文章目录
- 一、同步异步调用介绍
-
- [(1) 同步](#(1) 同步)
- [(2) 异步](#(2) 异步)
- 二、RabbitMQ基本介绍
- 三、快速入门
- 四、虚拟主机(数据隔离)
- 五、java客户端实战
- 六、WorkQueues模型
-
-
-
- [1. 测试一:一个队列多个消费者同时消费(Work模式)](#1. 测试一:一个队列多个消费者同时消费(Work模式))
- [2. 测试二:一个队列多个消费者同时消费(Work模式prefetch版本)](#2. 测试二:一个队列多个消费者同时消费(Work模式prefetch版本))
- [3. 总结](#3. 总结)
-
-
- 七、交换机类型(Exchange)
- 八、Fanout类型交换机
-
-
- [1. Fanout交换机案例实现](#1. Fanout交换机案例实现)
- [2. 总结](#2. 总结)
-
- 九、Direct类型交换机
-
-
- [1. Direct交换机案例实现](#1. Direct交换机案例实现)
- [2. 总结](#2. 总结)
-
- 十、Topic交换机
-
-
- [1. Topic交换机案例实现](#1. Topic交换机案例实现)
- [2. 总结](#2. 总结)
-
- 十一、声明队列和交换机
-
- 编码方式声明
- 基于注解声明
-
-
- (1)Fanout交换机
- (2)Direct交换机
- [(3) Topic交换机](#(3) Topic交换机)
-
- 十二、消息转换器
-
-
- [( 1 )默认转换器测试](#( 1 )默认转换器测试)
- [( 2 )配置JSON转换器](#( 2 )配置JSON转换器)
-
一、同步异步调用介绍
(1) 同步
latex
解读:
案例:支付服务》〉》〉》扣余额(需要等待结果)
扩展功能:
支付成功发短信
增加积分
优点:
可以立即得到结果的响应
缺点:
拓展性差(每增加一个功能都要修改之前的代码)
性能下降(同步需要等待结果,没有得到结果就需要一直等待,占用线程)
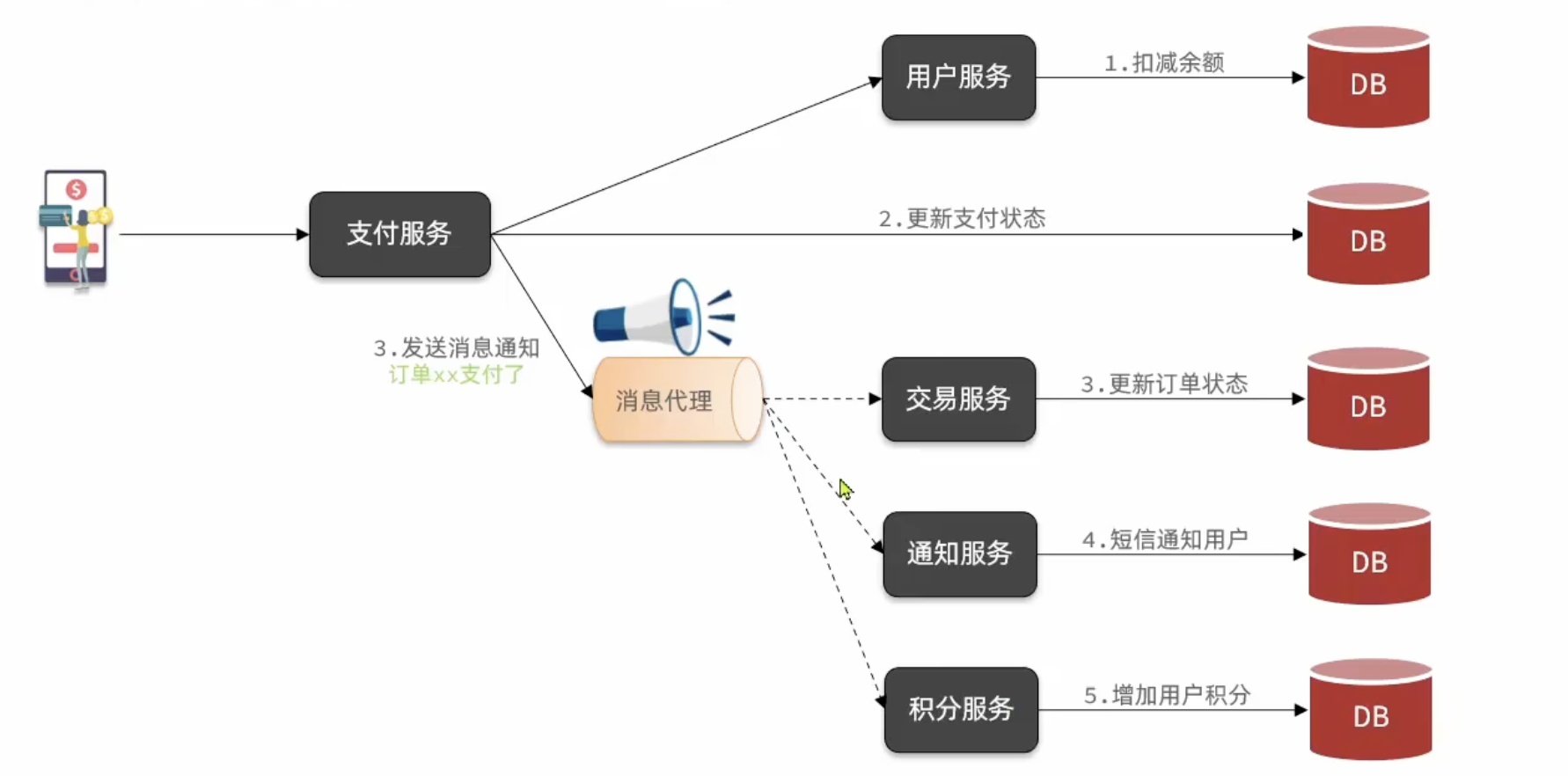
级联失败问题(在同步中的一个环节出现问题,可能后续的服务都出现问题)(2) 异步
消息代理可以将消息同时发送给交易、通知、积分服务
shell
综上,异步调用的优势包括:
● 耦合度更低
● 性能更好
● 业务拓展性强
● 故障隔离,避免级联失败
当然,异步通信也并非完美无缺,它存在下列缺点:
● 完全依赖于Broker的可靠性、安全性和性能
● 架构复杂,后期维护和调试麻烦二、RabbitMQ基本介绍
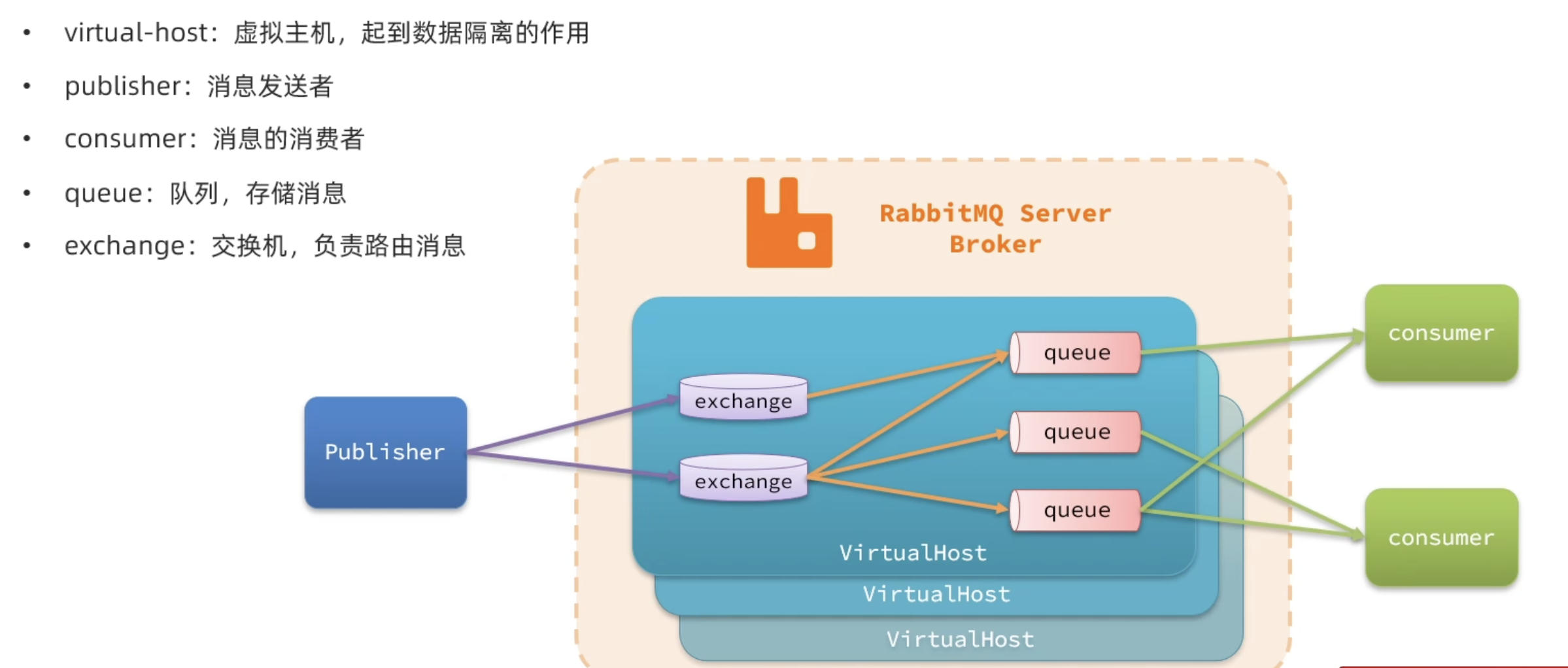
RabbitMQ是基于Erlang语言开发的开源消息通信中间件,官网地址:
Messaging that just works --- RabbitMQ接下来,我们就学习它的基本概念和基础用法。

三、快速入门
快速入门
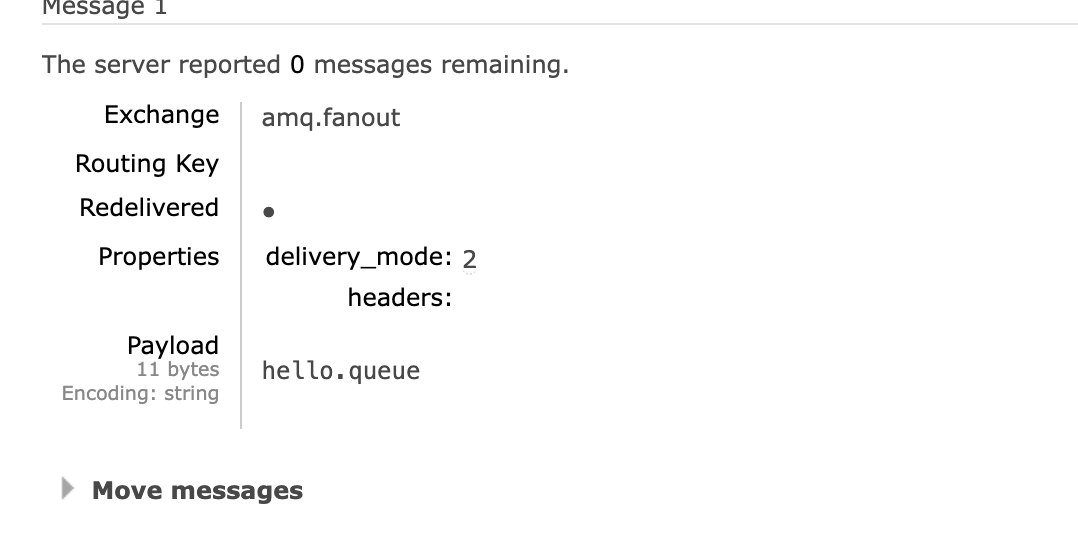
需求:在rabbitmq的控制台完成下列操作:
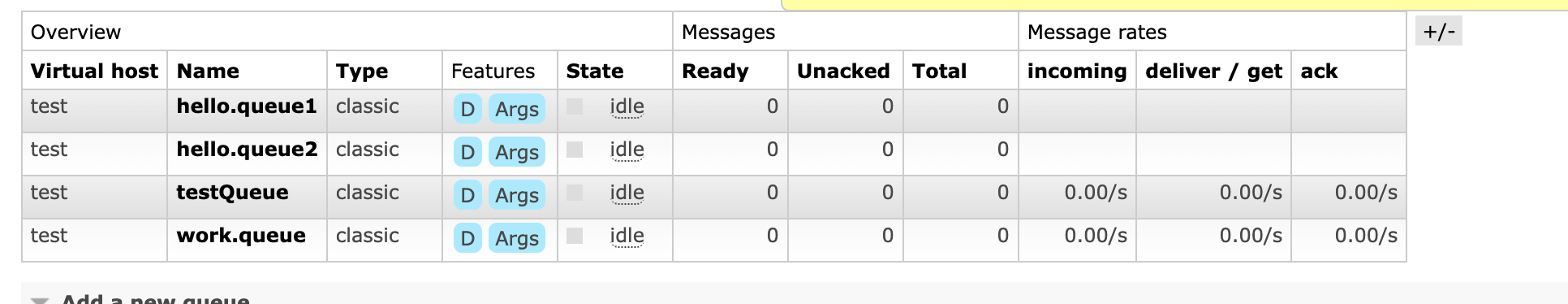
- 新建队列hello.queue1和hello.queue2 - 向默认的amp.fanout交换机发送一条消息 - 查看消息是否到达hello.queue1和hello.queue2
- 新建队列hello.queue1和hello.queue2
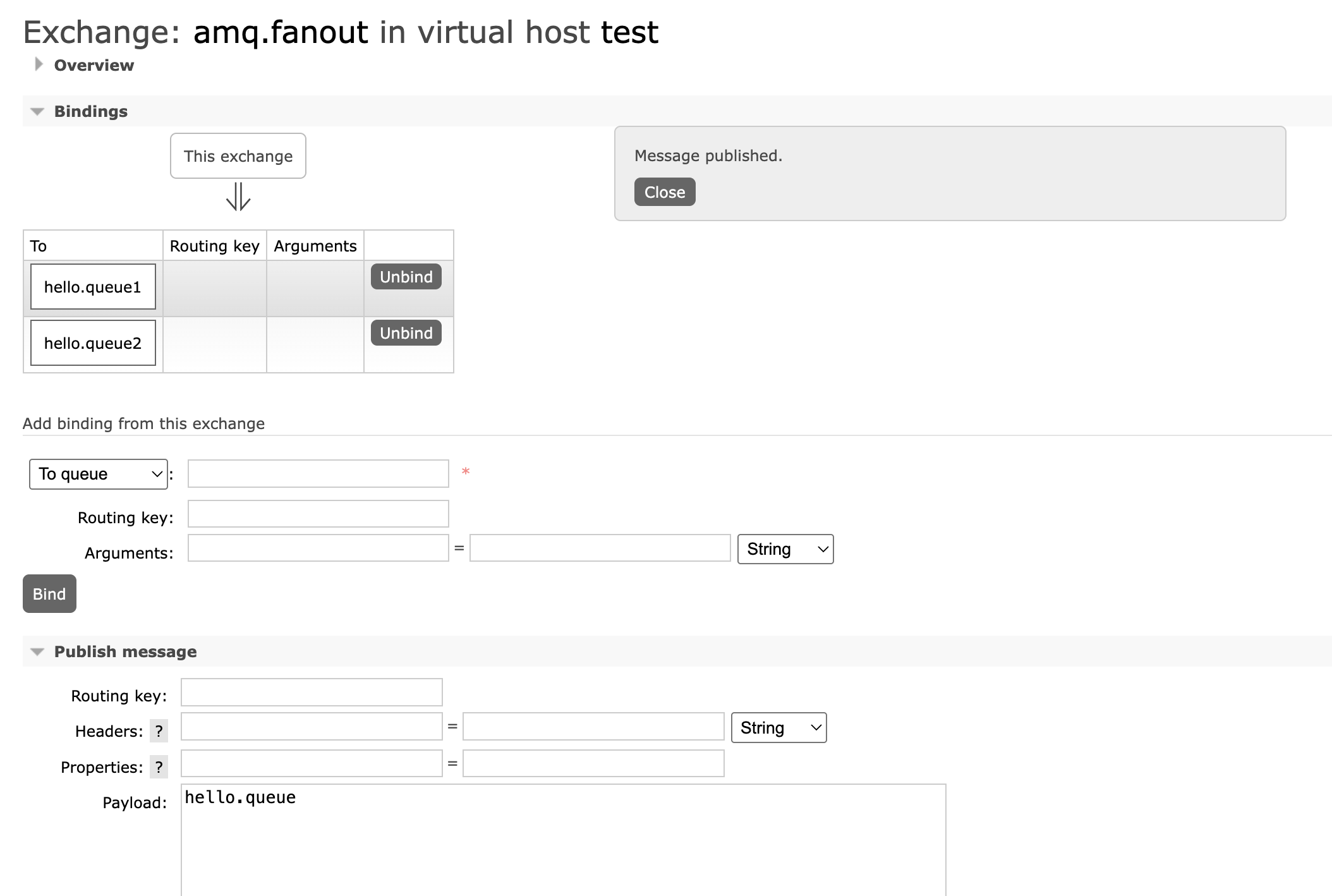
- 向默认的amp.fanout交换机发送一条消息
- 查看消息是否到达hello.queue1和hello.queue2
- 已经接收到了消息

四、虚拟主机(数据隔离)
virtual host的隔离特性,将不同项目隔离
五、java客户端实战
(1)名词解释:AMQT
由于
RabbitMQ采用了AMQP协议,因此它具备跨语言的特性。任何语言只要遵循AMQP协议收发消息,都可以与RabbitMQ交互。并且RabbitMQ官方也提供了各种不同语言的客户端。但是,RabbitMQ官方提供的Java客户端编码相对复杂,一般生产环境下我们更多会结合Spring来使用。而Spring的官方刚好基于RabbitMQ提供了这样一套消息收发的模板工具:SpringAMQP。并且还基于SpringBoot对其实现了自动装配,使用起来非常方便。
SpringAmqp的官方地址:
Spring AMQP
SpringAMQP提供了三个功能:
- 自动声明队列、交换机及其绑定关系
- 基于注解的监听器模式,异步接收消息
- 封装了RabbitTemplate工具,用于发送消息
(2)快速入门:通过队列直接发送接收消息
流程图:

springamqp如何收发消息?
实现流程:
- 引入spring-boot-starter-amgp依赖
- 创建publish模块和consumer模块
- 配置rabbitmg服务端信息
- 利用rabbittemplate发送消息
- 利用@rabbitlistener注解声明要监听的队列,监听消息
- 引入spring-boot-starter-amgp依赖
xml
<!-- rabbitmq核心依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>- 配置rabbitmg服务端信息
yaml
# bpulish 和consumer模块的配置一致
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: localhost # 主机
port: 5672 # 主机端口
username: test # 用户
password: test # 密码
virtual-host: test # 虚拟主机- 利用rabbittemplate发送消息(publish模块)
java
package cn.varin.rabbitmq.publish;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
@SpringBootTest
class PublishTestTest {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
/**
* 直接向队列中发送消息
testQueue为队列名称
*/
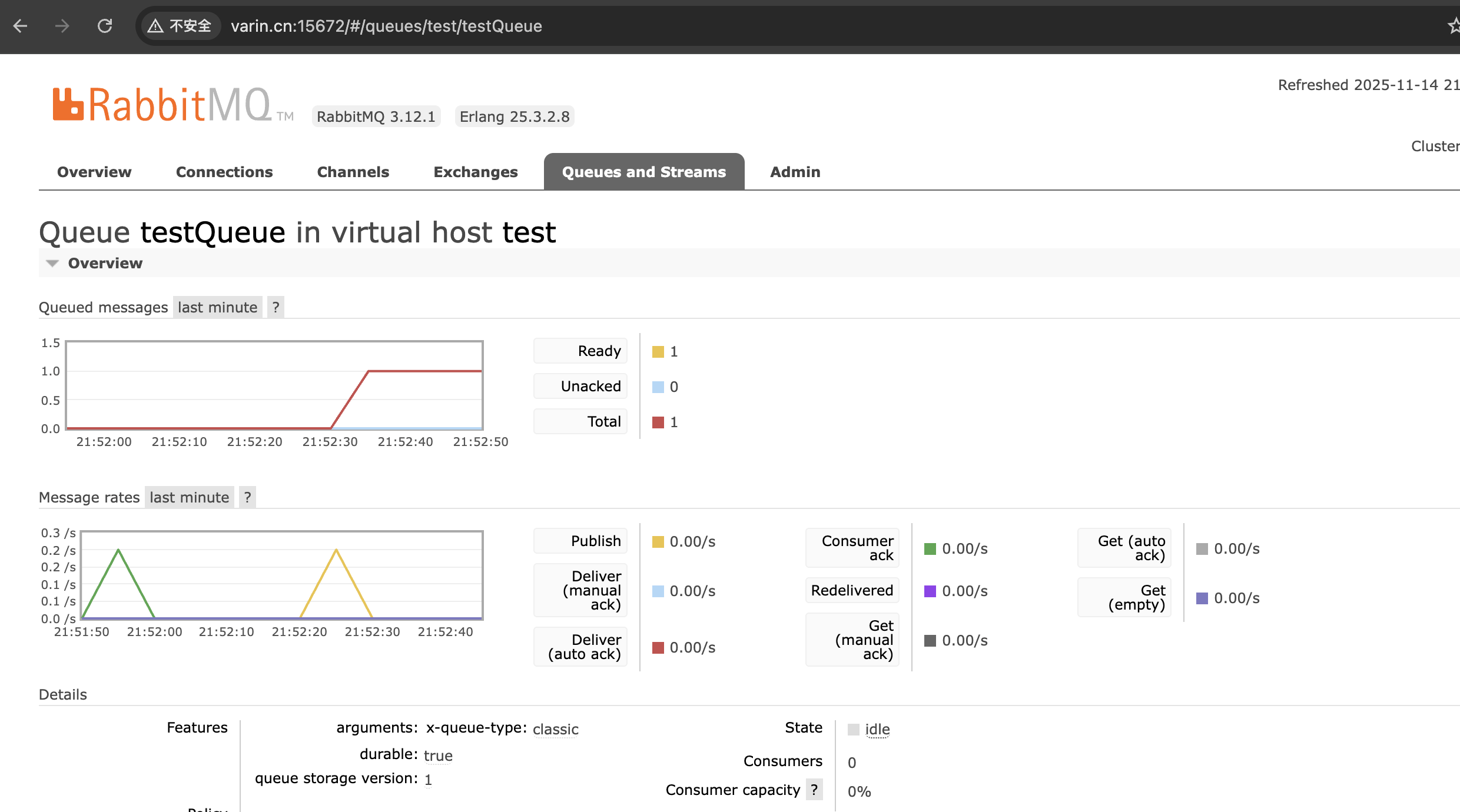
@Test
void send() {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("testQueue", "hello");
}
}
- 利用@rabbitlistener注解声明要监听的队列,监听消息(consumer模块)
java
package cn.varin.rabbitmq.consumer;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Slf4j
@Component
public class QueueConsumer {
/**
* 直接接收队列的消息
* @param message
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = {"testQueue"})
public void getMessage(String message) {
log.info("message:{}", message);
}
}
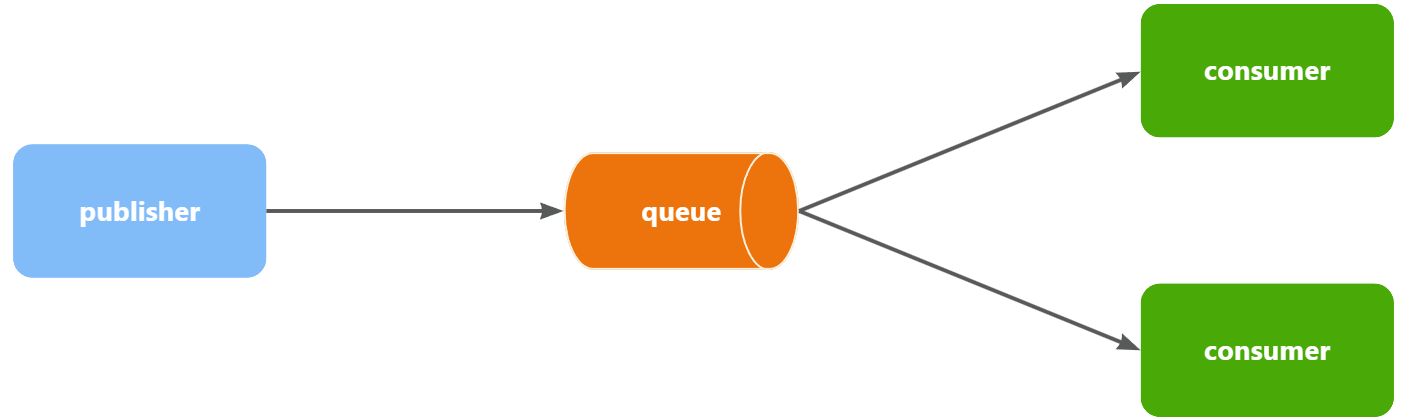
六、WorkQueues模型
解释:WorkQueues模型就是在一个队列绑定了多个消费者
解决问题:当生产者生产过多的消息,导致消息堆积的时候,多个消费者可以摊消息,从而提供消息的处理速度。
缺点:在默认情况下每个consumer消费消息时,是进行轮询等待的(你一个,我一个,平均分),这样的话如果某一consumer性能比较差的话,就会增加处理消息的时间。
优化:添加prefetch配置,将他设置为1
解释:表示每次只能获取一条消息,处理完成才能获取下一个消息
1. 测试一:一个队列多个消费者同时消费(Work模式)
- 建立simple.work队列

- 发送消息
java
@Test
void workQueueTest() throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("simple.work", "消息条数"+i);
}
}
- 接收消息(三个consumer)
java
/**
* 模拟work模型
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.work")
public void getWorkMessage(String message) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("message1:{}", message);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.work")
public void getWorkMessage2(String message) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("message2:{}", message);
}
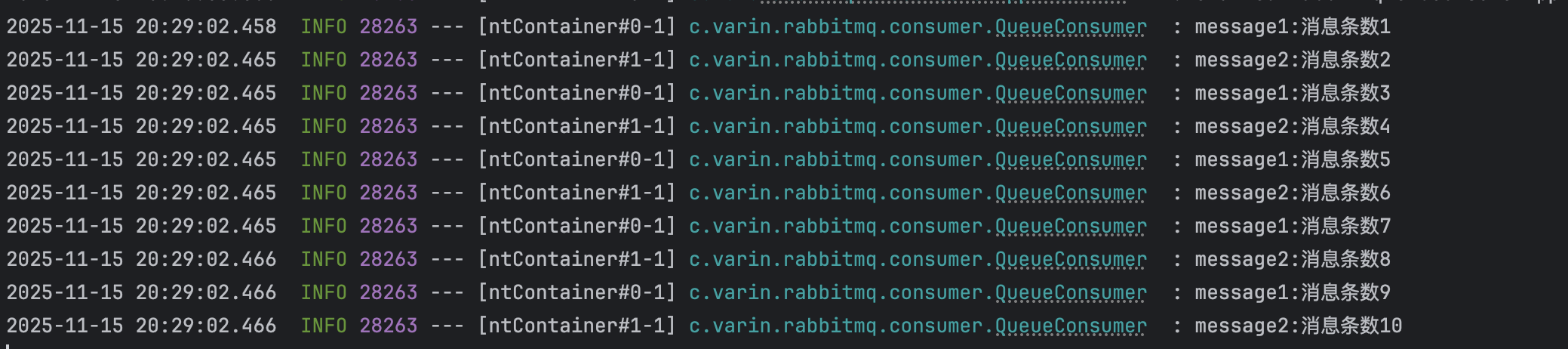
- 效果
2. 测试二:一个队列多个消费者同时消费(Work模式prefetch版本)
- consumer模块添加配置
yaml
server:
port: 9999
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: varin.cn # 主机
port: 5672 # 主机端口
username: test # 用户
password: test # 密码
virtual-host: test # 虚拟主机
listener:
simple:
prefetch: 1 #每次只能获取一条消息,处理完成才能获取下一个消息- 添加consumer延时时间(模拟性能不同)
java
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.work")
public void getWorkMessage(String message) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("message1:{}", message);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.work")
public void getWorkMessage2(String message) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("message2:{}", message);
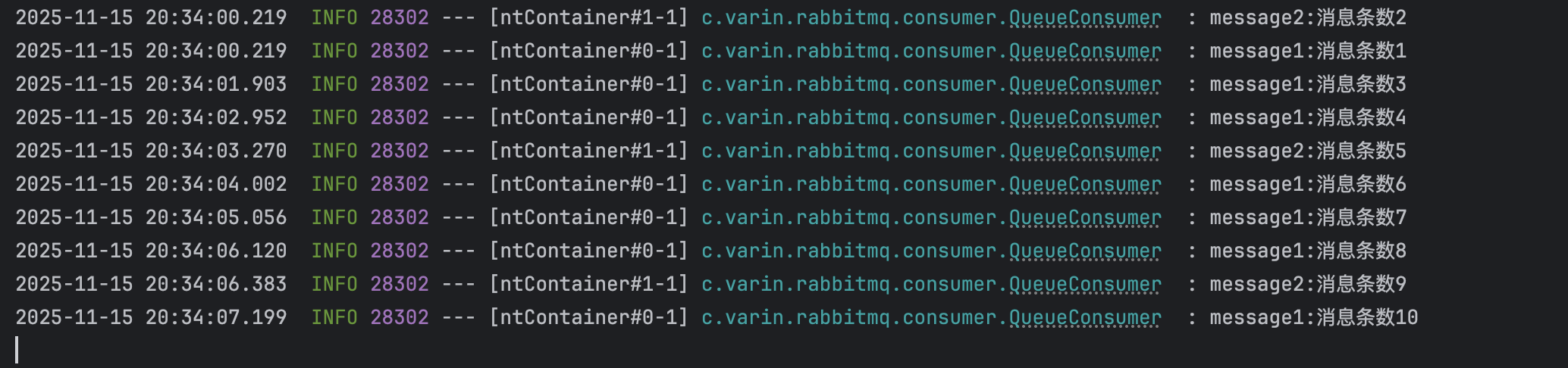
Thread.sleep(3000);- 测试效果
结果中可以看出:
message1消费了7条消息
message2消费了3条消息
3. 总结
Work模型的使用:
- 多个消费者绑定到一个队列,同一条消息只会被一个消费者处理
- 通过设置prefetch来控制消费者预取的消息数量
七、交换机类型(Exchange)
Exchange(交换机)只负责转发消息,不具备存储消息的能力,因此如果没有任何队列与Exchange绑定,或者没有符合路由规则的队列,那么消息会丢失!
交换机的类型有四种:
- Fanout:广播,将消息交给所有绑定到交换机的队列。我们最早在控制台使用的正是Fanout交换机
- Direct:订阅,基于RoutingKey(路由key)发送给订阅了消息的队列
- Topic:通配符订阅,与Direct类似,只不过RoutingKey可以使用通配符
- Headers:头匹配,基于MQ的消息头匹配,用的较少。
八、Fanout类型交换机
- 作用:消息发送到该类型的交换机,它会将消息通过广播的方式转发的它绑定的队列
1. Fanout交换机案例实现
- 实现流程图
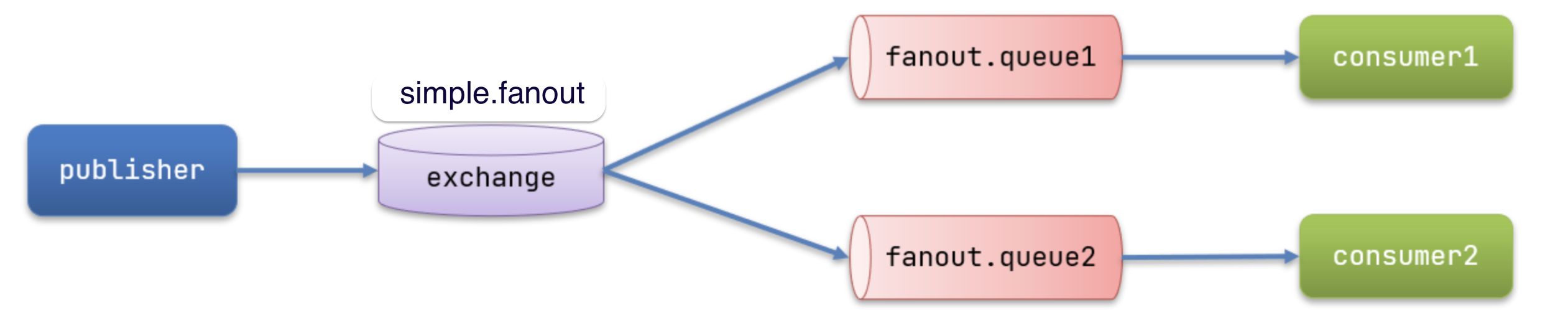
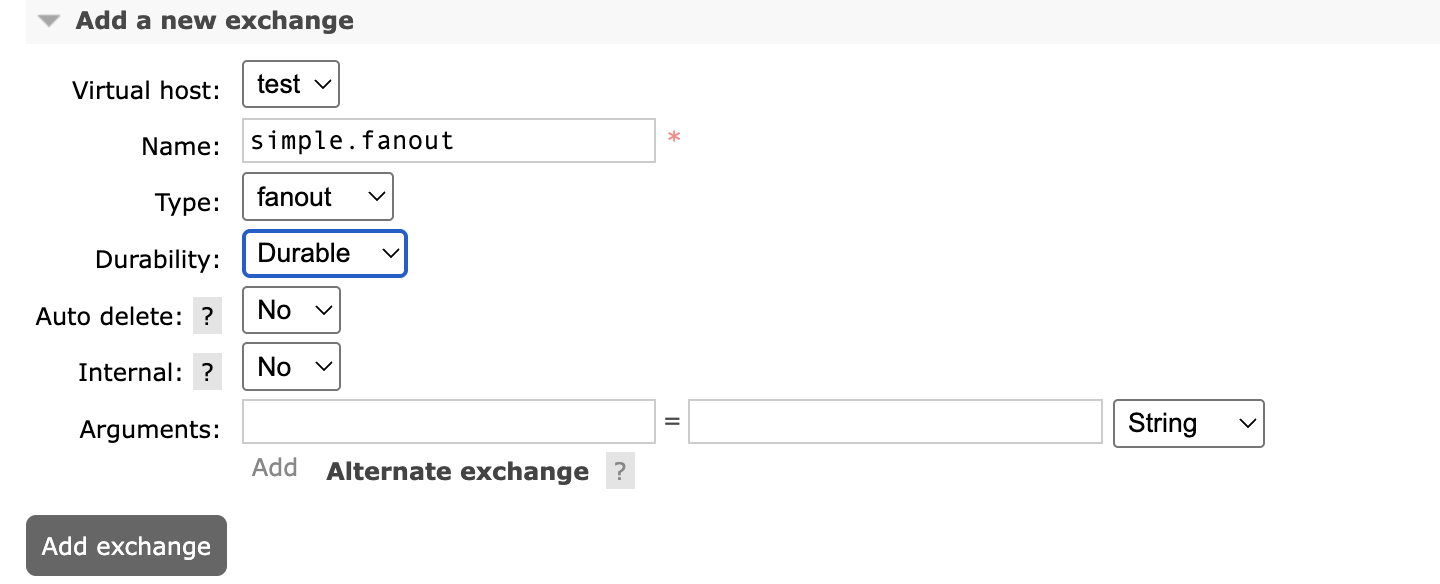
- 创建一个名为
simple.fanout的交换机,类型是Fanout

- 创建两个队列
fanout.queue1和fanout.queue2,绑定到交换机simple.fanout- 创建

- 绑定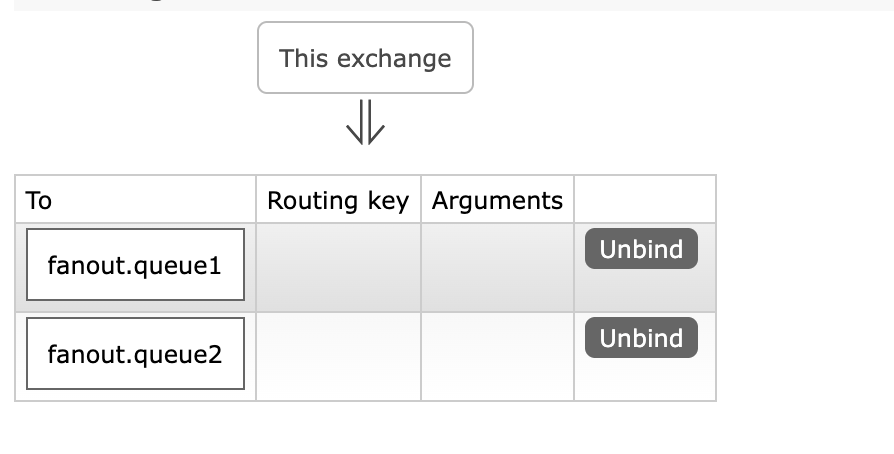
- publish发送
java
@Test
void fanoutExchangeToQueueTest() throws InterruptedException {
/**
* 参数一:交换机名称
* 参数三:消息内容
*/
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("simple.fanout","","fanoutExchangeToQueueTest");
}- consumer接收
java
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue1")
public void getFanoutMessage1(String message) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("fanout.queue1,message:{}", message);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue2")
public void getFanoutMessage2(String message) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("fanout.queue2,message:{}", message);
}- 结果

2. 总结
交换机的作用是什么?
- 接收publisher发送的消息
- 将消息按照规则路由到与之绑定的队列
- 不能缓存消息,路由失败,消息丢失
- FanoutExchange的会将消息路由到每个绑定的队列
九、Direct类型交换机
作用:通过
RoutingKey与队列进行绑定,根据消息的Routing Key进行判断,只有队列的Routingkey与消息的Routing key完全一致,才会接收到消息
1. Direct交换机案例实现
- 需求流程图:
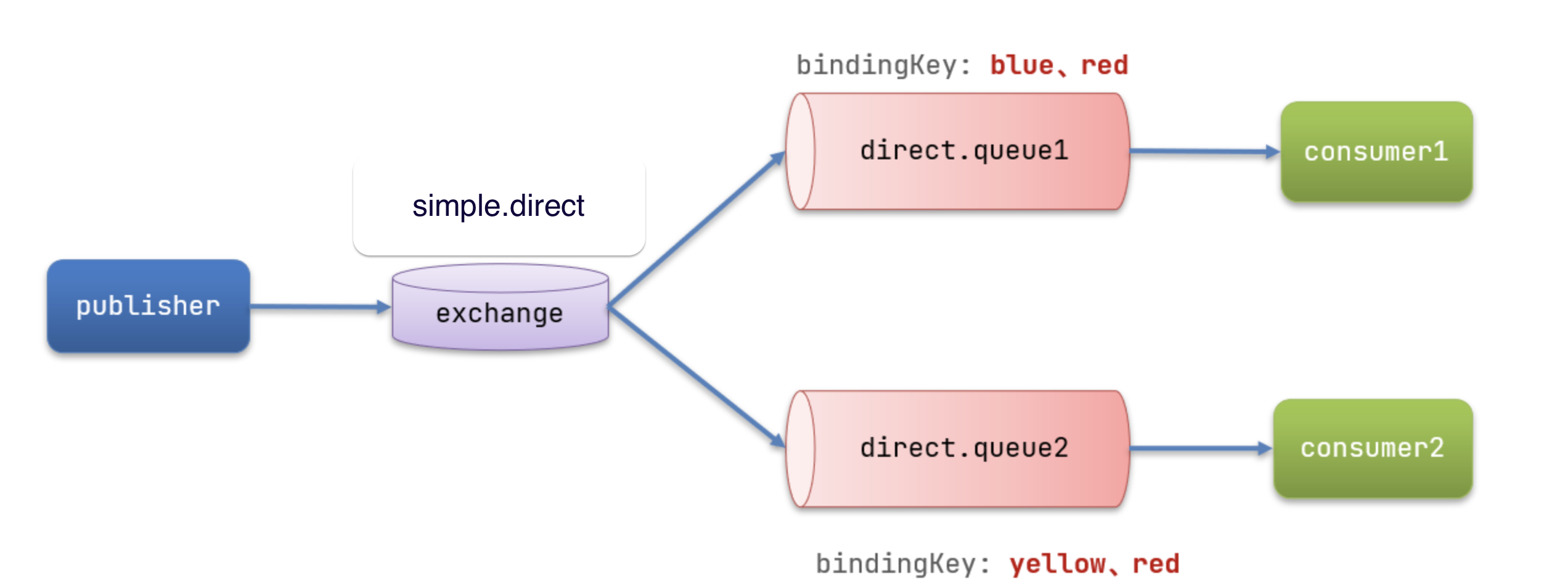
- 声明一个名为
simple.direct的交换机

- 声明队列
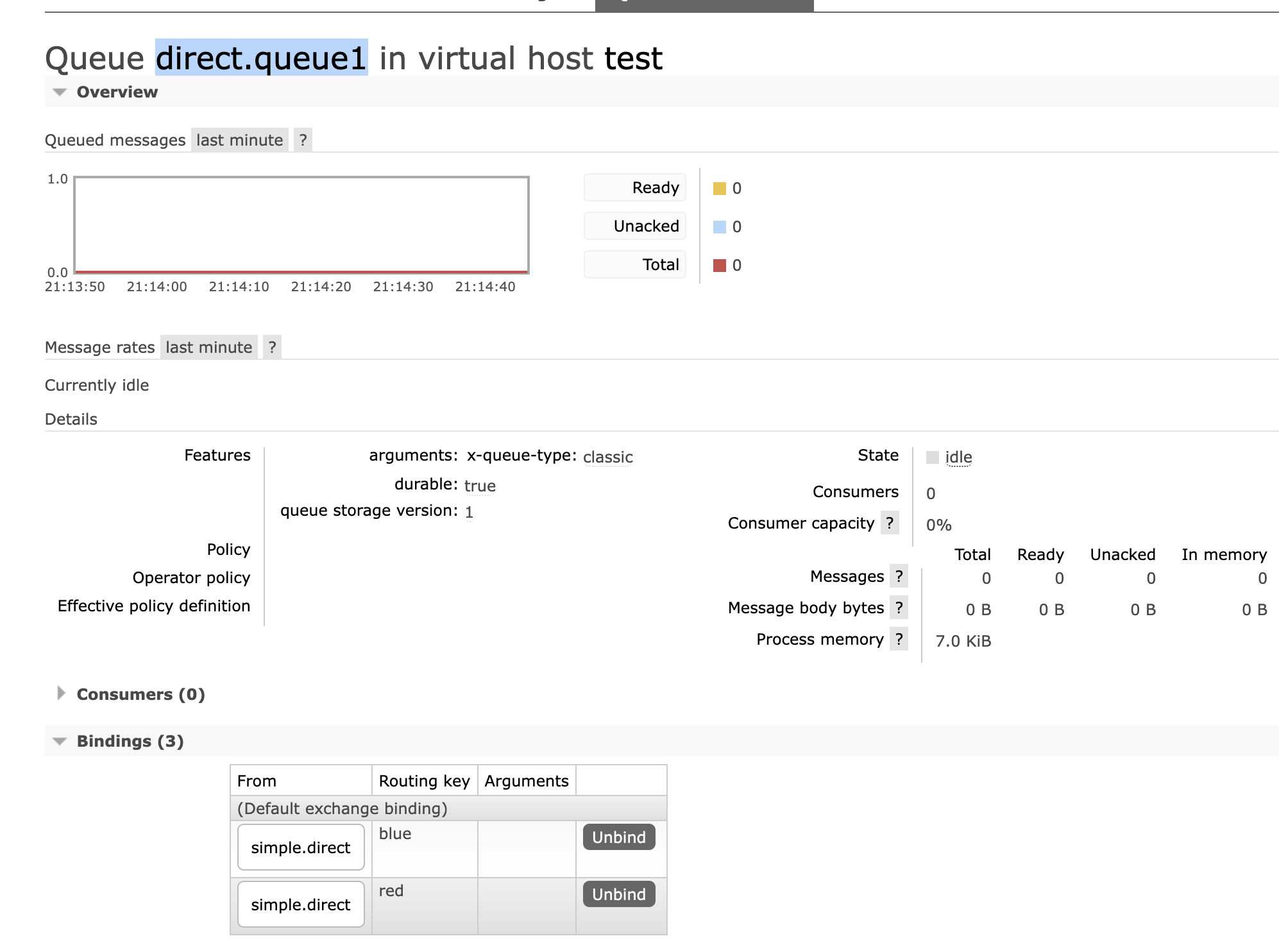
direct.queue1,绑定simple.direct,bindingKey为blud和red
- 声明队列
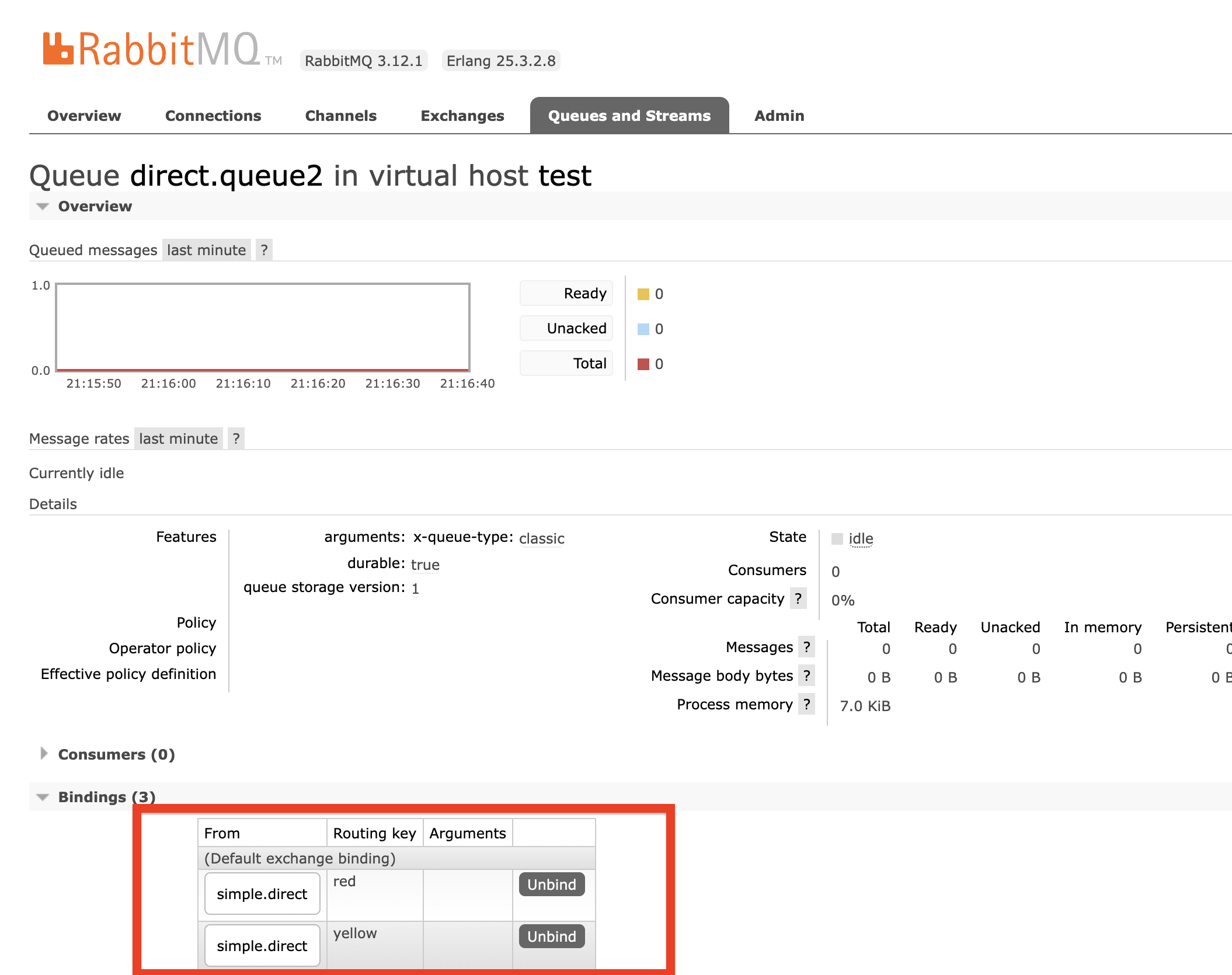
direct.queue2,绑定simple.direct,bindingKey为yellow和red
- 在publisher中编写测试方法,向
simple.direct发送消息
java
@Test
void directExchangeToQueueTest() throws InterruptedException {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("simple.direct","red","red");
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("simple.direct","yellow","yellow");
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("simple.direct","blue","blue");
}- 在
consumer服务中,编写两个消费者方法,分别监听direct.queue1和direct.queue2
java
/**
* direct交换机
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = "direct.queue1")
public void getDirectMessage1(String message) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("direct.queue1,message:{}", message);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "direct.queue2")
public void getDirectMessage2(String message) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("direct.queue2,message:{}", message);
}- 效果图

2. 总结
描述下Direct交换机与Fanout交换机的差异?
- Fanout交换机将消息路由给每一个与之绑定的队列
- Direct交换机根据RoutingKey判断路由给哪个队列
- 如果多个队列具有相同的RoutingKey,则与Fanout功能类似
十、Topic交换机
作用:topic交换机和direct交换机使用方法一致,不同点就是topic交换机在设置路由名称时,可以使用通配符代替。
通配符:
#:匹配一个或多个词*:匹配不多不少恰好1个词
1. Topic交换机案例实现
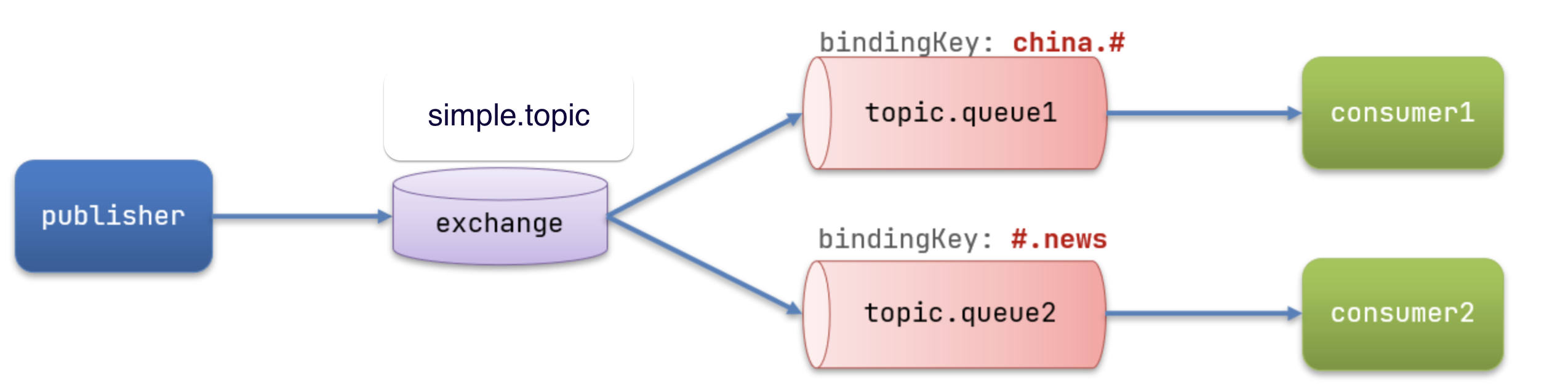
解释:
topic.queue1:绑定的是china.#,凡是以china.开头的routing key都会被匹配到,包括:china.newschina.weather
topic.queue2:绑定的是#.news,凡是以.news结尾的routing key都会被匹配。包括:china.newsjapan.news
- 声明一个名为
simple.topic的交换机

- 声明队列
topic.queue1,绑定china.#
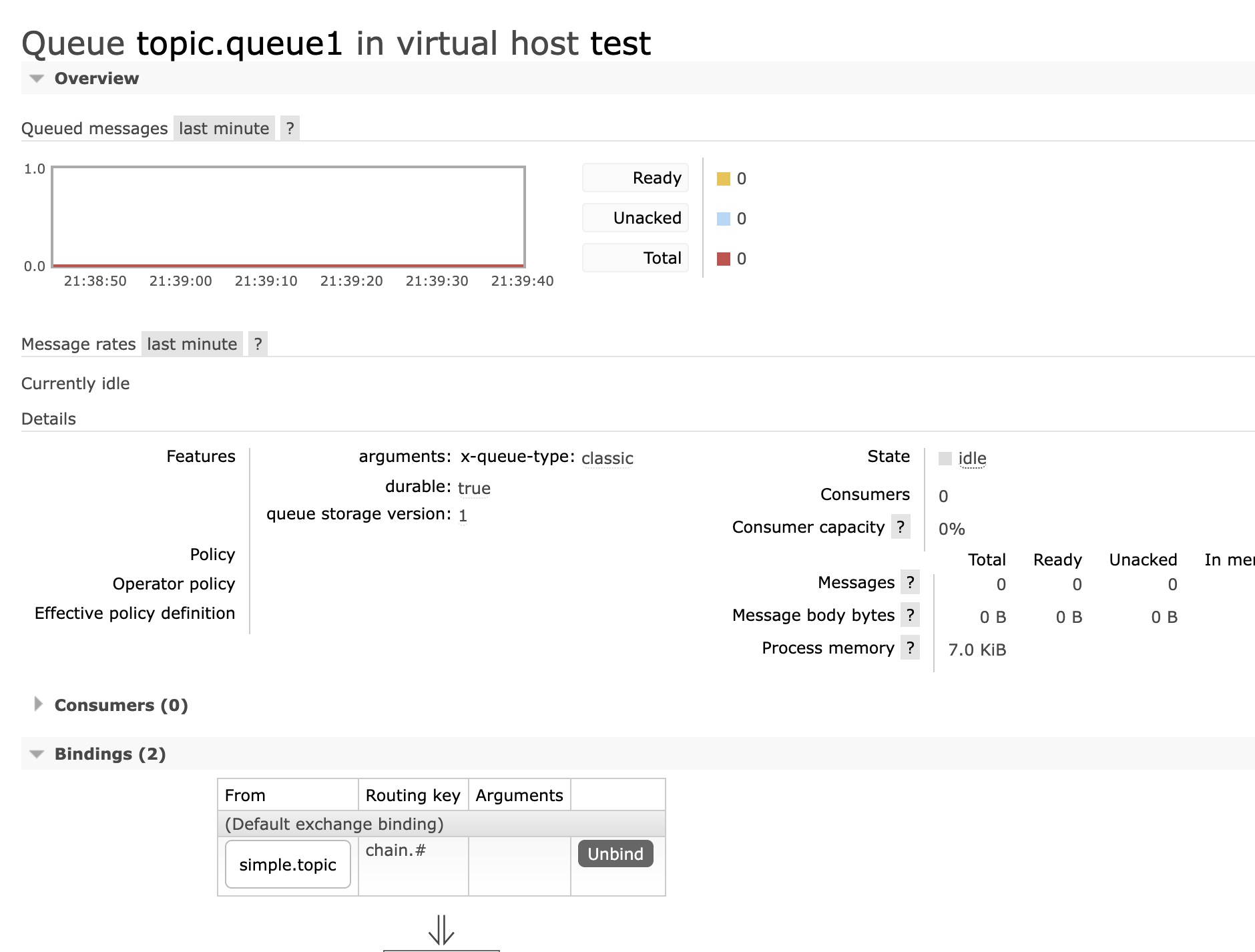
- 声明队列
topic.queue2,绑定#.news
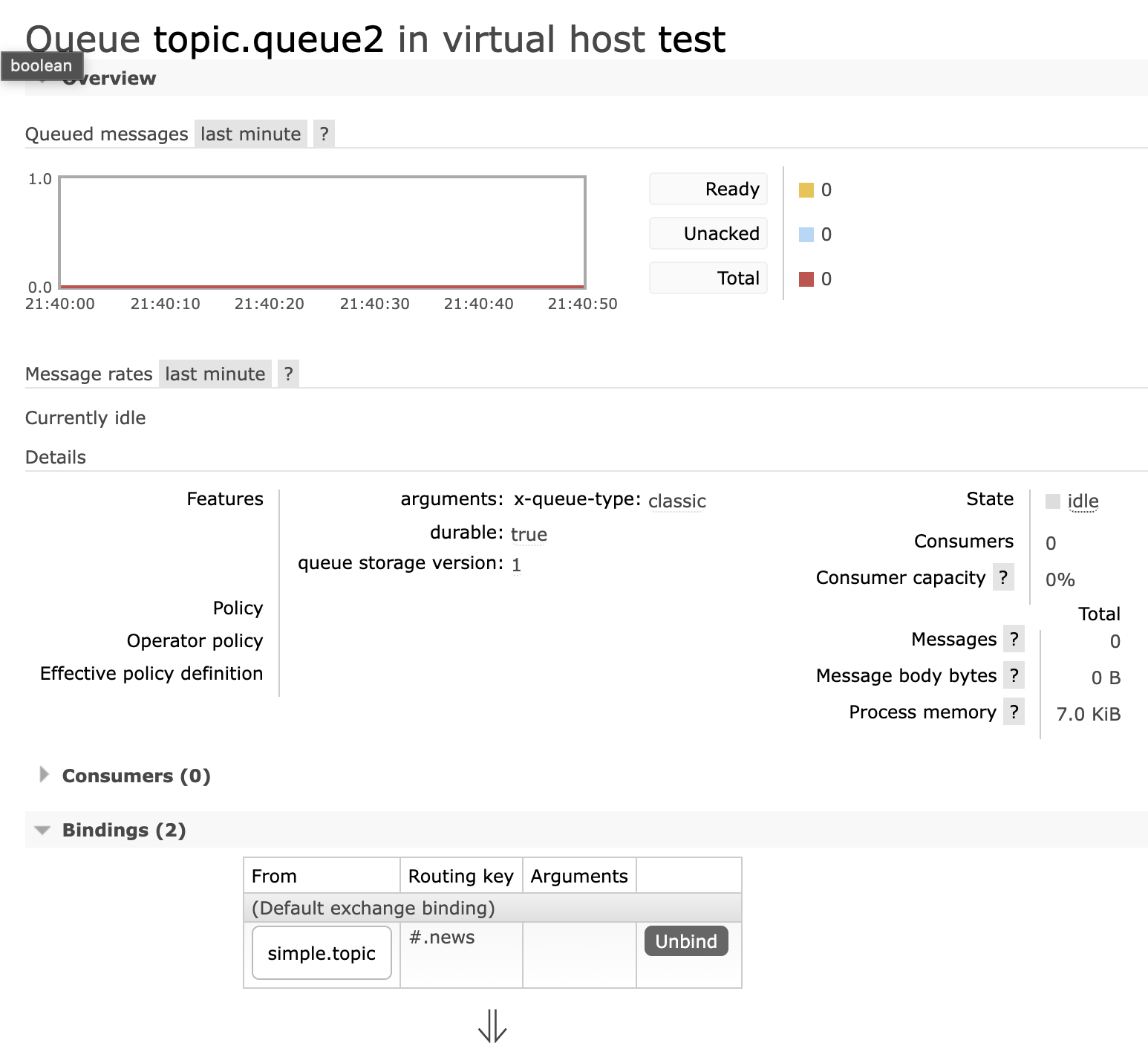
- 在publisher中编写测试方法,向
simple.topic发送消息
java
@Test
void topicExchangeToQueueTest() throws InterruptedException {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("simple.topic","chain.abc","chain.abc");
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("simple.topic","chain.news","chain.news");
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("simple.topic","fujian.news","fujian.news");
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("simple.topic","chain.fujian","chain.fujian");
}- 在
consumer服务中,编写两个消费者方法,分别监听topic.queue1和topic.queue2
java
/**
* topic交换机
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.queue1")
public void gettopicMessage1(String message) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("topic.queue1,message:{}", message);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.queue2")
public void gettopicMessage2(String message) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("topic.queue2,message:{}", message);- 效果
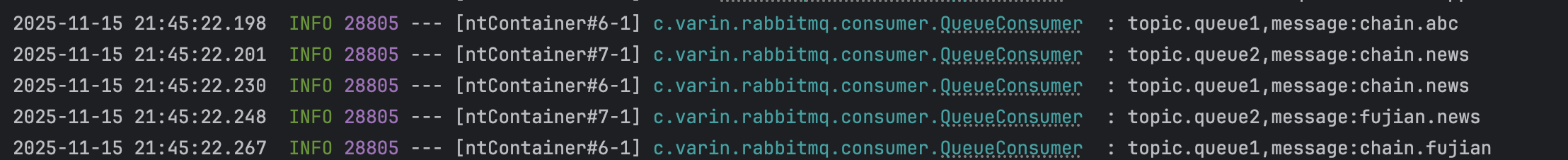
2. 总结
描述下Direct交换机与Topic交换机的差异?
- Topic交换机接收的消息RoutingKey必须是多个单词,以
**.**分割 - Topic交换机与队列绑定时的bindingKey可以指定通配符
#:代表0个或多个词*:代表1个词
十一、声明队列和交换机
由于之前都是使用web控制台的方式创建队列和交换机的,SpirngAMQT其实提供了代码自定义的方式。
编码方式声明
(1)fanout示例
java
package cn.varin.rabbitmq.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class FanoutConfig {
/**
* 创建fanout交换机
*/
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {
return ExchangeBuilder.fanoutExchange("customize.fanout").build();
}
@Bean
public Queue queue1() {
return new Queue("customize.queue1");
}
// 绑定
@Bean
public Binding binding1() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue1()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
}
(2)direct示例
注意:如果有多个routingKey需要绑定的话,就需要创建多个Binding
java
package cn.varin.rabbitmq.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class DirectConfig {
/**
* 创建Direct交换机
*/
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange() {
return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange("customize.direct").build();
}
@Bean
public Queue directQueue1() {
return new Queue("customize.direct.queue1");
}
// 绑定
@Bean
public Binding directBinding1() {
/**
* 目的地
* 类型
* 交换机
* routingkey
*/
return new Binding("customize.direct.queue1", Binding.DestinationType.QUEUE,"customize.direct", "red", null);
}
}基于注解声明
(1)Fanout交换机
java
/**
*基于注解声明fanout
*/
@RabbitListener(
bindings = @QueueBinding(
value =@Queue(name = "test.queue1"),// 创建队列
// 创建交换机并且指定类型
exchange = @Exchange(name = "test.fanout",type = ExchangeTypes.FANOUT)
)
)
public void getFanoutMessage(String message){
System.out.println(message);
}(2)Direct交换机
java
/**
*基于注解声明dirext
*/
@RabbitListener(
bindings = @QueueBinding(
value =@Queue(name = "test.direct.queue1"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "test.direct.exchange",type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT)
,
key = {"routing1,routing2"}
)
)
public void getDirectMessage(String message){
System.out.println(message);
}(3) Topic交换机
java
/**
*基于注解声明topic
*/
@RabbitListener(
bindings = @QueueBinding(
value =@Queue(name = "test.topic.queue1"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "test.topic.exchange",type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC)
,
key = {"#.topic"}
)
)
public void getTopicMessage(String message){
System.out.println(message);
}十二、消息转换器
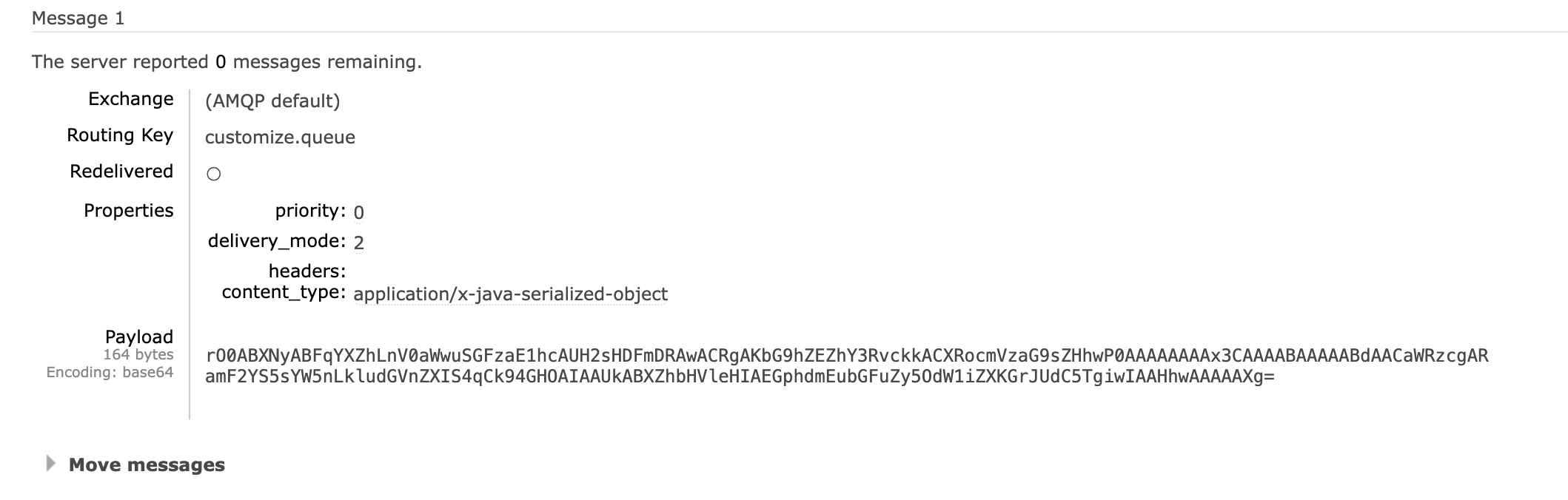
( 1 )默认转换器测试
- 默认情况下Spring采用的序列化方式是JDK序列化
- 存在问题:可能存在安全漏洞,以及序列化话后占用空间大
示例
- 建立一个队列:customize.queue

- 发送消息
java
@Test
void ToQueueTest() throws InterruptedException {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id",1);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("customize.queue",map);
}- 查看效果
( 2 )配置JSON转换器
注意,如果项目中引入了
spring-boot-starter-web依赖,则无需再次引入Jackson依赖。
- 引入依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>- 编写json配置Bean
java
package cn.varin.rabbitmq.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.Jackson2JsonMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.MessageConverter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class JsonConfig {
@Bean
public MessageConverter messageConverter() {
// 创建Jackson2JsonMessageConverter实例
Jackson2JsonMessageConverter jackson2JsonMessageConverter = new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
// 2.配置自动创建消息id,用于识别不同消息,也可以在业务中基于ID判断是否是重复消息
jackson2JsonMessageConverter.setCreateMessageIds(true);
return jackson2JsonMessageConverter;
}
}- 效果
