界面展示
更新中。。。
公共SDK
工具包放在common/core包下
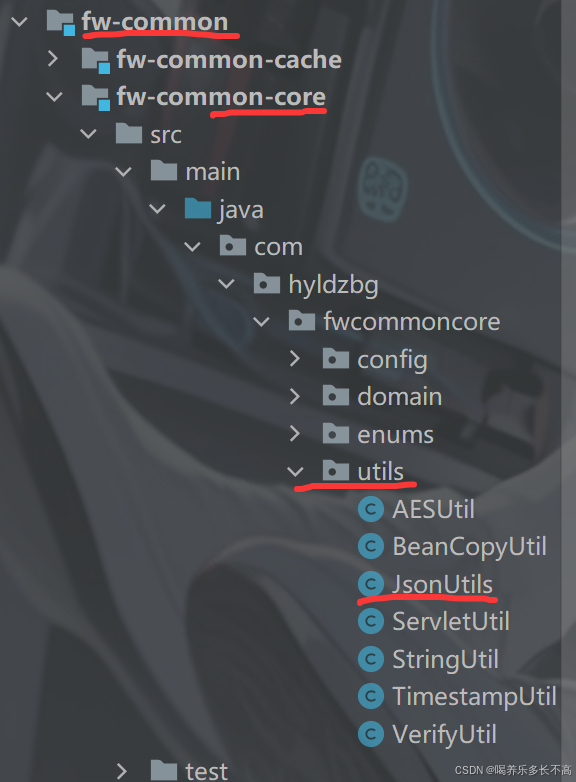
JSON工具包
为什么封装JSON工具包
- 在项目开发中我们经常会涉及到要将对象数据进行存储比如说要将对象存储到Redis等存储机制中描述同样的消息,json相比xml占用更少的空间
- 实际项目中,日志输出也是项目中很重要的一部分,日志中涉及到对象我们就可以采用JSON格式进行输出。
这里的JSON工具类使用的是Jackson
首先配置jackson
configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false)
反序列化时若 JSON 存在 Java 类未定义的属性,默认会抛异常;设为 false 则忽略未知属性,提升兼容性。configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false)
序列化日期时默认可能输出时间戳;设为 false 则按后续配置的日期格式输出,保持可读性。configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, false)
在序列化时当对象无任何属性时,默认可能抛异常;设为 false 允许序列化空对象,通常生成 {}。configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_INVALID_SUBTYPE, false)
反序列化时若类型标识与 Java 类型层次不匹配,默认抛异常;设为 false 提高容错性,尝试继续处理。configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATE_KEYS_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false)
在序列化时Map 以日期为键时,默认 false 即不使用时间戳形式,统一按配置的日期格式序列化键。configure(MapperFeature.USE_ANNOTATIONS, false)
禁用 Jackson 注解,完全依靠全局配置管理序列化/反序列化规则,减少注解带来的复杂性。
addModule(new JavaTimeModule())
注册 JSR310 模块,使 LocalDateTime、LocalDate等 Java 8 时间类可被正常序列化与反序列化。
defaultDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"))
统一全局日期格式为 yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss。addModule(new SimpleModule().addSerializer(LocalDateTime.class, new LocalDateTimeSerializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"))) //序列时起作用
.addDeserializer(LocalDateTime.class, new LocalDateTimeDeserializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")))) //反序列时起作用 对于 LocalDateTime 和 LocalDate 类型,序列化时可按指定格式转为 JSON 字符串,反序列化时也能将对应格式的字符串转回 LocalDateTime 或 LocalDate。serializationInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL)
序列化时仅输出非空值,忽略 null 字段,减少 JSON 体积
代码
java
@Slf4j
public class JsonUtils {
private static ObjectMapper OBJECT_MAPPER;
//jackson核心配置
static {
OBJECT_MAPPER =
JsonMapper.builder().configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false)
.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS, false)
.configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, false)
.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_INVALID_SUBTYPE, false)
.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATE_KEYS_AS_TIMESTAMPS,
false)
.configure(MapperFeature.USE_ANNOTATIONS, false)
.addModule(new JavaTimeModule())
.defaultDateFormat(new
SimpleDateFormat(CommonConstants.STANDARD_FORMAT))//TODO 魔法值
.serializationInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL)
.build();
}
/**
* 将对象转为json字符串
* @param obj 要转的对象
* @return 转换后的json
* @param <T> 泛型
*/
public static <T> String objectToJson(T obj){
//判空
if(obj == null){
return null;
}
//判断是否是String
if(obj instanceof String){
return (String) obj;
}
try {
return OBJECT_MAPPER.writeValueAsString(obj);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
log.warn("对象序列化出错 : {}",e.getMessage());
return null;
}
}
/**
* 对象转Json格式字符串(格式化的Json字符串)
* @param obj 对象
* @return 美化的Json格式字符串
* @param <T> 对象类型
*/
public static <T> String objectToJsonPretty(T obj) {
if (obj == null) {
return null;
}
try {
return obj instanceof String ? (String) obj :
OBJECT_MAPPER.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter().writeValueAsString(obj);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
log.warn("对象序列化出错 : {}", e.getMessage());
return null;
}
}
/**
* json转化为对象
* @param json
* @param tClass
* @return
* @param <T>
*/
public static <T> T jsonToObject(String json,Class<T> tClass){
//判空
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(json) || tClass == null){
return null;
}
//如果要转换成String类型,就直接返回json
if(tClass.equals(String.class)){
return (T)json;
}
try {
return OBJECT_MAPPER.readValue(json,tClass);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
log.warn("json序列化转换失败 : {}",e.getMessage());
return null;
}
}
/**
* 字符串转换为⾃定义对象,⽀持复杂的泛型嵌套
*
* @param json json字符串
* @param typeReference 对象模板信息
* @return 对象类对应的对象
* @param <T> 对象类
*/
public static <T> T jsonToObject(String json, TypeReference<T> typeReference){
//TODO
//判空
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(json) || typeReference == null){
return null;
}
try {
return OBJECT_MAPPER.readValue(json,typeReference);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
log.warn("json序列化转换失败 : {}",e.getMessage());
return null;
}
}
/**
* 字符串转换为⾃定义字段转为list,⽀持List嵌套简单对象
* @param str json字符串
* @param clazz 对象类
* @return 对象列表
* @param <T> 对象类型
*/
public static <T> List<T> stringTOList(String str, Class<T> clazz) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(str)|| clazz == null) {
return null;
}
//将clazz转化为List<clazz>
JavaType javaType = OBJECT_MAPPER.getTypeFactory().constructParametricType(List.class, clazz);
//将String转化为List<clazz>
try {
return OBJECT_MAPPER.readValue(str, javaType);
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("json序列化转换失败 : {}" + e.getMessage());
return null;
}
}
/**
* 字符串转换为⾃定义字段转为Map,⽀持Map嵌套简单对象
* @param json
* @param clazz
* @return
* @param <T>
*/
public static <T> Map<String,T> stringToMap(String json,Class<T> clazz){
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(json) || clazz == null) {
return null;
}
//将clazz转化为Map<String,clazz>
JavaType javaType =
OBJECT_MAPPER.getTypeFactory().constructMapType(LinkedHashMap.class, String.class,clazz);
//将String转化为Map<String,clazz>
try {
return OBJECT_MAPPER.readValue(json, javaType);
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("json序列化转换失败 : {}" + e.getMessage());
return null;
}
}
}在这里还会设计一个泛型擦除问题
泛型擦除问题
Bean拷贝工具包
在 Java Web 项目中,通常把代码分成 Controller 层、Service 层和 DAO 层;每层用的数据模型不同,因此经常要把数据从一个模型搬到另一个模型,这就需要进行 Bean 拷贝。
在本项目中共分了三种数据模型
DTO(Data Transfer Object):是一个用来传输数据的对象。DTO用来在不同层或不同系统之间传递数据,比如从Service层传递到Controller层或者Controller层传递到Service层等。DTO可以避免在层与层之间传递过多的不必要的数据,同时也可以隐藏内部的数据结构和实现细节。
VO(View Object:)是一个用来展示数据的对象(返回给前端的数据)。它是根据具体的视图(如Web页面、桌面应用的界面等)的要求,将数据以一种合适的形式进行组织和封装,以便于在视图中进行展示。
DO(Data Object):是与数据库表结构对应的对象,也叫持久化对象,通常在 DAO 层用于和数据库交互。
核心设计
- 提供级别对象拷贝功能(单个)
- 提供列表对象拷贝功能
java
public class BeanCopyUtil extends BeanUtils {
/**
* 单个bean拷贝,直接使用Springboot提供的方法
* @param source
* @param target
*/
public static void copyPropertie(Object source,Object target){
copyProperties(source,target);
}
/**
* Supplier<T> target传入的是一个创建目标对象方法的引用
* @param sources 源对象列表
* @param target 创建目标对象方法的引用
* @return 目标
* @param <S>源对象
* @param <T>目标对象
*/
public static <S,T> List<T> copyListProperties(List<S> sources, Supplier<T> target){
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>(sources.size());
//将源对象拷贝到目标对象
for(S source : sources){
T t = target.get();//目标对象
copyProperties(source,t);
list.add(t);
}
return list;
}
}BeanUtils.copyProperties注意事项
- 属性类型不⼀致会导致拷贝失败,实际开发里,同一个字段在不同类里类型可能不一样,比如 ID 在 A 类是 Long,在 B 类是 String,用 BeanUtils.copyProperties 拷贝就会失败,字段变成 null。而且假如一个类型时Long一个为long也会失败报FatalBeanException错
- 底层为反射实现效率较低,BeanUtils.copyProperties底层是通过反射获取到对象的set和get方法,然后通过get、set完成数据的拷贝,整体拷贝效率较低。
- BeanUtils.copyProperties是浅拷贝
时间戳工具类
核心设计
- 取当前时间戳
- 取未来 x 秒时间戳
- 取未来 x 天时间戳
- 取未来 x 月时间戳
- 取未来 x 年时间戳
- 算两时间戳差值
- 均支持秒级和毫秒级返回
java
/**
* 时间戳⼯具类
*/
public class TimestampUtil {
/**
* 获取当前时间戳(秒级)
*
* @return 当前时间戳(秒级)
*/
public static long getCurrentSeconds() {
return Instant.now().getEpochSecond();
}
/**
* 获取当前时间戳(毫秒级)
*
* @return 当前时间戳(毫秒级)
*/
public static long getCurrentMillis() {
return Instant.now().toEpochMilli();
}
/**
* 获取未来x秒的时间戳(秒级)
*
* @param seconds 秒
* @return 时间戳
*/
public static long getSecondsLaterSeconds(long seconds) {
ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));
ZonedDateTime secondsLater = now.plusSeconds(seconds);
return secondsLater.toEpochSecond();
}
/**
* 获取未来x秒的时间戳(毫秒级)
*
* @param seconds 秒
* @return 时间戳
*/
public static long getSecondsLaterMillis(long seconds) {
ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));
ZonedDateTime secondsLater = now.plusSeconds(seconds);
return secondsLater.toInstant().toEpochMilli();
}
/**
* 获取未来x天的时间戳(秒级)
* @param days 天
* @return 时间戳
*/
public static long getDaysLaterSeconds(long days) {
ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));
ZonedDateTime secondsLater = now.plusDays(days);
return secondsLater.toEpochSecond();
}
/**
* 获取未来x天的时间戳(毫秒级)
* @param days 天
* @return 时间戳
*/
public static long getDaysLaterMillis(long days) {
ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));
ZonedDateTime monthsLater = now.plusDays(days);
return monthsLater.toInstant().toEpochMilli();
}
/**
* 获取未来x⽉的时间戳(秒级)
* @param months ⽉
* @return 时间戳
*/
public static long getMonthsLaterSeconds(long months) {
ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));
ZonedDateTime monthsLater = now.plusMonths(months);
return monthsLater.toEpochSecond();
}
/**
* 获取未来x⽉的时间戳(毫秒级)
* @param months ⽉
* @return 时间戳
*/
public static long getMonthsLaterMillis(long months) {
ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));
ZonedDateTime monthsLater = now.plusMonths(months);
return monthsLater.toInstant().toEpochMilli();
}
/**
* 获取未来x年的时间戳(秒级)
* @param years 年
* @return 时间戳
*/
public static long getYearLaterSeconds(long years) {
ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));
ZonedDateTime yearLater = now.plusMonths(years);
return yearLater.toEpochSecond();
}
/**
* 获取未来x年的时间戳(毫秒级)
* @param years 年
* @return 时间戳
*/
public static long getYearLaterMillis(long years) {
ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("UTC"));
ZonedDateTime yearLater = now.plusMonths(years);
return yearLater.toInstant().toEpochMilli();
}
/**
* 计算两个时间戳之间的差异(毫秒)
*
* @param timestamp1 时间戳1
* @param timestamp2 时间戳2
* @return 时间戳差异(毫秒)
*/
public static long calculateDifferenceMillis(long timestamp1, long
timestamp2) {
return ChronoUnit.MILLIS.between(
Instant.ofEpochMilli(timestamp1),
Instant.ofEpochMilli(timestamp2));
}
/**
* 计算两个时间戳之间的差异(秒)
*
* @param timestamp1 时间戳1
* @param timestamp2 时间戳2
* @return 时间戳差异(秒)
*/
public static long calculateDifferenceSeconds(long timestamp1, long
timestamp2) {
return ChronoUnit.SECONDS.between(
Instant.ofEpochSecond(timestamp1),
Instant.ofEpochSecond(timestamp2));
}
}String工具类
核心设计
- 字符串常用操作
- 判断 URL 是否匹配规则:检查给定 URL 字符串是否命中规则链表中的任意一条匹配规则。
String工具类主要包含一下字符串的匹配和校验
依赖
XML
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId>
</dependency>代码
java
/**
* String工具类
*/
public class StringUtil {
/**
* 判断url是否符合匹配规则中的一个
* @param url
* @param patterns
* @return
*/
public static boolean matchs(String url, List<String> patterns){
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(url) || CollectionUtils.isEmpty(patterns)){
return false;
}
for(String pattern : patterns){
if(matchUrl(pattern,url)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判断url是否符合匹配规则
* 匹配规则
* ? 代表单个字符
* * 代表一层路径内的任意字符
* ** 表示任意路径内的任意字符
*
* @param pattern
* @param url
* @return
*/
public static boolean matchUrl(String pattern,String url){
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(pattern) || StringUtils.isEmpty(url)){
return false;
}
AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
return antPathMatcher.match(pattern,url);
}
}统一功能
放在common/domain包下,common/domain包里主要放一些,状态码,常量,以及后文提到的响应数据结构、自定义异常等,属于协议相关的内容。
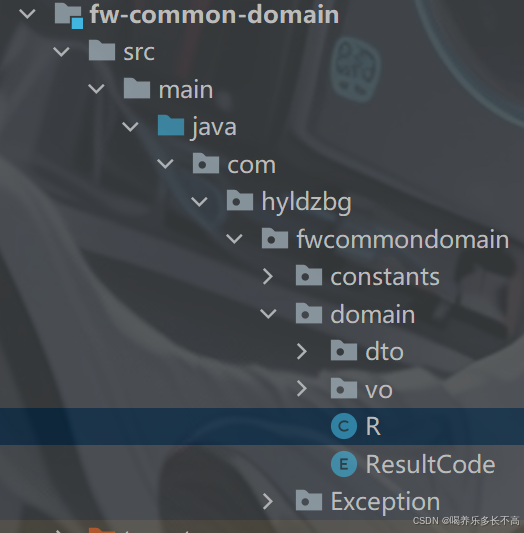
统一状态码
核心设计
定义状态枚举,添加状态编码和状态消息作为状态基本信息
比如400100(参数异常),500100(验证码发送失败)
状态码采用6位,前3位代表HTTP响应码,后面3位为项目中给出更加细致的区分。
java
/**
* 响应码
*/
@AllArgsConstructor
@Getter
public enum ResultCode {
//---------------------------2xx
/**
* 操作成功
*/
SUCCESS (200000, "操作成功"),
//------------------------4xx
//400
/**
* 无效的参数
*/
INVALID_PARA (400000, "无效的参数"),
/**
* 无效的验证码
*/
INVALID_CODE (400001, "无效的验证码"),
/**
* 错误的验证码
*/
ERROR_CODE (400002, "错误的验证码"),
/**
* 手机号格式错误
*/
ERROR_PHONE_FORMAT (400003, "手机号格式错误"),
/**
* 超过每日发送次数限制
*/
SEND_MSG_OVERLIMIT (400004, "超过每日发送次数限制"),
/**
* 无效的区划
*/
INVALID_REGION (400005, "无效的区划"),
/**
* 参数类型不匹配
*/
PARA_TYPE_MISMATCH (400006, "参数类型不匹配"),
/**
* 账号已停用,登录失败
*/
USER_DISABLE (400007, "账号已停用,登录失败"),
//401
/**
* 令牌不能为空
*/
TOKEN_EMPTY (401000, "令牌不能为空"),
/**
* 令牌已过期或验证不正确!
*/
TOKEN_INVALID (401001, "令牌已过期或验证不正确!"),
/**
* 令牌已过期!
*/
TOKEN_OVERTIME (401002, "令牌已过期!"),
/**
* 登录状态已过期!
*/
LOGIN_STATUS_OVERTIME (401003, "登录状态已过期!"),
/**
* 令牌验证失败!
*/
TOKEN_CHECK_FAILED (401004, "令牌验证失败!"),
//404
/**
* 服务未找到!
*/
SERVICE_NOT_FOUND (404000, "服务未找到"),
URL_NOT_FOUND (404001, "url未找到"),
//405
/**
* 请求方法不支持!
*/
REQUEST_METNHOD_NOT_SUPPORTED (405000, "请求方法不支持"),
//---------------------5xx
/**
* 服务繁忙请稍后重试!
*/
ERROR (500000, "服务繁忙请稍后重试"),
/**
* 操作失败
*/
FAILED (500001, "操作失败"),
/**
* 短信发送失败
*/
SEND_MSG_FAILED (500002, "短信发送失败"),
/**
* 获取直传地址失败
*/
PRE_SIGN_URL_FAILED (500003, "获取直传地址失败"),
/**
* 上传oss异常,请稍后重试
*/
OSS_UPLOAD_FAILED (500004, "上传oss异常,请稍后重试"),
/**
* 获取地图数据失败,请稍后重试
*/
QQMAP_QUERY_FAILED (500005, "获取地图数据失败,请稍后重试"),
/**
* 城市信息获取失败
*/
QQMAP_CITY_UNKNOW (500006, "城市信息获取失败"),
/**
* 根据位置获取城市失败
*/
QQMAP_LOCATE_FAILED (500007, "根据位置获取城市失败"),
/**
* 地图特性未开启
*/
MAP_NOT_ENABLED (500008, "地图特性未开启,开启方式参考使用手册"),
/**
* 地图区划特性未开启
*/
MAP_REGION_NOT_ENABLED (500009, "地图区划特性未开启,开启方式参考使用手册"),
//---------------------枚举占位
/**
* 占位专用
*/
RESERVED (99999999, "占位专用");
/**
* 响应码
*/
private int code;
/**
* 响应消息
*/
private String msg;
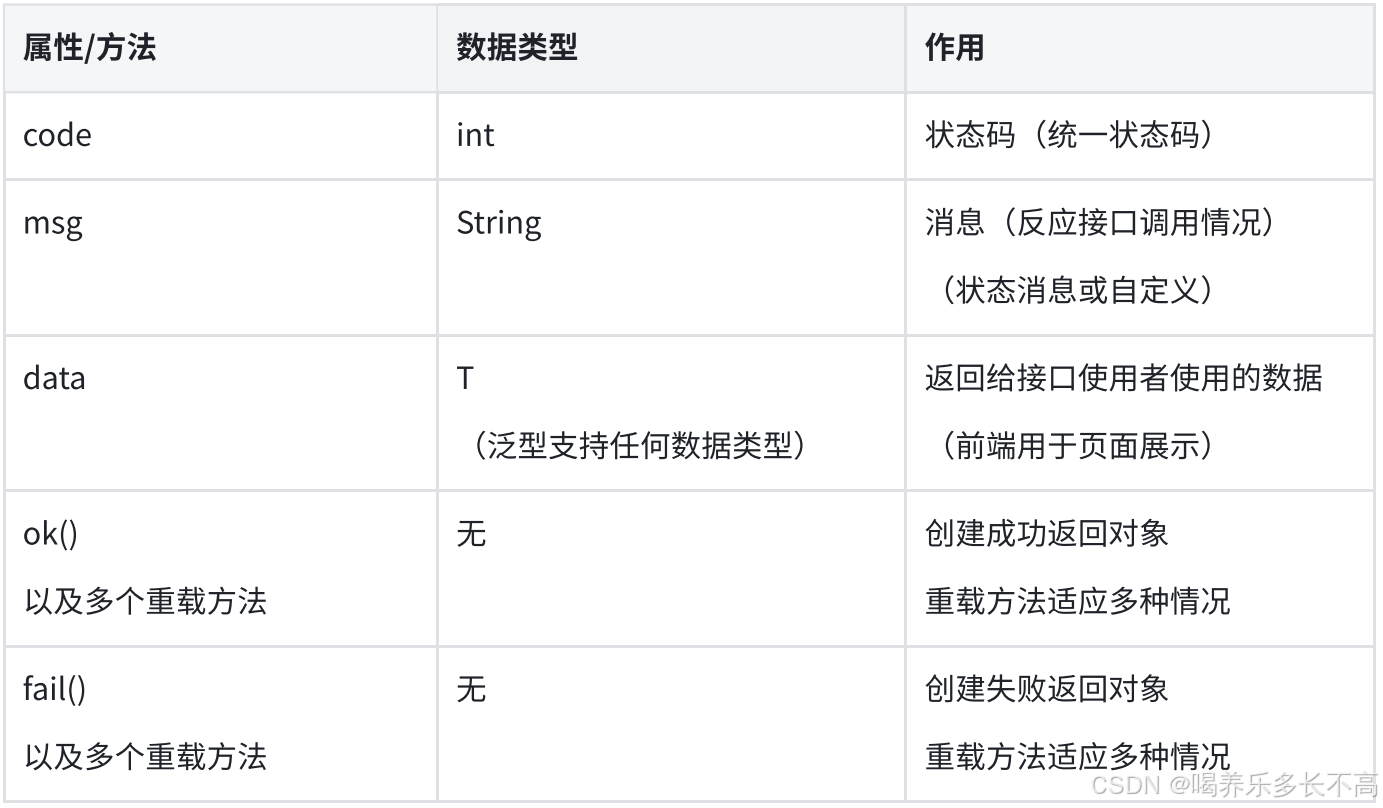
}统一响应数据结构
核心设计
- 使用统一状态码
- 消息默认取状态码对应文本,也可自定义,用于反映接口请求结果
- 通过泛型 `<T>` 支持返回任意数据类型
- 内置统一的成功 / 失败响应方法,一行代码即可生成标准结构
java
Data
public class R<T> {
/**
* 状态码
*/
private int code;
/**
* 返回消息
*/
private String msg;
/**
* 返回数据
*/
private T data;
/**
* 无参ok方法
* @return
* @param <T>
*/
public static <T> R<T> ok(){
return restResult(ResultCode.SUCCESS.getCode(), ResultCode.SUCCESS.getMsg(), null);
}
/**
* 自定义返回信息的ok方法
* @param msg
* @return
* @param <T>
*/
public static <T> R<T> ok(String msg,T data){
return restResult(ResultCode.SUCCESS.getCode(), msg, data);
}
/**
* 返回数据的ok方法
* @param data
* @return
* @param <T>
*/
public static <T> R<T> ok(T data){
return restResult(ResultCode.SUCCESS.getCode(), ResultCode.SUCCESS.getMsg(), data);
}
public static <T> R<T> restResult(int code,String msg,T data){
R result = new R();
result.setCode(code);
result.setMsg(msg);
result.setData(data);
return result;
}
/**
* 无参返回fail方法
* @return
* @param <T>
*/
public static <T> R<T> fail(){
return restResult(ResultCode.ERROR.getCode(), ResultCode.ERROR.getMsg(), null);
}
/**
* 有参fail方法
* @param msg
* @return
* @param <T>
*/
public static <T> R<T> fail(String msg){
return restResult(ResultCode.ERROR.getCode(), msg, null);
}
public static <T> R<T> fail(int code,String msg){
return restResult(code, msg, null);
}
public static <T> R<T> fail(String msg,T data){
return restResult(ResultCode.ERROR.getCode(), msg, data);
}
public static <T> R<T> fail(T data){
return restResult(ResultCode.ERROR.getCode(), ResultCode.ERROR.getMsg(), data);
}统一业务异常
统一异常处理完成后,接口抛出异常会自动转成统一响应结构,调用方就无需额外解析了。
一次请求经网关转发到微服务再操作数据库,共有 5 处可能抛异常:
- 网关自身处理异常
- 网关转发到微服务时网络异常
- 微服务内部处理异常
- 微服务调用数据库时操作异常
- 数据库自身网络或其他异常
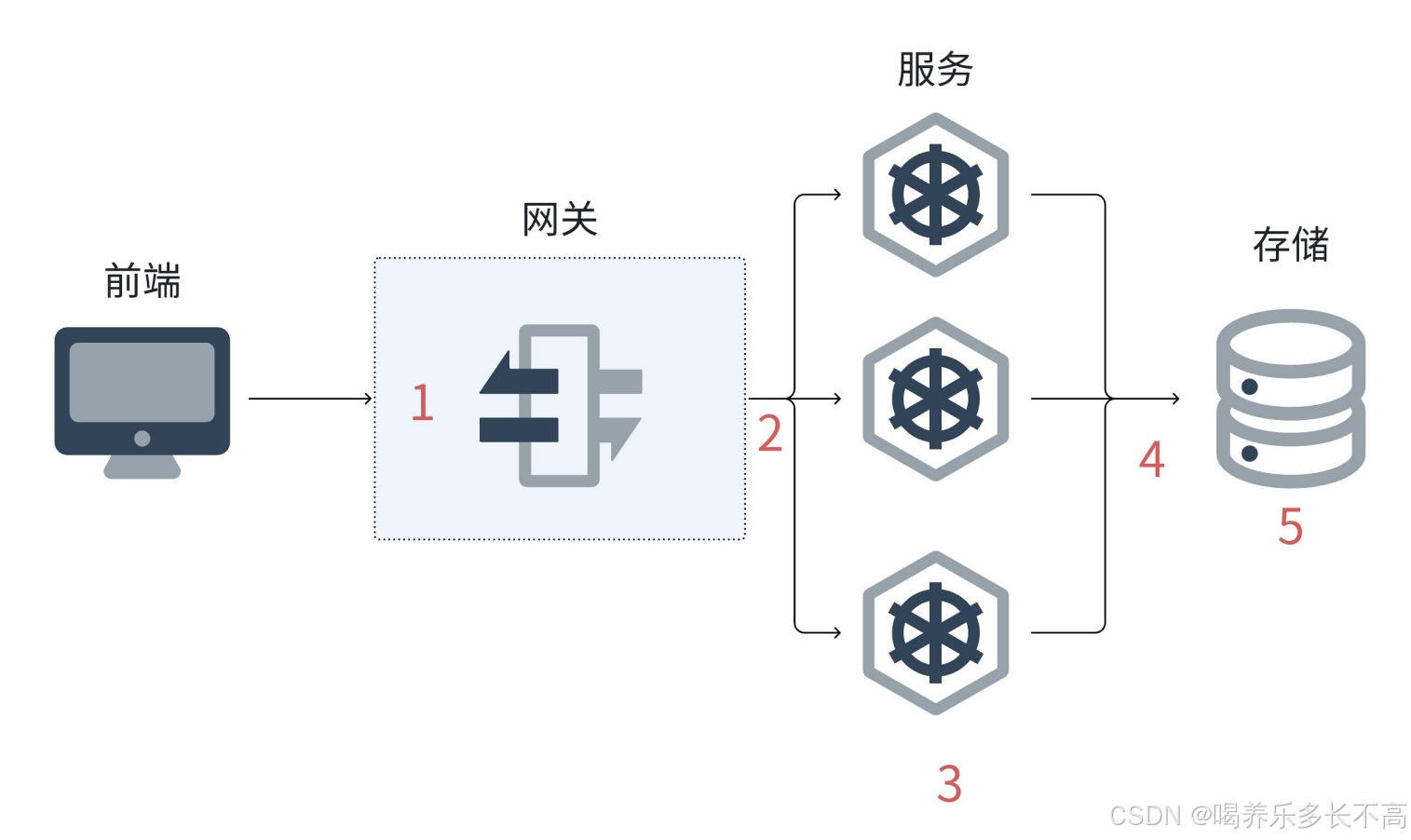
对于 3、4、5 处的异常,微服务直接用 RestControllerAdvice + @ExceptionHandler 捕获并返回统一响应结构;对于 1、2 处的异常,则需在网关层做全局异常处理,同样返回统一响应结构。
核心设计
- 使用RestControllerAdvice + ExceptionHandler 对微服务异常进行全局处理。并封装代码到 common/security下,异常处理应该属于安全类的所以我们将其封装到security包中。
- 网关层面进行全局异常处理,对于1、2处异常进行统一处理。(网关微服务)
- 对于异常处理后返回约定好的统一响应数据结构。
- 对于每种异常应该返回与之相对的状态码。
- 修改http状态码为异常对应状态码的前三位
各微服务全局异常处理解决
java
/**
* 全局异常处理器
*/
@RestControllerAdvice
@Slf4j
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
/**
* 设置http响应码
*
* @param response 响应信息
* @param errcode 响应码
*/
private void setResponseCode(HttpServletResponse response,Integer errcode)
{
int httpCode = Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(errcode).substring(0,3));
response.setStatus(httpCode);
}
/**
* 请求⽅式不⽀持
* @param e 异常信息
* @param request 请求
* @param response 响应
* @return 异常结果
*/
@ExceptionHandler(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class)
public R<?> handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupported(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException e,
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
log.error("请求地址'{}',不⽀持'{}'请求", requestURI, e.getMethod());
setResponseCode(response, ResultCode.REQUEST_METNHOD_NOT_SUPPORTED.getCode());
return R.fail(ResultCode.REQUEST_METNHOD_NOT_SUPPORTED.getCode(),
ResultCode.REQUEST_METNHOD_NOT_SUPPORTED.getMsg());
}
/**
* 类型不匹配异常
*
* @param e 异常信息
* @param response 响应
* @return 不匹配结果
*/
@ExceptionHandler({MethodArgumentTypeMismatchException.class})
public R<?> handleMethodArgumentTypeMismatchException(MethodArgumentTypeMismatchException e,
HttpServletResponse response) {
log.error("类型不匹配异常",e);
setResponseCode(response, ResultCode.PARA_TYPE_MISMATCH.getCode());
return R.fail(ResultCode.PARA_TYPE_MISMATCH.getCode(),
ResultCode.PARA_TYPE_MISMATCH.getMsg());
}
/**
* url未找到异常
*
* @param e 异常信息
* @param response 响应
* @return 异常结果
*/
@ExceptionHandler({NoResourceFoundException.class})
public R<?> handleMethodNoResourceFoundException(NoResourceFoundException e, HttpServletResponse response) {
log.error("url未找到异常",e);
setResponseCode(response, ResultCode.URL_NOT_FOUND.getCode());
return R.fail(ResultCode.URL_NOT_FOUND.getCode(),
ResultCode.URL_NOT_FOUND.getMsg());
}
/** 拦截运⾏时异常
*
* @param e 异常信息
* @param request 请求信息
* @param response 响应信息
* @return 响应结果
*/
@ExceptionHandler(RuntimeException.class)
public R<?> handleRuntimeException(RuntimeException e,
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
log.error("请求地址'{}',发⽣运⾏时异常.", requestURI, e);
setResponseCode(response, ResultCode.ERROR.getCode());
return R.fail(ResultCode.ERROR.getCode(), ResultCode.ERROR.getMsg());
}
/**
* 系统异常
* @param e 异常信息
* @param request 请求
* @param response 响应
* @return 响应结果
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public R<?> handleException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
log.error("请求地址'{}',发⽣异常.", requestURI, e);
setResponseCode(response, ResultCode.ERROR.getCode());
return R.fail(ResultCode.ERROR.getCode(), ResultCode.ERROR.getMsg());
}
/**
* 业务异常
*
* @param e 异常信息
* @param request 请求
* @param response 响应
* @return 业务异常结果
*/
@ExceptionHandler(ServiceException.class)
public R<?> handleServiceException(ServiceException e, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
log.error("请求地址'{}',发⽣业务异常", requestURI, e);
setResponseCode(response,e.getCode());
return R.fail(e.getCode(), e.getMessage());
}
/**
* 拿取报错信息里的DefaultMessage,并用","分割
* @param e
* @return
*/
public String joinMessage(MethodArgumentNotValidException e){
//拿取所有错误信息
List<ObjectError> allError = e.getAllErrors();
if(allError.isEmpty()){
return CommonConstants.EMPTY_STR;
}
//拿到DefaultMessage,并转成String类型用","分割
return allError.stream().map(ObjectError::getDefaultMessage)
.collect(Collectors.joining(CommonConstants.DEFAULT_DELIMITER));
}
/**
* 参数校验异常
* @param e
* @param request
* @param response
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public R<?> handleMethodArgumentNotValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
log.error("请求地址'{}',发⽣业务异常", requestURI, e);
setResponseCode(response,ResultCode.INVALID_PARA.getCode());
String message = joinMessage(e);
return R.fail(ResultCode.INVALID_PARA.getCode(), message);
}
/**
* 参数校验异常
* @param e
* @param request
* @param response
* @return
*/
@ExceptionHandler(ConstraintViolationException.class)
public R<?> handleMethodArgumentNotValidException(ConstraintViolationException e, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
log.error("请求地址'{}',发⽣业务异常", requestURI, e);
setResponseCode(response,ResultCode.INVALID_PARA.getCode());
String message = e.getMessage();
return R.fail(ResultCode.INVALID_PARA.getCode(), message);
}
}注意要把自己写的依赖提供给别的包使用,要记得添加spring文件
java
com.hyldzbg.fwcommonsecurity.handler.GlobalExceptionHandler网关层全局异常处理解决
java
package com.hyldzbg.fwgateway.handler;
import com.alibaba.nacos.shaded.io.grpc.internal.JsonUtil;
import com.hyldzbg.fwcommoncore.utils.JsonUtils;
import com.hyldzbg.fwcommondomain.Exception.ServiceException;
import com.hyldzbg.fwcommondomain.domain.R;
import com.hyldzbg.fwcommondomain.domain.ResultCode;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.core.io.buffer.DataBuffer;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.http.server.reactive.ServerHttpResponse;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.resource.NoResourceFoundException;
import org.springframework.web.server.ServerWebExchange;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
/**
* ⽹关统⼀异常处理
*/
@Order(-1)
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class GatewayExceptionHandler implements ErrorWebExceptionHandler {
/**
* 处理器
*
* @param exchange ServerWebExchange
* @param ex 异常信息
* @return ⽆
*/
@Override
//有异常时自动触发
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange, Throwable ex) {
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
//响应已经提交到客⼾端,⽆法再对这个响应进⾏常规的异常处理修改了,直接返回⼀个包含原始异常ex的Mono.error(ex)
if (response.isCommitted()) {
return Mono.error(ex);
}
String retMsg = ResultCode.ERROR.getMsg();;
int retCode = ResultCode.ERROR.getCode();
if (ex instanceof NoResourceFoundException) {
retCode = ResultCode.SERVICE_NOT_FOUND.getCode();
retMsg = ResultCode.SERVICE_NOT_FOUND.getMsg();
}else if (ex instanceof ServiceException) {
retMsg = ex.getMessage();
retCode = ((ServiceException) ex).getCode();
}
//按照统⼀状态码的特点,前三位是http状态码。从中截取http状态码
int httpCode = Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(retCode).substring(0, 3));
log.error("[⽹关异常处理]请求路径:{},异常信息:{}", exchange.getRequest().getPath(), ex.getMessage());
return webFluxResponseWriter(response,
HttpStatus.valueOf(httpCode), retMsg, retCode);
}
private static Mono<Void> webFluxResponseWriter(ServerHttpResponse
response, HttpStatus status, Object value, int code) {
return webFluxResponseWriter(response,
MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE, status, value, code);
}
private static Mono<Void> webFluxResponseWriter(ServerHttpResponse response,
String contentType, HttpStatus status,
Object value, int code) {
response.setStatusCode(status); //设置http响应
response.getHeaders().add(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE, contentType); //设置响应体内容类型为json
R<?> result = R.fail(code, value.toString()); //按照约定响应数据结构,构建响应体内容
DataBuffer dataBuffer =
response.bufferFactory().wrap(JsonUtils.objectToJson(result).getBytes());
return response.writeWith(Mono.just(dataBuffer)); //将响应体内容写⼊响应体
}
}统一自定义异常
为了满足业务需求,Java提供了一些内置的异常类,但是它们并不一定能够满足我们的具体业务需求,所以我们需要自定义异常类。
核心设计
- 给出一份自定义异常模板,项目可按自身需求扩展更多异常类型。
- 继承自 RuntimeException,异常一般在运行阶段抛出。
- 核心字段:状态码 + 提示信息,具体可随项目调整。
- 提供异常捕获:微服务和网关全局异常处理中应该应该分别提供自定义异常的捕获和处理
三种构造方式:
- 传入标准状态码,自动取用对应的 code 与 msg。
- 仅传入提示信息,code 使用默认状态码。
- 同时传入提示信息与标准状态码,自由组合。
推荐使用第一种
java
throw new ServiceException(ResultCode.ERROR_PHONE_FORMAT);
throw new ServiceException("字典数据键或值已存在");
throw new ServiceException("账号密码错误,请确认后重新登录",
ResultCode.INVALID_PARA.getCode());
java
package com.hyldzbg.fwcommondomain.Exception;
@Getter
@Setter
public class ServiceException extends RuntimeException{
/**
* 状态码
*/
private int code;
/**
* 状态信息
*/
private String message;
//推荐
public ServiceException(ResultCode resultCode){
this.code = resultCode.getCode();
this.message = resultCode.getMsg();
}
public ServiceException(String msg){
this.code = ResultCode.ERROR.getCode();
this.message = msg;
}
public ServiceException(int code,String msg){
this.code = code;
this.message = msg;
}
}异常捕获微服务侧(示例)
java
/**
* 业务异常,当报ServiceException异常时就会触发这个方法
*
* @param e 异常信息
* @param request 请求
* @param response 响应
* @return 业务异常结果
*/
@ExceptionHandler(ServiceException.class)
public R<?> handleServiceException(ServiceException e, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
log.error("请求地址'{}',发⽣业务异常", requestURI, e);
setResponseCode(response,e.getCode());
return R.fail(e.getCode(), e.getMessage());
}网关侧异常捕获(示例)
java
/**
* 处理器
*
* @param exchange ServerWebExchange
* @param ex 异常信息
* @return ⽆
*/
@Override
//有异常时自动触发
public Mono<Void> handle(ServerWebExchange exchange, Throwable ex) {
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
//响应已经提交到客⼾端,⽆法再对这个响应进⾏常规的异常处理修改了,直接返回⼀个包含原始异常ex的Mono.error(ex)
if (response.isCommitted()) {
return Mono.error(ex);
}
String retMsg = ResultCode.ERROR.getMsg();;
int retCode = ResultCode.ERROR.getCode();
if (ex instanceof NoResourceFoundException) {
retCode = ResultCode.SERVICE_NOT_FOUND.getCode();
retMsg = ResultCode.SERVICE_NOT_FOUND.getMsg();
}else if (ex instanceof ServiceException) {
retMsg = ex.getMessage();
retCode = ((ServiceException) ex).getCode();
}
//按照统⼀状态码的特点,前三位是http状态码。从中截取http状态码
int httpCode = Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(retCode).substring(0, 3));
log.error("[⽹关异常处理]请求路径:{},异常信息:{}", exchange.getRequest().getPath(), ex.getMessage());
return webFluxResponseWriter(response,
HttpStatus.valueOf(httpCode), retMsg, retCode);
}脚手架里只给出了一个 ServiceException,实际项目可按模块继续扩展,做到"见名知义"。
例如:UserAuthException ------ 一眼就能认出是用户认证异常。
统一参数校验
封装统一规范化参数校验的目的:
- 保证数据质量,拦截空值、越界等无效数据,防止脏数据进入业务层。
- 保障系统安全,统一过滤与校验规则,杜绝 SQL 注入、XSS 等参数级攻击入口。
- 增强系统稳定,在入口层提前暴露并处理非法参数,减少运行时异常,降低崩溃风险。
- 保持校验统一,一处定义、多处复用,避免散落在各层的重复校验逻辑,维护简单且风格一致。
本项目中通过spring-boot-validation进行辅助开发
spring-boot-validation 可一键完成统一、规范的参数校验。它基于 Java Bean Validation(JSR-380),通过注解即可快速声明规则,无需手写冗长校验代码。
例如:@NotEmpty 检查字符串非空,@Size 限定长度范围。
数据进入业务逻辑前自动执行校验,不合法立即抛异常,方便定位与处理。
接下来即使用 spring-boot-validation 实现统一参数校验。
核心设计
- 提供通用、规范的参数校验方案
- 通过注解一键完成接口参数校验
- 校验异常由统一异常处理捕获,向前端返回统一响应结构
依赖
java
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
</dependency一下是一些常用的校验注解
- @NotNull:值不能为 null
- @NotEmpty:字符串、集合或数组长度必须大于 0
- @NotBlank:字符串不能为空或仅空白字符
- @Size:字符串、集合或数组大小在指定范围内
- @Min:数值不低于最小值
- @Max:数值不超过最大值
- @Pattern:字符串符合指定正则表达式
- @Email:字符串为有效电子邮件地址
- @Future:日期必须是将来时间
- @Past:日期必须是过去时间
我们一般在 Controller 层做参数校验,大部分情况下,请求参数主要分为如下两种形式:
- POST、PUT 请求,使用 requestBody 传递参数。
- GET、Delete 请求,使用 requestParam/PathVariable 传递参数。
接下来,我们将依次展示这两种形式下如何通过注解进行参数校验。
requestBody
POST、PUT 请求一般会使用 requestBody 传递参数,这种情况下,后端使用 DTO 对象进行接收。比如,有一个接口,要求 name 不能为空,id 最小不能小于 1。如果校验失败,会抛出 MethodArgumentNotValidException 异常。
java
@Data
public class ValidationUserDTO {
@NotNull(message = "昵称不能为空")
private String name;
@NotBlank(message = "用户账号不能为空")
private String userAccount;
private String password;
@Min(value = 0, message = "年龄不能小于0岁")
@Max(value = 60, message = "年龄不能大于60岁")
private int age;
@NotEmpty(message = "用户密码不能为空")
@Size(min = 5, max = 10, message = "密码长度不能少于6位,不能大于10位")
@Pattern(regexp = "^(13[0-9]|14[01456879]|15[0-35-9]|16[2567]|17[08]|18[0-9]|19[0-35-9])\\d{8}$", message = "手机号码格式不正确")
private String phone;
@Email(message = "必须符合邮箱格式")
private String email;
@Past(message = "开始日期必须是过去的日期")
private LocalDate startDate;
@Future(message = "结束日期必须是未来的日期")
private LocalDate endDate;
}通过@Validated在controller层的方法参数上声明,就能实现自动参数校验
requestParam
这方式同样只在方法参数上加 @Validated 即可校验失败抛MethodArgumentNotValidException。
- 使用参数平铺方式
需在 Controller 类上加 @Validated,并在入参处写约束注解(如@Min) 等校验失败抛 ConstraintViolationException。
java
@RestController
@Validated
@RequestMapping("/test/validated")
public class TestValidatedController {
@GetMapping("/a3")
public int a3(@NotNull(message = "name不可为空") String name,
@Min(value = 1, message = "最⼩不能⼩于1") int id) {
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(id);
return 0;
}
}PathVariable
在这种情况下也需要在Controller类上加上@Validated注解。如果校验失败,也是会抛出ConstraintViolationException异常。
统一线程池
为什么需要线程池:
- 资源管理:有效管理线程资源,避免频繁创建和销毁带来的资源浪费。
- 性能提升:复用已创建的线程,减少系统开销,提高响应速度。
- 灵活性和可扩展性:可动态调整配置以适应不同负载,限制并发线程数,防止系统崩溃。
- 提供更强大功能:支持延时、定时等高级特性。
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 是Spring框架提供的一个用于执行异步任务的线程池实现类。它基于Java的线程池(java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor)进行了封装,使得在Spring应用中更方便地配置和使用线程池来处理异步任务。
使用时,使用配置类对ThreadPoolTaskExecutor进行定义和配置。在业务代码中使用@Async 完成多线程业务开发。
核心设计
- 把统一线程池代码fw-common-core
- 封装核心线程池配置类
- 线程池参数通过 Nacos 动态配置
- 提供注解,一键开启异步任务
- 支持各微服务按需自定义个性化配置
java
package com.hyldzbg.fwcommoncore.config;
@Configuration
@EnableAsync //启动异步开发
public class ThreadPoolConfig {
/**
* 核心线程数
*/
@Value("${thread.pool-executor.corePoolSize:5}")
private Integer corePoolSize;
/**
* 最大线程数
*/
@Value("${thread.pool-executor.maxPoolSize:100}")
private Integer maxPoolSize;
/**
* 工作队列大小
*/
@Value("${thread.pool-executor.queueCapacity:100}")
private Integer queueCapacity;
/**
* 空闲存活时间
*/
@Value("${thread.pool-executor.keepAliveSeconds:60}")
private Integer keepAliveSeconds;
/**
* 线程名称前缀
*/
@Value("${thread.pool-executor.prefixName:thread-service-}")
private String prefixName;
/**
* 拒绝策略 枚举取值参考:RejectType
*/
@Value("${thread.pool-executor.rejectHandler:2}")
private Integer rejectHandler;
/**
* 线程池执行器
* @return
*/
@Bean("ThreadPoolTaskExecutor")
public Executor getThreadExecutor(){
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
threadExecutor.setCorePoolSize(this.corePoolSize);
threadExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(this.maxPoolSize);
threadExecutor.setQueueCapacity(this.queueCapacity);
threadExecutor.setKeepAliveSeconds(this.keepAliveSeconds);
threadExecutor.setThreadNamePrefix(this.prefixName);
threadExecutor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(getRejectHandler());
return threadExecutor;
}
/**
* 拒绝策略
*
* @return 拒绝策略处理器
*/
public RejectedExecutionHandler getRejectHandler() {
if (RejectType.AbortPolicy.getValue().equals(rejectHandler)) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy(); //枚举
} else if
(RejectType.CallerRunsPolicy.getValue().equals(rejectHandler)) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy();
} else if
(RejectType.DiscardOldestPolicy.getValue().equals(rejectHandler)) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy();
} else {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy();
}
}
}如果需要队配置进行修改,可以将配置放在nacos中
java
thread:
pool-executor:
corePoolSize: 20
maxPoolSize: 50
queueCapacity: 80
keepAliveSeconds: 60
prefixName: thread-service
rejectHandler: 2