目录
[1.1 pytest介绍](#1.1 pytest介绍)
[1.2 pytest安装](#1.2 pytest安装)
[1.3 pytest安装用例运用规则](#1.3 pytest安装用例运用规则)
[1.4 pytest命令参数](#1.4 pytest命令参数)
[1.5 pytest安装配置文件](#1.5 pytest安装配置文件)
[1.6 前后置](#1.6 前后置)
[1.7 断言](#1.7 断言)
[1.8 参数化](#1.8 参数化)
[2.1 基本使用](#2.1 基本使用)
[2.2 嵌套](#2.2 嵌套)
[2.3 请求多个fixture](#2.3 请求多个fixture)
[2.4 yield fixture](#2.4 yield fixture)
[2.5 带参数的fixture](#2.5 带参数的fixture)
[4.JSON Schema](#4.JSON Schema)
[4.1 介绍](#4.1 介绍)
[4.2 数据类型](#4.2 数据类型)
[4.3 最大最小值](#4.3 最大最小值)
[4.4 字符串特殊校验](#4.4 字符串特殊校验)
[4.5 数组约束](#4.5 数组约束)
[4.6 对象约束](#4.6 对象约束)
[4.7 必须属性](#4.7 必须属性)
[4.8 依赖关系](#4.8 依赖关系)
[5.logging 日志模块](#5.logging 日志模块)
[5.1 介绍](#5.1 介绍)
[5.2 使用](#5.2 使用)
[6.测试报告 allure](#6.测试报告 allure)
[6.1 介绍](#6.1 介绍)
[6.2 安装](#6.2 安装)
[6.3 使用](#6.3 使用)
1.pytest
1.1 pytest介绍
pytest官方文档:https://docs.pytest.org/en/stable/getting-started.html
pytest是一个非常流行且高效的Python测试框架,它提供了丰富的功能和灵活的用法,使得编写和运行测试用例变得简单而高效。
pytest的特点:
- 简单易用 :pytest的语法简洁清晰,对于编写测试用例非常友好,几乎可以在几分钟内手。
- 强大的断言库 :pytest内置了丰富的断言库,可以轻松地进行测试结果的判断。
- 支持参数化测试 :pytest支持参数化测试,允许使用不同的参数多次运行同一个测试函数,这大大提高了测试效率。
- 丰富的插件生态系统 :pytest有着丰富的插件生态系统,可以通过插件扩展各种功能,比如覆盖率测试、测试报告生成(如pytest-html插件可以生成完美的HTML测试报告)、失败用例重复执行(如pytest-rerunfailures插件)等。此外,pytest还支持与selenium、requests、appinum等结合,实现Web自动化、接口自动化、App自动化测试。
- 灵活的测试控制 :pytest允许跳过指定用例,或对某些预期失败的case标记成失败,并支重复执行失败的case。
1.2 pytest安装
pip install pytest==8.3.2| pytest 版本 | 最低 Python 版本 |
|---|---|
| 8.0+ | 3.8+ |
| 7.1+ | 3.7+ |
| 6.2 - 7.0 | 3.6+ |
| 5.0 - 6.1 | 3.5+ |
| 3.3 - 4.6 | 2.7, 3.4+ |
安装好pytest后,确认pycharm中python解释器已经更新,来看一下有pytest框架和没有
pytest框架编写代码的区别:
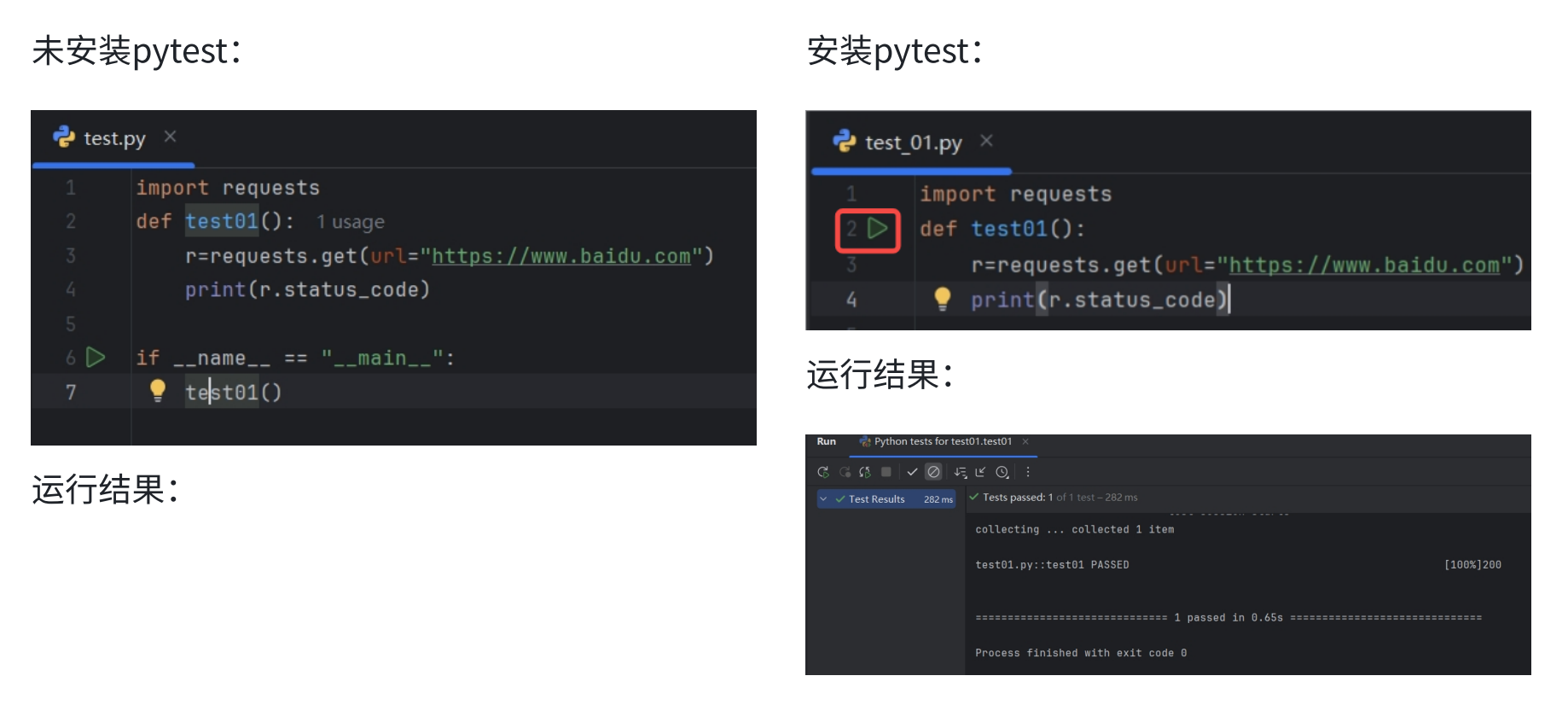
两张对比图可以明显看出来,未安装pytest框架的情况下需要编写main函数,在main函数中手动
调用测试用例testo1;安装了pytest框架后方法名前有直接运行标志。
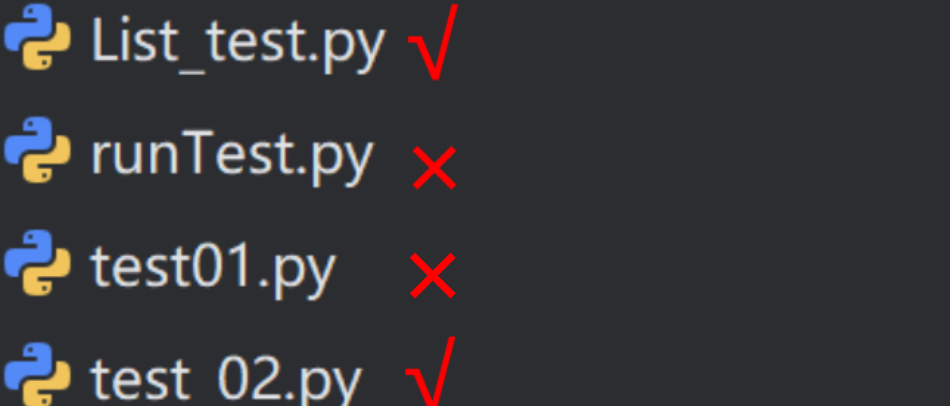
1.3 pytest安装用例运用规则
- 文件名必须以test_开头或者_test结尾
- 测试类必须以Test开头,并且不能有__init__方法。
- 测试方法必须以test开头
当满足以上要求后,可通过命令行参数pytest直接运行符合条件的用例
python
#测试类必须以Test开头,并且不能有__init__方法。
class Test03 :
def __init__(self):
print("-----init-------")
def test_03_01(self) :
print("test_03_01")
def test_03_02(self) :
print("test_03_02")
def test_03_03(self) :
print("test_03_03")
由于pytest的测试收集机制,测试类中不可以定义__init__方法。pytest采用自动发现机制来收集测试用例。它会自动实例化测试类并调用其所有以test结尾的方法作为测试用例。如果测试类中定义了_init__方法,那么当pytest实例化该类时,_init__方法会被调用,这可能会掩盖测试类的实际测试逻辑,并引入额外的副作用,影响测试结果的准确性。
python
#测试方法以test开头
def test_02_01() :
print("test_02_01")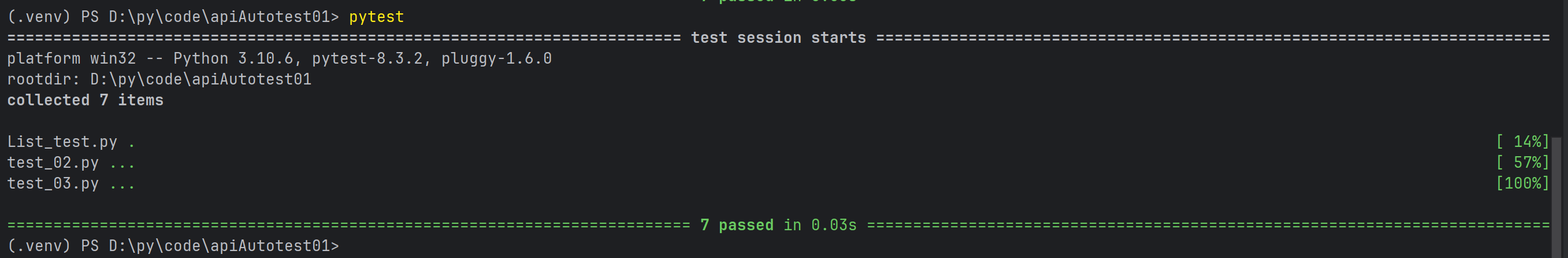
1.4 pytest命令参数
pytest提供了丰富的命令行选项来控制测试的执行。以下是一些常用的pytest命令行参数及其使用说明。
| 命令 | 描述 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| pytest | 在当前目录及其子目录中搜索并运行测试。 | |
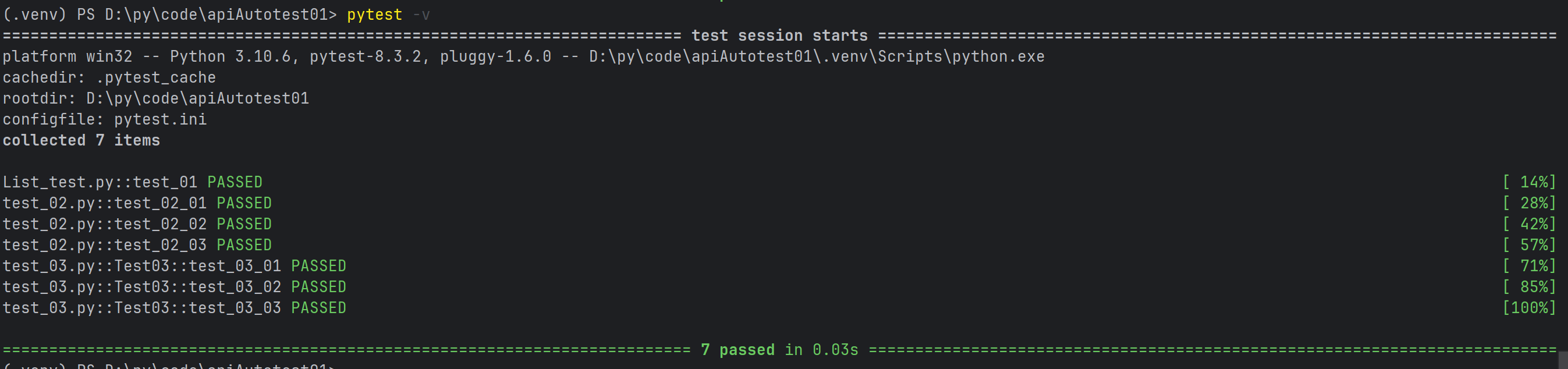
| pytest -v | 增加输出的详细程度。 | |
| pytest -s | 显示测试中的 print 语句。 | |
| pytest test_module.py | 运行指定的测试模块。 | |
| pytest test_dir/ | 运行指定目录下的所有测试。 | |
pytest -k <keyword> |
只运行测试名包含指定关键字的测试。 | |
pytest -m <marker> |
只运行标记为指定标记的测试。 | |
pytest -q |
减少输出的详细程度。 | |
pytest --html=report.html |
生成 HTML 格式的测试报告。 | 需要安装 pytest-html 插件 |
pytest --cov |
测量测试覆盖率 | 需要安装 pytest-cov 插件 |
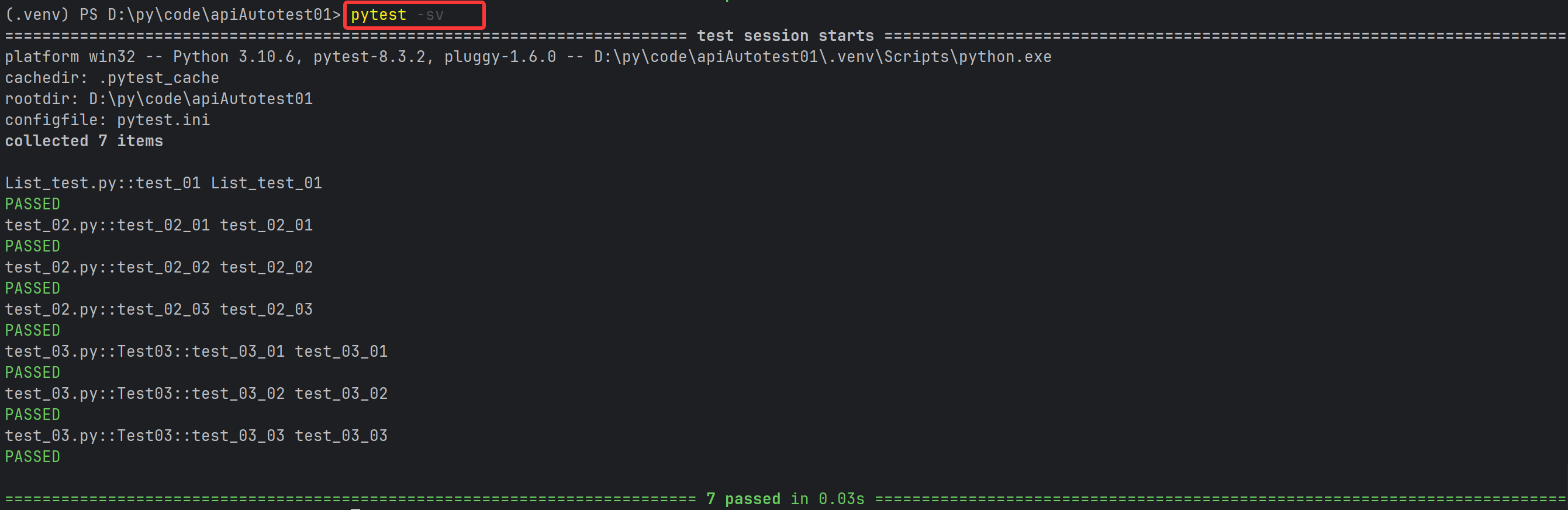
pytest -s -v 或者 pytest -sv (可以连写)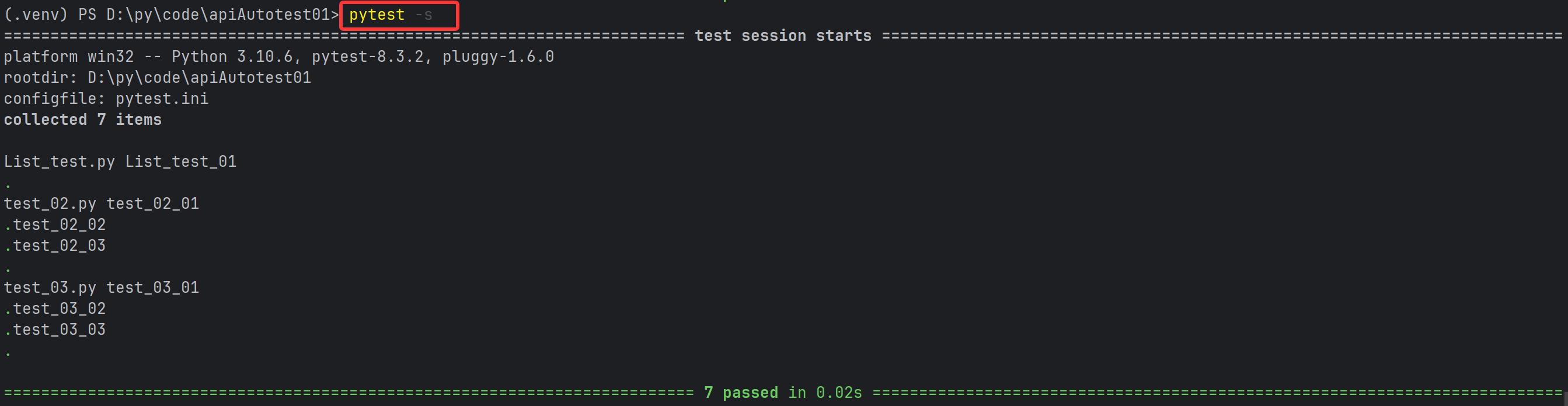
#指定⽂件:pytest 包名/⽂件名
pytest cases/test_01.py
#指定测试⽤例: pytest 包名/⽂件名::类名::⽅法名
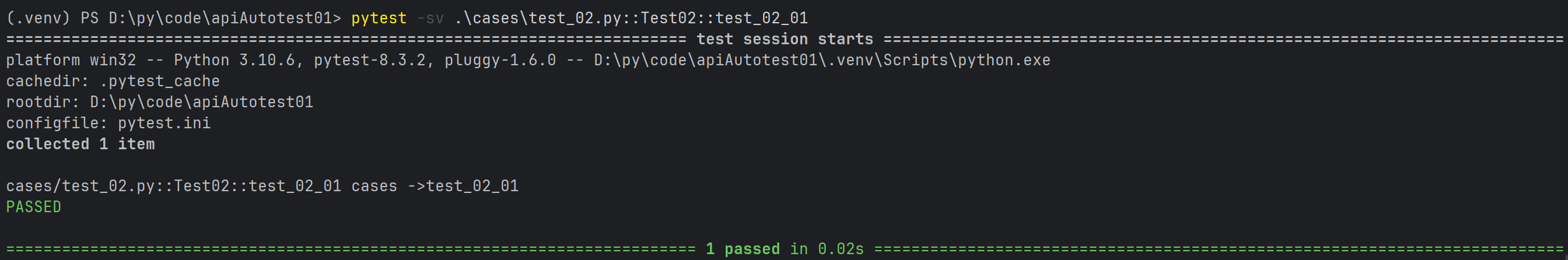
pytest cases/test_02.py::Test::test_a
python
def test_01_01() :
print("cases -> test_01_01")
def test_01_02() :
print("cases -> est_01_02")
def test_01_03() :
print("cases -> test_01_03")
python
class Test02:
def test_02_01(self):
print("cases ->test_02_01")
def test_02_02(self):
print("cases ->test_02_02")
def test_02_03(self):
print("cases ->test_02_03")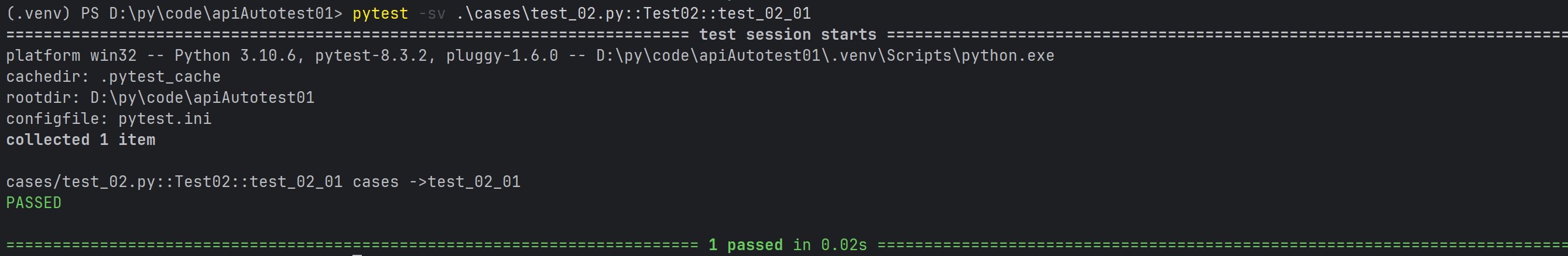
1.5 pytest安装配置文件
当我们既要详细输出,又要指定文件时,命令会又臭又长,而且每次运行都需要手动输入命
令,如何解决?
将需要的相关配置参数统一放到pytest配置文件中。
| 参数 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| addopts | 指定在命令行中默认包含的选项。 |
| testpaths | 指定搜索测试的目录。 |
| python_files | 指定发现测试模块时使用的文件匹配模式。 |
| python_classes | 指定发现测试类时使用的类名前缀或模式。 |
| python_functions | 指定发现测试函数和方法时使用的函数名前缀或模式。 |
norecursedirs |
指定在搜索测试时应该避免递归进入的目录模式。 |
markers |
定义测试标记,用于标记测试用例。 |
python
[pytest]
addopts = -vs
testpaths = ./cases
python_files = test_*.py
python_classes = Test*配置好pytest.ini文件后,命令行执行pytest命令即可,无需再额外指定其他参数
pytest.ini文件通常位于项目的根目录下。通过在pytest.ini中定义配置项,可以覆盖
pytest的默认行为,以满足项目的需求。
1.6 前后置
使用pytest框架,测试类中不可以添加init()方法,如何进行数据的初始化?
在测试框架中,前后置是指在执行测试用例前和测试用例后执行一些额外的操作,这些操作可以用于设置测试环境、准备测试数据等,以确保测试的可靠性
pytest框架提供三种方法做前后置的操作:
- setup_method 和 teardown_method:这两个方法用于类中的每个++测试方法的前置和后置操作++。
- setup_class 和 teardown_class:这两个方法用于整个++测试类的前置和后置操作++。
- fixture:这是pytest推荐的方式来实现测试用例的前置和后置操作。fixture提供了更灵活的控制和更强大的功能。
- 方法的前后置操作
python
class Test02:
def setup_method(self) :
print("setup_method")
def test_02_01(self):
print("cases ->test_02_01")
def test_02_02(self):
print("cases ->test_02_02")
def teardown_method(self) :
print("teardown_method")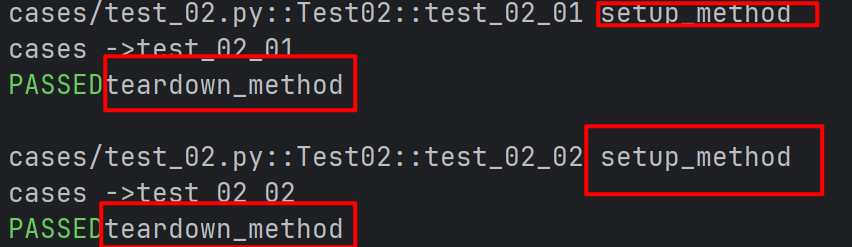
- 类的前后置操作
python
class Test02:
def setup_class(self) :
print("setup_class")
def test_02_01(self):
print("cases ->test_02_01")
def test_02_02(self):
print("cases ->test_02_02")
def teardown_class(self) :
print("teardown_class")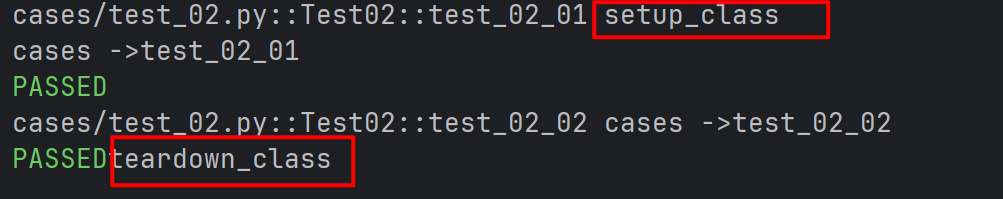
1.7 断言
断言(assert)是一种调试辅助工具,用于检查程序的状态是否符合预期。如果断言失(即条件为假),Python解释器将抛出一个AssertionError异常。断言通常用于检测程序中的逻辑错误。
pytest允许你在 Python测试中使用标准的 Pythonassert语句来验证预期和值。
pythonassert 条件, 错误信息
- 条件:必须是一个布尔表达式。
- 错误信息:当条件为假时显示的错误信息,可选。
免费学习API资源: http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/
- 基本数据类型的断言
python
def test_03_01():
a = 1
b = 2
assert a == b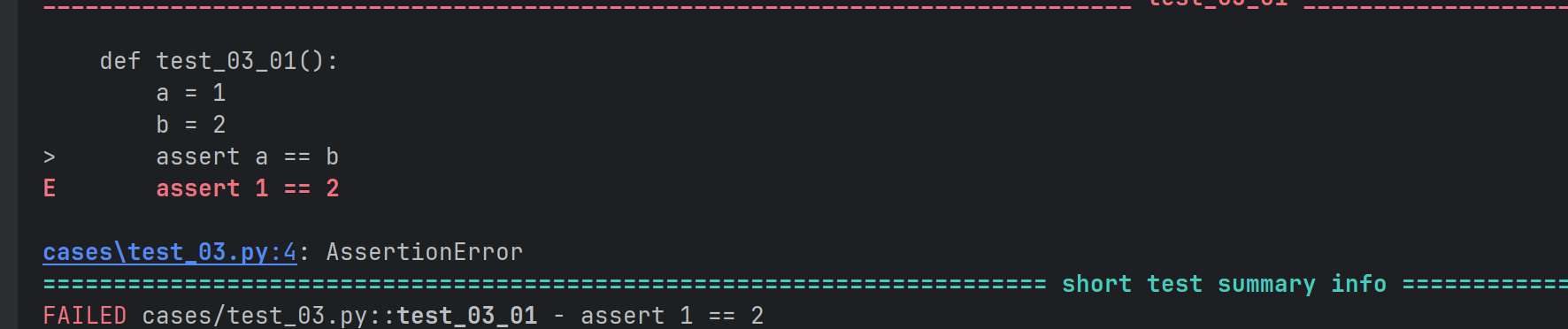
python
def test_03_01():
str1 = "hello"
str2 = "hallo"
assert str1 == str2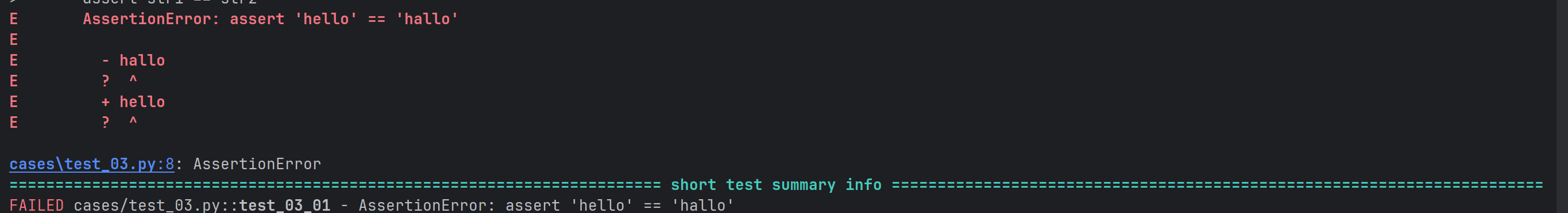
- 数据结构断言
python
def test_03_01():
# 断言列表
expect_list = [1, 'apple', 3.14]
actual_list = [1, 'apple', 3.14]
assert expect_list == actual_list
# 断言元组
expect_tuple = (1, 'apple', 3.14)
actual_tuple = (1, 'apple', 3.14)
assert expect_tuple == actual_tuple
# 断言字典
expect_dict = {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 25}
actual_dict = {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 25}
assert expect_dict == actual_dict
# 断⾔集合
expect_set = {1, 2, 3, 'apple'}
actual_set = {1, 2, 3, 'apple'}
assert expect_set == actual_set- 函数断言
python
def divide(a, b):
assert b != 0, "除数不能为0"
return a / b
def test_03_01():
# 正常情况
print(divide(10, 2)) # 输出 5.0
# 触发断⾔
print(divide(10, 0)) # 抛出 AssertionError: 除数不能为0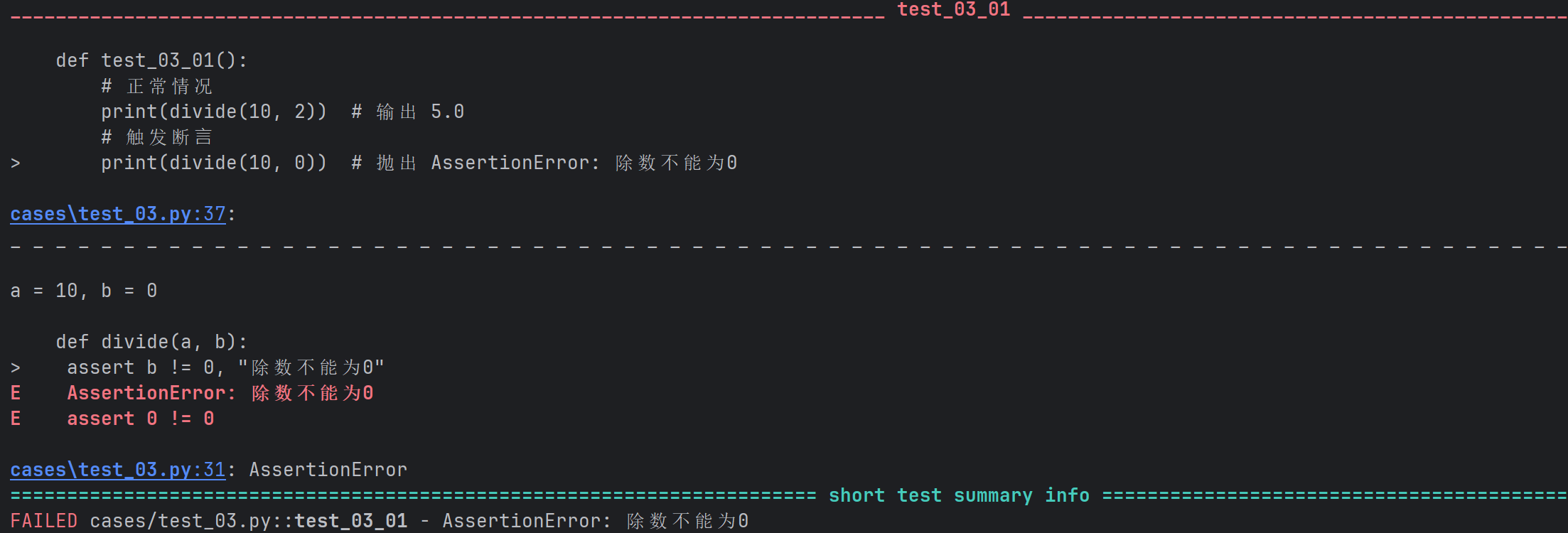
- 接口返回值引用
python
#断言接口返回值完整字段和值
def test():
url = "http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/1"
r = requests.get(url=url)
expect_data = {
"userId": 1,
"id": 1,
"title": "sunt aut facere repellat provident occaecati excepturi optio reprehenderit",
"body": "quia et suscipit\nsuscipit recusandae consequuntur expedita et cum\nreprehenderit molestiae ut ut quas totam\nnostrum rerum est autem sunt rem eveniet architecto"
}
actual_data = r.json()
assert expect_data == actual_data
# 断言接口返回值重要字段
def test2():
url = "http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/comments?postId=1"
r = requests.get(url=url)
print(r.json())
assert r.json()[0]['id'] == 1
#断言接口html返回值
def test3():
url = "http://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/"
r = requests.get(url=url)
assert "Use your own data" in r.text
1.8 参数化
参数化设计是自动化设计中的一个重要组成部分,它通过定义设计参数和规则,使得设计过程更加灵活和可控。
pytest中内置的pytest.mark.parametrize 装饰器允许对测试函数的参数进行参数化。
- 对单个参数的参数化
python
# 参数为同一类型
@pytest.mark.parametrize("data",(1,2,3))
def test(data):
print(data)
# 参数不是同一类型
@pytest.mark.parametrize("data",(1,"a",33.3))
def test2(data):
print(data)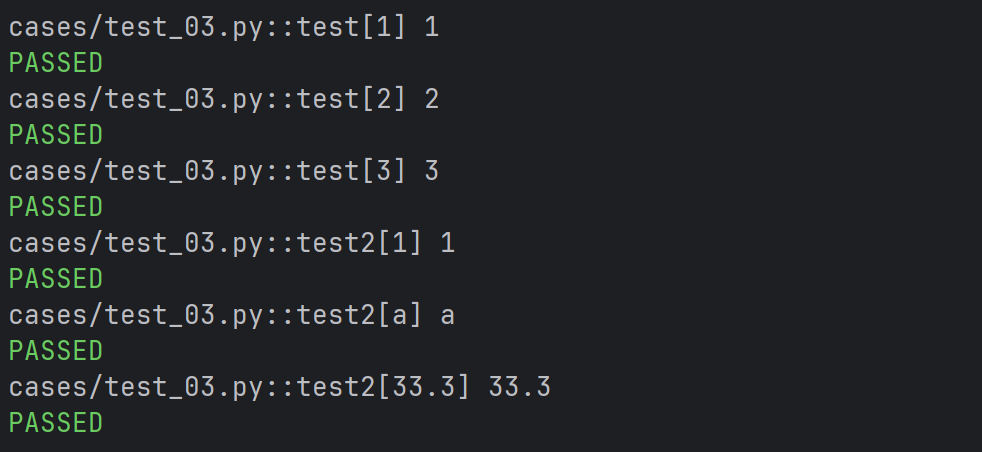
- 多组参数实现参数化
python
# 多组参数实现参数化
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_input,expected", [("3+5", 8), ("2+4", 6),("6*9", 42)])
def test_eval(test_input, expected):
assert eval(test_input) == expected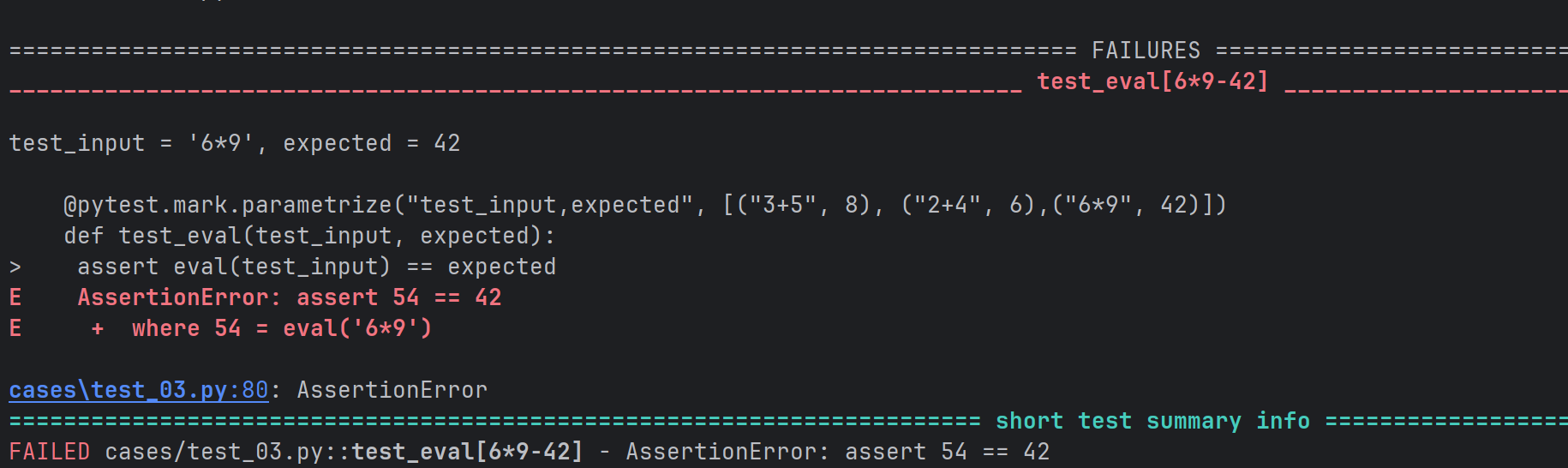
- 在类上使用参数化
python
@pytest.mark.parametrize("n,expected", [(1, 2), (3, 4)])
class TestClass:
def test_simple_case(self, n, expected):
assert n + 1 == expected
def test_weird_simple_case(self, n, expected):
assert (n * 1) + 1 == expected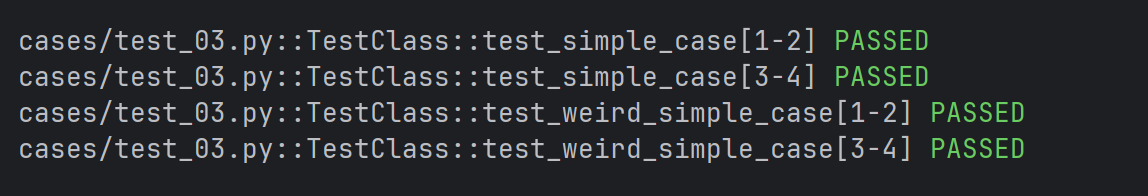
- 全局变量赋值参数
python
pytestmark = pytest.mark.parametrize("data",(1,2))
class Test_A:
def test_a01(self, data):
print(data)
def test_a02(self, data):
print("data")
class Test_B:
def test_b01(self, data):
print(data)
def test_b02(self, data):
print("data")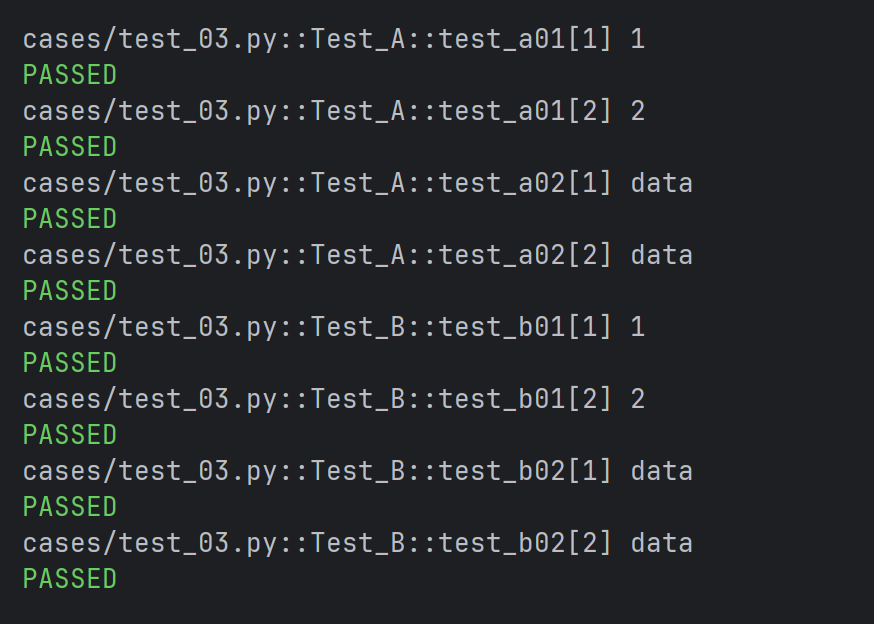
- 自定义参数化数据源
python
def data_provider():
return ["a", "b","c" ]
# 定义⼀个测试函数,它依赖于上⾯函数的返回值
@pytest.mark.parametrize("data", data_provider())
def test_data(data):
assert data != None
print(f"Testing with data provider: {data}")
2.fixture
2.1 基本使用
- 使用与不使用fixture标记
python
def fixture_01():
print("fixture_01")
def test_01():
fixture_01()
print("test_01")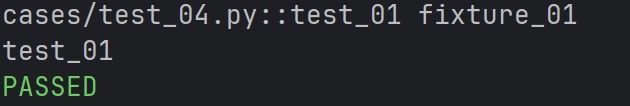
python
import pytest
@pytest.fixture
def fixture_01():
print("fixture_01")
def test_01(fixture_01):
print("test_01")
未标记fixture方法的调用与fixture标记的方法调用完全不一样,前者需要在方法体中调用,
而后者可以将函数名作为参数进行调用。
测试脚本中存在的很多重复的代码、公共的数据对象时,使用 fixture 最为合适
- 访问列表页和详情页之前都需要执行登录操作
python
import pytest
@pytest.fixture
def login():
print("---执⾏登陆操作-----")
def test_list(login):
print("---访问列表⻚")
def test_detail(login):
print("---访问详情⻚")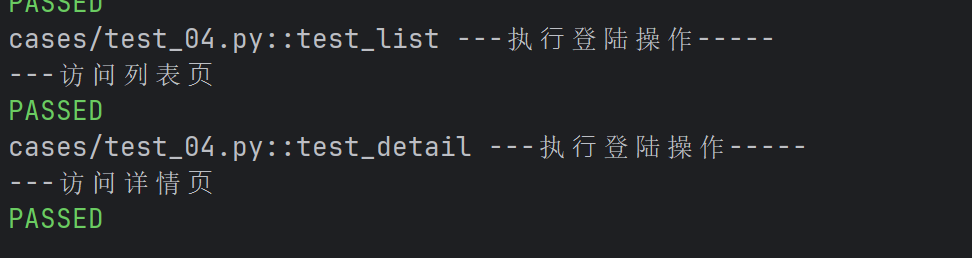
2.2 嵌套
python
@pytest.fixture
def first_entry() :
return "a"
@pytest.fixture
def order(first_entry) :
return [first_entry]
def test_string(order) :
order.append("b")
assert order == ["a", "b"]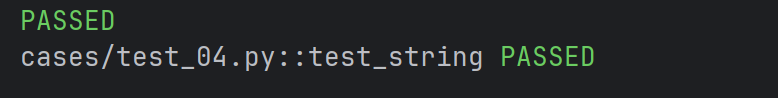
2.3 请求多个fixture
python
class Fruit :
def __init__(self, name, color) :
self.name = name
self.color = color
def __eq__(self, other):
#根据颜色判断
return self.color == other.color
@pytest.fixture
def my_fruit() :
return Fruit("apple", "red")
@pytest.fixture
def your_fruit() :
return [Fruit("banana","yellow"),Fruit("apple","green")]
def test_fruit(my_fruit, your_fruit) :
assert my_fruit in your_fruit2.4 yield fixture
当我们运行测试时,我们希望确保它们能够自我清理,以便它们不会干扰其他测试(同时也避免留下大量测试数据来膨胀系统)。pytest中的fixture提供了一个非常有用拆卸系统,它允许我们为每个fixture定义具体的清理步骤。
"Yield"fixture使用yield而不是return。有了这些fixture,我们可以运行一些代码,并将对象返回给请求的fixture/test,就像其他fixture一样。唯一的不同是:
- return被替换为yield。
- 该fixture的任何拆卸代码放置在yield之后。
执行顺序 :一旦pytest确定了fixture的线性顺序,它将运行每个fixture直到它返回或yield,然后继续执行列表中的下一个fixture做同样的事情。
测试完成后,pytest将逆向遍历fixture列表,对于每个yield的fixture,运行yield语句之后的代码。
- 返回数据/什么也不返回
python
@pytest.fixture
def operator():
print("数据的初始化")
yield 100
print("数据的清理")
def test_operator(operator):
print(100 + operator)
assert 100 == operator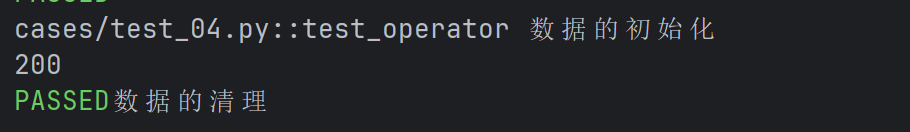
python
@pytest.fixture
def open_close():
print("前置操作,初始化.....")
yield
print("后置操作,清理数据.....")
def test_01(open_close):
print("第⼀个测试⽤例")
- 创建文件句柄和关闭文件
python
@pytest.fixture
def file_read() :
print("打开文件句柄")
f = open("test.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
yield f
print("关闭文件句柄")
f.close()
def test_file(file_read) :
r = file_read
str = r.read()
print(str)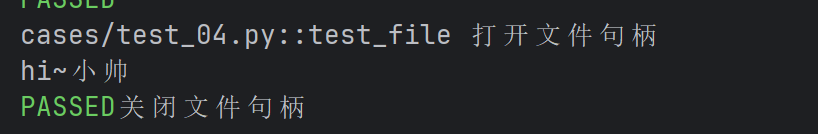
python
@pytest.fixture
def file_read() :
print("打开文件句柄")
f = open("test.txt","r",encoding="utf-8")
yield f
print("关闭文件句柄")
f.close()
@pytest.fixture
def file_write():
print("打开文件句柄")
f = open("test.txt","w",encoding="utf-8")
return f
def test_file(file_read,file_write) :
# 写⼊数据
w = file_write
w.write("测试数据")
w.close() # 写⼊后关闭⽂件句柄,以便读取
r = file_read
str = r.read()
print(str)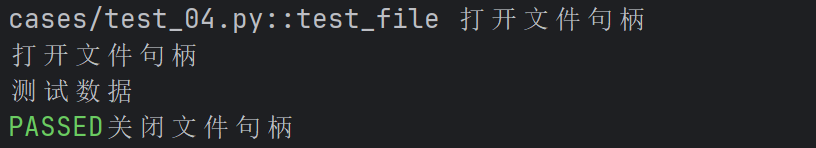
2.5 带参数的fixture
pytest.fixture(scope='', params='', autouse='', ids='', name='')- scope参数用于控制fixture的作用范围,决定了fixture的生命周期。可选值有:
- function(默认):每个测试函数都会调用一次fixture。
- class:在同一个测试类中共享这个fixture。
- module:在同一个测试模块中共享这个fixture。(一个文件里)
- session:整个测试会话中共享这个fixture。
- autouse参数默认为False。如果设置为True,则每个测试函数都会自动调用该fixture,
无需显式传入 - params参数用于参数化fixture,支持列表传入。每个参数值都会使fixture执行一次,类似于
for循环 - ids参数与params配合使用,为每个参数化实例指定可读的标识符(给参数取名字)
- name参数用于为fixture显式设置一个名称。如果使用了name,则在测试函数中需要使用这个
名称来引用fixture(给fixture取名字)
- scope的使用
python
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope="function")
def fixture_01() :
print("初始化")
yield
print("清理")
class TestCase() :
def test_01(self, fixture_01) :
print("第一个测试用例")
def test_02(self, fixture_01) :
print("第二个测试用例")
python
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope="class")
def fixture_01() :
print("初始化")
yield
print("清理")
class TestCase() :
def test_01(self, fixture_01) :
print("第一个测试用例")
def test_02(self, fixture_01) :
print("第二个测试用例")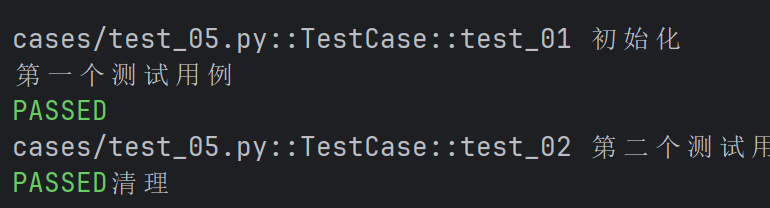
结论:
- scope默认为function,这里的function可以省略不写,当scope="function"时,每个测试函数都会调用一次fixture。
- scope="class"时,在同一个测试类中,fixture只会在类中的第一个测试函数开始前执行一次,并在类中的最后一个测试函数结束后执行清理。
- scope="moudle" scope="session"实现全局的前后置应用
- 当scope="moudle"、scope="session"时可用于实现全局的前后置应用,这里需要多个文件的配合
- conftest.py 和**@pytest.fixture** 结合使用实现全局的前后置应用
结合使用,可以实现在多个测试模块(py)文件中共享前后置操作,这种结合的方式使得可以在整个测试项目中定义和维护通用的前后置逻辑,使测试代码更加模块化和可维护。规则:
- conftest.py是一个单独存放的夹具配置文件,名称是固定的不能修改
- 你可以在项目中的不同目录下创建多个conftest.py文件,++每个conftest.py文件都会对其
所在目录及其子目录下的测试模块生效++- 在不同模块的测试中需要用到conftest.py的前后置功能时不需要做任何的import导入操作
- 作用:可以在不同的.py文件中使用同一个fixture函数
python
#conftest.py
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope="module", autouse=True)
def fixture_01():
print("初始化")
yield
print("清理")
python
def test_case01():
print("单独放出来的测试⽤例01")
class TestCase01():
def test_01(self):
print("第⼀个测试用例")
def test_02(self):
print("第二个测试用例")
def test_case02():
print("单独放出来的测试⽤例01")
class TestCase02():
def test_01(self):
print("第⼀个测试用例")
def test_02(self):
print("第二个测试用例")
python
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope="session", autouse=True)
def fixture_01():
print("初始化")
yield
print("清理")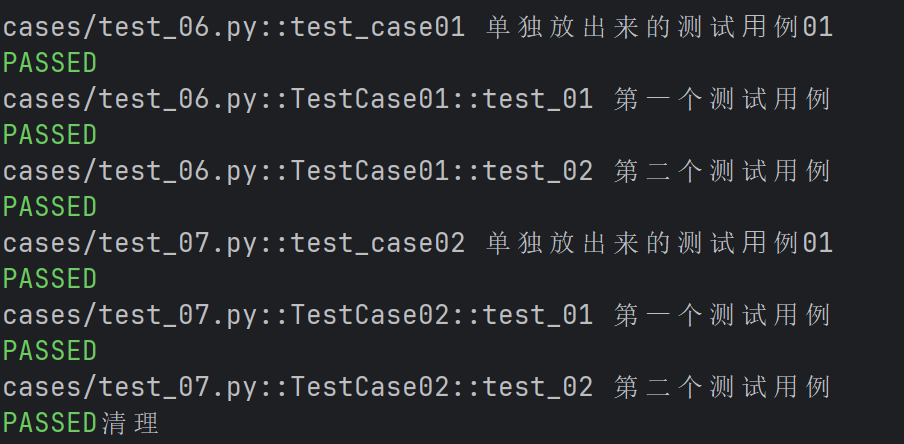
- autouse 的使用
python
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope="class", autouse=True)
def fixture_01() :
print("初始化")
yield
print("清理")
class Test_case():
def test_01(self):
print("第一个测试用例")
def test_02(self):
print("第二个测试用例")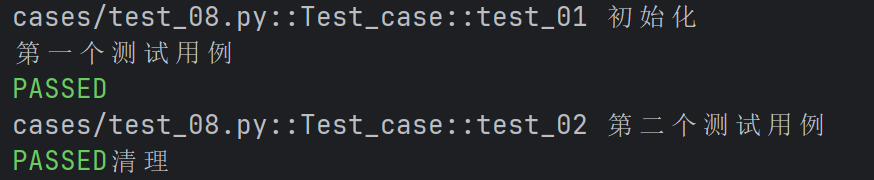
为False时:

autouse默认为False,即当前的fixture需要手动显示调用,在该案例之前我们默认使用的
都是autouse=False
当autouse=True时,fixture会在所有测试函数执行之前自动调用,无论这些测试函数是否显
式地引用了该fixture
- 通过 params 实现参数化
python
# 定义⼀个参数化的 fixture
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(params=["a", "b"])
def data_provider(request):
return request.param
# 定义⼀个测试函数,它依赖于上⾯的参数化 fixture
def test_data(data_provider):
assert data_provider != None
print(f"Testing with data provider: {data_provider}")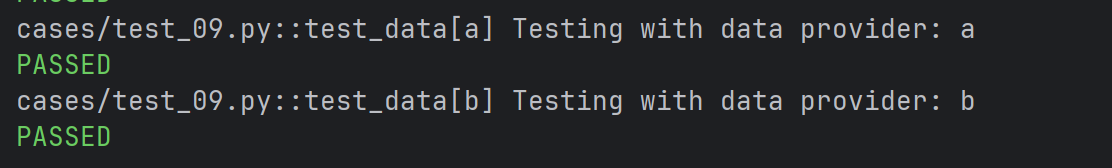
3.YAML
3.1YAML介绍
- 简单标量值
python
#yml文件
key: value
python
#JSON文件
{
"key": "value"
}
- 整数和浮点数
python
int_key: 123
float_key: 123.456
python
{
"int_key": 123,
"float_key": 123.456
}
- 布尔值
python
bool_key: true
python
{
"bool_key": true
}
- 字符串
python
string_key: "This is a string"
python
{
"string_key": "This is a string"
}
- 列表
python
list_key:
- item1
- item2
- item3
python
{
"list_key": ["item1", "item2", "item3"]
}
- 映射(字典)
python
map_key:
sub_key1: sub_value1
sub_key2: sub_value2
- 嵌套结构
python
nested_key:
list_key:
- item1
- item2
map_key:
sub_key1: sub_value1
sub_key2: sub_value2
python
{
"nested_key": {
"list_key": [
"item1",
"item2"
],
"map_key": {
"sub_key1": "sub_value1",
"sub_key2": "sub_value2"
}
}
}
3.2使用
- 安装 YAML 库
yaml文件通常作为配置文件来使用,可以使用yaml库来读取和写入YAML文件
python
pip install PyYAML==6.0.1- 创建 YAML 文件
- 写入 YAML 文件
python
#往yaml中写入数据
import yaml
def write_yaml(filename, data):
with open(file = filename, mode = 'a+', encoding = "utf-8") as f:
# 写入数据
yaml.safe_dump(data=data, stream=f)
# 测试往yaml文件中写入数据
def test_write() :
data = {
"name" : "zhangsan",
"age" : 22,
}
write_yaml("firstyaml.yml", data)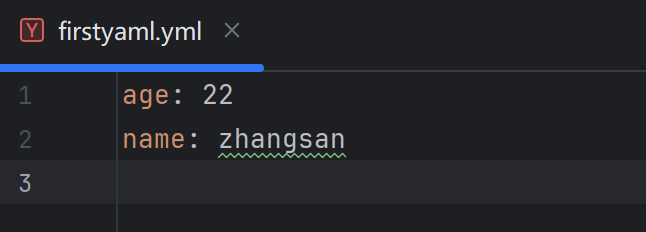
- 读取 YAML 文件
python
# 读取yaml文件中的数据
def read_yaml(filename):
with open(file = filename, mode = 'r', encoding = "utf-8") as f:
data = yaml.safe_load(stream = f)
return data
#测试读取yaml中的数据
def test_read() :
data = read_yaml("firstyaml.yml")
print(data)
注意:
Python的内置类型字典和json格式非常像
- JSON里key和字符串类型的值必须要用双引号
- Python里的单引号和双引号均可
因此当我们想要转为JSON时,就必须将Python中的字典格式数据转为JSON格式
pythondef test_read() : data = read_yaml("firstyaml.yml") json_str = json.dumps(data) print(json_str)
- 清空 YAML 文件
python
# 清空 yaml 文件中的数据
def clear_yaml(filename):
with open(file = filename, mode = 'w', encoding = "utf-8") as f:
f.truncate()
# 测试清空 yaml 文件中的数据
def test_clear() :
clear_yaml("firstyaml.yml")4.JSON Schema
JSON Schema一个用来定义和校验JSON的web规范,简而言之,JSON Schema是用来校验json是否符合预期。
根据json创建JSONSchema后,你可以使用你选择的语言中的验证器将示例数据与你的模式进行
验证。
4.1 介绍
python
#JSON
{
"code": "SUCCESS",
"errMsg": "",
"data": false
}
python
#schema
{
"type": "object",
"required": [],
"properties": {
"code": {
"type": "string"
},
"errMsg": {
"type": "string"
},
"data": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}json转JSON Schema太麻烦?使用现有工具自动转换:https://tooltt.com/json2schema/
注意:工具不是万能的,结果可能存在错误,要对自动生成的结果进行二次检查
python
def test_02():
url = "http://62.234.142.221:58080/board/topList"
header = {
"cookie" : "JSESSIONID=C8DD82EC03C9C3ABCC8D1C930FBD3C47"
}
r = requests.get(url,headers = header)
json_schema = {
"type": "object", # 响应根节点是对象
"required": ["code", "message", "data"], # 建议加上必选字段(根据接口实际返回调整)
"properties": {
"code": {"type": "number"},
"message": {"type": "string"}, # 注意:接口返回的message通常是字符串(比如"success"),之前写number可能报错,这里修正
"data": {
"type": "array", # data是数组
"items": { # 数组中的每个元素是对象
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {"type": "number"},
"name": {"type": "string"},
"articleCount": {"type": "number"},
"sort": {"type": "number"},
"state": {"type": "number"},
"deleteState": {"type": "number"},
"createTime": {"type": "string"},
"updateTime": {"type": "string"}
}
}
}
}
}
validate(r.json(), json_schema)
validate(json, json_schema)是用于验证 JSON 数据是否符合指定 JSON Schema 规则
- 待验证 JSON :你提供的包含
code、message、data的接口响应数据(code为数字 0,state和deleteState为数字 0 等)。- JSON Schema :你提供的用于描述 JSON 结构的规则(原 Schema 中
code、state、deleteState被错误定义为string类型)。
required:仅用于type: "object"中,指定对象必须包含的属性
4.2 数据类型
type 关键字指定了数据类型。 可以验证 JSON 数据中每个属性的数据类型是否符合预期。常用的数据类型包括:
| type | 解释 |
|---|---|
| string | 字符串类型,用于文本数据。 |
| number | 数字类型,用于表示浮点数。 |
| integer | 整数类型,用于表示整数。 |
| boolean | 布尔类型,值为 true 或 false。 |
| object | 对象类型,用于嵌套的 JSON 对象。 |
| array | 数组类型,用于列表或集合。 |
| null | 空值类型。 |
int只能表示整形数据,但是 number 表示数字:整数、浮点数...
python
def test_03():
json = {
"name":"zhangsan",
"height":178.5,
"female":False,
"hobby":{
"aaa":"aaa",
"bbb":"bbb",
}
}
json_schema = {
"type": "object",
"required": [],
"properties": {
"name": {"type": "string"},
"height": {"type": "number"},
"female": {"type": "boolean"},
"hobby":{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"aaa": {"type": "string"},
"bbb": {"type": "string"},
}
}
}
}
validate(json, json_schema)
"properties"是用于定义 "对象类型("type": "object")" 内部所包含的属性(字段)及其验证规则的关键字
python
def test_04():
json = {
"data":[
{
"name":"zhangsan",
"age":20
},
{
"name":"lisi",
"age":18
}
],
"addr":None
}
json_schema = {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"addr": {"type": "null"},
},
"data":{
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {"type": "string"},
"age": {"type": "number"},
}
}
}
}
validate(json, json_schema)
items:仅用于type: "array"中,定义数组内元素的验证规则(所有元素需符合同一规则)。
4.3 最大最小值
- minimum和maximum:指定数值的最小值和最大值。
- exclusiveMinimum和exclusiveMaximum:指定数值必须严格大于或小于某个值(不包含等于)。
python
def test_05():
json = {
"name":"zhangsan",
"age":10
}
json_schema= {
"type": "object",
"required": [],
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string"
},
"age": {
"type": "number",
# "minimum":0,
# "maximum":100
"exclusiveMinimum":0,
"exclusiveMaximum":100
}
}
}
validate(instance=json,schema=json_schema)4.4 字符串特殊校验
pattern:使用正则表达式来验证字符串是否符合特定的模式。
正则表达式在线测试工具:https://www.sojson.com/regex/check.html
| 代码 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| . | 匹配除换行符以外的任意字符 |
| \w | 匹配字母或数字或下划线 |
| \s | 匹配任意的空白符 |
| \d | 匹配数字 |
| \b | 匹配单词的开始或结束 |
| ^ | 匹配字符串的开始 |
| $ | 匹配字符串的结束 |
| 代码/语法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| * | 重复零次或更多次 |
| + | 重复一次或更多次 |
| ? | 重复零次或一次 |
| {n} | 重复n次 |
| {n,} | 重复n次或更多次 |
| {n,m} | 重复n到m次 |
python
def test_06():
json = {
"name": "zhangsa",
"age": 10
}
json_schema = {
"type": "object",
"required": [],
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string",
"pattern":"\S{20,}"
},
"age": {
"type": "number"
}
}
}
validate(instance=json,schema=json_schema)\S表示 "非空白字符"(即不能是空格、换行等),{20,}表示 "至少 20 个字符"。因此,"name"字段的值必须是**长度≥20 的非空白字符串,**所以此时会报错
4.5 数组约束
- minItems和maxItems:指定数组的最小和最大长度。
- uniqueItems:确保数组中的元素是唯一的。(默认情况下是允许重复False)
- items:定义数组中每个元素的类型和约束。
python
def test_07():
json = {
"data":[1,2,3,5,5],
"str":"hello"
}
json_schema = {
"type": "object",
"required": [],
"properties": {
"data": {
"type": "array",
# 针对数组添加最大和最小长度限制
"minItems":1,
"maxItems":5,
# 要求数组中元素唯一
"uniqueItems":True,
"items": {
"type": "number"
}
},
"str": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}
validate(instance=json,schema=json_schema)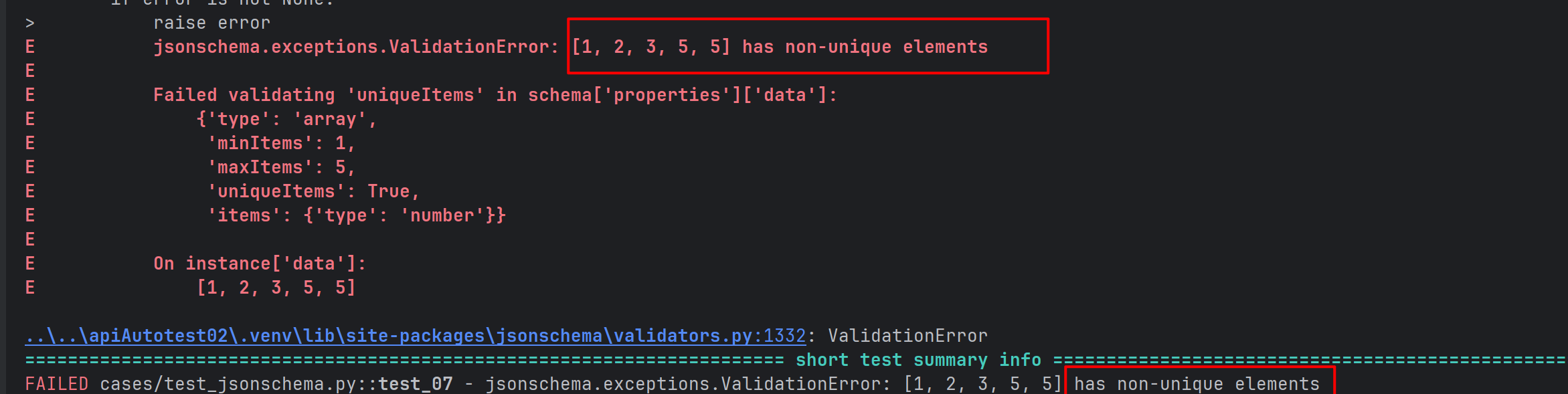
4.6 对象约束
- minProperties和maxProperties:指定对象的最小和最大属性数量。
- additionalProperties:控制是否允许对象中存在未在properties中定义的额外属性,默认为True。
python
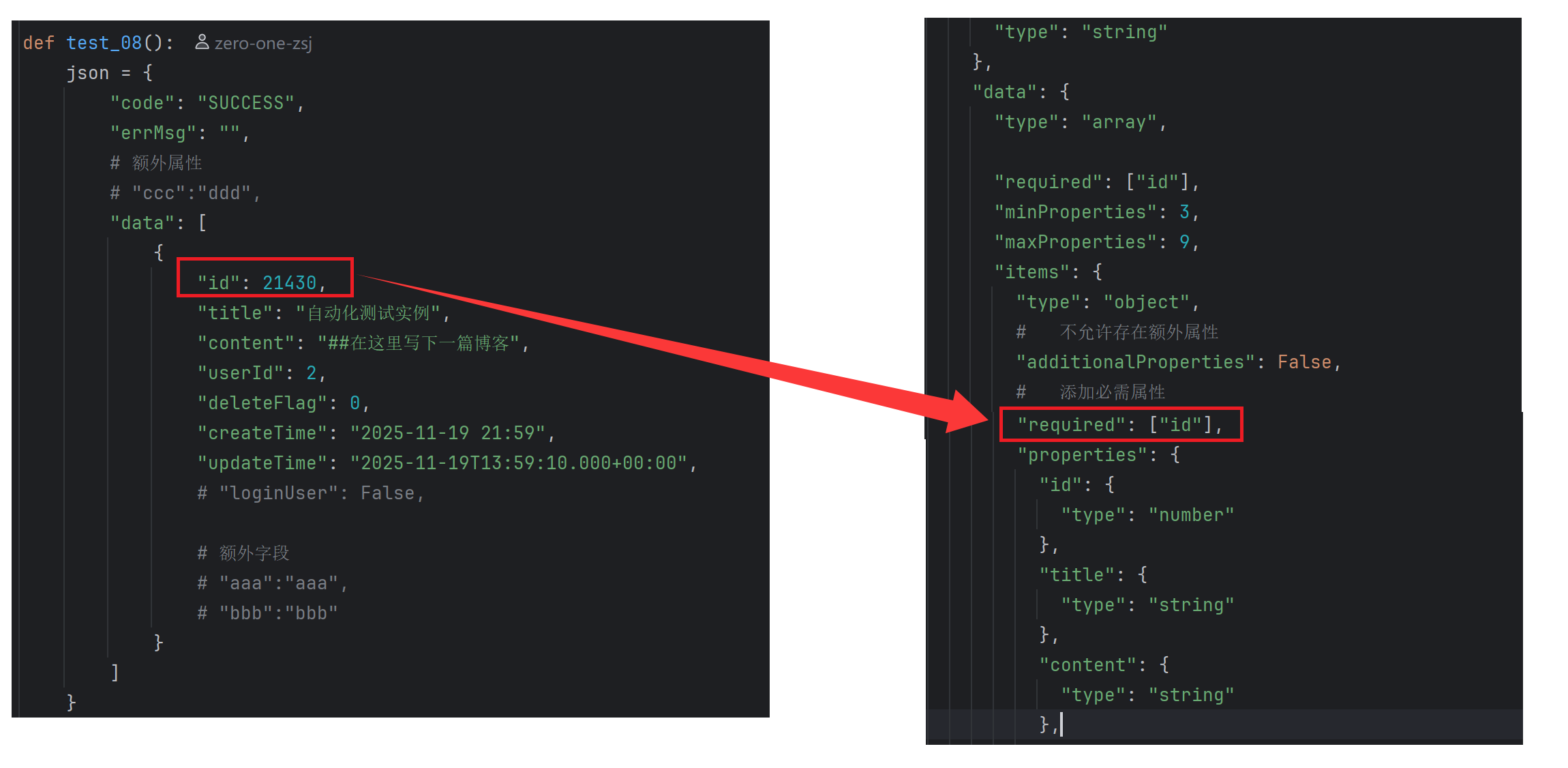
def test_08():
json = {
"code": "SUCCESS",
"errMsg": "",
# 额外属性
"ccc":"ddd",
"data": [
{
"id": 21430,
"title": "自动化测试实例",
"content": "##在这里写下一篇博客",
"userId": 2,
"deleteFlag": 0,
"createTime": "2025-11-19 21:59",
"updateTime": "2025-11-19T13:59:10.000+00:00",
"loginUser": False,
# 额外字段
"aaa":"aaa",
"bbb":"bbb"
}
]
}
json_schema ={
"type": "object",
# 不允许存在额外属性
"additionalProperties": False,
# 指定对象的最大最小属性数量
"minProperties": 3,
"maxProperties": 3,
# 添加必需属性
"required": [],
"properties": {
"code": {
"type": "string"
},
"errMsg": {
"type": "string"
},
"data": {
"type": "array",
"minProperties": 3,
"maxProperties": 9,
"items": {
"type": "object",
# 不允许存在额外属性
"additionalProperties": False,
"required": ["id","loginUser"],
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "number"
},
"title": {
"type": "string"
},
"content": {
"type": "string"
},
"userId": {
"type": "number"
},
"deleteFlag": {
"type": "number"
},
"createTime": {
"type": "string"
},
"updateTime": {
"type": "string"
},
"loginUser": {
"type": "boolean"
}
}
}
}
}
}
validate(instance=json,schema=json_schema)

4.7 必须属性
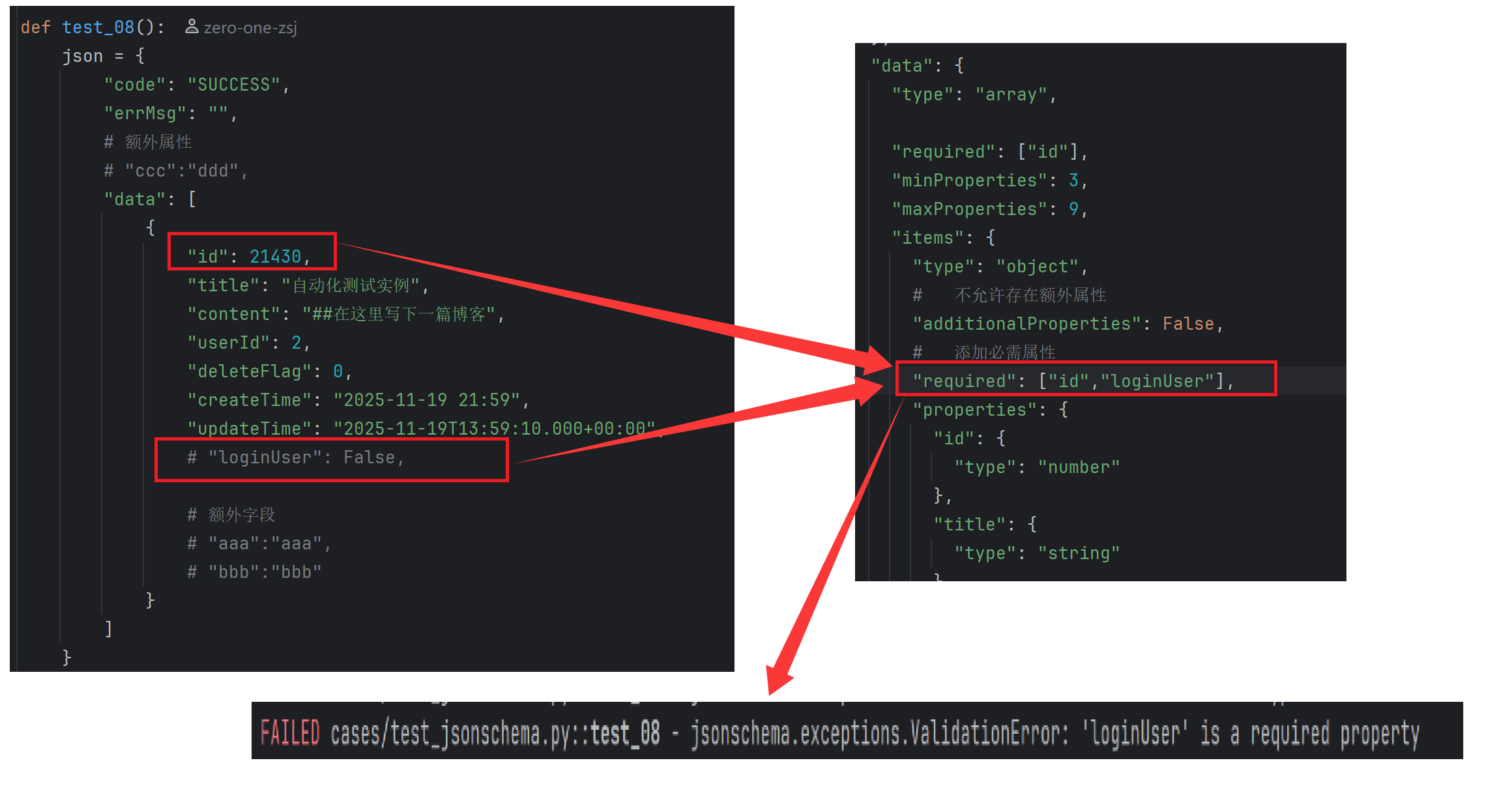
通过required关键字,JSONSchema可以指定哪些属性是必需的。如果JSON实例中缺少这些必需属性,验证将失败。
python
json_schema ={
"type": "object",
# 不允许存在额外属性
"additionalProperties": False,
# 指定对象的最大最小属性数量
"minProperties": 3,
"maxProperties": 3,
"properties": {
"code": {
"type": "string"
},
"errMsg": {
"type": "string"
},
"data": {
"type": "array",
"required": ["id"],
"minProperties": 3,
"maxProperties": 9,
"items": {
"type": "object",
# 不允许存在额外属性
"additionalProperties": False,
# 添加必需属性
# "required": ["id","loginUser"],
"required": ["id"],
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "number"
},
"title": {
"type": "string"
},
"content": {
"type": "string"
},
"userId": {
"type": "number"
},
"deleteFlag": {
"type": "number"
},
"createTime": {
"type": "string"
},
"updateTime": {
"type": "string"
},
"loginUser": {
"type": "boolean"
}
}
}
}
}
}
4.8 依赖关系
dependentRequired可以定义属性之间的依赖关系。例如,如果某个属性存在,则必须存在另一个属性。
python
def test_09():
json = {
"username":"zhangsan",
"age":20,
"height":178,
"gender":"male",
"hobby":{
"aaa":"aaa",
#"bbb":"bbb"
}
}
json_schema = {
"type": "object",
"required": [],
"properties": {
"username": {
"type": "string"
},
"age": {
"type": "number"
},
"height": {
"type": "number"
},
"gender": {
"type": "string"
},
"hobby":{
"type":"object",
"properties":{
"aaa":{
"type":"string"
},
"bbb":{
"type": "string"
}
},
"dependentRequired":{
"aaa":["bbb"]
}
}
},
"dependentRequired":{
"age":["height","gender"]
}
}
validate(instance=json,schema=json_schema)
5.logging 日志模块
5.1 介绍
logging是Python标准库中的一个模块,它提供了灵活的日志记录功能。通过logging,开发
者可以方便地将日志信息输出到控制台、文件、网络等多种目标,同时支持不同级别的日志记录,以满足不同场景下的需求。
5.2 使用
- 全局logging
python
import logging
# 指定输出级别,输出 info 及以上级别的日志
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
# 默认情况下 logging 输出 warning 及以上级别的日志
logging.debug("this is a debug message")
logging.info("this is a info message")
logging.warning("this is a warning message")
logging.error("this is a error message")
logging.critical("this is a critical message")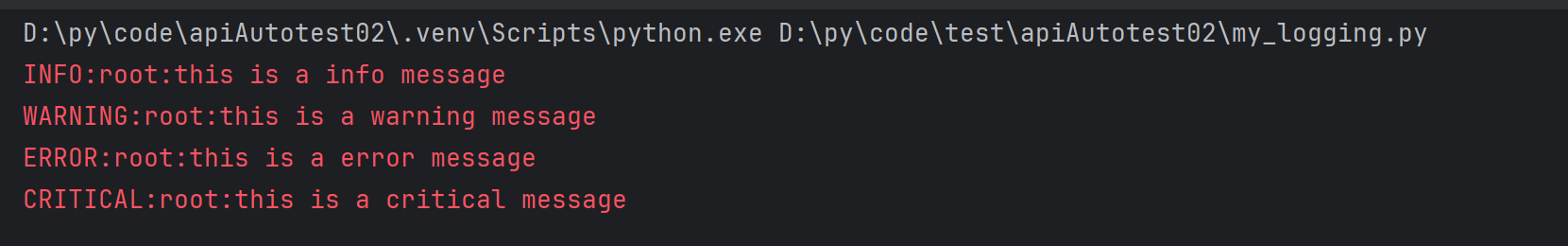
- 自定义logger并输出到控制台
python
logger = logging.getLogger("my_logger")
#给 logger 配置自己的日志级别
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
logger.debug("this is a debug message")
logger.info("this is a info message")
logger.warning("this is a warning message")
logger.error("this is a error message")
logger.critical("this is a critical message")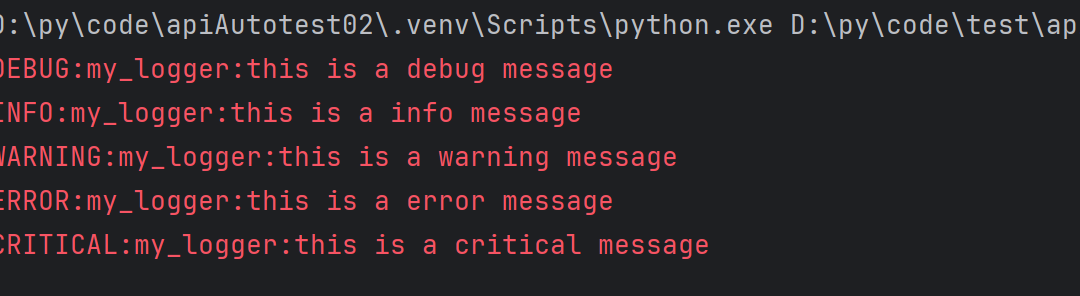
- 自定义logger并输出到日志文件
python
logger = logging.getLogger("my_logger")
#给 logger 配置自己的日志级别
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# 创建文件处理器 -- 将日志输出到 mylog.log 里(可以自动创建)
handler = logging.FileHandler(filename="mylog.log")
# 将处理器添加到日志记录器中
logger.addHandler(handler)
logger.debug("this is a debug message")
logger.info("this is a info message")
logger.warning("this is a warning message")
logger.error("this is a error message")
logger.critical("this is a critical message")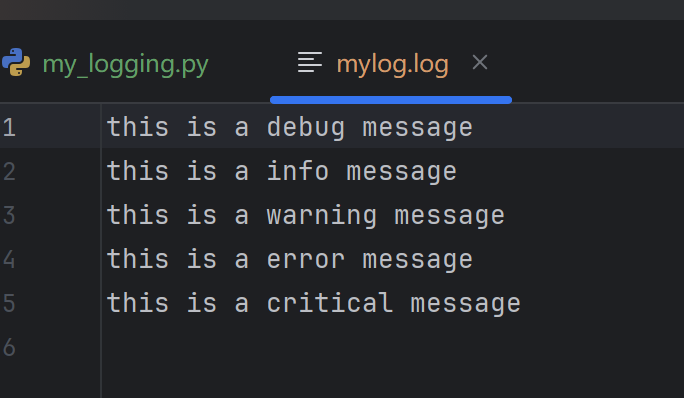
- 获取日志记录器:logging·getLogger(name_)获取一个日志记录器对象,name是当前模块的名称。使用模块名称作为日志记录器的名称有助于在大型项目中区分不同模块的日志。
- 设置日志级别 :logger.setLevel(logging.DEBuG)将日志记录器的级别设置为
DEBUG,这意味着所有DEBUG及以上级别的日志都会被记录。
- 日志级别金字塔:DEBUG<INFO<WARNING<ERROR<CRITICAL
高于设定级别的日志才会被处理- 创建文件处理器 :logging.FileHandler(filename="test.log")创建一个文件处理
器,将日志信息写入到名为test.log的文件中.- 添加处理器:logger.addHandler(handler)将文件处理器添加到日志记录器中,这样日志记录器就会使用这个处理器来处理日志信息,
- 设置日志格式
python
logger = logging.getLogger("my_logger")
#给 logger 配置自己的日志级别
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# 创建文件处理器 -- 将日志输出到 mylog.log 里(可以自动创建)
handler = logging.FileHandler(filename="mylog.log")
# 创建一个日志格式器对象
formatter = logging.Formatter(
"%(asctime)s %(levelname)s [%(name)s] [%(filename)s (%(funcName)s:%(lineno)d)] - %(message)s"
)
# 将格式器设置到处理器上
handler.setFormatter(formatter)
# 将处理器添加到日志记录器中
logger.addHandler(handler)
logger.debug("this is a debug message")
logger.info("this is a info message")
logger.warning("this is a warning message")
logger.error("this is a error message")
logger.critical("this is a critical message")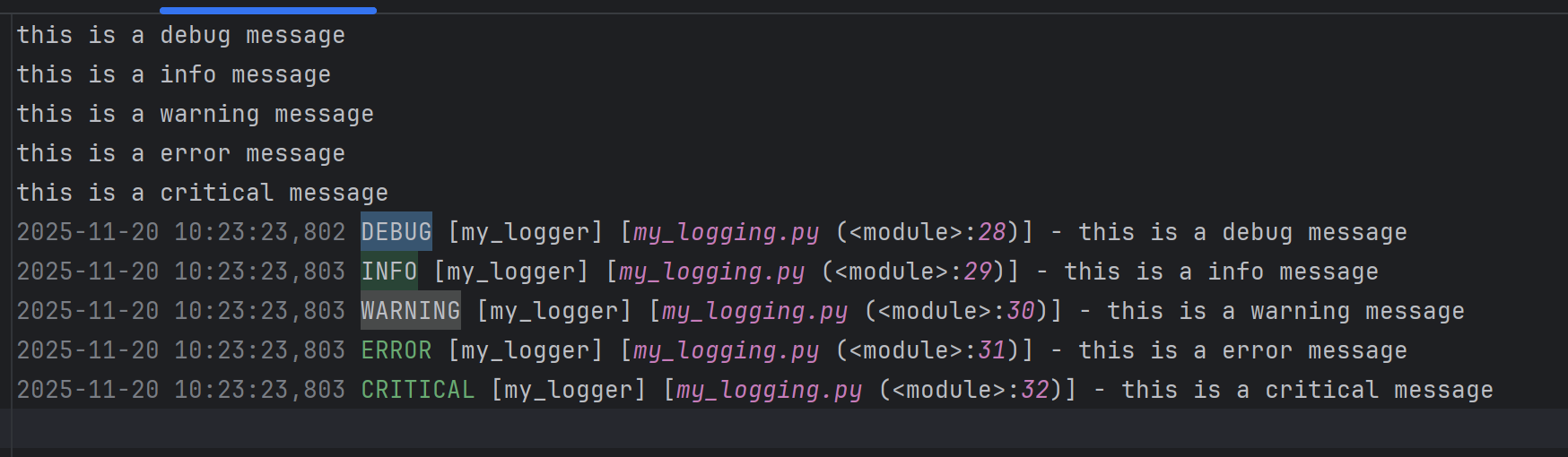
logging.Formatter是用于定义日志输出格式的类。在构造函数中,传递了一个格式字符串,用于指定日志信息的格式。格式字符串中使用了一些特殊的占位符(以开头),这些占位符会被替换为相应的日志信息内容
| 格式占位符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
%(asctime)s |
日志记录的时间戳,通常显示为日期和时间。 |
%(levelname)s |
日志级别(如 DEBUG、INFO、WARNING、ERROR、CRITICAL)。 |
%(name)s |
日志记录器的名称,通常为模块名称。 |
%(filename)s |
日志记录发生的文件名。 |
%(funcName)s |
日志记录发生的函数名。 |
%(lineno)d |
日志记录发生的行号。 |
%(message)s |
日志消息本身。 |
handler.setFormatter(formatter)将创建的格式器对象设置到处理器上。这意味着处理器在处理日志信息时,会使用这个格式器来格式化日志信息。
通过这种方式,你可以控制日志信息的输出格式,使其包含你感兴趣的信息,如时间戳、日志级别、文件名、函数名、行号等。
6.测试报告 allure
官方文档:https://allurereport.org/docs/pytest-configuration
6.1 介绍
AllureReport由一个框架适配器和allure命令行工具组成,是一个流行的开源工具,用于可视化
测试运行的结果。它可以以很少甚至零配置的方式添加到您的测试工作流中。它生成的报告可以在任何地方打开,并且任何人都可以阅读,无需深厚的技术知识。
6.2 安装
-
下载allure-pytest包
pip install allure-pytest==2.13.5 -
下载 Windows 版 Allure 报告
https://github.com/allure-framework/allure2/releases/download/2.30.0/allure2.30.0.zip
2.1解压后添加系统环境变量(将 allure-2.29.0 对应 bin 目录添加到系统环境变量中)
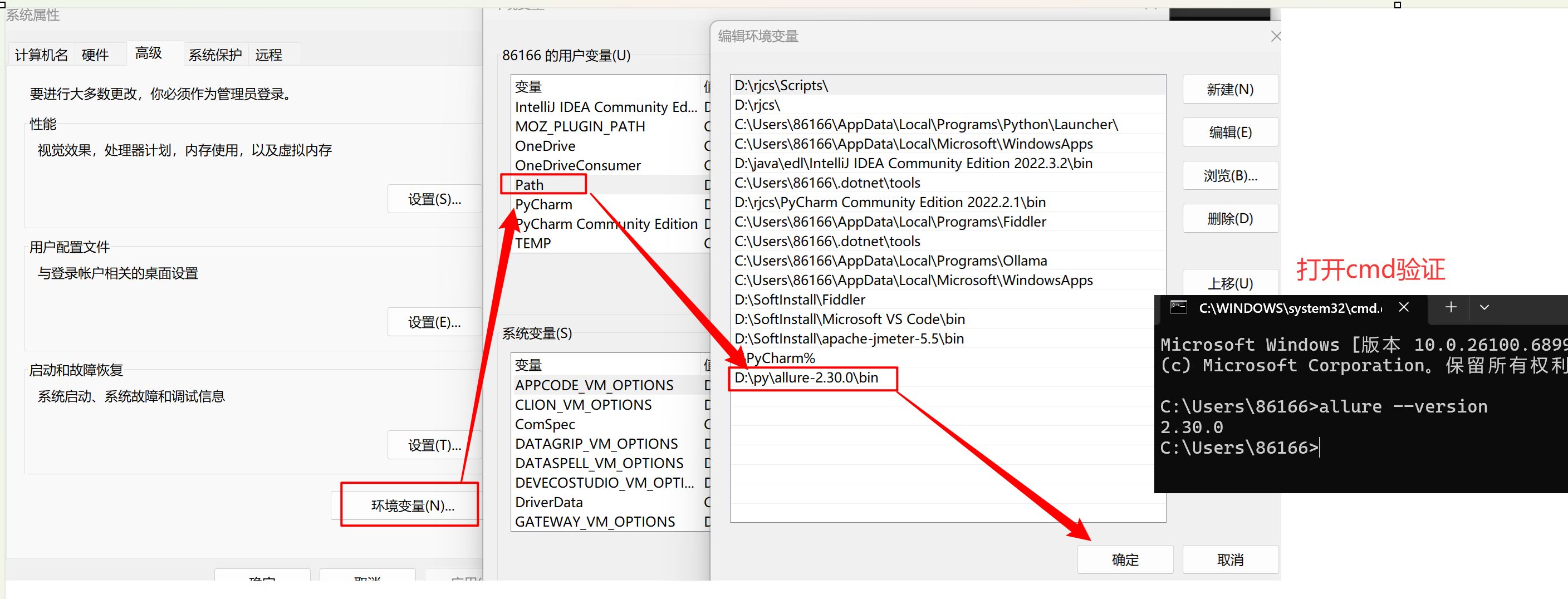
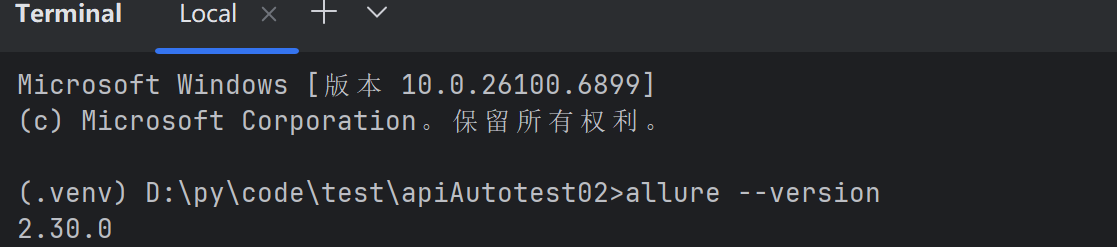
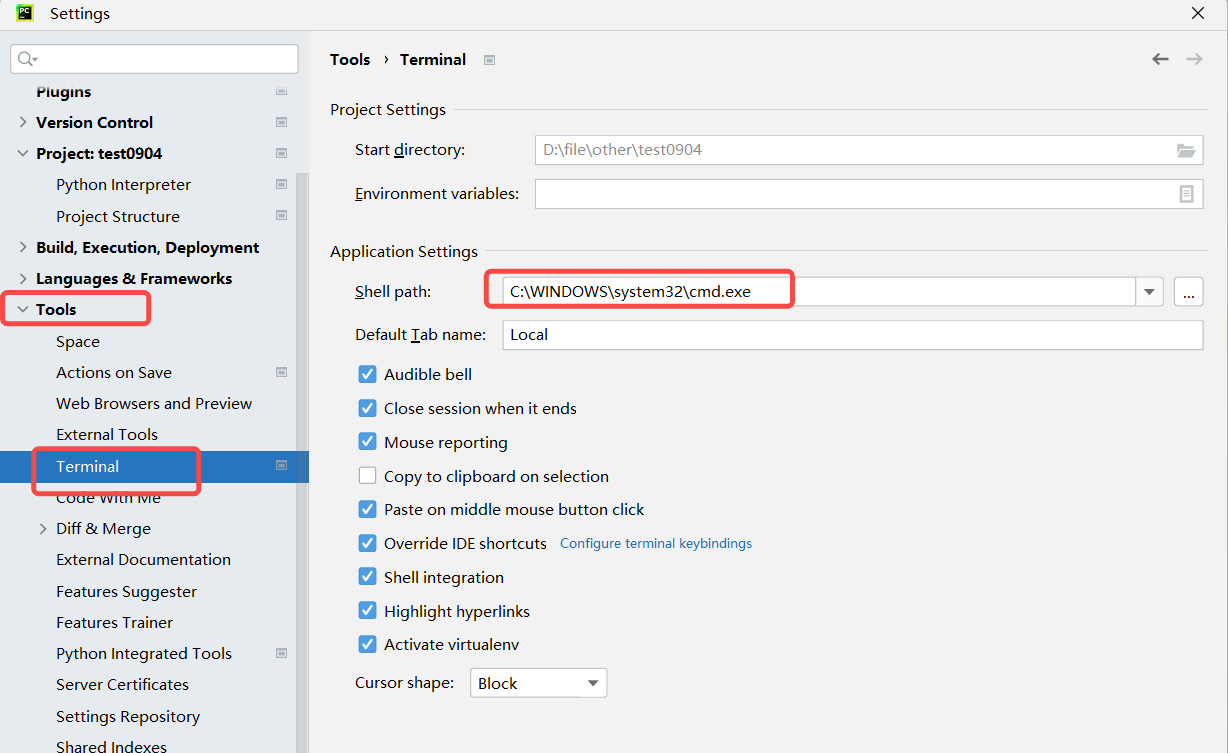
若出现cmd中执行allure--version可以打印版本,但是pycharm控制台执行命令提
示命题找不到,则需要修改pycharm中命令行环境,如下:
保存后需要重启pycharm!!!!!!
如果还不行则重启大法
6.3 使用
1.运行自动化,并指定测试报告放置路径
python
#allure-results(保存测试报告的路径)
pytest --alluredir=allure-results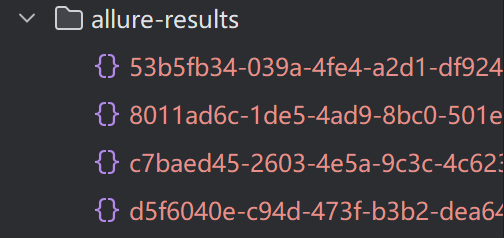
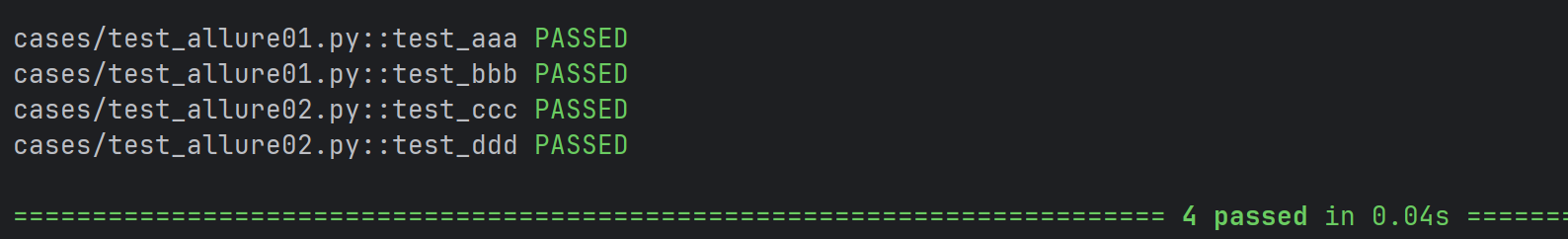
2. 查看测试报告
法一:启动⼀个本地服务器来在浏览器中展示测试报告
终端执行命令: allure serve [options] <allure-result>,自动在浏览器打开测试 报告
- --host:指定服务器监听的主机地址,默认为localhost。
- --port:指定服务器监听的端口号,默认为0(自动选择空闲端口)
- --clean-alluredir:清除上-次生成的测试报告
#不指定端口号和主机地址
allure serve .\allure-results\
#指定端口号
allure serve --port 8787 .\allure-results\
#清除上一次生成的测试报告
allure serve .\allure-results\ --clean-alluredir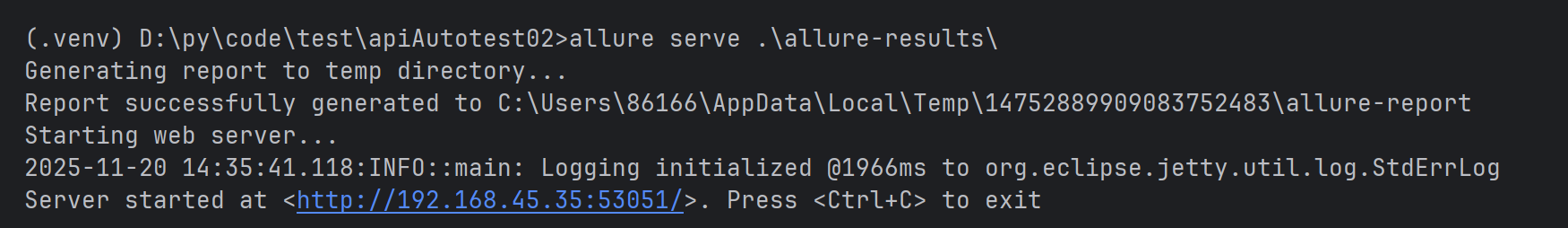

法二:从测试结果生成测试报告
终端执行命令:alluregenerate[options]<allure-results>-o <reports>
pythonallure generate .\allure-results\ -o .\allure-report --clean