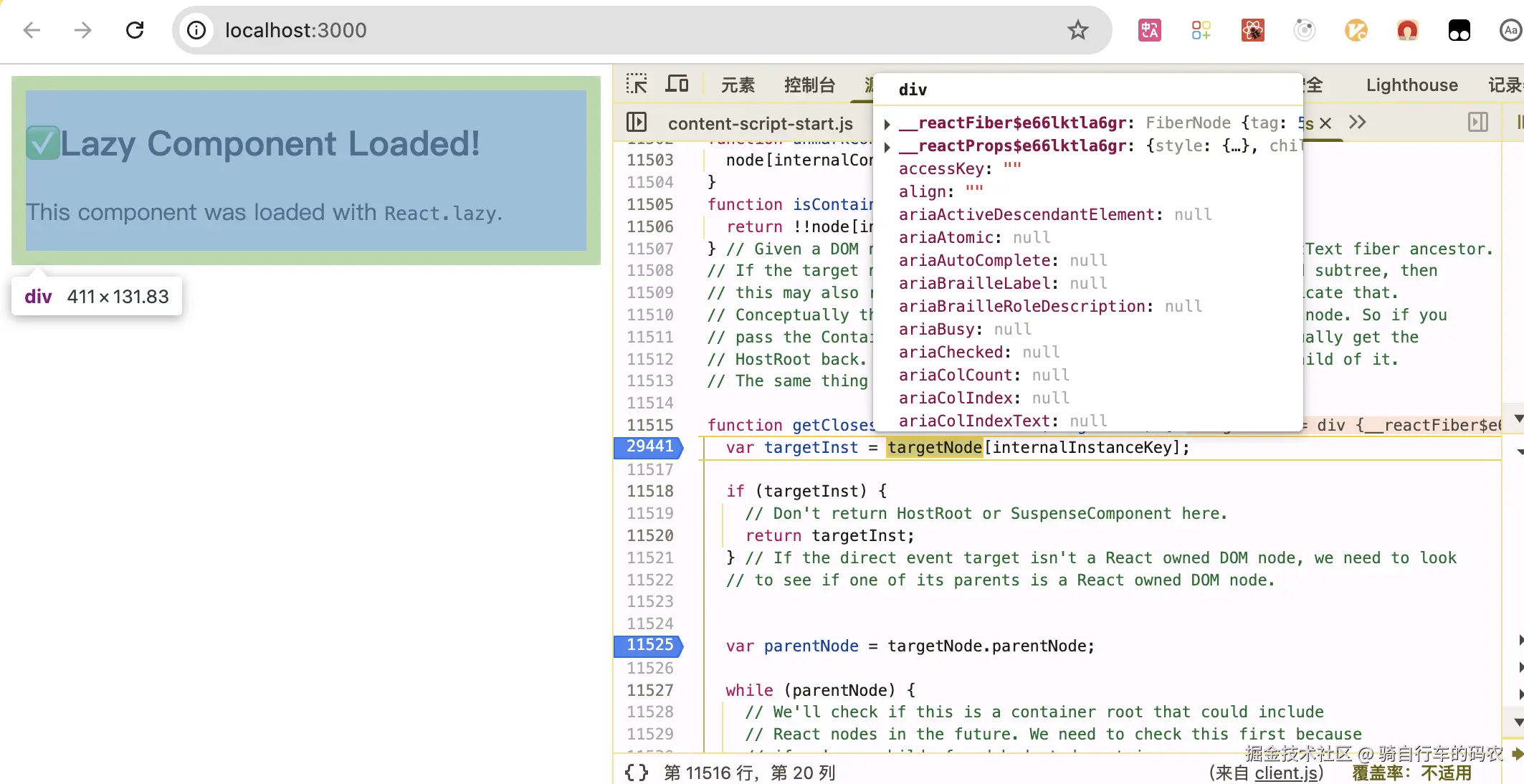 |
注释节点
SSR生成的HTML带有注释
html
<div>
<!-- $? --> 有internalInstanceKey、受到管理
<div> 没有internalInstanceKey、没有受到管理
Loading...
</div>
<!-- /$ -->
</div>
html
<div>
<!-- $ --> 有internalInstanceKey、受到管理
<h1> 没有internalInstanceKey、没有受到管理
Hello World!
</h1>
<!-- /$ -->
</div>React借助注释节点,快速找到SSR内容。如果没有注释节点,无法分辨SSR内容或者要从整个页面全部节点中一个一个查找。
React中专门查找注释节点的函数getParentSuspenseInstance:
html
<!--$--> ← Suspense A 开始 (pending) 找到这个节点
<div>Content A</div> 注释和内容是兄弟节点
<!--$--> ← Suspense B 开始 (pending)
<span>嵌套</span>
<!--/$--> ← Suspense B 结束
<p id="target">Target</p> ← targetInstance 从这里开始
<!--/$--> ← Suspense A 结束
js
function getParentSuspenseInstance(targetInstance) {
var node = targetInstance.previousSibling;
var depth = 0;
while (node) {
if (node.nodeType === COMMENT_NODE) {
var data = node.data;//node是`<!--$-->`, `<!--$!-->`, `<!--$?-->`, `<!--/$-->` 。data是`$``$!``$?``/$`。
if (data === SUSPENSE_START_DATA || // $
data === SUSPENSE_FALLBACK_START_DATA || // $!
data === SUSPENSE_PENDING_START_DATA) { // $?
// 遇到 Suspense 开始
if (depth === 0) {
return node; // 找到了最外层未闭合的 Suspense,返回
} else {
depth--; // 退出一层嵌套
}
} else if (data === SUSPENSE_END_DATA) { // /$
depth++; // 遇到结束,说明我们"进入"了一个更外层的 Suspense 范围
}
}
node = node.previousSibling; //从后往前找
}
return null;
}返回<!-- $ -->等的DOM。
第二部分
SSR核心概念
用官话来讲:
- 同构(Isomorphic / Universal Rendering)指 React 代码既能运行在服务端(Node.js)又能运行在客户端(浏览器)。其实就是在服务的执行一遍react组件。
- 注水 (Hydration)浏览器接收到服务端生成的 HTML 后,React 不会重新渲染 DOM ,而是"注水"------把 Fiber 树挂接到现有 DOM 上。给 DOM 节点加上 React 的事件绑定、内部状态,使 DOM 变"活"。
- 脱水 (Dehydration):在 React 18 里,Suspense 边界可以被"脱水" ,即保留 fallback 或 HTML 片段,但不立即 hydrate。等到用户交互或资源到达,再对局部进行 hydration。
同构是一个宏观目标: 它的目标是让同一套代码既能在服务器上运行(生成 HTML),又能在客户端上运行(处理交互)。它描述的是一种架构模式 。
脱水/注水是一个微观实现: 它是实现同构这个目标 所必须的技术手段。
其实就是服务端执行一遍React组件返回HTML。(服务端渲染)
HTML上的DOM找不到Fiber。(脱水的)
把Fiber关联到DOM,DOM能找到自己的Fiber(注水)
第三部分
实践例子
jsx
// src/App.jsx
import React, { Suspense, lazy } from 'react';
const LazyComp = lazy(() => {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('服务端和客户端都运行一次LazyComp');---运行两遍React组件:在vscode控制台打印一次,在浏览器控制台打印一次 第8秒在vscode打印,第16秒在浏览器打印
resolve(import('./LazyComp'));
}, 8000); // 模拟 8 秒延迟
});
});
function App() {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<LazyComp />
</Suspense>
);
}
export default App;
jsx
//client.jsx
import React from "react";
import { hydrateRoot } from "react-dom/client";
import App from "./App.jsx";
console.log(22222);
hydrateRoot(document.getElementById("root"), <App />);
jsx
// entry-server.jsx
import React from "react";
import { renderToPipeableStream } from "react-dom/server";
import App from "./App.jsx";
export function render(res) {
const { pipe } = renderToPipeableStream(<App />, {
onShellReady() {
res.setHeader("content-type", "text/html");
res.write(`<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My React App</title>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">`);
console.log(222);
pipe(res);//如果把const {pipe}注释掉,会报错 pipe is not defined;
res.write(`</div>
</body>
<script type="module" src="/dist/client.js"></script>
</html>`);
},
});
}
js
// LazyComp.jsx
import React from 'react';
export default function LazyComp() {
return <h1>✅Hello !</h1>;
}
js
//server.js 在根目录!
import express from "express";
import { createServer as createViteServer } from "vite";
import path from "path";
import { fileURLToPath } from "url";
const __dirname = path.dirname(fileURLToPath(import.meta.url));
async function start() {
const app = express();
// 1. 创建 Vite dev server (中间件模式)
const vite = await createViteServer({
server: { middlewareMode: true },
appType: "custom"
});
app.use(vite.middlewares);
// 2. SSR 路由
app.get("/", async (req, res) => {
try {
// const { render } = await vite.ssrLoadModule("/src/entry-server.jsx");
const { render } = await vite.ssrLoadModule("/dist/server.js");
render(res);
} catch (e) {
vite.ssrFixStacktrace(e);
console.error(e);
res.status(500).end(e.message);
}
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("🚀 SSR server running at http://localhost:3000");
});
}
start();
js
// vite.config.js
import { defineConfig } from 'vite';
// import react from '@vitejs/plugin-react';
export default defineConfig({
// plugins: [react()],//导入React
define: {
"process.env.NODE_ENV": '"development"',
},
// minify: false,
build: {
ssr: true,//必须是true,是false打包后entry-server.jsx返回render不返回
// sourcemap: true, // 生成 client.js.map
rollupOptions: {
input: {
server: 'src/entry-server.jsx',
client: "src/client.jsx"
},
output: {
entryFileNames: "[name].js",
}
}
},
});- 如果把const {pipe}注释掉,会报错 pipe is not defined;
- pipe的原理是res.write。内部借用TextEncoder.encodeInto()、unit8array最后res.write。
textEncoder.encodeInto()能把数据写入unit8array。
本例子的补充说明vite的index.html和打包:
为了简化,在我们的例子中虽然存在main.jsx、index.html,但是没有用到index.html,而是在entry-server.jsx手写的html。
这样的缺点是不能利用vite打包自动注入index.html的内容功能。
pipe的原理
- completeWriting把loading...和✅Hello发送过去。原理就是res.write。res是express请求的response。
js
//node_modules/react-dom/cjs/react-dom-server.node.development.js
function completeWriting(destination) {//destination就是res
if (currentView && writtenBytes > 0) {//currentView就是unit8Array
// console.log(destination.write(currentView.subarray(0, 64)));
// console.log(destination.write(currentView.subarray(0, 499)));
destination.write(currentView.subarray(0, writtenBytes));
}
currentView = null;
writtenBytes = 0;
destinationHasCapacity = true;
} |
 |
- send$1把文件发送过去 这似乎是vite干的
js
//node_modules/vite/dist/node/chunks/dep-BcnkIxro.js
function send$1(req, res, content, type, options) {
const {
etag = getEtag(content, { weak: true }),
cacheControl = "no-cache",
headers,
map
} = options;
if (res.writableEnded) {
return;
}
if (req.headers["if-none-match"] === etag) {
res.statusCode = 304;
res.end();
return;
}
res.setHeader("Content-Type", alias[type] || type);
res.setHeader("Cache-Control", cacheControl);
res.setHeader("Etag", etag);
if (headers) {
for (const name in headers) {
res.setHeader(name, headers[name]);
}
}
if (map && "version" in map && map.mappings) {
if (type === "js" || type === "css") {
content = getCodeWithSourcemap(type, content.toString(), map);
}
} else if (type === "js" && (!map || map.mappings !== "")) {
const code = content.toString();
if (convertSourceMap.mapFileCommentRegex.test(code)) {
debug$3?.(`Skipped injecting fallback sourcemap for ${req.url}`);
} else {
const urlWithoutTimestamp = removeTimestampQuery(req.url);
const ms = new MagicString(code);
content = getCodeWithSourcemap(
type,
code,
ms.generateMap({
source: path$d.basename(urlWithoutTimestamp),
hires: "boundary",
includeContent: true
})
);
}
}
res.statusCode = 200;
res.end(content);
return;
} |
待处理 |
状态码200  |
插入脚本片段
SSR多次用到了插入脚本片段的技术,也就是插入<script>,作为整个SSR技术实现的一部分。例如前面的插入client.js,例如前面的状态的注水,还有这里的$RC函数:
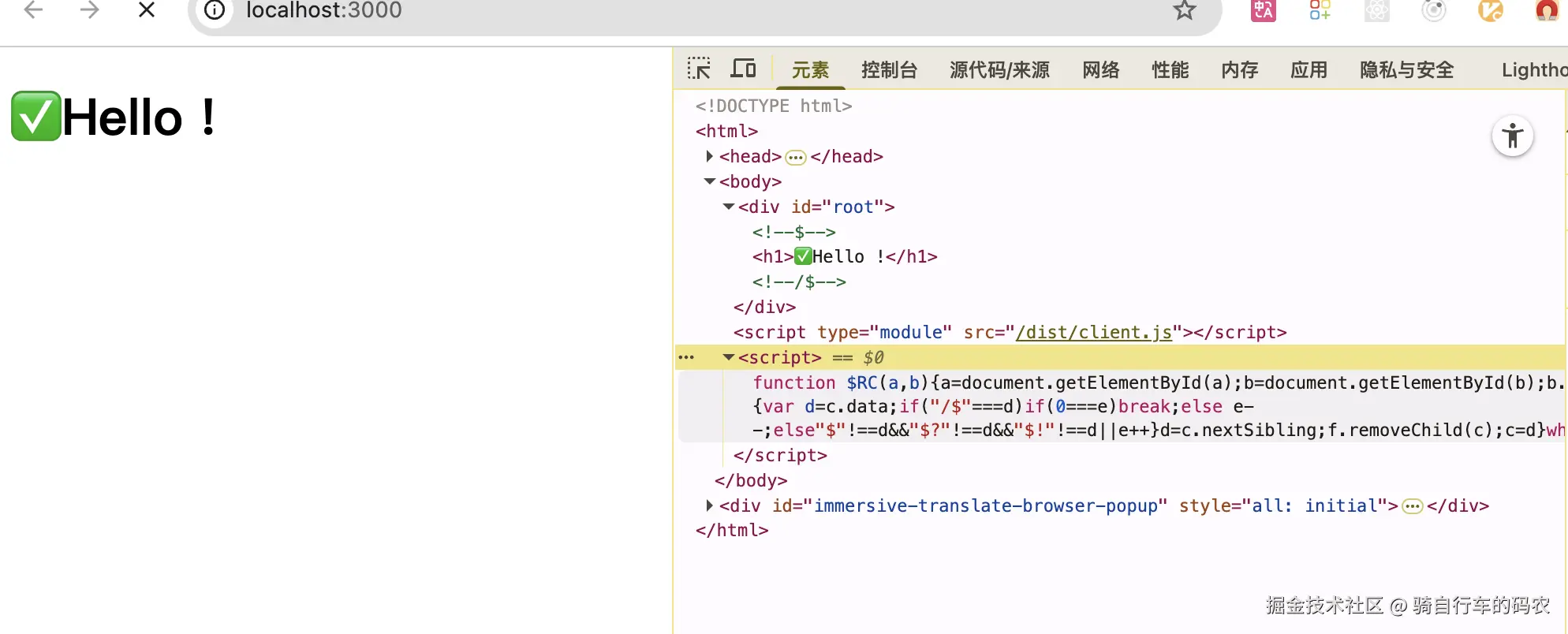
js
//node_modules/react-dom/cjs/react-dom-server.node.development.js
var completeBoundaryFunction = 'function $RC(a,b){a=document.getElementById(a);b=document.getElementById(b);b.parentNode.removeChild(b);if(a){a=a.previousSibling;var f=a.parentNode,c=a.nextSibling,e=0;do{if(c&&8===c.nodeType){var d=c.data;if("/$"===d)if(0===e)break;else e--;else"$"!==d&&"$?"!==d&&"$!"!==d||e++}d=c.nextSibling;f.removeChild(c);c=d}while(c);for(;b.firstChild;)f.insertBefore(b.firstChild,c);a.data="$";a._reactRetry&&a._reactRetry()}}';
var completeBoundaryScript1Full = stringToPrecomputedChunk(completeBoundaryFunction + ';$RC("');
function writeCompletedBoundaryInstruction(destination, responseState, boundaryID, contentSegmentID) {
writeChunk(destination, responseState.startInlineScript);
if (!responseState.sentCompleteBoundaryFunction) {
// The first time we write this, we'll need to include the full implementation.
responseState.sentCompleteBoundaryFunction = true;
writeChunk(destination, completeBoundaryScript1Full);
} else {
// Future calls can just reuse the same function.
writeChunk(destination, completeBoundaryScript1Partial);
}
if (boundaryID === null) {
throw new Error('An ID must have been assigned before we can complete the boundary.');
}
var formattedContentID = stringToChunk(contentSegmentID.toString(16));
writeChunk(destination, boundaryID);
writeChunk(destination, completeBoundaryScript2);
writeChunk(destination, responseState.segmentPrefix);
writeChunk(destination, formattedContentID);
return writeChunkAndReturn(destination, completeBoundaryScript3);
}把变量命名成有意义的变量名,取消掉压缩在看一下:
js
function $RC(a,b){a=document.getElementById(a);b=document.getElementById(b);b.parentNode.removeChild(b);if(a){a=a.previousSibling;var f=a.parentNode,c=a.nextSibling,e=0;do{if(c&&8===c.nodeType){var d=c.data;if("/$"===d)if(0===e)break;else e--;else"$"!==d&&"$?"!==d&&"$!"!==d||e++}d=c.nextSibling;f.removeChild(c);c=d}while(c);for(;b.firstChild;)f.insertBefore(b.firstChild,c);a.data="$";a._reactRetry&&a._reactRetry()}};$RC("B:0","S:0")
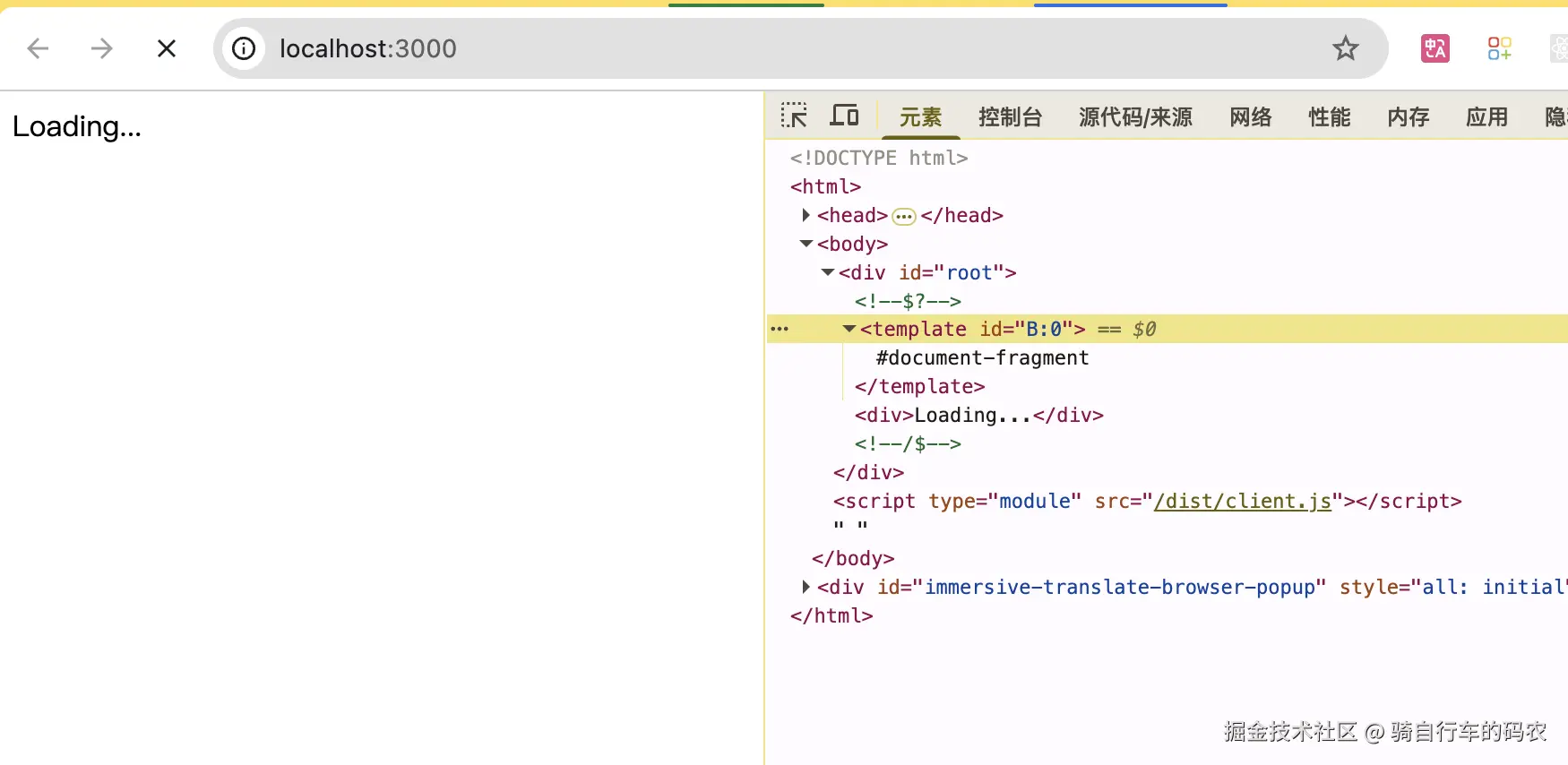
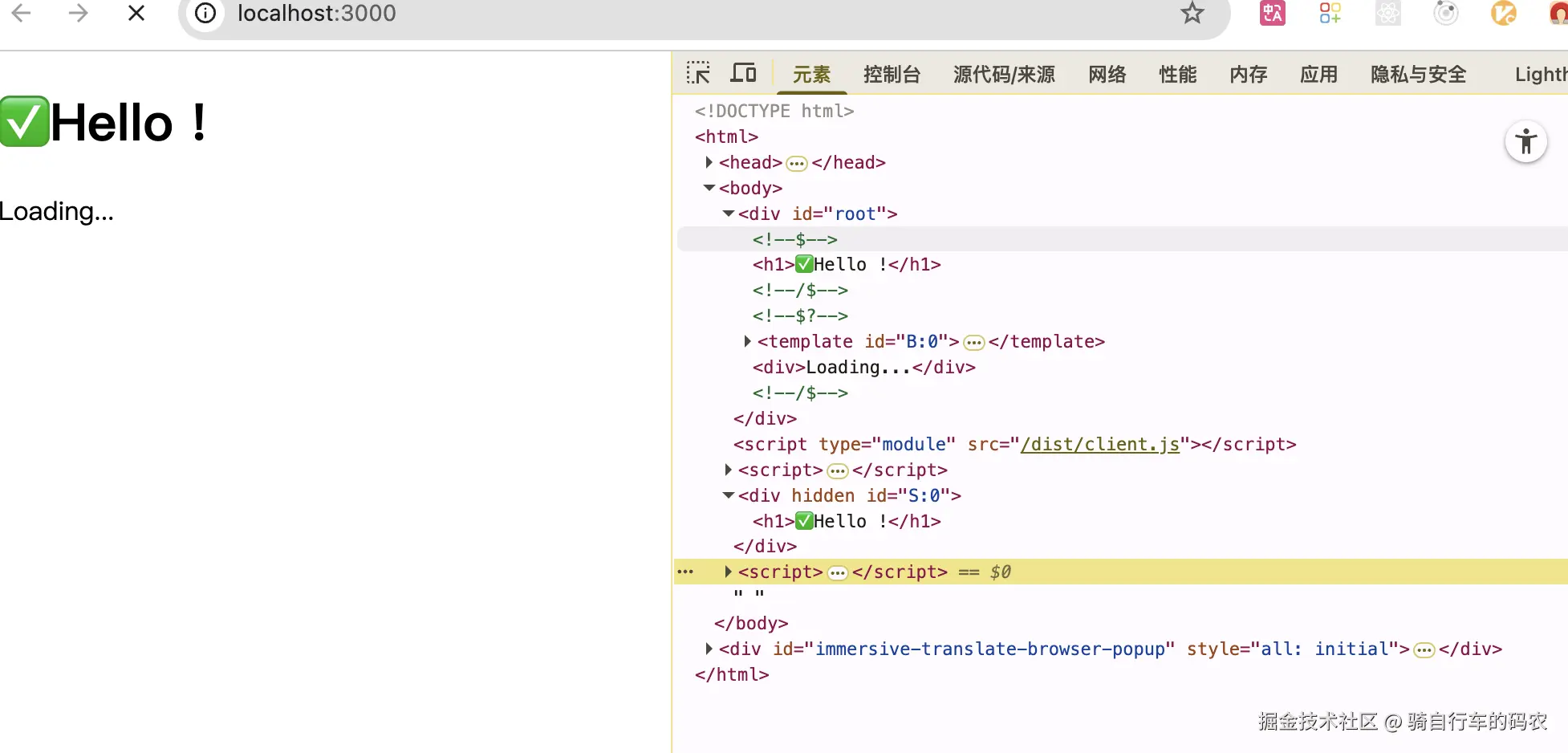
js
function replaceSegmentIntoBoundary(boundaryId, segmentId) {
const boundaryNode = document.getElementById(boundaryId);
const segmentTemplate = document.getElementById(segmentId);
// 移除 <template> 包裹
segmentTemplate.parentNode.removeChild(segmentTemplate);
if (boundaryNode) {
let marker = boundaryNode.previousSibling; // boundary 前的注释节点
const parent = marker.parentNode;
let current = marker.nextSibling;
let depth = 0;
// 删除 boundary 占位内容 (直到 "/$" 结束标记)
do {
if (current && current.nodeType === 8) { // 注释节点
const comment = current.data; //data就是注释节点的值<!-- 值 -->
if (comment === "/$") {
if (depth === 0) break;
else depth--;
} else if (comment === "$" || comment === "$?" || comment === "$!") {
depth++;
}
}
const next = current.nextSibling;
parent.removeChild(current);
current = next;
} while (current);
// 插入 segment 的内容
while (segmentTemplate.firstChild) {
parent.insertBefore(segmentTemplate.firstChild, current);
}
// 更新 marker,标记已完成
marker.data = "$";
if (marker._reactRetry) {
marker._reactRetry();
}
}
}
// 执行:把 S:0 (segment) 替换进 B:0 (boundary)
replaceSegmentIntoBoundary("B:0", "S:0");| B:0 | S:0 |
|---|---|
 |
 |
总结
SSR由四个角色组成,分别是:服务端和客户端公共的文件、HTTP服务器、客户端文件和服务端文件。
React组件创建了两遍,renderToPipeableStream+公共文件创建一遍,hydrateRoot+公共文件创建第二遍(完全没有用到createRoot)。
水合不过是把Fiber节点关联到DOM,所谓"关联"就是通过DOM能找到Fiber。
SSR技术的实现设计不过是 HTML文件 + 插入脚本 。
第一步,运行HTTP服务器,renderToPipeableStream + 公共文件 创建纯HTML文件
第二步,插入水合脚本client.js(客户端文件,里面是hydrateRoot())
第三步,插入替换脚本$RC。 HTTP服务器返回这个HTML文件,浏览器显示页面,执行脚本。
往后,再要其他功能,例如路由的管理、状态的管理,不过也是在HTML上插入新的脚本(不是全部都要插入新脚本)。
以状态管理为例,在服务端,正常创建了Store:
js
//服务端
import store from "./store";
const preloadedState = store.getState();给HTML文件插入脚本:
html
index.html
<body>
<div id="root">${content}</div>
<script> //插入
window.__PRELOAD_STATE__=${JSON.stringify(preloadedState)}//这样就被添加到了window
</script>
<script src="client.js"></script>
</body>客户端就能获取状态:
js
client.js
// 创建store时,如果有window?.__PRELOAD_STATE__,就以它为初始state,否则为空对象{}
const store = createStoreInstance(window?.__PRELOAD_STATE__);