有其他语言基础的快速入门GO
helloworld.go
Go
package main
// fmt 包用于格式化文本输出
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println("hello, world")
}运行
Go
go run helloworld.go等同于
Go
// Compile the program
go build helloworld.go
// Execute the compiled program
./helloworldfmt 包是 Go 中最常用的包之一,提供多种格式化输出的功能。
- fmt.Print()--输出无换行的文本
- fmt.Println()-带换行输出文本
- fmt.Printf()-输出格式化文本
显示机器上的 GOPATH 和 GOROOT 路径
Go
// Check the GOPATH directory
go env | grep GOPATH
// Check the GOROOT directory
go env | grep GOROOT为项目初始化 Go 模块
go mod init project_namego.mod的解释
Go
module test
go 1.15
require "helloWorld" v0.0.1
replace "helloWorld" => "../helloWorld"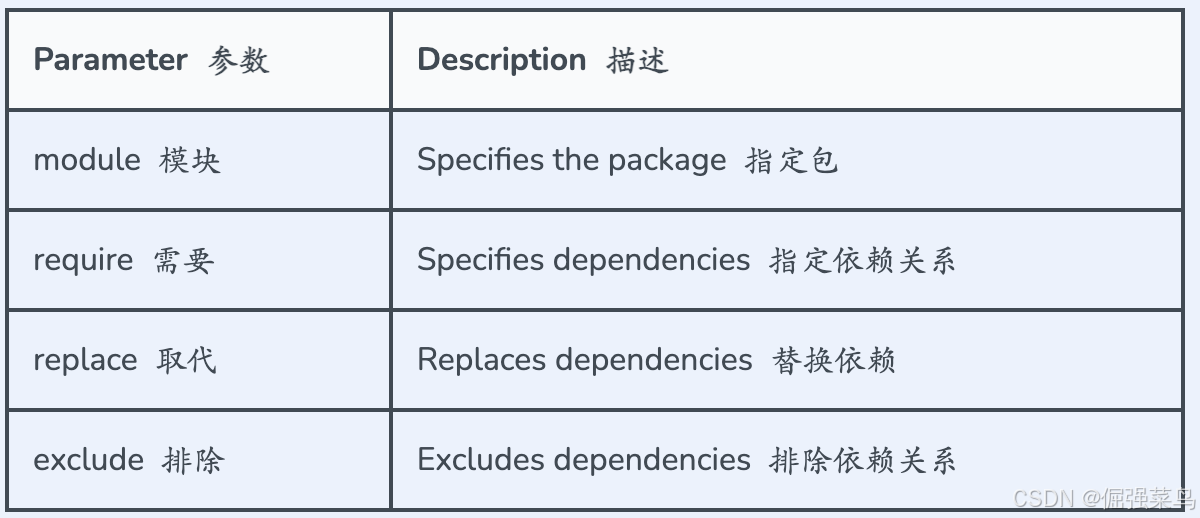
导入远程软件包
remote.go
Go
package main
import (
"github.com/labex-labs/golang-dev-code/chap02module"
)
func main() {
chap02module.StringTobase64("miiy")
}运行
Go
go get github.com/labex-labs/golang-dev-code/chap02module
go run -v remote.gogo get 命令会从 GitHub 下载 chap02module 包,并放到你的模块缓存中。完成后,go run命令会启动你的程序。
Go
import . "fmt"
// 意味着你可以直接使用 FMT 包中的函数和变量,而不带 FMT. 前缀。
func main() {
Println("xxxxxxx") // No `fmt.` prefix needed
}
import io "fmt" // 修改别名
func main() {
io.Println("xxxxxxx") 匿名导入(blank import)
只执行该包的 init() 函数,但不使用包里的任何符号。在代码里不能使用 time.XXX
Go
import (
_ "time" // Anonymous import
)
Go
go mod tidy
// 是保持 Go 项目依赖干净、正确、可构建的标准命令。自动整理依赖 、修复 go.mod/go.sum 、删除未使用依赖 、添加缺失依赖。
go mod vendor
// 把依赖复制到 vendor 目录| 命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| go mod tidy | 🔧 清理 go.mod/go.sum,让依赖记录正确("整理依赖") |
| go mod vendor | 📦 把所有依赖的源代码复制到 ./vendor 目录("本地依赖镜像") |
go语言中的赋值
| 运算符 | 是否声明新变量 | 是否允许类型推断 | 作用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
:= |
✔ 会声明新变量 | ✔ 会自动推断类型 | 新变量出现的地方(函数内) |
= |
✘ 不声明新变量 | ✔ 可以赋值给已有变量 | 已经声明过的变量重新赋值 |
:= 只能在函数内部使用,函数外一律用 var(不能用 :=)
Go
var variableName variableType.定义常数
Go
const Pi = 3.14159 // Using type inference initializationuintptr 是一个内置的无符号整数类型 ,用于表示 指针的数值形式(即内存地址) ,但它 本身不是指针类型,也不能被垃圾回收器(GC)追踪。
Go
var ptr uintptr
x := 42
// Convert the pointer to x to uintptr
ptr = uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(&x))
fmt.Printf("The address of x stored in ptr is: %v\n", ptr)
// The address of x stored in ptr is: 824634175224-
len(str)→ 计算字节数(byte length) -
utf8.RuneCountInString(str)→ 计算字符数(rune count)
把字符串 a 转换成 int 类型
i, err := strconv.Atoi("123")
执行结果:
-
i→ int 类型,值为 123 -
err→ 如果转换成功,为 nil;如果字符串不是数字,会返回错误
定义常数:
Go
const name [type] = value
Go
package main
import "fmt"
const (
monday = "MONDAY"
tuesday = "TUESDAY"
wednesday = "WEDNESDAY"
thursday
friday
)
func main() {
fmt.Println(monday, tuesday, wednesday, thursday, friday)
}
// MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY WEDNESDAY WEDNESDAYthursday, friday没有明确的数值。根据 Go 规则,当常数未被显式初始化时,它继承了之前常量的值
iota 常数发生器
iota 是 Go 语言中一个预声明的标识符,仅在常量声明(const)中使用,用于生成一系列自增的无类型整数常量(从 0 开始)。
Go
package main
import "fmt"
const (
monday = iota // initial value is 0
tuesday = iota // increments by 1 each time
wednesday = iota
thursday = iota
friday = iota
)
func main() {
fmt.Println(monday, tuesday, wednesday, thursday, friday)
}
// 0 1 2 3 4
// 跳过某个特定值
package main
import "fmt"
const (
monday = iota // 0
tuesday // 1
_
thursday // 3
friday // 4
)
func main() {
fmt.Println(monday, tuesday, thursday, friday)
}if else 语句的格式
Go
if condition {
code
} else {
code
}else if statement
Go
if condition {
code
} else if condition {
code
} else {
code
}IF 语句中的初始化语句
Go
if initialization statement; condition {
code
}switch语法
Go
switch condition {
case val1:
// code block
case val2:
// code block
...
default:
// code block
}case可以多个值
Go
switch condition {
case val1, val2:
// code block
...
}当省略条件变量时,switch 语句的行为类似于 if-else 语句,示例:
Go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
today := time.Now().Weekday()
switch {
case today == time.Monday:
fmt.Println("Today is Monday.")
case today == time.Tuesday:
fmt.Println("Today is Tuesday.")
case today == time.Wednesday:
fmt.Println("Today is Wednesday.")
case today == time.Thursday:
fmt.Println("Today is Thursday.")
case today == time.Friday:
fmt.Println("Today is Friday.")
case today == time.Saturday:
fmt.Println("Today is Saturday.")
default:
fmt.Println("Today is Sunday.")
}
}fallthrough:继续执行下一个 case,一个 case 只能 fallthrough 到下一个 case。
Go
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func main() {
n := 10
switch n {
case 10:
fmt.Println(10)
fallthrough
case 3:
fmt.Println(3)
}
}
// 10
// 3for 循环语句的语法
Go
for initialization; condition; post {
// code block
}
Go
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
// Output numbers from 0 to 9
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
fmt.Println(i)
}
}