在分布式系统中,一次请求可能被重复执行多次,导致数据不一致、资金损失等严重后果。本文将深入探讨Dubbo服务调用如何保证幂等性,从原理到实践,为你提供完整的解决方案。
文章目录
-
- [🎯 引言:一个价值百万的教训](#🎯 引言:一个价值百万的教训)
- 一、Dubbo幂等性基础:为什么需要特殊处理?🤔
-
- [1.1 Dubbo的默认行为分析](#1.1 Dubbo的默认行为分析)
- [1.2 Dubbo重试机制详解](#1.2 Dubbo重试机制详解)
- [1.3 幂等性的数学原理](#1.3 幂等性的数学原理)
- [二、幂等性解决方案全景图 🗺️](#二、幂等性解决方案全景图 🗺️)
-
- [2.1 各类方案对比分析](#2.1 各类方案对比分析)
- [三、基于业务设计的幂等方案 💡](#三、基于业务设计的幂等方案 💡)
-
- [3.1 状态机幂等设计](#3.1 状态机幂等设计)
- [3.2 唯一业务编号方案](#3.2 唯一业务编号方案)
- [四、基于Dubbo框架的幂等实现 ⚙️](#四、基于Dubbo框架的幂等实现 ⚙️)
-
- [4.1 Dubbo幂等过滤器(Filter)](#4.1 Dubbo幂等过滤器(Filter))
- [4.2 自定义幂等注解](#4.2 自定义幂等注解)
- [五、分布式环境下的高级幂等方案 🚀](#五、分布式环境下的高级幂等方案 🚀)
-
- [5.1 基于Redis的分布式锁幂等](#5.1 基于Redis的分布式锁幂等)
- [5.2 数据库乐观锁幂等方案](#5.2 数据库乐观锁幂等方案)
- [六、Dubbo幂等性最佳实践 📋](#六、Dubbo幂等性最佳实践 📋)
-
- [6.1 不同场景下的方案选择](#6.1 不同场景下的方案选择)
- [6.2 幂等性实施检查清单](#6.2 幂等性实施检查清单)
- [6.3 配置文件示例](#6.3 配置文件示例)
- [6.4 监控与告警配置](#6.4 监控与告警配置)
- [七、常见问题与解决方案 ❓](#七、常见问题与解决方案 ❓)
-
- [7.1 幂等键冲突问题](#7.1 幂等键冲突问题)
- [7.2 分布式环境下的时钟同步问题](#7.2 分布式环境下的时钟同步问题)
- [7.3 幂等结果反序列化问题](#7.3 幂等结果反序列化问题)
- [八、总结与展望 🎓](#八、总结与展望 🎓)
-
- [8.1 核心要点回顾](#8.1 核心要点回顾)
- [8.2 幂等性决策矩阵](#8.2 幂等性决策矩阵)
- [8.3 未来发展趋势](#8.3 未来发展趋势)
- [8.4 最后的建议](#8.4 最后的建议)
- [参考资料 📚](#参考资料 📚)
🎯 引言:一个价值百万的教训
先从一个真实的生产事故说起:
2020年,某电商平台在"双十一"大促期间,由于网络抖动和客户端重试机制,同一笔订单被重复扣款3次 ,导致数千名用户投诉,直接经济损失超过百万元💰。事后排查发现,根本原因是支付服务没有做好幂等性控制。
什么是幂等性?
幂等性(Idempotence) 是分布式系统中的核心概念,它指的是:无论一次操作执行多少次,其结果都应与执行一次相同。
举个生活中的例子:
- ✅ 幂等操作:按下电视遥控器的"关机"按钮,无论按多少次,电视都会关机
- ❌ 非幂等操作:用遥控器将音量调高5格,每按一次音量就增加5格
为什么微服务中幂等性如此重要?
在分布式系统中,网络不可靠是常态。Dubbo服务调用可能因为以下原因产生重复请求:
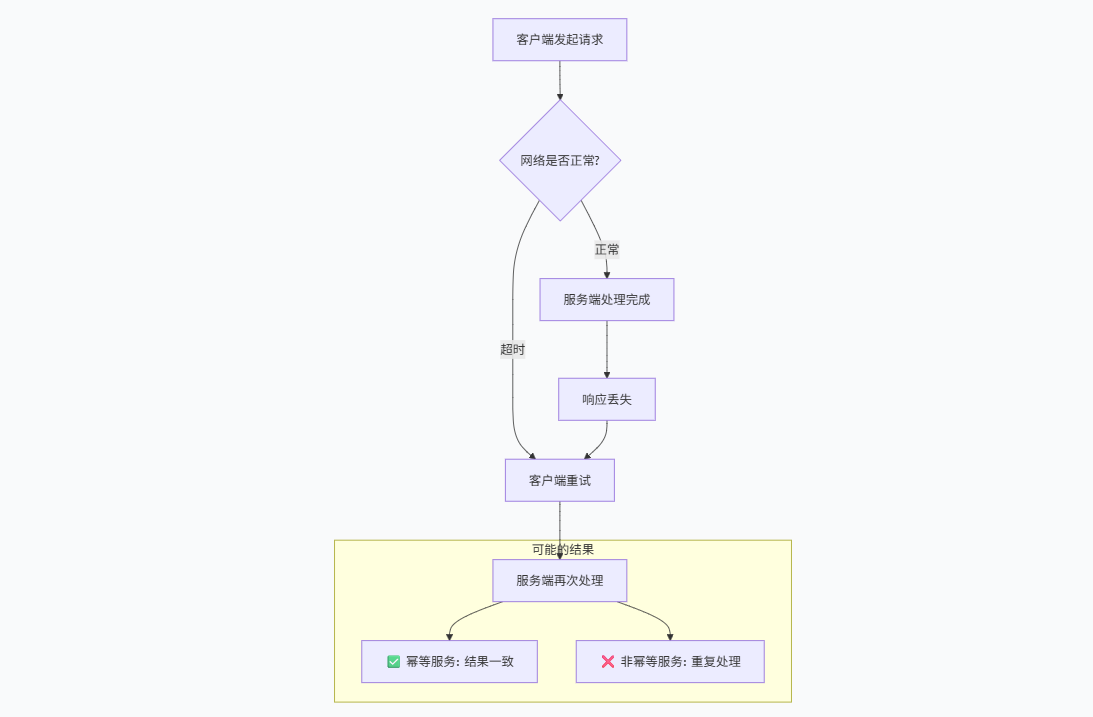
常见的重复请求场景:
| 场景 | 原因 | 影响 |
|---|---|---|
| 网络超时重试 | 客户端未收到响应,自动重试 | 数据重复处理 |
| 负载均衡重试 | Dubbo集群容错机制(如failover) | 同一请求发送到多个实例 |
| 消息队列重投 | 消息中间件重试机制 | 消费者重复消费 |
| 用户重复提交 | 用户连续点击提交按钮 | 业务逻辑重复执行 |
一、Dubbo幂等性基础:为什么需要特殊处理?🤔
1.1 Dubbo的默认行为分析
让我们先看看Dubbo在默认情况下的调用行为:
java
// 一个简单的Dubbo服务接口
public interface PaymentService {
/**
* 支付接口 - 默认情况下是非幂等的!
* @param orderId 订单ID
* @param amount 支付金额
* @return 支付结果
*/
PaymentResult pay(Long orderId, BigDecimal amount);
}
// Dubbo消费者调用示例
@Service
public class OrderService {
@DubboReference(retries = 3) // 默认重试3次
private PaymentService paymentService;
public void processPayment(Long orderId, BigDecimal amount) {
// 网络抖动时可能被多次调用!
PaymentResult result = paymentService.pay(orderId, amount);
// ...
}
}关键问题 :当pay()方法因为网络超时被重试时,用户可能会被重复扣款!
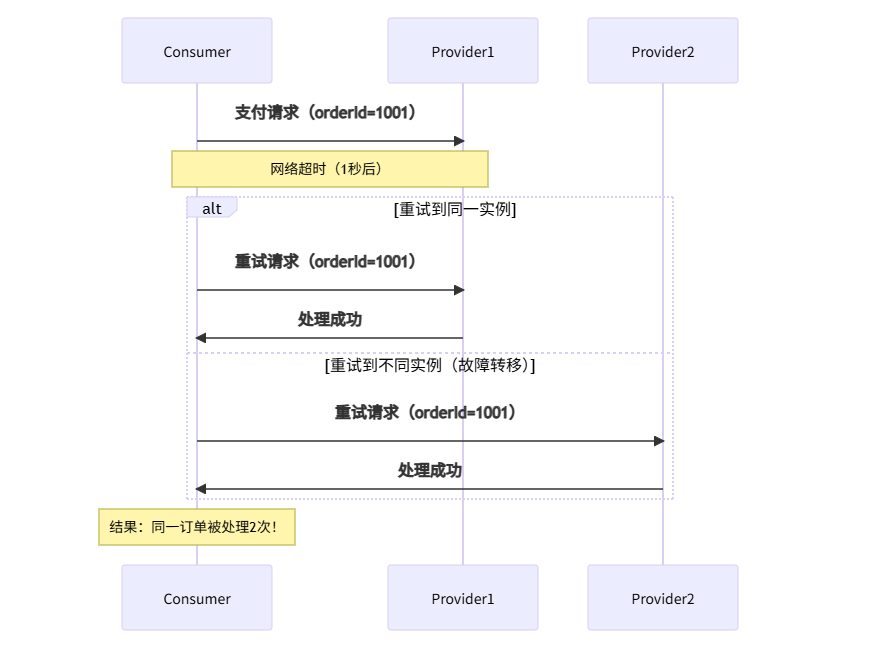
1.2 Dubbo重试机制详解
Dubbo提供了丰富的集群容错模式,其中一些会导致重复调用:
java
@DubboReference(
cluster = "failover", // 失败自动切换,默认值
retries = 2, // 重试2次
timeout = 1000 // 1秒超时
)
private PaymentService paymentService;Dubbo重试场景分析:
1.3 幂等性的数学原理
从数学角度理解幂等性:
对于函数 f(x),如果满足:f(f(x)) = f(x)
那么函数 f 是幂等的在Dubbo服务中的体现:
java
// 幂等服务:多次调用结果相同
paymentService.deductBalance(userId, 100); // 余额减少100
paymentService.deductBalance(userId, 100); // 再次调用,余额不变
// 非幂等服务:多次调用结果累积
paymentService.addBalance(userId, 100); // 余额增加100
paymentService.addBalance(userId, 100); // 再次调用,余额变为200二、幂等性解决方案全景图 🗺️
在深入Dubbo具体实现前,我们先了解完整的幂等性解决方案体系:
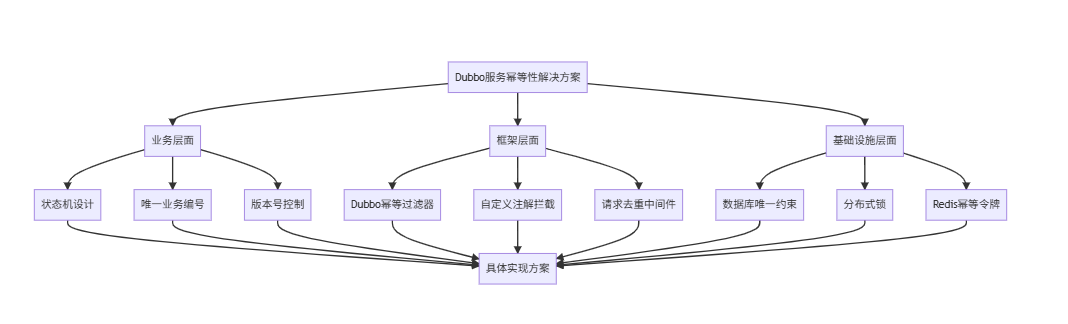
2.1 各类方案对比分析
| 方案类别 | 具体技术 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数据库层 | 唯一索引、乐观锁 | 实现简单,可靠性高 | 数据库压力大,性能影响 | 数据强一致性要求 |
| 分布式锁 | Redis锁、ZooKeeper锁 | 保证强一致性,通用性强 | 实现复杂,可能死锁 | 并发控制,临界资源 |
| 令牌机制 | Redis token、雪花算法 | 轻量级,性能好 | 需要额外存储,有状态 | 高并发,短时操作 |
| 框架拦截 | Dubbo Filter、Spring AOP | 无侵入,透明化 | 需要框架支持,配置复杂 | 全局限流,统一处理 |
| 业务设计 | 状态机、版本号 | 业务语义清晰 | 业务耦合度高 | 复杂业务流程 |
三、基于业务设计的幂等方案 💡
3.1 状态机幂等设计
通过状态流转控制,确保同一状态的操作只执行一次:
java
// 订单状态定义
public enum OrderStatus {
CREATED(1, "已创建"),
PAID(2, "已支付"),
SHIPPED(3, "已发货"),
COMPLETED(4, "已完成"),
CANCELED(5, "已取消");
// 状态流转规则
private static final Map<OrderStatus, Set<OrderStatus>> STATE_FLOW = new HashMap<>();
static {
STATE_FLOW.put(CREATED, Set.of(PAID, CANCELED));
STATE_FLOW.put(PAID, Set.of(SHIPPED, CANCELED));
STATE_FLOW.put(SHIPPED, Set.of(COMPLETED));
STATE_FLOW.put(COMPLETED, Set.of());
STATE_FLOW.put(CANCELED, Set.of());
}
public static boolean canTransfer(OrderStatus from, OrderStatus to) {
return STATE_FLOW.getOrDefault(from, Collections.emptySet()).contains(to);
}
}
// 幂等的订单服务实现
@Service
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
@Override
@Transactional
public boolean payOrder(Long orderId, BigDecimal amount) {
Order order = orderDao.selectById(orderId);
// 检查当前状态是否允许支付
if (!OrderStatus.canTransfer(order.getStatus(), OrderStatus.PAID)) {
// 已经是支付状态,直接返回成功(幂等)
if (order.getStatus() == OrderStatus.PAID) {
log.info("订单{}已经是支付状态,幂等返回", orderId);
return true;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("订单当前状态不允许支付");
}
// 执行支付逻辑
boolean paymentResult = paymentGateway.pay(orderId, amount);
if (paymentResult) {
// 更新订单状态为已支付
int rows = orderDao.updateStatus(orderId, OrderStatus.CREATED, OrderStatus.PAID);
if (rows == 0) {
// 乐观锁更新失败,说明状态已被其他请求修改
throw new ConcurrentUpdateException("订单状态并发修改");
}
}
return paymentResult;
}
}状态机幂等优势:
- ✅ 业务语义清晰
- ✅ 天然支持幂等(同一状态操作返回相同结果)
- ✅ 容易实现并发控制
3.2 唯一业务编号方案
为每个操作分配全局唯一ID,通过数据库唯一约束保证幂等:
java
// 支付记录表设计
CREATE TABLE payment_record (
id BIGINT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
payment_no VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL UNIQUE COMMENT '支付流水号,唯一标识一次支付',
order_id BIGINT NOT NULL COMMENT '订单ID',
amount DECIMAL(10, 2) NOT NULL COMMENT '支付金额',
status TINYINT NOT NULL COMMENT '支付状态',
create_time DATETIME NOT NULL,
update_time DATETIME NOT NULL,
INDEX idx_order_id (order_id),
INDEX idx_payment_no (payment_no)
) COMMENT='支付记录表';
// Dubbo服务实现
@DubboService
@Service
public class PaymentServiceImpl implements PaymentService {
@Autowired
private PaymentRecordDao paymentRecordDao;
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public PaymentResult pay(String paymentNo, Long orderId, BigDecimal amount) {
// 1. 先尝试插入支付记录(利用唯一约束实现幂等)
try {
PaymentRecord record = new PaymentRecord();
record.setPaymentNo(paymentNo);
record.setOrderId(orderId);
record.setAmount(amount);
record.setStatus(PaymentStatus.PROCESSING.getCode());
record.setCreateTime(new Date());
record.setUpdateTime(new Date());
paymentRecordDao.insert(record);
} catch (DuplicateKeyException e) {
// 2. 如果记录已存在,说明是重复请求
PaymentRecord existingRecord = paymentRecordDao.selectByPaymentNo(paymentNo);
log.info("重复支付请求,paymentNo={}, 返回已有结果", paymentNo);
// 根据已有状态返回结果
return buildResultFromRecord(existingRecord);
}
// 3. 执行实际的支付逻辑
try {
boolean success = thirdPartyPaymentGateway.execute(orderId, amount);
// 4. 更新支付状态
PaymentStatus status = success ? PaymentStatus.SUCCESS : PaymentStatus.FAILED;
paymentRecordDao.updateStatus(paymentNo, status);
return PaymentResult.builder()
.paymentNo(paymentNo)
.success(success)
.message(success ? "支付成功" : "支付失败")
.build();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 支付异常,更新为失败状态
paymentRecordDao.updateStatus(paymentNo, PaymentStatus.FAILED);
throw e;
}
}
private PaymentResult buildResultFromRecord(PaymentRecord record) {
boolean success = record.getStatus() == PaymentStatus.SUCCESS.getCode();
return PaymentResult.builder()
.paymentNo(record.getPaymentNo())
.success(success)
.message(success ? "支付成功(幂等返回)" : "支付失败(幂等返回)")
.build();
}
}客户端调用示例:
java
@Service
public class OrderPaymentService {
@DubboReference
private PaymentService paymentService;
/**
* 生成唯一的支付流水号
*/
private String generatePaymentNo(Long orderId) {
// 使用订单ID + 时间戳 + 随机数保证唯一性
return String.format("PAY-%d-%d-%04d",
orderId,
System.currentTimeMillis(),
ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(1000));
}
public PaymentResult processPayment(Long orderId, BigDecimal amount) {
// 为每次支付请求生成唯一ID
String paymentNo = generatePaymentNo(orderId);
// 调用支付服务
PaymentResult result = paymentService.pay(paymentNo, orderId, amount);
// 如果支付失败且原因是重复请求,记录日志但不抛出异常
if (!result.isSuccess() && "重复支付请求".equals(result.getMessage())) {
log.warn("订单{}支付重复请求,paymentNo={}", orderId, paymentNo);
}
return result;
}
}四、基于Dubbo框架的幂等实现 ⚙️
4.1 Dubbo幂等过滤器(Filter)
Dubbo的Filter机制是实现幂等性的理想位置:
java
/**
* Dubbo幂等过滤器
* 通过请求ID和业务键实现幂等控制
*/
@Activate(group = {CommonConstants.PROVIDER, CommonConstants.CONSUMER})
public class IdempotentFilter implements Filter {
private static final String HEADER_REQUEST_ID = "X-Request-ID";
private static final String HEADER_BUSINESS_KEY = "X-Business-Key";
@Autowired
private IdempotentService idempotentService;
@Override
public Result invoke(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
// 1. 只在提供者端进行幂等校验
if (!RpcContext.getContext().isProviderSide()) {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
// 2. 获取请求ID和业务键
String requestId = RpcContext.getContext().getAttachment(HEADER_REQUEST_ID);
String businessKey = RpcContext.getContext().getAttachment(HEADER_BUSINESS_KEY);
// 3. 如果请求没有幂等标识,直接放行
if (StringUtils.isBlank(requestId) || StringUtils.isBlank(businessKey)) {
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
// 4. 生成幂等键:服务名 + 方法名 + 业务键
String serviceName = invoker.getInterface().getName();
String methodName = invocation.getMethodName();
String idempotentKey = String.format("%s:%s:%s", serviceName, methodName, businessKey);
// 5. 检查是否已处理过
IdempotentRecord record = idempotentService.getRecord(idempotentKey, requestId);
if (record != null) {
// 已处理过,直接返回之前的结果
log.info("幂等请求命中,key={}, requestId={}", idempotentKey, requestId);
return deserializeResult(record.getResultData());
}
// 6. 执行前保存处理标记(防止并发)
boolean acquired = idempotentService.acquireLock(idempotentKey, requestId);
if (!acquired) {
// 获取锁失败,说明正在处理中
throw new RpcException("请求正在处理中,请稍后重试");
}
try {
// 7. 执行业务逻辑
Result result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
// 8. 保存处理结果(无论成功还是异常)
if (result.hasException()) {
idempotentService.saveFailure(idempotentKey, requestId, result.getException());
} else {
idempotentService.saveSuccess(idempotentKey, requestId, serializeResult(result));
}
return result;
} finally {
// 9. 释放锁
idempotentService.releaseLock(idempotentKey, requestId);
}
}
private String serializeResult(Result result) {
// 序列化结果对象
try {
return JSON.toJSONString(result.getValue());
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
}
}
private Result deserializeResult(String resultData) {
// 反序列化结果对象
if (StringUtils.isBlank(resultData)) {
return new AppResponse();
}
try {
Object value = JSON.parseObject(resultData, Object.class);
return new AppResponse(value);
} catch (Exception e) {
return new AppResponse();
}
}
}幂等服务实现:
java
@Service
public class RedisIdempotentServiceImpl implements IdempotentService {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
// 请求结果保存时间(24小时)
private static final long RESULT_EXPIRE_SECONDS = 24 * 60 * 60;
// 处理锁超时时间(30秒)
private static final long LOCK_EXPIRE_SECONDS = 30;
@Override
public IdempotentRecord getRecord(String idempotentKey, String requestId) {
String recordKey = buildRecordKey(idempotentKey, requestId);
String recordJson = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(recordKey);
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(recordJson)) {
return JSON.parseObject(recordJson, IdempotentRecord.class);
}
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean acquireLock(String idempotentKey, String requestId) {
String lockKey = buildLockKey(idempotentKey);
// 使用SETNX实现分布式锁
Boolean acquired = redisTemplate.opsForValue()
.setIfAbsent(lockKey, requestId, LOCK_EXPIRE_SECONDS, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return Boolean.TRUE.equals(acquired);
}
@Override
public void saveSuccess(String idempotentKey, String requestId, String resultData) {
String recordKey = buildRecordKey(idempotentKey, requestId);
IdempotentRecord record = new IdempotentRecord();
record.setIdempotentKey(idempotentKey);
record.setRequestId(requestId);
record.setSuccess(true);
record.setResultData(resultData);
record.setProcessTime(new Date());
String recordJson = JSON.toJSONString(record);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(recordKey, recordJson, RESULT_EXPIRE_SECONDS, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 清理锁
String lockKey = buildLockKey(idempotentKey);
redisTemplate.delete(lockKey);
}
@Override
public void saveFailure(String idempotentKey, String requestId, Throwable exception) {
String recordKey = buildRecordKey(idempotentKey, requestId);
IdempotentRecord record = new IdempotentRecord();
record.setIdempotentKey(idempotentKey);
record.setRequestId(requestId);
record.setSuccess(false);
record.setErrorMessage(exception.getMessage());
record.setProcessTime(new Date());
String recordJson = JSON.toJSONString(record);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(recordKey, recordJson, RESULT_EXPIRE_SECONDS, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 清理锁
String lockKey = buildLockKey(idempotentKey);
redisTemplate.delete(lockKey);
}
@Override
public void releaseLock(String idempotentKey, String requestId) {
String lockKey = buildLockKey(idempotentKey);
// 只有锁的持有者才能释放锁
String lockHolder = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(lockKey);
if (requestId.equals(lockHolder)) {
redisTemplate.delete(lockKey);
}
}
private String buildRecordKey(String idempotentKey, String requestId) {
return String.format("idempotent:record:%s:%s", idempotentKey, requestId);
}
private String buildLockKey(String idempotentKey) {
return String.format("idempotent:lock:%s", idempotentKey);
}
}4.2 自定义幂等注解
更优雅的方式是通过注解实现幂等控制:
java
/**
* 幂等注解
* 标注在Dubbo服务方法上,自动实现幂等控制
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface DubboIdempotent {
/**
* 幂等键的生成策略
*/
KeyStrategy keyStrategy() default KeyStrategy.BUSINESS_KEY;
/**
* 业务键参数位置(从0开始)
*/
int[] keyParams() default {0};
/**
* 结果保存时间(秒)
*/
long expireSeconds() default 3600;
/**
* 错误时的重试策略
*/
RetryStrategy retryStrategy() default RetryStrategy.FAIL_FAST;
enum KeyStrategy {
/**
* 基于业务参数生成
*/
BUSINESS_KEY,
/**
* 基于请求ID生成
*/
REQUEST_ID,
/**
* 自定义生成器
*/
CUSTOM
}
enum RetryStrategy {
/**
* 快速失败,直接抛出异常
*/
FAIL_FAST,
/**
* 返回上次执行结果
*/
RETURN_PREVIOUS,
/**
* 等待重试
*/
WAIT_RETRY
}
}
// 使用示例
@DubboService
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
@Override
@DubboIdempotent(
keyStrategy = DubboIdempotent.KeyStrategy.BUSINESS_KEY,
keyParams = {0}, // 使用第一个参数(orderId)作为业务键
expireSeconds = 7200,
retryStrategy = DubboIdempotent.RetryStrategy.RETURN_PREVIOUS
)
public PaymentResult pay(Long orderId, BigDecimal amount) {
// 业务逻辑
return doPay(orderId, amount);
}
}注解处理器实现:
java
/**
* 幂等注解的AOP处理器
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class IdempotentAspect {
@Autowired
private IdempotentService idempotentService;
@Autowired
private IdempotentKeyGenerator keyGenerator;
@Around("@annotation(idempotentAnnotation)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, DubboIdempotent idempotentAnnotation) throws Throwable {
// 1. 生成幂等键
String idempotentKey = generateIdempotentKey(joinPoint, idempotentAnnotation);
// 2. 获取请求ID(从Dubbo上下文或生成)
String requestId = getRequestId();
// 3. 检查是否已处理
IdempotentRecord record = idempotentService.getRecord(idempotentKey, requestId);
if (record != null) {
return handleExistingRecord(record, idempotentAnnotation.retryStrategy());
}
// 4. 获取处理锁
boolean lockAcquired = idempotentService.acquireLock(idempotentKey, requestId);
if (!lockAcquired) {
return handleLockNotAcquired(idempotentAnnotation.retryStrategy());
}
try {
// 5. 执行业务逻辑
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
// 6. 保存成功结果
idempotentService.saveSuccess(idempotentKey, requestId, serializeResult(result));
return result;
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
// 7. 保存失败结果
idempotentService.saveFailure(idempotentKey, requestId, throwable);
throw throwable;
} finally {
// 8. 释放锁
idempotentService.releaseLock(idempotentKey, requestId);
}
}
private String generateIdempotentKey(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, DubboIdempotent annotation) {
Method method = ((MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature()).getMethod();
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
switch (annotation.keyStrategy()) {
case BUSINESS_KEY:
return keyGenerator.generateBusinessKey(method, args, annotation.keyParams());
case REQUEST_ID:
return keyGenerator.generateRequestIdKey(method, getRequestId());
case CUSTOM:
return keyGenerator.generateCustomKey(method, args);
default:
return keyGenerator.generateDefaultKey(method, args);
}
}
private String getRequestId() {
// 从Dubbo上下文中获取请求ID
String requestId = RpcContext.getContext().getAttachment("X-Request-ID");
if (StringUtils.isBlank(requestId)) {
// 生成新的请求ID
requestId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
RpcContext.getContext().setAttachment("X-Request-ID", requestId);
}
return requestId;
}
private Object handleExistingRecord(IdempotentRecord record, DubboIdempotent.RetryStrategy retryStrategy) {
switch (retryStrategy) {
case RETURN_PREVIOUS:
if (record.isSuccess()) {
return deserializeResult(record.getResultData());
} else {
throw new IdempotentException("前次执行失败: " + record.getErrorMessage());
}
case FAIL_FAST:
throw new IdempotentException("重复请求");
case WAIT_RETRY:
// 等待一段时间后重试
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
return null; // 返回null让调用方重试
default:
throw new IdempotentException("重复请求");
}
}
private Object handleLockNotAcquired(DubboIdempotent.RetryStrategy retryStrategy) {
switch (retryStrategy) {
case WAIT_RETRY:
// 等待后抛出异常,让Dubbo重试机制处理
throw new TemporaryException("服务繁忙,请重试");
case FAIL_FAST:
case RETURN_PREVIOUS:
default:
throw new IdempotentException("请求正在处理中");
}
}
private String serializeResult(Object result) {
try {
return JSON.toJSONString(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
}
}
private Object deserializeResult(String resultData) {
try {
return JSON.parseObject(resultData, Object.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
}
}
}五、分布式环境下的高级幂等方案 🚀
5.1 基于Redis的分布式锁幂等
java
/**
* 基于Redis分布式锁的幂等控制器
*/
@Component
public class RedisIdempotentController {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
private static final String IDEMPOTENT_PREFIX = "idempotent:";
private static final long DEFAULT_EXPIRE_TIME = 3600; // 1小时
/**
* 尝试获取幂等锁并执行操作
*/
public <T> T executeWithIdempotent(String key, Supplier<T> supplier, Class<T> clazz) {
return executeWithIdempotent(key, supplier, clazz, DEFAULT_EXPIRE_TIME);
}
public <T> T executeWithIdempotent(String key, Supplier<T> supplier,
Class<T> clazz, long expireSeconds) {
String redisKey = IDEMPOTENT_PREFIX + key;
// 1. 尝试设置NX,如果已存在则直接返回
Boolean setSuccess = redisTemplate.opsForValue()
.setIfAbsent(redisKey, "processing", expireSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(setSuccess)) {
// 2. 检查是否已处理完成
String resultJson = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(redisKey);
if (!"processing".equals(resultJson)) {
// 已处理完成,反序列化返回结果
return deserializeResult(resultJson, clazz);
}
// 3. 还在处理中,根据策略处理
return handleProcessing(key, clazz);
}
try {
// 4. 执行业务逻辑
T result = supplier.get();
// 5. 保存处理结果
String resultJson = serializeResult(result);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(redisKey, resultJson, expireSeconds, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
// 6. 处理失败,删除key(允许重试)
redisTemplate.delete(redisKey);
throw e;
}
}
/**
* 支持重入的幂等锁
*/
public <T> T executeWithReentrantIdempotent(String key, String requestId,
Supplier<T> supplier, Class<T> clazz) {
String redisKey = IDEMPOTENT_PREFIX + key;
String lockKey = IDEMPOTENT_PREFIX + "lock:" + key;
// 使用Hash结构存储,支持重入
String currentRequestId = redisTemplate.<String, String>opsForHash()
.get(redisKey, "requestId");
if (requestId.equals(currentRequestId)) {
// 同一个请求重入,直接返回缓存结果
String resultJson = redisTemplate.<String, String>opsForHash()
.get(redisKey, "result");
if (resultJson != null) {
return deserializeResult(resultJson, clazz);
}
}
// 尝试获取分布式锁
boolean lockAcquired = tryAcquireLock(lockKey, requestId, 30);
if (!lockAcquired) {
throw new ConcurrentRequestException("请求正在处理中");
}
try {
// 设置当前请求ID
redisTemplate.<String, String>opsForHash()
.put(redisKey, "requestId", requestId);
redisTemplate.expire(redisKey, DEFAULT_EXPIRE_TIME, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 执行业务逻辑
T result = supplier.get();
// 保存结果
String resultJson = serializeResult(result);
redisTemplate.<String, String>opsForHash()
.put(redisKey, "result", resultJson);
return result;
} finally {
// 释放锁
releaseLock(lockKey, requestId);
}
}
private boolean tryAcquireLock(String lockKey, String requestId, long expireSeconds) {
String script =
"if redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0 then " +
" redis.call('hset', KEYS[1], 'owner', ARGV[1]) " +
" redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], 'count', 1) " +
" redis.call('expire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) " +
" return 1 " +
"elseif redis.call('hget', KEYS[1], 'owner') == ARGV[1] then " +
" redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], 'count', 1) " +
" redis.call('expire', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) " +
" return 1 " +
"else " +
" return 0 " +
"end";
Long result = redisTemplate.execute(
new DefaultRedisScript<>(script, Long.class),
Collections.singletonList(lockKey),
requestId,
String.valueOf(expireSeconds)
);
return result != null && result == 1;
}
private void releaseLock(String lockKey, String requestId) {
String script =
"if redis.call('hget', KEYS[1], 'owner') == ARGV[1] then " +
" local count = redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], 'count', -1) " +
" if count <= 0 then " +
" redis.call('del', KEYS[1]) " +
" end " +
" return 1 " +
"else " +
" return 0 " +
"end";
redisTemplate.execute(
new DefaultRedisScript<>(script, Long.class),
Collections.singletonList(lockKey),
requestId
);
}
private String serializeResult(Object result) {
try {
return JSON.toJSONString(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
}
}
private <T> T deserializeResult(String resultJson, Class<T> clazz) {
try {
return JSON.parseObject(resultJson, clazz);
} catch (Exception e) {
return null;
}
}
private <T> T handleProcessing(String key, Class<T> clazz) {
// 实现等待或快速失败策略
// 这里实现等待策略,最多等待5秒
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new IdempotentException("等待中断");
}
String resultJson = redisTemplate.opsForValue()
.get(IDEMPOTENT_PREFIX + key);
if (!"processing".equals(resultJson)) {
return deserializeResult(resultJson, clazz);
}
}
throw new IdempotentException("处理超时");
}
}5.2 数据库乐观锁幂等方案
java
/**
* 基于数据库乐观锁的幂等实现
*/
@Service
public class OptimisticLockIdempotentService {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**
* 使用版本号实现乐观锁幂等
*/
public boolean updateWithVersion(String tableName, Long id,
Map<String, Object> updates,
int expectedVersion) {
// 构建SET子句
StringBuilder setClause = new StringBuilder();
List<Object> params = new ArrayList<>();
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : updates.entrySet()) {
if (!"version".equals(entry.getKey())) {
setClause.append(entry.getKey()).append(" = ?, ");
params.add(entry.getValue());
}
}
// 添加版本更新
setClause.append("version = version + 1, update_time = NOW() ");
// 构建WHERE条件
String whereClause = "WHERE id = ? AND version = ? AND is_deleted = 0";
params.add(id);
params.add(expectedVersion);
// 执行更新
String sql = String.format("UPDATE %s SET %s %s", tableName, setClause, whereClause);
int rows = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, params.toArray());
return rows > 0;
}
/**
* 使用状态机的乐观锁实现
*/
public boolean updateOrderStatus(Long orderId, String fromStatus,
String toStatus, String requestId) {
String sql =
"UPDATE orders " +
"SET status = ?, " +
" update_time = NOW(), " +
" last_request_id = ? " +
"WHERE id = ? " +
" AND status = ? " +
" AND (last_request_id IS NULL OR last_request_id != ?) " +
" AND is_deleted = 0";
int rows = jdbcTemplate.update(sql,
toStatus, requestId, orderId, fromStatus, requestId);
if (rows > 0) {
return true;
} else {
// 检查是否已经被当前请求处理过
String checkSql =
"SELECT COUNT(1) FROM orders " +
"WHERE id = ? AND status = ? AND last_request_id = ?";
Integer count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(
checkSql, Integer.class, orderId, toStatus, requestId);
return count != null && count > 0;
}
}
/**
* 插入幂等记录表
*/
public boolean insertIdempotentRecord(String requestId, String businessType,
String businessKey, String initStatus) {
String sql =
"INSERT INTO idempotent_record (" +
" request_id, business_type, business_key, " +
" status, create_time, update_time" +
") VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, NOW(), NOW()) " +
"ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE " +
" update_time = NOW()";
try {
int rows = jdbcTemplate.update(sql,
requestId, businessType, businessKey, initStatus);
return rows > 0;
} catch (DuplicateKeyException e) {
// 记录已存在,幂等返回成功
return true;
}
}
}六、Dubbo幂等性最佳实践 📋
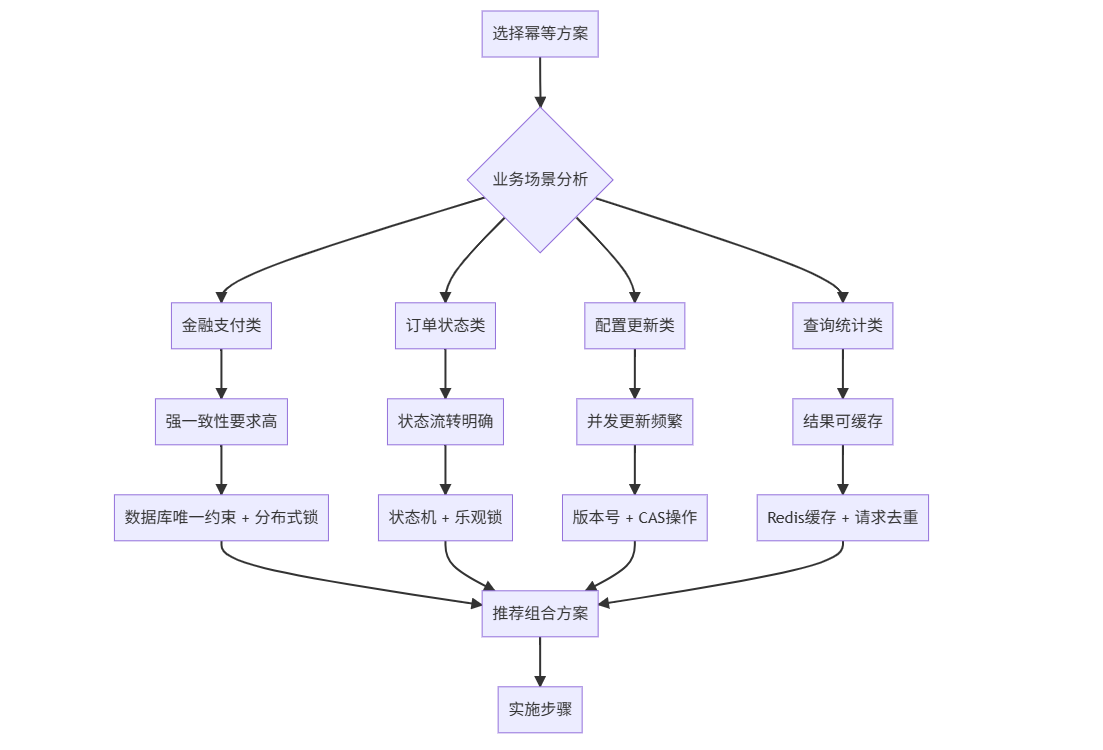
6.1 不同场景下的方案选择
6.2 幂等性实施检查清单
| 检查项 | 是否完成 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 业务分析 | ☐ | 识别出需要幂等性的服务和方法 |
| 方案设计 | ☐ | 选择适合业务场景的幂等方案 |
| 唯一键设计 | ☐ | 设计全局唯一的业务键或请求ID |
| 异常处理 | ☐ | 定义重复请求的响应策略 |
| 并发控制 | ☐ | 实现分布式锁或乐观锁 |
| 结果缓存 | ☐ | 缓存处理结果,支持快速返回 |
| 过期策略 | ☐ | 设置合理的缓存过期时间 |
| 监控告警 | ☐ | 监控幂等拦截情况和重复请求率 |
| 性能测试 | ☐ | 验证幂等方案对性能的影响 |
| 回滚方案 | ☐ | 准备方案失效时的应急措施 |
6.3 配置文件示例
yaml
# application-idempotent.yml
dubbo:
idempotent:
enabled: true
# 默认策略配置
default:
enabled: true
strategy: redis # 使用Redis实现
expire-time: 3600 # 结果缓存1小时
lock-timeout: 30 # 锁超时30秒
retry-strategy: return_previous # 重复请求返回上次结果
# 服务级配置
services:
com.example.PaymentService:
enabled: true
methods:
pay:
strategy: database # 支付使用数据库唯一约束
key-generator: business # 使用业务键
key-params: [0, 1] # 使用前两个参数生成键
refund:
strategy: redis_lock # 退款使用Redis锁
expire-time: 7200 # 缓存2小时
# Redis配置
redis:
host: ${REDIS_HOST:localhost}
port: ${REDIS_PORT:6379}
database: 1 # 使用专用数据库
timeout: 2000
# 集群配置
cluster:
nodes: ${REDIS_CLUSTER_NODES:}
# 哨兵配置
sentinel:
master: ${REDIS_SENTINEL_MASTER:}
nodes: ${REDIS_SENTINEL_NODES:}
# 监控配置
monitor:
enabled: true
# Prometheus指标
metrics:
enabled: true
path: /actuator/idempotent-metrics
# 日志记录
logging:
enabled: true
level: INFO6.4 监控与告警配置
java
/**
* 幂等性监控指标
*/
@Component
public class IdempotentMetrics {
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
// 计数器指标
private final Counter totalRequests;
private final Counter idempotentHits;
private final Counter concurrentBlocks;
private final Timer processingTimer;
public IdempotentMetrics(MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
// 初始化指标
this.totalRequests = Counter.builder("dubbo.idempotent.requests.total")
.description("总请求数")
.register(meterRegistry);
this.idempotentHits = Counter.builder("dubbo.idempotent.hits.total")
.description("幂等命中数")
.register(meterRegistry);
this.concurrentBlocks = Counter.builder("dubbo.idempotent.blocks.total")
.description("并发阻塞数")
.register(meterRegistry);
this.processingTimer = Timer.builder("dubbo.idempotent.processing.time")
.description("处理时间")
.publishPercentiles(0.5, 0.95, 0.99)
.register(meterRegistry);
}
public void recordRequest(String service, String method) {
totalRequests.increment();
// 添加标签
meterRegistry.counter("dubbo.idempotent.requests",
"service", service,
"method", method).increment();
}
public void recordIdempotentHit(String service, String method) {
idempotentHits.increment();
meterRegistry.counter("dubbo.idempotent.hits",
"service", service,
"method", method).increment();
}
public void recordConcurrentBlock(String service, String method) {
concurrentBlocks.increment();
meterRegistry.counter("dubbo.idempotent.blocks",
"service", service,
"method", method).increment();
}
public Timer.Sample startProcessingTimer() {
return Timer.start(meterRegistry);
}
public void stopProcessingTimer(Timer.Sample sample, String service, String method) {
sample.stop(processingTimer);
meterRegistry.timer("dubbo.idempotent.processing",
"service", service,
"method", method);
}
/**
* 获取幂等命中率
*/
public double getIdempotentHitRate() {
double total = totalRequests.count();
double hits = idempotentHits.count();
return total > 0 ? hits / total : 0.0;
}
/**
* 获取并发阻塞率
*/
public double getConcurrentBlockRate() {
double total = totalRequests.count();
double blocks = concurrentBlocks.count();
return total > 0 ? blocks / total : 0.0;
}
}七、常见问题与解决方案 ❓
7.1 幂等键冲突问题
问题:不同业务使用相同键导致冲突
解决方案:设计层级化的键结构
java
public class IdempotentKeyGenerator {
/**
* 生成层级化的幂等键
*/
public String generateHierarchicalKey(String service, String method,
String businessType, String businessKey) {
// 格式:服务:方法:业务类型:业务键
return String.format("%s:%s:%s:%s",
sanitize(service),
sanitize(method),
sanitize(businessType),
sanitize(businessKey));
}
/**
* 支持通配符的键匹配
*/
public boolean matchKey(String pattern, String key) {
// 将*替换为正则表达式.*
String regex = pattern.replace(".", "\\.").replace("*", ".*");
return key.matches(regex);
}
/**
* 生成带时间窗口的键(防止历史数据影响)
*/
public String generateTimeWindowKey(String baseKey, long windowMinutes) {
long windowIndex = System.currentTimeMillis() / (windowMinutes * 60 * 1000);
return String.format("%s:window:%d", baseKey, windowIndex);
}
private String sanitize(String input) {
if (input == null) return "";
// 替换可能引起问题的字符
return input.replace(":", "_").replace("*", "_").replace("?", "_");
}
}7.2 分布式环境下的时钟同步问题
问题:不同服务器时钟不同步,导致时间相关逻辑出错
解决方案:使用逻辑时钟或统一时间源
java
public class DistributedTimeService {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
/**
* 获取分布式递增ID(替代时间戳)
*/
public long getDistributedId(String businessType) {
String key = "distributed:id:" + businessType;
Long id = redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(key);
return id != null ? id : 0L;
}
/**
* 获取逻辑时间戳(避免时钟回拨)
*/
public long getLogicalTimestamp(String instanceId) {
String key = "logical:timestamp:" + instanceId;
String current = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
long logicalTime = current != null ? Long.parseLong(current) : now;
// 确保逻辑时间单调递增
if (now > logicalTime) {
logicalTime = now;
} else {
logicalTime++; // 如果当前时间小于逻辑时间,递增逻辑时间
}
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, String.valueOf(logicalTime));
return logicalTime;
}
/**
* 使用Redis的时间(相对准确)
*/
public long getRedisTime() {
try {
// Redis TIME命令返回当前服务器时间
List<Object> time = redisTemplate.execute(
(RedisCallback<List<Object>>) connection ->
connection.serverCommands().time()
);
if (time != null && time.size() >= 2) {
long seconds = Long.parseLong(time.get(0).toString());
long microSeconds = Long.parseLong(time.get(1).toString());
return seconds * 1000 + microSeconds / 1000;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// 降级到本地时间
log.warn("获取Redis时间失败,使用本地时间", e);
}
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}7.3 幂等结果反序列化问题
问题:缓存的结果无法正确反序列化
解决方案:使用类型安全的序列化方案
java
public class TypeSafeSerializer {
private static final String TYPE_INFO_KEY = "__type__";
/**
* 带类型信息的序列化
*/
public String serializeWithType(Object obj) {
if (obj == null) return null;
Map<String, Object> data = new HashMap<>();
data.put(TYPE_INFO_KEY, obj.getClass().getName());
data.put("data", obj);
return JSON.toJSONString(data);
}
/**
* 带类型信息的反序列化
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T deserializeWithType(String json) {
if (json == null) return null;
try {
Map<String, Object> data = JSON.parseObject(json, Map.class);
String className = (String) data.get(TYPE_INFO_KEY);
Object dataObj = data.get("data");
if (className != null && dataObj != null) {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
String dataJson = JSON.toJSONString(dataObj);
return (T) JSON.parseObject(dataJson, clazz);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("反序列化失败: {}", json, e);
}
return null;
}
/**
* 兼容性反序列化(尝试多种类型)
*/
public Object deserializeCompatible(String json, Class<?>... candidateTypes) {
if (candidateTypes == null || candidateTypes.length == 0) {
return JSON.parseObject(json, Object.class);
}
for (Class<?> clazz : candidateTypes) {
try {
return JSON.parseObject(json, clazz);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 尝试下一个类型
}
}
// 都失败,返回Map
return JSON.parseObject(json, Map.class);
}
}八、总结与展望 🎓
8.1 核心要点回顾
通过本文的详细讲解,我们掌握了Dubbo服务调用幂等性的完整解决方案:
✅ 理解幂等性 :无论操作执行多少次,结果都与执行一次相同
✅ 识别幂等场景 :支付、下单、状态变更等关键业务
✅ 掌握多种方案 :数据库唯一约束、分布式锁、状态机、版本控制
✅ 实现Dubbo集成 :通过Filter、注解、AOP等方式无缝集成
✅ 处理复杂情况 :分布式环境、时钟同步、反序列化等
✅ 建立监控体系:指标收集、告警设置、性能分析
8.2 幂等性决策矩阵
| 业务特征 | 推荐方案 | 技术实现 | 注意事项 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 强一致性金融业务 | 数据库唯一约束 + 分布式锁 | 唯一索引 + Redis锁 | 注意死锁和性能 |
| 订单状态流转 | 状态机 + 乐观锁 | 状态枚举 + 版本号 | 设计合理的状态流转 |
| 配置批量更新 | 版本号 + CAS操作 | 版本字段 + 条件更新 | 处理更新冲突 |
| 高并发查询 | 请求去重 + 结果缓存 | Redis + 内存缓存 | 缓存一致性问题 |
| 异步消息处理 | 消息ID幂等 + 去重表 | 消息中间件 + 数据库 | 消息顺序和重复 |
8.3 未来发展趋势
随着技术发展,幂等性方案也在不断演进:
- 服务网格集成:通过Istio等服务网格实现透明的幂等控制
- 云原生方案:利用云服务的原生幂等特性(如AWS Lambda)
- 智能幂等:基于AI预测的智能重试和幂等决策
- 标准化协议:HTTP/3等新协议对幂等的原生支持
- 区块链应用:利用区块链的不可篡改性实现天然幂等
8.4 最后的建议
🚨 重要提醒:幂等性不是银弹,需要根据具体业务场景选择合适的方案。建议从小范围试点开始,逐步推广到全系统。同时,完善的监控和告警机制是幂等方案成功的保障。
参考资料 📚
💡 扩展阅读建议:除了本文介绍的技术方案,还可以深入学习分布式事务(如Seata)、事件溯源(Event Sourcing)等高级主题,它们提供了另一种视角来解决数据一致性问题。
标签 : Dubbo 幂等性 分布式系统 微服务 Java