原型链是JavaScript中最重要的概念之一,本文将循序渐进地带你掌握这个核心概念!
文章目录
-
- [🤔 什么是原型链?](#🤔 什么是原型链?)
-
- [🎯 基本定义](#🎯 基本定义)
- [🐕 **生活化理解:宠物的"血统链"**](#🐕 生活化理解:宠物的"血统链")
- [🌟 核心概念](#🌟 核心概念)
- [🔍 核心概念:`proto` vs `prototype`](#🔍 核心概念:
__proto__vsprototype) -
- [🎯 **`prototype` 属性:构造函数的"模板"** 英文翻译为"原型"](#🎯
prototype属性:构造函数的"模板" 英文翻译为"原型") -
- [**什么是 `prototype`?**](#什么是
prototype?)
- [**什么是 `prototype`?**](#什么是
- [🔗 **`proto` 属性:对象的"寻根"指针**](#🔗
__proto__属性:对象的"寻根"指针) -
- [**什么是 `proto`?**](#什么是
__proto__?)
- [**什么是 `proto`?**](#什么是
- [🚨 **重要澄清:实例对象没有prototype属性!**](#🚨 重要澄清:实例对象没有prototype属性!)
- [💡 **关键区别:**](#💡 关键区别:)
- [🌟 **总结对比表**](#🌟 总结对比表)
- [🎯 **`prototype` 属性:构造函数的"模板"** 英文翻译为"原型"](#🎯
- [🏗️ 原型链的工作原理](#🏗️ 原型链的工作原理)
-
- [🎬 **完整的创建过程解析**](#🎬 完整的创建过程解析)
- [🔍 **属性查找过程**](#🔍 属性查找过程)
- [🎭 **设计原理**](#🎭 设计原理)
- [🎯 为什么需要原型链?](#🎯 为什么需要原型链?)
-
- [💡 设计初衷](#💡 设计初衷)
- [🤔 没有原型链会怎样?](#🤔 没有原型链会怎样?)
- [✅ 有了原型链的好处](#✅ 有了原型链的好处)
- [🎯 解决的核心问题](#🎯 解决的核心问题)
- [💻 实战演示:从简单到复杂](#💻 实战演示:从简单到复杂)
-
- [🧪 **基础演示**](#🧪 基础演示)
- [🧬 **继承演示**](#🧬 继承演示)
- [🔗 原型链查找机制](#🔗 原型链查找机制)
-
- [🔍 查找算法演示](#🔍 查找算法演示)
- [🎮 实际应用场景](#🎮 实际应用场景)
-
- [🎮 游戏角色系统](#🎮 游戏角色系统)
- [🛠️ 最佳实践](#🛠️ 最佳实践)
-
- [✅ 正确的继承方式](#✅ 正确的继承方式)
- [❌ 常见错误](#❌ 常见错误)
- [🔧 现代ES6+写法](#🔧 现代ES6+写法)
- [📈 总结](#📈 总结)
-
- [🎯 核心要点](#🎯 核心要点)
- [🎯 **记忆口诀**](#🎯 记忆口诀)
- [💡 **学习建议**](#💡 学习建议)
- [🌟 **最终理解**](#🌟 最终理解)
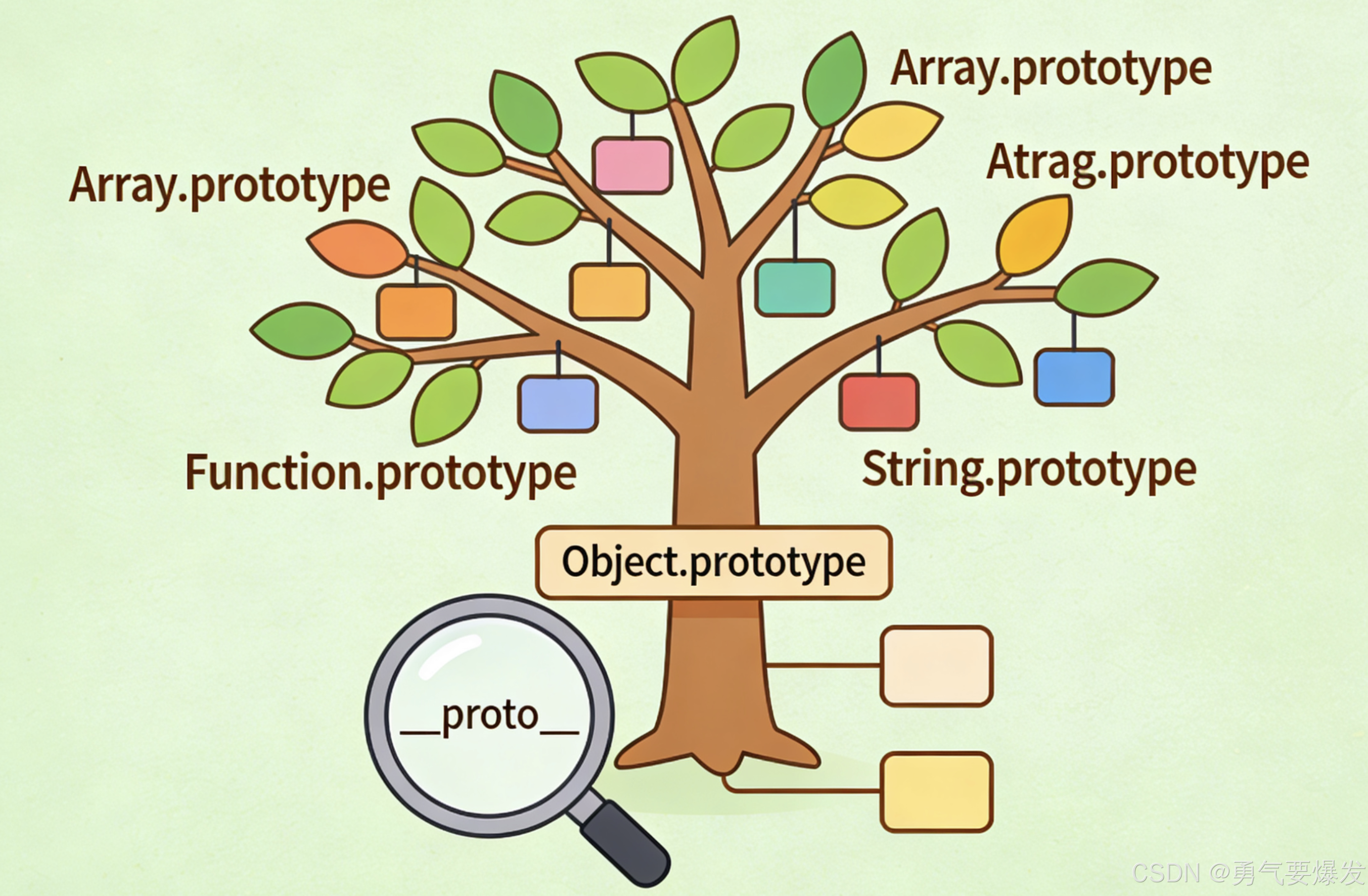
🤔 什么是原型链?
🎯 基本定义
原型链 :JavaScript中对象通过原型(prototype)连接起来的链式结构,用于实现属性和方法的继承。
🐕 生活化理解:宠物的"血统链"
想象一下宠物的血统关系:
🐕 旺财(具体的狗)
↓ 原型链
🐕🦺 哈士奇(品种特征)
↓ 原型链
🐕 狗(物种特征)
↓ 原型链
🐾 动物(生物特征)
↓ 原型链
🌍 生物(最基本特征)
↓ 原型链
null (链的终点)对应到JavaScript中:
- 旺财 = 具体的对象实例
myDog - 哈士奇 = 构造函数的原型
Husky.prototype - 狗 = 父类原型
Dog.prototype - 动物 = 更高层的父类原型
Animal.prototype - 生物 = 根对象原型
Object.prototype - null = 原型链的终点
🌟 核心概念
每个JavaScript对象都有一个隐藏的属性 __proto__(它是一个指针),它指向该对象的原型。这样就形成了一条链:
对象 → 原型对象 → 原型的原型 → ... → null🔍 核心概念:__proto__ vs prototype
🎯 prototype 属性:构造函数的"模板" 英文翻译为"原型"
什么是 prototype?
- 只有函数才有
prototype属性 - 它是一个对象,存储了将来实例对象要继承的属性和方法
- 相当于一个"模板"或"蓝图"
javascript
// 🏭 构造函数 = 工厂
function Husky(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 📋 prototype = 工厂的生产模板
Husky.prototype.breed = '哈士奇';
Husky.prototype.howl = function() {
console.log(`${this.name} 在嚎叫: 嗷呜~~~`);
};
// 🔍 查看prototype的内容
console.log('Husky.prototype:', Husky.prototype);
// 输出: { breed: '哈士奇', howl: function, constructor: Husky }🔗 __proto__ 属性:对象的"寻根"指针
什么是 __proto__?
- 每个对象都有
__proto__属性 - 它是一个指针,指向该对象的原型
- 用于在原型链上查找属性和方法
javascript
// 🐕 创建实例
const myDog = new Husky('旺财');
// 🔍 __proto__ = 寻根指针
console.log('myDog.__proto__:', myDog.__proto__);
// 输出: { breed: '哈士奇', howl: function, constructor: Husky }
// ✅ 验证关系
console.log(myDog.__proto__ === Husky.prototype); // true🚨 重要澄清:实例对象没有prototype属性!
javascript
// ❌ 错误理解
myDog.prototype.prototype // undefined.prototype → 报错!
// ✅ 正确的原型链访问方式
myDog.__proto__ // → Husky.prototype (哈士奇特征)
myDog.__proto__.__proto__ // → Dog.prototype (狗特征)
myDog.__proto__.__proto__.__proto__ // → Animal.prototype (动物特征)💡 关键区别:
- 实例对象 (如
myDog):只有__proto__属性,没有prototype属性 - 构造函数 (如
Husky):既有prototype属性,也有__proto__属性
🌟 总结对比表
| 特性 | prototype |
__proto__ |
|---|---|---|
| 拥有者 | 只有函数 | 所有对象 |
| 作用 | 存储共享属性和方法 | 指向对象的原型 |
| 类型 | 对象 | 指针/引用 |
| 用途 | 定义继承内容 | 查找继承内容 |
| 比喻 | 哈士奇(哈士奇品种的基因库) | 旺财脖子上铭牌"品种:哈士奇"(旺财的血统追溯线) |
🏗️ 原型链的工作原理
🎬 完整的创建过程解析
javascript
// 步骤1: 定义构造函数
function Husky(name) {
this.name = name; // 实例属性
}
// 步骤2: 在prototype上添加共享方法
Husky.prototype.breed = '哈士奇';
Husky.prototype.howl = function() {
console.log(`${this.name} 在嚎叫`);
};
// 步骤3: 创建实例(new的魔法)
const myDog = new Husky('旺财');
// 🔍 new操作符做了什么?
// 1. 创建空对象: const myDog = {};
// 2. 设置__proto__: myDog.__proto__ = Husky.prototype;
// 3. 执行构造函数: Husky.call(myDog, '旺财');
// 4. 返回对象: return myDog;
console.log('=== 验证结果 ===');
console.log('myDog.name:', myDog.name); // '旺财' (实例属性)
console.log('myDog.breed:', myDog.breed); // '哈士奇' (从prototype继承)
console.log('myDog.howl:', myDog.howl); // function (从prototype继承)🔍 属性查找过程
当我们访问 myDog.breed 时,JavaScript的查找路径:
- myDog对象本身 ❌ 没有breed属性
- myDog.__ proto__ (即Husky.prototype) ✅ 找到breed属性
🎭 设计原理
角色分工明确
- 构造函数:负责创建实例特有的属性
- prototype:负责存储所有实例共享的方法
- proto:负责连接到原型,实现继承
验证共享机制
javascript
const dog1 = new Husky('旺财');
const dog2 = new Husky('二哈');
// ✅ 每个实例有自己的name属性
console.log(dog1.name !== dog2.name); // true
// ✅ 所有实例共享同一个howl方法
console.log(dog1.howl === dog2.howl); // true🎯 为什么需要原型链?
💡 设计初衷
JavaScript创造原型链的根本原因是为了解决代码复用 和继承的问题。
🤔 没有原型链会怎样?
javascript
// ❌ 没有原型链的世界
function createPerson1(name) {
return {
name: name,
sayHello: function() { console.log(`Hello, I'm ${this.name}`); },
walk: function() { console.log(`${this.name} is walking`); },
sleep: function() { console.log(`${this.name} is sleeping`); }
};
}
function createPerson2(name) {
return {
name: name,
sayHello: function() { console.log(`Hello, I'm ${this.name}`); }, // 重复代码
walk: function() { console.log(`${this.name} is walking`); }, // 重复代码
sleep: function() { console.log(`${this.name} is sleeping`); } // 重复代码
};
}
// 每个对象都有自己的方法副本,浪费内存!✅ 有了原型链的好处
javascript
// ✅ 有原型链的世界
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 方法只定义一次,所有实例共享
Person.prototype.sayHello = function() {
console.log(`Hello, I'm ${this.name}`);
};
Person.prototype.walk = function() {
console.log(`${this.name} is walking`);
};
Person.prototype.sleep = function() {
console.log(`${this.name} is sleeping`);
};
// 所有实例共享相同的方法,节省内存
const person1 = new Person('张三');
const person2 = new Person('李四');
console.log(person1.sayHello === person2.sayHello); // true - 同一个方法!🎯 解决的核心问题
- 内存效率 💾 - 方法只存储一份,所有实例共享
- 代码复用 🔄 - 避免重复定义相同的方法
- 继承机制 🧬 - 实现面向对象的继承关系
💻 实战演示:从简单到复杂
🧪 基础演示
javascript
// 1. 创建构造函数
function Animal(name) {
this.name = name;
this.type = 'animal';
}
// 2. 在原型上添加方法
Animal.prototype.eat = function() {
console.log(`${this.name} is eating`);
};
Animal.prototype.sleep = function() {
console.log(`${this.name} is sleeping`);
};
// 3. 创建实例
const dog = new Animal('旺财');
// 4. 验证原型链关系
console.log('=== 原型链关系验证 ===');
console.log('dog.__proto__ === Animal.prototype:', dog.__proto__ === Animal.prototype);
console.log('Animal.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype:', Animal.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype);
console.log('Object.prototype.__proto__ === null:', Object.prototype.__proto__ === null);
// 5. 属性查找演示
console.log('\n=== 属性查找演示 ===');
console.log('dog.name:', dog.name); // 自身属性
console.log('dog.type:', dog.type); // 自身属性
dog.eat(); // 原型方法
dog.sleep(); // 原型方法
console.log('dog.toString():', dog.toString()); // Object.prototype的方法🧬 继承演示
javascript
// 📊 原型链继承关系图
/*
┌─────────────────────┐
│ Object.prototype │ ← 所有对象的根原型
│ (toString, etc.) │
└──────────┬──────────┘
│ __proto__
┌─────────────────────┐
│ Animal.prototype │ ← 父类原型对象
│ { eat: function } │
└──────────┬──────────┘
│ __proto__
┌─────────────────────┐
│ Dog.prototype │ ← 子类原型对象
│ { bark: function } │
│ constructor: Dog │
└──────────┬──────────┘
│ __proto__
┌─────────────────────┐
│ myDog │ ← 实例对象
│ name: '旺财' │
│ breed: '金毛' │
└─────────────────────┘
🔍 方法查找路径 (myDog.eat()):
myDog → Dog.prototype → Animal.prototype ✅ 找到eat方法
🎯 继承关系:
myDog instanceof Dog → true (直接继承)
myDog instanceof Animal → true (原型链继承)
myDog instanceof Object → true (最终继承)
*/
// 🐾 步骤1:定义父类(动物)
function Animal(name) {
// 所有动物都有名字这个基本属性
this.name = name;
}
// 🍽️ 步骤2:给父类添加共同行为(所有动物都会吃)
Animal.prototype.eat = function() {
console.log(`${this.name} is eating`);
};
// 🐕 步骤3:定义子类(狗)
function Dog(name, breed) {
// 🔗 关键:调用父类构造函数,继承父类的属性
// Animal.call(this, name) 相当于在Dog中执行 this.name = name
Animal.call(this, name);
// 🆕 子类特有的属性
this.breed = breed;
}
// 🧬 步骤4:建立原型链继承关系(最关键的一步)
// Object.create(Animal.prototype) 创建一个新对象,其__proto__指向Animal.prototype
// 这样Dog的实例就能通过原型链访问到Animal的方法
Dog.prototype = Object.create(Animal.prototype);
// 🔧 步骤5:修复constructor指向
// 因为上一步覆盖了Dog.prototype,所以需要手动设置constructor
// 让Dog.prototype.constructor重新指向Dog构造函数
Dog.prototype.constructor = Dog;
// 🎵 步骤6:给子类添加特有方法
Dog.prototype.bark = function() {
console.log(`${this.name} is barking`);
};
// 🎉 步骤7:创建实例并测试继承
const myDog = new Dog('旺财', '金毛');
// 📊 继承验证:
myDog.eat(); // 继承自Animal - 输出: 旺财 is eating
myDog.bark(); // Dog自己的方法 - 输出: 旺财 is barking
// 🔍 原型链查找过程:
// myDog.eat() 的查找路径:
// 1. myDog对象本身 ❌ 没有eat方法
// 2. myDog.__proto__ (即Dog.prototype) ❌ 没有eat方法
// 3. Dog.prototype.__proto__ (即Animal.prototype) ✅ 找到eat方法!
console.log('继承关系验证:');
console.log('myDog instanceof Dog:', myDog instanceof Dog); // true
console.log('myDog instanceof Animal:', myDog instanceof Animal); // true
console.log('myDog.name:', myDog.name); // 旺财 (继承自Animal)
console.log('myDog.breed:', myDog.breed); // 金毛 (Dog特有属性)🔗 原型链查找机制
🔍 查找算法演示
javascript
// 演示属性查找的完整过程
function demonstratePropertyLookup() {
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.species = 'Homo sapiens';
Person.prototype.greet = function() {
return `Hi, I'm ${this.name}`;
};
const alice = new Person('Alice');
// 查找 name 属性
console.log('查找 alice.name:');
console.log('1. 在 alice 自身查找 name ✅ 找到:', alice.name);
// 查找 species 属性
console.log('\n查找 alice.species:');
console.log('1. 在 alice 自身查找 species ❌ 未找到');
console.log('2. 在 Person.prototype 查找 species ✅ 找到:', alice.species);
// 查找 toString 方法
console.log('\n查找 alice.toString:');
console.log('1. 在 alice 自身查找 toString ❌ 未找到');
console.log('2. 在 Person.prototype 查找 toString ❌ 未找到');
console.log('3. 在 Object.prototype 查找 toString ✅ 找到');
console.log('结果:', alice.toString());
// 查找不存在的属性
console.log('\n查找 alice.nonExistent:');
console.log('1. 在 alice 自身查找 ❌ 未找到');
console.log('2. 在 Person.prototype 查找 ❌ 未找到');
console.log('3. 在 Object.prototype 查找 ❌ 未找到');
console.log('4. 到达 null,查找结束');
console.log('结果:', alice.nonExistent); // undefined
}
demonstratePropertyLookup();🎮 实际应用场景
🎮 游戏角色系统
javascript
// 基础角色类
function Character(name, health) {
this.name = name;
this.health = health;
this.level = 1;
}
Character.prototype.attack = function() {
return `${this.name} 发起攻击!`;
};
Character.prototype.heal = function(amount) {
this.health += amount;
console.log(`${this.name} 恢复了 ${amount} 点生命值`);
};
// 战士类
function Warrior(name, health, strength) {
Character.call(this, name, health);
this.strength = strength;
this.weapon = '剑';
}
Warrior.prototype = Object.create(Character.prototype);
Warrior.prototype.constructor = Warrior;
Warrior.prototype.powerAttack = function() {
return `${this.name} 使用 ${this.weapon} 发起强力攻击!造成 ${this.strength * 2} 点伤害!`;
};
// 法师类
function Mage(name, health, mana) {
Character.call(this, name, health);
this.mana = mana;
this.spells = ['火球术', '冰箭术'];
}
Mage.prototype = Object.create(Character.prototype);
Mage.prototype.constructor = Mage;
Mage.prototype.castSpell = function(spellIndex) {
if (this.mana >= 10) {
this.mana -= 10;
const spell = this.spells[spellIndex] || this.spells[0];
return `${this.name} 施放了 ${spell}!`;
} else {
return `${this.name} 魔法值不足!`;
}
};
// 创建角色
const warrior = new Warrior('亚瑟', 100, 15);
const mage = new Mage('梅林', 80, 50);
// 测试继承的方法
console.log(warrior.attack()); // 继承自 Character
console.log(warrior.powerAttack()); // Warrior 特有方法
warrior.heal(20); // 继承自 Character
console.log(mage.attack()); // 继承自 Character
console.log(mage.castSpell(0)); // Mage 特有方法
mage.heal(15); // 继承自 Character🛠️ 最佳实践
✅ 正确的继承方式
javascript
// ✅ 推荐:使用 Object.create()
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Parent.prototype.sayHello = function() {
return `Hello, I'm ${this.name}`;
};
function Child(name, age) {
Parent.call(this, name); // 调用父构造函数
this.age = age;
}
// 正确设置原型链
Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype);
Child.prototype.constructor = Child;
Child.prototype.sayAge = function() {
return `I'm ${this.age} years old`;
};❌ 常见错误
javascript
// ❌ 错误1:直接赋值原型
Child.prototype = Parent.prototype; // 会影响父类原型
// ❌ 错误2:使用 new 创建原型
Child.prototype = new Parent(); // 会调用父构造函数
// ❌ 错误3:忘记设置 constructor
// Child.prototype.constructor 指向错误🔧 现代ES6+写法
javascript
// ES6 Class 语法(推荐)
class Animal {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
speak() {
return `${this.name} makes a sound`;
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
constructor(name, breed) {
super(name); // 调用父类构造函数
this.breed = breed;
}
speak() {
return `${this.name} barks`;
}
getBreed() {
return `${this.name} is a ${this.breed}`;
}
}
const myDog = new Dog('旺财', '金毛');
console.log(myDog.speak()); // 旺财 barks
console.log(myDog.getBreed()); // 旺财 is a 金毛📈 总结
🎯 核心要点
| 概念 | 作用 | 生活例子 | 关键点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原型链 | 实现继承和属性查找 | 家族血统 | 从子到父的链式查找 |
| prototype | 存储共享方法 | 家族族谱 | 只有函数才有 |
| proto | 指向原型对象 | 血缘关系 | 所有对象都有 |
| constructor | 指向构造函数 | 知道"父亲" | 标识对象来源 |
🎯 记忆口诀
prototype:我是模板,定义别人继承什么__proto__:我是指针,指向我要继承的模板
💡 学习建议
- 先理解概念 :搞清楚
prototype和__proto__的区别 - 动手实践:写代码验证原型链关系
- 循序渐进:从简单的单层继承到复杂的多层继承
- 现代写法:掌握ES6 Class语法,但理解底层原理
- 实际应用:在项目中合理使用继承,避免过度设计
🌟 最终理解
原型链就像是JavaScript对象的"家族关系网",每个对象都知道自己的"祖先"是谁,当自己没有某个特征时,就去问祖先要。这种设计让JavaScript既保持了灵活性,又实现了代码的复用和继承!
🎉 恭喜!你已经掌握了JavaScript原型链的核心概念!