再回不去vs2010,只能用vs2015!
感谢csdn博主ouliten cudnn的普及!我的第一个cudnn就是抄他的!
cuda-NCCL笔记(3)-- 分布式训练LeNet_分布式训练中,nccl梯度反传更新的原理-CSDN博客
人生得意先show一下:
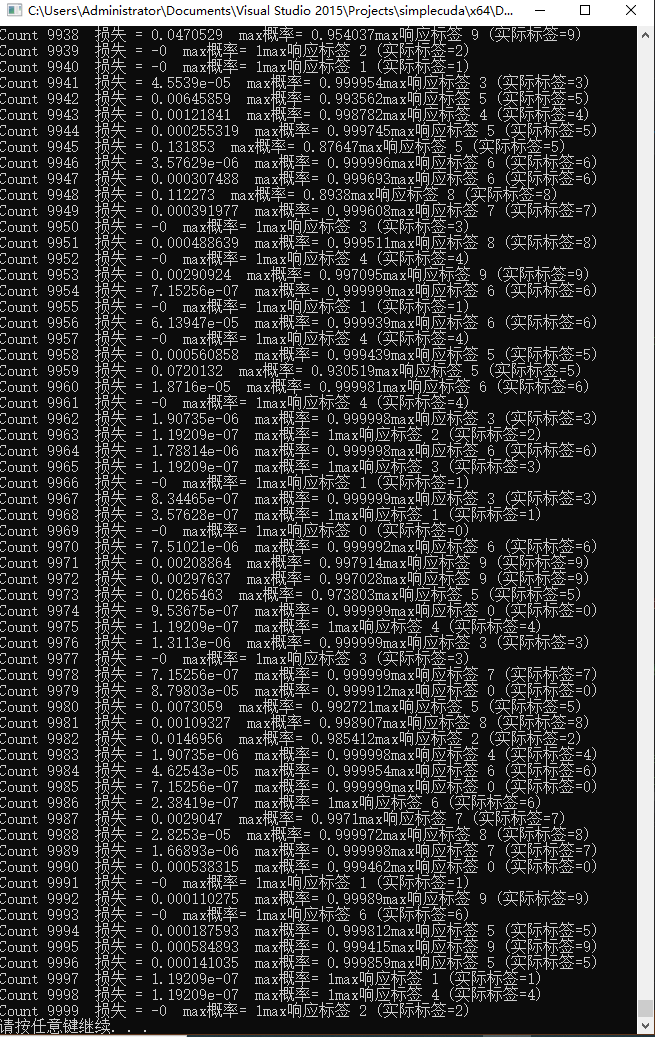
使用cudnn搞定lenet训练手写数字!真是快的不得了!gpu真是干活好手!
训练两次,test10000张图片成绩98.1!不错!平时我train成绩达到这个成绩,我就满足了!
作者ouliten原版是,linux版本,是为2线程服务的,即2个gpu
我改成windows10专业版,vs2015 c++,英伟达显卡1060(6g),cuda9.0,cudnn7.1.4!
这个老师ouliten真不错!
cudnn一次成功!花一周时间就差不多了!人有时就是懒,一拖一年,我就是这样!python拖了十年!今年是自己的人工智能元年,定下目标,一切事情都要为这个目标让路!
python+pytorch(也是第一次学)版本的cifar10,残差训练也达成了新高度84分!
真是走过千难万险!人工智能,不好玩!人生还是要发大愿望!才足够耐风寒!
第一回使用.cu文件,真的不适应!
还是lenet写(抄)过十几遍了,熟得很!所以才能走得这么快!
用星爷的话说,几百遍了,熟得很!
好,先看mnist数据加载:使用下面这个类:
//load minist
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <random>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdint>
struct MNISTSamlpe
{
MNISTSamlpe(const std::vector<float>& image_, const unsigned char &label_) :image(image_), label(label_) {}
std::vector<float> image;//28*28
unsigned char label;
};
class MNISTDataset {
public:
MNISTDataset(const std::string &image_file, const std::string &label_file) {
load_images(image_file);
load_labels(label_file);
if (images.size() != labels.size()) {
throw std::runtime_error("Number of images and labels mismatch");
}
indices.resize(images.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i<indices.size(); i++)
indices[i] = i;
}
////随机打乱
//void shuffle(unsigned seed = 42) {
// std::shuffle(indices.begin(), indices.end(), std::default_random_engine(seed));
// current_idx = 0;
//}
//Get next batch(获取下一批数据)
std::vector<MNISTSamlpe> next_batch(size_t batch_size) {
std::vector<MNISTSamlpe> batch;
batch.reserve(batch_size);
for (size_t i = 0; i<batch_size; i++) {
if (current_idx >= indices.size()) current_idx = 0;
size_t idx = indices[current_idx++];
batch.emplace_back(MNISTSamlpe{ images[idx], labels[idx] });
}
return batch;
}
size_t size() const { return images.size(); }
private:
std::vector<std::vector<float>> images;
std::vector<unsigned char> labels;
std::vector<size_t> indices;
size_t current_idx = 0;
void load_images(const std::string &path) {
FILE* mnist_file = NULL;
int err = fopen_s(&mnist_file, "c:\\train-images.idx3-ubyte", "rb");
unsigned char image_buffer[784]; //保存图片信息
int head_info[1000]; //读取出文件的头信息,该信息不参与计算
fread(head_info, 1, 16, mnist_file); //读取16字节头部信息
if (mnist_file == NULL)
{
// cout << "load data from your file err..." << endl;
return;
}
else
{
//cout << "loading data...[in func -->> load_mnist_data]" << endl;
}
int num = 60000; int rows = 28; int cols = 28;
images.resize(num, std::vector<float>(rows*cols));
for (int i = 0; i < 60000; i++)
{
/*sample[i].data = (double*)malloc(padded_matrix_size * sizeof(double));
memset(sample[i].data, 0, padded_matrix_size * sizeof(double));*/
fread(image_buffer, 1, 784, mnist_file);
unsigned int value;
//int index = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 28; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < 28; k++)
{
int shuffle_index = (j + 0) * 28 + k + 0;
//value = (unsigned int)image_buffer[index++];
///*images[j][k] = value / 255.0f;*/
images[i][shuffle_index] = image_buffer[shuffle_index] / 255.0f;
/*images[i][j] = value / 255.0f;*/
/*if (value < 128)
{
sample[i].data[shuffle_index] = 0;
}
else
{
sample[i].data[shuffle_index] = 1;
}*/
}
}
}
/*fclose(mnist_file);
mnist_file = NULL;*/
//std::ifstream file(path, std::ios::binary);
//if (!file) throw std::runtime_error("Cannot open image file");
/* uint32_t magic, num, rows, cols;
file.read((char *)&magic, 4);
file.read((char*)&num, 4);
file.read((char*)&rows, 4);
file.read((char*)&cols, 4);
magic = __builtin_bswap32(magic);
num = __builtin_bswap32(num);
rows = __builtin_bswap32(rows);
cols = __builtin_bswap32(cols);
if (magic != 2051) throw std::runtime_error("Invalid MNIST image file");*/
//int num = 60000; int rows = 28; int cols = 28;
//images.resize(num, std::vector<float>(rows*cols));
///*images.resize(num, std::vector<float>(rows*cols));*/
//for (uint32_t i = 0; i<num; i++) {
// for (uint32_t j = 0; j<rows*cols; j++) {
// unsigned char pixel;
// file.read((char*)&pixel, 1);
// images[i][j] = pixel / 255.0f;
// }
//}
fclose(mnist_file);
mnist_file = NULL;
}
void load_labels(const std::string &path) {
FILE* mnist_file = NULL;
int err = fopen_s(&mnist_file, "c:\\train-labels.idx1-ubyte", "rb");
unsigned char label;
if (mnist_file == NULL)
{
//cout << "load label from your file err..." << endl;
return;
}
else
{
// cout << "loading label...[in func -->> load_mnist_label]" << endl;
}
int head_info[1000]; //读取出文件的头信息,该信息不参与计算
fread(head_info, 1, 8, mnist_file); //读取8字节头部信息
int num = 60000;
labels.resize(num);
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
// sample[i].label = (double*)malloc(class_count * sizeof(double));
/* for (int k = 0; k < 10; k++)
{
sample[i].label[k] = 0;
}*/
fread((char*)&label, sizeof(label), 1, mnist_file);
//int value_index = (unsigned int)label;
//sample[i].label[value_index] = 1;
labels[i] = label;
//show_pic(sample[i],value_index); //test
}
fclose(mnist_file);
mnist_file = NULL;
/* std::ifstream file(path, std::ios::binary);
if (!file) throw std::runtime_error("Cannot open label file");
uint32_t magic, num;
file.read((char*)&magic, 4);
file.read((char*)&num, 4);
magic = __builtin_bswap32(magic);
num = __builtin_bswap32(num);
if (magic != 2049) throw std::runtime_error("Invalid MNIST label file");*/
/* labels.resize(num);
for (uint32_t i = 0; i<num; i++) {
unsigned char lbl;
file.read((char*)&lbl, 1);
labels[i] = lbl;
}*/
}
};
因为我对这个数据集很熟悉,所以也就改成自己的加载方式!否则,自己哪里挂都不知道!
其次,cudnn上场了:为lenet所作的准备工作:
#include <vector>
#include<memory>
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cudnn.h>
#include <cublas_v2.h>
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include"device_launch_parameters.h"
bool InitCUDA() {
int count;
cudaGetDeviceCount(&count);
if (count == 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "There is no device.\n");
return false;
}
int i;
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
cudaDeviceProp prop;
if (cudaGetDeviceProperties(&prop, i) == cudaSuccess) {
if (prop.major >= 1)
{
break;
}
}
}
if (i == count)
{
fprintf(stderr, "There is no device supporting CUDA 1.x.\n");
return false;
}
cudaSetDevice(i);
return true;
}
global void add(int *a, int *b, int *c, int N) {
int index = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (index < N) {
c[index] = a[index] + b[index];
}
}
//以上是cuda测试
//以下测试lenet
void error_handling(cudaError_t res) {
if (res != cudaSuccess) {
std::cout << "error! " << cudaGetErrorString(res) << std::endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
void error_handling(cudnnStatus_t status) {
if (status != CUDNN_STATUS_SUCCESS) {
std::cout << "error! " << cudnnGetErrorString(status) << std::endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
void error_handling(cublasStatus_t status) {
if (status != CUBLAS_STATUS_SUCCESS) {
std::cout << "error! " << (status) << std::endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
//功能:将数组 p 初始化为 [a,b] 区间的均匀分布随机数。
global void init_uniform(float* p, int n, unsigned seed, float a = -0.05f, float b = 0.05f) {
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (i < n) {
// 线性同余伪随机(教学用)
unsigned s = seed ^ (i * 747796405u + 2891336453u);
s ^= s >> 17; s *= 0xed5ad4bbU; s ^= s >> 11; s *= 0xac4c1b51U; s ^= s >> 15; s *= 0x31848babU; s ^= s >> 14;
float r = (s & 0x00FFFFFF) / float(0x01000000); // [0,1)
p[i] = a + (b - a) * r;
}
}
//张量清零 功能:把数组 p 清零。常用于梯度初始化。
global void zero_kernel(float* p, int n) {
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (i < n) {
p[i] = 0.0f;
}
}
//功能:在卷积 / 全连接的输出上加上对应的 bias 偏置。
//原理:根据 idx 反推当前像素属于哪个通道 c,然后加上对应的 b[c]。(因为bias是根据通道划分的,一个通道共用一个bias)
global void add_bias_nchw(float* y, const float* b, int N, int C, int H, int W) {//b数组的大小是C
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
int total = N * C * H * W;
if (i < total) {
int c = (i / (H * W)) % C;//计算当前像素属于哪个同搭配channel
y[i] += b[c];
}
}
// Softmax 前向 + 交叉熵损失(单样本),logits->prob, 返回loss
//功能:计算 softmax 概率,同时得到交叉熵损失。
//原理:标准 softmax + CE,做了 max 平移避免指数溢出。
global void softmax_forward_loss(const float* logits, const int* label, float* prob, float* loss, int num_classes) {
// 单样本简化
// 1) 减去最大值防溢出
float mx = logits[0];
for (int i = 1; i < num_classes; i++)
mx = fmaxf(mx, logits[i]);
float sum = 0.f;
for (int i = 0; i < num_classes; i++) {
float e = expf(logits[i] - mx);
prob[i] = e;
sum += e;
}
for (int i = 0; i < num_classes; i++)
prob[i] /= sum;
int y = *label;
float l = -logf(fmaxf(prob[y], 1e-12f));//这是损失
*loss = l;
}
// softmax + CE 的反向:dlogits(损失函数对logits的导数) = prob - onehot(推导过程自行学习)
//功能:计算 dL / dlogits。
global void softmax_ce_backward(const float* prob, const int* label, float* dlogits, int num_classes) {
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (i < num_classes) {
int y = *label;
dlogits[i] = prob[i] - (i == y ? 1.f : 0.f);//详见softmax的梯度公式
}
}
// softmax + cross entropy loss (batch)
// logits: [batch_size, num_classes]
// labels: [batch_size]
// prob: [batch_size, num_classes]
// loss: [batch_size] (每个样本的loss,外面可以再取均值)
global void softmax_forward_loss_batch(
const float* logits, const unsigned* labels,
float* prob, float* loss,
int batch_size, int num_classes)
{
int b = blockIdx.x; // 每个block处理一个样本
if (b >= batch_size) return;
const float* logit_row = logits + b * num_classes;
float* prob_row = prob + b * num_classes;
// 1) 找最大值防止溢出
float mx = logit_row[0];
for (int i = 1; i < num_classes; i++)
mx = fmaxf(mx, logit_row[i]);
// 2) exp & sum
float sum = 0.f;
for (int i = 0; i < num_classes; i++) {
float e = expf(logit_row[i] - mx);
prob_row[i] = e;
sum += e;
}
// 3) 归一化 softmax
for (int i = 0; i < num_classes; i++)
prob_row[i] /= sum;
// 4) cross entropy loss
unsigned y = labels[b];
float l = -logf(fmaxf(prob_row[y], 1e-12f));
loss[b] = l;
}
// backward: dlogits = prob - onehot
// prob: [batch_size, num_classes]
// labels: [batch_size]
// dlogits: [batch_size, num_classes]
global void softmax_ce_backward_batch(
const float* prob, const unsigned* labels,
float* dlogits,
int batch_size, int num_classes)
{
int b = blockIdx.x; // 样本编号
int i = threadIdx.x; // 类别编号
if (b >= batch_size || i >= num_classes) return;
int y = labels[b];
const float* prob_row = prob + b * num_classes;
float* dlogit_row = dlogits + b * num_classes;
dlogit_row[i] = prob_row[i] - (i == y ? 1.f : 0.f);
}
// SGD 参数更新:W -= lr * dW
//功能:梯度下降更新参数。
global void sgd_update(float* W, const float* dW, float lr, int n) {
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (i < n) {
W[i] -= lr * dW[i];
}
}
// 功能是计算卷积层的 bias 梯度
// 逻辑:把输出梯度 dy 在 N、H、W 上做 sum,得到每个通道的偏置梯度。**每个通道一个线程**
//dy:上层传下来的梯度,形状是(N, C, H, W)
//数学上,db[c]=dy在N*H*W维度上的总和
global void reduce_bias_grad(const float* dy, float* db, int N, int C, int H, int W) {
int c = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (c >= C) return;
float s = 0.f;
for (int n = 0; n < N; n++) {//遍历 batch 内的每个样本 n
const float* p = dy + (n * C + c) * H * W;//p 指向第 n 个样本、第 c 个通道的起始地址
for (int i = 0; i < H * W; i++)//内层循环:遍历该通道的所有空间位置(H * W)
s += p[i];//累加梯度到 s
}
db[c] = s;
}
//张量展平 (Flatten): 将特征图 (N,C,H,W) flatten 成 (N, C*H*W) 行优先缓冲(简单拷贝)
//这里简化为 N=1,只是拷贝。
global void nchw_to_nxk(const float* x, float* y, int N, int C, int H, int W) {
// N=1 简化
int k = C * H * W;
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (i < k) y[i] = x[i];
}
//功能:反展平,主要用在调试或反向传播时。
global void nxk_to_nchw(const float* x, float* y, int N, int C, int H, int W) {
int k = C * H * W;
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (i < k) y[i] = x[i];
}
// 初始化 GPU 上的 ones 向量
global void init_ones_kernel(float* data, int n) {
int idx = blockIdx.x*blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (idx < n) data[idx] = 1.0f;
}
//缩放
global void scale_kernel(float* data, int n, float factor) {
int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (idx < n) {
data[idx] *= factor;
}
}
//作者最后加了这个,有没有用?
/* Tensor Bias addition : C = alpha * A + beta * C */
cudnnStatus_t
cudnnAddTensor(cudnnHandle_t handle,
const void *alpha,
const cudnnTensorDescriptor_t aDesc,
const void *A,
const void *beta,
const cudnnTensorDescriptor_t cDesc,
void *C);
////类方式实现
//// 初始化 GPU 上的 ones 向量
//global void init_ones_kernel(float* data, int n) {
// int idx = blockIdx.x*blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
// if (idx < n) data[idx] = 1.0f;
//}
class Layer {//抽象的层
public:
//输入的逻辑:调用者传入分配内存空间的输入,输出存在类里
virtual void forward(float* input) = 0;
//反向传播的逻辑亦是如此,只是名字反了一下,参数名字是output
virtual void backward(float* grad_output) = 0;
virtual float* get_output() = 0;
virtual float* get_grad_input() = 0;
virtual void update(float lr) = 0;
virtual~Layer() {}
};
class Conv2D :public Layer {
public:
Conv2D(cudnnHandle_t &handle, int batch, int in_channels, int out_channels, int in_h, int in_w, int kernel_size, int stride = 1, int padding = 0) :
_handle(handle), _batch(batch), _in_channels(in_channels), _out_channels(out_channels), _in_h(in_h), _in_w(in_w), _kernel_size(kernel_size), _stride(stride), _padding(padding)
{
//初始化描述符
error_handling(cudnnCreateTensorDescriptor(&_input_desc));//I
error_handling(cudnnCreateTensorDescriptor(&_output_desc));//O
error_handling(cudnnCreateTensorDescriptor(&_bias_desc));//bias
error_handling(cudnnCreateFilterDescriptor(&_filter_desc));//filter
error_handling(cudnnCreateConvolutionDescriptor(&_conv_desc));//con ker
//设置描述符
error_handling(cudnnSetTensor4dDescriptor(_input_desc, CUDNN_TENSOR_NCHW, CUDNN_DATA_FLOAT, _batch, _in_channels, _in_h, _in_w));
error_handling(cudnnSetTensor4dDescriptor(_bias_desc, CUDNN_TENSOR_NCHW, CUDNN_DATA_FLOAT, 1, out_channels, 1, 1));
error_handling(cudnnSetFilter4dDescriptor(_filter_desc, CUDNN_DATA_FLOAT, CUDNN_TENSOR_NCHW, _out_channels, _in_channels, _kernel_size, _kernel_size));
error_handling(cudnnSetConvolution2dDescriptor(_conv_desc, padding, padding, stride, stride, 1, 1, CUDNN_CROSS_CORRELATION, CUDNN_DATA_FLOAT));
error_handling(cudnnGetConvolution2dForwardOutputDim(_conv_desc, _input_desc, _filter_desc, &_batch, &_out_channels, &_out_h, &_out_w));//获得输出维度
error_handling(cudnnSetTensor4dDescriptor(_output_desc, CUDNN_TENSOR_NCHW, CUDNN_DATA_FLOAT, _batch, _out_channels, _out_h, _out_w));
//分配GPU内存
www = (float*)malloc(sizeof(float)*_out_channels* _in_channels*_kernel_size*_kernel_size);
//还应该有个置零的动作
error_handling(cudaMalloc(&_weight, sizeof(float)*_out_channels* _in_channels*_kernel_size*_kernel_size));
error_handling(cudaMalloc(&_bias, sizeof(float) * _out_channels));
error_handling(cudaMalloc(&_grad_weight, sizeof(float) * _out_channels * _in_channels * _kernel_size * _kernel_size));//参数的梯度维度和参数是一样的
error_handling(cudaMalloc(&_grad_bias, sizeof(float) * _out_channels));
error_handling(cudaMalloc(&_output, sizeof(float) * _batch * _out_channels * _out_h * _out_w));
error_handling(cudaMalloc(&_grad_input, sizeof(float) * _batch * _in_channels * _in_h * _in_w));
//初始化参数
int w_size = _out_channels * _in_channels * _kernel_size * _kernel_size;
int b_size = _out_channels;
init_uniform << <(w_size + 255) / 256, 256 >> > (_weight, w_size, time(NULL), -0.05f, 0.05f);
init_uniform << <(b_size + 255) / 256, 256 >> > (_bias, b_size, time(NULL) + 1, -0.05f, 0.05f);
zero_kernel << <(w_size + 255) / 256, 256 >> > (_grad_weight, w_size);
zero_kernel << <(_batch * _out_channels * _out_h * _out_w + 255) / 256, 256 >> > (_output, _batch * _out_channels * _out_h * _out_w);
zero_kernel << <(_batch * _in_channels * _in_h * _in_w + 255) / 256, 256 >> > (_grad_input, _batch * _in_channels * _in_h * _in_w);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
//TODO:检测结果的事情后面再说吧
//获取算法
cudnnConvolutionFwdAlgoPerf_t fwdPerf[8]; int retFwd = 0;
cudnnGetConvolutionForwardAlgorithm_v7(_handle, _input_desc, _filter_desc, _conv_desc, _output_desc, 8, &retFwd, fwdPerf);
_fwd_algo = fwdPerf[0].algo;
cudnnConvolutionBwdFilterAlgoPerf_t bwdFiltPerf[8]; int retBF = 0;
cudnnConvolutionBwdDataAlgoPerf_t bwdDataPerf[8]; int retBD = 0;
cudnnGetConvolutionBackwardFilterAlgorithm_v7(_handle, _input_desc, _output_desc, _conv_desc, _filter_desc, 8, &retBF, bwdFiltPerf);
_bwd_filter_algo = bwdFiltPerf[0].algo;
cudnnGetConvolutionBackwardDataAlgorithm_v7(_handle, _filter_desc, _output_desc, _conv_desc, _input_desc, 8, &retBD, bwdDataPerf);
_bwd_data_algo = bwdDataPerf[0].algo;
//工作空间的内存分配
cudnnGetConvolutionForwardWorkspaceSize(_handle, _input_desc, _filter_desc, _conv_desc, _output_desc, _fwd_algo, &_fwd_ws_size);
cudnnGetConvolutionBackwardFilterWorkspaceSize(_handle, _input_desc, _output_desc, _conv_desc, _filter_desc, _bwd_filter_algo, &_bwd_filter_ws_size);
cudnnGetConvolutionBackwardDataWorkspaceSize(_handle, _filter_desc, _output_desc, _conv_desc, _input_desc, _bwd_data_algo, &_bwd_data_ws_size);
if (_fwd_ws_size > 0)
cudaMalloc(&_fwd_ws, _fwd_ws_size);
else _fwd_ws = nullptr;
if (_bwd_filter_ws_size > 0)
cudaMalloc(&_bwd_filter_ws, _bwd_filter_ws_size);
else _bwd_filter_ws = nullptr;
if (_bwd_data_ws_size > 0)
cudaMalloc(&_bwd_data_ws, _bwd_data_ws_size);
else _bwd_data_ws = nullptr;
}
void forward(float* input)override {
_input = input;
const float alpha = 1.0f, beta = 0.0f;
//向前
cudnnConvolutionForward(_handle, &alpha,
_input_desc, _input,
_filter_desc, _weight,
_conv_desc, _fwd_algo, _fwd_ws, _fwd_ws_size, &beta,
_output_desc, _output);
//加偏置
cudnnAddTensor(_handle, &alpha, _bias_desc, _bias, &alpha, _output_desc, _output);//注意这里两个都是alpha,详情查看函数接口
}
void backward(float* grad_output)override {
const float alpha = 1.0f, beta = 0.0f;
// grad_bias
cudnnConvolutionBackwardBias(_handle, &alpha, _output_desc, grad_output, &beta, _bias_desc, _grad_bias);
// grad_weight
cudnnConvolutionBackwardFilter(_handle, &alpha, _input_desc, _input, _output_desc, grad_output,
_conv_desc, _bwd_filter_algo, _bwd_filter_ws, _bwd_filter_ws_size, &beta, _filter_desc, _grad_weight);
// grad_input 这个输出 是要传到外面去给下一层用的
cudnnConvolutionBackwardData(_handle, &alpha, _filter_desc, _weight, _output_desc, grad_output,
_conv_desc, _bwd_data_algo, _bwd_data_ws, _bwd_data_ws_size, &beta, _input_desc, _grad_input);
}
float* get_output() override { return _output; }
float* get_grad_input() override { return _grad_input; }
float* getwgh() { return www; }//很久没用类了,还搞个重载,有点懵,更新后取www才有意义
void update(float lr) override {
int w_size = _out_channels * _in_channels * _kernel_size * _kernel_size;
int b_size = _out_channels;
// 简单 SGD
sgd_update << <(w_size + 255) / 256, 256 >> > (_weight, _grad_weight, lr, w_size);//权重应该从这里取出来20251006
sgd_update << <(b_size + 255) / 256, 256 >> > (_bias, _grad_bias, lr, b_size);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
// ---- 打印中间输出 ----
cudaMemcpy(www, _weight, _out_channels* _in_channels*_kernel_size*_kernel_size * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);//取出权重,可以一试,保存加载不必再训练喽
}
/*getwgh()
{
}*/
~Conv2D() {
cudaFree(_weight);
cudaFree(_bias);
cudaFree(_grad_weight);
cudaFree(_grad_bias);
cudaFree(_output);
cudaFree(_grad_input);
if (_fwd_ws) cudaFree(_fwd_ws);
if (_bwd_filter_ws) cudaFree(_bwd_filter_ws);
if (_bwd_data_ws) cudaFree(_bwd_data_ws);
cudnnDestroyTensorDescriptor(_input_desc);
cudnnDestroyTensorDescriptor(_output_desc);
cudnnDestroyTensorDescriptor(_bias_desc);
cudnnDestroyFilterDescriptor(_filter_desc);
cudnnDestroyConvolutionDescriptor(_conv_desc);
}
private:
int _in_channels, _out_channels, _kernel_size, _stride, _padding, _batch;//卷积核的参数(kernel暂时是正方形的)
int _in_h, _in_w, _out_h, _out_w;//输入输出的形状
float* _weight, *_bias;//卷积核的参数和偏置
float* _input, *_output, *_grad_input;//x的输入、输出,反向传播时向外输出的梯度
float* _grad_weight, *_grad_bias;//参数的梯度,偏置的梯度
cudnnHandle_t& _handle;//引用外部的handle,这样一个程序只用创建一个handle
cudnnTensorDescriptor_t _input_desc, _output_desc, _bias_desc;//三个张量描述子:输入张量,输出张量,偏置张量
cudnnFilterDescriptor_t _filter_desc;//卷积核描述子
cudnnConvolutionDescriptor_t _conv_desc;//卷积描述子
cudnnConvolutionFwdAlgo_t _fwd_algo;//前向操作的算法
cudnnConvolutionBwdFilterAlgo_t _bwd_filter_algo;//反向求导中,对参数求导的算法
cudnnConvolutionBwdDataAlgo_t _bwd_data_algo;//反向求导中,对输入求导的算法
size_t _fwd_ws_size, _bwd_filter_ws_size, _bwd_data_ws_size;//各个工作空间的大小
void* _fwd_ws = nullptr, *_bwd_filter_ws = nullptr, *_bwd_data_ws = nullptr;//各个工作空间的指针
float * www;
};
class ReLU :public Layer {
public:
ReLU(cudnnHandle_t& handle, int n, int c, int h, int w) :_handle(handle), _n(n), _c(c), _h(h), _w(w) {
//描述子初始化
cudnnCreateTensorDescriptor(&_input_desc);
cudnnCreateActivationDescriptor(&_act_desc);
//描述子设置
cudnnSetTensor4dDescriptor(_input_desc, CUDNN_TENSOR_NCHW, CUDNN_DATA_FLOAT, _n, _c, _h, _w);
cudnnSetActivationDescriptor(_act_desc, CUDNN_ACTIVATION_RELU, CUDNN_PROPAGATE_NAN, 0.0f);
//分配GPU内存
cudaMalloc(&_output, sizeof(float) * _n * _c * _h * _w);
cudaMalloc(&_grad_input, sizeof(float) * _n * _c * _h * _w);
}
void forward(float* input)override {
_input = input;
const float alpha = 1.0f, beta = 0.0f;
//执行激活操作,结果保存在_output
cudnnActivationForward(_handle, _act_desc, &alpha,
_input_desc, _input, &beta,
_input_desc, _output);
}
void backward(float* grad_output)override {
//执行反向梯度计算,结果存在_grad_input
const float alpha = 1.0f, beta = 0.0f;
cudnnActivationBackward(_handle, _act_desc, &alpha,
_input_desc, _output, // yDesc, y (forward 输出)
_input_desc, grad_output, // dyDesc, dy (来自上层的梯度)
_input_desc, _input, // xDesc, x (forward 输入)
&beta,
_input_desc, _grad_input); // dxDesc, dx
}
float* get_output()override { return _output; }
float* get_grad_input()override { return _grad_input; }
void update(float lr) override {}
~ReLU() {
cudaFree(_output);
cudaFree(_grad_input);
cudnnDestroyTensorDescriptor(_input_desc);
cudnnDestroyActivationDescriptor(_act_desc);
}
private:
float* _input;
float* _output;
float* _grad_input;
int _n, _c, _h, _w;
cudnnHandle_t& _handle;
cudnnTensorDescriptor_t _input_desc;//输入(同时也是输出)张量的描述子
cudnnActivationDescriptor_t _act_desc;//激活描述子
};
class MaxPool2D :public Layer {
public:
MaxPool2D(cudnnHandle_t &handle, int n, int c, int h, int w, int ph, int pw, int padding, int stride) :
_handle(handle), _n(n), _c(c), _h(h), _w(w), _ph(ph), _pw(pw), _padding(padding), _stride(stride) {
//描述子初始化
cudnnCreateTensorDescriptor(&_input_desc);
cudnnCreateTensorDescriptor(&_output_desc);
cudnnCreatePoolingDescriptor(&_pool_desc);
//描述子设置
cudnnSetPooling2dDescriptor(_pool_desc, CUDNN_POOLING_MAX, CUDNN_PROPAGATE_NAN, _ph, _pw, _padding, _padding, _stride, _stride);
cudnnSetTensor4dDescriptor(_input_desc, CUDNN_TENSOR_NCHW, CUDNN_DATA_FLOAT, _n, _c, _h, _w);
cudnnGetPooling2dForwardOutputDim(_pool_desc, _input_desc, &_n, &_c, &_out_h, &_out_w);
cudnnSetTensor4dDescriptor(_output_desc, CUDNN_TENSOR_NCHW, CUDNN_DATA_FLOAT, _n, _c, _out_h, _out_w);
//分配内存
cudaMalloc(&_output, sizeof(float)*_n*_c*_out_h*_out_w);
cudaMalloc(&_grad_input, sizeof(float)*_n*_c*_h*_w);
}
void forward(float *input) override {
_input = input;
const float alpha = 1.0f, beta = 0.0f;
cudnnPoolingForward(_handle, _pool_desc, &alpha,
_input_desc, _input, &beta,
_output_desc, _output);
}
void backward(float *grad_output) override {
const float alpha = 1.0f, beta = 0.0f;
cudnnPoolingBackward(_handle, _pool_desc, &alpha, _output_desc, _output, _output_desc, grad_output, _input_desc, _input, &beta, _input_desc, _grad_input);
}
float *get_output()override { return _output; }
float *get_grad_input()override { return _grad_input; }
void update(float lr)override {}
~MaxPool2D() {
cudaFree(_output);
cudaFree(_grad_input);
cudnnDestroyTensorDescriptor(_input_desc);
cudnnDestroyTensorDescriptor(_output_desc);
cudnnDestroyPoolingDescriptor(_pool_desc);
}
private:
int _n, _c, _h, _w, _ph, _pw, _padding, _stride;//输入维度,池化的padding和stride
int _out_h, _out_w;//输出维度
float *_input, *_output, *_grad_input;
cudnnHandle_t &_handle;
cudnnTensorDescriptor_t _input_desc, _output_desc;//输入输出张量描述子
cudnnPoolingDescriptor_t _pool_desc;//池化描述子
};
class Linear : public Layer {
public:
Linear(cublasHandle_t &handle_, int batch_, int in_f, int out_f)
: handle(handle_), batch(batch_), in_features(in_f), out_features(out_f)
{
www = (float*)malloc(sizeof(float) * in_features * out_features);
//还应该有个置零的动作
// 参数和输出内存
cudaMalloc(&weight, sizeof(float) * in_features * out_features);
cudaMalloc(&bias, sizeof(float) * out_features);
cudaMalloc(&grad_weight, sizeof(float) * in_features * out_features);
cudaMalloc(&grad_bias, sizeof(float) * out_features);
cudaMalloc(&output, sizeof(float) * batch * out_features);
cudaMalloc(&grad_input, sizeof(float) * batch * in_features);
cudaMalloc(&ones, sizeof(float) * batch);
//初始化参数,为什么前面类中没有?可以参考没写类之前
init_uniform << <(in_features*out_features + 255) / 256, 256 >> > (weight, in_features*out_features, 1, -0.05f, 0.05f);//先同意设置为1
init_uniform << <(out_features + 255) / 256, 256 >> > (bias, out_features, 1, -0.05f, 0.05f);
// 初始化 ones 向量
init_ones_kernel << <(batch + 255) / 256, 256 >> >(ones, batch);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
}
void forward(float* input_) override {
//input: [batch, in_features]
// weight: [in_features, out_features]
// bias: [out_features]
// output: [batch, out_features]
input = input_;
const float alpha = 1.0f, beta = 0.0f;
// output = input * weight
cublasSgemm(handle, CUBLAS_OP_N, CUBLAS_OP_N,
out_features, batch, in_features,
&alpha,
weight, out_features,
input, in_features,
&beta,
output, out_features);
// add bias:
const float beta2 = 1.0f;
for (int i = 0; i < batch; i++)
cublasSaxpy(handle, out_features, &alpha, bias, 1, output + i*out_features, 1);
}
void backward(float* grad_output) override {
//input [batch, in_features]
//grad_output [batch, out_features]
//grad_weight [in_features, out_features]
const float alpha = 1.0f, beta = 0.0f;
// grad_weight = input^T * grad_output
cublasSgemm(handle, CUBLAS_OP_N, CUBLAS_OP_T,
out_features, in_features, batch,
&alpha,
grad_output, out_features,
input, in_features,
&beta,
grad_weight, out_features);
// weight: [in_features, out_features]
//grad_output [batch, out_features]
//grad_input [batch, in_features]
// grad_input = grad_output * weight^T
cublasSgemm(handle, CUBLAS_OP_T, CUBLAS_OP_N,
in_features, batch, out_features,
&alpha,
weight, out_features,
grad_output, out_features,
&beta,
grad_input, in_features);
// grad_bias = grad_output^T * ones
cublasSgemv(handle, CUBLAS_OP_N,
batch, out_features,
&alpha,
grad_output, out_features,
ones, 1,
&beta,
grad_bias, 1);
}
float* get_output() override { return output; }
float* get_grad_input() override { return grad_input; }
void update(float lr) override {
const float alpha = -lr;
// weight -= lr * grad_weight
cublasSaxpy(handle, in_features*out_features, &alpha, grad_weight, 1, weight, 1);
// bias -= lr * grad_bias
cublasSaxpy(handle, out_features, &alpha, grad_bias, 1, bias, 1);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();//需要这句话吗?先试一试
cudaMemcpy(www, weight, sizeof(float) * in_features * out_features, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);//暂时未获取bias
}
float* getwgh() { return www; }//很久没用类了,还搞个重载,有点懵,更新后取www才有意义
~Linear() {
cudaFree(weight);
cudaFree(bias);
cudaFree(grad_weight);
cudaFree(grad_bias);
cudaFree(output);
cudaFree(grad_input);
cudaFree(ones);
// delete www;
}
private:
cublasHandle_t &handle;
int in_features, out_features, batch;
float *weight, *bias;
float *grad_weight, *grad_bias;
float *input, *output, *grad_input;
float *ones;
float * www;
};
cublasStatus_t cublasSaxpy(
cublasHandle_t handle,
int n,
const float *alpha,
const float *x, int incx,
float *y, int incy);
void checkCuda(cudaError_t res) {
if (res != cudaSuccess) {
std::cerr << "CUDA Error: " << cudaGetErrorString(res) << std::endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
第三步,就是在上面cudnn api(应用程序接口)的准备工作上,构建lenet网络:
class LeNet :public Layer {
public:
LeNet(cublasHandle_t &cublas_, cudnnHandle_t &cudnn_, int batch_) :cublas(cublas_), cudnn(cudnn_), batch(batch_) {
layers.emplace_back(std::make_shared<Conv2D>(cudnn, batch, 1, 6, 28, 28, 5));//0,有权重
layers.emplace_back(std::make_shared<ReLU>(cudnn, batch, 6, 24, 24));
layers.emplace_back(std::make_shared<MaxPool2D>(cudnn, batch, 6, 24, 24, 2, 2, 0, 2));
layers.emplace_back(std::make_shared<Conv2D>(cudnn, batch, 6, 16, 12, 12, 5));//3,有权重
layers.emplace_back(std::make_shared<ReLU>(cudnn, batch, 16, 8, 8));
layers.emplace_back(std::make_shared<MaxPool2D>(cudnn, batch, 16, 8, 8, 2, 2, 0, 2));
layers.emplace_back(std::make_shared<Linear>(cublas, batch, 16 * 4 * 4, 120));//6,,有权重
layers.emplace_back(std::make_shared<ReLU>(cudnn, batch, 120, 1, 1));
layers.emplace_back(std::make_shared<Linear>(cublas, batch, 120, 84));//8,,有权重
layers.emplace_back(std::make_shared<ReLU>(cudnn, batch, 84, 1, 1));
layers.emplace_back(std::make_shared<Linear>(cublas, batch, 84, 10));//10,,有权重
cudaMalloc(&output, batch * 10 * sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&grad_input, batch * 1 * 28 * 28 * sizeof(float));
}
void forward(float *input_)override {
input = input_;
for (const auto &l : layers) {
l->forward(input);
input = l->get_output();
}
cudaMemcpy(output, input, sizeof(float)*batch * 10, cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice);
}
void backward(float *grad_output)override {
float* grad = grad_output;
for (int i = layers.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
layers[i]->backward(grad);
grad = layers[i]->get_grad_input();
}
cudaMemcpy(grad_input, grad, sizeof(float)*batch * 1 * 28 * 28, cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice);
}
float* get_output() override { return output; }
float* get_grad_input() override { return grad_input; }
void update(float lr) {
for (const auto &l : layers) {
l->update(lr);
}
}
/*void getWghL1() {
layersWgh1= layers[0]->getwgh();
}
void getWghL2() {
layersWgh2 = layers[3]->getwgh();
}
void getWghL3() {
layersWgh3 = layers[6]->getwgh();
}
void getWghL4() {
layersWgh4 = layers[8]->getwgh();
}
void getWghL5() {
layersWgh5 = layers[10]->getwgh();
}*/
~LeNet() {
cudaFree(output);
cudaFree(grad_input);
}
//float* get_w_grad() {
// return nullptr;
//}
//float* get_b_grad() {
// return nullptr;
//}
//int get_w_grad_size() {
// return 0;
//}
//int get_b_grad_size() {
// return 0;
//}
//void allreduce_grads(ncclComm_t comm, int num_gpus, cudaStream_t stream) {//专门用来同步分布训练梯度的函数
// for (const auto &layer : layers) {
// int w_size = layer->get_w_grad_size();
// if (w_size) {//有参数的梯度
// float *w_grad = layer->get_w_grad();//这是获取已经算好的梯度
// ncclAllReduce(w_grad, w_grad, w_size, ncclFloat, ncclSum, comm, stream);
// //归一化
// scale_kernel << <(w_size + 255) / 256, 256 >> >(w_grad, w_size, 1.0 / num_gpus);
// }
// int b_size = layer->get_b_grad_size();
// if (b_size) {
// float *b_grad = layer->get_b_grad();//这是获取已经算好的梯度
// ncclAllReduce(b_grad, b_grad, b_size, ncclFloat, ncclSum, comm, stream);
// //归一化
// scale_kernel << <(b_size + 255) / 256, 256 >> >(b_grad, b_size, 1.0 / num_gpus);
// }
// }
// cudaStreamSynchronize(stream);
//}
private:
cublasHandle_t &cublas;
cudnnHandle_t &cudnn;
int batch;
float *input, *output, *grad_input;
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<Layer>> layers;
float * layersWgh1; float * layersWgh2; float * layersWgh3; float * layersWgh4; float * layersWgh5;
};
厉害,这把c++的重载搞得是炉火纯青!我想改成笨办法,试了三次没成功!又简洁又高效,好,随他去!
第四步,就是训练了:
//#include<thread>
void train(int epochs, int batch_size, float lr, LeNet &net, int rank, cudaStream_t stream, MNISTDataset &Dataset) {
float *d_inputs;
unsigned *d_labels;
//输出的预测概率,softmax后的结果,损失,预测概率的梯度(作为LeNet反向传播的输入)
float *d_logits, *d_prob, *loss, *dlogits;
int num_classes = 10;
cudaMalloc(&d_inputs, batch_size * 28 * 28 * sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&d_labels, batch_size*sizeof(unsigned));
cudaMalloc(&d_logits, batch_size*num_classes*sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&d_prob, batch_size*num_classes*sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&loss, batch_size*sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&dlogits, batch_size*num_classes*sizeof(float));
std::vector<float> h_loss(batch_size);
for (int epoch = 0; epoch<epochs; epoch++) {
auto batch = Dataset.next_batch(batch_size);
std::vector<unsigned> h_labels(batch_size);
for (int batch_idx = 0; batch_idx<batch_size; batch_idx++) {
cudaMemcpy(d_inputs + batch_idx * 28 * 28, batch[batch_idx].image.data(), 28 * 28 * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
h_labels[batch_idx] = batch[batch_idx].label;
}
cudaMemcpy(d_labels, h_labels.data(),
batch_size*sizeof(unsigned), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
net.forward(d_inputs);
cudaMemcpy(d_logits, net.get_output(), batch_size*num_classes*sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice);
softmax_forward_loss_batch << <batch_size, 1 >> >(d_logits, d_labels, d_prob, loss, batch_size, num_classes);
softmax_ce_backward_batch << <batch_size, num_classes >> >(d_prob, d_labels, dlogits, batch_size, num_classes);
net.backward(dlogits);
// net.allreduce_grads(comm, nDev, stream);
cudaStreamSynchronize(stream);
net.update(lr);
// ---- 打印中间输出 ----
cudaMemcpy(h_loss.data(), loss, batch_size*sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
float avg_loss = 0.f;
for (float l : h_loss) avg_loss += l;
avg_loss /= batch_size;
if (epoch % 1 == 0) { // 每个 epoch 打印一次
std::cout << "[Rank " << rank << "] Epoch " << epoch
<< " Avg Loss = " << avg_loss
<< " (first label=" << h_labels[0] << ")"
<< std::endl;
}
}
cudaFree(d_inputs);
cudaFree(d_labels);
cudaFree(d_logits);
cudaFree(d_prob);
cudaFree(loss);
cudaFree(dlogits);
}
第五步,测试10000张:
int last[10000];
void test( LeNet &net, cudaStream_t stream, MNISTDataset &Dataset) {//使用10000
float *d_inputs;
unsigned *d_labels;
for (int x = 0; x<10000; x++)
{
last[x] = 0;
}
//输出的预测概率,softmax后的结果,损失,预测概率的梯度(作为LeNet反向传播的输入)
float *d_logits, *d_prob, *loss, *dlogits;
int num_classes = 10;
cudaMalloc(&d_inputs, 1 * 28 * 28 * sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&d_labels, 1*sizeof(unsigned));
cudaMalloc(&d_logits, 1*10*sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&d_prob, 1*10*sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&loss, 1*sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&dlogits, 1*10*sizeof(float));
std::vector<float> h_loss(1); std::vector<float> h_prob(10);
for (int epoch = 0; epoch<10000; epoch++) {
auto batch = Dataset.next_batch(1);
std::vector<unsigned> h_labels(1);//取了一个图像一个标签,也可以是train数据取10000
for (int batch_idx = 0; batch_idx<1; batch_idx++) {
cudaMemcpy(d_inputs + batch_idx * 28 * 28, batch[batch_idx].image.data(), 28 * 28 * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
h_labels[batch_idx] = batch[batch_idx].label;
}
cudaMemcpy(d_labels, h_labels.data(),
1*sizeof(unsigned), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
net.forward(d_inputs);
cudaMemcpy(d_logits, net.get_output(), 1*10*sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice);
softmax_forward_loss_batch << <1, 1 >> >(d_logits, d_labels, d_prob, loss, 1, num_classes);
cudaStreamSynchronize(stream);
// ---- 打印中间输出 ----
cudaMemcpy(h_loss.data(), loss, 1*sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaMemcpy(h_prob.data(), d_prob, 1 * 10 * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
if (h_prob[i] > h_prob[ans]) ans = i;//找到最大概率标号
if (h_labels[0] == ans)
last[epoch] = 1;
//找出最大概率是不是与标签同?同,则ok
//否则失败
/* float avg_loss = 0.f;
for (float l : h_loss) avg_loss += l;
avg_loss /= 1;*/
if (epoch % 1 == 0) { // 每个 epoch 打印一次
std::cout << "Count " << epoch
<< " 损失 = " << h_loss[0]
<< " max概率= " << h_prob[ans]
<< "max响应标签 " << ans
<< " (实际标签=" << h_labels[0] << ")"
<< std::endl;
}
}
cudaFree(d_inputs);
cudaFree(d_labels);
cudaFree(d_logits);
cudaFree(d_prob);
cudaFree(loss);
cudaFree(dlogits);
int P = 100;
int 得分数组[9];
int he = 9100;//统计最后1000,十次
float junzhi = 0;
for (int n = 0; n < 9; n++)
{
int hh = 0; //double wucha = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < P; i++)
{
hh += last[he + i];
// wucha += erT[he + i];
}
// textBox47.Text += he.ToString() + "," + hh.ToString() +":"+ ((float)wucha / 100).ToString()+ "\r\n";
he += 100;
junzhi += hh;
得分数组[n] = hh;
}
junzhi = junzhi / (float)9;
}
最后,mian函数上场:
int main() {
MNISTDataset Datasets = MNISTDataset{ "c:\\train-images.idx3-ubyte", "c:\\train-labels.idx1-ubyte" };
//所以我就不要线程了,也不要他的minist了
int dev = 0;
cudaSetDevice(dev);
// 创建流
cudaStream_t stream;
checkCuda(cudaStreamCreate(&stream));
cublasHandle_t cublas;
cudnnHandle_t cudnn;
cublasCreate(&cublas);//句柄是与当前上下文绑定的,不能一个句柄执行在不同GPU
cudnnCreate(&cudnn);
/*int batch_size = 8;*/
int batch_size = 10;
float lr = 0.018f;
LeNet LeNet_net(cublas, cudnn, batch_size);
train(6000, batch_size, lr, LeNet_net, 0, stream, Datasets);
test(LeNet_net,stream, Datasets);
//第二次训练和测试,看成绩会不会提升
train(6000, batch_size, lr, LeNet_net, 0, stream, Datasets);
test(LeNet_net, stream, Datasets);
cublasDestroy(cublas);
cudnnDestroy(cudnn);
cudaStreamDestroy(stream);
}
上面要解释的是:我训练了两次,叫epoch,而程序中的epoch循环了6000次,并不是真正的轮次,批处理是10,so,6000(epochs)*10(batch_size)=60000,这正好是60000万张训练图像!