前言
在前面2篇文章
我们看了Init、Zygote进程,本文是Android 15 Framework解析系列的第三篇,一起来看看 SystemServer 进程的启动与核心服务的初始化全流程吧。
注意:本文出现的源码基于Android - 15.0.0_r1。另外本文关注主要逻辑,省略部分代码。
一、 Android系统启动流程
本文是介绍SystemServer,照例先看下Android系统启动流程: 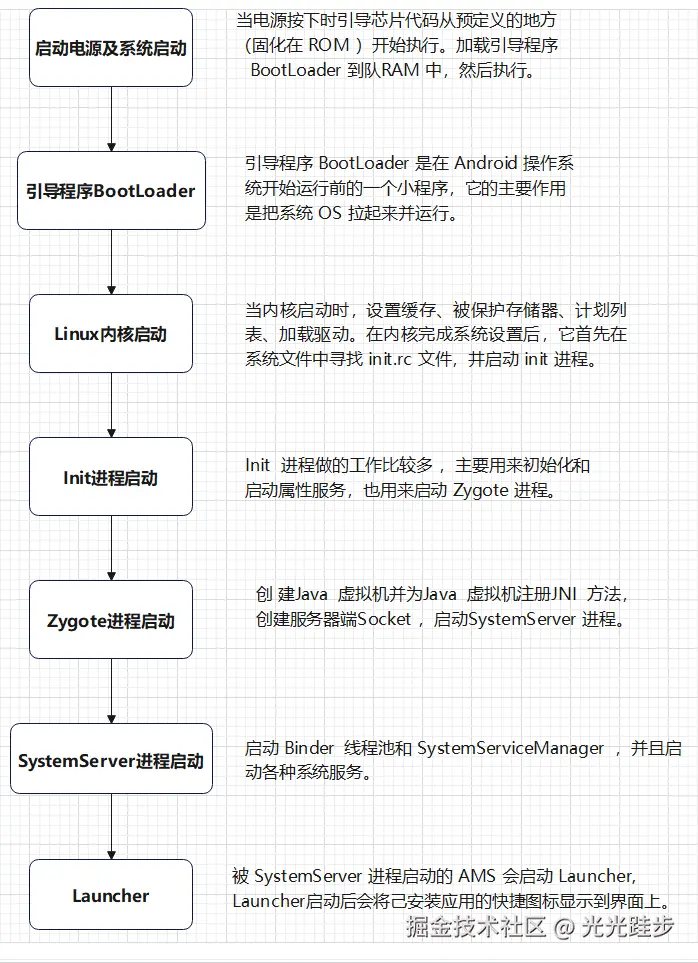
启动电源及系统启动 -> Bootloader -> Linux内核启动 -> Init -> Zygote -> SystemServer -> Launcher
二、 SystemServer
SystemServer 是 Android 系统的核心进程,它会启动并管理几乎所有关键的系统服务,如 AMS、WMS等。
我们就从SystemServer的启动开始看吧。
2.1 SystemServer的启动
SystemServer的启动是在ZygoteInit::main方法中,调用了forkSystemServer方法 /frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
Java
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public static void main(String[] argv) {
...
if (startSystemServer) {
// 此处调用了forkSystemServer
Runnable r = forkSystemServer(abiList, zygoteSocketName, zygoteServer);
...
}
...
}
private static Runnable forkSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName,
ZygoteServer zygoteServer) {
// 特权能力
long capabilities = posixCapabilitiesAsBits(
OsConstants.CAP_IPC_LOCK,
OsConstants.CAP_KILL,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_ADMIN,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_BIND_SERVICE,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_BROADCAST,
OsConstants.CAP_NET_RAW,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_MODULE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_NICE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_PTRACE,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TIME,
OsConstants.CAP_SYS_TTY_CONFIG,
OsConstants.CAP_WAKE_ALARM,
OsConstants.CAP_BLOCK_SUSPEND
);
/* Containers run without some capabilities, so drop any caps that are not available. */
StructCapUserHeader header = new StructCapUserHeader(
OsConstants._LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_3, 0);
StructCapUserData[] data;
try {
data = Os.capget(header);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to capget()", ex);
}
capabilities &= Integer.toUnsignedLong(data[0].effective) |
(Integer.toUnsignedLong(data[1].effective) << 32);
/* Hardcoded command line to start the system server */
String[] args = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1023,"
+ "1024,1032,1065,3001,3002,3003,3005,3006,3007,3009,3010,3011,3012",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--nice-name=system_server",
"--runtime-args",
"--target-sdk-version=" + VMRuntime.SDK_VERSION_CUR_DEVELOPMENT,
"com.android.server.SystemServer",
};
ZygoteArguments parsedArgs;
int pid;
try {
ZygoteCommandBuffer commandBuffer = new ZygoteCommandBuffer(args);
try {
parsedArgs = ZygoteArguments.getInstance(commandBuffer);
} catch (EOFException e) {
throw new AssertionError("Unexpected argument error for forking system server", e);
}
commandBuffer.close();
Zygote.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
Zygote.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
if (Zygote.nativeSupportsMemoryTagging()) {
String mode = SystemProperties.get("persist.arm64.memtag.system_server", "");
if (mode.isEmpty()) {
/* The system server has ASYNC MTE by default, in order to allow
* system services to specify their own MTE level later, as you
* can't re-enable MTE once it's disabled. */
mode = SystemProperties.get("persist.arm64.memtag.default", "async");
}
if (mode.equals("async")) {
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.MEMORY_TAG_LEVEL_ASYNC;
} else if (mode.equals("sync")) {
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.MEMORY_TAG_LEVEL_SYNC;
} else if (!mode.equals("off")) {
/* When we have an invalid memory tag level, keep the current level. */
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.nativeCurrentTaggingLevel();
Slog.e(TAG, "Unknown memory tag level for the system server: \"" + mode + "\"");
}
} else if (Zygote.nativeSupportsTaggedPointers()) {
/* Enable pointer tagging in the system server. Hardware support for this is present
* in all ARMv8 CPUs. */
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.MEMORY_TAG_LEVEL_TBI;
}
/* Enable gwp-asan on the system server with a small probability. This is the same
* policy as applied to native processes and system apps. */
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.GWP_ASAN_LEVEL_LOTTERY;
if (shouldProfileSystemServer()) {
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags |= Zygote.PROFILE_SYSTEM_SERVER;
}
/* Request to fork the system server process */
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.mUid, parsedArgs.mGid,
parsedArgs.mGids,
parsedArgs.mRuntimeFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.mPermittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.mEffectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
/* For child process */
if (pid == 0) {
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
return handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
return null;
}
static int forkSystemServer(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int runtimeFlags,
int[][] rlimits, long permittedCapabilities, long effectiveCapabilities) {
ZygoteHooks.preFork();
int pid = nativeForkSystemServer(
uid, gid, gids, runtimeFlags, rlimits,
permittedCapabilities, effectiveCapabilities);
// Set the Java Language thread priority to the default value for new apps.
Thread.currentThread().setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
ZygoteHooks.postForkCommon();
return pid;
}
// com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp
static jint com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeForkSystemServer(
JNIEnv* env, jclass, uid_t uid, gid_t gid, jintArray gids,
jint runtime_flags, jobjectArray rlimits, jlong permitted_capabilities,
jlong effective_capabilities) {
...
// ForkCommon会调用fork函数
pid_t pid = zygote::ForkCommon(env, true,
fds_to_close,
fds_to_ignore,
true);
...
return pid;
}
pid_t zygote::ForkCommon(JNIEnv* env, bool is_system_server,
const std::vector<int>& fds_to_close,
const std::vector<int>& fds_to_ignore,
bool is_priority_fork,
bool purge) {
...
pid_t pid = fork();
...
return pid;
}在forkSystemServer中,调用了nativeForkSystemServer方法,最后会调用fork,并将返回pid。执行完forkSystemServer之后,会继续看后面的代码,会执行handleSystemServerProcess
Java
private static Runnable handleSystemServerProcess(ZygoteArguments parsedArgs) {
// set umask to 0077 so new files and directories will default to owner-only permissions.
Os.umask(S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO);
if (parsedArgs.mNiceName != null) {
Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.mNiceName);
}
final String systemServerClasspath = Os.getenv("SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH");
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
// Capturing profiles is only supported for debug or eng builds since selinux normally
// prevents it.
if (shouldProfileSystemServer() && (Build.IS_USERDEBUG || Build.IS_ENG)) {
try {
Log.d(TAG, "Preparing system server profile");
final String standaloneSystemServerJars =
Os.getenv("STANDALONE_SYSTEMSERVER_JARS");
final String systemServerPaths = standaloneSystemServerJars != null
? String.join(":", systemServerClasspath, standaloneSystemServerJars)
: systemServerClasspath;
prepareSystemServerProfile(systemServerPaths);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "Failed to set up system server profile", e);
}
}
}
// parsedArgs.mInvokeWith 为null,走else分支
if (parsedArgs.mInvokeWith != null) {
String[] args = parsedArgs.mRemainingArgs;
// If we have a non-null system server class path, we'll have to duplicate the
// existing arguments and append the classpath to it. ART will handle the classpath
// correctly when we exec a new process.
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
String[] amendedArgs = new String[args.length + 2];
amendedArgs[0] = "-cp";
amendedArgs[1] = systemServerClasspath;
System.arraycopy(args, 0, amendedArgs, 2, args.length);
args = amendedArgs;
}
WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.mInvokeWith,
parsedArgs.mNiceName, parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion,
VMRuntime.getCurrentInstructionSet(), null, args);
throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected return from WrapperInit.execApplication");
} else {
// 创建SystemServerClassLoader, 实现是构建的PathClassLoader对象
ClassLoader cl = getOrCreateSystemServerClassLoader();
if (cl != null) {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
}
// 调用ZygoteInit.zygoteInit
return ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion,
parsedArgs.mDisabledCompatChanges,
parsedArgs.mRemainingArgs, cl);
}
/* should never reach here */
}
public static Runnable zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, long[] disabledCompatChanges,
String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (RuntimeInit.DEBUG) {
Slog.d(RuntimeInit.TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.redirectLogStreams();
RuntimeInit.commonInit();
ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();
return RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, disabledCompatChanges, argv,
classLoader);
}
protected static Runnable applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, long[] disabledCompatChanges,
String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) {
// If the application calls System.exit(), terminate the process
// immediately without running any shutdown hooks. It is not possible to
// shutdown an Android application gracefully. Among other things, the
// Android runtime shutdown hooks close the Binder driver, which can cause
// leftover running threads to crash before the process actually exits.
nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup(true);
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion);
VMRuntime.getRuntime().setDisabledCompatChanges(disabledCompatChanges);
final Arguments args = new Arguments(argv);
// The end of of the RuntimeInit event (see #zygoteInit).
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
// Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main
return findStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
}
protected static Runnable findStaticMain(String className, String[] argv,
ClassLoader classLoader) {
Class<?> cl;
try {
// 根据类名动态加载目标类
cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
ex);
}
Method m;
try {
// 获取目标类的 main 方法
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing static main on " + className, ex);
} catch (SecurityException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);
}
int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
// 验证方法修饰符:必须是 public static
if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Main method is not public and static on " + className);
}
// MethodAndArgsCaller实现了Runnable接口,后续ZygoteInit会调用run() 方法
// 最终结果:子进程直接从目标类的 main 方法开始执行, 这里就是SystemServer::main方法
return new MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
}
// RuntimeInit.java
static class MethodAndArgsCaller implements Runnable {
/** method to call */
private final Method mMethod;
/** argument array */
private final String[] mArgs;
public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String[] args) {
mMethod = method;
mArgs = args;
}
public void run() {
try {
mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs });
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
Throwable cause = ex.getCause();
if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) cause;
} else if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) cause;
}
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}从上面代码可以看到,先通过fork创建子进程,再通过反射找到SystemServer::main方法,后续在ZygoteInit.main()中,调用run方法,会执行mMethod.invoke,从而也就到了SystemServer::main,即启动了SystemServer
还记得在handleSystemServerProcess方法中,调用了getOrCreateSystemServerClassLoader,去创建SystemServerClassLoader,这个方法调用链,我贴下面吧,感兴趣可以自己看看,也可以越过这部分,直接看2.2小节,不影响Android启动流程
Java
private static ClassLoader getOrCreateSystemServerClassLoader() {
if (sCachedSystemServerClassLoader == null) {
final String systemServerClasspath = Os.getenv("SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH");
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
sCachedSystemServerClassLoader = createPathClassLoader(systemServerClasspath,
VMRuntime.SDK_VERSION_CUR_DEVELOPMENT);
}
}
return sCachedSystemServerClassLoader;
}
static ClassLoader createPathClassLoader(String classPath, int targetSdkVersion) {
String libraryPath = System.getProperty("java.library.path");
// We use the boot class loader, that's what the runtime expects at AOT.
ClassLoader parent = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getParent();
// 注意这里的classLoaderName传的是null,后面会根据这个参数来判断使用哪种ClassLoader
return ClassLoaderFactory.createClassLoader(classPath, libraryPath, libraryPath,
parent, targetSdkVersion, true /* isNamespaceShared */, null /* classLoaderName */);
}
// classLoaderName为null
public static ClassLoader createClassLoader(String dexPath,
String librarySearchPath, String libraryPermittedPath, ClassLoader parent,
int targetSdkVersion, boolean isNamespaceShared, String classLoaderName) {
List<String> nativeSharedLibraries = new ArrayList<>();
nativeSharedLibraries.add("ALL");
return createClassLoader(dexPath, librarySearchPath, libraryPermittedPath,
parent, targetSdkVersion, isNamespaceShared, classLoaderName, null,
nativeSharedLibraries, null);
}
// classLoaderName为null
public static ClassLoader createClassLoader(String dexPath,
String librarySearchPath, String libraryPermittedPath, ClassLoader parent,
int targetSdkVersion, boolean isNamespaceShared, String classLoaderName,
List<ClassLoader> sharedLibraries, List<String> nativeSharedLibraries,
List<ClassLoader> sharedLibrariesAfter) {
final ClassLoader classLoader = createClassLoader(dexPath, librarySearchPath, parent,
classLoaderName, sharedLibraries, sharedLibrariesAfter);
...
return classLoader;
}
// classLoaderName为null
public static ClassLoader createClassLoader(String dexPath,
String librarySearchPath, ClassLoader parent, String classloaderName,
List<ClassLoader> sharedLibraries, List<ClassLoader> sharedLibrariesLoadedAfter) {
ClassLoader[] arrayOfSharedLibraries = (sharedLibraries == null)
? null
: sharedLibraries.toArray(new ClassLoader[sharedLibraries.size()]);
ClassLoader[] arrayOfSharedLibrariesLoadedAfterApp = (sharedLibrariesLoadedAfter == null)
? null
: sharedLibrariesLoadedAfter.toArray(
new ClassLoader[sharedLibrariesLoadedAfter.size()]);
// 在createPathClassLoader方法调用ClassLoaderFactory.createClassLoader时,传递的classloaderName为null
// isPathClassLoaderName判断这个参数为null,会返回true
if (isPathClassLoaderName(classloaderName)) {
// 因此SystemServerClassLoader是用的PathClassLoader
return new PathClassLoader(dexPath, librarySearchPath, parent, arrayOfSharedLibraries,
arrayOfSharedLibrariesLoadedAfterApp);
} else if (isDelegateLastClassLoaderName(classloaderName)) {
return new DelegateLastClassLoader(dexPath, librarySearchPath, parent,
arrayOfSharedLibraries, arrayOfSharedLibrariesLoadedAfterApp);
}
throw new AssertionError("Invalid classLoaderName: " + classloaderName);
}
// 这里的参数name,也就是从传下来classloaderName,为null,此方法返回true
public static boolean isPathClassLoaderName(String name) {
return name == null || PATH_CLASS_LOADER_NAME.equals(name) ||
DEX_CLASS_LOADER_NAME.equals(name);
}2.2 SystemServer
通过上一小节的调用,就跑到了SystemServer::main方法中
Java
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
public SystemServer() {
...
mStartCount = SystemProperties.getInt(SYSPROP_START_COUNT, 0) + 1;
// 设备启动(开机)以来经过的真实时间
mRuntimeStartElapsedTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
// 设备启动以来经过的有效运行时间
mRuntimeStartUptime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
Process.setStartTimes(mRuntimeStartElapsedTime, mRuntimeStartUptime,
mRuntimeStartElapsedTime, mRuntimeStartUptime);
// Remember if it's runtime restart or reboot.
mRuntimeRestart = mStartCount > 1;
}
private void run() {
TimingsTraceAndSlog t = new TimingsTraceAndSlog();
try {
t.traceBegin("InitBeforeStartServices");
// 设置一些属性值
SystemProperties.set(SYSPROP_START_COUNT, String.valueOf(mStartCount));
SystemProperties.set(SYSPROP_START_ELAPSED, String.valueOf(mRuntimeStartElapsedTime));
SystemProperties.set(SYSPROP_START_UPTIME, String.valueOf(mRuntimeStartUptime));
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.SYSTEM_SERVER_START,
mStartCount, mRuntimeStartUptime, mRuntimeStartElapsedTime);
// Set the device's time zone (a system property) if it is not set or is invalid.
SystemTimeZone.initializeTimeZoneSettingsIfRequired();
// If the system has "persist.sys.language" and friends set, replace them with
// "persist.sys.locale". Note that the default locale at this point is calculated
// using the "-Duser.locale" command line flag. That flag is usually populated by
// AndroidRuntime using the same set of system properties, but only the system_server
// and system apps are allowed to set them.
//
// NOTE: Most changes made here will need an equivalent change to
// core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
if (!SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.language").isEmpty()) {
final String languageTag = Locale.getDefault().toLanguageTag();
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.locale", languageTag);
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.language", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.country", "");
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.localevar", "");
}
// The system server should never make non-oneway calls
Binder.setWarnOnBlocking(true);
// The system server should always load safe labels
PackageItemInfo.forceSafeLabels();
// Default to FULL within the system server.
SQLiteGlobal.sDefaultSyncMode = SQLiteGlobal.SYNC_MODE_FULL;
// Deactivate SQLiteCompatibilityWalFlags until settings provider is initialized
SQLiteCompatibilityWalFlags.init(null);
// Here we go!
Slog.i(TAG, "Entered the Android system server!");
final long uptimeMillis = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_SYSTEM_RUN, uptimeMillis);
if (!mRuntimeRestart) {
FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME_REPORTED,
FrameworkStatsLog
.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME__EVENT__SYSTEM_SERVER_INIT_START,
uptimeMillis);
}
// In case the runtime switched since last boot (such as when
// the old runtime was removed in an OTA), set the system
// property so that it is in sync. We can't do this in
// libnativehelper's JniInvocation::Init code where we already
// had to fallback to a different runtime because it is
// running as root and we need to be the system user to set
// the property. http://b/11463182
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.dalvik.vm.lib.2", VMRuntime.getRuntime().vmLibrary());
// Mmmmmm... more memory!
VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();
// Some devices rely on runtime fingerprint generation, so make sure
// we've defined it before booting further.
Build.ensureFingerprintProperty();
// Within the system server, it is an error to access Environment paths without
// explicitly specifying a user.
Environment.setUserRequired(true);
// Within the system server, any incoming Bundles should be defused
// to avoid throwing BadParcelableException.
BaseBundle.setShouldDefuse(true);
// Within the system server, when parceling exceptions, include the stack trace
Parcel.setStackTraceParceling(true);
// Ensure binder calls into the system always run at foreground priority.
BinderInternal.disableBackgroundScheduling(true);
// Increase the number of binder threads in system_server
BinderInternal.setMaxThreads(sMaxBinderThreads);
// Prepare the main looper thread (this thread).
android.os.Process.setThreadPriority(
android.os.Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);
android.os.Process.setCanSelfBackground(false);
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
Looper.getMainLooper().setSlowLogThresholdMs(
SLOW_DISPATCH_THRESHOLD_MS, SLOW_DELIVERY_THRESHOLD_MS);
SystemServiceRegistry.sEnableServiceNotFoundWtf = true;
// 加载libandroid_servers.so
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
// Allow heap / perf profiling.
initZygoteChildHeapProfiling();
// Debug builds - spawn a thread to monitor for fd leaks.
if (Build.IS_DEBUGGABLE) {
spawnFdLeakCheckThread();
}
// Check whether we failed to shut down last time we tried.
// This call may not return.
performPendingShutdown();
// 创建 system context.
createSystemContext();
// Call per-process mainline module initialization.
ActivityThread.initializeMainlineModules();
// Sets the dumper service
ServiceManager.addService("system_server_dumper", mDumper);
mDumper.addDumpable(this);
// Create the system service manager.
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
mSystemServiceManager.setStartInfo(mRuntimeRestart,
mRuntimeStartElapsedTime, mRuntimeStartUptime);
mDumper.addDumpable(mSystemServiceManager);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
// Prepare the thread pool for init tasks that can be parallelized
SystemServerInitThreadPool tp = SystemServerInitThreadPool.start();
mDumper.addDumpable(tp);
// Lazily load the pre-installed system font map in SystemServer only if we're not doing
// the optimized font loading in the FontManagerService.
if (!com.android.text.flags.Flags.useOptimizedBoottimeFontLoading()
&& Typeface.ENABLE_LAZY_TYPEFACE_INITIALIZATION) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Loading pre-installed system font map.");
Typeface.loadPreinstalledSystemFontMap();
}
// Attach JVMTI agent if this is a debuggable build and the system property is set.
if (Build.IS_DEBUGGABLE) {
// Property is of the form "library_path=parameters".
String jvmtiAgent = SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.dalvik.jvmtiagent");
if (!jvmtiAgent.isEmpty()) {
int equalIndex = jvmtiAgent.indexOf('=');
String libraryPath = jvmtiAgent.substring(0, equalIndex);
String parameterList =
jvmtiAgent.substring(equalIndex + 1, jvmtiAgent.length());
// Attach the agent.
try {
Debug.attachJvmtiAgent(libraryPath, parameterList, null);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.e("System", "*************************************************");
Slog.e("System", "********** Failed to load jvmti plugin: " + jvmtiAgent);
}
}
}
} finally {
t.traceEnd(); // InitBeforeStartServices
}
// Setup the default WTF handler
RuntimeInit.setDefaultApplicationWtfHandler(SystemServer::handleEarlySystemWtf);
// 启动服务
try {
t.traceBegin("StartServices");
// 引导服务,如ATMS, AMS,DMS
startBootstrapServices(t);
// 核心服务,如BatteryService
startCoreServices(t);
// 其他服务,如WMS, IMS
startOtherServices(t);
startApexServices(t);
// Only update the timeout after starting all the services so that we use
// the default timeout to start system server.
updateWatchdogTimeout(t);
CriticalEventLog.getInstance().logSystemServerStarted();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
t.traceEnd(); // StartServices
}
StrictMode.initVmDefaults(null);
if (!mRuntimeRestart && !isFirstBootOrUpgrade()) {
final long uptimeMillis = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME_REPORTED,
FrameworkStatsLog.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME__EVENT__SYSTEM_SERVER_READY,
uptimeMillis);
final long maxUptimeMillis = 60 * 1000;
if (uptimeMillis > maxUptimeMillis) {
Slog.wtf(SYSTEM_SERVER_TIMING_TAG,
"SystemServer init took too long. uptimeMillis=" + uptimeMillis);
}
}
// Set binder transaction callback after starting system services
Binder.setTransactionCallback(new IBinderCallback() {
@Override
public void onTransactionError(int pid, int code, int flags, int err) {
mActivityManagerService.frozenBinderTransactionDetected(pid, code, flags, err);
}
});
// Loop forever.
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}在SystemServer::main中,先调用SystemServer的构造方法,然后再调用了SystemServer::run。run方法中,做了很多事,我们还是只看比较重要的。
- createSystemContext
- startBootstrapServices
- startCoreServices
- startOtherServices
- startApexServices
那么就依次看看具体代码吧
2.2.1 createSystemContext
Java
private void createSystemContext() {
// 获取ActivityThread
ActivityThread activityThread = ActivityThread.systemMain();
mSystemContext = activityThread.getSystemContext();
mSystemContext.setTheme(DEFAULT_SYSTEM_THEME);
final Context systemUiContext = activityThread.getSystemUiContext();
systemUiContext.setTheme(DEFAULT_SYSTEM_THEME);
Trace.registerWithPerfetto();
}
// ActivityThread.java
public static ActivityThread systemMain() {
ThreadedRenderer.initForSystemProcess();
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(true, 0);
return thread;
}
private void attach(boolean system, long startSeq) {
sCurrentActivityThread = this;
mConfigurationController = new ConfigurationController(this);
mSystemThread = system;
mStartSeq = startSeq;
mDdmSyncStageUpdater.next(Stage.Attach);
// system为true,执行eles分支
if (!system) {
...
} else {
// Don't set application object here -- if the system crashes,
// we can't display an alert, we just want to die die die.
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("system_process",
UserHandle.myUserId());
try {
mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation();
mInstrumentation.basicInit(this);
// 创建ContextImpl
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(
this, getSystemContext().mPackageInfo);
// 通过反射创建mInitialApplication,调用onCreate()
mInitialApplication = context.mPackageInfo.makeApplicationInner(true, null);
mInitialApplication.onCreate();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate Application():" + e.toString(), e);
}
}
...
}
public ContextImpl getSystemContext() {
synchronized (this) {
if (mSystemContext == null) {
mSystemContext = ContextImpl.createSystemContext(this);
}
return mSystemContext;
}
}
// ContextImpl.java
static ContextImpl createSystemContext(ActivityThread mainThread) {
LoadedApk packageInfo = new LoadedApk(mainThread);
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(null, mainThread, packageInfo,
ContextParams.EMPTY, null, null, null, null, null, 0, null, null,
DEVICE_ID_DEFAULT, false);
context.setResources(packageInfo.getResources());
context.mResources.updateConfiguration(context.mResourcesManager.getConfiguration(),
context.mResourcesManager.getDisplayMetrics());
context.mContextType = CONTEXT_TYPE_SYSTEM_OR_SYSTEM_UI;
return context;
}在createSystemContext方法中,会创建System Context, 并且还通过反射创建mInitialApplication,调用它的onCreate()。
2.2.2 startBootstrapServices
Java
private void startBootstrapServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
...
// 启动看门狗
final Watchdog watchdog = Watchdog.getInstance();
watchdog.start();
...
// 开启Installer
Installer installer = mSystemServiceManager.startService(Installer.class);
...
// 开启PowerStatsService
mSystemServiceManager.startService(PowerStatsService.class);
...
// 开启ATMS, AMS
ActivityTaskManagerService atm = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
ActivityTaskManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService();
mActivityManagerService = ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.startService(
mSystemServiceManager, atm);
mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager(mSystemServiceManager);
mActivityManagerService.setInstaller(installer);
...
mDisplayManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(DisplayManagerService.class);
...
// 添加一个设备重启监听
watchdog.init(mSystemContext, mActivityManagerService);
...
}
public <T extends SystemService> T startService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
try {
final String name = serviceClass.getName();
Slog.i(TAG, "Starting " + name);
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER, "StartService " + name);
// Create the service.
if (!SystemService.class.isAssignableFrom(serviceClass)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create " + name
+ ": service must extend " + SystemService.class.getName());
}
final T service;
try {
// 获取构造方法
Constructor<T> constructor = serviceClass.getConstructor(Context.class);
// 构造实例
service = constructor.newInstance(mContext);
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service could not be instantiated", ex);
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service must have a public constructor with a Context argument", ex);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service must have a public constructor with a Context argument", ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to create service " + name
+ ": service constructor threw an exception", ex);
}
// 启动服务
startService(service);
// 返回服务实例
return service;
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
}
}
public void startService(@NonNull final SystemService service) {
// Check if already started
String className = service.getClass().getName();
// mServiceClassnames是一个Set, 防止反复启动同一服务
if (mServiceClassnames.contains(className)) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Not starting an already started service " + className);
return;
}
mServiceClassnames.add(className);
// Register it.
mServices.add(service);
// Start it.
long time = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
try {
// 调用启动服务的onStart方法,实际就是往ServiceManager中注册当前启动的服务
service.onStart方法();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to start service " + service.getClass().getName()
+ ": onStart threw an exception", ex);
}
warnIfTooLong(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() - time, service, "onStart");
}在startBootstrapServices中, 会启动看门狗以及启动一些服务,比如ATMS, AMS,DMS等。看门狗的作用是进程监听并管理, 如果监听的进程出现了问题,会把SystemServer杀死,而Zygote收到SystemServer被杀死之后,会把自己也杀死,然后Init会重新启动Zygote,Zygote再重新启动SystemServer。
而在startBootstrapServices中启动服务是通过mSystemServiceManager.startService(xxx.class)的方式,会通过反射获取服务实例,后续还会调用service.onStart方法(),向ServiceManager中注册当前启动的服务。这样client端才能通过Binder和Server端通信。
后续还会写Binder的文章,到时再一起讲ServiceManage
2.2.3 startCoreServices
Java
private void startCoreServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
t.traceBegin("startCoreServices");
// Service for system config
t.traceBegin("StartSystemConfigService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(SystemConfigService.class);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("StartBatteryService");
// Tracks the battery level. Requires LightService.
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BatteryService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Tracks application usage stats.
t.traceBegin("StartUsageService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(UsageStatsService.class);
mActivityManagerService.setUsageStatsManager(
LocalServices.getService(UsageStatsManagerInternal.class));
t.traceEnd();
// Tracks whether the updatable WebView is in a ready state and watches for update installs.
if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_WEBVIEW)) {
t.traceBegin("StartWebViewUpdateService");
mWebViewUpdateService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(WebViewUpdateService.class);
t.traceEnd();
}
// Tracks and caches the device state.
t.traceBegin("StartCachedDeviceStateService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(CachedDeviceStateService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Tracks cpu time spent in binder calls
t.traceBegin("StartBinderCallsStatsService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BinderCallsStatsService.LifeCycle.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Tracks time spent in handling messages in handlers.
t.traceBegin("StartLooperStatsService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(LooperStatsService.Lifecycle.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Manages apk rollbacks.
t.traceBegin("StartRollbackManagerService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(RollbackManagerService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Tracks native tombstones.
t.traceBegin("StartNativeTombstoneManagerService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(NativeTombstoneManagerService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Service to capture bugreports.
t.traceBegin("StartBugreportManagerService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BugreportManagerService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Service for GPU and GPU driver.
t.traceBegin("GpuService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(GpuService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// Handles system process requests for remotely provisioned keys & data.
t.traceBegin("StartRemoteProvisioningService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(RemoteProvisioningService.class);
t.traceEnd();
// TODO(b/277600174): Start CpuMonitorService on all builds and not just on debuggable
// builds once the Android JobScheduler starts using this service.
if (Build.IS_DEBUGGABLE || Build.IS_ENG) {
// Service for CPU monitor.
t.traceBegin("CpuMonitorService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(CpuMonitorService.class);
t.traceEnd();
}
t.traceEnd(); // startCoreServices
}在startCoreServices中,同样是通过SystemServiceManager::startService启动了很多服务,如SystemConfigService,BatteryService...
2.2.4 startOtherServices
Java
private void startOtherServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
t.traceBegin("startOtherServices");
mSystemServiceManager.updateOtherServicesStartIndex();
final Context context = mSystemContext;
DynamicSystemService dynamicSystem = null;
IStorageManager storageManager = null;
NetworkManagementService networkManagement = null;
VpnManagerService vpnManager = null;
VcnManagementService vcnManagement = null;
NetworkPolicyManagerService networkPolicy = null;
WindowManagerService wm = null;
NetworkTimeUpdateService networkTimeUpdater = null;
InputManagerService inputManager = null;
...
try {
...
t.traceBegin("StartInputManagerService");
inputManager = new InputManagerService(context);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("DeviceStateManagerService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(DeviceStateManagerService.class);
t.traceEnd();
if (!disableCameraService) {
t.traceBegin("StartCameraServiceProxy");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(CameraServiceProxy.class);
t.traceEnd();
}
t.traceBegin("StartWindowManagerService");
// WMS needs sensor service ready
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(t, SystemService.PHASE_WAIT_FOR_SENSOR_SERVICE);
// 启动WMS,WMS需要IMS的协助处理,因此会将IMS对象传入WMS中
wm = WindowManagerService.main(context, inputManager, !mFirstBoot,
new PhoneWindowManager(), mActivityManagerService.mActivityTaskManager);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE, wm, /* allowIsolated= */ false,
DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL | DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_HIGH
| DUMP_FLAG_PROTO);
ServiceManager.addService(Context.INPUT_SERVICE, inputManager,
/* allowIsolated= */ false, DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("SetWindowManagerService");
mActivityManagerService.setWindowManager(wm);
t.traceEnd();
t.traceBegin("WindowManagerServiceOnInitReady");
wm.onInitReady();
t.traceEnd();
...
t.traceBegin("StartInputManager");
inputManager.setWindowManagerCallbacks(wm.getInputManagerCallback());
// 启动InputManagerService
inputManager.start();
}
...
t.traceBegin("StartSystemUI");
try {
// 启动SystemUi
startSystemUi(context, windowManagerF);
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("starting System UI", e);
}
t.traceEnd();
t.traceEnd(); // startOtherServices
}
private static void startSystemUi(Context context, WindowManagerService windowManager) {
PackageManagerInternal pm = LocalServices.getService(PackageManagerInternal.class);
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setComponent(pm.getSystemUiServiceComponent());
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_DEBUG_TRIAGED_MISSING);
//Slog.d(TAG, "Starting service: " + intent);
context.startServiceAsUser(intent, UserHandle.SYSTEM);
windowManager.onSystemUiStarted();
}
// InputManagerService.java
public void start() {
Slog.i(TAG, "Starting input manager");
mNative.start();
// Add ourselves to the Watchdog monitors.
Watchdog.getInstance().addMonitor(this);
}
// com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
static void nativeStart(JNIEnv* env, jobject nativeImplObj) {
NativeInputManager* im = getNativeInputManager(env, nativeImplObj);
status_t result = im->getInputManager()->start();
if (result) {
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "Input manager could not be started.");
}
}在startOtherServices中,同样也是启动了很多服务,比较重要的有WMS, IMS等,最后还会启动SystemUI
2.2.5 startApexServices
Java
private void startApexServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
if (Flags.recoverabilityDetection()) {
// For debugging RescueParty
if (Build.IS_DEBUGGABLE
&& SystemProperties.getBoolean("debug.crash_system", false)) {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
t.traceBegin("startApexServices");
// TODO(b/192880996): get the list from "android" package, once the manifest entries
// are migrated to system manifest.
List<ApexSystemServiceInfo> services = ApexManager.getInstance().getApexSystemServices();
for (ApexSystemServiceInfo info : services) {
String name = info.getName();
String jarPath = info.getJarPath();
t.traceBegin("starting " + name);
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(jarPath)) {
mSystemServiceManager.startService(name);
} else {
mSystemServiceManager.startServiceFromJar(name, jarPath);
}
t.traceEnd();
}
// make sure no other services are started after this point
mSystemServiceManager.sealStartedServices();
t.traceEnd(); // startApexServices
}startApexServices其实就是去遍历List<ApexSystemServiceInfo>,启动此list中的services。
贴下官网APEX的图: 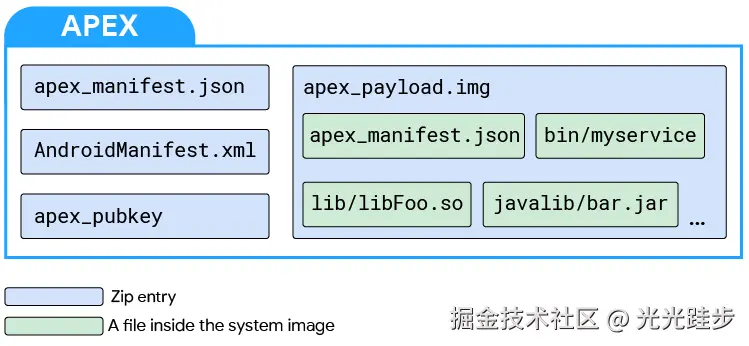
具体APEX的说明,请去官网了解: APEX 文件格式 | Android Open Source Project
这里就简单介绍下APEX
定义 :APEX(Android Pony EXpress)是从 Android 10 (Q) 开始引入的系统模块更新容器格式 。它与APK类似,但专为更新底层系统模块(如运行时库、硬件抽象层HAL)而设计。
目的 :用于支持无需完整OTA的系统模块动态更新。这解决了传统APK模型无法在系统启动早期加载、以及对底层模块更新不灵活的问题。
启动时机:在 startOtherServices 之后, 所有常规服务启动完成之后,会调用 startApexServices, 这避免 APEX 被正在初始化的核心服务所依赖,从而保证系统启动流程稳定。
三、小结
本文介绍了Andorid系统启动流程中的SystemServer,它创建System Context了,并启动各种服务,比如AMS, WMS,IMS等等,最后还启动SystemUi。
用一个时序图总结下SystemServer吧 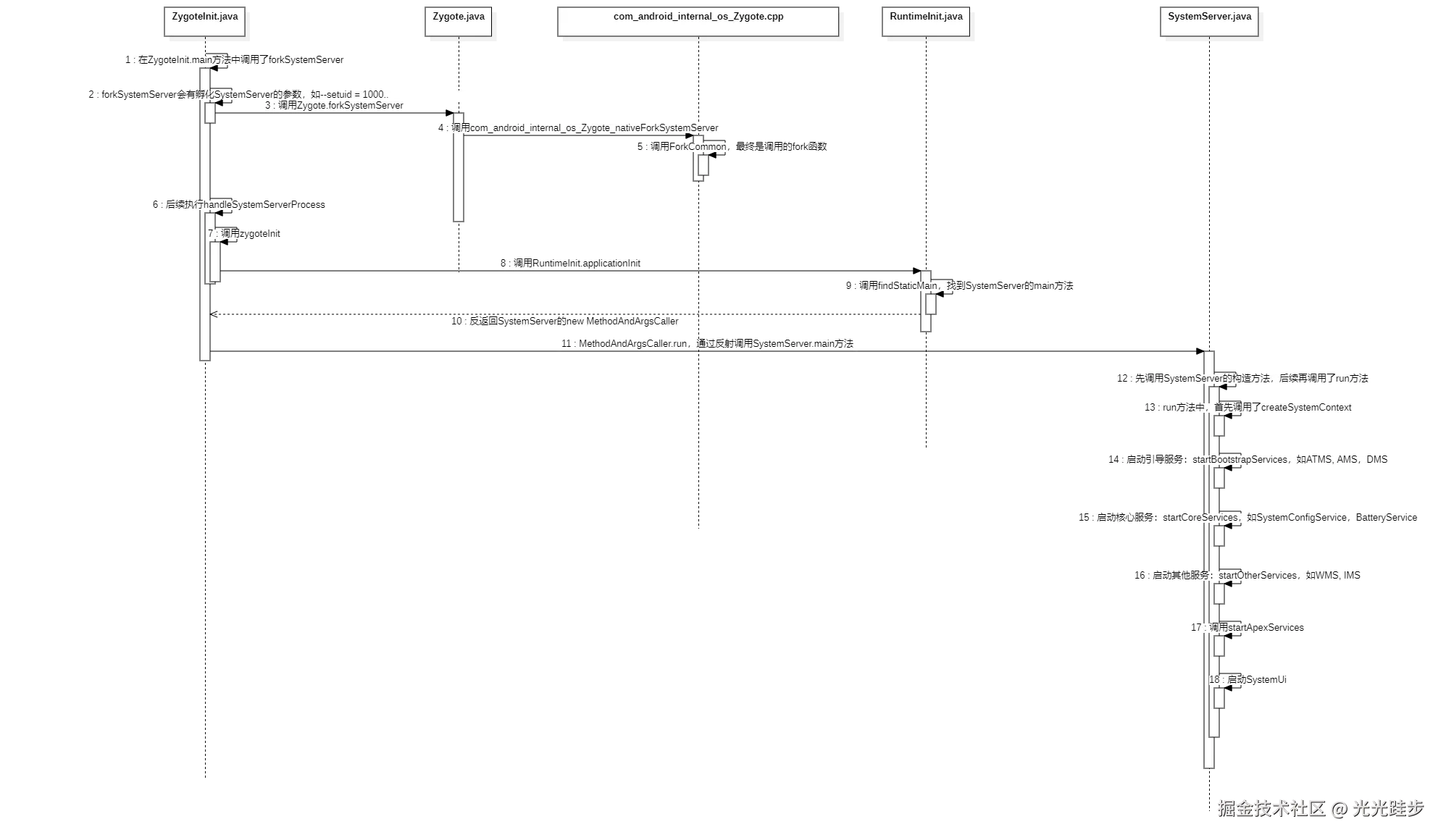
感谢阅读,希望本文对你有所帮助,如有任何不对的地方,欢迎大家指出。
四、参考资料
- 《Android进阶解密》
- APEX 文件格式 | Android Open Source Project