在日常的开发任务中,我们常常需要存储和操作大量的数据,Java本身提供了许多的集合框架,我们可以灵活运用这些集合框架和常用的库函数简化我们的开发流程。
Java集合框架是一个用于存储和操作数据的强大工具。它主要由两个根接口Collection和Map派生出来。Collection接口进一步分为List、Set和Queue三种子接口,而Map接口则用于存储键值对。本次我们主要介绍List和Map的核心常用函数。
一、List 核心常用函数
接口:java.util.List
主流实现:ArrayList、 LinkedList
ArrayList是动态数组,支持根据填充的数据自动扩容、根据编号删除等增删改查的功能。
LinkedList是链表结构,同样支持各种增删改查的功能。
核心函数表
| 函数签名 | 功能说明 | 核心场景 |
|---|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | 尾部添加元素 | 基础元素插入 |
| void add(int index, E element) | 指定索引插入元素 | 中间位置插入 |
| E get(int index) | 获取指定索引元素 | 随机访问(ArrayList 优势) |
| E remove(int index) | 删除指定索引元素 | 按位置删除 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 删除首个匹配的元素 | 按值删除 |
| int size() | 获取元素个数 | 遍历/边界判断 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 判断是否为空 | 空值校验 |
| void clear() | 清空所有元素 | 重置列表 |
| int indexOf(Object o) | 查找元素首次出现的索引 (无则返回-1) | 元素存在性+位置查 找 |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | 查找元素最后出现的索引 | 反向查找元素 |
| List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 截取子列表(视图,原列表修改同步) | 列表切片(如旋转数 组) |
| default void sort(Comparator c) | 自定义比较器排序 | 自定义规则排序 (JDK8+) |
| default boolean removeIf(Predicate filter) | 按条件批量删除 | 过滤元素(如移除所 有偶数) |
部分方法实现示例
我们用示例代码实现后面三种方法:(以LinkedList为例)
1、subList
java
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class List_Study {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> num=new LinkedList<>();
num.add(100);
num.add(1000);
num.add(10000);
num.add(29);
num.add(39);
num.add(49);
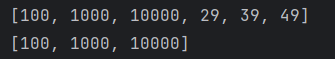
List<Integer> slice1 =num.subList(0,3);
System.out.println(num.stream().toList());
System.out.println(slice1.stream().toList());
}
}
2、sort
java
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class List_Study {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> num=new LinkedList<>();
num.add(100);
num.add(1000);
num.add(10000);
num.add(29);
num.add(39);
num.add(49);
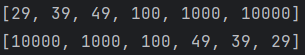
num.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a->a));//升序排列
System.out.println(num.stream().toList());
num.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a->-a));//降序排列
System.out.println(num.stream().toList());
}
}
3、removeIf
java
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class List_Study {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> num=new LinkedList<>();
num.add(100);
num.add(1000);
num.add(10000);
num.add(29);
num.add(39);
num.add(49);
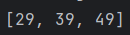
num.removeIf(a->a>=100);
System.out.println(num.stream().toList());
}
}
二、Map 核心常用函数
接口:java.util.Map
主流实现:HashMap、 TreeMap、LinkedHashMap
Map的主要功能是K-V存储:Key不能重复 ,存入的数据与存入时顺序的顺序无关,位置是结构内部通过固定的算法来排列 ,可以通过Key查找对应的Value。
核心函数表
|-------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------|------------------|
| 函数签名 | 功能说明 | 核心场景 |
| V put(K key, V value) | 存入键值对(键 存在则覆盖值) | 基础映射存储 |
| V get(Object key) | 获取键对应值(无则返回 null) | 基础映射查找 |
| V getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) | 获取值,无则返回默认值 | 计数场景避免空指针 |
| boolean containsKey(Object key) | 判断是否包含指定键 | 键存在性校验 |
| boolean containsValue(Object value) | 判断是否包含指 定值 | 值存在性校验 (效率低,慎 用) |
| V remove(Object key) | 删除指定键的键值对 | 移除映射 |
| Set<K> keySet() | 获取所有键的Set 集合 | 遍历所有键 |
| Collection<V> values() | 获取所有值的 Collection集合 | 遍历所有值 |
| Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() | 获取所有键值对 的Set集合 | 遍历所有键值对 (高效) |
| int size() | 获取键值对个数 | 映射数量统计 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 判断是否为空 | 空值校验 |
| void clear() | 清空所有键值对 | 重置映射 |
| default void forEach(BiConsumer<?super K,?super V> action | 遍历键值对 (Lambda) | 批量处理映射元素 |
| default V putIfAbsent(K key, V value) | 键不存在时才存 入值 | 避免覆盖已有映射 |
部分方法实现示例
1、entrySet()
java
import java.util.*;
public class HashMap_Study {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer,String> student=new HashMap<>();
student.put(10,"张三");
student.put(20,"李四");
student.put(30,"王五");
student.put(40,"赵六");
//根据需要的返回值定义一个Set集合
Set<Map.Entry<Integer,String>> stu;
stu=student.entrySet();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(stu.toArray()));
}
}
2、forEach
java
import java.util.*;
public class HashMap_Study {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer,String> student=new HashMap<>();
student.put(10,"张三");
student.put(20,"李四");
student.put(30,"王五");
student.put(40,"赵六");
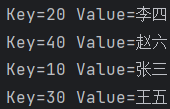
student.forEach((key,value)->{
System.out.println("Key="+key+" "+"Value="+value);
});
}
}
注:foreach不可以直接修改Map里面的键值对!
3、putIfAbsent
java
import java.util.*;
public class HashMap_Study {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer,String> student=new HashMap<>();
student.put(10,"张三");
student.put(20,"李四");
student.put(30,"王五");
student.put(40,"赵六");
student.putIfAbsent(40,"你好");
student.putIfAbsent(50,"刘七");
student.forEach((key,value)->{
System.out.println("Key="+key+" "+"Value="+value);
});
}
}
可以看到,(40,"你好")这一键值对没有成功添加,因为已经存在40这个key了。
三、补充知识
1、Lambda表达式
Lambda表达式是一种简洁的编程语言特性,它允许我们以匿名方法的形式快速定义和实现功能。其使用的符号是->。其实可以把他理解为只写方法的参数和方法体,避免了单独写方法的麻烦。例如上面在foreach方法中用到的
(key,value)->{
System.out.println("Key="+key+" "+"Value="+value);
}
就是对传入的key和value进行大括号里面的操作,本质上就是一个简化版的方法。
2、Set的重要应用
Set是集合,区别于Collection,Set中不允许有重复的元素出现,利用这一特性,我们可以用Set来执行去重、集合运算等操作。
①去重
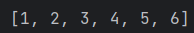
例如现在有一个线性表,里面有{1,2,2,3,3,4,5,6}的元素,现在要将所有的重复元素去除到只剩一个,那就可以将这个线性表的元素全部添加到一个Set中,这样就可以实现去重操作了。
java
import java.util.*;
public class delete {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> number = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 6));
Set<Integer> num=new HashSet<>(number);
System.out.println(num);
}
}
②集合运算
集合的运算包括求交集和并集:交集是两个集合共有的元素,并集是两个集合含有的所有元素。
java
import java.util.*;
public class delete {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> number = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4));
Set<Integer> num1=new HashSet<>(number);
Set<Integer> num2=new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList(3,4,5,6));
Set<Integer> UnionNum=new HashSet<>(num1);
UnionNum.addAll(num2);
Set<Integer> intersectSet=new HashSet<>(num1);
intersectSet.retainAll(num2);
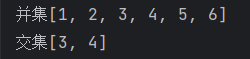
System.out.println("并集"+UnionNum);
System.out.println("交集"+intersectSet);
}
}
并集:调用addAll方法 交集:调用retainAll方法