文章目录
-
- [一、unordered_set 和 unordered_map](#一、unordered_set 和 unordered_map)
-
-
- [1、unordered_set 类的介绍](#1、unordered_set 类的介绍)
- [2、unordered_set 和 set 的差异](#2、unordered_set 和 set 的差异)
- 3、unordered_map的介绍
- [4、unordered_multiset 和 unordered_multimap](#4、unordered_multiset 和 unordered_multimap)
-
- 二、哈希概念
- 三、哈希函数
- 四、处理哈希冲突
- 五、封装哈希
一、unordered_set 和 unordered_map
1、unordered_set 类的介绍
unordered_set 是无序的,而set中序遍历是有序的

这里 Hash 和 Pred 是两个仿函数

2、unordered_set 和 set 的差异
- unordered_set和set的第⼀个差异是对key的要求不同,set要求Key⽀持⼩于⽐较,⽽unordered_set要求Key⽀持转成整形且⽀持等于⽐较。
- unordered_set和set的第⼆个差异是迭代器的差异,set的iterator是双向迭代器,unordered_set是单向迭代器,其次set底层是红⿊树,红⿊树是⼆叉搜索树,⾛中序遍历是有序的,所以set迭代器遍历是有序+去重。⽽unordered_set底层是哈希表,迭代器遍历是⽆序+去重。
- unordered_set和set的第三个差异是性能的差异,整体⽽⾔⼤多数场景下,unordered_set的增删查改更快⼀些,因为红⿊树增删查改效率是 ,⽽哈希表增删查平均效率是。
3、unordered_map的介绍
结构:
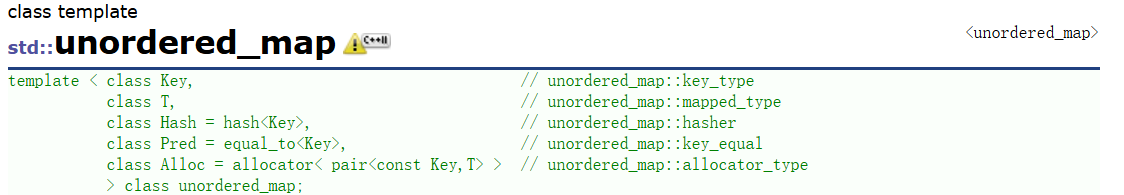
差异:

4、unordered_multiset 和 unordered_multimap
- unordered_multimap/unordered_multiset跟multimap/multiset功能完全类似,⽀持Key冗余。
- unordered_multimap/unordered_multiset跟multimap/multiset的差异也是三个⽅⾯的差异,key的要求的差异,iterator及遍历顺序的差异,性能的差异。
二、哈希概念
哈希(hash)⼜称散列,是⼀种组织数据的⽅式。从译名来看,有散乱排列的意思。本质就是通过哈希函数把关键字Key跟存储位置建⽴⼀个映射关系,查找时通过这个哈希函数计算出Key存储的位置,进⾏快速查找。
1、直接定址法
当关键字的范围⽐较集中时,直接定址法就是⾮常简单⾼效的⽅法,⽐如⼀组关键字都在[0,99]之间,那么我们开⼀个100个数的数组,每个关键字的值直接就是存储位置的下标。再⽐如⼀组关键字值都在[a,z]的⼩写字⺟,那么我们开⼀个26个数的数组,每个关键字acsii码-aascii码就是存储位置的下标。也就是说直接定址法本质就是⽤关键字计算出⼀个绝对位置或者相对位置。这个⽅法我们在计数排序部分已经⽤过了,其次在string章节的下⾯OJ也⽤过了。
387. 字符串中的第一个唯一字符
2、哈希冲突
N个值通过哈希函数,映射到M个空间

3、负载因⼦

4、将关键字转为整数

三、哈希函数

1、除法散列法/除留余数法

2、乘法散列法

3、全域散列法

四、处理哈希冲突

1、开放定址法

线性探测

二次探测

双重散列

代码实现
cpp
namespace open_address
{
enum State
{
EXIST,
EMPTY,
DELETE
};
template<class K,class V>
struct HashData
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
State _state = EMPTY;
};
template<class K>
struct HashFun
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
//特化
template<>
struct HashFun<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string key)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto& e : key)
{
hash += e;
hash *= 131;
}
return hash;
}
};
template<class K,class V,class Hash = HashFun<K>>
class HashTable
{
public:
HashTable()
{
_tables.resize(__stl_next_prime(1));
}
//素数表
inline unsigned long __stl_next_prime(unsigned long n)
{
// Note: assumes long is at least 32 bits.
static const int __stl_num_primes = 28;
static const unsigned long __stl_prime_list[__stl_num_primes] =
{
53, 97, 193, 389, 769,
1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433,
1572869, 3145739, 6291469, 12582917, 25165843,
50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457,
1610612741, 3221225473, 4294967291
};
const unsigned long* first = __stl_prime_list;
const unsigned long* last = __stl_prime_list + __stl_num_primes;
const unsigned long* pos = lower_bound(first, last, n);
return pos == last ? *(last - 1) : *pos;
}
//插入
bool Insert(const pair<K,V> kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first))
{
return false;
}
//if(_n*10 / _table.size() >= 7)
if ((double)_n / (double)_tables.size() >= 0.7)
{
size_t newsize = __stl_next_prime(_tables.size() + 1);
HashTable<K, V,Hash> newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newsize);
//遍历旧表重新映射到新表
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
if(_tables[i]._state == EXIST)
newHT.Insert(_tables[i]._kv);
}
_tables.swap(newHT._tables);
}
Hash hs;
size_t hash0 = hs(kv.first) % _tables.size();
size_t i = 1;
size_t hashi = hash0;
while (_tables[hashi]._state == EXIST)
{
//线性探索
hashi = hash0+ i % _tables.size();
++i;
}
_tables[hashi]._kv = kv;
_tables[hashi]._state = EXIST;
_n++;
return true;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
HashData<K, V>* ret = Find(key);
if (ret == nullptr)
{
return false;
}
--_n;
ret->_state = DELETE;
return true;
}
HashData<K, V>* Find(const K& key)
{
Hash hs;
size_t hash0 = hs(key) % _tables.size();
size_t i = 1;
size_t hashi = hash0;
while (_tables[hashi]._state != EMPTY)
{
if (_tables[hashi]._state == EXIST && _tables[hashi]._kv.first == key)
return &_tables[hashi];
hashi = (hash0 + i) % _tables.size();
++i;
}
return nullptr;
}
private:
vector <HashData<K,V>> _tables;
size_t _n = 0;
};
}2、链地址法
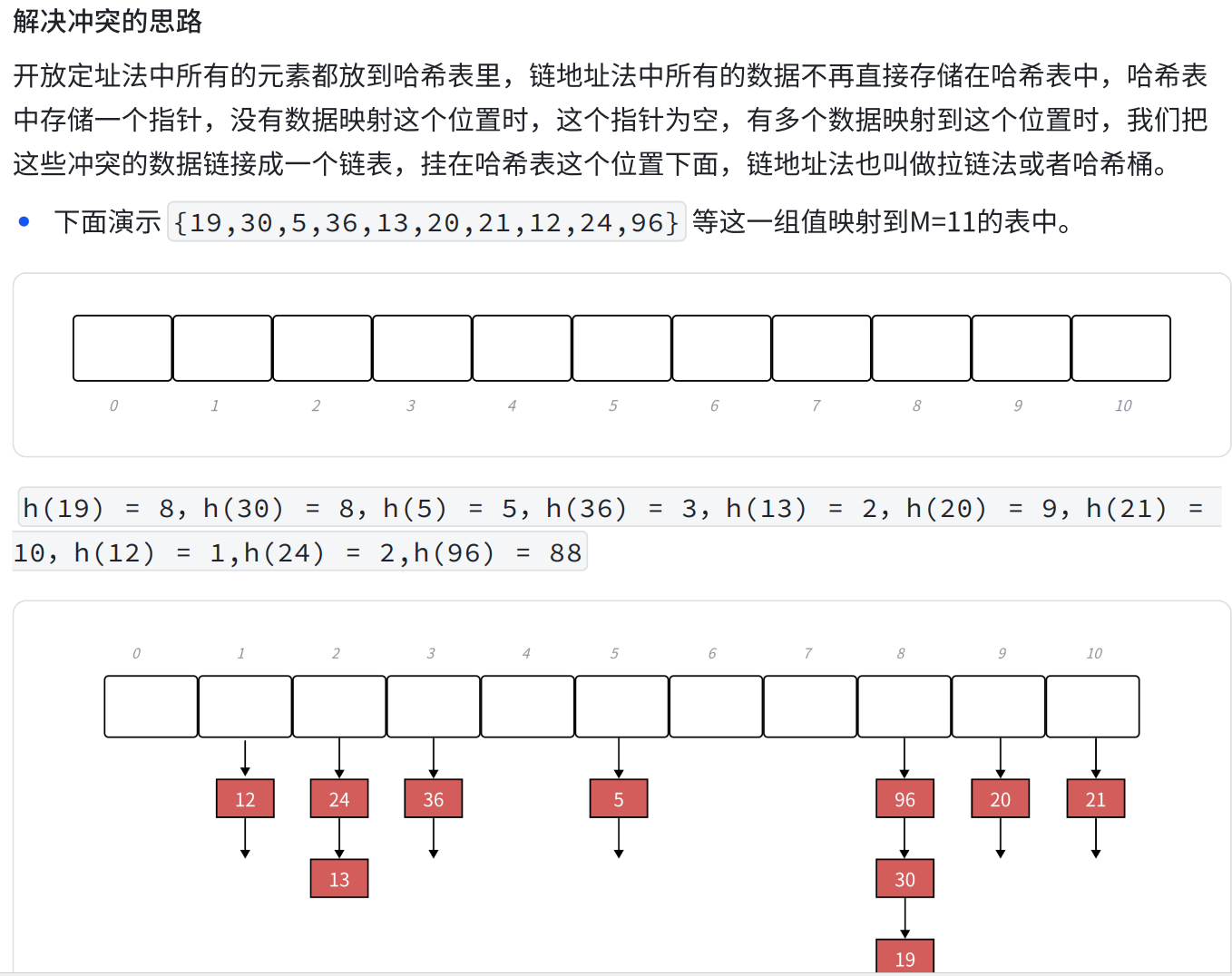
代码实现
cpp
namespace hash_bucket
{
template<class K,class V>
struct HashNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
HashNode<K, V>* _next;
HashNode(const pair<K, V> kv)
:_kv(kv)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
};
template<class K,class V>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<K,V> Node;
public:
HashTable()
{
_tables.resize(__stl_next_prime(1),nullptr);
}
~HashTable()
{
for (int i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
}
//素数表
inline unsigned long __stl_next_prime(unsigned long n)
{
// Note: assumes long is at least 32 bits.
static const int __stl_num_primes = 28;
static const unsigned long __stl_prime_list[__stl_num_primes] =
{
53, 97, 193, 389, 769,
1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433,
1572869, 3145739, 6291469, 12582917, 25165843,
50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457,
1610612741, 3221225473, 4294967291
};
const unsigned long* first = __stl_prime_list;
const unsigned long* last = __stl_prime_list + __stl_num_primes;
const unsigned long* pos = lower_bound(first, last, n);
return pos == last ? *(last - 1) : *pos;
}
bool Insert(const pair<K,V> kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first))
return false;
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
size_t newsize = __stl_next_prime(_tables.size() + 1);
HashTable<K, V> newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newsize, nullptr);
for (int i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t j = cur->_kv.first % newsize;
cur->_next = newHT._tables[j];
newHT._tables[j] = cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
_tables.swap(newHT._tables);
}
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);
size_t i = (kv.first) % _tables.size();
newnode->_next = _tables[i];
_tables[i] = newnode;
++_n;
return true;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
size_t i = key % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
return cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
int hashi = key % _tables.size();
Node* prev = nullptr;
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
if (prev == nullptr)
{
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
--_n;
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return false;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
size_t _n;
};
}五、封装哈希
1、unordered_map的模拟实现
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
namespace lsh
{
template<class K>
struct DefHashF
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
template<>
struct DefHashF<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto e : key)
{
hash *= 31;
hash += e;
}
return hash;
}
};
template<class V>
struct HashBucketNode
{
HashBucketNode(const V& data)
:_data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
V _data;
HashBucketNode<V>* _next;
};
// 为了实现简单,在哈希桶的迭代器类中需要用到hashBucket本身,
template<class K, class V, class KeyOfValue, class HF>
class HashBucket;
// 注意:因为哈希桶在底层是单链表结构,所以哈希桶的迭代器不需要--操作
template <class K, class V, class KeyOfValue, class HF>
struct HBIterator
{
typedef HashBucket<K, V, KeyOfValue, HF> HashBucket;
typedef HashBucketNode<V>* PNode;
typedef HBIterator<K, V, KeyOfValue, HF> Self;
HBIterator(PNode pNode = nullptr, HashBucket* pHt = nullptr)
:_pNode(pNode)
, _pHt(pHt)
{
}
Self& operator++()
{
HF HashFunc;
KeyOfValue KOV;
// 当前迭代器所指节点后还有节点时直接取其下一个节点
if (_pNode->_next)
_pNode = _pNode->_next;
else
{
// 找下一个不空的桶,返回该桶中第一个节点
size_t bucketNo = HashFunc(KOV(_pNode->_data)) % _pHt->bucket_count() + 1;
for (; bucketNo < _pHt->bucket_count(); ++bucketNo)
{
if (_pNode = _pHt->_tables[bucketNo])
break;
}
if (bucketNo == _pHt->bucket_count())
{
_pNode = nullptr;
}
}
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
HF HashFunc;
KeyOfValue KOV;
Self h(_pNode, _pHt);
if (_pNode->_next)
{
_pNode = _pNode->_next;
}
else
{
size_t bucketNo = HashFunc(KOV(_pNode->_data)) % _pHt->bucket_count() + 1;
for (; bucketNo < _pHt->bucket_count(); ++bucketNo)
{
if (_pNode = _pHt->_tables[bucketNo])
break;
}
if (bucketNo == _pHt->bucket_count())
{
_pNode = nullptr;
}
}
return h;
}
V& operator*()
{
return _pNode->_data;
}
V* operator->()
{
return &_pNode->_data;
}
bool operator==(const Self& it) const
{
return it._pNode == _pNode;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it) const
{
return it._pNode != _pNode;
}
PNode _pNode; // 当前迭代器关联的节点
HashBucket* _pHt; // 哈希桶--主要是为了找下一个空桶时候方便
};
template<class K,class V,class KeyOfValue, class HF>
class HashBucket
{
typename typedef HashBucketNode<V> Node;
template <class K, class V, class KeyOfValue, class HF>
friend struct HBIterator;
public:
typename typedef HBIterator<K, V, KeyOfValue, HF> Iterator;
HashBucket()
:_n(0)
{
_tables.resize(1, nullptr);
}
//素数表
inline unsigned long __stl_next_prime(unsigned long n)
{
// Note: assumes long is at least 32 bits.
static const int __stl_num_primes = 28;
static const unsigned long __stl_prime_list[__stl_num_primes] =
{
53, 97, 193, 389, 769,
1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433,
1572869, 3145739, 6291469, 12582917, 25165843,
50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457,
1610612741, 3221225473, 4294967291
};
const unsigned long* first = __stl_prime_list;
const unsigned long* last = __stl_prime_list + __stl_num_primes;
const unsigned long* pos = lower_bound(first, last, n);
return pos == last ? *(last - 1) : *pos;
}
Iterator begin() {
for (int i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
if (_tables[i] != nullptr)
{
return Iterator(_tables[i],this);
}
}
return end();
}
Iterator end() { return Iterator(nullptr, this); }
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// capacity
size_t size()const { return _n; }
bool empty()const { return _n == 0; }
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// lookup
Iterator find(const K& key)
{
HF H;
KeyOfValue KV;
size_t hash0 = H(key) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hash0];
while (cur)
{
if (key == KV(cur->_data))
return Iterator(cur, this);
cur = cur->_next;
}
return Iterator(nullptr, nullptr);
}
size_t count(const K& key)
{
if (find(key)!=end())return 1;
else return 0;
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////
// modify
pair<Iterator, bool> insert(const V& value)
{
HF H;
KeyOfValue KV;
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
size_t newsize = __stl_next_prime(_tables.size() + 1);
HashBucket<K, V, KeyOfValue, HF> newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newsize);
//遍历旧表重新映射到新表
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* next = _tables[i];
while (next != nullptr)
{
Node* cur = next->_next;
size_t hash0 = H(KV(next->_data)) % newHT._tables.size();
next->_next = newHT._tables[hash0];
newHT._tables[hash0] = next;
next = cur;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
_tables.swap(newHT._tables);
}
Iterator it = find(KV(value));
if(it != end())return {it,false};
Node* newnode = new Node(value);
size_t hash0 = H(KV(value)) % _tables.size();
newnode->_next = _tables[hash0];
_tables[hash0] = newnode;
_n++;
return { Iterator(newnode,this),true };
}
Iterator erase(Iterator position)
{
Iterator it = position;
++it;
HF H;
KeyOfValue KV;
size_t hash0 = H(KV(position._pNode->_data)) % position._pHt->_tables.size();
if (position._pHt->_tables[hash0] == position._pNode)
{
position._pHt->_tables[hash0] = position._pNode->_next;
}
else
{
Node* cur = position._pHt->_tables[hash0];
Node* next = cur->_next;
while (next != position._pNode)
{
cur = next;
next = next->_next;
}
cur->_next = next->_next;
}
position._pHt->_n--;
delete position._pNode;
return it;
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// bucket
size_t bucket_count()
{
return _tables.size();
}
size_t bucket_size(const K& key)
{
HF H;
size_t cnt = 0;
size_t hash0 = H(key) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hash0];
while (cur)
{
++cnt;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return cnt;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
size_t _n;
};
// unordered_map中存储的是pair<K, V>的键值对,K为key的类型,V为value的类型,HF哈希函数类型
// unordered_map在实现时,只需将hashbucket中的接口重新封装即可
template<class K, class V, class HF = DefHashF<K>>
class unordered_map
{
struct KeyOfValue
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& data)
{
return data.first;
}
};
typedef HashBucket<K, pair<K, V>, KeyOfValue, HF> HT;
public:
typename typedef HT::Iterator iterator;
public:
unordered_map() : _ht()
{}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////
iterator begin() { return _ht.begin(); }
iterator end() { return _ht.end(); }
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// capacity
size_t size()const { return _ht.size(); }
bool empty()const { return _ht.empty(); }
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Acess
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _ht.insert(pair<K, V>(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
const V& operator[](const K& key)const
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _ht.insert(pair<K, V>(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// lookup
iterator find(const K& key) { return _ht.find(key); }
size_t count(const K& key) { return _ht.count(key); }
/////////////////////////////////////////////////
// modify
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& valye)
{
return _ht.insert(valye);
}
iterator erase(iterator position)
{
return _ht.erase(position);
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// bucket
size_t bucket_count() { return _ht.bucket_count(); }
size_t bucket_size(const K& key) { return _ht.bucket_size(key); }
private:
HT _ht;
};
}2、unordered_set的模拟实现
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
namespace lsh
{
template<class V>
struct HashBucketNode
{
HashBucketNode(const V& data)
:_data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
{}
V _data;
HashBucketNode<V>* _next;
};
// 为了实现简单,在哈希桶的迭代器类中需要用到hashBucket本身,
template<class K, class V, class KeyOfValue, class HF>
class HashBucket;
// 注意:因为哈希桶在底层是单链表结构,所以哈希桶的迭代器不需要--操作
template <class K, class V, class KeyOfValue, class HF>
struct HBIterator
{
typedef HashBucket<K, V, KeyOfValue, HF> HashBucket;
typedef HashBucketNode<V>* PNode;
typedef HBIterator<K, V, KeyOfValue, HF> Self;
HBIterator(PNode pNode = nullptr, HashBucket* pHt = nullptr)
{
_pNode = pNode;
_pHt = pHt;
}
Self& operator++()
{
KeyOfValue KV;
HF HashFunc;
// 当前迭代器所指节点后还有节点时直接取其下一个节点
if (_pNode->_next)
_pNode = _pNode->_next;
else
{
// 找下一个不空的桶,返回该桶中第一个节点
size_t bucketNo = HashFunc(KV(_pNode->_data))%_pHt->_tables.size() + 1;
for (; bucketNo < _pHt->BucketCount(); ++bucketNo)
{
if (_pNode = _pHt->_tables[bucketNo])
break;
}
if (bucketNo == _pHt->BucketCount())
{
_pNode = nullptr;
}
}
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self t = *this;
KeyOfValue KV;
HF HashFunc;
if (_pNode->_next)
_pNode = _pNode->_next;
else
{
// 找下一个不空的桶,返回该桶中第一个节点
size_t bucketNo = HashFunc(KV(_pNode->_data)) % _pHt->_tables.size() + 1;
for (; bucketNo < _pHt->BucketCount(); ++bucketNo)
{
if (_pNode = _pHt->_tables[bucketNo])
break;
}
if (bucketNo == _pHt->BucketCount())
{
_pNode = nullptr;
}
}
return t;
}
V& operator*()
{
return _pNode->_data;
}
V* operator->()
{
return &_pNode->_data;
}
bool operator==(const Self& it) const
{
return _pNode == it._pNode;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& it) const
{
return _pNode != it._pNode;
}
PNode _pNode; // 当前迭代器关联的节点
HashBucket* _pHt; // 哈希桶--主要是为了找下一个空桶时候方便
};
// unordered_set中存储的是K类型,HF哈希函数类型
template<class K>
struct DefHashF
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
template<>
struct DefHashF<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto& e : key)
{
hash *= 31;
hash += e;
}
return hash;
}
};
template<class K, class V, class KeyOfValue, class HF>
class HashBucket
{
typedef HashBucketNode<V> Node;
template <class K, class V, class KeyOfValue, class HF>
friend struct HBIterator;
public:
typedef HBIterator<K, V, KeyOfValue, HF> Iterator;
HashBucket()
:_n(0)
{
_tables.resize(1,nullptr);
}
Iterator begin()
{
Node* r = nullptr;
for (int i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
if (_tables[i] != nullptr)
{
r = _tables[i];
break;
}
}
return Iterator({ r,this });
}
Iterator end() { return Iterator({nullptr,this}); }
size_t size()const { return _n; }
bool empty()const { return _n == 0; }
Iterator Find(const K& key)
{
HF H;
KeyOfValue KV;
size_t hash = H(key)%_tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hash];
while (cur)
{
if (key == KV(cur->_data))return Iterator({ cur,this });
cur = cur->_next;
}
return end();
}
size_t Count(const K& key) { return Find(key) != end(); }
//素数表
inline unsigned long __stl_next_prime(unsigned long n)
{
// Note: assumes long is at least 32 bits.
static const int __stl_num_primes = 28;
static const unsigned long __stl_prime_list[__stl_num_primes] =
{
53, 97, 193, 389, 769,
1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433,
1572869, 3145739, 6291469, 12582917, 25165843,
50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457,
1610612741, 3221225473, 4294967291
};
const unsigned long* first = __stl_prime_list;
const unsigned long* last = __stl_prime_list + __stl_num_primes;
const unsigned long* pos = lower_bound(first, last, n);
return pos == last ? *(last - 1) : *pos;
}
pair<Iterator, bool> Insert(const V& value)
{
HF H;
KeyOfValue KV;
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
size_t newsize = __stl_next_prime(_n + 1);
HashBucket<K, V, KeyOfValue, HF> newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newsize);
for (int i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t hash = H(KV(cur->_data)) % newsize;
cur->_next = newHT._tables[hash];
newHT._tables[hash] = cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
_tables.swap(newHT._tables);
}
Iterator e = Find(KV(value));
if (e != end())return { e,false };
size_t hash = H(KV(value)) % _tables.size();
Node* newnode = new Node(value);
newnode->_next = _tables[hash];
_tables[hash] = newnode;
_n++;
return { Iterator(newnode,this),true };
}
Iterator Erase(Iterator position)
{
Iterator it = position;
it++;
HF H;
KeyOfValue KV;
size_t hash = H(KV(position._pNode->_data)) % _tables.size();
if (position._pNode == _tables[hash])
{
_tables[hash] = _tables[hash]->_next;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _tables[hash];
Node* next = cur->_next;
while (next != position._pNode)
{
cur = next;
next = cur->_next;
}
cur->_next = next->_next;
}
delete position._pNode;
_n--;
return it;
}
size_t BucketCount() { return _tables.size(); }
size_t BucketSize(const K& key)
{
HF H;
size_t cnt = 0;
size_t hash = H(key) % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hash];
while (cur)
{
cnt++;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return cnt;
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
size_t _n;
};
// unordered_set在实现时,只需将hashbucket中的接口重新封装即可
template<class K, class HF = DefHashF<K>>
class unordered_set
{
// 通过key获取value的操作
struct KeyOfValue
{
const K& operator()(const K& data)
{
return data;
}
};
typedef HashBucket<K, K, KeyOfValue, HF> HT;
public:
typename typedef HT::Iterator iterator;
public:
unordered_set() : _ht()
{}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////
iterator begin() { return _ht.begin(); }
iterator end() { return _ht.end(); }
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// capacity
size_t size()const { return _ht.size(); }
bool empty()const { return _ht.empty(); }
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// lookup
iterator find(const K& key) { return _ht.Find(key); }
size_t count(const K& key) { return _ht.Count(key); }
/////////////////////////////////////////////////
// modify
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& value)
{
return _ht.Insert(value);
}
iterator erase(iterator position)
{
return _ht.Erase(position);
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// bucket
size_t bucket_count() { return _ht.BucketCount(); }
size_t bucket_size(const K& key) { return _ht.BucketSize(key); }
private:
HT _ht;
};
}