文本分类
-
- 安装前置包
- 数据加载
- 使用表征模型进行文本分类
-
- [1. 使用特定任务模型](#1. 使用特定任务模型)
- [2. 性能评估函数](#2. 性能评估函数)
- 基于嵌入向量的分类方法
-
- [1. 监督分类(使用逻辑回归)](#1. 监督分类(使用逻辑回归))
使用表征模型和生成模型进行文本分类
安装前置包
python
# %%capture
# !pip install transformers sentence-transformers openai
# !pip install -U datasets数据加载
python
from datasets import load_dataset
# 加载数据集
data = load_dataset("rotten_tomatoes")
data上述代码直接运行可能会报错
requests.exceptions.SSLError:(MaxRetryError("HTTPSConnectionPool(host='huggingface.co', port=443)
原因是因为网络不能下载,可以引入梯子端口,代理端口的查看方式如下
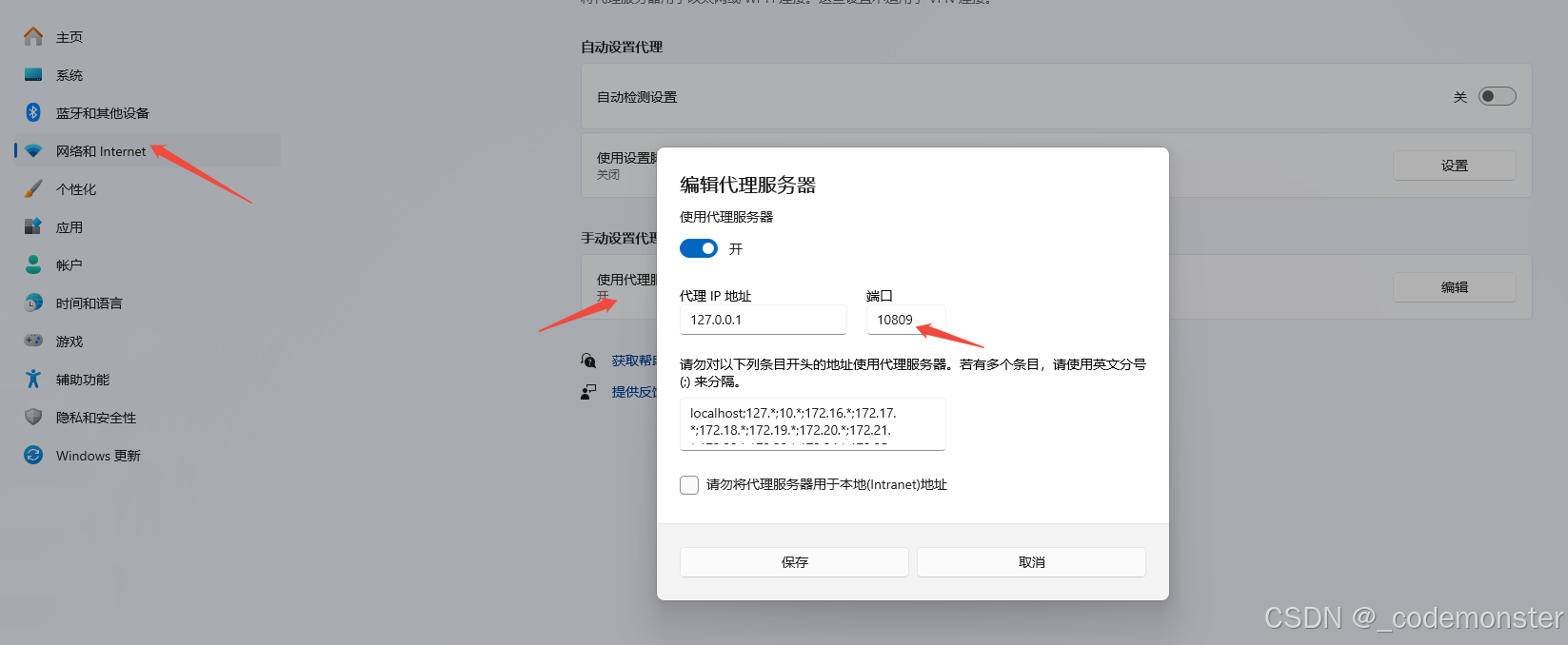
并将缓存地址改为自己有权限的指定地址
python
from datasets import load_dataset
import os
os.environ['HTTP_PROXY'] = 'http://127.0.0.1:10809'
os.environ['HTTPS_PROXY'] = 'http://127.0.0.1:10809'
# Load our data
# data = load_dataset("rotten_tomatoes")
os.environ['HF_HOME'] = 'D:/huggingface_cache' # 改为你喜欢的目录
# 或者使用数据集加载时的参数
data = load_dataset(
"rotten_tomatoes",
cache_dir="D:/huggingface_cache/datasets"
)
data如果已经将数据rotten_tomatoes下载到本地了,也可以直接用本地地址进行加载
python
from datasets import load_dataset
import os
# Load our data
data = load_dataset("/workspace/huggingface_cache/datasets/rotten_tomatoes")
data输出:
DatasetDict({
train: Dataset({
features: ['text', 'label'],
num_rows: 8530
})
validation: Dataset({
features: ['text', 'label'],
num_rows: 1066
})
test: Dataset({
features: ['text', 'label'],
num_rows: 1066
})
})
python
# 查看训练集样本
data["train"][0:2]输出:
{'text': ['the rock is destined to be the 21st century\'s new " conan " and that he\'s going to make a splash even greater than arnold schwarzenegger , jean-claud van damme or steven segal .',
'things really get weird , though not particularly scary : the movie is all portent and no content .'],
'label': [1, 0]}使用表征模型进行文本分类
1. 使用特定任务模型
python
from transformers import pipeline
import numpy as np
from tqdm import tqdm
from transformers.pipelines.pt_utils import KeyDataset
# 加载预训练模型(已针对情感分析进行微调)
model_path = "cardiffnlp/twitter-roberta-base-sentiment-latest"
# 创建推理管道
pipe = pipeline(
model=model_path,
tokenizer=model_path,
task="text-classification",
return_all_scores=True,
device="cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
)上面代码如果网络不给力的话,可能没办法把模型下载下来,可以在网络行得通的电脑上用下面电脑下载下来后离线加载。
python
from huggingface_hub import snapshot_download
import os
os.environ['HTTP_PROXY'] = 'http://127.0.0.1:10809'
os.environ['HTTPS_PROXY'] = 'http://127.0.0.1:10809'
# 设置模型路径
model_id = "cardiffnlp/twitter-roberta-base-sentiment-latest"
local_dir = "D:/huggingface_cache/models/twitter-roberta-base-sentiment-latest"
# 确保目录存在
os.makedirs(local_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 下载模型(对应 hf download 命令)
print(f"开始下载模型: {model_id}")
print(f"保存到: {local_dir}")
try:
snapshot_download(
repo_id=model_id,
local_dir=local_dir,
local_dir_use_symlinks=False, # 不使用符号链接
force_download=True, # 强制重新下载
resume_download=False # 不续传
)
print("✅ 模型下载完成!")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 下载失败: {e}")local_dir 改成自己的本地存储路径就行
离线加载
和之前我们做的入门实验一样,不过之前的AutoModelForCausalLM(用于因果语言模型)是用来来加载一个分类模型的。而twitter-roberta-base-sentiment-latest 是一个文本分类模型,应该用 AutoModelForSequenceClassification来进行加载。
python
model_path = "/workspace/models/twitter-roberta-base-sentiment-latest"
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification, AutoTokenizer
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
model_path, # 本地路径
device_map="cuda",
torch_dtype="auto",
trust_remote_code=False,
local_files_only=True # 关键参数:只使用本地文件
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_path, local_files_only=True)然后再用加载的模型创建一个文本分类管道
注意这里是text-classification而不是之前的 text-generation 。
python
from transformers import pipeline
# 创建一个文本分类管道
pipe = pipeline(
model=model_path,
tokenizer=model_path,
task="text-classification",
return_all_scores=True,
device="cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
)推理
python
# 在测试集上进行推理
y_pred = []
for output in tqdm(pipe(KeyDataset(data["test"], "text"),
batch_size=32),
total=len(data["test"]),
desc="模型推理"):
# 提取负面和正面情感得分
negative_score = output[0]["score"]
positive_score = output[2]["score"]
# 选择得分较高的类别
assignment = 0 if negative_score > positive_score else 1
y_pred.append(assignment)2. 性能评估函数
python
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
def evaluate_performance(y_true, y_pred):
"""评估分类性能并打印报告"""
performance = classification_report(
y_true,
y_pred,
target_names=["负面评价", "正面评价"],
digits=4
)
print("分类性能报告:")
print(performance)
# 评估模型性能
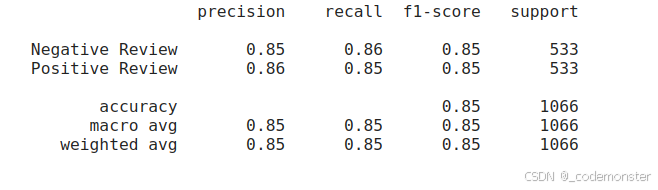
evaluate_performance(data["test"]["label"], y_pred)输出:
基于嵌入向量的分类方法
在前面的示例中,我们使用了预训练的特定任务模型twitter-roberta-base-sentiment-latest进行情感分析。但如果找不到针对这个特定任务预训练的模型呢?是否需要自己微调表示模型?答案是否定的。如果你有足够的计算资源,可能会有想要自己微调模型的时候。然而,并非每个人都能获得大量的计算资源。这就是通用嵌入模型发挥作用的地方。
我们将通用嵌入模型进行冻结也就是不进行训练,只是用它来提取特征并将输入文本转换为嵌入向量。
1. 监督分类(使用逻辑回归)
补丁1:apply_monkey_patches
python
import sys
import types
def apply_monkey_patches():
"""应用猴子补丁解决所有导入问题"""
print("应用猴子补丁...")
# 1. 补丁 torch._six
import torch
class TorchSixPatch:
string_classes = (str,)
int_classes = int
def is_integer(self, obj):
return isinstance(obj, int)
if not hasattr(torch, '_six'):
torch._six = types.ModuleType('_six')
patch = TorchSixPatch()
torch._six.string_classes = patch.string_classes
torch._six.int_classes = patch.int_classes
torch._six.is_integer = patch.is_integer
# 2. 预导入可能会出问题的模块
try:
# 提前导入这些模块以避免循环导入
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from typing import Any, Dict, List, Optional, Tuple, Union
except:
pass
# 3. 创建简化版的 trainer 模块
create_simple_trainer_module()
print("✅ 猴子补丁应用完成")
def create_simple_trainer_module():
"""创建简化版的 trainer 模块"""
# 创建模拟的 trainer 模块
trainer_module = types.ModuleType('transformers.trainer')
# 添加必要的类和函数
class TrainerStub:
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
pass
trainer_module.Trainer = TrainerStub
trainer_module.__version__ = "4.30.0"
# 注入到 sys.modules
sys.modules['transformers.trainer'] = trainer_module
# 也更新 transformers 模块的引用
import transformers
transformers.trainer = trainer_module
transformers.Trainer = TrainerStub
# 在导入任何 transformers 模块之前调用补丁2:apply_comprehensive_patches
python
import sys
import types
import warnings
# 抑制警告
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
def apply_comprehensive_patches():
"""应用全面的兼容性补丁"""
print("=" * 60)
print("应用全面的兼容性补丁")
print("=" * 60)
# 1. 修复 torch._six
import torch
if not hasattr(torch, '_six'):
print("1. 修复 torch._six...")
torch._six = types.ModuleType('torch._six')
torch._six.string_classes = (str, bytes)
torch._six.int_classes = int
torch._six.is_integer = lambda x: isinstance(x, int)
torch._six.PY2 = False
torch._six.PY3 = True
print(" ✅ 完成")
# 2. 修复 transformers.trainer 模块
print("2. 修复 transformers.trainer...")
fix_transformers_trainer()
# 3. 修复其他可能的问题
print("3. 设置环境变量...")
import os
os.environ['TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE'] = '1'
os.environ['HF_DATASETS_OFFLINE'] = '1'
print("✅ 所有补丁应用完成")
return True
def fix_transformers_trainer():
"""修复 transformers.trainer 模块"""
# 创建完整的 trainer 模拟模块
trainer_module = types.ModuleType('transformers.trainer')
# 添加必要的常量
trainer_module.TRAINING_ARGS_NAME = "training_args.bin"
trainer_module.WEIGHTS_NAME = "pytorch_model.bin"
trainer_module.CONFIG_NAME = "config.json"
# 添加 Trainer 类(简化版)
class TrainerStub:
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
self.args = kwargs.get('args', None)
self.model = kwargs.get('model', None)
self.data_collator = kwargs.get('data_collator', None)
def train(self):
print("Trainer.train() - 简化版")
return None
def evaluate(self):
print("Trainer.evaluate() - 简化版")
return {}
def predict(self):
print("Trainer.predict() - 简化版")
return []
trainer_module.Trainer = TrainerStub
# 添加其他必要的类和函数
trainer_module.set_seed = lambda x: None
trainer_module.EvalPrediction = type('EvalPrediction', (), {})
trainer_module.IntervalStrategy = type('IntervalStrategy', (), {
'NO': 'no',
'STEPS': 'steps',
'EPOCH': 'epoch'
})
# 添加版本信息
trainer_module.__version__ = "4.30.0"
# 注入到 sys.modules
sys.modules['transformers.trainer'] = trainer_module
# 更新 transformers 模块
if 'transformers' in sys.modules:
import transformers
transformers.trainer = trainer_module
transformers.Trainer = TrainerStub
transformers.trainer.TRAINING_ARGS_NAME = "training_args.bin"
return trainer_module加载离线模型
python
apply_monkey_patches()
apply_comprehensive_patches()
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
# Load model
model = SentenceTransformer('/workspace/models/all-mpnet-base-v2')
# Convert text to embeddings
train_embeddings = model.encode(data["train"]["text"], show_progress_bar=True)
test_embeddings = model.encode(data["test"]["text"], show_progress_bar=True)apply_monkey_patches()和apply_comprehensive_patches()是两个补丁,由于版本不兼容的问题,可能会报错Failed to import transformers.trainer because of the following error (look up to see its traceback):No module named 'torch._six'以及报错ImportError: cannot import name 'TRAINING_ARGS_NAME' from 'transformers.trainer' (unknown location),这两个补丁是为了解决这两个问题的。
all-mpnet-base-v2充当的就是前面讲的通用嵌入模型进行冻结也就是不进行训练,只是用它来提取特征并将输入文本转换为嵌入向量。
python
print(f"训练集嵌入维度: {train_embeddings.shape}")输出
(8530, 768)
引入逻辑回归分类器对前面得到的向量进行训练
python
# 训练逻辑回归分类器
clf = LogisticRegression(random_state=42, max_iter=1000)
clf.fit(train_embeddings, data["train"]["label"])预测并评估所训练出来的模型
python
# 预测并评估
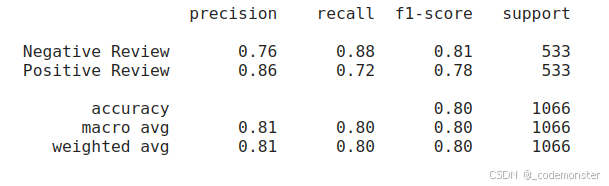
y_pred = clf.predict(test_embeddings)
evaluate_performance(data["test"]["label"], y_pred)输出