1 原理
对极几何描述了通过两个不同视角或相机拍摄同一场景时,两个视图之间内在的、纯粹的几何关系。它不依赖于场景的具体内容,只与相机的内参数和两个视图或相机之间的相对位置(外参数)有关。
如图1-1所示[2]^{[2]}[2],O和O'表示相机的光心,X表示真实场景中的一个三维点,x和x'是X在两个视图中的投影点,e和e'是极点,平面OO'X是极平面,极平面与视图的交线l和l'是极线。
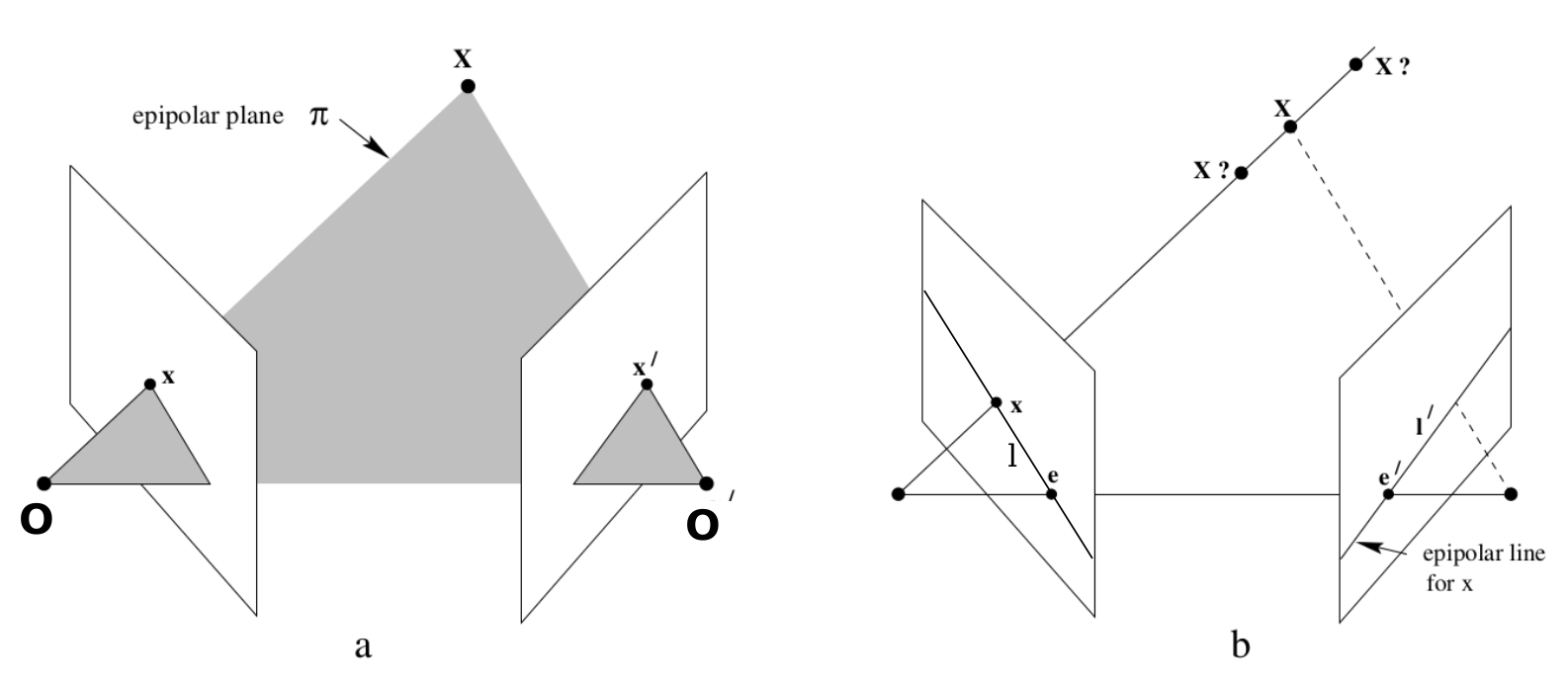
图1-1 对极几何的原理图
参考[1, 2],推导极线约束的原理:
假设真实场景中有一个点X,在两个相机(分别称其为相机1和相机2)的相机坐标系中的三维坐标,采用向量分别表示为C1=[X1,Y1,Z1]TC_1=[X_1, Y_1, Z_1]^{\mathrm{T}}C1=[X1,Y1,Z1]T,C2=[X2,Y2,Z2]TC_2=[X_2, Y_2, Z_2]^{\mathrm{T}}C2=[X2,Y2,Z2]T,相机1到相机2的坐标转换,用旋转矩阵R和平移向量t表示,t=[tx,ty,tz]Tt=[t_x, t_y, t_z]^{\mathrm{T}}t=[tx,ty,tz]T。两个三维点的转换关系为
C2=RC1+t(1.1) C_2=RC_1+t \tag{1.1} C2=RC1+t(1.1)
方程(1.1)的两边同时乘以[t]×[t]_{\times}[t]×,得
t\]×C2=\[t\]×RC1+\[t\]×t(1.2) \[t\]_{\\times}C_2=\[t\]_{\\times}RC_1+\[t\]_{\\times}t \\tag{1.2} \[t\]×C2=\[t\]×RC1+\[t\]×t(1.2)
其中,\[t\]×\[t\]_{\\times}\[t\]×表示由向量t转化而来的反对称矩阵
\[t\]×=\[0−tztytz0−tx−tytx0\](1.3) \[t\]_{\\times}= \\begin{bmatrix} 0 \& -t_z \& t_y \\\\ t_z \& 0 \& -t_x \\\\ -t_y \& t_x \& 0 \\end{bmatrix} \\tag{1.3} \[t\]×=⎣⎡0tz−ty−tz0txty−tx0⎦⎤(1.3)
向量的叉乘,可采用矩阵表示为
t×t=\[t\]×t=0(1.4) t \\times t =\[t\]_{\\times}t=0 \\tag{1.4} t×t=\[t\]×t=0(1.4)
所以直接把方程(1.2)右边的第二项约去,即
\[t\]×C2=\[t\]×RC1(1.5) \[t\]_{\\times}C_2=\[t\]_{\\times}RC_1 \\tag{1.5} \[t\]×C2=\[t\]×RC1(1.5)
方程(1.5)的两边同时乘以C2TC_2\^{\\mathrm{T}}C2T,得
C2T\[t\]×C2=C2T\[t\]×RC1(1.6) C_2\^{\\mathrm{T}}\[t\]_{\\times}C_2=C_2\^{\\mathrm{T}}\[t\]_{\\times}RC_1 \\tag{1.6} C2T\[t\]×C2=C2T\[t\]×RC1(1.6)
可以证明,C2T\[t\]×C2=0C_2\^{\\mathrm{T}}\[t\]_{\\times}C_2=0C2T\[t\]×C2=0,所以
C2T\[t\]×RC1=0(1.7) C_2\^{\\mathrm{T}}\[t\]_{\\times}RC_1=0 \\tag{1.7} C2T\[t\]×RC1=0(1.7)
方程(1.7)中的\[t\]×R\[t\]_{\\times}R\[t\]×R被定义为**本质矩阵**(Essential Matrix)。
使用E表示本质矩阵,可将方程(1.7)简化为
C2TEC1=0(1.8) C_2\^{\\mathrm{T}}EC_1=0 \\tag{1.8} C2TEC1=0(1.8)
这就是对极约束。
本质矩阵体现了三维空间中任意一点X、两个相机光心O和O'必须共面这一根本性的几何约束。这种共面性是视觉系统能够估计深度信息的数学基础,也是"对极几何"概念的核心体现。
本质矩阵描述了两个相机坐标系之间纯粹的旋转和平移关系,即相对位姿,体现了三维空间点在两个相机之间的刚体运动约束,是相机位姿估计中最"本质"的数学表达。
本质矩阵具有尺度等价性(尺度不变性)------对E乘以任意非零常数后,对极约束仍然满足。这反映了单目相机系统无法确定绝对尺度的本质特性,所能恢复的只是与具体尺度无关的相对位置关系。
虽然旋转和平移各有3个自由度,但由于尺度等价性,本质矩阵实际只有5个自由度。这一特性揭示了视觉系统理论上最少需要5对匹配点才能唯一确定相机相对位姿的本质限制。
本质矩阵的旋转矩阵分量是单位正交矩阵,另一个分量\[t\]×\[t\]_{\\times}\[t\]×是反对称矩阵,所以可以证明,本质矩阵的秩为2,且其奇异值必定是\[σ,σ,0\]T\[σ, σ, 0\]\^{\\mathrm{T}}\[σ,σ,0\]T的形式,这些内在性质是本质矩阵区别于普通矩阵的关键特征,反映了对极几何的深层数学结构。
本质矩阵之所以"本质",还在于它剥离了相机内参等因素,直接聚焦于视觉系统中最核心的几何关系------两相机坐标系之间的相对变换。这种变换关系是实现立体视觉、三维重建和相机位姿估计的数学基石,也是从二维图像中恢复三维信息的关键桥梁。通过本质矩阵,计算机视觉系统能够将图像中的像素对应关系转化为有意义的几何约束,从而解决"如何通过二维图像感知三维世界"这一本质问题。
C1C_1C1和C2C_2C2投影到图像之后的二维点,分别用向量p1p_1p1和p2p_2p2表示。假设两个相机的图像都是理想图像,即无畸变的图像。根据针孔相机模型
Z1p1=K1C1(1.9) Z_1p_1=K_1C_1 \\tag{1.9} Z1p1=K1C1(1.9)
Z2p2=K2C2(1.10) Z_2p_2=K_2C_2 \\tag{1.10} Z2p2=K2C2(1.10)
其中,K1K_1K1和K2K_2K2分别为两个相机的内参数矩阵。
分别对方程(1.9)和(1.10)进行矩阵变换:
C1=Z1K1−1p1(1.11) C_1=Z_1K_1\^{-1}p_1 \\tag{1.11} C1=Z1K1−1p1(1.11)
C2=Z2K2−1p2(1.12) C_2=Z_2K_2\^{-1}p_2 \\tag{1.12} C2=Z2K2−1p2(1.12)
将方程(1.11)和(1.12)代入方程(1.8):
p2TK2−TEK1−1p1=0(1.13) p_2\^{\\mathrm{T}}K_2\^{-\\mathrm{T}}EK_1\^{-1}p_1=0 \\tag{1.13} p2TK2−TEK1−1p1=0(1.13)
其中,K2−TEK1−1K_2\^{-\\mathrm{T}}EK_1\^{-1}K2−TEK1−1被定义为**基础矩阵**(Fundamental Matrix)。
基础矩阵描述了两个图像像素坐标系之间对应点的约束关系,它直接作用于图像像素点,可将一幅图像中的点映射到另一幅图像中的极线上。
使用F表示基础矩阵,将方程(1.13)简化为
p2TFp1=0(1.14) p_2\^{\\mathrm{T}}Fp_1=0 \\tag{1.14} p2TFp1=0(1.14)
这是对极约束的另一种表达形式。
## 2 应用
### 2.1 在双目立体相机中的应用
在双目相机中,对极几何最重要的应用就是极线校正。
1. 目的
极线校正的目的是将两个相机非共面行对准的原始图像,变换成理想的双目配置,即两个图像平面严格平行,且光轴平行。
2. 意义
(1)极大简化立体匹配: 寻找左图某点 (x, y) 在右图中的匹配点时,只需要在右图的同一行上进行水平搜索即可。这使算法变得非常简单、高效。
(2)提升匹配速度和精度: 搜索范围从二维降为一维,大大减少了计算量,并降低了错误匹配的概率。这是实现实时深度计算的关键。几乎所有实用的双目立体系统,例如自动驾驶车辆、机器人中使用的双目立体相机,都必须先进行极线校正。
3. 效果
左右图像的极线变为水平线,左右图像中的对应点具有相同的纵坐标,即行对齐。
使用大模型Grok Code生成C++代码,实现极线校正。
stereo_rectification.h
```cpp
#ifndef STEREO_RECTIFICATION_H
#define STEREO_RECTIFICATION_H
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
struct StereoCameraConfig
{
// 左相机内参
cv::Mat left_camera_matrix;
cv::Mat left_dist_coeffs;
// 右相机内参
cv::Mat right_camera_matrix;
cv::Mat right_dist_coeffs;
// 左右相机间的旋转矩阵和平移向量
cv::Mat rotation_matrix; // 3x3
cv::Mat translation_vector; // 3x1
// 图像尺寸
cv::Size image_size;
};
struct StereoRectificationResult
{
// 校正后的旋转矩阵
cv::Mat left_rectification_matrix; // 3x3
cv::Mat right_rectification_matrix; // 3x3
// 校正后的投影矩阵
cv::Mat left_projection_matrix; // 3x4
cv::Mat right_projection_matrix; // 3x4
// 重投影矩阵 (4x4, 用于计算深度)
cv::Mat disparity_to_depth_matrix; // 4x4
// 有效像素区域
cv::Rect left_valid_roi;
cv::Rect right_valid_roi;
// 校正映射矩阵
cv::Mat left_map_x, left_map_y;
cv::Mat right_map_x, right_map_y;
};
class StereoRectifier
{
public:
StereoRectifier();
~StereoRectifier();
/**
* @brief 从YAML文件加载立体相机配置
* @param config_file 配置文件路径
* @return 是否加载成功
*/
bool loadStereoConfig(const std::string& config_file);
/**
* @brief 从参数直接设置立体相机配置
* @param config 立体相机配置结构体
*/
void setStereoConfig(const StereoCameraConfig& config);
/**
* @brief 执行极线校正
* @param alpha 自由缩放参数 (0-1), 0表示裁剪以获得有效像素, 1表示保留所有像素
* @return 校正结果
*/
StereoRectificationResult rectify(double alpha = 0.0);
/**
* @brief 应用校正到图像对
* @param left_image 左图像
* @param right_image 右图像
* @param rectified_left 校正后的左图像
* @param rectified_right 校正后的右图像
* @return 是否成功
*/
bool applyRectification(const cv::Mat& left_image, const cv::Mat& right_image,
cv::Mat& rectified_left, cv::Mat& rectified_right);
/**
* @brief 保存校正结果到文件
* @param result 校正结果
* @param filename 保存文件名
* @return 是否保存成功
*/
bool saveRectificationResult(const StereoRectificationResult& result,
const std::string& filename);
/**
* @brief 从文件加载校正结果
* @param filename 文件名
* @return 校正结果
*/
StereoRectificationResult loadRectificationResult(const std::string& filename);
/**
* @brief 验证极线校正效果
* @param left_image 左图像
* @param right_image 右图像
* @param result 校正结果
*/
void validateRectification(const cv::Mat& left_image, const cv::Mat& right_image,
const StereoRectificationResult& result);
/**
* @brief 计算深度图
* @param disparity_map 视差图
* @param result 校正结果
* @return 深度图
*/
cv::Mat computeDepthMap(const cv::Mat& disparity_map,
const StereoRectificationResult& result);
private:
StereoCameraConfig stereo_config_;
bool is_config_loaded_;
/**
* @brief 检查配置是否有效
* @return 是否有效
*/
bool validateConfig() const;
/**
* @brief 创建校正映射矩阵
* @param result 校正结果
* @param alpha 自由缩放参数
*/
void createRectificationMaps(StereoRectificationResult& result, double alpha);
};
#endif // STEREO_RECTIFICATION_H
```
stereo_rectification.cpp
```cpp
#include "../include/stereo_rectification.h"
#include
#include
#include
StereoRectifier::StereoRectifier() : is_config_loaded_(false)
{
}
StereoRectifier::~StereoRectifier()
{
}
bool StereoRectifier::loadStereoConfig(const std::string& config_file)
{
try
{
cv::FileStorage fs(config_file, cv::FileStorage::READ);
if (!fs.isOpened())
{
std::cerr << "无法打开配置文件: " << config_file << std::endl;
return false;
}
// 读取左相机内参
fs["left_camera_matrix"] >> stereo_config_.left_camera_matrix;
fs["left_dist_coeffs"] >> stereo_config_.left_dist_coeffs;
// 读取右相机内参
fs["right_camera_matrix"] >> stereo_config_.right_camera_matrix;
fs["right_dist_coeffs"] >> stereo_config_.right_dist_coeffs;
// 读取外参
fs["rotation_matrix"] >> stereo_config_.rotation_matrix;
fs["translation_vector"] >> stereo_config_.translation_vector;
// 读取图像尺寸
fs["image_width"] >> stereo_config_.image_size.width;
fs["image_height"] >> stereo_config_.image_size.height;
fs.release();
is_config_loaded_ = validateConfig();
return is_config_loaded_;
}
catch (const cv::Exception& e)
{
std::cerr << "加载配置时发生错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
return false;
}
}
void StereoRectifier::setStereoConfig(const StereoCameraConfig& config)
{
stereo_config_ = config;
is_config_loaded_ = validateConfig();
}
StereoRectificationResult StereoRectifier::rectify(double alpha)
{
StereoRectificationResult result;
if (!is_config_loaded_)
{
std::cerr << "立体相机配置未加载,无法进行校正" << std::endl;
return result;
}
try
{
// 执行双目立体校正
cv::stereoRectify(
stereo_config_.left_camera_matrix, stereo_config_.left_dist_coeffs,
stereo_config_.right_camera_matrix, stereo_config_.right_dist_coeffs,
stereo_config_.image_size,
stereo_config_.rotation_matrix, stereo_config_.translation_vector,
result.left_rectification_matrix, result.right_rectification_matrix,
result.left_projection_matrix, result.right_projection_matrix,
result.disparity_to_depth_matrix,
cv::CALIB_ZERO_DISPARITY, alpha,
stereo_config_.image_size, &result.left_valid_roi, &result.right_valid_roi
);
// 创建校正映射矩阵
createRectificationMaps(result, alpha);
std::cout << "立体校正完成" << std::endl;
std::cout << "左相机有效区域: " << result.left_valid_roi << std::endl;
std::cout << "右相机有效区域: " << result.right_valid_roi << std::endl;
}
catch (const cv::Exception& e)
{
std::cerr << "立体校正过程中发生错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
return result;
}
bool StereoRectifier::applyRectification(const cv::Mat& left_image, const cv::Mat& right_image,
cv::Mat& rectified_left, cv::Mat& rectified_right)
{
if (!is_config_loaded_)
{
std::cerr << "立体相机配置未加载,无法应用校正" << std::endl;
return false;
}
try
{
// 获取校正结果(这里可以优化为缓存结果)
StereoRectificationResult result = rectify(0.0);
if (result.left_map_x.empty() || result.right_map_x.empty())
{
std::cerr << "校正映射矩阵为空,无法应用校正" << std::endl;
return false;
}
// 应用校正到左右图像
cv::remap(left_image, rectified_left, result.left_map_x, result.left_map_y, cv::INTER_LINEAR);
cv::remap(right_image, rectified_right, result.right_map_x, result.right_map_y, cv::INTER_LINEAR);
return true;
}
catch (const cv::Exception& e)
{
std::cerr << "应用校正时发生错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
return false;
}
}
bool StereoRectifier::saveRectificationResult(const StereoRectificationResult& result,
const std::string& filename)
{
try
{
cv::FileStorage fs(filename, cv::FileStorage::WRITE);
if (!fs.isOpened())
{
std::cerr << "无法打开文件保存校正结果: " << filename << std::endl;
return false;
}
// 保存校正矩阵
fs << "left_rectification_matrix" << result.left_rectification_matrix;
fs << "right_rectification_matrix" << result.right_rectification_matrix;
fs << "left_projection_matrix" << result.left_projection_matrix;
fs << "right_projection_matrix" << result.right_projection_matrix;
fs << "disparity_to_depth_matrix" << result.disparity_to_depth_matrix;
// 保存有效区域
fs << "left_valid_roi_x" << result.left_valid_roi.x;
fs << "left_valid_roi_y" << result.left_valid_roi.y;
fs << "left_valid_roi_width" << result.left_valid_roi.width;
fs << "left_valid_roi_height" << result.left_valid_roi.height;
fs << "right_valid_roi_x" << result.right_valid_roi.x;
fs << "right_valid_roi_y" << result.right_valid_roi.y;
fs << "right_valid_roi_width" << result.right_valid_roi.width;
fs << "right_valid_roi_height" << result.right_valid_roi.height;
fs.release();
std::cout << "校正结果已保存到: " << filename << std::endl;
return true;
}
catch (const cv::Exception& e)
{
std::cerr << "保存校正结果时发生错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
return false;
}
}
StereoRectificationResult StereoRectifier::loadRectificationResult(const std::string& filename)
{
StereoRectificationResult result;
try
{
cv::FileStorage fs(filename, cv::FileStorage::READ);
if (!fs.isOpened())
{
std::cerr << "无法打开文件加载校正结果: " << filename << std::endl;
return result;
}
// 加载校正矩阵
fs["left_rectification_matrix"] >> result.left_rectification_matrix;
fs["right_rectification_matrix"] >> result.right_rectification_matrix;
fs["left_projection_matrix"] >> result.left_projection_matrix;
fs["right_projection_matrix"] >> result.right_projection_matrix;
fs["disparity_to_depth_matrix"] >> result.disparity_to_depth_matrix;
// 加载有效区域
result.left_valid_roi.x = (int)fs["left_valid_roi_x"];
result.left_valid_roi.y = (int)fs["left_valid_roi_y"];
result.left_valid_roi.width = (int)fs["left_valid_roi_width"];
result.left_valid_roi.height = (int)fs["left_valid_roi_height"];
result.right_valid_roi.x = (int)fs["right_valid_roi_x"];
result.right_valid_roi.y = (int)fs["right_valid_roi_y"];
result.right_valid_roi.width = (int)fs["right_valid_roi_width"];
result.right_valid_roi.height = (int)fs["right_valid_roi_height"];
fs.release();
// 重新创建校正映射矩阵
createRectificationMaps(result, 0.0);
std::cout << "校正结果已从文件加载: " << filename << std::endl;
}
catch (const cv::Exception& e)
{
std::cerr << "加载校正结果时发生错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
return result;
}
void StereoRectifier::validateRectification(const cv::Mat& left_image, const cv::Mat& right_image,
const StereoRectificationResult& result)
{
if (left_image.empty() || right_image.empty())
{
std::cerr << "输入图像为空,无法验证校正效果" << std::endl;
return;
}
try
{
// 创建验证图像
cv::Mat validation_image;
cv::Size image_size = left_image.size();
// 水平拼接校正后的图像用于验证
cv::Mat canvas(image_size.height, image_size.width * 2, left_image.type());
// 应用校正
cv::Mat rectified_left, rectified_right;
cv::remap(left_image, rectified_left, result.left_map_x, result.left_map_y, cv::INTER_LINEAR);
cv::remap(right_image, rectified_right, result.right_map_x, result.right_map_y, cv::INTER_LINEAR);
// 复制到画布
rectified_left.copyTo(canvas(cv::Rect(0, 0, image_size.width, image_size.height)));
rectified_right.copyTo(canvas(cv::Rect(image_size.width, 0, image_size.width, image_size.height)));
// 在图像上绘制水平线来验证极线对齐
for (int y = 50; y < canvas.rows; y += 50)
{
cv::line(canvas, cv::Point(0, y), cv::Point(canvas.cols - 1, y), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1);
}
// 显示验证结果
cv::imshow("Rectification Validation", canvas);
cv::waitKey(0);
std::cout << "校正验证完成。水平绿线应与特征点对齐。" << std::endl;
std::cout << "如果极线不平行,可能需要重新标定相机。" << std::endl;
}
catch (const cv::Exception& e)
{
std::cerr << "验证校正时发生错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
}
cv::Mat StereoRectifier::computeDepthMap(const cv::Mat& disparity_map,
const StereoRectificationResult& result)
{
cv::Mat depth_map;
if (disparity_map.empty())
{
std::cerr << "视差图为空,无法计算深度图" << std::endl;
return depth_map;
}
try
{
// 使用重投影矩阵计算深度图
cv::reprojectImageTo3D(disparity_map, depth_map, result.disparity_to_depth_matrix, true);
std::cout << "深度图计算完成" << std::endl;
}
catch (const cv::Exception& e)
{
std::cerr << "计算深度图时发生错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
return depth_map;
}
bool StereoRectifier::validateConfig() const
{
// 检查相机内参矩阵
if (stereo_config_.left_camera_matrix.empty() || stereo_config_.right_camera_matrix.empty())
{
std::cerr << "相机内参矩阵为空" << std::endl;
return false;
}
// 检查矩阵尺寸
if (stereo_config_.left_camera_matrix.size() != cv::Size(3, 3) ||
stereo_config_.right_camera_matrix.size() != cv::Size(3, 3))
{
std::cerr << "相机内参矩阵尺寸不正确,应为3x3" << std::endl;
return false;
}
// 检查外参
if (stereo_config_.rotation_matrix.empty() || stereo_config_.translation_vector.empty())
{
std::cerr << "旋转矩阵或平移向量为空" << std::endl;
return false;
}
if (stereo_config_.rotation_matrix.size() != cv::Size(3, 3) ||
stereo_config_.translation_vector.size() != cv::Size(1, 3))
{
std::cerr << "外参矩阵尺寸不正确" << std::endl;
return false;
}
// 检查图像尺寸
if (stereo_config_.image_size.width <= 0 || stereo_config_.image_size.height <= 0)
{
std::cerr << "图像尺寸无效" << std::endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
void StereoRectifier::createRectificationMaps(StereoRectificationResult& result, double alpha)
{
if (!is_config_loaded_)
{
std::cerr << "配置未加载,无法创建校正映射" << std::endl;
return;
}
try
{
// 为左右相机创建校正映射
cv::initUndistortRectifyMap(
stereo_config_.left_camera_matrix, stereo_config_.left_dist_coeffs,
result.left_rectification_matrix, result.left_projection_matrix,
stereo_config_.image_size, CV_32FC1,
result.left_map_x, result.left_map_y
);
cv::initUndistortRectifyMap(
stereo_config_.right_camera_matrix, stereo_config_.right_dist_coeffs,
result.right_rectification_matrix, result.right_projection_matrix,
stereo_config_.image_size, CV_32FC1,
result.right_map_x, result.right_map_y
);
std::cout << "校正映射矩阵创建完成" << std::endl;
}
catch (const cv::Exception& e)
{
std::cerr << "创建校正映射时发生错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
}
```
stereo_rectification_example.cpp
```cpp
#include "../include/stereo_rectification.h"
#include
#include
/**
* 双目立体相机极线校正示例程序
* 演示如何使用StereoRectifier类进行立体校正
*/
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
// 检查命令行参数
if (argc < 4)
{
std::cout << "用法: " << argv[0] << " <配置文件> <左图像> <右图像>" << std::endl;
std::cout << "例如: " << argv[0] << " stereo_config.yaml left.jpg right.jpg" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
std::string config_file = argv[1];
std::string left_image_path = argv[2];
std::string right_image_path = argv[3];
try
{
// 1. 创建立体校正器对象
StereoRectifier rectifier;
// 2. 加载立体相机配置
std::cout << "加载立体相机配置: " << config_file << std::endl;
if (!rectifier.loadStereoConfig(config_file))
{
std::cerr << "加载配置文件失败" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// 3. 读取测试图像
cv::Mat left_image = cv::imread(left_image_path, cv::IMREAD_COLOR);
cv::Mat right_image = cv::imread(right_image_path, cv::IMREAD_COLOR);
if (left_image.empty() || right_image.empty())
{
std::cerr << "无法读取输入图像" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
std::cout << "左图像尺寸: " << left_image.size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "右图像尺寸: " << right_image.size() << std::endl;
// 4. 执行立体校正
std::cout << "执行立体校正..." << std::endl;
StereoRectificationResult result = rectifier.rectify(0.0); // alpha=0 表示裁剪获得最大有效像素
// 5. 应用校正到图像
cv::Mat rectified_left, rectified_right;
if (!rectifier.applyRectification(left_image, right_image, rectified_left, rectified_right))
{
std::cerr << "应用校正失败" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// 6. 显示原始图像和校正后的图像
// 创建对比显示的画布
cv::Mat original_canvas(left_image.rows, left_image.cols * 2, left_image.type());
left_image.copyTo(original_canvas(cv::Rect(0, 0, left_image.cols, left_image.rows)));
right_image.copyTo(original_canvas(cv::Rect(left_image.cols, 0, right_image.cols, right_image.rows)));
cv::Mat rectified_canvas(rectified_left.rows, rectified_left.cols * 2, rectified_left.type());
rectified_left.copyTo(rectified_canvas(cv::Rect(0, 0, rectified_left.cols, rectified_left.rows)));
rectified_right.copyTo(rectified_canvas(cv::Rect(rectified_left.cols, 0, rectified_right.cols, rectified_right.rows)));
// 在校正后的图像上绘制水平线以验证极线对齐
for (int y = 50; y < rectified_canvas.rows; y += 50)
{
cv::line(rectified_canvas, cv::Point(0, y), cv::Point(rectified_canvas.cols - 1, y), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1);
}
// 显示结果
cv::imshow("原始图像 (左 | 右)", original_canvas);
cv::imshow("校正后图像 (左 | 右)", rectified_canvas);
// 7. 保存校正结果
std::string result_file = "stereo_rectification_result.yaml";
if (rectifier.saveRectificationResult(result, result_file))
{
std::cout << "校正结果已保存到: " << result_file << std::endl;
}
// 8. 保存校正后的图像
cv::imwrite("rectified_left.jpg", rectified_left);
cv::imwrite("rectified_right.jpg", rectified_right);
std::cout << "校正后的图像已保存" << std::endl;
// 9. 验证校正效果
std::cout << "按任意键验证校正效果..." << std::endl;
cv::waitKey(0);
rectifier.validateRectification(left_image, right_image, result);
// 10. 示例:从文件加载校正结果
std::cout << "测试从文件加载校正结果..." << std::endl;
StereoRectificationResult loaded_result = rectifier.loadRectificationResult(result_file);
if (!loaded_result.left_rectification_matrix.empty())
{
std::cout << "成功从文件加载校正结果" << std::endl;
}
std::cout << "立体校正示例完成!" << std::endl;
cv::destroyAllWindows();
}
catch (const cv::Exception& e)
{
std::cerr << "OpenCV错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;
return -1;
}
catch (const std::exception& e)
{
std::cerr << "标准异常: " << e.what() << std::endl;
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
```
stereo_config_sample.yaml
```yaml
%YAML:1.0
# 双目立体相机配置示例文件
# 这个文件包含了进行立体校正所需的所有参数
# 参数通常通过双目相机标定获得
# 左相机内参矩阵 (3x3)
left_camera_matrix: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 3
cols: 3
dt: d
data: [ 615.0, 0.0, 310.0,
0.0, 615.0, 240.0,
0.0, 0.0, 1.0 ]
# 左相机畸变系数 [k1, k2, p1, p2, k3]
left_dist_coeffs: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 1
cols: 5
dt: d
data: [ -0.1, 0.05, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 ]
# 右相机内参矩阵 (3x3)
right_camera_matrix: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 3
cols: 3
dt: d
data: [ 615.0, 0.0, 310.0,
0.0, 615.0, 240.0,
0.0, 0.0, 1.0 ]
# 右相机畸变系数 [k1, k2, p1, p2, k3]
right_dist_coeffs: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 1
cols: 5
dt: d
data: [ -0.1, 0.05, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 ]
# 左右相机间的旋转矩阵 (3x3)
rotation_matrix: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 3
cols: 3
dt: d
data: [ 0.9998, -0.0012, 0.0198,
0.0012, 0.9999, 0.0123,
-0.0198, -0.0123, 0.9997 ]
# 左右相机间的平移向量 (3x1),单位通常为毫米或米
translation_vector: !!opencv-matrix
rows: 3
cols: 1
dt: d
data: [ -120.0, 5.0, 10.0 ]
# 图像尺寸
image_width: 640
image_height: 480
```
### 2.2 在视觉SLAM中的应用
对极几何在SLAM中主要用于解决相机运动中的位姿估计问题。
1. 基本过程
(1)系统采集两帧图像,视为两个不同位置的相机,内参数矩阵K1=K2K_1=K_2K1=K2。
(2)提取并匹配两帧图像的特征点。
(3)使用匹配点对,通过八点法等算法计算基础矩阵F或本质矩阵E。
(4)从本质矩阵E中分解出相机从第一帧到第二帧的旋转矩阵R和平移向量 t(带一个未知的尺度因子)。
2. 意义
对极几何提供了SLAM系统两个关键帧之间的运动估计,并由此可以通过三角测量生成3D地图点。
## 参考文献
\[1\] 高翔,张涛 等. 视觉SLAM十四讲:从理论到实践,第2版. 电子工业出版社. 2019.
\[2\] Richard Hartley, Andrew Zisserman. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, Second Edition. Cambridge University Press. 2003.
