在当前的大模型(LLM)领域,如何让模型具备更强的逻辑推理能力(Chain-of-Thought, CoT)是一个热门话题。DeepSeek-R1 等模型的成功证明了**强化学习(RL)**在提升推理能力方面的巨大潜力。
今天我们将深入解析一段使用 Unsloth 框架和 GRPO (Generative Reward-Paired Optimization) 算法微调 Qwen2.5-7B 的代码。我们将解释为什么这种方法比传统的 PPO 更高效,并逐步拆解代码。
📖 第一部分:什么是 GRPO?
在通过强化学习微调 LLM 时,最著名的算法莫过于 PPO (Proximal Policy Optimization)。然而,PPO 极其消耗资源,因为它通常需要加载四个模型:
- Policy Model (当前训练的模型)
- Reference Model (用于计算 KL 散度,防止模型跑偏)
- Reward Model (用于打分)
- Value Model / Critic (用于估计预期收益)
GRPO 的核心原理
GRPO (Generative Reward-Paired Optimization) 是一种旨在去除 "Critic"(价值模型)的优化算法,由 DeepSeek 团队提出。
它的工作流程如下:
- 输入:给定一个问题(Prompt)。
- 采样(Group Sampling):模型针对该问题生成一组(Group)回复(例如生成 6 个不同的答案)。
- 打分:使用奖励函数(Reward Function)对这 6 个答案分别打分。
- 优势计算(Advantage Estimation) :
- 它不依赖 Critic 模型来预测基准分数。
- 它直接计算这组答案的平均分作为基准。
- 得分高于平均分的答案被"鼓励"(正向更新),低于平均分的被"抑制"。
- 更新:利用这些优势值更新模型参数。
📊 图解:PPO vs GRPO
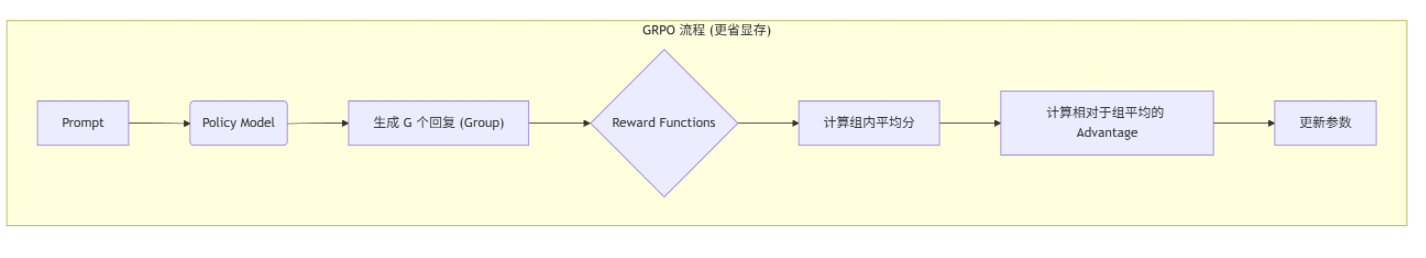
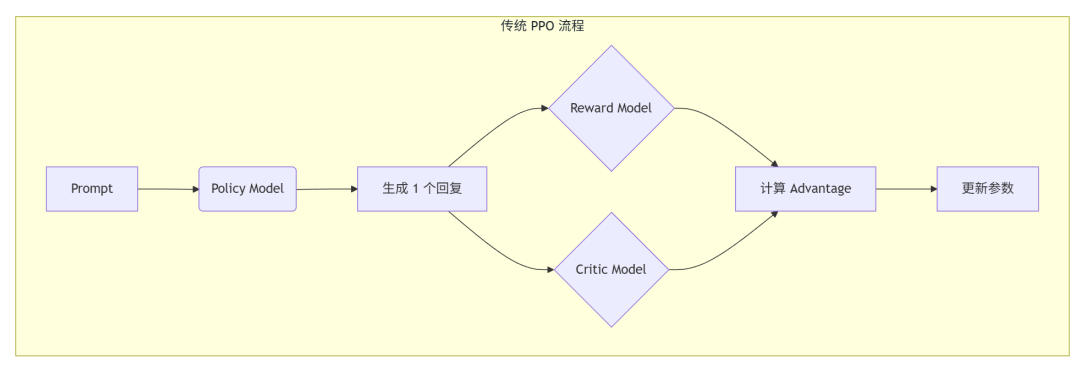
GRPO 的优势
- 显存占用更低:不需要加载巨大的 Critic 模型,这使得在单卡上进行 RL 微调成为可能。
- 训练更稳定:通过组内归一化(Group Normalization),减少了方差。
- 适合推理任务:通过对同一个数学问题生成多个解题路径,模型能自动学会哪种路径更能推导出正确答案。
💻 第二部分:代码详细解析
以下代码使用了 Unsloth(加速训练)和 TRL(Transformer Reinforcement Learning)库。
1. 环境初始化与模型加载
python
import unsloth
from unsloth import FastLanguageModel
import torch
# ---------------- 配置参数 ----------------
max_seq_length = 1024 # 序列最大长度,包含Prompt和生成的答案
lora_rank = 32 # LoRA的秩,值越大参数越多,表现可能越好但训练越慢
# ---------------- 加载模型 ----------------
# 使用 Unsloth 的 FastLanguageModel 加载 Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct
model, tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained(
model_name = "/root/autodl-tmp/models/Qwen/Qwen2___5-7B-Instruct", # 本地模型路径或 HuggingFace ID
max_seq_length = max_seq_length,
load_in_4bit = True, # 核心优化:使用 4bit 量化加载,显存占用极大降低
fast_inference = True, # 启用 vLLM 加速推理(GRPO 需要大量推理生成,这步很关键)
max_lora_rank = lora_rank,
gpu_memory_utilization = 0.6, # 显存占用限制,防止 OOM
)
# ---------------- 配置 LoRA ----------------
# 将模型转换为 PEFT (Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning) 模型
model = FastLanguageModel.get_peft_model(
model,
r = lora_rank,
# 针对所有线性层进行微调,通常能获得更好的效果
target_modules = [
"q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj",
"gate_proj", "up_proj", "down_proj",
],
lora_alpha = lora_rank,
use_gradient_checkpointing = "unsloth", # 显存优化技术
random_state = 3407,
)2. 数据集准备与格式化
GRPO 需要模型不仅输出答案,还要学会"思考"。我们通过 System Prompt 强制模型输出 XML 格式的思维链(CoT)。
python
import re
from datasets import load_dataset, Dataset
# ---------------- 定义提示词模板 ----------------
# 强制模型按照 <reasoning>...</reasoning> <answer>...</answer> 的格式输出
SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
Respond in the following format:
<reasoning>
...
</reasoning>
<answer>
...
</answer>
"""
def extract_hash_answer(text: str) -> str | None:
"""处理 GSM8K 数据集原本的 '#### 答案' 格式"""
if "####" not in text:
return None
return text.split("####")[1].strip()
def get_gsm8k_questions(split = "train") -> Dataset:
"""加载并预处理 GSM8K 数据集"""
# 加载本地或云端数据集
data = load_dataset('/root/autodl-tmp/datasets/gsm8k', 'main')[split]
# 映射数据格式:添加 System Prompt
data = data.map(lambda x: {
'prompt': [
{'role': 'system', 'content': SYSTEM_PROMPT},
{'role': 'user', 'content': x['question']}
],
'answer': extract_hash_answer(x['answer']) # 提取标准答案用于后续奖励计算
})
return data
dataset = get_gsm8k_questions()3. 定义奖励函数 (Reward Functions)
这是强化学习的灵魂。我们定义了 5 个函数来指导模型的行为。模型生成的每一个回复都会经过这 5 个函数打分。
- Hard Rewards (硬性指标): 答案对不对?格式是不是 XML?
- Soft Rewards (软性指标): 标签是否完整?是否是整数?
python
# ---------------- 辅助函数 ----------------
def extract_xml_answer(text: str) -> str:
"""从模型生成的 XML 中提取 <answer> 标签内的内容"""
answer = text.split("<answer>")[-1]
answer = answer.split("</answer>")[0]
return answer.strip()
# ---------------- 奖励函数群 ----------------
# 1. 正确性奖励:最核心的指标,答案对给 2.0 分,不对给 0 分
def correctness_reward_func(prompts, completions, answer, **kwargs) -> list[float]:
responses = [completion[0]['content'] for completion in completions]
extracted_responses = [extract_xml_answer(r) for r in responses]
# 打印日志以便观察训练过程
print('-'*20, f"\nResponse:\n{responses[0]}", f"\nExtracted:\n{extracted_responses[0]}")
return [2.0 if r == a else 0.0 for r, a in zip(extracted_responses, answer)]
# 2. 整数奖励:鼓励生成整数答案
def int_reward_func(completions, **kwargs) -> list[float]:
responses = [completion[0]['content'] for completion in completions]
extracted_responses = [extract_xml_answer(r) for r in responses]
return [0.5 if r.isdigit() else 0.0 for r in extracted_responses]
# 3. 严格格式奖励:正则匹配完整的 XML 结构
def strict_format_reward_func(completions, **kwargs) -> list[float]:
pattern = r"^<reasoning>\n.*?\n</reasoning>\n<answer>\n.*?\n</answer>\n$"
responses = [completion[0]["content"] for completion in completions]
matches = [re.match(pattern, r) for r in responses]
return [0.5 if match else 0.0 for match in matches]
# 4. 宽松格式奖励:只要有标签就行,防止训练初期过严导致模型学不会
def soft_format_reward_func(completions, **kwargs) -> list[float]:
pattern = r"<reasoning>.*?</reasoning>\s*<answer>.*?</answer>"
responses = [completion[0]["content"] for completion in completions]
matches = [re.match(pattern, r) for r in responses]
return [0.5 if match else 0.0 for match in matches]
# 5. XML 计数奖励:引导模型逐步写出完整的标签
def xmlcount_reward_func(completions, **kwargs) -> list[float]:
def count_xml(text):
count = 0.0
# 每写对一个标签给 0.125 分
if text.count("<reasoning>\n") == 1: count += 0.125
if text.count("\n</reasoning>\n") == 1: count += 0.125
if text.count("\n<answer>\n") == 1: count += 0.125
if text.count("\n</answer>") == 1: count += 0.125
return count
return [count_xml(c[0]["content"]) for c in completions]4. 配置 GRPOTrainer 并开始训练
这里是最关键的配置部分。
python
from trl import GRPOConfig, GRPOTrainer
# ---------------- 训练参数 ----------------
training_args = GRPOConfig(
learning_rate = 5e-6, # 学习率通常比 SFT 低
adam_beta1 = 0.9,
adam_beta2 = 0.99,
weight_decay = 0.1,
warmup_ratio = 0.1,
lr_scheduler_type = "cosine",
optim = "paged_adamw_8bit", # 使用 8bit 优化器节省显存
logging_steps = 1,
per_device_train_batch_size = 1,
gradient_accumulation_steps = 1,
# --- GRPO 特有参数 ---
num_generations = 6, # 核心参数 G:每个 Prompt 采样 6 个回复进行对比
max_prompt_length = 256,
max_completion_length = 1024 - 256,
max_steps = 250, # 演示用,设得较小
save_steps = 250,
max_grad_norm = 0.1,
report_to = "none",
output_dir = "outputs",
)
# ---------------- 初始化训练器 ----------------
trainer = GRPOTrainer(
model = model,
processing_class = tokenizer,
# 将所有奖励函数传入
reward_funcs = [
xmlcount_reward_func,
soft_format_reward_func,
strict_format_reward_func,
int_reward_func,
correctness_reward_func,
],
args = training_args,
train_dataset = dataset,
)
# ---------------- 开始训练 ----------------
# 在训练过程中,你会看到 loss 和各个 reward 函数的平均分
trainer.train()5. 推理与保存
训练完成后,我们使用 vLLM 进行快速推理来验证效果,并保存 LoRA 权重。
python
# 保存 LoRA
model.save_lora("grpo_saved_lora")
# ---------------- 推理测试 ----------------
# 构造测试输入
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template([
{"role" : "system", "content" : SYSTEM_PROMPT},
{"role" : "user", "content" : "Calculate pi."}, # 测试问题
], tokenize = False, add_generation_prompt = True)
from vllm import SamplingParams
sampling_params = SamplingParams(
temperature = 0.8,
top_p = 0.95,
max_tokens = 2048,
)
# 加载刚训练好的 LoRA 进行推理
output = model.fast_generate(
text,
sampling_params = sampling_params,
lora_request = model.load_lora("grpo_saved_lora"),
)[0].outputs[0].text
print(output)📝 总结
通过这段代码,我们实现了一个基于 GRPO 的强化学习流程:
- Unsloth 提供了极速的训练环境和 4bit 量化支持。
- GRPO 省去了 Critic 模型,利用组内采样的相对优势(Advantage)来优化策略。
- 多重奖励函数 就像老师的指挥棒,不仅要求模型"做对题"(Correctness),还要求模型"写规范"(XML Format)并"写出过程"(Reasoning)。
这种方法特别适合数学、代码等客观题场景,能够有效激发大模型的潜在推理能力。如果你在显存有限的情况下(如 24GB 显存显卡)想要尝试 RLHF/RLAIF,这套方案是目前的最佳实践之一。
完整代码:
python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# coding: utf-8
"""
Qwen2.5-7B GRPO 微调完整脚本
基于 Unsloth 框架和 TRL 库进行 Generative Reward-Paired Optimization (GRPO) 训练。
环境依赖安装建议:
pip install unsloth
pip install --no-deps "trl<0.9.0" peft accelerate bitsandbytes
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121
"""
import re
import torch
import torchvision
from datasets import load_dataset, Dataset
from unsloth import FastLanguageModel
from trl import GRPOConfig, GRPOTrainer
from vllm import SamplingParams
# ==========================================
# 1. 配置与环境检查
# ==========================================
print(f"PyTorch version: {torch.__version__}")
print(f"CUDA available: {torch.cuda.is_available()}")
# 核心参数配置
MAX_SEQ_LENGTH = 1024 # 最大序列长度 (Prompt + Completion)
LORA_RANK = 32 # LoRA 秩
GPU_MEMORY_UTILIZATION = 0.6 # 显存占用限制 (防止 vLLM 和训练抢显存 OOM)
# 路径配置 (请根据实际情况修改,如果没有下载好权重,可直接填 HuggingFace ID)
# MODEL_PATH = "Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct"
MODEL_PATH = "/root/autodl-tmp/models/Qwen/Qwen2___5-7B-Instruct"
# DATASET_PATH = "openai/gsm8k"
DATASET_PATH = "/root/autodl-tmp/datasets/gsm8k"
# ==========================================
# 2. 模型加载与 LoRA 配置
# ==========================================
print("Loading model...")
model, tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained(
model_name = MODEL_PATH,
max_seq_length = MAX_SEQ_LENGTH,
load_in_4bit = True, # 4bit 量化加载,节省显存
fast_inference = True, # 启用 vLLM 加速推理 (GRPO 必须)
max_lora_rank = LORA_RANK,
gpu_memory_utilization = GPU_MEMORY_UTILIZATION,
)
# 配置 LoRA 适配器
model = FastLanguageModel.get_peft_model(
model,
r = LORA_RANK,
target_modules = [
"q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj",
"gate_proj", "up_proj", "down_proj",
],
lora_alpha = LORA_RANK,
use_gradient_checkpointing = "unsloth", # 显存优化
random_state = 3407,
)
# ==========================================
# 3. 数据集准备
# ==========================================
# 定义系统提示词:强制模型输出 XML 格式的思维链
SYSTEM_PROMPT = """
Respond in the following format:
<reasoning>
...
</reasoning>
<answer>
...
</answer>
"""
def extract_hash_answer(text: str) -> str | None:
"""从 GSM8K 的 '#### 答案' 格式中提取标准答案"""
if "####" not in text:
return None
return text.split("####")[1].strip()
def get_gsm8k_questions(split = "train") -> Dataset:
"""加载 GSM8K 数据集并格式化"""
try:
data = load_dataset(DATASET_PATH, 'main')[split]
except Exception:
print(f"本地路径 {DATASET_PATH} 加载失败,尝试在线加载 openai/gsm8k...")
data = load_dataset('openai/gsm8k', 'main')[split]
data = data.map(lambda x: {
'prompt': [
{'role': 'system', 'content': SYSTEM_PROMPT},
{'role': 'user', 'content': x['question']}
],
'answer': extract_hash_answer(x['answer'])
})
return data
print("Processing dataset...")
dataset = get_gsm8k_questions()
# ==========================================
# 4. 定义奖励函数 (Reward Functions)
# ==========================================
def extract_xml_answer(text: str) -> str:
"""从 XML 中提取答案部分"""
answer = text.split("<answer>")[-1]
answer = answer.split("</answer>")[0]
return answer.strip()
# 1. 正确性奖励:答案是否与标准答案一致
def correctness_reward_func(prompts, completions, answer, **kwargs) -> list[float]:
responses = [completion[0]['content'] for completion in completions]
q = prompts[0][-1]['content']
extracted_responses = [extract_xml_answer(r) for r in responses]
# 打印样例以便监控 (仅打印 batch 中的第一个)
print('-'*20, f"Question:\n{q}", f"\nAnswer:\n{answer[0]}", f"\nResponse:\n{responses[0]}", f"\nExtracted:\n{extracted_responses[0]}")
return [2.0 if r == a else 0.0 for r, a in zip(extracted_responses, answer)]
# 2. 整数奖励:答案是否为整数
def int_reward_func(completions, **kwargs) -> list[float]:
responses = [completion[0]['content'] for completion in completions]
extracted_responses = [extract_xml_answer(r) for r in responses]
return [0.5 if r.isdigit() else 0.0 for r in extracted_responses]
# 3. 严格格式奖励:完全符合 XML 结构
def strict_format_reward_func(completions, **kwargs) -> list[float]:
pattern = r"^<reasoning>\n.*?\n</reasoning>\n<answer>\n.*?\n</answer>\n$"
responses = [completion[0]["content"] for completion in completions]
matches = [re.match(pattern, r) for r in responses]
return [0.5 if match else 0.0 for match in matches]
# 4. 宽松格式奖励:包含基本的 XML 标签
def soft_format_reward_func(completions, **kwargs) -> list[float]:
pattern = r"<reasoning>.*?</reasoning>\s*<answer>.*?</answer>"
responses = [completion[0]["content"] for completion in completions]
matches = [re.match(pattern, r) for r in responses]
return [0.5 if match else 0.0 for match in matches]
# 5. XML 计数奖励:奖励标签的完整性
def xmlcount_reward_func(completions, **kwargs) -> list[float]:
def count_xml(text):
count = 0.0
if text.count("<reasoning>\n") == 1: count += 0.125
if text.count("\n</reasoning>\n") == 1: count += 0.125
if text.count("\n<answer>\n") == 1: count += 0.125
if text.count("\n</answer>") == 1: count += 0.125
# 稍微惩罚过长的 XML 尾部垃圾字符
count -= (len(text.split("\n</answer>")[-1]) - 1)*0.001
return count
return [count_xml(c[0]["content"]) for c in completions]
# ==========================================
# 5. 训练配置与启动
# ==========================================
max_prompt_length = 256
training_args = GRPOConfig(
learning_rate = 5e-6,
adam_beta1 = 0.9,
adam_beta2 = 0.99,
weight_decay = 0.1,
warmup_ratio = 0.1,
lr_scheduler_type = "cosine",
optim = "paged_adamw_8bit",
logging_steps = 1,
per_device_train_batch_size = 1,
gradient_accumulation_steps = 1,
# GRPO 关键参数
num_generations = 6, # 每个 Prompt 采样 6 个结果进行对比
max_prompt_length = max_prompt_length,
max_completion_length = MAX_SEQ_LENGTH - max_prompt_length,
max_steps = 250, # 训练步数
save_steps = 250,
max_grad_norm = 0.1,
report_to = "none",
output_dir = "grpo_outputs",
)
print("Initializing GRPOTrainer...")
trainer = GRPOTrainer(
model = model,
processing_class = tokenizer,
reward_funcs = [
xmlcount_reward_func,
soft_format_reward_func,
strict_format_reward_func,
int_reward_func,
correctness_reward_func,
],
args = training_args,
train_dataset = dataset,
)
print("Starting training...")
trainer.train()
# 保存 LoRA 适配器
print("Saving LoRA model...")
model.save_lora("grpo_saved_lora")
# ==========================================
# 6. 推理测试
# ==========================================
print("Running inference test...")
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template([
{"role" : "system", "content" : SYSTEM_PROMPT},
{"role" : "user", "content" : "Calculate pi."}, # 简单测试题
], tokenize = False, add_generation_prompt = True)
sampling_params = SamplingParams(
temperature = 0.8,
top_p = 0.95,
max_tokens = 1024,
)
# 加载保存的 LoRA 进行生成
try:
output = model.fast_generate(
text,
sampling_params = sampling_params,
lora_request = model.load_lora("grpo_saved_lora"),
)[0].outputs[0].text
print("\nInference Output:")
print(output)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Inference failed: {e}")
# ==========================================
# 7. 模型导出选项 (按需取消注释)
# ==========================================
# model.save_pretrained_merged("merged_model", tokenizer, save_method="merged_16bit")
# model.push_to_hub_gguf("hf/model", tokenizer, quantization_method="q4_k_m", token="")相关资源:
百度网盘:https://pan.baidu.com/s/15x0FyYRRr4aL3W7U6CrRSA?pwd=1mu9