序言
循环时编程语言的核心,for、while等各大语言都支持,也是每个开发人员都必须掌握的基础,所以本章将以案例为主,特别之处再辅以文档。
For loops
dart
void main() {
var message = StringBuffer('Dart is fun');
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
message.write('!');
}
print(message);//Dart is fun!!!!!
}这是一个十分常见的循环,需要注意下StringBuffer的添加不再是append()
dart
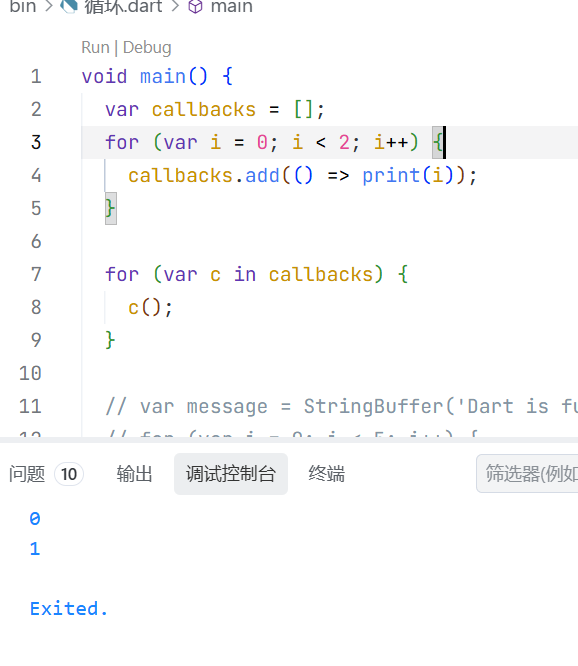
var callbacks = [];
for (var i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
callbacks.add(() => print(i));
}
for (final c in callbacks) {
c();
}这里输出了0,1
这是关于循环中的索引问题,Dart for循环中的闭包捕获索引的值,而不是索引。kotlin中也是这样的。
dart
for (var candidate in candidates) {
candidate.interview();
}同样支持for in,在不需要下标时可以使用这种方式。
dart
for (final Candidate(:name, :yearsExperience) in candidates) {
print('$name has $yearsExperience of experience.');
}可以将上篇文章中学习到的 pattern用到for循环中,以简单快捷的方式获得对象的值。
dart
var collection = [1, 2, 3];
collection.forEach(print); // 1 2 3接下来是我们之前的案例修改的,foreach的入参是Function
dart
var callbacks = [];
for (var i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
callbacks.add(() => print(i));
}
callbacks.forEach((dynamic c){
c();
});可迭代的类可以使用forEach函数。
While
dart
while (!isDone()) {
doSomething();
}
dart
do {
printLine();
} while (!atEndOfPage());这是两个基本的写法,这里顺带回顾下
while:先判断,后执行
do-while:先执行,后判断
Break and continue
dart
while (true) {
if (shutDownRequested()) break;
processIncomingRequests();
}break跳出循环
dart
for (int i = 0; i < candidates.length; i++) {
var candidate = candidates[i];
if (candidate.yearsExperience < 5) {
continue;
}
candidate.interview();
}continue跳到下次迭代。
dart
candidates
.where((c) => c.yearsExperience >= 5)
.forEach((c) => c.interview());当使用foreach时的条件写法,下面是我自己的一个例子:
dart
var list = [];
for(var i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
list.add(i);
list.add(9-i);
}
print(list);//[0, 9, 1, 8, 2, 7, 3, 6, 4, 5, 5, 4, 6, 3, 7, 2, 8, 1]
list.where((i)=> i < 5).forEach((i){
print(i);
});下面看输出:

无关顺序,所有<5的值都在控制台输出了,所以where只是每一次迭代的先判断。
Labels
A label is an identifier followed by a colon (labelName:) that you can place before a statement to create a labeled statement. Loops and switch cases are often used as labeled statements. A labeled statement can be referenced later in a break or continue statement as follows:
break labelName; Terminates the execution of the labeled statement. This is useful for breaking out of a specific outer loop when you're within a nested loop.
continue labelName; Skips the rest of the current iteration of the labeled statement loop and continues with the next iteration.
Labels are used to manage control flow. They are often used with loops and switch cases and allow you to specify which statement to break out of or continue, rather than affecting the innermost loop by default.
译文:标签(label)是后跟冒号(labelName:)的标识符,可以放在语句之前创建标签语句。循环和switch分支经常被用作带标签的语句。标签语句可以在后面的break或continue语句中引用,如下所示:
打破labelName;终止已标记语句的执行。当你处于嵌套循环中时,这有助于跳出特定的外循环。
继续labelName;跳过标记语句循环的当前迭代的其余部分,继续进行下一次迭代。
标签用于管理控制流。它们通常与循环和switch case一起使用,允许你指定退出或继续哪个语句,而默认情况下不会影响最内层的循环。
又是一个新奇的东西,但是作用还是很清晰的
直接看案例:
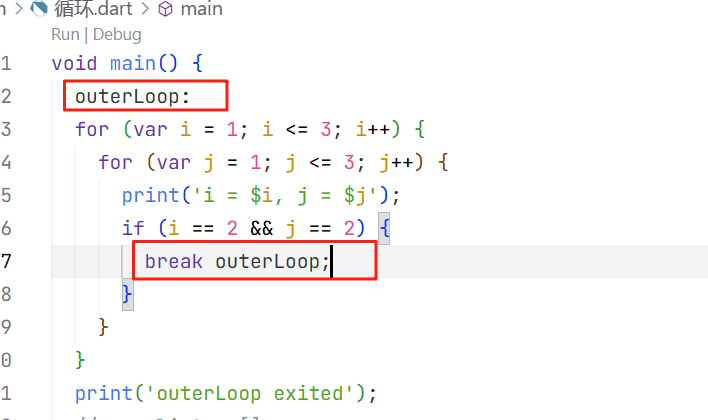
可以看到它允许我们为一个循环起个名字,主要应用于多层嵌套的场景下。
下面是continue和label的使用
dart
outerLoop:
for (var i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
for (var j = 1; j <= 3; j++) {
if (i == 2 && j == 2) {
continue outerLoop;
}
print('i = $i, j = $j');
}
}下面是label在while中的使用
dart
var i = 1;
outerLoop:
while (i <= 3) {
var j = 1;
while (j <= 3) {
print('i = $i, j = $j');
if (i == 2 && j == 2) {
break outerLoop;
}
j++;
}
i++;
}
print('outerLoop exited');
dart
var i = 1;
outerLoop:
while (i <= 3) {
var j = 1;
while (j <= 3) {
if (i == 2 && j == 2) {
i++;
continue outerLoop;
}
print('i = $i, j = $j');
j++;
}
i++;
}在do-while中也是可以的
dart
var i = 1;
outerLoop:
do {
var j = 1;
do {
if (i == 2 && j == 2) {
i++;
continue outerLoop;
}
print('i = $i, j = $j');
j++;
} while (j <= 3);
i++;
} while (i <= 3);switch嵌套也是可以使用label的
dart
dynamic? i = null;
outerSwitch:
switch (i) {
case null:
break;
case num:
switch (i + 1) {
case 3:
break outerSwitch;
}
print('i is a number');
break;
}小结
和其他语言都差不多,foreach的语法稍有不同,label属于新东西,但我们一般也不提倡循环多层嵌套,属于一种没有办法的办法。