初识C++
一、C++的第一个程序
由于C++兼容C绝大部分语言,使用C语言实现的hello world依旧可以运行
- C语言后缀为
.c - C++后缀为
.cpp
C++中C语言版本的输出:
cpp
/*test.cpp*/
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello world");
return 0;
}C++版本的输出:
cpp
/*test.cpp*/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "hello world" << endl;
return 0;
}二、命名空间
1、namespace的价值
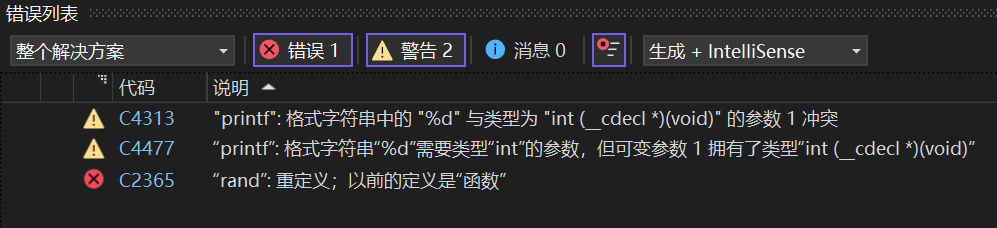
在C/C++中,由于变量、函数和类是大量存在的,在全局作用域中大量存在,可能会导致很多冲突。命名空间的目的就是对标识符的名称进行本地化,避免命名冲突,所以用namespace关键字来解决此类问题。
以下是C语言中的命名冲突
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int rand = 9;
int main()
{
printf("%d", rand);
return 0;
}
2、namespace的定义
- 定义命名空间,需要使用到namespace关键字,后面跟命名空间的名字,然后接一对即可,中
即为命名空间的成员。命名空间中可以定义变量/函数/类型等。 - namespace本质是定义出一个域,这个域跟全局域各自独立,不同的域可以定义同名变量,所以下面的rand不在冲突了。
- C++中域有函数局部域,全局域,命名空间域,类域;域影响的是编译时语法查找一个变量/函数/类型出处(声明或定义)的逻辑,所有有了域隔离,名字冲突就解决了。局部域和全局域除了会影响编译查找逻辑,还会影响变量的生命周期,命名空间域和类域不影响变量生命周期。
- namespace只能定义在全局,当然他还可以嵌套定义。
- 项目工程中多文件中定义的同名namespace会认为是一个namespace,不会冲突。
- C++标准库都放在一个叫std(standard)的命名空间中。
(1)正常的命名空间定义
C版本
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//域
namespace yuuki
{
// 命名空间中可以定义变量/函数/类型
int rand = 10; //常量
//函数
int Add(int left, int right)
{
return left + right;
}
//结构体
struct Node
{
struct Node* next;
int val;
};
}//注意:没有分号
int main()
{
// 这里默认是访问的是全局的rand函数指针
printf("rand = %p\n", rand);
// 这里指定bit命名空间中的rand
printf("yuuki::rand = %d\n", yuuki::rand);
printf("yuuki::Add = %p\n", yuuki::Add);
printf("yuuki::Add(1, 2) = %d\n", yuuki::Add(1, 2));
struct yuuki::Node node;
return 0;
}
C++版本
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//域
namespace yuuki
{
int rand = 10;
}
int a = 0;
int main()
{
int a = 1;
cout << "a = " << a << endl; //1
// ::域作用限定符
cout << "::a = " << ::a << endl; //0
cout << "yuuki::rand = " << yuuki::rand << endl; //10
return 0;
}
(2)命名空间可以嵌套
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
namespace yuuki
{
namespace A
{
int rand = 10;
int Add(int x, int y)
{
return x + y;
}
}
namespace B
{
int rand = 20;
int Sub(int x, int y)
{
return x - y;
}
}
}
int main()
{
printf("yuuki->A->rand = %d\n", yuuki::A::rand);
printf("yuuki->B->rand = %d\n", yuuki::B::rand);
printf("yuuki->A->Add = %d\n", yuuki::A::Add(1, 1));
printf("yuuki->B->Sub = %d\n", yuuki::B::Sub(1, 1));
return 0;
}
- 多文件中可以定义同名namespace,他们会默认合并到一起,就像同一个namespace一样
3、命名空间的使用
编译查找一个变量的声明/定义时,默认只会在局部或者全局查找,不会到命名空间里面去查找。所以下面程序会编译报错。所以我们要使用命名空间中定义的变量/函数,有三种方式:
- 指定命名空间访问,项目中推荐这种方式
- using将命名空间中某个成员展开,项目中经常访问的不存在冲突的成员推荐这种方式
- 展开命名空间中全部成员,项目不推荐,冲突风险很大,日常小练习程序为了方便推荐使用
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
namespace yuuki
{
int a = 0;
int b = 1;
}
int main()
{
// 编译报错:error C2065: "a": 未声明的标识符
printf("%d\n", a);
return 0;
}(1)指定命名空间访问
cpp
// 指定命名空间访问
#include<stdio.h>
namespace N
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
}
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", N::a); //10
return 0;
}(2)将命名空间中某个成员展开
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
namespace N
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
}
// using将命名空间中某个成员展开
using N::b;
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", N::a); //10
printf("%d\n", b); //20
return 0;
}(3)展开命名空间中全部成员
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
namespace N
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
}
// 展开命名空间中全部成员
using namespce N;
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", a); //10
printf("%d\n", b); //20
return 0;
}三、C++输入&输出
<iostream>是Input Output Stream的缩写,是标准的输入、输出流库,定义了标准的输入、输出对象。std::cin是istream类的对象,它主要面向窄字符的标准输入流。std:cout是ostream类的对象,它主要面向窄字符的标准输出流。std::endl是一个函数,流插入输出时,相当于插入一个换行字符加刷新缓冲区。- <<是流插入运算符,>>是流提取运算符。(C语言还用这两个运算符做位运算左移/右移)
- 使用C++输入输出更方便,不需要像printf/scanf输入输出时那样,需要手动指定格式,C++的输入输出可以自动识别变量类型(本质是通过函数重载实现的),其实最重要的是C++的流能更好的支持自定义类型对象的输入输出。
- 1O流涉及类和对象,运算符重载、继承等很多面向对象的知识,所以这里我们只能简单认识一下C++IO流的用法。
cout/cin/endl等都属于C++标准库,C++标准库都放在一个叫std(standard)的命名空间中,所以要通过命名空间的使用方式去用他们。- 一般日常练习中我们可以
using namespace std,实际项目开发中不建议using namespace std。 - 这里我们没有包含
<stdio.h>,也可以使用printf和scanf,在包含<iostream>间接包含了。vs系列编译器是这样的,其他编译器可能会报错。
1.输出
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 0;
double b = 0.1;
char c = 'x';
cout << a << " " << b << " " << c << endl;
std::cout << a << " " << b << " " << c << std::endl;
return 0;
}2.输入
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 0;
double b = 0.1;
char c = 'x';
cout << a << " " << b << " " << c << endl;
std::cout << a << " " << b << " " << c << std::endl;
// 可以⾃动识别变量的类型
cin >> a >> b >> c;
cout << a << " " << b << " " << c << endl;
return 0;
}在io需求比较高的地方,如部分大量输入的竞赛题中,加上以下3行代码可以提高C++IO效率
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 在io需求⽐较⾼的地⽅,如部分⼤量输⼊的竞赛题中,加上以下3⾏代码
// 可以提⾼C++IO效率
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
return 0;
}四、缺省参数
- 缺省参数是声明或定义函数时为函数的参数指定一个缺省值。在调用该函数时,如果没有指定实参则采用该形参的缺省值,否则使用指定的实参,缺省参数分为全缺省和半缺省参数。(有些地方把缺省参数也叫默认参数)
- 全缺省就是全部形参给缺省值,半缺省就是部分形参给缺省值。C++规定半缺省参数必须从右往左依次连续缺省,不能间隔跳跃给缺省值。
- 带缺省参数的函数调用,C++规定必须从左到右依次给实参,不能跳跃给实参。
- 函数声明和定义分离时,缺省参数不能在函数声明和定义中同时出现,规定必须函数声明给缺省值。
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
void Func(int a = 0)
{
cout << a << endl;
}
int main()
{
Func(); //没有传参时,使用参数的默认值
Func(10); //传参时,使用指定的实参
return 0;
}输出结果为:
0
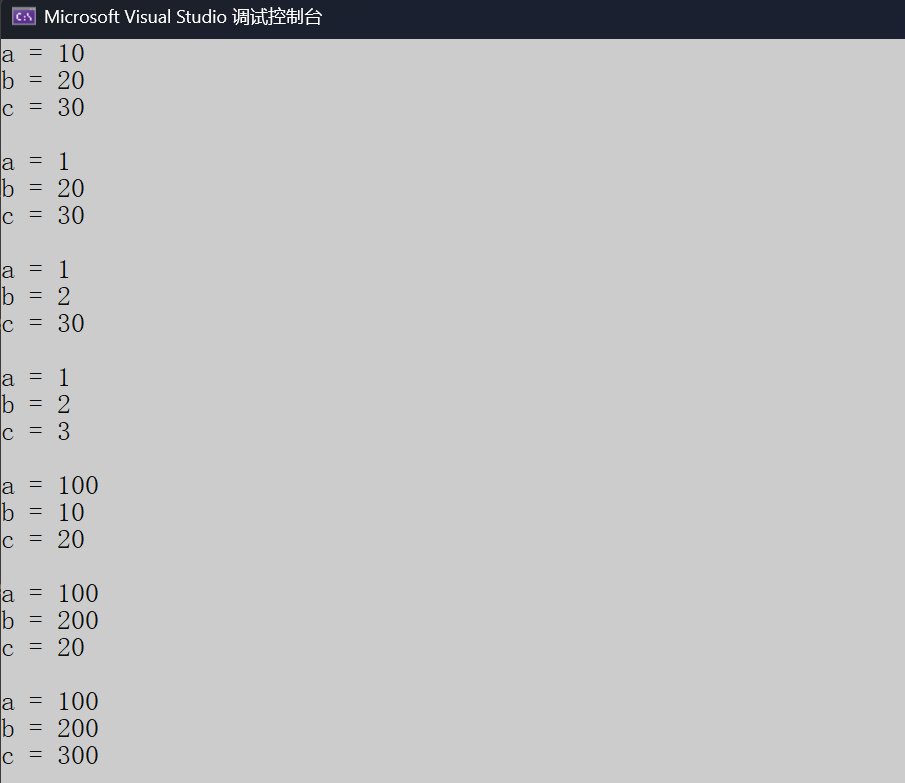
101.全缺省和半缺省
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 全缺省
void Func1(int a = 10, int b = 20, int c = 30)
{
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
cout << "c = " << c << endl << endl;
}
// 半缺省
void Func2(int a, int b = 10, int c = 20)
{
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
cout << "c = " << c << endl << endl;
}
int main()
{
Func1();
Func1(1);
Func1(1, 2);
Func1(1, 2, 3);
Func2(100);
Func2(100, 200);
Func2(100, 200, 300);
return 0;
}
错误方式
cpp
//半缺省时,不能传空
Func2(int a, int b = 10, int c = 20);
Func2();
//缺省是从右到左,不能跳跃缺省
Func2(int a, int b = 10, int c);2.实际运用
cpp
// Stack.h
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
void STInit(ST* pS, int n = 4);
// Stack.cpp
#include"Stack.h"
//缺省参数不能声明和定义同时给
void STInit(ST* pS,int n)
{
assert(ps && n > 0);
ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(n * sizeof(STDataType));
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = n;
}
//test.cpp
#include"Stack.h"
int main()
{
ST s1;
STInit(&s1);
//确定知道要插入1000个数据,初始化时一把开好,避免扩容
ST s2;
STInit(&s2, 1000);
return 0;
}五、函数重载
C++支持在同一作用域中出现同名函数,但是要求这些同名函数的形参不同,可以是参数个数不同或者类型不同。这样C++函数调用就表现出了多态行为,使用更灵活。C语言是不支持同一作用域中出现同名函数的
1.参数类型不同
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int Add(int left, int right)
{
return left + right;
}
double Add(double left, double right)
{
return left + right;
}
int main()
{
cout << Add(1, 2) << endl; //3
cout << Add(1.1, 2.2) << endl; //3.3
}2.参数个数不同
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void f()
{
cout << "f()" << endl;
}
void f(int a)
{
cout << "f(int a)" << endl;
}
int main()
{
f(); //f()
f(1); //f(int a)
return 0;
}3.参数的顺序不同
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void f(int a, char b)
{
cout << "f(int a, char b)" << endl;
}
void f(char b, int a)
{
cout << "f(char b, int a)" << endl;
}
int main()
{
f(1, 'a'); //f(int a, char b)
f('a', 1); //f(char b, int a)
return 0;
}4.编译器无法区分
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// 下⾯两个函数构成重载
void Func()
{
cout << "Func()" << endl;
}
//缺省参数 + 函数重载
void Func(int a = 10)
{
cout << "Func(int a = 10)" << endl;
}
int main()
{
// f()但是调用时,会报错,存在歧义,编译器不知道调用谁
Func();
//调用Func(int a = 10)
Func(1);
return 0;
}六、引用
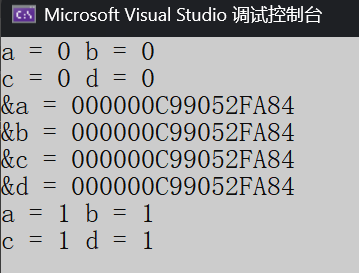
1、引用的概念和定义
引用不是新定义一个变量,而是给已存在变量取了一个别名 ,编译器不会为引用变量开辟内存间,
它和它引用的变量共用同一块内存空间 。
**类型& 引用别名 = 引用对象;
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 0;
// 引用:b和c是a的别名
int& b = a;
int& c = a;
// 也可以给别名b取别名,d相当于还是a的别名
int& d = b;
cout << "a = " << a << " b = " << b << endl;
cout << "c = " << c << " d = " << d << endl;
d++;
cout << "&a = " << &a << endl;
cout << "&b = " << &b << endl;
cout << "&c = " << &c << endl;
cout << "&d = " << &d << endl;
cout << "a = " << a << " b = " << b << endl;
cout << "c = " << c << " d = " << d << endl;
return 0;
}
2、引用的特性
- 引用在定义时必须初始化
- 一个变量可以有多个引用
- 引用一旦引用一个实体,再不能引用其他实体
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 10;
//编译报错:"ra"必须初始化引用
//int& b;
//正确引用
int& b = a;
int c = 20;
//这里并非让b引用c,因为C++引用不能改变指向
//这里是一个赋值
b = c;
cout << &a << endl;
cout << &b << endl;
cout << &c << endl;
return 0;
}3、引用的使用
1.交换函数
(1)指针版
cpp
void Swap(int* px, int* py)
{
int tmp = *px;
*px = *py;
*py = tmp;
}(2)引用版
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void Swap(int& rx, int& ry)
{
int tmp = rx;
rx = ry;
ry = tmp;
}
int main()
{
int x = 3, y = 6;
cout << "x = " << x << endl;
cout << "y = " << y << endl;
Swap(x, y);
cout << "x = " << x << endl;
cout << "y = " << y << endl;
return 0;
}2.栈
引用可以简化指针
cpp
#include"Stack.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
//rs相当于st1
void STInit(ST& rs, int n = 4)
{
rs.a = (STDataType*)malloc(n * sizeof(STDataType));
rs.top = 0;
rs.capacity = n;
}
//栈顶
void STPush(ST& rs, STDataType x)
{
if (rs.top == rs.capacity)
{
int newcapacity = rs.capacity == 0 ? 4 : rs.capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(rs.a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
rs.a = tmp;
rs.capacity = newcapacity;
}
rs.a[rs.top] = x;
rs.top++;
}
//int STTop(ST& rs)
int& STTop(ST& rs)
{
assert(rs.top > 0);
return rs.a[rs.top];
}
int main()
{
//调用全局的
ST st1;
STInit(st1);
STPush(st1, 1);
STPush(st1, 2);
cout << STTop(st1) << endl;
STTop(st1) += 10;
cout << STTop(st1) << endl;
return 0;
}3.顺序表
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct SeqList
{
int a[10];
int size;
}STL;
//一些主要用C代码实现版本数据结构教材中,使用C++引用替代指针传参,目的是简化程序,避开复杂的指针
void SeqPushBack(SLT& sl, int x)
{}
typedef struct ListNode
{
int val;
struct ListNode* next;
}LTNode, *PNode;
//指针变量也可以取别名,这里LTNode*&phead就是给指针变量取别名
//这样就不需要用二级指针了,相对而言简化了程序
//void ListPushBack(LTNode**phead,int x)
//void ListPushBack(LTNode*&phead,int x)
void ListPushBack(PNode& phead, int x)
{
PNode newnode = (PNode)malloc(sizeof(LTNode));
newnode->val = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if(phead == NULL)
{
phead = newnode;
}
else
{
//...
}
}
int main()
{
PNode plist = NULL;
ListPushBack(plist, 1);
return 0;
}4、const引用
- 可以引用一个const对象,但是必须用const引用。const引用也可以引用普通对象,因为对象的访问权限在引用过程中可以缩小,但是不能放大
- 不需要注意的是类型
int& rb = a*3; double d = 12.34; int& rb = d;这样有些场景下a * 3的和结果保存在一个临时对象中,int& rd = d也是类似,在类型转换中会产生临时对象存储中间值,也就是时,rb和rd引用的都是临时对象,而C++规定临时对象具有常性,使用这里就触发了权限放大,必须要用常引用才可以。 - 所谓临时对象就是编译器需要一个空间暂存表达式的求值结果时临时创建的一个未命名的对象,C++中把这个未命名对象叫做临时对象。
cpp
int main()
{
const int a = 10;
// 编译报错:error C2440: "初始化": 无法从"const int"转换为"int &"
// 这里的引用是对a访问权限的放大
//int& ra = a;
const int& ra = a;
//编译器报错:不能给常量赋值
//ra++;
//这里的引用时对b访问权限的缩小
int b = 20;
const int& rb = b;
//编译报错:不能给常量赋值
//rb++;
return 0;
}
cpp
int main()
{
int a = 10;
const int& ra = 30;
//编译报错:无法从int转换为int&
//int& rb = a * 3;
const int& rb = a * 3;//因为a*3要创建临时对象
double d = 12.34;
//编译报错:无法从int转换为int&
//int& rd = d;
const int& rd = d;//因为类型的转变,需要创建临时变量
return 0;
}5、指针和引用的关系
C++中的指针和引用在实践中相辅相成,功能有重叠性,但是各有自己的特点,互相不可替代。
- 语法概念上引用是一个变量的取别名不开空间;指针是存储一个变量地址,要开空间
- 定义引用时必须初始化;指针建议初始化,但是语法上不是必须的
- 引用在初始化时引用一个对象后,就不能再引用其他对象;而指针可以在不断地改变指向对象
- 引用可以直接访问对象,指针需要解引用才能访问对象
- sizeof中含义不同,引用结果为引用类型的大小,但指针始终是地址空间所占字节个数(32位平台占4个字节,64位下是8byte)
- 指针很容易出现空指针和野指针的情况;而引用很少出现,使用起来相对更安全
七、lnline
- 用liline修饰的函数叫做内联函数,编译时C++编译器会在调用的地方展开内联函数,这样调用内联函数就需要建立栈帧了,就可以提高效率
- inline对于编译器而言只是一个建议,也就是说,你加了inline编译器也可以选择在调用的地方不展开,不同编译器关于inline什么情况展开各不相同,因为C++标准没有规定这个。inline适用于频繁调用的短小函数,对于递归函数,代码相对多一些的函数,加上inline也会被编译器忽略。
- C语言实现宏函数也会在预处理时替换展开,但是宏函数实现很复杂很容易出错的,且不方便调试,C++设计了inline目的就是替代C的宏函数。
- vs编译器debug版本下面默认是不展开inline的,这样方便调试,debug版本想展开需要设置一下以下两个地方。
- inline不建议声明和定义分离到两个文件,分离会导致链接错误。因为inline被展开,就没有函数地址,链接时会出现报错。
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
inline int Add(int x, int y)
{
int ret = x + y;
ret += 1;
ret += 1;
ret += 1;
return ret; //6
}
int main()
{
//可以通过汇编观察程序是否展开
//有call Add语句就是没有展开
int ret = Add(1, 2);
cout << Add(1, 2) * 5 << endl; //30
return 0;
}
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define ADD(a, b) ((a) + (b))
//不能在末尾加分号,加分号在C++中导致错误
//外面要加括号,可能会因为运算符优先级问题,导致数据错误
//里面要加括号,在比较运算符时,会导致问题
int main()
{
int ret = ADD(1, 2);
cout << ADD(1, 2) << endl; //3
cout << ADD(1, 2) * 5 << endl; //如果不在外层加括号则是11
int x = 1, y = 2;
ADD(x & y, x | y); // -> (x&y + x|y);
//+的优先级大于&和|
return 0;
}
cpp
/*test.h*/
inline void Func(int x);
/*test.cpp*/
#include"test.h";
void Func(int x)
{
cout << x << endl;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//链接错误:无法解析的外部符号
Func(1);
return 0;
}八、nullptr
NULL实际是一个宏,在传统的C头文件中,可以看到如下代码:
C
#ifndef NULL
#ifdef __cplusplus
#define NULL 0
#else
#define NULL ((void *)0)
#endif
#endif
- C++中NULL可能被定义为字面常量0,或者C中被定义为无类型指针
(void*)的常量。不论采取何种定义,在使用空值的指针时,都不可避免的会遇到一些麻烦,本想通过f(NULL)调用指针版本的f(int*)函数,但是由于NULL被定义成0,调用了f(intx),因此与程序的初衷相悖。f((void*)NULL);调用会报错。- C++11中引入
nullptr,nullptr是一个特殊的关键字,nullptr是一种特殊类型的字面量,它可以换成任意其他类型的指针类型。使用nullptr定义空指针可以避免类型转换的问题,因为nullptr只能被隐式地转换为指针类型,而不能被转换为整数类型。
cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void f(int x)
{
cout << "f(int x)" << endl;
}
void f(int* ptr)
{
cout << "f(int* ptr)" << endl;
}
int main()
{
f(0);//f(int x)
//本想通过f(NULL)调用指针版本的f(int*)函数,但是由于NULL被定义成0,
f(NULL);//f(int x)
f((int*)NULL);//f(int* ptr)
//error:2个重载中没有一个可以转换所有参数类型
//f((void*)NULL);
f(nullptr); //f(int* ptr)
return 0;
}