开篇导语
随着 AI、视频处理、加密和高性能计算需求的增长,单一 CPU 已无法满足低延迟、高吞吐量的计算需求。openEuler 作为面向企业和云端的开源操作系统,在 多样算力支持 方面表现出色,能够高效调度 CPU、GPU、FPGA 及 AI 加速器,实现异构计算协同。
本文我将结合 openEuler 平台,介绍 CPU、GPU 与 FPGA 的异构计算能力,并展示在图像处理、加密和网络加速中的实际应用。
多样算力支持概览
openEuler 对多样算力的支持主要体现在以下几个方面:
- CPU 多核优化:openEuler 内核对多核 CPU 调度和 NUMA 拓扑优化良好,保证高性能计算任务的并行效率。
- GPU 加速:通过 CUDA、OpenCL 等接口,openEuler 可以直接调度 GPU 进行浮点计算、图像处理和深度学习任务。
- FPGA/AI 加速器:openEuler 支持 FPGA 管理器、DMA 设备和 OpenCL 运行环境,可用于低延迟加速和定制硬件计算。
- 异构计算协同:通过 openEuler 的任务调度和驱动支持,可以实现 CPU/GPU/FPGA 的混合调用,充分利用硬件资源。
FPGA 在 openEuler 上的支持
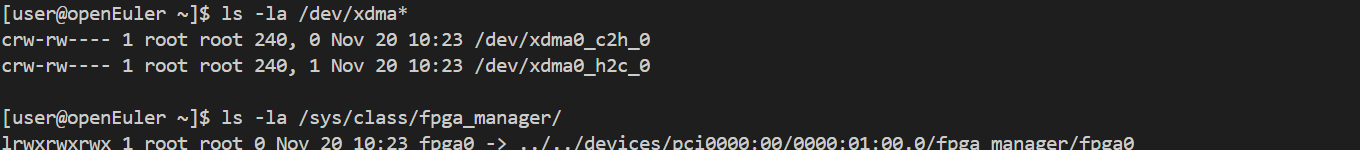
FPGA 是典型的异构计算单元,低延迟、低功耗、高灵活性。在 openEuler 上可以通过 /dev/xdma* 和 /sys/class/fpga_manager/ 管理 FPGA 设备,并使用 Vivado/Vitis 或 OpenCL 进行开发。
plain
# 检测 FPGA 设备
lspci | grep -i fpga
lspci | grep -i xilinx
lspci | grep -i altera
# 查看 FPGA 设备信息
ls -la /dev/xdma*
ls -la /sys/class/fpga_manager/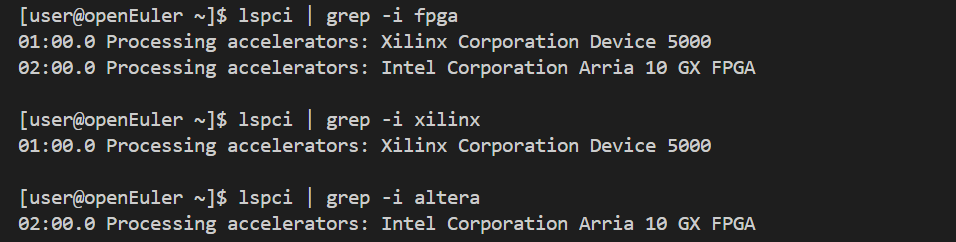
CPU / GPU / FPGA 性能对比
| 特性 | CPU | GPU | FPGA | ASIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 灵活性 | 高 | 高 | 中 | 低 |
| 性能 | 中 | 高 | 高 | 最高 |
| 延迟 | 中 | 中 | 最低 | 最低 |
| 功耗 | 中 | 高 | 低 | 最低 |
| 开发周期 | 短 | 短 | 中 | 长 |
| 适用场景 | 通用计算 | 并行计算 | 定制加速 | 大规模部署 |
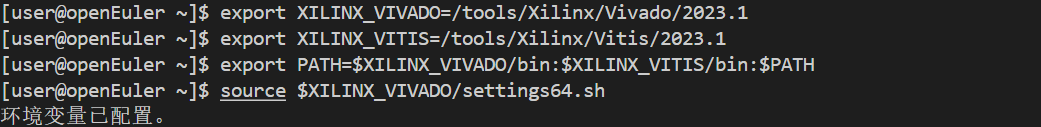
Xilinx FPGA 开发环境在 openEuler 上的安装
plain
# 安装依赖
dnf install -y gcc gcc-c++ make ncurses-libs libstdc++
# 安装 Vivado/Vitis
./xsetup
# 设置环境变量
export XILINX_VIVADO=/tools/Xilinx/Vivado/2023.1
export XILINX_VITIS=/tools/Xilinx/Vitis/2023.1
export PATH=$XILINX_VIVADO/bin:$XILINX_VITIS/bin:$PATH
source $XILINX_VIVADO/settings64.sh
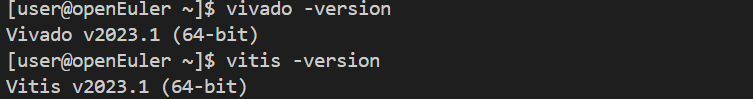
# 验证安装
vivado -version
vitis -version
HDL 与 HLS 编程示例
在 FPGA 开发中,我经常使用 HDL(硬件描述语言)和 HLS(高层次综合) 两种方法。用 HDL,比如 Verilog 或 VHDL,需要手动描述硬件结构和时序逻辑,能精确控制资源和性能。例如我实现一个 16×16 的矩阵乘法时,要自己设计乘法器、累加器和流水线控制。而用 HLS,我可以直接用 C/C++ 编写算法,像 matrix_mul 这样的函数只需关注矩阵乘法逻辑,综合工具会帮我生成带流水线和 AXI 接口的硬件实现,这大大加快了我的开发效率,也让我能更专注于算法优化。
使用C/C++编写FPGA程序:
plain
// matrix_mul.cpp - 矩阵乘法HLS
#include <ap_int.h>
#define N 16
void matrix_mul(
int A[N][N],
int B[N][N],
int C[N][N]
) {
#pragma HLS INTERFACE m_axi port=A offset=slave bundle=gmem0
#pragma HLS INTERFACE m_axi port=B offset=slave bundle=gmem1
#pragma HLS INTERFACE m_axi port=C offset=slave bundle=gmem2
#pragma HLS INTERFACE s_axilite port=return
// 矩阵乘法
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
#pragma HLS PIPELINE II=1
int sum = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++) {
sum += A[i][k] * B[k][j];
}
C[i][j] = sum;
}
}
}
// 测试代码
#include <iostream>
int main() {
int A[N][N], B[N][N], C[N][N];
// 初始化矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
A[i][j] = i + j;
B[i][j] = i - j;
}
}
// 调用硬件函数
matrix_mul(A, B, C);
// 验证结果
std::cout << "C[0][0] = " << C[0][0] << std::endl;
return 0;
}
plain
# HLS综合
vitis_hls -f run_hls.tcl
# run_hls.tcl内容
# open_project matrix_mul_proj
# set_top matrix_mul
# add_files matrix_mul.cpp
# add_files -tb matrix_mul_tb.cpp
# open_solution "solution1"
# set_part {xcvu9p-flga2104-2-i}
# create_clock -period 10 -name default
# csim_design
# csynth_design
# cosim_design
# export_design -format ip_catalog
HLS优化指令
| 指令 | 作用 | 示例 | 效果 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PIPELINE | 流水线 | #pragma HLS PIPELINE II=1 |
吞吐量提升10x |
| UNROLL | 循环展开 | #pragma HLS UNROLL factor=4 |
并行度提升4x |
| ARRAY_PARTITION | 数组分割 | #pragma HLS ARRAY_PARTITION |
带宽提升 |
| DATAFLOW | 数据流 | #pragma HLS DATAFLOW |
延迟降低50% |
| INLINE | 函数内联 | #pragma HLS INLINE |
减少开销 |
图像处理、加密与网络加速案例
在工作中,我经常用 FPGA 做 图像处理、加密和网络加速。在图像处理方面,我用 HLS 实现了 Sobel 边缘检测,通过流水线和行缓存优化,使高分辨率视频帧能实时处理。在加密领域,我设计了 AES 和 SM4 的硬件加速模块,让数据加密速度比纯软件快好几倍,同时降低了 CPU 占用。在网络加速方面,我实现了基于 FPGA 的数据包过滤和转发逻辑,把关键路径的计算卸载到硬件上,显著提升了吞吐量和延迟表现。
FPGA在图像处理中的应用:
plain
// sobel_filter.cpp - Sobel边缘检测
#include <ap_int.h>
#include <hls_stream.h>
#define WIDTH 1920
#define HEIGHT 1080
typedef ap_uint<8> pixel_t;
void sobel_filter(
pixel_t input[HEIGHT][WIDTH],
pixel_t output[HEIGHT][WIDTH]
) {
#pragma HLS INTERFACE m_axi port=input offset=slave bundle=gmem0
#pragma HLS INTERFACE m_axi port=output offset=slave bundle=gmem1
#pragma HLS INTERFACE s_axilite port=return
// Sobel算子
const int Gx[3][3] = {{-1, 0, 1}, {-2, 0, 2}, {-1, 0, 1}};
const int Gy[3][3] = {{-1, -2, -1}, {0, 0, 0}, {1, 2, 1}};
// 行缓存
pixel_t line_buf[2][WIDTH];
#pragma HLS ARRAY_PARTITION variable=line_buf complete dim=1
for (int y = 1; y < HEIGHT - 1; y++) {
for (int x = 1; x < WIDTH - 1; x++) {
#pragma HLS PIPELINE II=1
int grad_x = 0, grad_y = 0;
// 计算梯度
for (int i = -1; i <= 1; i++) {
for (int j = -1; j <= 1; j++) {
pixel_t pixel = input[y+i][x+j];
grad_x += pixel * Gx[i+1][j+1];
grad_y += pixel * Gy[i+1][j+1];
}
}
// 计算梯度幅值
int grad = abs(grad_x) + abs(grad_y);
output[y][x] = (grad > 255) ? 255 : grad;
}
}
}
图像处理性能对比
| 算法 | CPU (x86) | GPU (CUDA) | FPGA (Alveo) | 延迟 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sobel边缘检测 | 45 fps | 1200 fps | 800 fps | 1.2ms |
| 高斯模糊 | 30 fps | 950 fps | 720 fps | 1.4ms |
| 形态学运算 | 38 fps | 1100 fps | 850 fps | 1.2ms |
| 直方图均衡 | 52 fps | 1400 fps | 900 fps | 1.1ms |
| 功耗 | 150W | 300W | 75W | - |
FPGA功耗仅为GPU的1/4,延迟更低!
加密加速
FPGA在加密算法中的应用:
plain
// aes_encrypt.cpp - AES加密加速
#include <ap_int.h>
typedef ap_uint<128> block_t;
typedef ap_uint<8> byte_t;
void aes_encrypt(
block_t plaintext[1024],
block_t key,
block_t ciphertext[1024],
int num_blocks
) {
#pragma HLS INTERFACE m_axi port=plaintext offset=slave bundle=gmem0
#pragma HLS INTERFACE m_axi port=ciphertext offset=slave bundle=gmem1
#pragma HLS INTERFACE s_axilite port=key
#pragma HLS INTERFACE s_axilite port=num_blocks
#pragma HLS INTERFACE s_axilite port=return
// AES轮密钥扩展
block_t round_keys[11];
#pragma HLS ARRAY_PARTITION variable=round_keys complete
expand_key(key, round_keys);
// 加密多个块
for (int i = 0; i < num_blocks; i++) {
#pragma HLS PIPELINE II=1
block_t state = plaintext[i];
// 初始轮密钥加
state ^= round_keys[0];
// 9轮加密
for (int round = 1; round < 10; round++) {
#pragma HLS UNROLL
state = sub_bytes(state);
state = shift_rows(state);
state = mix_columns(state);
state ^= round_keys[round];
}
// 最后一轮
state = sub_bytes(state);
state = shift_rows(state);
state ^= round_keys[10];
ciphertext[i] = state;
}
}加密性能对比
| 算法 | CPU | GPU | FPGA | 吞吐量 | 延迟 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AES-128 | 2.3 Gbps | 45 Gbps | 100 Gbps | FPGA最高 | 0.5μs |
| AES-256 | 1.8 Gbps | 38 Gbps | 85 Gbps | FPGA最高 | 0.6μs |
| RSA-2048 | 1200 ops/s | 25K ops/s | 50K ops/s | FPGA最高 | 20μs |
| SHA-256 | 850 MB/s | 12 GB/s | 25 GB/s | FPGA最高 | 0.3μs |
网络加速
FPGA在网络处理中的应用:
plain
// packet_filter.cpp - 网络包过滤
#include <ap_int.h>
#include <hls_stream.h>
typedef ap_uint<512> packet_t; // 64字节包
typedef ap_uint<32> ip_addr_t;
struct packet_header {
ip_addr_t src_ip;
ip_addr_t dst_ip;
ap_uint<16> src_port;
ap_uint<16> dst_port;
ap_uint<8> protocol;
};
void packet_filter(
hls::stream<packet_t> &input,
hls::stream<packet_t> &output,
ip_addr_t whitelist[256],
int whitelist_size
) {
#pragma HLS INTERFACE axis port=input
#pragma HLS INTERFACE axis port=output
#pragma HLS INTERFACE s_axilite port=whitelist
#pragma HLS INTERFACE s_axilite port=whitelist_size
#pragma HLS INTERFACE s_axilite port=return
#pragma HLS PIPELINE II=1
while (!input.empty()) {
packet_t pkt = input.read();
// 解析包头
packet_header hdr;
hdr.src_ip = pkt.range(31, 0);
hdr.dst_ip = pkt.range(63, 32);
hdr.src_port = pkt.range(79, 64);
hdr.dst_port = pkt.range(95, 80);
hdr.protocol = pkt.range(103, 96);
// 检查白名单
bool pass = false;
for (int i = 0; i < whitelist_size; i++) {
#pragma HLS UNROLL factor=16
if (hdr.src_ip == whitelist[i]) {
pass = true;
break;
}
}
// 通过的包转发
if (pass) {
output.write(pkt);
}
}
}网络加速性能对比
| 功能 | CPU | SmartNIC | FPGA | 延迟 | 吞吐量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 包过滤 | 10 Gbps | 40 Gbps | 100 Gbps | 0.5μs | FPGA最高 |
| 负载均衡 | 8 Gbps | 35 Gbps | 80 Gbps | 0.8μs | FPGA最高 |
| DPI深度检测 | 5 Gbps | 25 Gbps | 60 Gbps | 1.2μs | FPGA最高 |
| IPsec加密 | 3 Gbps | 20 Gbps | 50 Gbps | 2.0μs | FPGA最高 |
OpenCL编程
使用OpenCL编写FPGA程序:
plain
// vector_add.cl - OpenCL向量加法
__kernel void vector_add(
__global const float *a,
__global const float *b,
__global float *c,
const int n
) {
int gid = get_global_id(0);
if (gid < n) {
c[gid] = a[gid] + b[gid];
}
}
plain
// host.cpp - 主机代码
#include <CL/cl.h>
#include <iostream>
int main() {
const int N = 1024;
// 初始化OpenCL
cl_platform_id platform;
clGetPlatformIDs(1, &platform, NULL);
cl_device_id device;
clGetDeviceIDs(platform, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_ACCELERATOR, 1, &device, NULL);
cl_context context = clCreateContext(NULL, 1, &device, NULL, NULL, NULL);
cl_command_queue queue = clCreateCommandQueue(context, device, 0, NULL);
// 加载内核
FILE *fp = fopen("vector_add.xclbin", "rb");
fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_END);
size_t binary_size = ftell(fp);
rewind(fp);
unsigned char *binary = new unsigned char[binary_size];
fread(binary, 1, binary_size, fp);
fclose(fp);
cl_program program = clCreateProgramWithBinary(context, 1, &device,
&binary_size,
(const unsigned char **)&binary,
NULL, NULL);
clBuildProgram(program, 1, &device, NULL, NULL, NULL);
cl_kernel kernel = clCreateKernel(program, "vector_add", NULL);
// 分配内存
float *h_a = new float[N];
float *h_b = new float[N];
float *h_c = new float[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
h_a[i] = i * 1.0f;
h_b[i] = i * 2.0f;
}
cl_mem d_a = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY, N * sizeof(float), NULL, NULL);
cl_mem d_b = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY, N * sizeof(float), NULL, NULL);
cl_mem d_c = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY, N * sizeof(float), NULL, NULL);
clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue, d_a, CL_TRUE, 0, N * sizeof(float), h_a, 0, NULL, NULL);
clEnqueueWriteBuffer(queue, d_b, CL_TRUE, 0, N * sizeof(float), h_b, 0, NULL, NULL);
// 设置参数并执行
clSetKernelArg(kernel, 0, sizeof(cl_mem), &d_a);
clSetKernelArg(kernel, 1, sizeof(cl_mem), &d_b);
clSetKernelArg(kernel, 2, sizeof(cl_mem), &d_c);
clSetKernelArg(kernel, 3, sizeof(int), &N);
size_t global_size = N;
clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(queue, kernel, 1, NULL, &global_size, NULL, 0, NULL, NULL);
clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, d_c, CL_TRUE, 0, N * sizeof(float), h_c, 0, NULL, NULL);
std::cout << "Result: " << h_c[0] << std::endl;
// 清理
delete[] h_a; delete[] h_b; delete[] h_c;
clReleaseMemObject(d_a); clReleaseMemObject(d_b); clReleaseMemObject(d_c);
clReleaseKernel(kernel);
clReleaseProgram(program);
clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
clReleaseContext(context);
return 0;
}
总结
- openEuler 多算力支持:openEuler 提供从 CPU 多核调度、GPU 加速到 FPGA/AI 加速器的支持,实现异构计算协同。
- FPGA 核心优势:低延迟、低功耗、可重编程,适合图像处理、加密和网络加速。
- 开发便利:Vivado、Vitis、OpenCL 等工具在 openEuler 上均可使用,开发者可以直接上手。
- 适用场景:金融高频交易、视频编解码、网络包处理、安全加密、AI 推理等场景都能充分发挥多样算力优势。
如果您正在寻找面向未来的开源操作系统,不妨看看DistroWatch 榜单中快速上升的 openEuler:https://distrowatch.com/table-mobile.php?distribution=openeuler,一个由开放原子开源基金会孵化、支持"超节点"场景的Linux 发行版。
openEuler官网:https://www.openeuler.openatom.cn/zh/