SHELL概述和基本功能
- 可以是命令解释器:将用户在终端输入的字符串翻译成机器可移植性的命令。
- 也可是所谓shell脚本: shell脚本本质上就是多个构成的一个文件而已,这个文件中可以有 条件结构 循环结构 函数。
书写规范
-
shell脚本必须是.sh结尾
-
第一行必须是 指定脚本由哪个命令解释器来执行。
shell[root@server ~]# echo $SHELL #打印当前使用的shell /bin/bash vim test.sh --------------------------------------------------------- 1 #!/bin/bash
运行脚本的四种方式
方法1
- 使用相对路径运行脚本【脚本必须得有可执行权限】
shell
# 脚本第一行必须指明使用哪个命令解释器 如 #!/bin/bash
[root@server ~]# ./test.sh
-bash: ./test.sh: 权限不够
# 使用此种方式运行的脚本必须具备可执行权限
[root@server ~]# ll test.sh
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 222 11月 22 17:15 test.sh
[root@server ~]# chmod +x test.sh
[root@server ~]# ./test.sh方法2
- 使用sh或bash命令执行脚本,不需要执行权限(建议使用),第一行命令解释器注释也非必要
- 可以使用bash -n 脚本名 ,进行语法检测,且不执行脚本
- 可以使用bash -x 脚本名 ,进行脚本执行跟踪,逐条语句的跟踪执行
shell
[root@server ~]# vim set_net.sh
------------------------------------------
1 nmcli connection modify enp0s5 ipv4.method manual ipv4.address 192.168.10.$1/24
2 nmcli connection modify enp0s5 ipv4.dns 8.8.8.8
3 nmcli connection modify enp0s5 ipv4.gateway 192.168.1.2
4 nmcli connection up ens160
------------------------------------------
# 使用 sh/bash/csh/zsh 脚本名称 参数
[root@server ~]# sh set_net.sh 150方法3
- 绝对路径执行脚本
- 脚本第一行必须指明使用哪个命令解释器 如 #!/bin/bash
- 脚本必须得有可执行权限
shell
[root@server ~]# chmod +x set_net.sh
[root@server ~]# /root/set_net.sh 101方法4
- 使用 . 脚本名称 或 source 脚本名称
- 使用这种方式 脚本不需要可执行权限
shell
[root@server ~]# . set_net.sh 101
连接已成功激活(D-Bus 活动路径:/org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/10)
[root@server ~]# source set_net.sh 100
连接已成功激活(D-Bus 活动路径:/org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/13)bash shell基本功能
echo打印命令
格式
- echo -参数 内容
参数
- -n : 输出内容时不再在尾部添加\n换行。
- -e : 会将字符串中\x进行转义(\x得有具体转义功能)
shell
[root@server ~]# echo -e "i\tam\tsuper\tman"
i am super man
[root@server ~]# echo "i\tam\tsuper\tman"
i\tam\tsuper\tmanecho的字体颜色修改
\e[数字;数字m 内容 \e[0m- 数字:1.加粗高亮 4.下划线 5.闪烁 40-47 是7种背景色
- 数字m:30-37 是7中字体色
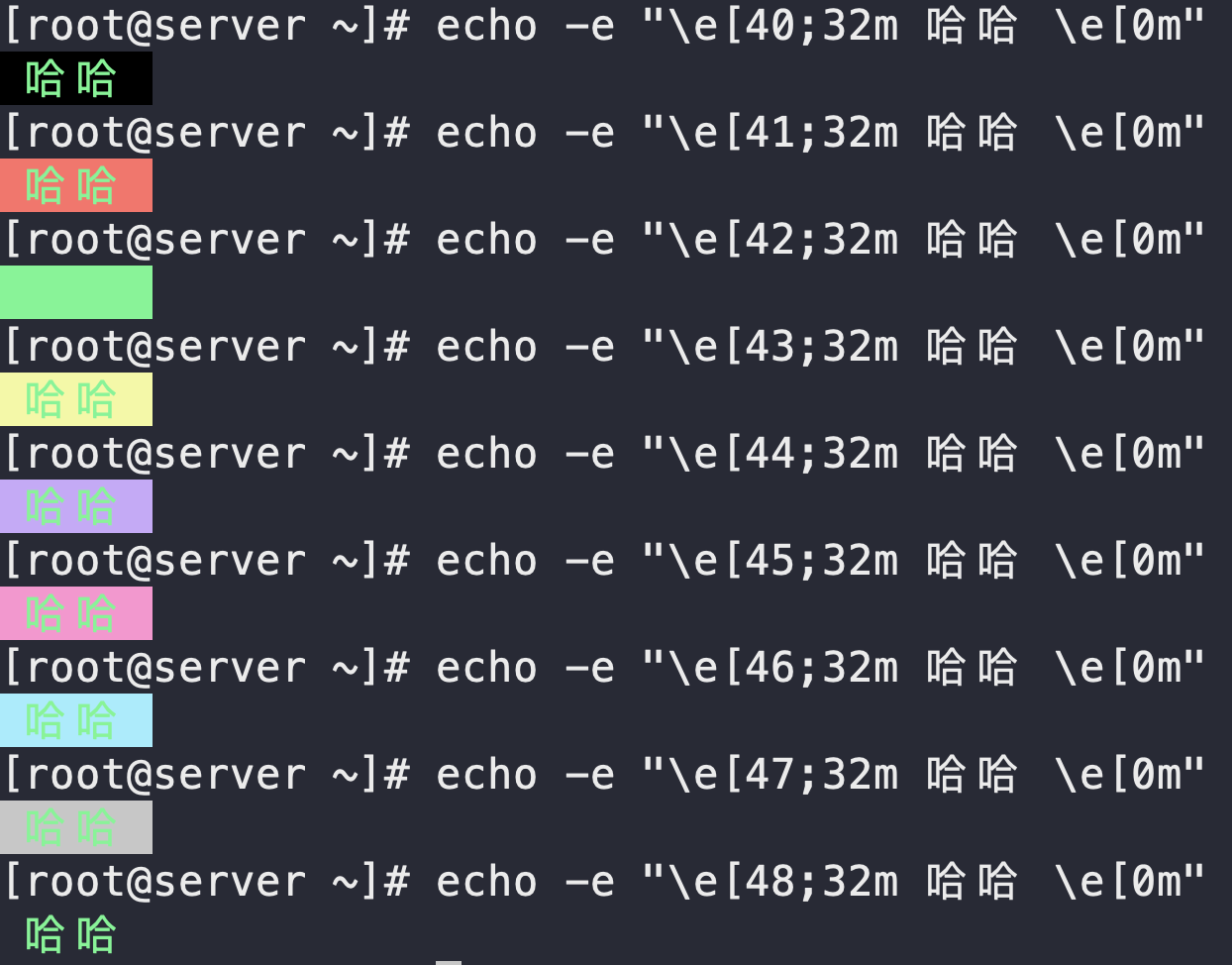
printf 命令
printf 模仿的就是C中printf,但是shell中printf不需要小括号
格式:
shell
printf 格式控制字符串 参数列表例:
shell
[root@server ~]# echo "Hello ,Shell"
Hello ,Shell
[root@server ~]# printf "Hello ,Shell\n"
Hello ,Shell
[root@server ~]# printf "Hello ,Shell"
Hello ,Shell[root@server ~]#
[root@server ~]# printf "%d %s\n" 1 "abc"
1 abc
[root@server ~]# printf '%d %s\n' 1 "abc"
1 abc # 单引号双引号效果一样
[root@server ~]# printf %s abcdef
abcdef[root@server ~]# #没有双引号也可输出,没有\n会续连下一个提示符
[root@server ~]# printf "%-10s %-8s %-4s\n" 姓名 性别 体重kg
姓名 性别 体重kg
# %s %c %d %f 都是格式替代符,%s 输出一个字符串,%d 整型输出,%c 输出一个字符,%f 输出实数,以小数形式输出。
# %-10s 指一个宽度为 10 个字符(- 表示左对齐,没有则表示右对齐),任何字符都会被显示在 10 个字符宽的字符内,如果不足则自动以空格填充,超过也会将内容全部显示出来。
[root@server ~]# printf "%-10s %-8s %-4.2f\n" 郭靖 男 66.1234
郭靖 男 66.12
# %-4.2f 指格式化为小数,其中 .2 指保留2位小数
[root@server ~]# printf "我今年%d岁,我体重%.1fkg,%s %c \n" 18 180 qwer ty
我今年18岁,我体重180.0kg,qwer t
[root@server ~]#vim 1.sh
------------------------------------------
#!/bin/sh
age=18;
weight=180;
echo "我今年${age}岁,我体重${weight}kg"
printf "我今年%d岁,我体重%fkg" $age $weight
------------------------------------------
${} : 一般用于引用扩号中变量的值
$() : 一般用于将括号中的命令的执行结果进行返回
$变量名: 引用变量的值read【常用于多参数脚本】
脚本传参
sh 脚本名 参数1 参数2 参数3...参数n
参数1 传给脚本中 $1
参数2 传给脚本中 $2
参数3 传给脚本中 $3
...
参数n 传给脚本中 $n作用
- read 命令可从标准输入读取字符串等信息,然后传递给shell程序内部定义的变量使用。
- read 是一个重要的 bash 命令,用于从键盘或标准输入读取文本,我们可以使用 read 命令以交互形式读取来自用户的输入,当然 read 能做的远不止这些。
- 通常我们按下回车键表示命令输入完成,但是很特殊情况下,我们需要基于字符数或者特定字符来表示命令输入完成
语法
bash
read [选项]
常用选项:
-a 读取的内容存入数组
-d 持续读取直到读入 DELIM 变量中的第一个字符,而不是换行符
-n/N 读取N个字符
-p 指定提示信息,用于等待输入
-r 不允许反斜杠转义任何字符
-s 从标准输入中读取密码而不在屏幕上显示输入的字符
-t 设置读取输入的超时时间,单位为秒例
shell
#1. 读取单个或多个变量
[root@server ~]# read a
123
[root@server ~]# echo $a
123
[root@server ~]# read a b c
1 2 3
[root@server ~]# echo $a $b $c
1 2 3
#2. 将读取的数据存入数组中
-a 传入数组
[root@server ~]# read -a array
1 2 3 4 5
[root@server ~]# echo ${array[@]} #@获取数组中的所有元素
1 2 3 4 5
[root@server ~]# echo ${array[0]}
1
[root@server ~]# echo ${array[2]}
3
#3. -d 指定结束符 只能是一个字符
[root@server ~]# read -d end -p "请输入值" a
请输入值laskjdfkl
qwlkje[root@server ~]# echo $a
laskjdfkl qwlkj
#4. -n num 指定变量的长度 读到足够字符后自动停止命令
[root@server ~]# read -n 6 -p "请输入变量的值:" a
请输入变量的值:abcdef[root@server ~]# echo $a
abcdef
#5. -r 原意字符串(原来写的什么就打印出什么)
[root@server ~]# read a
i\tam\tsuperman\t
[root@server ~]# echo $a
itamtsupermant
[root@server ~]# read -r a
i\tam\tsuperman\t
#6. -s 密码输入(不显示输入的内容)
[root@server ~]# read -s -p "请输入密码:" pwd
请输入密码:[root@server ~]# echo $pwd
asldjfklasjdfklajsdklfjqkl;werjlxcljvjweldsvwlksdflkjasldfalksjdfjlasdfasdfasdfasf
#7. -t 指定输入的过期时间
[root@server ~]# read -t 3 -p "请输入密码" pwd
请输入密码12331232134312[root@server ~]# 12331232134312实验
shell
编写一个 Shell 脚本,实现以下功能:
1.使用 read命令提示用户输入姓名、年龄和职业
2.使用echo不同颜色输出标题 | 姓名 | 年龄 | 职业 |
3.使用printf输出用户的数据 | xxx | xxx | xxxx |
[root@server ~]# vim exercise.sh
----------------------------------------------
1 read -p "请输入用户的姓名,年龄,职业" name age career
2 echo -e "\e[40;32m|name\t|age\t|career\t| \e[0m"
3 printf "|%s\t|%d\t|%s\t|\n" $name $age $career
----------------------------------------------
[root@server ~]# sh exercise.sh
请输入用户的姓名,年龄,职业哈哈 19 学生
|name |age |career |
|哈哈 |19 |学生 |命令执行顺序
- 顺序执行: ;
shell
[root@server ~]# date ; ls -l /etc/passwd- 前面命令执行不成功,后面的命令不执行: &&
shell
[root@server ~]# mkdir /mnt/iso && mount /dev/sr0 /mnt/iso- 前面命令成功,后面就不执行,如果前面不成功后面就执行: ||
shell
[root@server ~]# mkdir tt || ls /
[root@server ~]# mkdir tt || ls / # 可以再次执行export
- export 创建环境变量
- 所谓的环境变量类似于全局变量,但是没有全局变量范围广,只在当前进程及其子孙进程中可以使用。
shell
[root@server ~]# a=1
[root@server ~]# echo $a
1
[root@server ~]# sh
sh-5.1# echo $a
#在子进程中显示不出来
sh-5.1# exit
exit
#用export创建环境变量
[root@server ~]# mingzi=hehe
[root@server ~]# export mingzi
[root@server ~]# sh
sh-5.1# echo $mingzi
hehe
sh-5.1# exit
exitlscpu
- 在Linux系统中,lscpu命令是用于显示和收集有关CPU(中央处理器)架构和相关信息的命令。它提供了关于CPU的详细信息,包括处理器类型、架构、核心数、线程数、缓存大小等。
shell
[root@server ~]# lscpu
架构: x86_64
CPU 运行模式: 32-bit, 64-bit
Address sizes: 45 bits physical, 48 bits virtual
字节序: Little Endian
CPU: 2
在线 CPU 列表: 0,1
厂商 ID: GenuineIntel
BIOS Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
型号名称: Intel(R) Core(TM) Ultra 5 125H
BIOS Model name: Intel(R) Core(TM) Ultra 5 125H
CPU 系列: 6
型号: 170
每个核的线程数: 1
每个座的核数: 1
座: 2
步进: 4
BogoMIPS: 7200.00
标记: fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep m
trr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush mmx fxsr s
se sse2 ss syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm const
ant_tsc arch_perfmon rep_good nopl xtopology
tsc_reliable nonstop_tsc cpuid tsc_known_freq
pni pclmulqdq ssse3 fma cx16 pcid sse4_1 sse
4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer ae
s xsave avx f16c rdrand hypervisor lahf_lm ab
m 3dnowprefetch invpcid_single ssbd ibrs ibpb
stibp ibrs_enhanced fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1
avx2 smep bmi2 erms invpcid rdseed adx smap
clflushopt clwb sha_ni xsaveopt xsavec xgetbv
1 xsaves avx_vnni arat umip pku ospke gfni va
es vpclmulqdq rdpid movdiri movdir64b fsrm md
_clear serialize flush_l1d arch_capabilities
Virtualization features:
超管理器厂商: VMware
虚拟化类型: 完全
Caches (sum of all):
L1d: 96 KiB (2 instances)
L1i: 128 KiB (2 instances)
L2: 4 MiB (2 instances)
L3: 36 MiB (2 instances)
NUMA:
NUMA 节点: 1
NUMA 节点0 CPU: 0,1
Vulnerabilities:
Gather data sampling: Not affected
Itlb multihit: KVM: Mitigation: VMX unsupported
L1tf: Not affected
Mds: Not affected
Meltdown: Not affected
Mmio stale data: Unknown: No mitigations
Retbleed: Not affected
Spec store bypass: Mitigation; Speculative Store Bypass disabled
via prctl
Spectre v1: Mitigation; usercopy/swapgs barriers and __us
er pointer sanitization
Spectre v2: Mitigation; Enhanced / Automatic IBRS, IBPB c
onditional, RSB filling, PBRSB-eIBRS SW seque
nce
Srbds: Not affected
Tsx async abort: Not affectedxargs
- 管道符 |:管道符的作用是将 管道左侧命令的 标准输出 作为 管道右侧命令的标准输入
- xargs的作用:将标准输入 转为为命令可用的参数。
格式
shell
xargs [选项] [命令]
常用选项:
-I:用于指定替换字符串,将输入数据中的特定字符串替换为命令行参数。
-n:用于指定每次执行命令的参数个数。
-t:用于打印执行的命令。
-p:用于提示用户确认是否执行命令。
-r:当标准输入为空时,不执行命令。示例
shell
[root@server ~]# touch {1..100}
[root@server ~]# ls
1 14 2 25 30 36 41 47 52 58 63 69 74 8 85 90 96
10 15 20 26 31 37 42 48 53 59 64 7 75 80 86 91 97
100 16 21 27 32 38 43 49 54 6 65 70 76 81 87 92 98
11 17 22 28 33 39 44 5 55 60 66 71 77 82 88 93 99
12 18 23 29 34 4 45 50 56 61 67 72 78 83 89 94
13 19 24 3 35 40 46 51 57 62 68 73 79 84 9 95
[root@server ~]# ls | rm
rm: 缺少操作数
请尝试执行 "rm --help" 来获取更多信息。
# xargs 将标准输入 转为为命令可用的参数。
[root@server ~]# ls | xargs rm
[root@server ~]# ls
# -I 创建一个{}代表元素集合中的每一个元素
[root@server ~]# ls
1 2 4 6 8 a c e g i k m o q s u w y
10 3 5 7 9 b d f h j l n p r t v x z
[root@server ~]# ls | xargs -I {} rm -rf {}
[root@server ~]# ls
# xargs可以对文件的显示格式 重新进行整理
[root@server ~]# cat > 1.txt << EOF
>
> a b c d e f g
> h i j k l m n
> o p q
> r s t
> u v w x y z
>
> EOF
[root@server ~]# cat 1.txt | xargs
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
[root@server ~]# cat 1.txt | xargs -n 3
a b c
d e f
g h i
j k l
m n o
p q r
s t u
v w x
y z
[root@server ~]# cat 1.txt | xargs -n 4
a b c d
e f g h
i j k l
m n o p
q r s t
u v w x
y z
[root@server ~]# cat 1.txt | xargs -n 5
a b c d e
f g h i j
k l m n o
p q r s t
u v w x y
zexit退出程序
- 作用:终止Shell程序的执行
- 格式:exit 状态码
- 状态码:是表示命令执行状态的一组数字,他跟命令的返回值没有任何关系。该参数是一个整数值,其取值范围为0~255
- 注意:Shell程序的退出状态码储存在系统变量$?中,因此,用户可以通过该变量取得Shell程序返回给父进程的退出状态码
- 所有的命令执行完毕时都会有状态码。
- 常见状态码:
shell
0----------------命令运行成功
1----------------通知未知错误
2----------------误用shell命令
126--------------命令不可执行
127--------------没有找到命令
128--------------无效退出参数
128+x------------linux信号x的严重错误
130--------------命令通过Ctrl+C终止
255--------------退出状态码越界- 演示在不同的情况下,程序返回不同的状态码
shell
#? 表示上一条命令的执行状态
0 --------- 表示命令执行成功
非0 ------------ 表示命令执行失败
[root@server ~]# echo "china"
china
[root@server ~]# echo $?
0
[root@server ~]# ehco "china"
bash: ehco: command not found...
Similar command is: 'echo'
[root@server ~]# echo $?
127
#自己创建一个脚本返回状态码
[root@server ~]# vim test.sh
----------------------------------------------
1 exit $1
----------------------------------------------
[root@server ~]#sh test.sh 22
[root@server ~]#echo $?
22
[root@server ~]#sh test.sh 255
[root@server ~]#echo $?
255
[root@server ~]#sh test.sh 256
[root@server ~]#echo $?
0
[root@server ~]#sh test.sh 257
[root@server ~]#echo $?
1