如果跟着我完成了前面的一些学习,相信你也对ai有一定程度的了解了,话不多说我们下一步继续学手搓一个简单的ReAct Agent,如果你不了解什么是ReAct的话可以百度或者问一下AI,相信AI可以给你很详细的解答。
起步
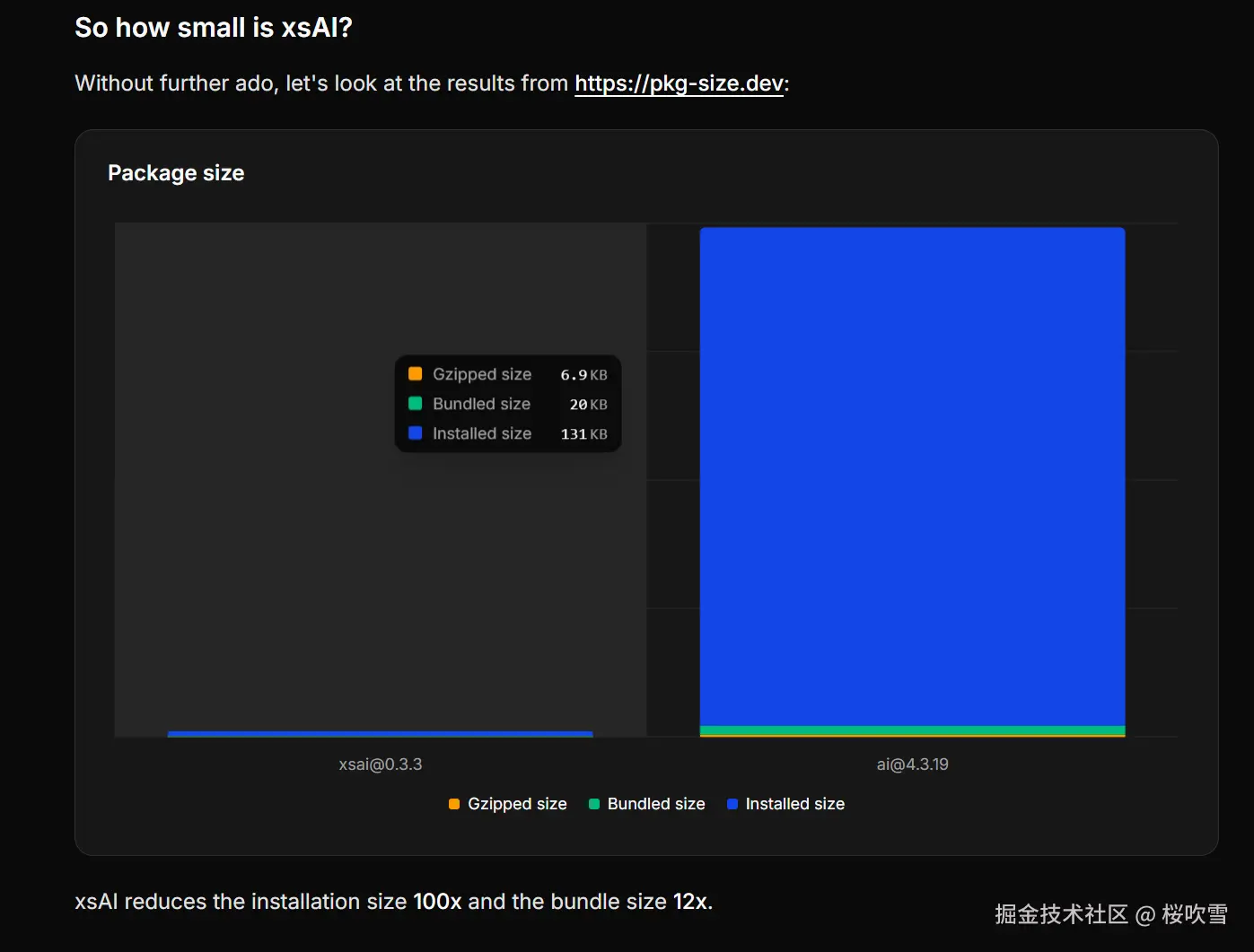
既然是手搓的话,咱们就先不用前面用到的Langchain.js了(手搓完再展示Langchain.js v1.0的createAgent),这里使用一个非常轻便的库:xsai,相对于Langchain.js动不动几十MB的安装依赖,xsai就要小很多了
然后js运行时咱们选非常好用的Bun,因为内置了很多好用的工具,比如Monorepo、env管理等等
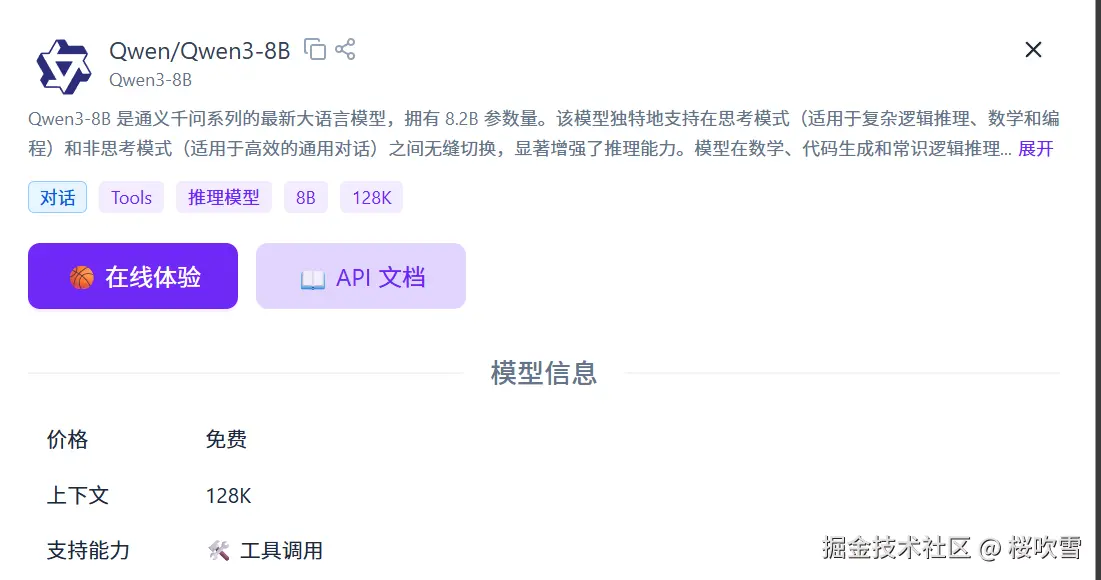
然后模型选择,既然叫ReAct,那么我们需要一个能够推理思考的模型,当然你也可以写提示词让非推理模型生成推理链,不过现在是5202年末,各大厂商都有推出非常牛逼的推理模型,那么咱们简单点选个推理模型就好了,这里我选择了Qwen3-8B,使用ollama本地运行(其实是最近换了新显卡发现本地跑小模型也挺快的),当然也可以选择一些云计算平台,比如火山、百炼等等,都有几十上百万的免费token,要是用完了想白嫖也可以选择硅基流动的免费模型!
除此之外也没啥多余的东西了,那么开始操作吧
sh
bun init
✓ Select a project template: Blank
+ .gitignore
+ index.ts
+ tsconfig.json (for editor autocomplete)
+ README.md
To get started, run:
bun run index.ts
sh
bun add @xsai/shared-chat @xsai/tool @xsai/utils-chat zod编写代码
为了方便演示,代码就不拆分文件了,直接写到底,并用简单说明一下:
ts
import {
chat,
type AssistantMessage,
type FinishReason,
type Message,
type Tool,
type Usage,
} from "@xsai/shared-chat";
import { tool } from "@xsai/tool";
import { message } from "@xsai/utils-chat";
import * as z from "zod";
//#region openai 返回结构
export interface Choice {
finish_reason: FinishReason;
index: number;
message: AssistantMessage;
}
export interface ChatCompletionsResponse {
choices: Choice[];
created: number;
id: string;
model: string;
object: "chat.completion";
system_fingerprint: string;
usage: Usage;
}
//#endregion
// 方便生成message
export const assistant = message.assistant;
export const system = message.system;
export const user = message.user;
// 用来创建agent
export function createAgent(options: {
provider: {
baseURL: string;
apiKey: string;
model: string;
};
tools?: Tool[];
}) {
// call:让agent开始工作
async function call(
messages: Message[],
callOptions: { maxRoundTrip: number } = { maxRoundTrip: 10 }
) {
let count = 0;
// 限制一下agent最大运行步数
while (count < callOptions.maxRoundTrip) {
const res = await chat({
...options.provider,
baseURL: options.provider.baseURL,
model: options.provider.model,
messages,
tools: options.tools,
});
const cmplResp = (await res.json()) as ChatCompletionsResponse;
console.log(JSON.stringify(cmplResp.choices[0], null, 2));
const toolCalls = cmplResp.choices[0]?.message.tool_calls;
// 判断是否函数调用,如果没有函数调用说明结束工作,已经得到结果
if (!toolCalls?.length) {
return cmplResp;
}
// 将tool_calls加入到messages上下文中,方便ai判读已经调用过说明函数
messages.push(assistant(toolCalls[0]));
for (const choice of cmplResp.choices) {
if (!choice.message.tool_calls) {
continue;
}
for (const toolCall of choice.message.tool_calls) {
// 找到tool
const foundTool = options.tools?.find(
(tool) => tool.function.name === toolCall.function.name
);
if (!foundTool) {
continue;
}
// 调用tool拿到结果
const invokeResult = await foundTool.execute(
JSON.parse(toolCall.function.arguments || "{}"),
{
messages,
toolCallId: toolCall.id,
}
);
// 将结果加入到上下文中
messages.push({
role: "tool",
content:
invokeResult === "string"
? invokeResult
: JSON.stringify(invokeResult),
tool_call_id: toolCall.id,
});
}
}
// 完成一次函数调用
count++;
}
}
return { call };
}
async function main() {
// 创建工具
const getCity = await tool({
name: "getCity",
description: "Get the user's city",
execute: () => "广州",
parameters: z.object({}),
});
const getCityCode = await tool({
name: "getCityCode",
description: "Get the user's city code with search",
execute: () => "Guangzhou",
parameters: z.object({
location: z
.string()
.min(1)
.describe("Get the user's city code with search"),
}),
});
const getWeather = await tool({
name: "getWeather",
description: "Get the city code weather",
execute: ({ cityCode }) => ({
city: `广州`,
cityCode,
weather: "sunny",
degreesCelsius: 26,
}),
parameters: z.object({
cityCode: z.string().min(1).describe("Get the city code weather"),
}),
});
// 创建agent
const { call } = createAgent({
provider: {
baseURL: "http://localhost:11434/v1",
apiKey: "unused",
model: "qwen3:8b",
},
tools: [getCity, getCityCode, getWeather],
});
// 运行
const res = await call([
system(
"我是一名乐于助人的助手,负责为用户提供所需信息。用户可能提出任何问题,请识别用户的需求,并选用合适的工具来获取必要信息。"
),
user("今天天气怎么样?"),
]);
// 观察执行结果
console.log(res?.choices[0]?.message.content);
}
main();执行一下,查看结果:
sh
bun index.ts
今天广州的天气是晴天,气温28摄氏度。是不是很简单通俗易懂。
邪修(bushi)快捷办法
当然你可以参考上面的办法简单封装一下,或者,也不是不可以用别人写好的办法,比如langchain.js的办法
sh
bun add langchain @langchain/openai编写代码!
ts
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { createAgent, tool } from "langchain";
import * as z from "zod";
const getCity = tool(() => "广州", {
name: "getCity",
description: "Get the user's city",
schema: z.object({}),
});
const getCityCode = tool(() => "Guangzhou", {
name: "getCityCode",
description: "Get the user's city code with search",
schema: z.object({
location: z
.string()
.min(1)
.describe("Get the user's city code with search"),
}),
});
const getWeather = tool(
({ cityCode }) => ({
city: `广州`,
cityCode,
weather: "sunny",
degreesCelsius: 28,
}),
{
name: "getWeather",
description: "Get the city code weather",
schema: z.object({
cityCode: z.string().min(1).describe("Get the city code weather"),
}),
}
);
const agent = createAgent({
model: new ChatOpenAI({
configuration: {
baseURL: "http://localhost:11434/v1",
},
apiKey: "unused",
model: "qwen3:8b",
}),
tools: [getCity, getCityCode, getWeather],
systemPrompt: "You are a helpful assistant.",
});
const result = await agent.invoke({
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "今天天气怎么样" }],
});
console.log(result.messages.at(-1)?.content);
sh
bun langchain-agent.ts
今天广州的天气晴朗,气温28摄氏度。嗯,很简单粗暴,很邪修(
你学废了吗!