一.日志与策略模式


像我们的linux中,也保存有相关的日志,如(/var/log/dmesg /var/log/syslog等)

二.日志封装
1.makefile
bash
bin=test_log
cc=g++
SRC=$(wildcard *.cc)
OBJ=$(SRC:.cc=.o)
$(bin):$(OBJ)
$(cc) -o $@ $^ -std=c++17 -lpthread
%.o:%.cc
$(cc) -c $< -std=c++17
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -rf $(bin) $(OBJ)2.日志框架实现
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "Mutex.hpp"
namespace LogModule
{
using namespace LockModule;
//构成: 1. 构建日志字符串 2.刷新落盘(screen,file)
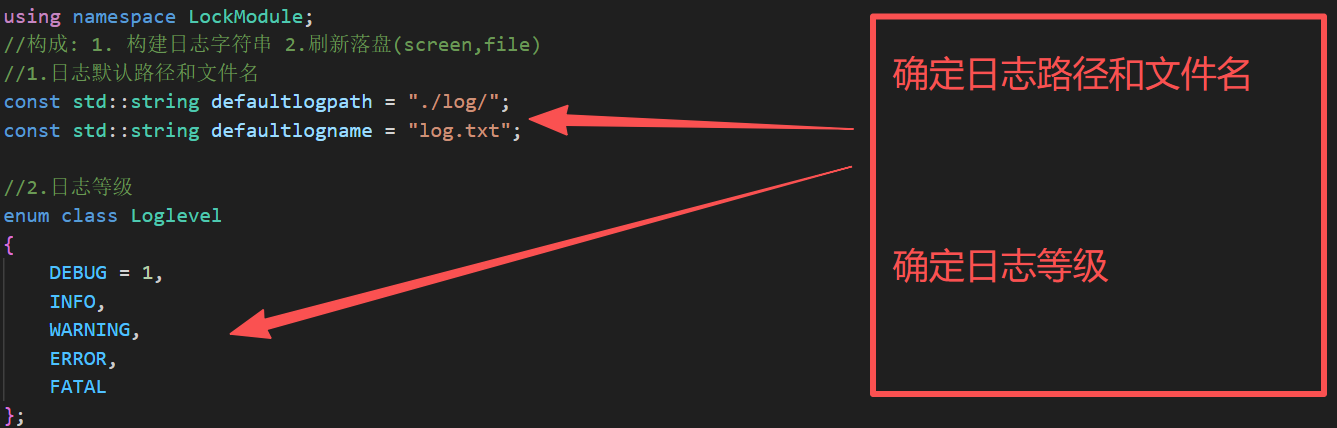
//1.日志默认路径和文件名
const std::string defaultlogpath = "./log/";
const std::string defaultlogname = "log.txt";
//2.日志等级
enum class Loglevel
{
DEBUG = 1,
INFO,
WARNING,
ERROR,
FATAL
};
//3.刷新策略
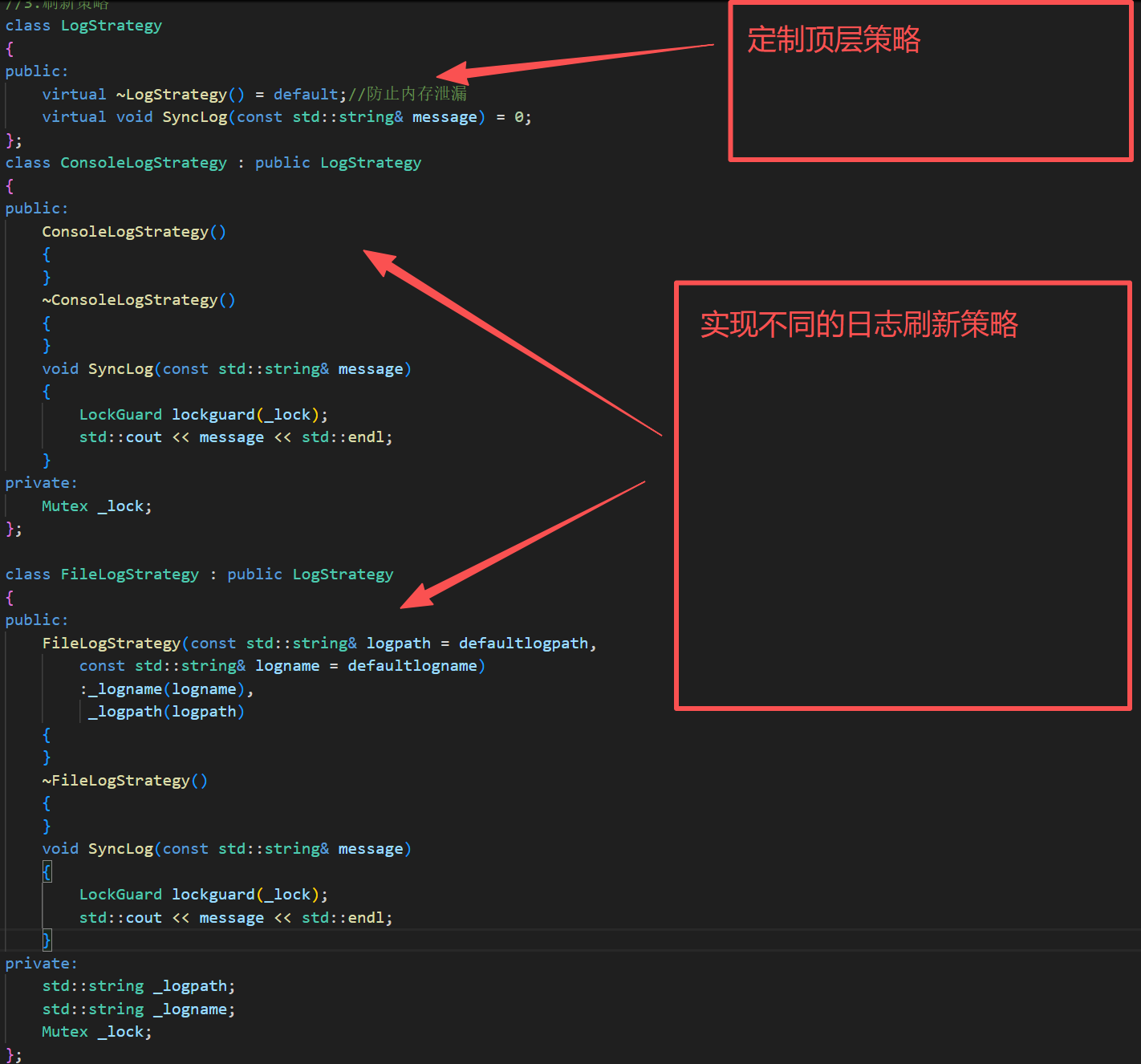
class LogStrategy
{
public:
virtual ~LogStrategy() = default;//防止内存泄漏
virtual void SyncLog(const std::string& message) = 0;
};
class ConsoleLogStrategy : public LogStrategy
{
public:
ConsoleLogStrategy()
{
}
~ConsoleLogStrategy()
{
}
void SyncLog(const std::string& message)
{
LockGuard lockguard(_lock);
std::cout << message << std::endl;
}
private:
Mutex _lock;
};
class FileLogStrategy : public LogStrategy
{
public:
FileLogStrategy(const std::string& logpath = defaultlogpath,
const std::string& logname = defaultlogname)
:_logname(logname),
_logpath(logpath)
{
}
~FileLogStrategy()
{
}
void SyncLog(const std::string& message)
{
LockGuard lockguard(_lock);
std::cout << message << std::endl;
}
private:
std::string _logpath;
std::string _logname;
Mutex _lock;
};
}
3.文件日志实现
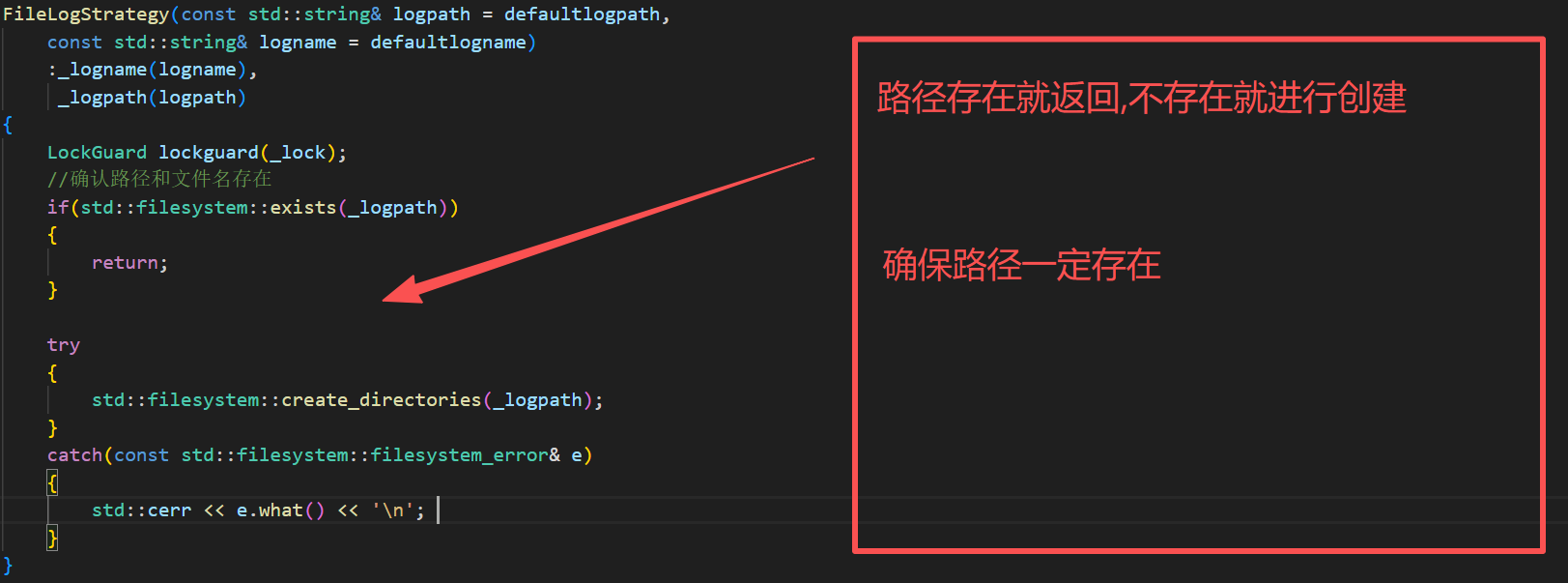
a.确定文件和路径存在
cpp
FileLogStrategy(const std::string& logpath = defaultlogpath,
const std::string& logname = defaultlogname)
:_logname(logname),
_logpath(logpath)
{
LockGuard lockguard(_lock);
//确认路径和文件名存在
if(std::filesystem::exists(_logpath))
{
return;
}
try
{
std::filesystem::create_directories(_logpath);
}
catch(const std::filesystem::filesystem_error& e)
{
std::cerr << e.what() << '\n';
}
}
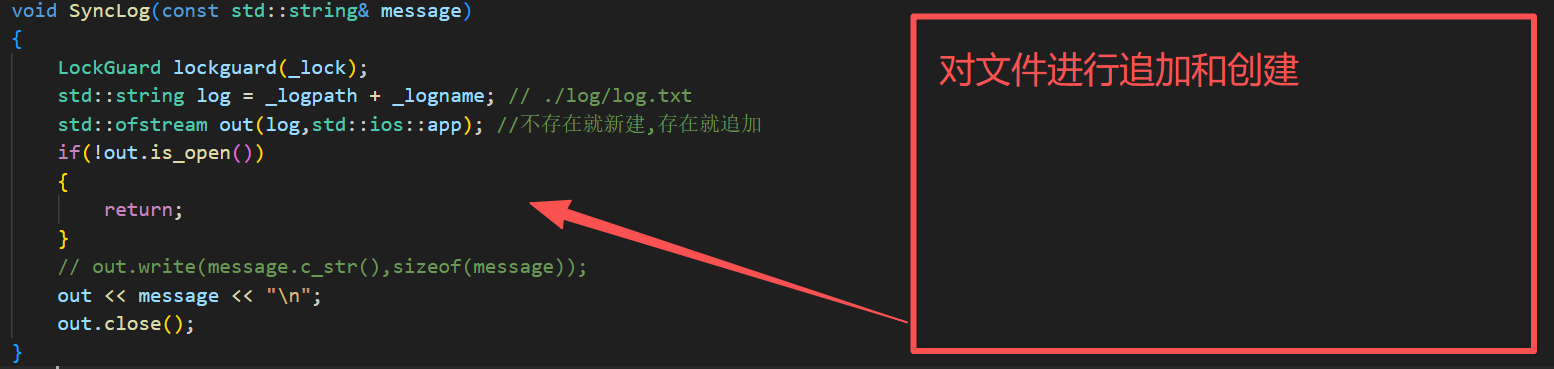
cpp
void SyncLog(const std::string& message)
{
LockGuard lockguard(_lock);
std::string log = _logpath + _logname; // ./log/log.txt
std::ofstream out(log,std::ios::app); //不存在就新建,存在就追加
if(!out.is_open())
{
return;
}
// out.write(message.c_str(),sizeof(message));
out << message << "\n";
out.close();
}
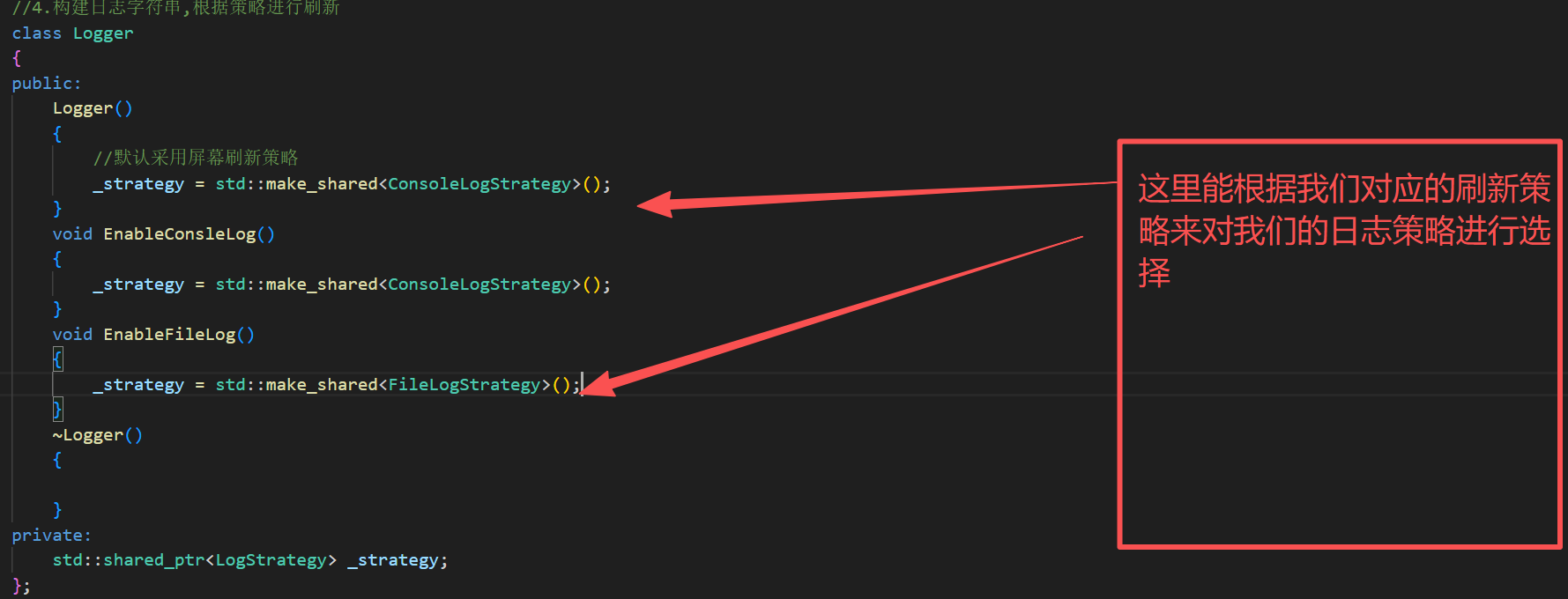
b.根据策略进行刷新
cpp
class Logger
{
public:
Logger()
{
//默认采用屏幕刷新策略
_strategy = std::make_shared<ConsoleLogStrategy>();
}
void EnableConsleLog()
{
_strategy = std::make_shared<ConsoleLogStrategy>();
}
void EnableFileLog()
{
_strategy = std::make_shared<FileLogStrategy>();
}
~Logger()
{
}
private:
std::shared_ptr<LogStrategy> _strategy;
}
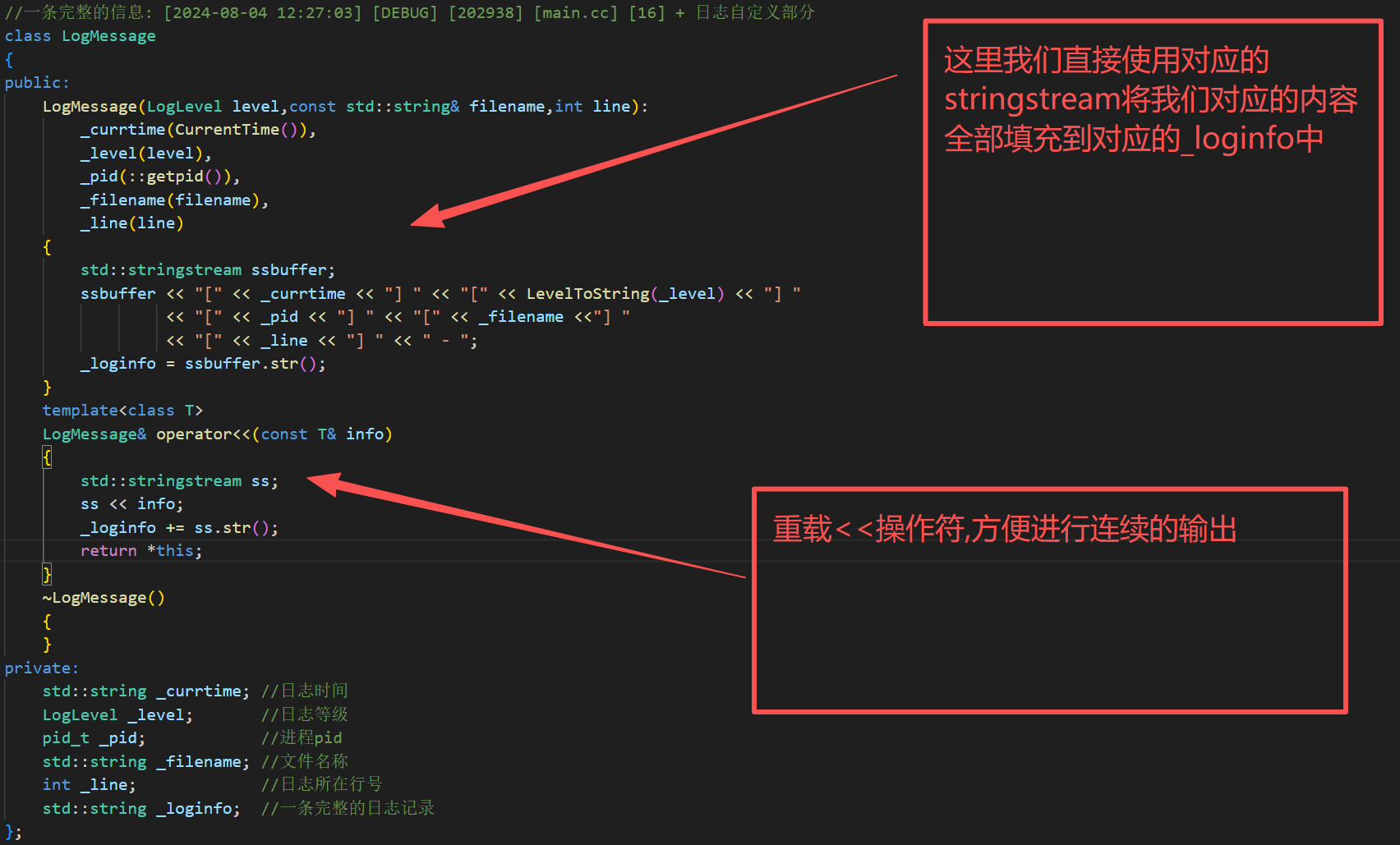
c.构建日志字符串
我们在Logger类的内部进行定义我们对应的日志字符串类
cpp
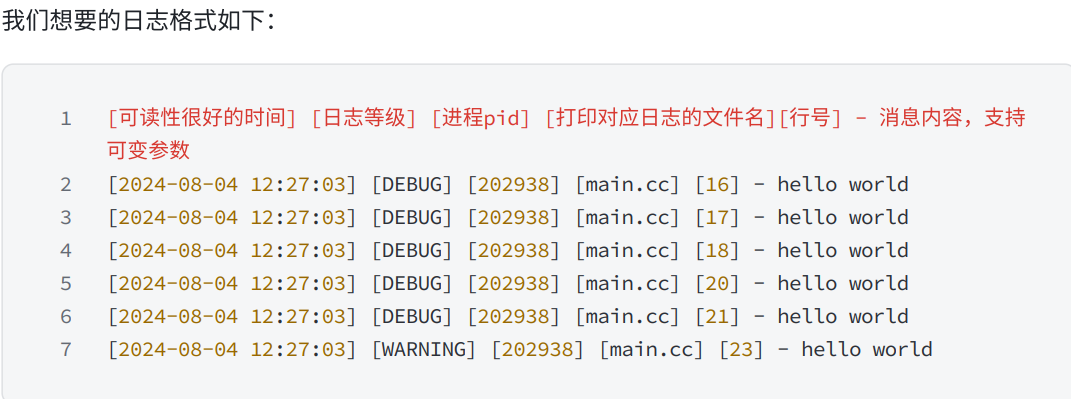
//一条完整的信息: [2024-08-04 12:27:03] [DEBUG] [202938] [main.cc] [16] + 日志自定义部分
class LogMessage
{
public:
LogMessage(LogLevel level,const std::string& filename,int line):
_currtime(CurrentTime()),
_level(level),
_pid(::getpid()),
_filename(filename),
_line(line)
{
std::stringstream ssbuffer;
ssbuffer << "[" << _currtime << "] " << "[" << LevelToString(_level) << "] "
<< "[" << _pid << "] " << "[" << _filename <<"] "
<< "[" << _line << "] " << " - ";
_loginfo = ssbuffer.str();
}
template<class T>
LogMessage& operator<<(const T& info)
{
std::stringstream ss;
ss << info;
_loginfo += ss.str();
return *this;
}
~LogMessage()
{
}
private:
std::string _currtime; //日志时间
LogLevel _level; //日志等级
pid_t _pid; //进程pid
std::string _filename; //文件名称
int _line; //日志所在行号
std::string _loginfo; //一条完整的日志记录
};
d.()的重载
cpp
LogMessage operator()(LogLevel level,const std::string& filename,int line)
{
return LogMessage(level,filename,line);
}这里就是要进行拷贝返回

e.定义LOD()
cpp
Logger logger;
#define LOG(Level) logger(Level,__FILE__,__LINE__)
这里定义宏的好处:

在该文件进行调用时,会将代码进行宏替换到对应的文件,然后__FILE__和__LINE__就能识别是哪个代码的哪一行
f.__FILE__和__LINE__的使用
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__LINE__);
printf("%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__LINE__);
printf("%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__LINE__);
return 0;
}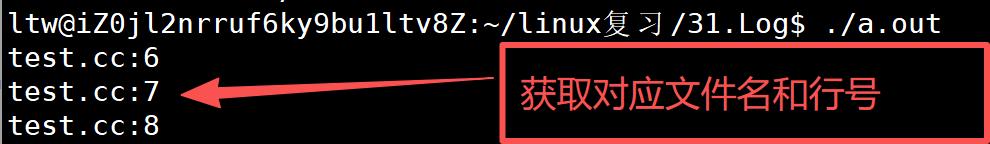
__FILE__就能获取我们对应的文件名,__LINE__能获取我们对应的文件行号
g.根据刷新策略进行刷新
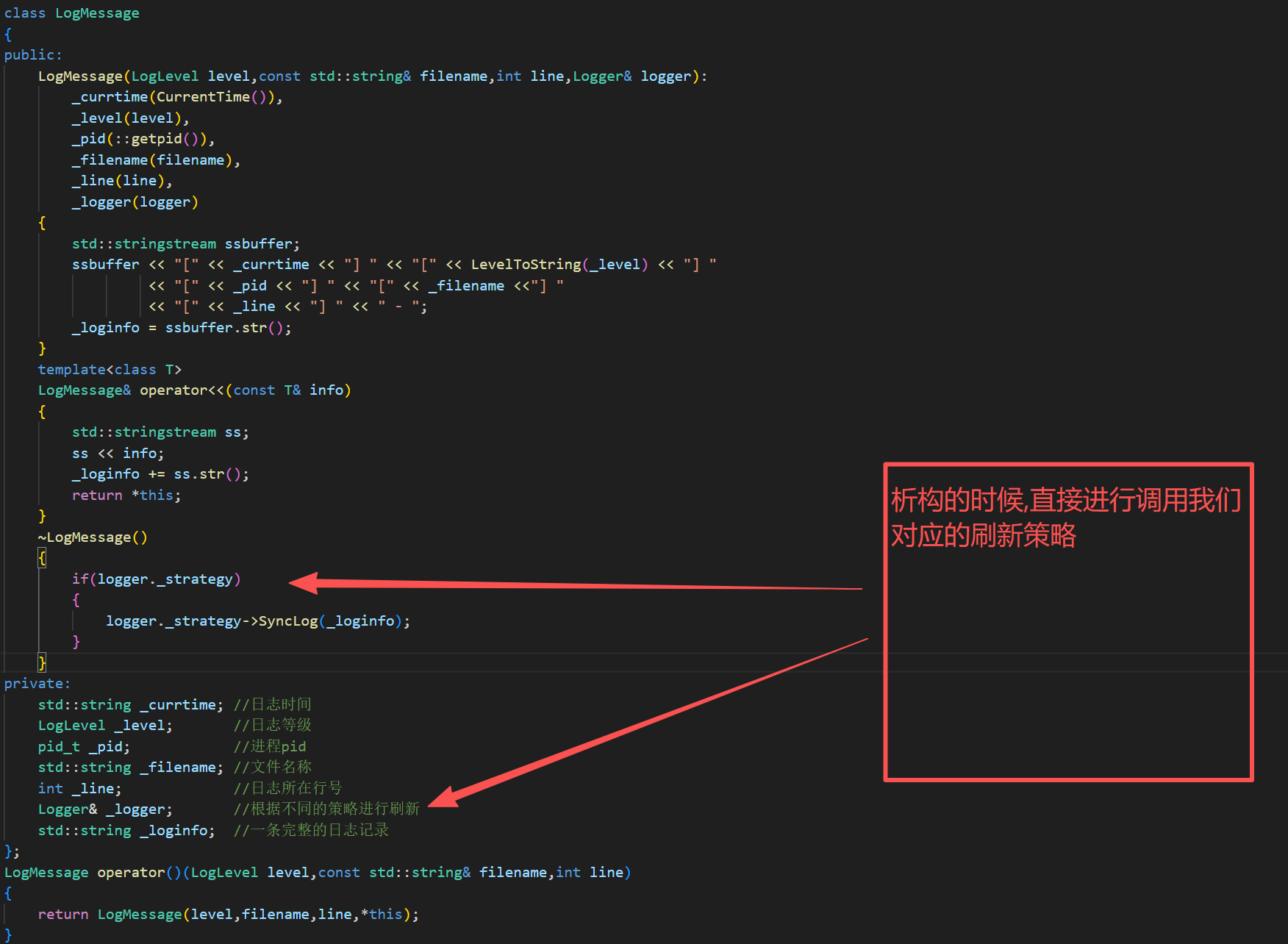
cpp
class LogMessage
{
public:
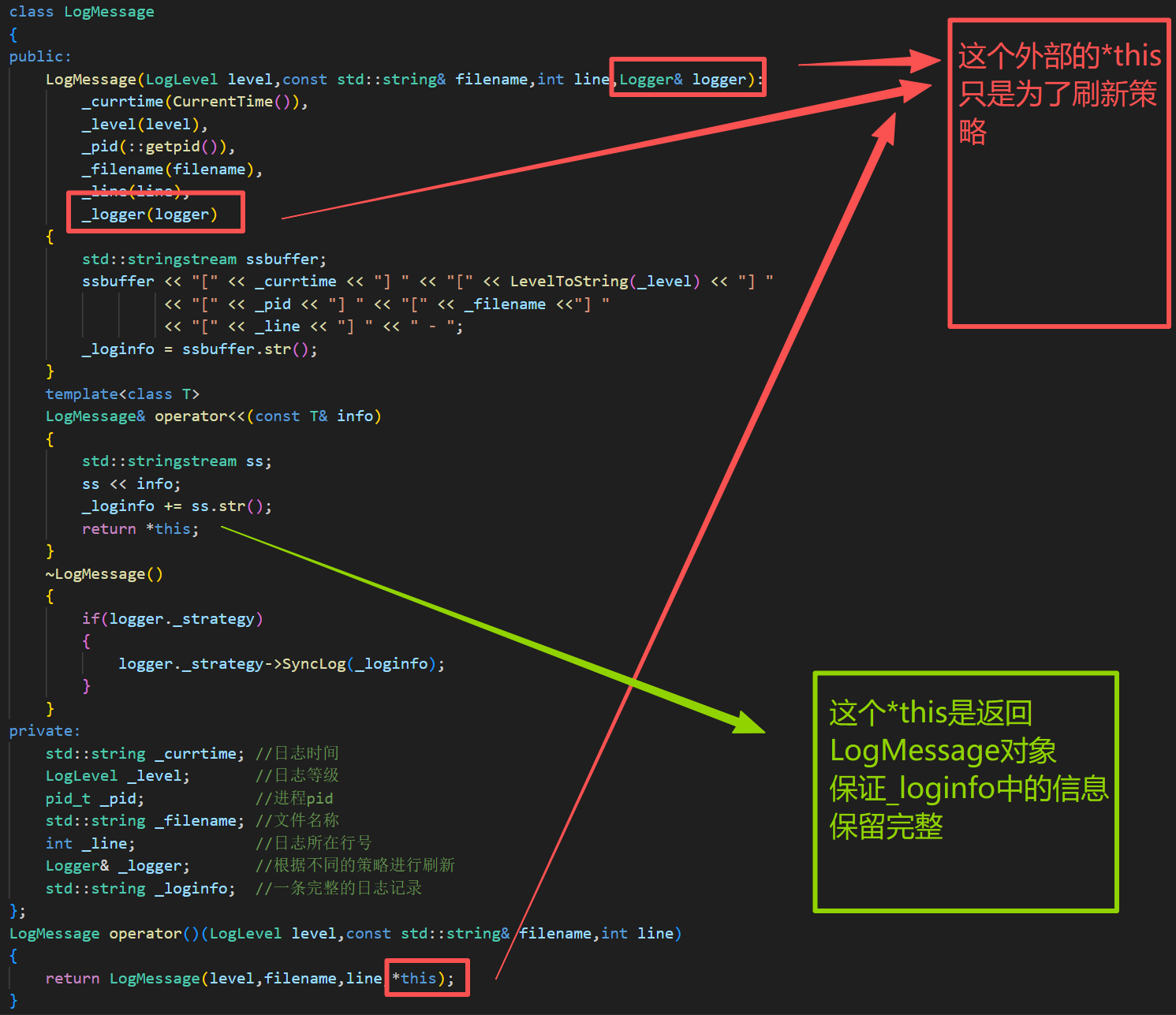
LogMessage(LogLevel level,const std::string& filename,int line,Logger& logger):
_currtime(CurrentTime()),
_level(level),
_pid(::getpid()),
_filename(filename),
_line(line),
_logger(logger)
{
std::stringstream ssbuffer;
ssbuffer << "[" << _currtime << "] " << "[" << LevelToString(_level) << "] "
<< "[" << _pid << "] " << "[" << _filename <<"] "
<< "[" << _line << "] " << " - ";
_loginfo = ssbuffer.str();
}
template<class T>
LogMessage& operator<<(const T& info)
{
std::stringstream ss;
ss << info;
_loginfo += ss.str();
return *this;
}
~LogMessage()
{
if(logger._strategy)
{
logger._strategy->SyncLog(_loginfo);
}
}
private:
std::string _currtime; //日志时间
LogLevel _level; //日志等级
pid_t _pid; //进程pid
std::string _filename; //文件名称
int _line; //日志所在行号
Logger& _logger; //根据不同的策略进行刷新
std::string _loginfo; //一条完整的日志记录
};
h.获取时间
cpp
//获取一些当前系统时间
std::string CurrentTime()
{
time_t time_stamp = ::time(nullptr);
struct tm curr;
localtime_r(&time_stamp,&curr);
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer,sizeof(buffer),"%4d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d",
curr.tm_year + 1900,
curr.tm_mon + 1,
curr.tm_mday,
curr.tm_hour,
curr.tm_min,
curr.tm_sec
);
return buffer;
}
// std::string GetCurrTime()
// {
// time_t t = time(nullptr);
// struct tm* curr = ::localtime(&t);
// char currtime[32];
// snprintf(currtime,sizeof(currtime),"%d-%d-%d %d:%d:%d",
// curr->tm_year + 1900,
// curr->tm_mon + 1,
// curr->tm_mday,
// curr->tm_hour,
// curr->tm_min,
// curr->tm_sec
// );
// return currtime;
// }I.测试代码
cpp
#include "Log.hpp"
using namespace LogModule;
int main()
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "hello world " << 3.14;
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "hello world " << 5.21382;
return 0;
}
J.查看宏替换(预处理)

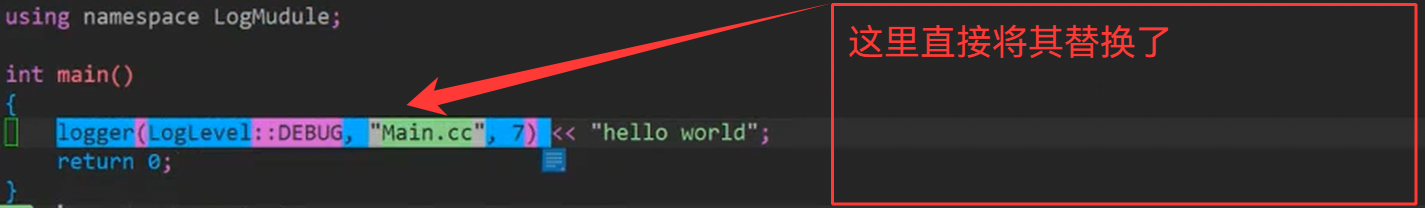
k.转换刷新策略定义
cpp
#define ENABLE_CONSOLE_LOG() logger.EnableConsleLog()
#define ENABLE_FILE_LOG() logger.EnableFileLog()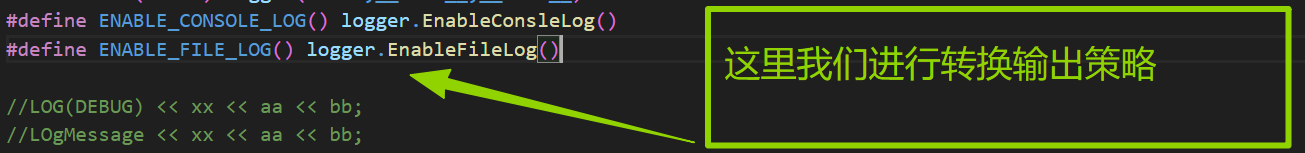
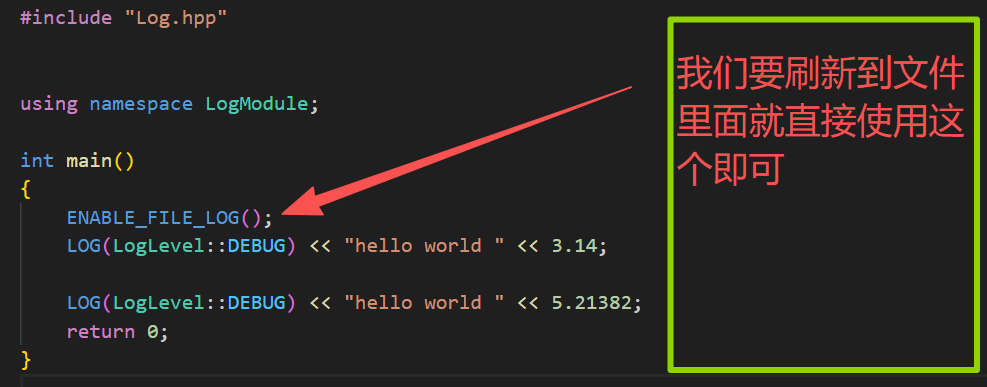
cpp
#include "Log.hpp"
using namespace LogModule;
int main()
{
ENABLE_FILE_LOG();
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "hello world " << 3.14;
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "hello world " << 5.21382;
return 0;
}
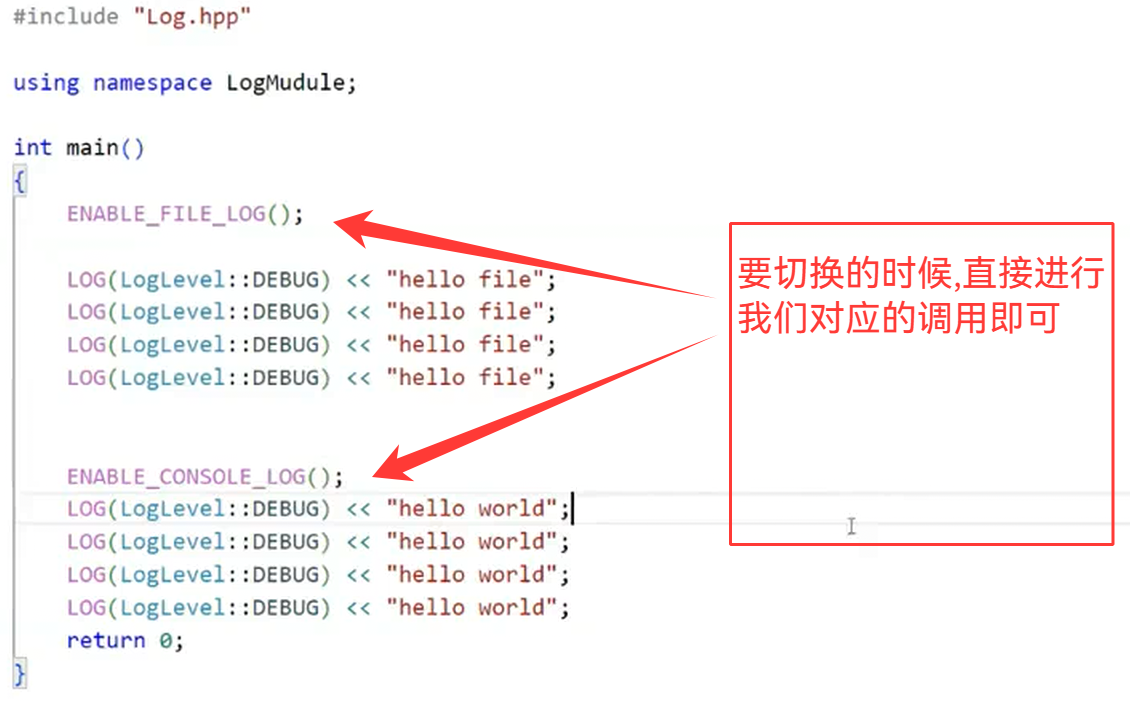
三.线程池介绍


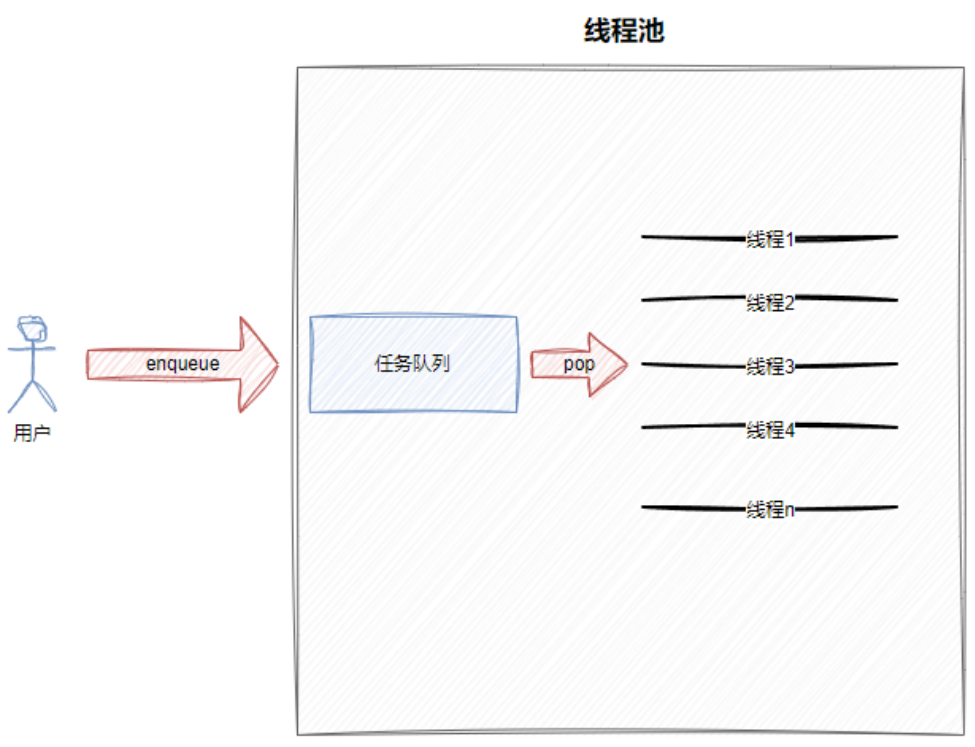
四.线程池封装
1.将对应的Mutex.hpp等代码拷贝
cpp
"Thread.hpp"
#ifndef _THREAD_HPP__
#define _THREAD_HPP__
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <functional>
namespace ThreadModule
{
using func_t = std::function<void()>;
static int number = 1;
enum class TSTATUS
{
NEW,
RUN,
STOP
};
class Thread
{
private:
//这个地方不能写成成员方法
// void* Routine(Threadthis,void* args)
// {
// }
static void* Routine(void* args)
{
Thread* t = static_cast<Thread*>(args);
t->_func();
return nullptr;
}
void EnableDetach()
{
_joinable = false;
}
public:
Thread(func_t func):_func(func),_status(TSTATUS::NEW),_joinable(true)
{
_name = "Thread-" + std::to_string(number++);
_pid = getpid();
}
bool Start()
{
if(_status != TSTATUS::RUN)
{
int n = pthread_create(&_tid,nullptr,Routine,this);
if(n != 0)
{
return false;
}
_status = TSTATUS::RUN;
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool Stop()
{
if(_status == TSTATUS::RUN)
{
int n = pthread_cancel(_tid);
if(n != 0)
{
return false;
}
_status = TSTATUS::STOP;
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool Join()
{
if(_joinable)
{
int n = pthread_join(_tid,nullptr);
if(n != 0)
{
return false;
}
_status = TSTATUS::STOP;
return true;
}
return false;
}
void Detach()
{
EnableDetach();
pthread_detach(_tid);
}
bool IsJoinable()
{
return _joinable;
}
std::string Name()
{
return _name;
}
~Thread()
{
}
private:
std::string _name;
pthread_t _tid;
pid_t _pid;
bool _joinable;//默认不分离
func_t _func;
TSTATUS _status;
};
};
#endif
cpp
"Mutex.hpp"
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
namespace LockModule
{
class Mutex
{
public:
Mutex(const Mutex&) = delete;
const Mutex& operator=(const Mutex&) = delete;
Mutex()
{
int n = ::pthread_mutex_init(&_lock,nullptr);
(void)n;
}
void Lock()
{
int n = ::pthread_mutex_lock(&_lock);
(void)n;
}
void Unlock()
{
int n = ::pthread_mutex_unlock(&_lock);
(void)n;
}
pthread_mutex_t* LockPtr()
{
return &_lock;
}
~Mutex()
{
int n = ::pthread_mutex_destroy(&_lock);
(void)n;
}
private:
pthread_mutex_t _lock;
};
class LockGuard
{
public:
LockGuard(Mutex& mtx):_mtx(mtx)
{
_mtx.Lock();
}
~LockGuard()
{
_mtx.Unlock();
}
private:
Mutex& _mtx;
};
};
cpp
"Log.hpp"
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdio>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <filesystem>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <memory>
#include <time.h>
#include "Mutex.hpp"
namespace LogModule
{
using namespace LockModule;
//构成: 1. 构建日志字符串 2.刷新落盘(screen,file)
//1.日志默认路径和文件名
const std::string defaultlogpath = "./log/";
const std::string defaultlogname = "log.txt";
//2.日志等级
enum LogLevel
{
DEBUG = 1,
INFO,
WARNING,
ERROR,
FATAL
};
std::string LevelToString(LogLevel level)
{
switch(level)
{
case LogLevel::DEBUG:
return "DEBUG";
case LogLevel::INFO:
return "INFO";
case LogLevel::WARNING:
return "WARNING";
case LogLevel::ERROR:
return "ERROR";
case LogLevel::FATAL:
return "FATAL";
default:
return "None";
}
}
//3.刷新策略
class LogStrategy
{
public:
virtual ~LogStrategy() = default;//防止内存泄漏
virtual void SyncLog(const std::string& message) = 0;
};
class ConsoleLogStrategy : public LogStrategy
{
public:
ConsoleLogStrategy()
{
}
~ConsoleLogStrategy()
{
}
void SyncLog(const std::string& message)
{
LockGuard lockguard(_lock);
std::cout << message << std::endl;
}
private:
Mutex _lock;
};
class FileLogStrategy : public LogStrategy
{
public:
FileLogStrategy(const std::string& logpath = defaultlogpath,
const std::string& logname = defaultlogname)
:_logname(logname),
_logpath(logpath)
{
LockGuard lockguard(_lock);
//确认路径和文件名存在
if(std::filesystem::exists(_logpath))
{
return;
}
try
{
std::filesystem::create_directories(_logpath);
}
catch(const std::filesystem::filesystem_error& e)
{
std::cerr << e.what() << '\n';
}
}
~FileLogStrategy()
{
}
void SyncLog(const std::string& message)
{
LockGuard lockguard(_lock);
std::string log = _logpath + _logname; // ./log/log.txt
std::ofstream out(log,std::ios::app); //不存在就新建,存在就追加
if(!out.is_open())
{
return;
}
// out.write(message.c_str(),sizeof(message));
out << message << "\n";
out.close();
}
private:
std::string _logpath;
std::string _logname;
Mutex _lock;
};
//获取一些当前系统时间
std::string CurrentTime()
{
time_t time_stamp = ::time(nullptr);
struct tm curr;
localtime_r(&time_stamp,&curr);
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer,sizeof(buffer),"%4d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d",
curr.tm_year + 1900,
curr.tm_mon + 1,
curr.tm_mday,
curr.tm_hour,
curr.tm_min,
curr.tm_sec
);
return buffer;
}
// std::string GetCurrTime()
// {
// time_t t = time(nullptr);
// struct tm* curr = ::localtime(&t);
// char currtime[32];
// snprintf(currtime,sizeof(currtime),"%d-%d-%d %d:%d:%d",
// curr->tm_year + 1900,
// curr->tm_mon + 1,
// curr->tm_mday,
// curr->tm_hour,
// curr->tm_min,
// curr->tm_sec
// );
// return currtime;
// }
//4.构建日志字符串,根据策略进行刷新
class Logger
{
public:
Logger()
{
//默认采用屏幕刷新策略
_strategy = std::make_shared<ConsoleLogStrategy>();
}
void EnableConsleLog()
{
_strategy = std::make_shared<ConsoleLogStrategy>();
}
void EnableFileLog()
{
_strategy = std::make_shared<FileLogStrategy>();
}
~Logger()
{
}
//一条完整的信息: [2024-08-04 12:27:03] [DEBUG] [202938] [main.cc] [16] + 日志自定义部分
class LogMessage
{
public:
LogMessage(LogLevel level,const std::string& filename,int line,Logger& logger):
_currtime(CurrentTime()),
_level(level),
_pid(::getpid()),
_filename(filename),
_line(line),
_logger(logger)
{
std::stringstream ssbuffer;
ssbuffer << "[" << _currtime << "] " << "[" << LevelToString(_level) << "] "
<< "[" << _pid << "] " << "[" << _filename <<"] "
<< "[" << _line << "] " << " - ";
_loginfo = ssbuffer.str();
}
template<class T>
LogMessage& operator<<(const T& info)
{
std::stringstream ss;
ss << info;
_loginfo += ss.str();
return *this;
}
~LogMessage()
{
if(_logger._strategy)
{
_logger._strategy->SyncLog(_loginfo);
}
}
private:
std::string _currtime; //日志时间
LogLevel _level; //日志等级
pid_t _pid; //进程pid
std::string _filename; //文件名称
int _line; //日志所在行号
Logger& _logger; //根据不同的策略进行刷新
std::string _loginfo; //一条完整的日志记录
};
LogMessage operator()(LogLevel level,const std::string& filename,int line)
{
return LogMessage(level,filename,line,*this);
}
private:
std::shared_ptr<LogStrategy> _strategy;
};
Logger logger;
#define LOG(Level) logger(Level,__FILE__,__LINE__)
#define ENABLE_CONSOLE_LOG() logger.EnableConsleLog()
#define ENABLE_FILE_LOG() logger.EnableFileLog()
//LOG(DEBUG) << xx << aa << bb;
//LOgMessage << xx << aa << bb;
}
cpp
"Cond.hpp"
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "Mutex.hpp"
namespace CondModule
{
using namespace LockModule;
class Cond
{
public:
Cond()
{
int n = ::pthread_cond_init(&_cond,nullptr);
(void)n;
}
void Wait(Mutex& mutex)//让线程曾经的锁释放曾经的锁
{
int n = ::pthread_cond_wait(&_cond,mutex.LockPtr());
(void)n;
}
void Notify()
{
int n = ::pthread_cond_signal(&_cond);
(void)n;
}
void NotifyAll()
{
int n = ::pthread_cond_broadcast(&_cond);
(void)n;
}
~Cond()
{
int n = ::pthread_cond_destroy(&_cond);
(void)n;
}
private:
pthread_cond_t _cond;
};
}2.线程池框架设计
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "Log.hpp"
#include "Mutex.hpp"
#include "Cond.hpp"
#include "Thread.hpp"
namespace ThreadPoolModule
{
using namespace LogModule;
using namespace ThreadModule;
using namespace LockModule;
using namespace CondModule;
const static int defaultnum = 5;
class ThreadPool
{
public:
ThreadPool()
{
}
void Equeue()
{
}
void Start()
{
}
void Stop()
{
}
~ThreadPool()
{
}
private:
};
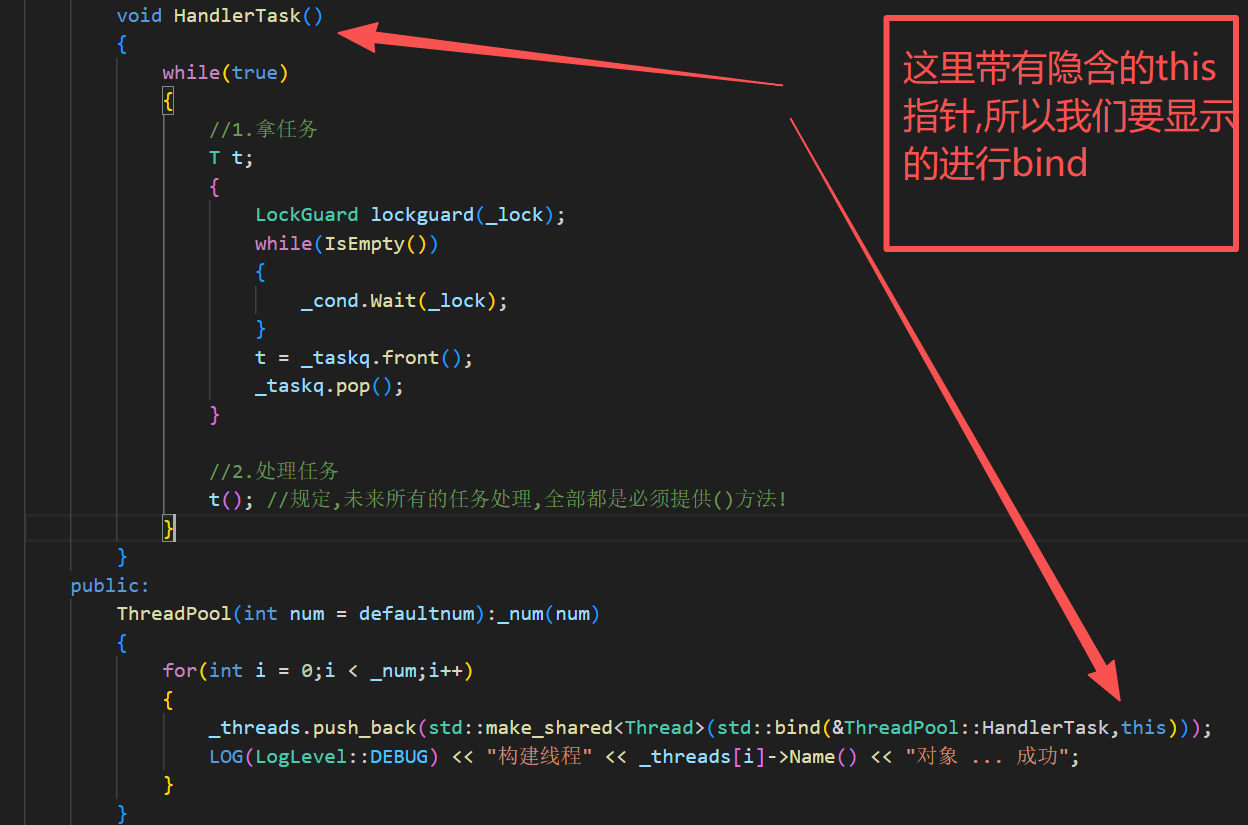
}3.构造函数
cpp
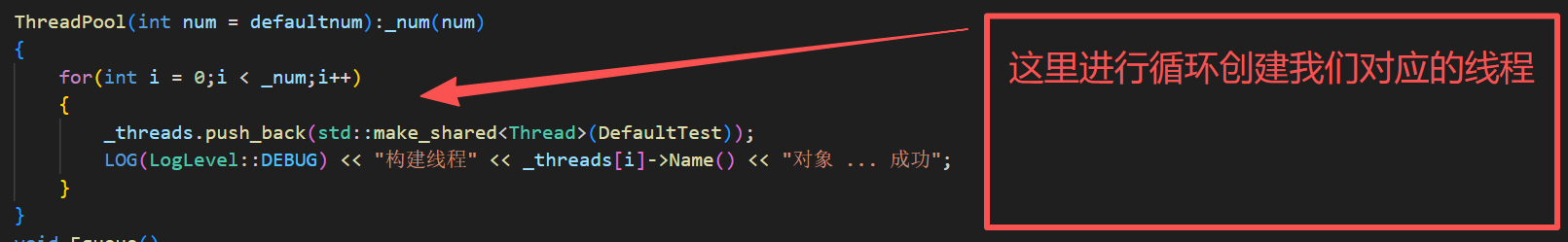
ThreadPool(int num = defaultnum):_num(num)
{
for(int i = 0;i < _num;i++)
{
_threads.push_back(std::make_shared<Thread>(DefaultTest));
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "构建线程" << _threads[i]->Name() << "对象 ... 成功";
}
}
4.Start()
cpp
void Start()
{
for(auto& thread_ptr : _threads)
{
thread_ptr->Start();
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "启动线程" << thread_ptr->Name() << " ... 成功";
}
}5.Wait()
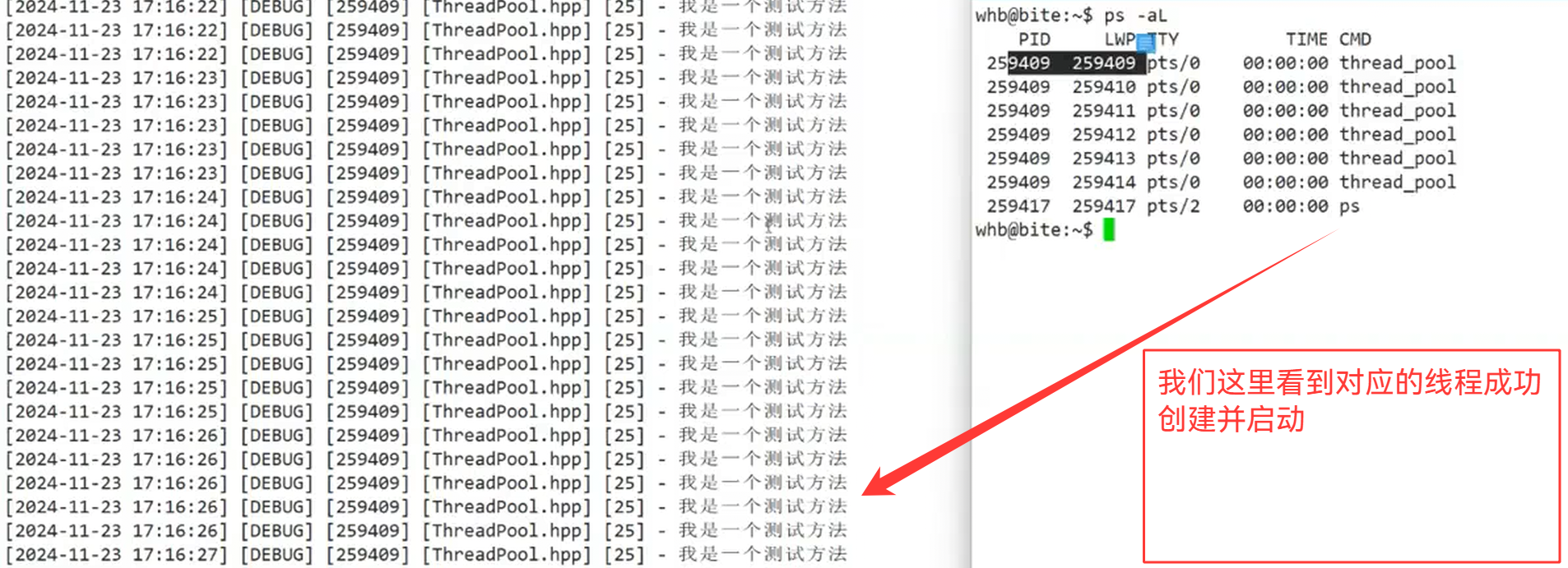
cpp
void Wait()
{
for(auto& thread_ptr : _threads)
{
thread_ptr->Join();
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "停止线程" << thread_ptr->Name() << " ... 成功";
}
}
6.线程处理任务
cpp
bool IsEmpty()
{
return _taskq.empty();
}
void HandlerTask()
{
while(true)
{
//1.拿任务
T t;
{
LockGuard lockguard(_lock);
while(IsEmpty())
{
_cond.Wait(_lock);
}
t = _taskq.front();
_taskq.pop();
}
//2.处理任务
t(); //规定,未来所有的任务处理,全部都是必须提供()方法!
}
}
7.唤醒线程
cpp
void Equeue(T& in)
{
LockGuard lockguard(_lock);
_taskq.push(std::move(in));
if(_wait_num > 0)
{
_cond.Notify();
}
}
8.任务类的创建
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include "Log.hpp"
using task_t = std::function<void()>;
using namespace LogModule;
void Push()
{
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "我是一个推送数据到服务器的一个任务,我正在被执行";
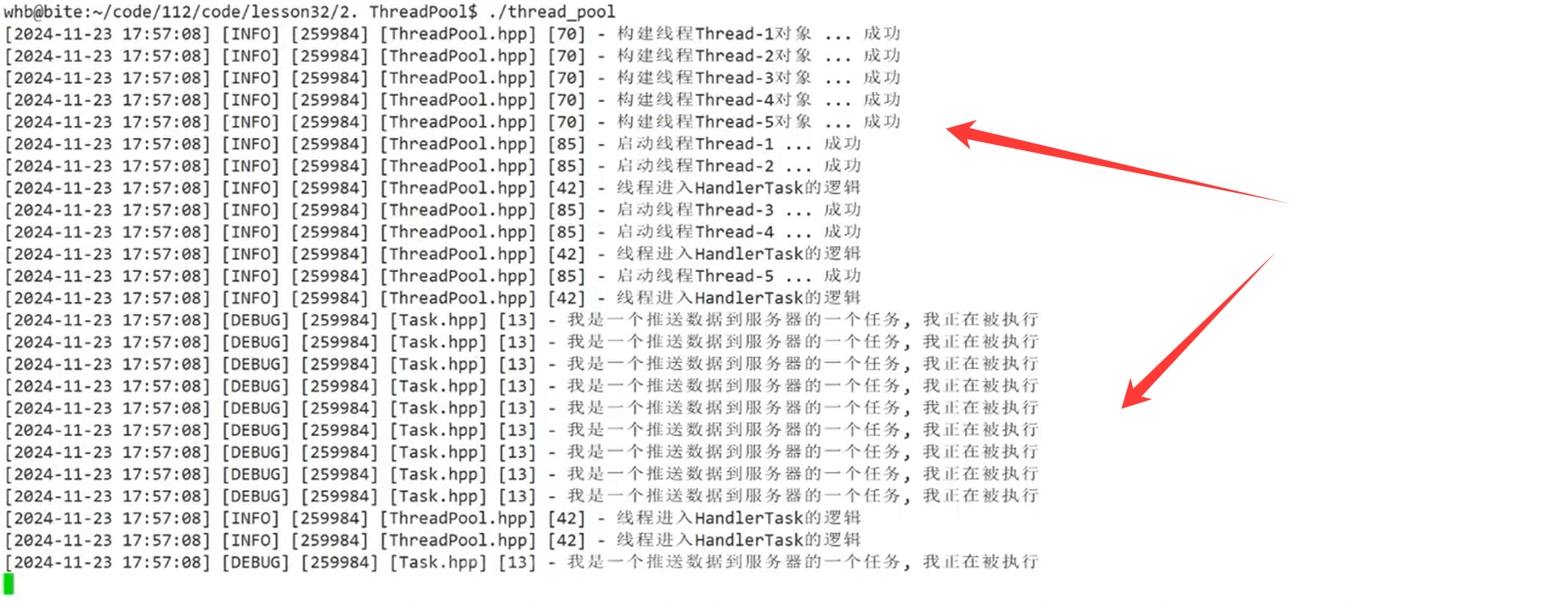
}9.测试代码
cpp
#include "ThreadPool.hpp"
#include "Task.hpp"
#include <memory>
using namespace ThreadPoolModule;
int main()
{
ENABLE_CONSOLE_LOG();
std::unique_ptr<ThreadPool<task_t>> tp = std::make_unique<ThreadPool<task_t>>();
tp->Start();
int cnt = 10;
while(cnt)
{
tp->Equeue(Push);
cnt--;
}
// tp->Stop();
tp->Wait();
return 0;
}