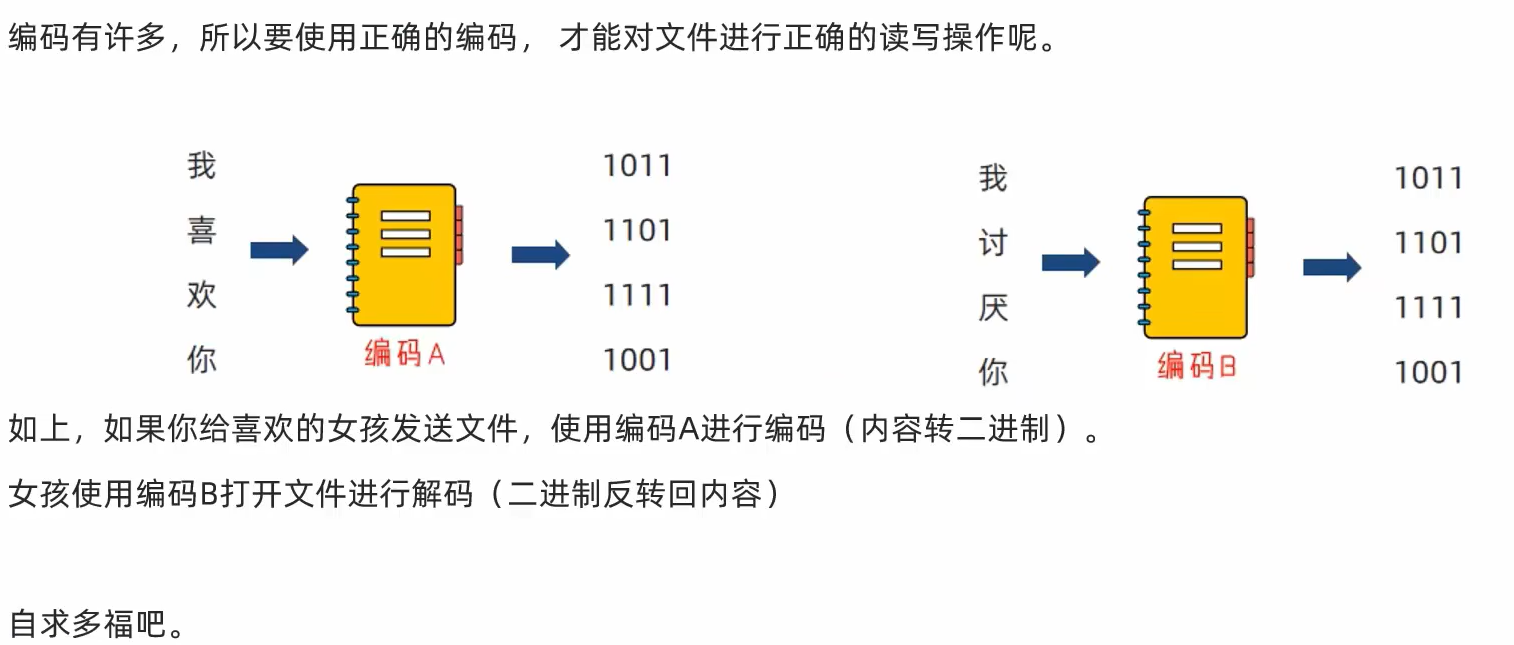
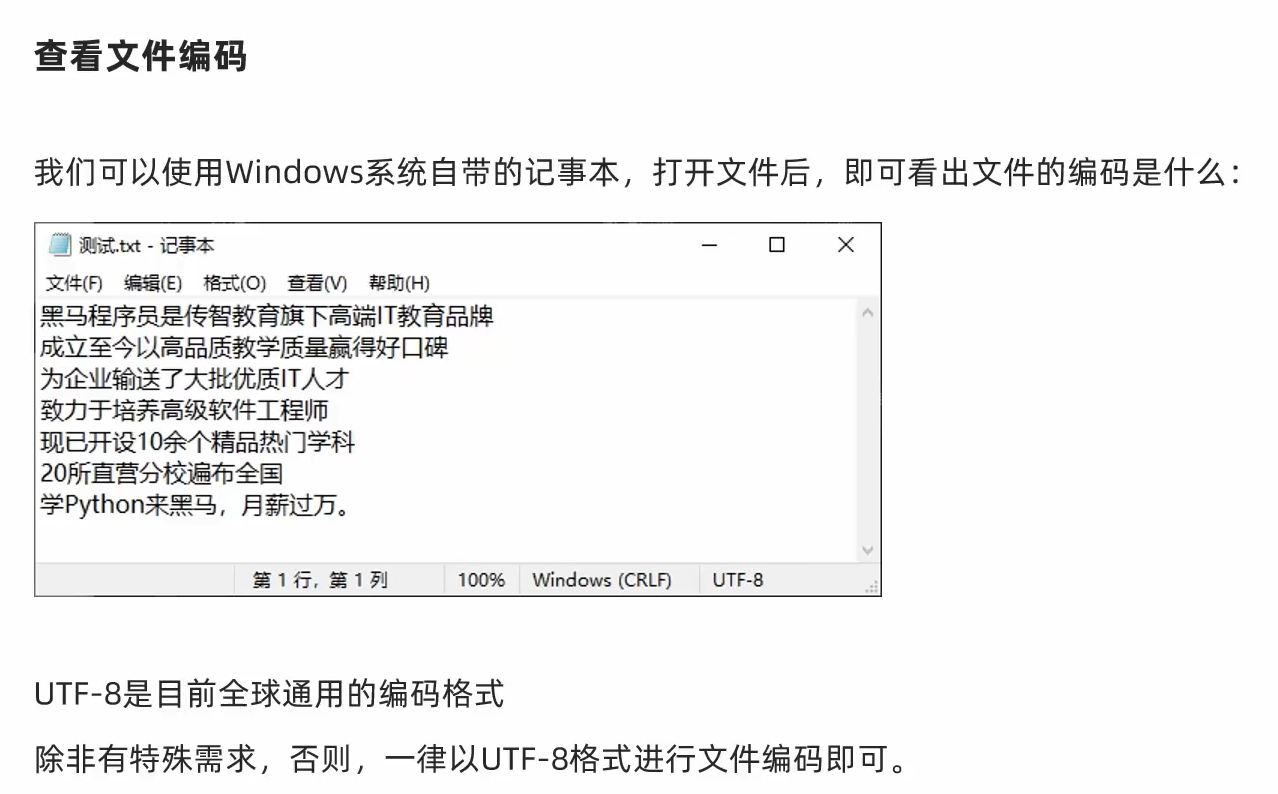
1. 文件的编码



2.文件的读取
2.1 文件操作的作用
2.1.1 什么是文件

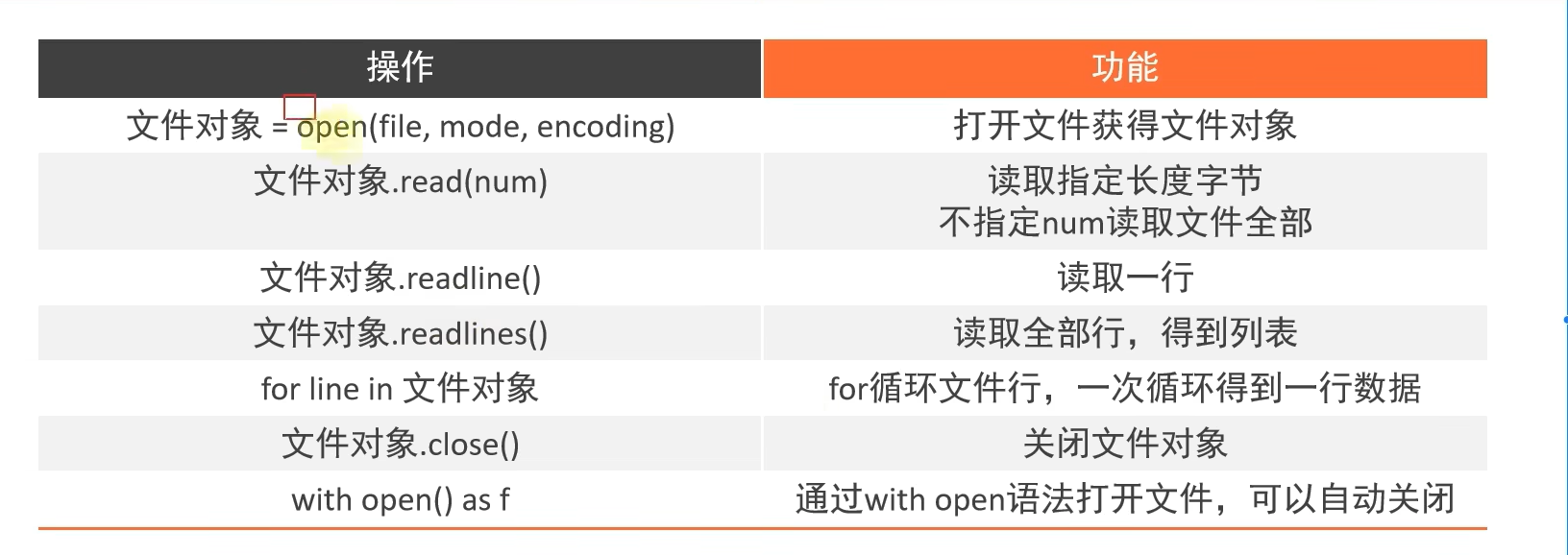
2.2 文件的打开、读取、关闭操作

2.2.1 open()打开函数


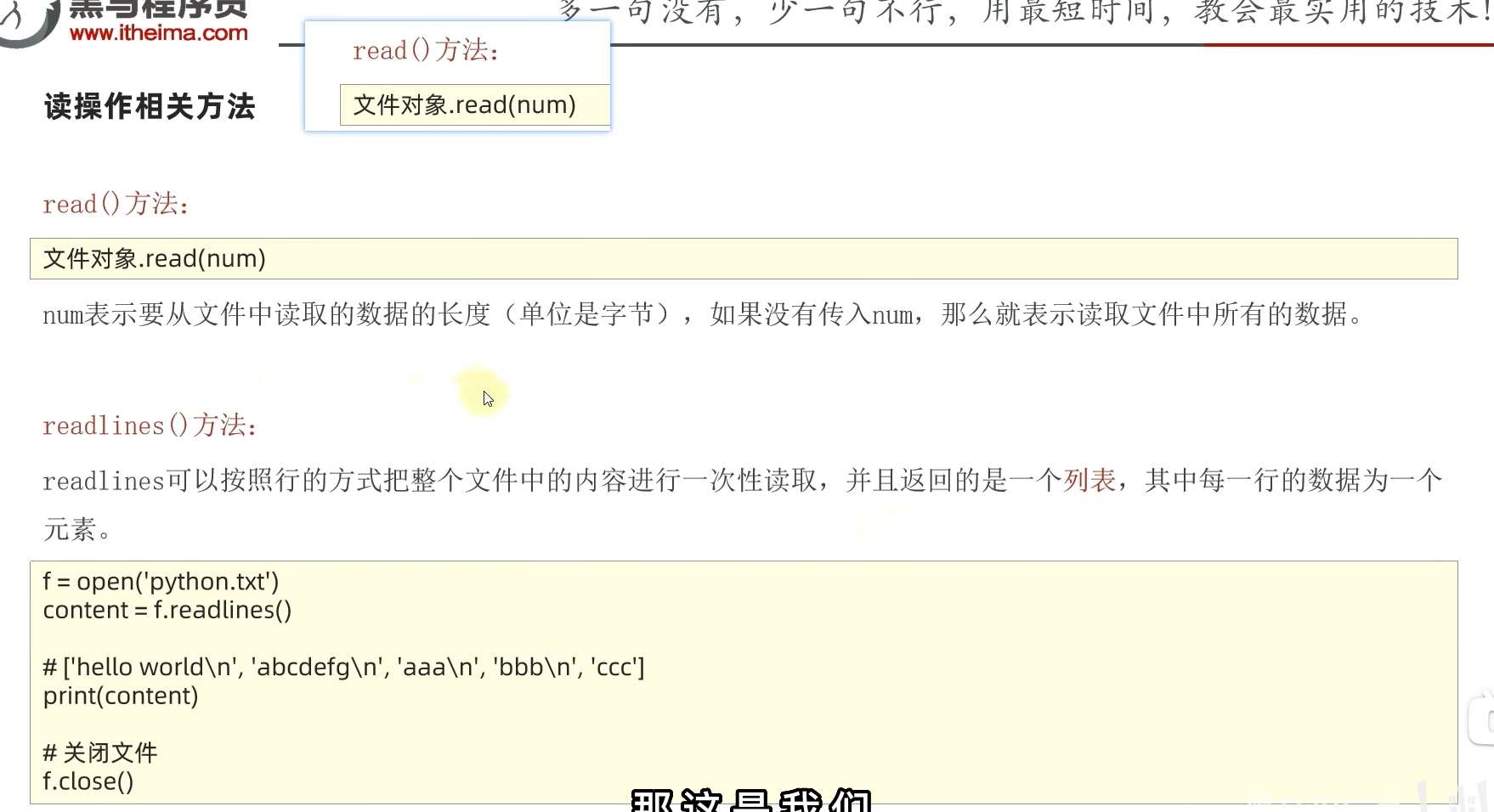
2.2.2 read()和readlines()方法
2.2.3 readline()方法

2.2.4 for循环读取行

2.2.5 关闭文件对象

2.2.6 with open语法

python
# 打开文件
# 将其赋给f这个对象
f = open("F:/测试.txt","r",encoding="UTF-8")
#<class '_io.TextIOWrapper'> 对文本文件进行IO操作功能的一个类
print(type(f))
# 读取文件 -read()
print(f"读取5个字节的结果:{f.read(5)}")
#如果连续读取,会从上次读取的位置继续读取
print(f"读取全部内容:{f.read()}")
# 读取文件 -readLines()
lines = f.readlines() #读取文件的全部行,封装到列表中
"""
lines对象的类型:<class 'list'>
lines对象的内容:['黑马程序员\n', '哈哈\n', '球球你了\n', '不要再刷视频了\n', '太智障了']"""
print(f"lines对象的类型:{type(lines)}")
print(f"lines对象的内容:{lines}")
#关闭文件
f.close()2.2.7 总结

2.3 案例

python
f = open("F:/测试.txt","r",encoding="UTF-8")
# 方式1:读取全部内容,通过字符串count方法进行统计itheima单词数量
content = f.read()
print(content.count("itheima"))
# 方式2: 读取内容,一行一行的读取
count =0 #用count进行累加
for line in f:
line = line.strip() #去除头和尾的空格以及换行符
words = line.split(" ") #将字符串按照空格进行分割,返回一个列表
for word in words:
if word == "itheima":
count += 1
print(count)
f.close()3.文件的写入


python
# 可以写一个不存在的文件,会自动创建
# 若文件已经存在,会将文件内容清空,再重新写
f =open("F:/测试1.txt","w",encoding="UTF-8")
f.write("hell第三方的o world")#内容写到内存中
f.flush()#将内存积攒的内容,写到硬盘的文件中
f.close()#close方法,其实内置了flush方法,在关闭文件之前,会将内存积攒的内容,写到硬盘的文件中4.文件的追加
想要换行,最后添加\n就可以了

5.文件操作综合案例
文件备份


python
f = open("F:/测试1.txt","r",encoding="UTF-8")
f1 = open("F:/测试.txt","w",encoding="UTF-8")
for line in f:
content=line
if content.count("正式")>0:
f1.write(content)
f.close()
f1.close()