
基于SpringBoot的企业考勤管理系统设计与实现
🌟 你好,我是 励志成为糕手 !
🌌 在代码的宇宙中,我是那个追逐优雅与性能的星际旅人。
✨ 每一行代码都是我种下的星光,在逻辑的土壤里生长成璀璨的银河;
🛠️ 每一个算法都是我绘制的星图,指引着数据流动的最短路径;
🔍 每一次调试都是星际对话,用耐心和智慧解开宇宙的谜题。
🚀 准备好开始我们的星际编码之旅了吗?
目录
摘要
在现代企业管理中,考勤管理作为人力资源管理的重要组成部分,直接关系到企业的运营效率和员工的工作积极性。传统的纸质考勤记录方式不仅效率低下,而且容易出错,难以进行数据分析和统计。随着企业规模的扩大和信息化程度的提高,开发一套高效、准确、易用的考勤管理系统显得尤为重要。
本文详细介绍了基于Spring Boot框架的企业考勤管理系统的设计与实现过程。系统采用经典的MVC架构模式,后端使用Spring Boot 2.6.13作为核心框架,结合Spring Data JPA进行数据持久化操作,前端采用Thymeleaf模板引擎和Bootstrap 5构建响应式用户界面。数据库选用MySQL 5.7+,确保数据的安全性和可靠性。
系统主要包含三大核心模块:员工管理模块负责员工信息的增删改查和唯一性验证;考勤记录模块支持每日考勤记录、考勤状态管理和请假记录管理;月度统计模块提供出勤统计、请假日期列表和出勤率计算等功能。系统通过数据库唯一约束确保同一员工同一天只能有一条考勤记录,使用Java 8的LocalDate和LocalTime处理日期时间,关键业务操作采用Spring事务管理机制。
在技术实现方面,系统充分运用了Spring Boot的自动配置特性,简化了开发配置过程。通过JPA注解实现对象关系映射,减少了SQL编写工作量。前端界面采用响应式设计,适配不同尺寸的设备。系统还提供了RESTful API接口,便于后续移动端应用的集成开发。
通过本系统的设计与实现,不仅解决了企业考勤管理的实际问题,也为类似管理系统的开发提供了可复用的技术方案和架构参考。系统具有良好的扩展性,可以方便地添加权限管理、考勤规则配置、报表导出等高级功能。
系统架构设计
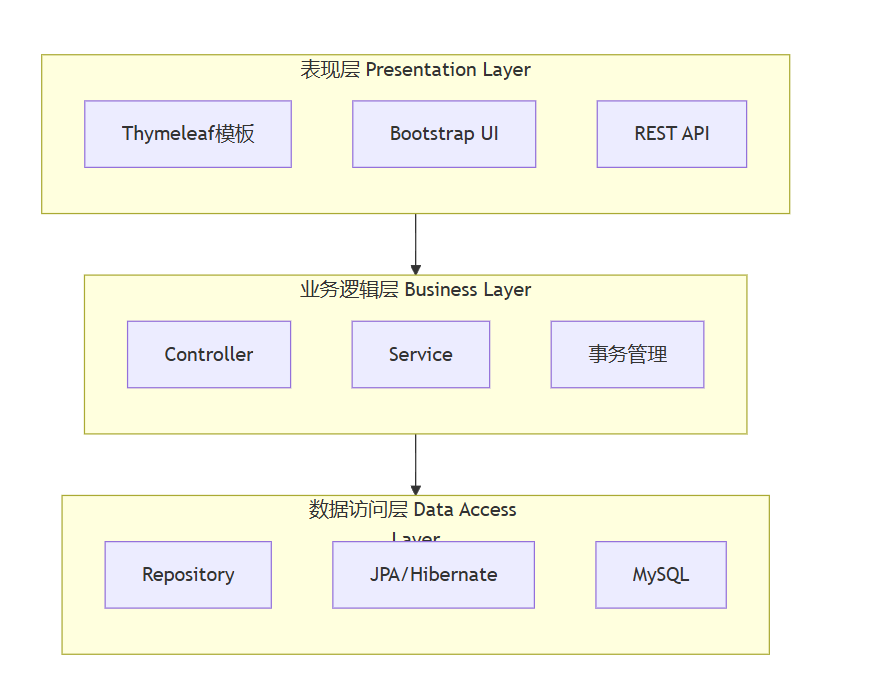
整体架构概览
本系统采用经典的三层架构模式,将应用分为表现层、业务逻辑层和数据访问层,各层之间职责明确,耦合度低,便于维护和扩展。
核心业务流程
考勤管理系统的核心业务流程涉及员工信息管理、考勤记录操作和统计报表生成三个主要环节。
管理员 普通用户 正常 请假 其他 用户登录系统 身份验证 员工管理 考勤操作 添加员工信息 验证员工编号唯一性 保存到数据库 选择考勤日期 记录考勤状态 状态判断 记录打卡时间 填写请假信息 记录特殊情况 生成考勤记录 月度统计计算 生成统计报表 数据可视化展示
数据库设计
实体关系模型
系统采用规范化的数据库设计,确保数据的一致性和完整性。主要包含员工表和考勤记录表两个核心实体。
数据表结构设计
系统设计了两个核心数据表,分别存储员工基本信息和考勤记录数据。
员工表结构设计:
sql
CREATE TABLE employees (
id BIGINT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
employee_id VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
department VARCHAR(50),
position VARCHAR(50),
created_at DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
updated_at DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
INDEX idx_department (department),
UNIQUE INDEX uk_employee_id (employee_id)
);考勤记录表结构设计:
sql
CREATE TABLE attendance_records (
id BIGINT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
employee_id BIGINT NOT NULL,
record_date DATE NOT NULL,
attendance_status VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL,
check_in_time TIME,
check_out_time TIME,
leave_type VARCHAR(20),
leave_reason VARCHAR(200),
created_at DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
updated_at DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
UNIQUE INDEX uk_employee_date (employee_id, record_date),
INDEX idx_record_date (record_date),
INDEX idx_attendance_status (attendance_status),
FOREIGN KEY fk_attendance_employee (employee_id) REFERENCES employees(id)
);核心代码实现
实体类设计
系统采用JPA注解方式定义实体类,实现对象关系映射。以下是员工实体类的完整实现:
java
package org.example.attendance_system.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
/**
* 员工实体类
* 负责存储员工基本信息,包括编号、姓名、部门、职位等
*/
@Entity
@Table(name = "employees")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String name;
@Column(nullable = false, unique = true)
private String employeeId;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String department;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String position;
@Column(name = "created_at")
private LocalDateTime createdAt;
@Column(name = "updated_at")
private LocalDateTime updatedAt;
// 默认构造函数
public Employee() {
}
// 带参构造函数
public Employee(String name, String employeeId, String department, String position) {
this.name = name;
this.employeeId = employeeId;
this.department = department;
this.position = position;
}
// Getter和Setter方法
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
this.updatedAt = LocalDateTime.now();
}
// 其他getter/setter方法...
/**
* 实体保存前自动设置创建时间和更新时间
*/
@PrePersist
protected void onCreate() {
createdAt = LocalDateTime.now();
updatedAt = LocalDateTime.now();
}
/**
* 实体更新前自动设置更新时间
*/
@PreUpdate
protected void onUpdate() {
updatedAt = LocalDateTime.now();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", employeeId='" + employeeId + '\'' +
", department='" + department + '\'' +
", position='" + position + '\'' +
'}';
}
}关键代码点评:
- 使用
@PrePersist和@PreUpdate注解实现自动时间戳管理 - 通过
@Column注解定义字段约束,确保数据完整性 - 实体类设计符合JPA规范,便于Spring Data JPA操作
业务逻辑层实现
考勤记录服务类封装了核心的业务逻辑,包括考勤记录管理、统计计算等功能:
java
package org.example.attendance_system.service;
import org.example.attendance_system.entity.AttendanceRecord;
import org.example.attendance_system.entity.Employee;
import org.example.attendance_system.repository.AttendanceRecordRepository;
import org.example.attendance_system.repository.EmployeeRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* 考勤记录服务类
* 负责考勤记录的增删改查、统计计算等业务逻辑
*/
@Service
public class AttendanceRecordService {
@Autowired
private AttendanceRecordRepository attendanceRecordRepository;
@Autowired
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
/**
* 记录考勤信息
* 检查是否已存在当天的考勤记录,避免重复记录
*/
public AttendanceRecord recordAttendance(AttendanceRecord attendanceRecord) {
// 检查是否已存在当天的考勤记录
if (attendanceRecordRepository.existsByEmployeeAndRecordDate(
attendanceRecord.getEmployee(), attendanceRecord.getRecordDate())) {
throw new RuntimeException("该员工当天考勤记录已存在");
}
return attendanceRecordRepository.save(attendanceRecord);
}
/**
* 统计员工某月的出勤情况
* 返回各种出勤状态的统计数量
*/
public Map<String, Integer> getAttendanceSummaryByEmployeeAndMonth(
Employee employee, int year, int month) {
List<Object[]> results = attendanceRecordRepository
.countAttendanceByStatusAndMonth(employee, year, month);
Map<String, Integer> summary = new HashMap<>();
// 初始化所有状态为0
summary.put("正常", 0);
summary.put("迟到", 0);
summary.put("早退", 0);
summary.put("请假", 0);
summary.put("缺勤", 0);
// 填充实际数据
for (Object[] result : results) {
String status = (String) result[0];
Long count = (Long) result[1];
summary.put(status, count.intValue());
}
return summary;
}
/**
* 获取员工某月的请假日期列表
* 用于月度统计和日历展示
*/
public List<LocalDate> getLeaveDatesByEmployeeAndMonth(
Employee employee, int year, int month) {
List<AttendanceRecord> leaveRecords =
getLeaveRecordsByEmployeeAndMonth(employee, year, month);
return leaveRecords.stream()
.map(AttendanceRecord::getRecordDate)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
// 其他业务方法...
}关键代码点评:
- 使用
@Service注解标识业务逻辑组件 - 通过Repository进行数据访问,实现业务逻辑与数据访问的分离
- 异常处理机制确保业务操作的可靠性
- 使用Stream API进行集合操作,代码简洁高效
控制器层实现
考勤记录控制器负责处理HTTP请求,协调业务逻辑和视图渲染:
java
package org.example.attendance_system.controller;
import org.example.attendance_system.entity.AttendanceRecord;
import org.example.attendance_system.entity.Employee;
import org.example.attendance_system.service.AttendanceRecordService;
import org.example.attendance_system.service.EmployeeService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Optional;
/**
* 考勤记录控制器
* 处理考勤相关的HTTP请求,包括列表展示、添加、编辑、删除等操作
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/attendance")
public class AttendanceRecordController {
@Autowired
private AttendanceRecordService attendanceRecordService;
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
/**
* 显示考勤记录列表页面
* 支持按年月筛选考勤记录
*/
@GetMapping
public String listAttendanceRecords(
@RequestParam(required = false) Integer year,
@RequestParam(required = false) Integer month,
Model model) {
// 如果没有指定年月,使用当前年月
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
int currentYear = year != null ? year : today.getYear();
int currentMonth = month != null ? month : today.getMonthValue();
List<AttendanceRecord> records = attendanceRecordService
.getAttendanceRecordsByMonth(currentYear, currentMonth);
List<Employee> employees = employeeService.getAllEmployees();
model.addAttribute("records", records);
model.addAttribute("employees", employees);
model.addAttribute("currentYear", currentYear);
model.addAttribute("currentMonth", currentMonth);
model.addAttribute("attendanceRecord", new AttendanceRecord());
return "attendance/list";
}
/**
* 显示月度统计页面
* 提供员工出勤情况的详细统计信息
*/
@GetMapping("/summary")
public String showMonthlySummary(
@RequestParam(required = false) Integer year,
@RequestParam(required = false) Integer month,
@RequestParam(required = false) Long employeeId,
Model model) {
// 如果没有指定年月,使用当前年月
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
int currentYear = year != null ? year : today.getYear();
int currentMonth = month != null ? month : today.getMonthValue();
List<Employee> employees = employeeService.getAllEmployees();
model.addAttribute("employees", employees);
model.addAttribute("currentYear", currentYear);
model.addAttribute("currentMonth", currentMonth);
if (employeeId != null) {
Optional<Employee> employee = employeeService.getEmployeeById(employeeId);
if (employee.isPresent()) {
// 获取月度统计
Map<String, Integer> summary = attendanceRecordService
.getAttendanceSummaryByEmployeeAndMonth(
employee.get(), currentYear, currentMonth);
// 获取请假日期
List<LocalDate> leaveDates = attendanceRecordService
.getLeaveDatesByEmployeeAndMonth(
employee.get(), currentYear, currentMonth);
model.addAttribute("selectedEmployee", employee.get());
model.addAttribute("summary", summary);
model.addAttribute("leaveDates", leaveDates);
}
}
return "attendance/summary";
}
// REST API接口...
}关键代码点评:
- 使用
@Controller和@RequestMapping注解定义控制器 - 通过
@RequestParam处理请求参数,提供灵活的筛选功能 - 使用Model对象向视图传递数据
- 清晰的URL映射和页面跳转逻辑
系统功能特性
出勤状态管理
系统支持多种出勤状态,每种状态都有明确的定义和对应的处理逻辑:
| 出勤状态 | 状态说明 | 处理逻辑 | 颜色标识 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 正常 | 按时上下班 | 记录打卡时间 | 绿色 (#28a745) |
| 迟到 | 上班打卡时间晚于规定时间 | 记录实际打卡时间 | 黄色 (#ffc107) |
| 早退 | 下班打卡时间早于规定时间 | 记录实际打卡时间 | 橙色 (#fd7e14) |
| 请假 | 因事假、病假等请假 | 填写请假类型和原因 | 蓝色 (#17a2b8) |
| 缺勤 | 未打卡且未请假 | 自动标记为缺勤 | 红色 (#dc3545) |
月度统计功能
系统提供详细的月度统计功能,帮助管理人员了解员工的出勤情况:
72% 12% 8% 4% 4% 图2:月度出勤状态分布图 正常 请假 迟到 早退 缺勤
技术选型对比
在项目开发过程中,我们对不同的技术方案进行了评估和选择:
| 技术组件 | 选型方案 | 优势 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 后端框架 | Spring Boot | 快速开发、自动配置、生态丰富 | 企业级应用、微服务 |
| 数据持久化 | Spring Data JPA | 简化数据库操作、面向对象 | 关系型数据库应用 |
| 前端模板 | Thymeleaf | 自然模板、与Spring集成好 | 服务端渲染应用 |
| UI框架 | Bootstrap 5 | 响应式设计、组件丰富 | 现代化Web界面 |
| 数据库 | MySQL | 稳定性好、生态成熟 | 事务性应用 |
系统部署与配置
环境配置
系统采用标准的Spring Boot配置方式,通过application.properties文件进行配置:
properties
# 数据库配置
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/attendance_system?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.username=your_username
spring.datasource.password=your_password
# JPA配置
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL8Dialect
# 服务器配置
server.port=8080
# Thymeleaf配置
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html
spring.thymeleaf.mode=HTML
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8
spring.thymeleaf.servlet.content-type=text/html
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false项目依赖管理
系统使用Maven进行依赖管理,核心依赖包括:
xml
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot Starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Data JPA -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Thymeleaf模板引擎 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 测试依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>系统性能优化
数据库优化策略
为了提高系统性能,我们采用了多种数据库优化策略:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 索引优化 查询优化 缓存策略 连接池优化 分库分表 高优先级 中优先级 低优先级 图3:数据库优化策略实施时间线
缓存策略设计
为了提升系统响应速度,我们设计了多级缓存策略:
- 应用级缓存:使用Spring Cache注解缓存热点数据
- 数据库查询缓存:配置MySQL查询缓存
- 静态资源缓存:配置HTTP缓存头优化前端资源加载
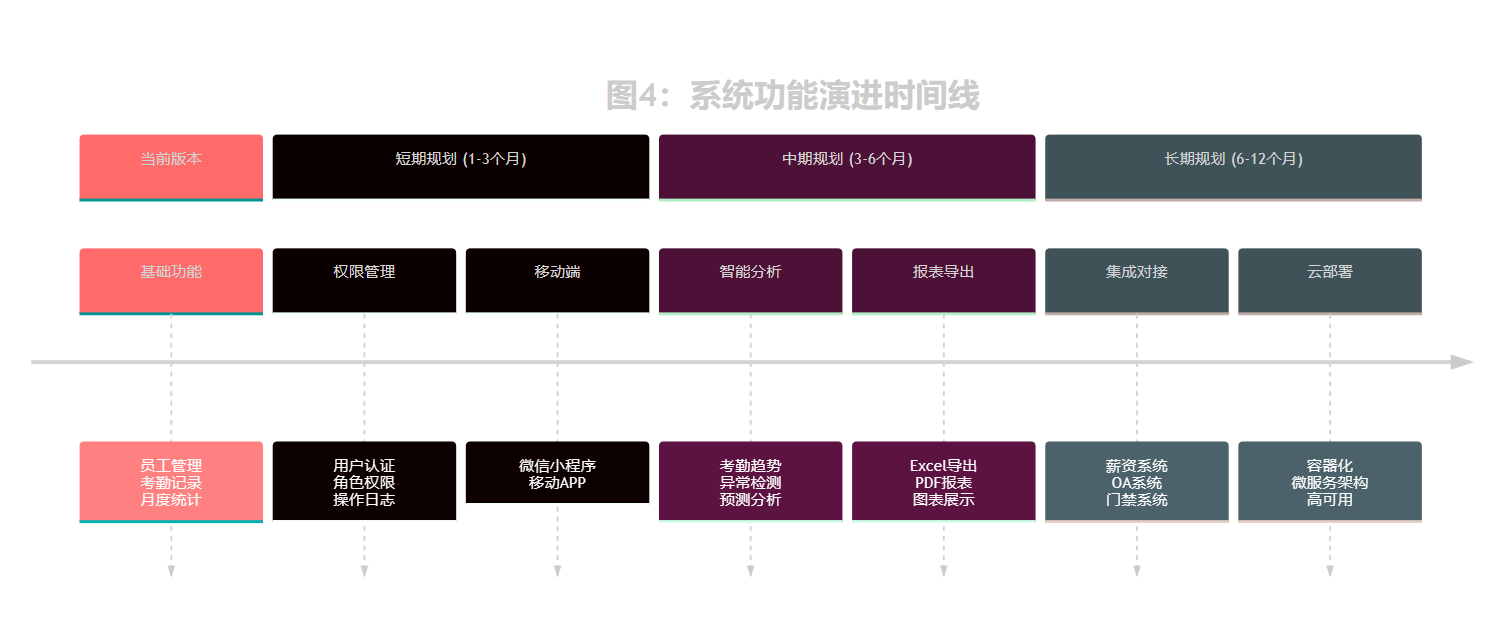
扩展功能规划
未来功能演进
系统具有良好的扩展性,可以方便地添加以下高级功能:
这里放一个实际运行的截图吧:
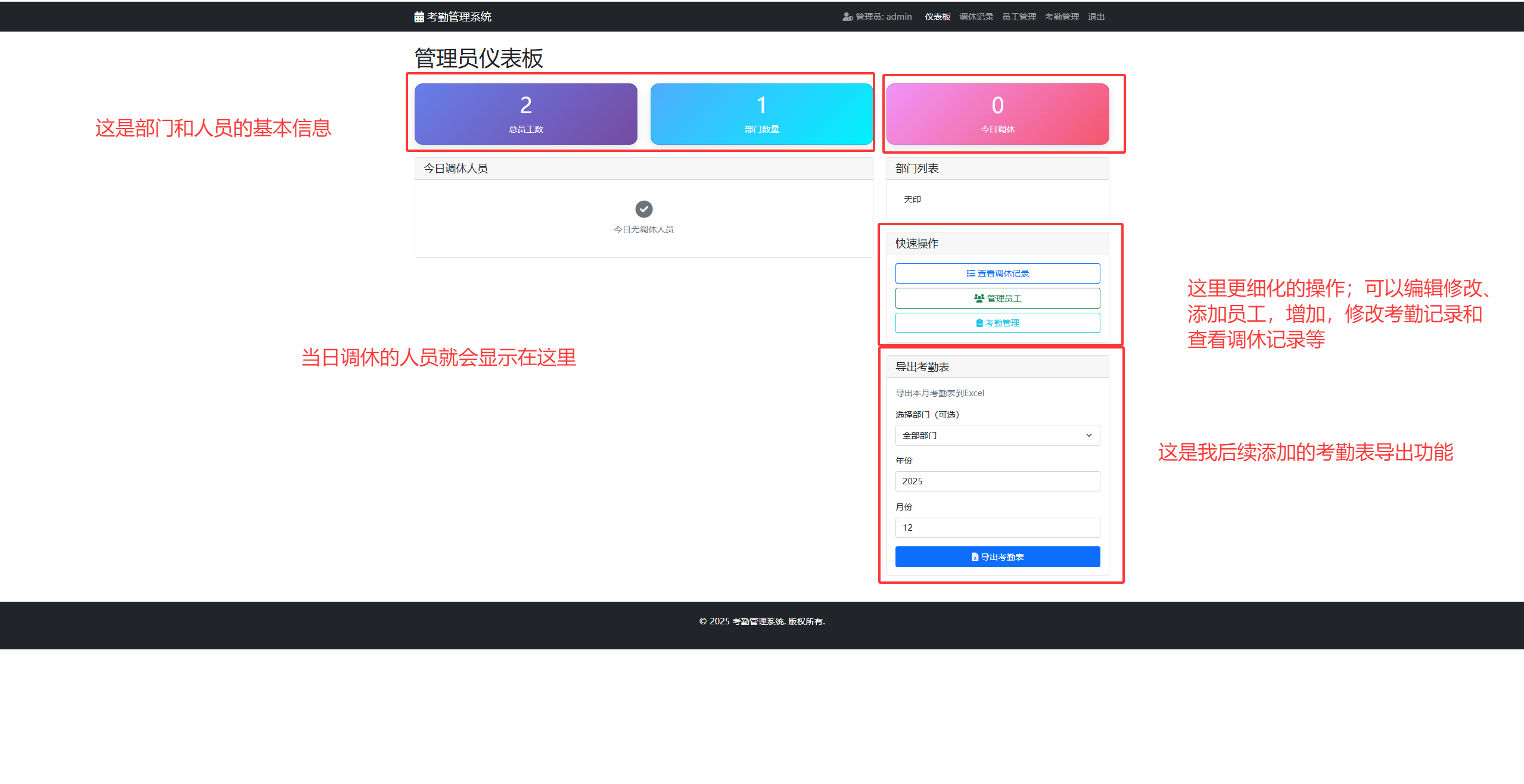
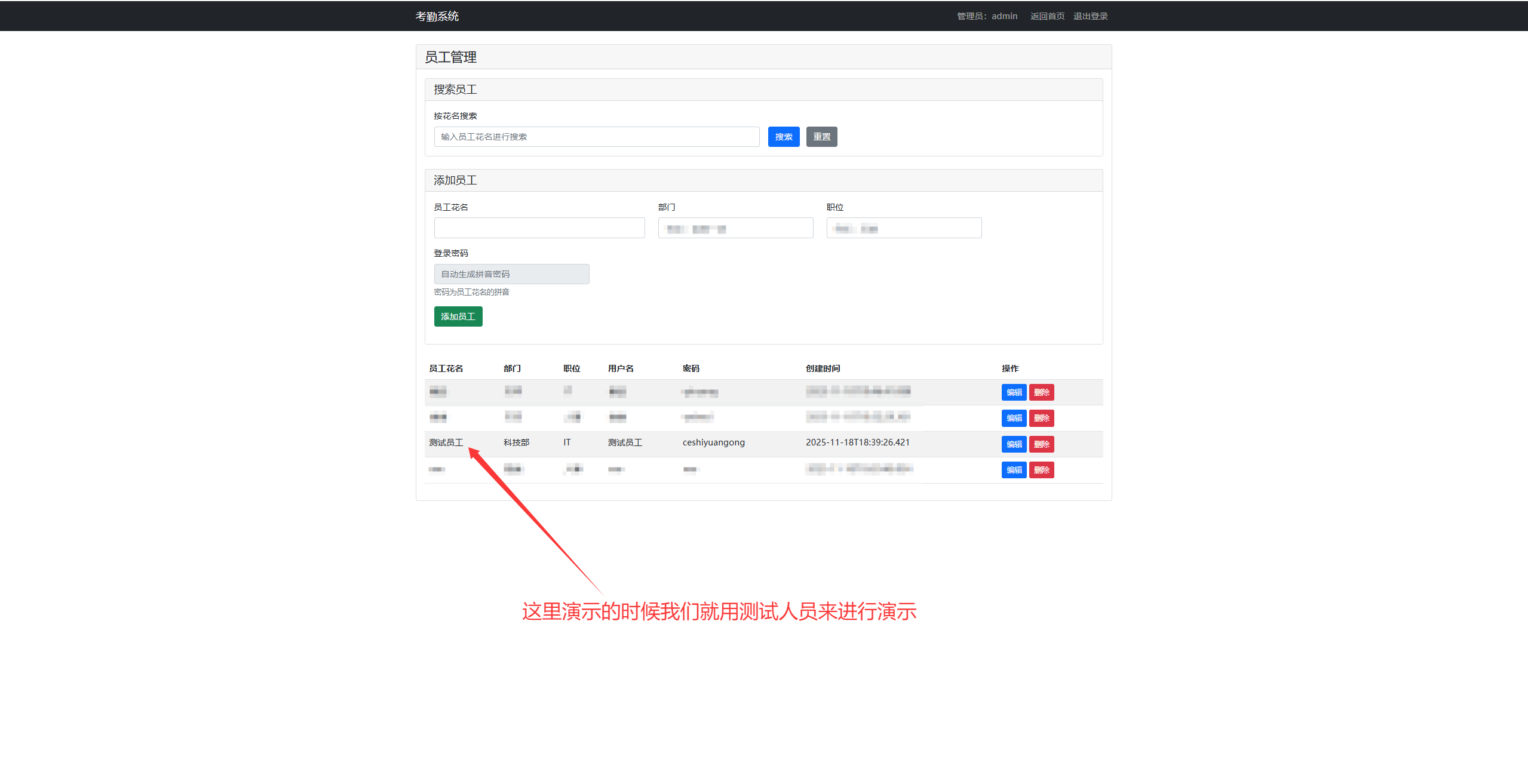
大致就是这个样子,不同的细化功能可以在后续完善。而且这个是超级管理员的界面。超级管理员admin有修改,添加员工、修改,添加员工记录等操作,方便统计和管理;
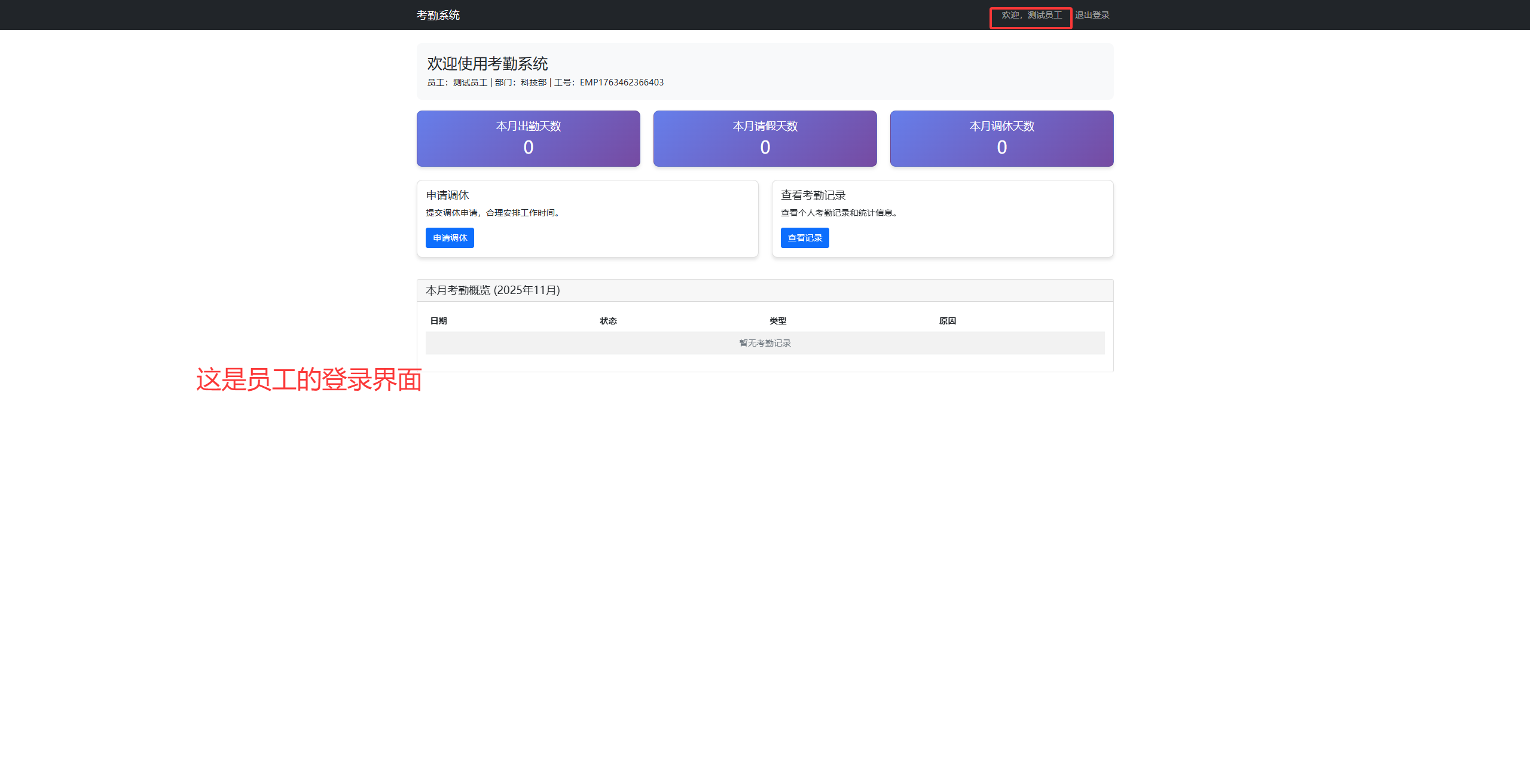
如果是员工要申请调休的界面则如下图这样:(前提是在管理员工页面内有这个员工)
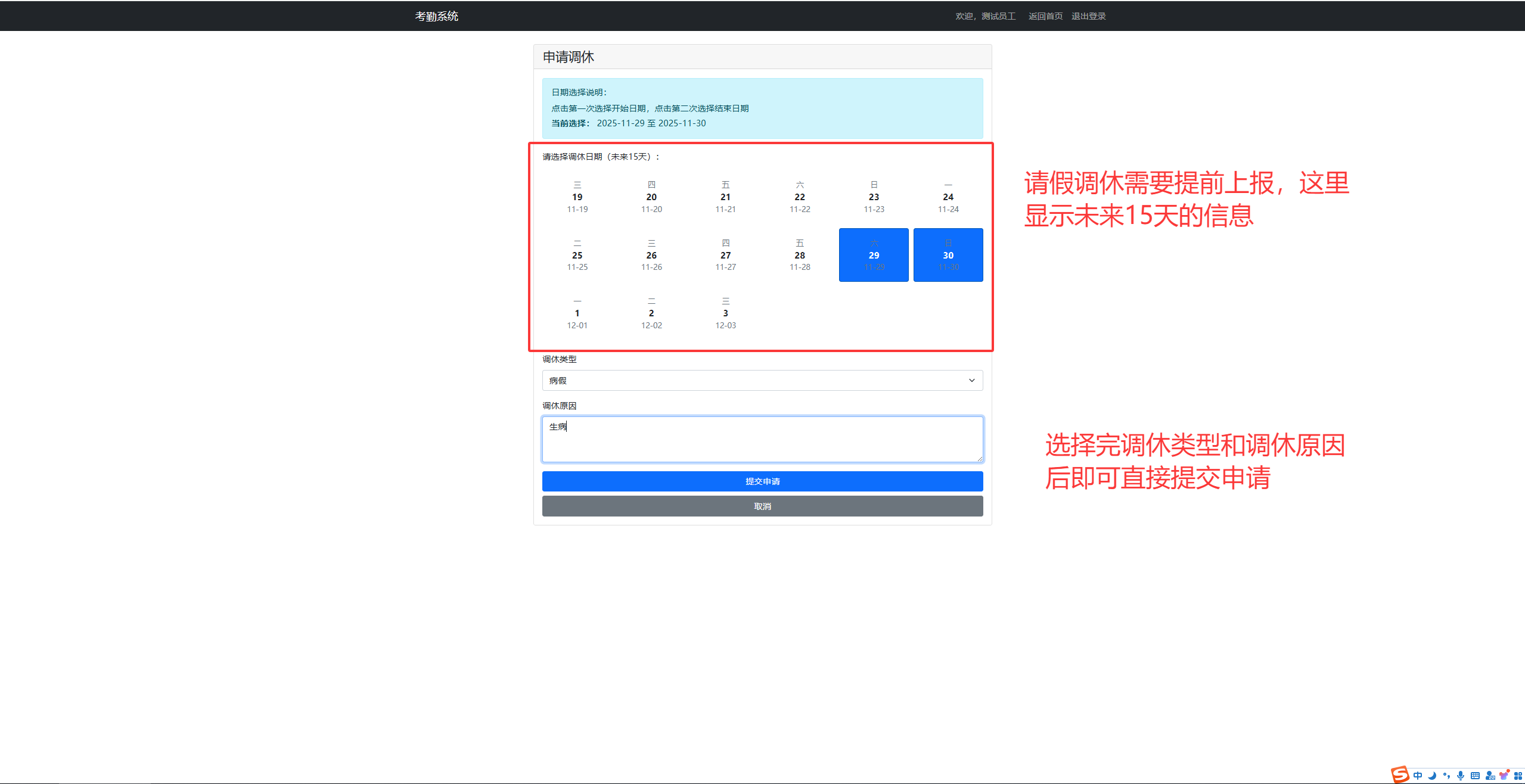
点击申请调休后,会来到如下的界面,只用选择好调休日期,调休类型后点击提交:
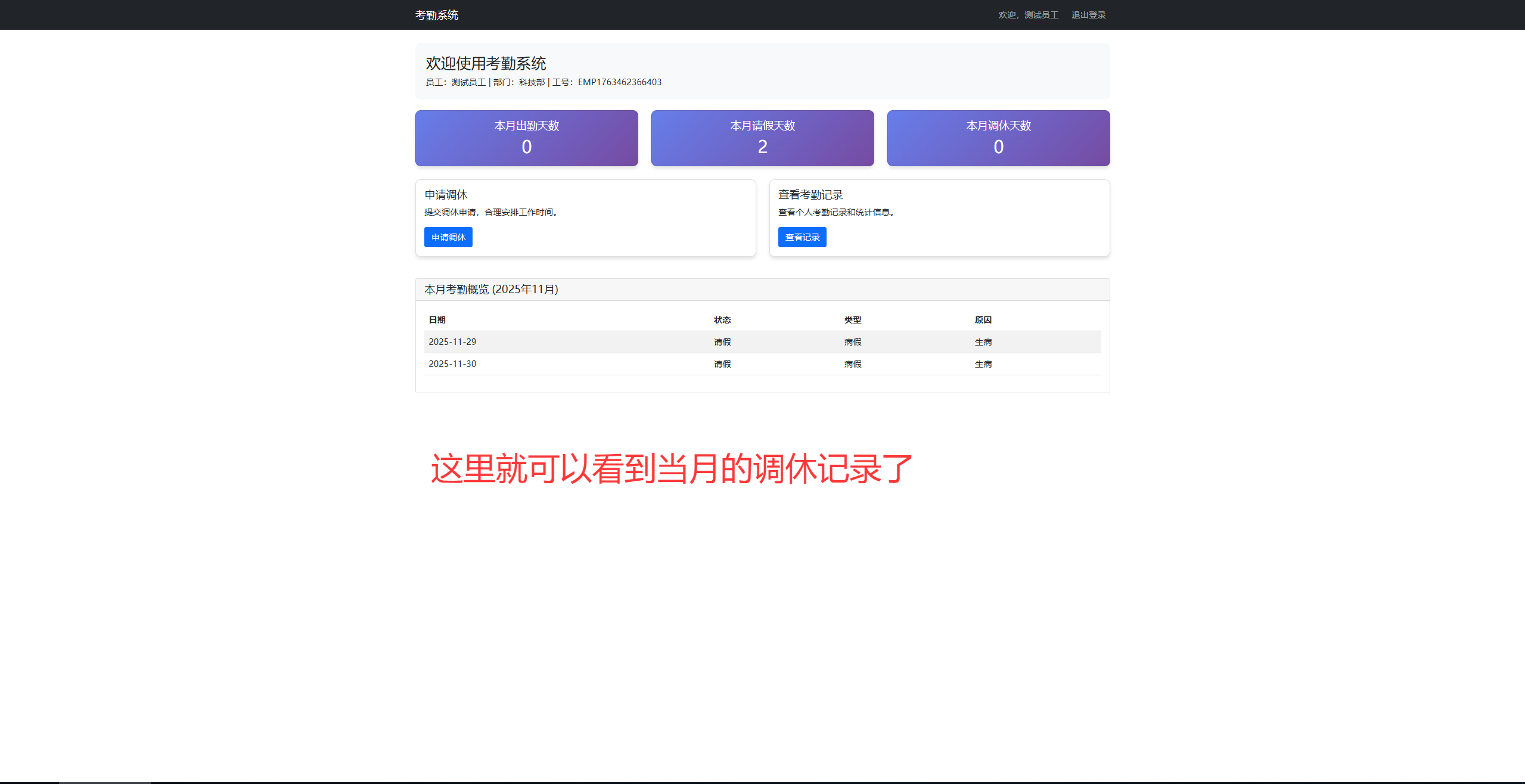
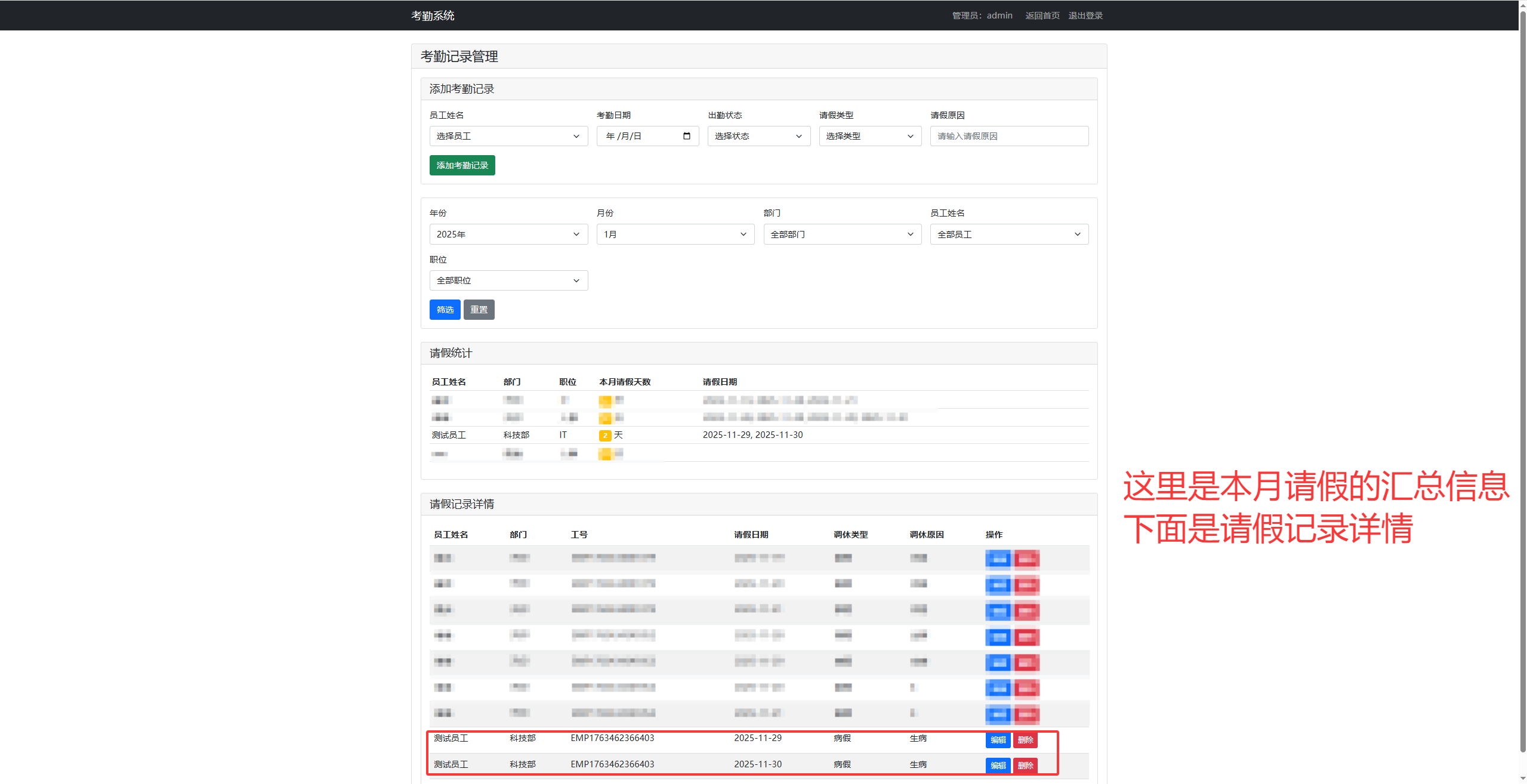
总结
通过本项目的设计与实现,我们成功开发了一套功能完善、性能优良的企业考勤管理系统。系统采用Spring Boot框架,结合现代Web开发技术,实现了员工管理、考勤记录、月度统计等核心功能。
在技术实现方面,系统充分体现了Spring Boot的快速开发优势,通过自动配置和约定优于配置的原则,大大减少了开发工作量。采用JPA进行数据持久化,简化了数据库操作,提高了开发效率。前端使用Thymeleaf和Bootstrap构建了美观、易用的用户界面。
系统设计遵循了软件工程的最佳实践,包括分层架构、模块化设计、异常处理、数据验证等。通过合理的数据库设计和索引优化,确保了系统的性能和稳定性。系统还提供了RESTful API接口,为后续的移动端开发和系统集成奠定了基础。
在项目开发过程中,我们遇到了诸多挑战,如数据一致性保证、性能优化、用户体验设计等。通过不断的学习和实践,我们找到了有效的解决方案,积累了宝贵的开发经验。这些经验不仅适用于考勤管理系统,也可以推广到其他类似的企业管理系统中。
最后,希望本文能给您提供帮助!
参考链接
关键词标签
#SpringBoot #考勤管理系统 #企业应用 #Java开发 #Web开发