1. 常规情况
基础知识:
- 考虑到模型输出位置量化损失对模型精度的影响较大,工具链推荐模型以 linear/conv 结尾,此时支持高精度 int32 输出(在 quantized.onnx 中,转定点为 int32,在前面 calib+qat 阶段都是 float32),这几乎可以做到无损。
- 征程 6 工具链量化 setter 模板支持自动设置高精度输出,前提是 conv 输出直接 接 dequant,不作为其他 node 的输入。
输出位置结构示意图:
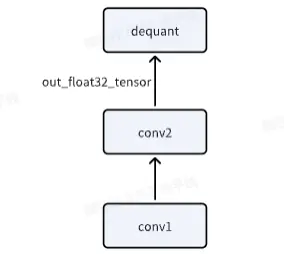
全流程代码如下:
Plain
import torch
from horizon_plugin_pytorch import set_march, March
set_march(March.NASH_M)
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization import prepare, set_fake_quantize, FakeQuantState
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization import QuantStub
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization.hbdk4 import export
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization.qconfig_template import (
calibration_8bit_weight_16bit_act_qconfig_setter,
qat_8bit_weight_16bit_fixed_act_qconfig_setter,
default_calibration_qconfig_setter,
ModuleNameQconfigSetter
)
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization.qconfig import get_qconfig, MSEObserver, MinMaxObserver
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.dtype import qint8, qint16
from torch.quantization import DeQuantStub
import torch.nn as nn
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization import hbdk4 as hb4
from hbdk4.compiler import convert, save, hbm_perf, visualize, compile
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# 定义网络结构
class SmallModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SmallModel, self).__init__()
# 第一个 Linear: 输入 [2, 100, 256] -> 输出 [2, 100, 256]
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(256, 256)
self.layernorm = nn.LayerNorm(256) # 对最后一维进行归一化
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
# 第二个 Linear: 输入 [2, 100, 256] -> 输出 [2, 100, 60]
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(256, 60)
# 第三个 Linear: 输入 [2, 100, 60] -> 输出 [2, 100, 60]
self.linear3 = nn.Linear(60, 60)
self.quant = QuantStub()
self.dequant = DeQuantStub()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.quant(x)
# 第一个 Linear
x = self.linear1(x) # [2, 100, 256]
x = self.layernorm(x) # [2, 100, 256]
x = self.relu(x) # [2, 100, 256]
# 第二个 Linear
y = self.linear2(x) # [2, 100, 60]
# 第三个 Linear
z = self.linear3(y)
z = self.dequant(z)
return z
# 设置随机种子,保证每次生成的数据相同
torch.manual_seed(42)
example_input = torch.randn(2, 100, 256)
model = SmallModel()
# 前向传播
output_x = model(example_input)
print("输入形状:", example_input.shape)
print("输出形状:", output_x.shape)
# A global march indicating the target hardware version must be setted before prepare qat.
set_march(March.NASH_M)
calib_model = prepare(model.eval(), example_input,
qconfig_setter=(
default_calibration_qconfig_setter,
),
)
calib_model.eval()
set_fake_quantize(calib_model, FakeQuantState.CALIBRATION)
calib_model(example_input)
calib_model.eval()
set_fake_quantize(calib_model, FakeQuantState.VALIDATION)
calib_out_x = calib_model(example_input)
print("calib输出shape:", calib_out_x.shape)
qat_bc = export(calib_model, example_input)
# save(qat_bc, "qat.bc")
# visualize(qat_bc, "qat.onnx")
hb_quantized_model = convert(qat_bc, March.NASH_M)
# save(hb_quantized_model,"quantized.bc")
visualize(hb_quantized_model, "quantized_single.onnx")查看 quantized.onnx,可以看到最后一个 conv 确实是 int32 高精度输出
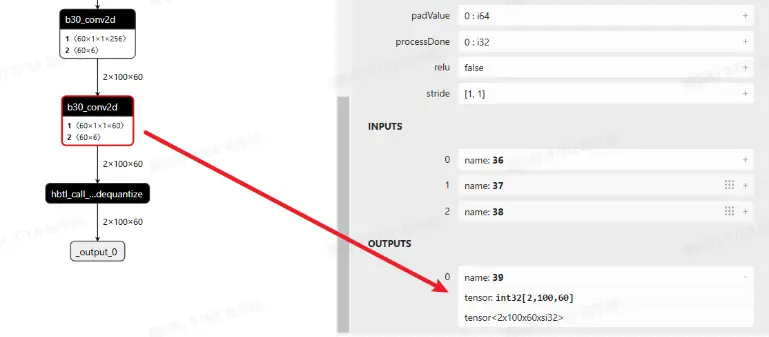
2. 输出又输入
如果 conv1,既作为模型输出,又作为后续 conv2 的输入,此时应该怎么办?
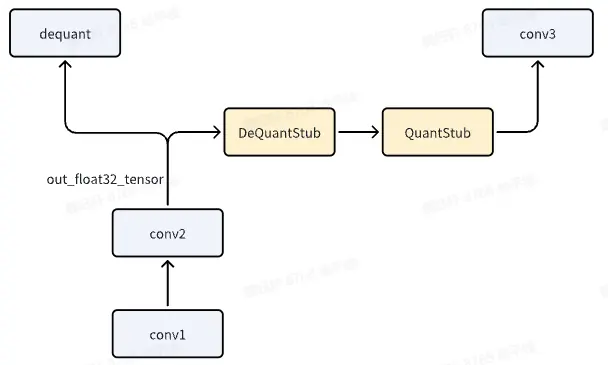
关键代码如下:
Plain
def forward(self, x):
x = self.quant(x)
# 第一个 Linear
x = self.linear1(x) # [2, 100, 256]
x = self.layernorm(x) # [2, 100, 256]
x = self.relu(x) # [2, 100, 256]
# 第二个 Linear
y = self.linear2(x) # [2, 100, 60]
y_out = self.dequant(y)
y = self.quant_out(y_out)
# y = self.quant_out(y)
# 第三个 Linear
z = self.linear3(y)
z = self.dequant(z)
return x, y_out注意,y_out = self.dequant(y)是必须要添加的,否则无法实现该效果。
全流程代码如下:
Plain
import torch
from horizon_plugin_pytorch import set_march, March
set_march(March.NASH_M)
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization import prepare, set_fake_quantize, FakeQuantState
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization import QuantStub
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization.hbdk4 import export
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization.qconfig_template import (
calibration_8bit_weight_16bit_act_qconfig_setter,
qat_8bit_weight_16bit_fixed_act_qconfig_setter,
default_calibration_qconfig_setter,
ModuleNameQconfigSetter
)
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization.qconfig import get_qconfig, MSEObserver, MinMaxObserver
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.dtype import qint8, qint16
from torch.quantization import DeQuantStub
import torch.nn as nn
from horizon_plugin_pytorch.quantization import hbdk4 as hb4
from hbdk4.compiler import convert, save, hbm_perf, visualize, compile
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# 定义网络结构
class SmallModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SmallModel, self).__init__()
# 第一个 Linear: 输入 [2, 100, 256] -> 输出 [2, 100, 256]
self.linear1 = nn.Linear(256, 256)
self.layernorm = nn.LayerNorm(256) # 对最后一维进行归一化
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
# 第二个 Linear: 输入 [2, 100, 256] -> 输出 [2, 100, 60]
self.linear2 = nn.Linear(256, 60)
# 第三个 Linear: 输入 [2, 100, 60] -> 输出 [2, 100, 60]
self.linear3 = nn.Linear(60, 60)
self.quant = QuantStub()
self.quant_out = QuantStub()
self.dequant = DeQuantStub()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.quant(x)
# 第一个 Linear
x = self.linear1(x) # [2, 100, 256]
x = self.layernorm(x) # [2, 100, 256]
x = self.relu(x) # [2, 100, 256]
# 第二个 Linear
y = self.linear2(x) # [2, 100, 60]
y_out = self.dequant(y)
y = self.quant_out(y_out)
# 第三个 Linear
z = self.linear3(y)
z = self.dequant(z)
return z, y_out
# 设置随机种子,保证每次生成的数据相同
torch.manual_seed(42)
example_input = torch.randn(2, 100, 256)
model = SmallModel()
# 前向传播
output_x, output_y = model(example_input)
print("输入形状:", example_input.shape)
print("输出形状:", output_x.shape, output_y.shape)
# A global march indicating the target hardware version must be setted before prepare qat.
set_march(March.NASH_M)
calib_model = prepare(model.eval(), example_input,
qconfig_setter=(
default_calibration_qconfig_setter,
),
)
calib_model.eval()
set_fake_quantize(calib_model, FakeQuantState.CALIBRATION)
calib_model(example_input)
calib_model.eval()
set_fake_quantize(calib_model, FakeQuantState.VALIDATION)
calib_out_x, calib_out_y= calib_model(example_input)
print("calib输出shape:", calib_out_x.shape)
qat_bc = export(calib_model, example_input)
# save(qat_bc, "qat.bc")
# visualize(qat_bc, "qat.onnx")
hb_quantized_model = convert(qat_bc, March.NASH_M)
# save(hb_quantized_model,"quantized.bc")
visualize(hb_quantized_model, "quantized.onnx")查看 quantized.onnx,linear2 符合预期,确实是 int32 高精度输出。
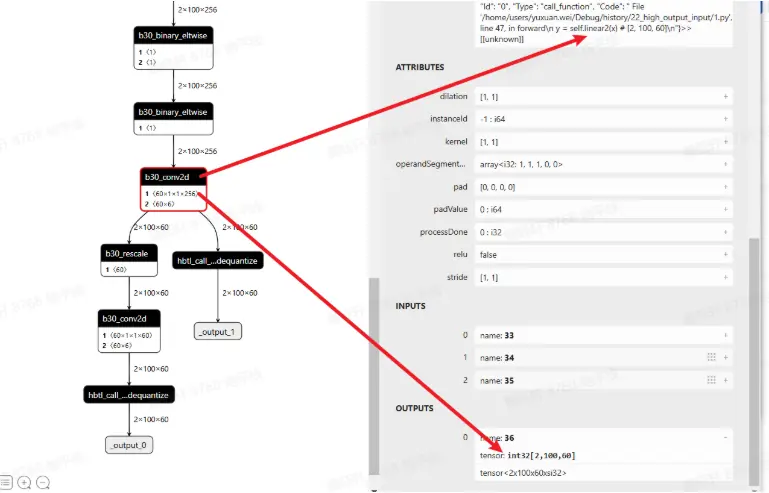
新加入的 dequant 与 quant 会变成 rescale
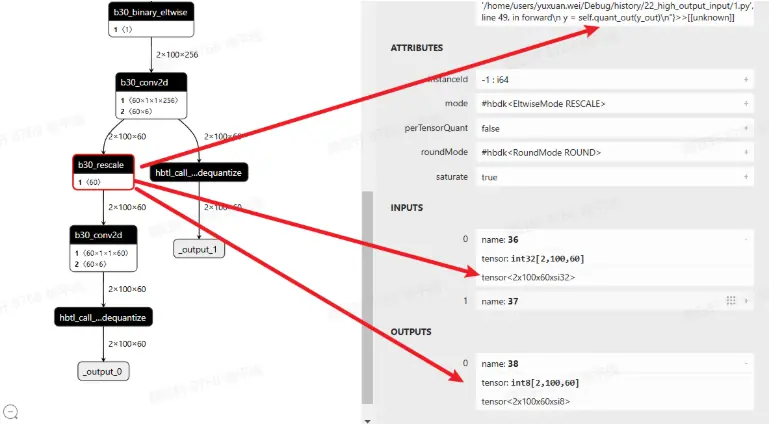
以上是征程 6EM 的默认做法,如果使用的是征程 6PH,conv like 算子输出直接就是 float32,在既作为输出,又作为下一阶段输入时,会存在 vpu 的 quantize(float32->int16/int8),如下图所示
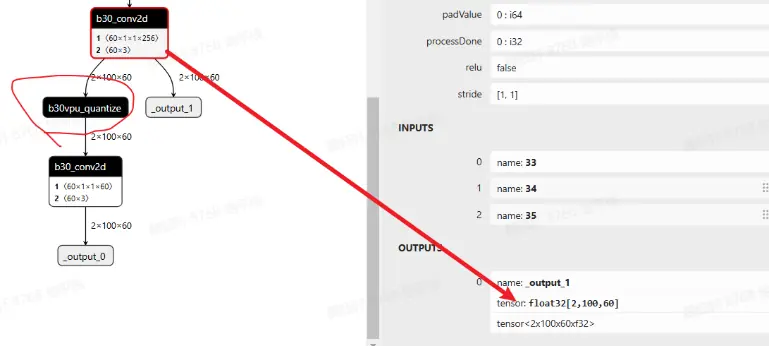
如果想依旧沿用征程 6EM 的方式,可进行如下配置:
Plain
qat_bc._integer_conv = True
hb_quantized_model = convert(qat_bc, "nash-h")具体选择哪种方式可实测 latency(建议考虑将模型 conv like 算子 c++ 反量化的耗时减少也加进去对比)