前言
在 Flutter 混合开发中,原生端(Android/iOS)与 Flutter 端的通信是一个核心话题。本文以 Android 分享功能为例,介绍从简单实现到生产级优化的完整过程。
方案对比
方案一:使用第三方包
示例:share_handler 包
dart
SharedMedia? _sharedMedia;
Future<void> _initShareHandler() async {
// 监听热启动(App在前台/后台)
handler.sharedMediaStream.listen((SharedMedia media) {
_handleSharedData(media);
});
// 处理冷启动(App被分享唤醒)
final media = await handler.getInitialSharedMedia();
if (media != null) {
_handleSharedData(media);
}
}优点:
- 开箱即用,无需编写原生代码
- 跨平台支持(iOS + Android)
缺点:
- 无法自定义原生端逻辑
- 功能受限于包的实现
方案二:MethodChannel 自定义通信
适合需要精细控制原生逻辑的场景。
核心概念
1. MethodChannel 通信机制
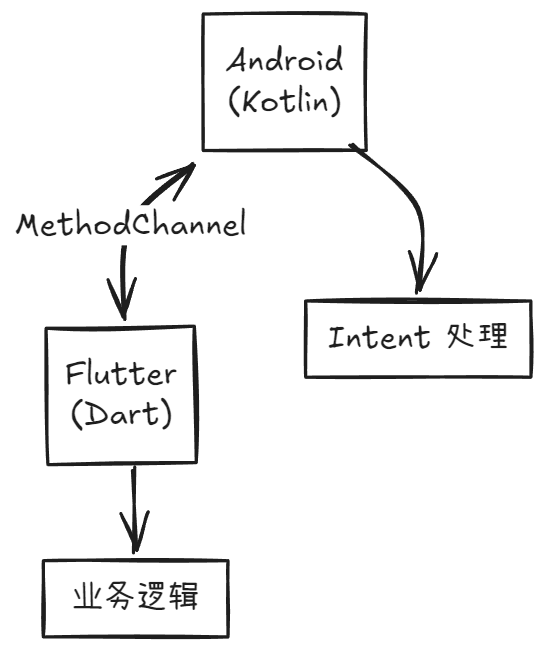
关键要素:
- Channel Name:通信的唯一标识,两端必须一致
- Method Name:具体调用的方法名
- Arguments:传递的数据(Map/List/基本类型)
- Result Callback:处理返回值
2. Flutter Engine 生命周期
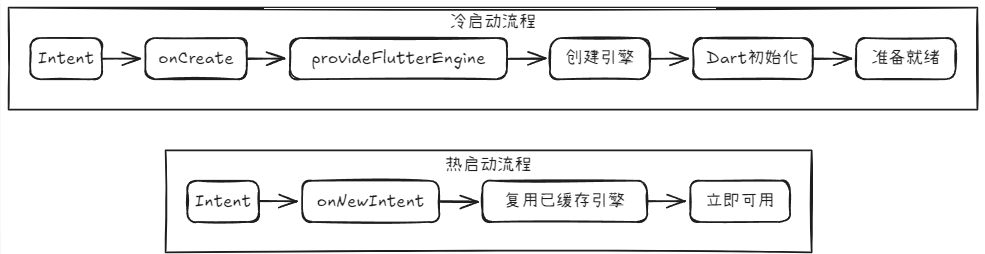
核心问题:如何判断引擎何时真正准备好?
前置配置
配置 AndroidManifest.xml
首先,你需要声明一个新的 Activity 作为分享入口。我们不使用 MainActivity,而是创建一个专用的 ShareActivity。
打开 android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml,在 <application> 标签内添加:
xml
<activity
android:name=".ShareActivity"
android:theme="@style/Theme.Flutter.Transparent"
android:launchMode="singleTask"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.SEND" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:mimeType="text/*" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>关键点解释:
-
android:name=".ShareActivity": 指向我们即将创建的ShareActivity.kt类。 -
android:theme="@style/Theme.Flutter.Transparent": 使用透明主题,即使用于后台处理,也能避免启动时出现白屏/黑屏闪烁,体验更佳。 -
android:launchMode="singleTask": 这是实现鲁棒性的第一步 。它确保ShareActivity在任务栈中只有一个实例。 -
<intent-filter>: 声明此 Activity 可以响应ACTION_SEND动作和text/*(纯文本) 类型的数据。
你还可以添加其他的配置,全部如下:
xml
<!-- 透明分享接收 Activity - 单一 FlutterActivity 架构 -->
<activity
android:name=".ShareActivity"
android:theme="@style/Theme.Transparent"
android:exported="true"
android:launchMode="singleTask"
android:taskAffinity=""
android:excludeFromRecents="true"
android:configChanges="orientation|keyboardHidden|keyboard|screenSize|locale|layoutDirection|fontScale|screenLayout|density|uiMode"
android:hardwareAccelerated="true"
android:windowSoftInputMode="adjustResize">
<intent-filter>
<!-- 接收单个分享项目 -->
<action android:name="android.intent.action.SEND" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<!-- 支持的MIME类型 -->
<data android:mimeType="text/*" />
<data android:mimeType="image/*" />
<data android:mimeType="video/*" />
<data android:mimeType="application/*" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<!-- 接收多个分享项目 -->
<action android:name="android.intent.action.SEND_MULTIPLE" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<!-- 支持的MIME类型 -->
<data android:mimeType="text/*" />
<data android:mimeType="image/*" />
<data android:mimeType="video/*" />
<data android:mimeType="application/*" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>步骤 2: 理解 Activity 生命周期 (鲁棒性的关键)
launchMode="singleTask" 决定了 ShareActivity 如何被启动,这直接关系到我们必须覆盖哪些方法:
-
冷启动 (Cold Start):
-
场景: 你的 App 进程完全未运行。
-
触发 : 用户分享,系统创建新进程和
ShareActivity实例。 -
调用 :
onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?)
-
-
热启动 (Hot Start):
-
场景: 你的 App 已经在后台运行(之前分享过,或打开过主 App)。
-
触发: 用户再次分享。
-
调用 :
onNewIntent(intent: Intent)(系统不会创建新实例,而是复用现有实例,并通过此方法传入新的Intent)。
-
常见的陷阱 :如果只在
onCreate中处理intent,这会导致所有热启动 的分享都被忽略,造成"第二次分享失灵"的 Bug。
基础实现
Android 端核心代码
1. 定义通信常量
kotlin
class ShareActivity : FlutterActivity() {
companion object {
// 通道标识
private const val CHANNEL = "com.doublez.pocketmind/share"
// 引擎缓存 ID
private const val ENGINE_ID = "share_engine"
}
private var methodChannel: MethodChannel? = null
}2. 初始化引擎和通道
kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
initFlutterBackgroundEngine()
// ⚠️ 问题:延迟处理是为了等待引擎,但不可靠,详见后面的
Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()).postDelayed({
handleShareIntent(intent)
}, 300)
}
private fun initFlutterBackgroundEngine() {
// 尝试复用缓存引擎
flutterEngine = FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().get(ENGINE_ID)
if (flutterEngine == null) {
// 冷启动:创建新引擎
flutterEngine = FlutterEngine(this).apply {
dartExecutor.executeDartEntrypoint(
DartExecutor.DartEntrypoint.createDefault()
)
}
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().put(ENGINE_ID, flutterEngine)
}
// 创建 MethodChannel
// 这里会导致无论冷热启动,都重新创建 MethodChannel,旧监听器丢失,消息无法接收,博主遇到这个坑,单独放这边提醒读者
flutterEngine?.dartExecutor?.binaryMessenger?.let { messenger ->
methodChannel = MethodChannel(messenger, CHANNEL)
}
}3. 解析并发送数据
kotlin
private fun handleShareIntent(intent: Intent?) {
val action = intent?.action
val type = intent?.type
when {
action == Intent.ACTION_SEND && type?.startsWith("text/") == true -> {
val text = intent.getStringExtra(Intent.EXTRA_TEXT) ?: return
val title = intent.getStringExtra(Intent.EXTRA_SUBJECT) ?: "分享内容"
sendToFlutter(title, text)
}
}
}
private fun sendToFlutter(title: String, content: String) {
val data = mapOf(
"title" to title,
"content" to content,
"timestamp" to System.currentTimeMillis()
)
methodChannel?.invokeMethod("saveAndSync", data, object : MethodChannel.Result {
override fun success(result: Any?) {
Log.d(TAG, "✅ 成功")
}
override fun error(code: String, message: String?, details: Any?) {
Log.e(TAG, "❌ 失败: $message")
}
override fun notImplemented() {
Log.w(TAG, "⚠️ 方法未实现")
}
})
}Flutter 端核心代码
dart
void main() async {
WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
ShareBackgroundService.initialize(); // 初始化通信服务
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class ShareBackgroundService {
static const MethodChannel _channel = MethodChannel(
'com.doublez.pocketmind/share', // 与 Android 端一致
);
static void initialize() {
_channel.setMethodCallHandler(_handleMethodCall);
}
static Future<dynamic> _handleMethodCall(MethodCall call) async {
switch (call.method) {
case 'saveAndSync': // 匹配 Android 端的方法名
return await _processSh areData(call.arguments);
default:
throw PlatformException(code: 'UNKNOWN_METHOD');
}
}
static Future<Map<String, dynamic>> _processShareData(dynamic args) async {
final data = args as Map;
final title = data['title'] as String;
final content = data['content'] as String;
// 处理业务逻辑...
return {'success': true};
}
}Version 1.0 存在的问题
| 问题 | 表现 | 原因 |
|---|---|---|
| 时序问题 | 数据偶尔丢失 | 固定延迟 300ms 无法保证引擎就绪 |
| 冷热启动混淆 | 热启动时重复初始化 | 未区分引擎状态 |
| 生命周期错乱 | onNewIntent 未处理 |
只在 onCreate 处理数据 |
优化实现
核心优化:双向握手机制
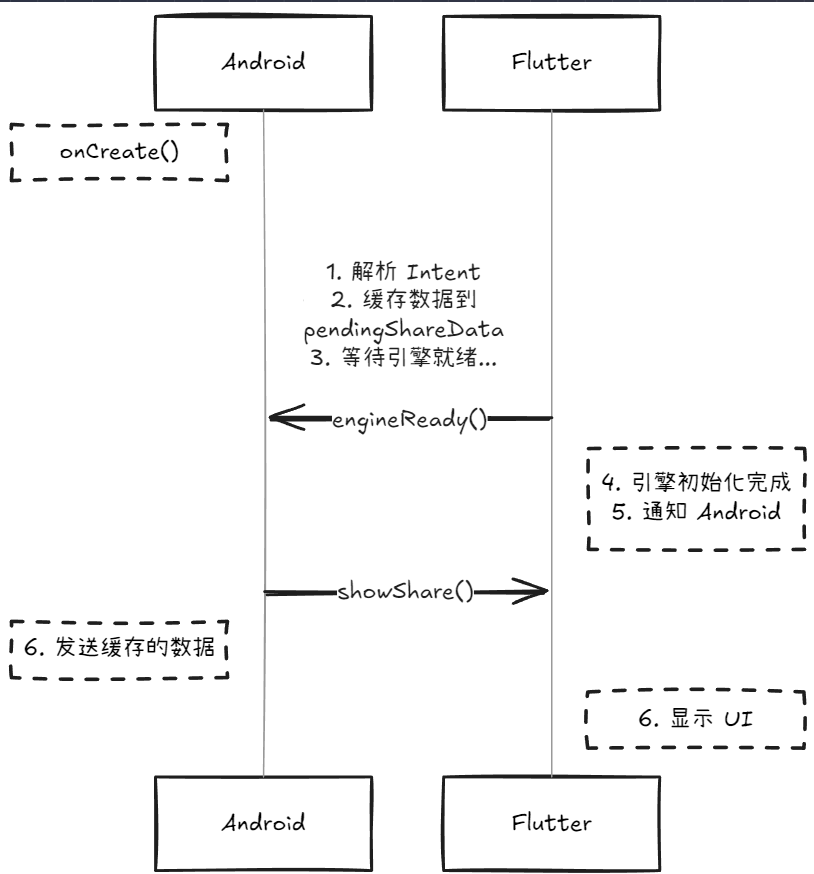
Android 端优化代码
1. 状态管理
kotlin
class ShareActivity : FlutterActivity() {
private var methodChannel: MethodChannel? = null
private var pendingShareData: ShareData? = null // 待处理数据队列
private var isEngineReady = false // 引擎状态标志
data class ShareData(val title: String, val content: String)
}2. 生命周期处理
kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// 1. 解析并缓存数据(不立即发送)
val shareData = parseShareIntent(intent)
if (shareData != null) {
pendingShareData = shareData
// 2. 如果是热启动,引擎可能已就绪
if (isEngineReady && methodChannel != null) {
notifyDartToShowShare(shareData)
// 发送的数据置为null,防止下次干扰
pendingShareData = null
}
}
}
override fun onNewIntent(intent: Intent) {
super.onNewIntent(intent)
// 处理热启动
val shareData = parseShareIntent(intent)
if (shareData != null) {
pendingShareData = shareData
if (isEngineReady) {
notifyDartToShowShare(shareData)
pendingShareData = null
}
}
}3. 引擎初始化与通道设置
kotlin
override fun provideFlutterEngine(context: Context): FlutterEngine? {
var engine = FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().get(ENGINE_ID)
val isHotStart = engine != null
if (engine == null) {
// 冷启动:创建引擎
val flutterLoader = FlutterInjector.instance().flutterLoader()
//确保 FlutterLoader 已初始化
if (!flutterLoader.initialized()) {
flutterLoader.startInitialization(applicationContext)
flutterLoader.ensureInitializationComplete(context, null)
}
engine = FlutterEngine(this).apply {
dartExecutor.executeDartEntrypoint(
DartExecutor.DartEntrypoint(
flutterLoader.findAppBundlePath(),
"main_share" // 可选:独立入口
)
)
}
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().put(ENGINE_ID, engine)
} else {
// 热启动:引擎已就绪
isEngineReady = true
}
setupMethodChannel(engine)
return engine
}
private fun setupMethodChannel(engine: FlutterEngine) {
engine.dartExecutor.binaryMessenger.let { messenger ->
methodChannel = MethodChannel(messenger, CHANNEL)
// ⚡ 关键:监听 Flutter 端的就绪信号
methodChannel?.setMethodCallHandler { call, result ->
when (call.method) {
"engineReady" -> {
isEngineReady = true
result.success(null)
// 处理待发送的数据
pendingShareData?.let { data ->
notifyDartToShowShare(data)
pendingShareData = null
}
}
else -> result.notImplemented()
}
}
// 热启动场景:立即处理
if (isEngineReady) {
pendingShareData?.let { data ->
notifyDartToShowShare(data)
pendingShareData = null
}
}
}
}4. 发送数据
kotlin
private fun notifyDartToShowShare(data: ShareData) {
val payload = mapOf(
"title" to data.title,
"content" to data.content,
"timestamp" to System.currentTimeMillis()
)
methodChannel?.invokeMethod("showShare", payload, object : MethodChannel.Result {
override fun success(result: Any?) {
Log.d(TAG, "✅ Flutter 已接收数据")
}
override fun error(code: String, msg: String?, details: Any?) {
Log.e(TAG, "❌ 错误: $msg")
}
override fun notImplemented() {
Log.w(TAG, "⚠️ 方法未实现")
}
})
}Flutter 端优化代码
dart
class _MyShareAppState extends State<MyShareApp> {
static const _channel = MethodChannel('com.example.notebook/share');
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_channel.setMethodCallHandler(_handleMethodCall);
// ⚡ 关键:渲染完成后通知原生端
WidgetsBinding.instance.addPostFrameCallback((_) {
_notifyEngineReady();
});
}
Future<void> _notifyEngineReady() async {
try {
await _channel.invokeMethod('engineReady');
print("✅ 已通知 Android:引擎就绪");
} catch (e) {
print("❌ 通知失败: $e");
}
}
Future<dynamic> _handleMethodCall(MethodCall call) async {
switch (call.method) {
case 'showShare':
final args = call.arguments as Map;
// 处理分享数据...
return "Success";
default:
throw PlatformException(code: 'UNKNOWN_METHOD');
}
}
}最佳实践总结
1. 通道设计原则
| 原则 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 唯一性 | Channel Name 全局唯一 | com.company.app/feature |
| 语义化 | Method Name 清晰表意 | showShare vs method1 |
| 版本兼容 | 支持多版本协议 | 在参数中添加 version 字段 |
2. 数据传递规范
kotlin
// ✅ 推荐:使用结构化数据
val data = mapOf(
"type" to "text",
"payload" to mapOf(
"title" to title,
"content" to content
),
"metadata" to mapOf(
"timestamp" to System.currentTimeMillis(),
"source" to packageName
)
)
// ❌ 避免:直接传递复杂对象
methodChannel.invokeMethod("share", customObject) // 可能会序列化失败3. 错误处理策略
dart
Future<T> safeInvoke<T>(
String method,
dynamic arguments,
) async {
try {
return await _channel.invokeMethod<T>(method, arguments);
} on PlatformException catch (e) {
// 处理原生端抛出的错误
log.error('Platform error: ${e.code} - ${e.message}');
rethrow;
} catch (e) {
// 处理其他错误
log.error('Unknown error: $e');
rethrow;
}
}4. 生命周期同步
| 场景 | Android 端 | Flutter 端 |
|---|---|---|
| 冷启动 | 缓存数据 → 等待就绪信号 | 初始化完成 → 发送就绪信号 |
| 热启动 | 检查引擎状态 → 立即发送 | 复用已有实例 |
5. 性能优化建议
kotlin
// 1. 引擎预热(在 Application 中)
class MyApp : Application() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
FlutterInjector.instance().flutterLoader()
.startInitialization(this)
}
}
// 2. 引擎复用
FlutterEngineCache.getInstance().put(ENGINE_ID, engine)
// 3. 避免阻塞主线程
Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()).post {
methodChannel?.invokeMethod(...)
}更近一步
极端情况下的数据丢失怎么办?
使用
pendingData+isEngineReady双重保险机制。
安卓端代码:
kotlin
class ChannelHealthMonitor(
private val methodChannel: MethodChannel,
private val onHealthChanged: (Boolean) -> Unit
) {
private var isHealthy = false
private val handler = Handler(Looper.getMainLooper())
private val checkInterval = 5000L // 5 秒检查一次
private val healthCheckRunnable = object : Runnable {
override fun run() {
checkHealth()
handler.postDelayed(this, checkInterval)
}
}
fun start() {
Log.d(TAG, "开始健康检查")
handler.post(healthCheckRunnable)
}
fun stop() {
Log.d(TAG, "停止健康检查")
handler.removeCallbacks(healthCheckRunnable)
}
private fun checkHealth() {
val startTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
methodChannel.invokeMethod("ping", null, object : MethodChannel.Result {
override fun success(result: Any?) {
val latency = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime
val healthy = latency < 1000 // 延迟小于 1 秒视为健康
if (isHealthy != healthy) {
isHealthy = healthy
onHealthChanged(healthy)
Log.d(TAG, if (healthy) "✅ 通道健康" else "❌ 通道异常")
}
}
override fun error(code: String, message: String?, details: Any?) {
if (isHealthy) {
isHealthy = false
onHealthChanged(false)
Log.e(TAG, "❌ 通道错误: $message")
}
}
override fun notImplemented() {
if (isHealthy) {
isHealthy = false
onHealthChanged(false)
Log.w(TAG, "⚠️ ping 方法未实现")
}
}
})
}
companion object {
private const val TAG = "ChannelHealthMonitor"
}
}
// 在 ShareActivity 中使用
class ShareActivity : FlutterActivity() {
private var healthMonitor: ChannelHealthMonitor? = null
private fun setupMethodChannel(engine: FlutterEngine) {
// ... 创建 methodChannel ...
// 启动健康检查
healthMonitor = ChannelHealthMonitor(methodChannel!!) { isHealthy ->
if (!isHealthy) {
// 通道异常,尝试恢复
Log.w(TAG, "检测到通道异常,尝试重新初始化")
recreateChannel(engine)
}
}
healthMonitor?.start()
}
private fun recreateChannel(engine: FlutterEngine) {
methodChannel = MethodChannel(engine.dartExecutor.binaryMessenger, CHANNEL)
// 重新设置监听器...
}
override fun onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy()
healthMonitor?.stop()
}
}flutter端代码(不重试版本):
dart
class ChannelHealthService {
static const _channel = MethodChannel('com.example.notebook/share');
static Timer? _heartbeatTimer;
static int _pingCount = 0;
static int _failCount = 0;
// 启动健康监控
static void startMonitoring() {
// 响应 Android 的 ping
_channel.setMethodCallHandler((call) async {
if (call.method == 'ping') {
_pingCount++;
print('[$_pingCount] 收到 ping,通道健康');
return 'pong'; // 返回响应
}
});
// 主动发送心跳
_heartbeatTimer = Timer.periodic(const Duration(seconds: 10), (_) {
_sendHeartbeat();
});
}
static Future<void> _sendHeartbeat() async {
try {
final result = await _channel.invokeMethod('heartbeat');
_failCount = 0;
print('✅ 心跳成功: $result');
} catch (e) {
_failCount++;
print('❌ 心跳失败 ($_failCount): $e');
if (_failCount >= 3) {
print('⚠️ 连续失败 3 次,通道可能断开');
_onChannelDisconnected();
}
}
}
static void _onChannelDisconnected() {
// 尝试恢复连接
print('尝试恢复通道连接...');
// 重新初始化
_channel.setMethodCallHandler(null);
Future.delayed(const Duration(seconds: 1), () {
startMonitoring();
});
}
static void stopMonitoring() {
_heartbeatTimer?.cancel();
_heartbeatTimer = null;
}
}
// 在 main.dart 中启动
void main() {
WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
ChannelHealthService.startMonitoring();
runApp(const MyApp());
}flutter端重试版本
dart
class SmartChannelHealthChecker {
final MethodChannel channel;
final Duration timeout;
final int maxRetries;
SmartChannelHealthChecker({
required this.channel,
this.timeout = const Duration(seconds: 3),
this.maxRetries = 3,
});
Future<HealthStatus> checkHealth() async {
int attempts = 0;
while (attempts < maxRetries) {
try {
final stopwatch = Stopwatch()..start();
await channel
.invokeMethod('ping')
.timeout(timeout);
stopwatch.stop();
return HealthStatus(
isHealthy: true,
latency: stopwatch.elapsedMilliseconds,
attempts: attempts + 1,
);
} catch (e) {
attempts++;
if (attempts >= maxRetries) {
return HealthStatus(
isHealthy: false,
error: e.toString(),
attempts: attempts,
);
}
// 指数退避
await Future.delayed(Duration(milliseconds: 100 * attempts));
}
}
return HealthStatus(isHealthy: false, attempts: attempts);
}
}
class HealthStatus {
final bool isHealthy;
final int? latency;
final String? error;
final int attempts;
HealthStatus({
required this.isHealthy,
this.latency,
this.error,
required this.attempts,
});
@override
String toString() {
if (isHealthy) {
return '✅ 健康 (延迟: ${latency}ms, 尝试: $attempts)';
} else {
return '❌ 异常 (错误: $error, 尝试: $attempts)';
}
}
}
// 使用示例
Future<void> performHealthCheck() async {
final checker = SmartChannelHealthChecker(
channel: _channel,
timeout: const Duration(seconds: 2),
maxRetries: 3,
);
final status = await checker.checkHealth();
print(status);
if (!status.isHealthy) {
// 触发恢复机制
await _attemptReconnection();
}
}通过本文的优化方案,我们实现了:
✅ 可靠的时序控制 :双向握手机制
✅ 完整的生命周期管理 :支持冷/热启动
✅ 健壮的错误处理 :多层级异常捕获
✅ 高性能:引擎复用 + 预热
核心思想:不要假设时序,通过显式信号量进行同步状态。