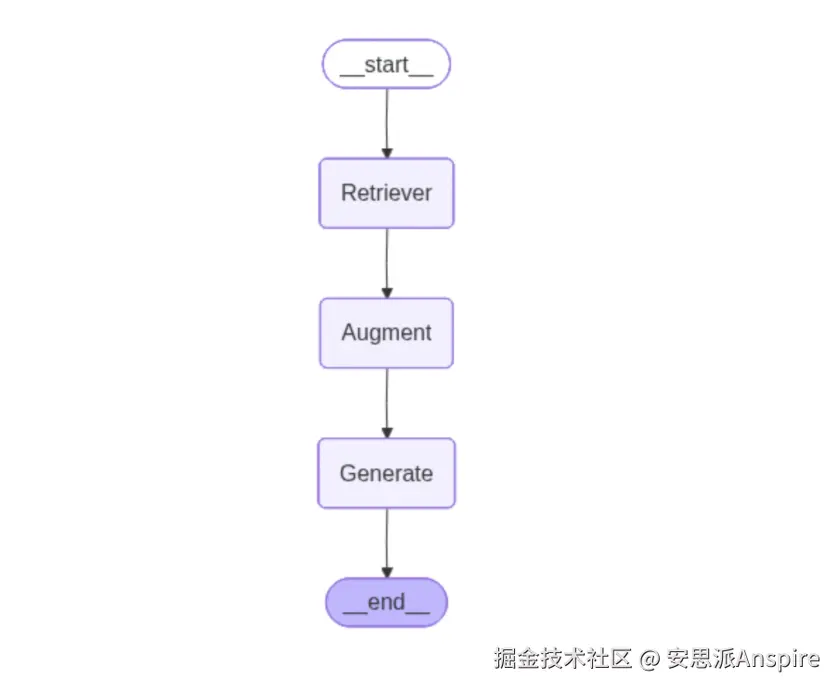
简单的RAG代码实现
在这个简单的RAG中,流程如下:
查询 → 检索 → 提示构建(增强) → 生成
该流程使用LangGraph的状态图实现,包含三个节点(步骤):
-
检索器:对 `medical_q_n_a` 集合执行相似性查询,并将排名靠前的文档合并为一个上下文字符串。
-
PromptBuilder:创建一个简单的RAG提示,该提示注入检索到的上下文和用户问题,并带有长度限制。
-
大语言模型:调用 `get_llm_response(prompt)` 并将模型输出保存到工作流状态中。
python
from typing import Literal
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph,MessagesState, START, END
from openai import OpenAI
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from typing import List
# === Define workflow node functions ===
def retrieve_context(state):
"""Retrieve top documents from ChromaDB based on query."""
print("---RETRIEVING CONTEXT---")
query = state["query"] # last user message
results = collection1.query(query_texts=[query], n_results=3)
context = "\n".join(results["documents"][0])
#state["query"] = query
state["context"] = context
print(context)
# Save context in the state for later nodes
return state
def build_prompt(state):
"""Construct the RAG-style prompt."""
print("---AUGMENT (BUILDING PROMPT)---")
query = state["query"]
context = state["context"]
prompt = f"""
Answer the following question using the context below.
Context:
{context}
Question: {query}
please limit your answer in 50 words.
"""
state["prompt"] = prompt
print(prompt)
return state
def call_llm(state):
"""Call your existing LLM function."""
print("---GENERATE (CALLING LLM)---")
prompt = state["prompt"]
answer = get_llm_response(prompt)
state["response"] = answer
return state
# === Build the workflow ===
## Define the state structure
class GraphState(TypedDict):
query : str
prompt : str
context : List[str]
response : str
workflow = StateGraph(GraphState)
# Add nodes
workflow.add_node("Retriever", retrieve_context)
workflow.add_node("Augment", build_prompt)
workflow.add_node("Generate", call_llm)
# Define edges
workflow.add_edge(START, "Retriever")
workflow.add_edge("Retriever", "Augment")
workflow.add_edge("Augment", "Generate")
workflow.add_edge("Generate", END)
# Compile agent
rag_agent = workflow.compile()
# === Run it ===
from IPython.display import Image, display
display(Image(rag_agent.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))按回车键或点击以查看全尺寸图像
简单的检索增强生成(图片由作者提供)
测试简单RAG:
css
input_state = {"query": "What are the treatments for Kawasaki disease ?"}
from pprint import pprint
for step in rag_agent.stream(input_state):
for key, value in step.items():
pprint(f"Finished running: {key}:")
pprint(value["response"])输出:
scala
---RETRIEVING CONTEXT---
Question: What are the treatments for Kawasaki disease ?. Answer: These resources address the diagnosis or management of Kawasaki disease: - Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center - Genetic Testing Registry: Acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome - National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute: How is Kawasaki Disease Treated? These resources from MedlinePlus offer information about the diagnosis and management of various health conditions: - Diagnostic Tests - Drug Therapy - Surgery and Rehabilitation - Genetic Counseling - Palliative Care. Type: treatment.
Question: What are the treatments for Krabbe Disease ?. Answer: There is no cure for Krabbe disease. Results of a very small clinical trial of children with infantile Krabbe disease found that children who received umbilical cord blood stem cells from unrelated donors prior to symptom onset developed with little neurological impairment. Bone marrow transplantation may help some people. Generally, treatment for the disorder is symptomatic and supportive. Physical therapy may help maintain or increase muscle tone and circulation.. Type: treatment.
Question: What are the treatments for Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, progeroid type ?. Answer: How might Ehlers-Danlos syndrome progeroid type be treated? Individuals with Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome progeroid type can benefit from a variety of treatments depending on their symptoms. Affected children with weak muscle tone and delayed development might benefit from physiotherapy to improve muscle strength and coordination. Affected individuals with joint pain might benefit from anti-inflammatory drugs. Lifestyle changes or precautions during exercise or intense physical activity may be advised to reduce the chance of accidents to the skin and bone. It is recommended that affected individuals discuss treatment options with their healthcare provider.. Type: treatment.
'Finished running: Retriever:'
---AUGMENT (BUILDING PROMPT)---
Answer the following question using the context below.
Context:
Question: What are the treatments for Kawasaki disease ?. Answer: These resources address the diagnosis or management of Kawasaki disease: - Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center - Genetic Testing Registry: Acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome - National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute: How is Kawasaki Disease Treated? These resources from MedlinePlus offer information about the diagnosis and management of various health conditions: - Diagnostic Tests - Drug Therapy - Surgery and Rehabilitation - Genetic Counseling - Palliative Care. Type: treatment.
Question: What are the treatments for Krabbe Disease ?. Answer: There is no cure for Krabbe disease. Results of a very small clinical trial of children with infantile Krabbe disease found that children who received umbilical cord blood stem cells from unrelated donors prior to symptom onset developed with little neurological impairment. Bone marrow transplantation may help some people. Generally, treatment for the disorder is symptomatic and supportive. Physical therapy may help maintain or increase muscle tone and circulation.. Type: treatment.
Question: What are the treatments for Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, progeroid type ?. Answer: How might Ehlers-Danlos syndrome progeroid type be treated? Individuals with Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome progeroid type can benefit from a variety of treatments depending on their symptoms. Affected children with weak muscle tone and delayed development might benefit from physiotherapy to improve muscle strength and coordination. Affected individuals with joint pain might benefit from anti-inflammatory drugs. Lifestyle changes or precautions during exercise or intense physical activity may be advised to reduce the chance of accidents to the skin and bone. It is recommended that affected individuals discuss treatment options with their healthcare provider.. Type: treatment.
Question: What are the treatments for Kawasaki disease ?
please limit your answer in 50 words.
'Finished running: Augment:'
---GENERATE (CALLING LLM)---
'Finished running: Generate:'
('Kawasaki disease is treated mainly with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) '
'and high-dose aspirin to reduce inflammation and prevent coronary artery '
'aneurysms. If fever recurs or IVIG resistance occurs, additional treatments '
'(repeat IVIG, steroids) may be considered; ongoing monitoring with '
'echocardiograms is recommended.')公平又简单,对吧。但要是有人问出超出大纲的问题呢!!
是的,系统彻底失败了。
别担心,我们有智能增强检索生成(Agentic RAG)作为救星。
能动RAG - 代码实现
核心思想:不是始终使用同一个检索器,而是使用一个小型路由代理,它在多个检索选项中进行决策,然后验证检索到的上下文是否相关。
流程如下:
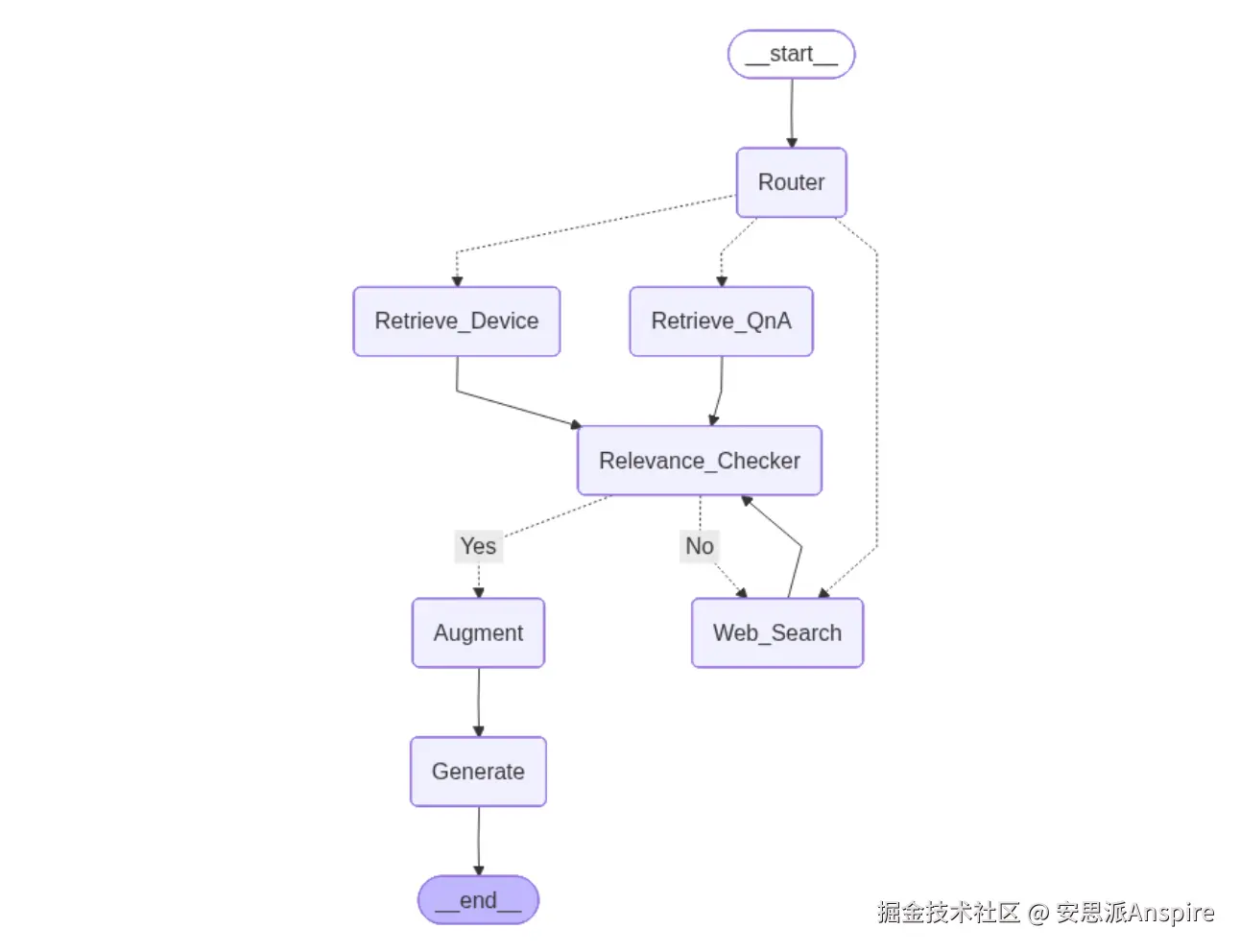
查询 → 路由器(源选择) → 检索 → 相关性检查器 → 如果相关:生成,如果不相关:转到网络搜索 → 结束
这些是使用LangGraph的StateGraph节点实现的。条件是使用"conditional_edge"实现的。
以下是关键节点:
1. 路由节点:构建一个简短的决策提示,并要求大语言模型返回三个标签之一:`Retrieve_QnA`、`Retrieve_Device`或`Web_Search`。
2. 检索器节点:一个用于问答Chroma集合,一个用于设备手册Chroma集合,一个用于网络搜索API。每个节点都会返回一个上下文字符串并设置一个 `source` 标签。
3. 相关性检查器:询问大语言模型(LLM)检索到的上下文是否相关(答案应为`是`或`否`)。
4. 条件路由:如果相关性为`是`,则继续进行提示构建和大语言模型处理。如果为`否`,则回退到`网络搜索`并重新运行相关性检查;流程将迭代次数限制为最多3次尝试。
能动流将这些节点组合成一个带有条件边的状态图。
python
from typing import Literal
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph,MessagesState, START, END
from openai import OpenAI
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
from typing import List
# === Define workflow node functions ===
def retrieve_context_q_n_a(state):
"""Retrieve top documents from ChromaDB Collection 1 (Medical Q&A Data) based on query."""
print("---RETRIEVING CONTEXT---")
query = state["query"] # last user message
results = collection1.query(query_texts=[query], n_results=3)
context = "\n".join(results["documents"][0])
state["context"] = context
state["source"] = "Medical Q&A Collection"
print(context)
# Save context in the state for later nodes
return state
# === Define workflow node functions ===
def retrieve_context_medical_device(state):
"""Retrieve top documents from ChromaDB Collection 2 (Medical Device Manuals Data) based on query."""
print("---RETRIEVING CONTEXT---")
query = state["query"] # last user message
results = collection2.query(query_texts=[query], n_results=3)
context = "\n".join(results["documents"][0])
state["context"] = context
state["source"] = "Medical Device Manual"
print(context)
# Save context in the state for later nodes
return state
def web_search(state):
"""Perform web search using Google Serper API."""
print("---PERFORMING WEB SEARCH---")
query = state["query"]
search_results = search.run(query=query)
state["context"] = search_results
state["source"] = "Web Search"
print(search_results)
return state
def router(state: GraphState) -> Literal[
"Retrieve_QnA", "Retrieve_Device", "Web_Search"
]:
"""Agentic router: decides which retrieval method to use."""
query = state["query"]
# A lightweight decision LLM - you can replace this with GPT-4o-mini, etc.
decision_prompt = f"""
You are a routing agent. Based on the user query, decide where to look for information.
Options:
- Retrieve_QnA: if it's about general medical knowledge, symptoms, or treatment.
- Retrieve_Device: if it's about medical devices, manuals, or instructions.
- Web_Search: if it's about recent news, brand names, or external data.
Query: "{query}"
Respond ONLY with one of: Retrieve_QnA, Retrieve_Device, Web_Search
"""
router_decision = get_llm_response(decision_prompt).strip()
print(f"---ROUTER DECISION: {router_decision}---")
print(router_decision)
state["source"] = router_decision
return state
# Define the routing function for the conditional edge
def route_decision(state: GraphState) -> str:
return state["source"]
def build_prompt(state):
"""Construct the RAG-style prompt."""
print("---AUGMENT (BUILDING GENERATIVE PROMPT)---")
query = state["query"]
context = state["context"]
prompt = f"""
Answer the following question using the context below.
Context:
{context}
Question: {query}
please limit your answer in 50 words.
"""
state["prompt"] = prompt
print(prompt)
return state
def call_llm(state):
"""Call your existing LLM function."""
print("---GENERATE (CALLING LLM)---")
prompt = state["prompt"]
answer = get_llm_response(prompt)
state["response"] = answer
return state
def check_context_relevance(state):
"""Determine whether to retrieved context is relevant or not."""
print("---CONTEXT RELEVANCE CHECKER---")
query = state["query"]
context = state["context"]
relevance_prompt = f"""
Check the below context if the context is relevent to the user query or.
####
Context:
{context}
####
User Query: {query}
Options:
- Yes: if the context is relevant.
- No: if the context is not relevant.
Please answer with only 'Yes' or 'No'.
"""
relevance_decision_value = get_llm_response(relevance_prompt).strip()
print(f"---RELEVANCE DECISION: {relevance_decision_value}---")
state["is_relevant"] = relevance_decision_value
return state
# Define the check_context_relevance function for the conditional edge
def relevance_decision(state: GraphState) -> str:
iteration_count = state.get("iteration_count", 0)
iteration_count += 1
state["iteration_count"] = iteration_count
## Limiting to max 3 iterations
if iteration_count >= 3:
print("---MAX ITERATIONS REACHED, FORCING 'Yes'---")
state["is_relevant"] = "Yes"
return state["is_relevant"]
# === Build the workflow ===
## Define the state structure
class GraphState(TypedDict):
query: str
context: str
prompt: str
response: str
source: str # Which retriever/tool was used
is_relevant: str
iteration_count: int
workflow = StateGraph(GraphState)
# Add nodes
workflow.add_node("Router", router)
workflow.add_node("Retrieve_QnA", retrieve_context_q_n_a)
workflow.add_node("Retrieve_Device", retrieve_context_medical_device)
workflow.add_node("Web_Search", web_search)
workflow.add_node("Relevance_Checker", check_context_relevance)
workflow.add_node("Augment", build_prompt)
workflow.add_node("Generate", call_llm)
# Define edges
workflow.add_edge(START, "Router")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"Router",
route_decision, # this function decides the path dynamically
{
"Retrieve_QnA": "Retrieve_QnA",
"Retrieve_Device": "Retrieve_Device",
"Web_Search": "Web_Search",
}
)
workflow.add_edge("Retrieve_QnA", "Relevance_Checker")
workflow.add_edge("Retrieve_Device", "Relevance_Checker")
workflow.add_edge("Web_Search", "Relevance_Checker")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"Relevance_Checker",
relevance_decision, # this function decides the path dynamically
{
"Yes": "Augment",
"No": "Web_Search",
}
)
workflow.add_edge("Augment", "Generate")
workflow.add_edge("Generate", END)
# Compile the dynamic RAG agent
agentic_rag = workflow.compile()
# ===================================
# === Visualize Workflow (Optional) ===
# ===================================
# === Run it ===
from IPython.display import Image, display
display(Image(agentic_rag.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png()))按回车键或点击以查看全尺寸图像