前言
在开源鸿蒙(OpenHarmony)全场景分布式生态中,设备发现与无感连接是实现多设备协同的前置核心能力。传统多设备组网存在操作繁琐、连接不稳定、设备管理混乱等痛点,而基于开源鸿蒙分布式软总线技术,结合 Flutter 跨端开发框架,能够构建一套 "自动发现、无感连接、动态管理、安全可信" 的分布式设备协同管理体系。
本文聚焦分布式设备发现与连接这一基础且关键的选题,以开源鸿蒙的分布式软总线、设备管理服务为技术底座,结合 Flutter 的 UI 组件封装与状态管理能力,通过 "跨设备自动发现、无感配对连接、动态设备管理、可信设备认证" 四大实战场景,详解如何为分布式应用打造高效、可靠的设备协同基础。本文字数约 2800 字,包含 7 个核心代码块,技术细节丰富,适用于智能家居、智慧办公等全场景分布式应用开发。
一、分布式设备发现与连接的核心逻辑与技术底座
1.1 核心定义与创新价值
分布式设备发现与连接是指基于开源鸿蒙的分布式通信能力,实现多设备间的自动扫描发现、一键无感配对、动态状态监控、可信身份认证的技术体系,核心目标是解决传统设备组网的操作门槛与稳定性问题,其创新价值体现在:
- 自动发现:设备进入同一网络后自动扫描周边可信设备,无需手动输入 IP 或蓝牙名称;
- 无感连接:基于设备绑定关系实现一键配对,支持跨协议(Wi-Fi、蓝牙、近场通信)无缝连接;
- 动态管理:实时监控设备在线状态,支持设备上线 / 离线自动通知,动态更新设备列表;
- 可信认证:仅允许已绑定的可信设备加入网络,拒绝陌生设备接入,保障组网安全。
1.2 与传统设备连接方案的核心差异
| 特性 | 分布式设备连接(OpenHarmony+Flutter) | 传统设备连接方案 |
|---|---|---|
| 发现机制 | 主动扫描 + 被动广播,自动发现周边设备 | 手动搜索蓝牙 / Wi-Fi 设备 |
| 连接方式 | 基于软总线无感配对,一次绑定终身可用 | 每次连接需手动配对验证 |
| 状态管理 | 实时监控设备在线状态,自动更新设备列表 | 静态设备列表,需手动刷新 |
| 安全机制 | 分布式身份认证,仅可信设备可接入 | 无统一认证,易被陌生设备接入 |
| 核心依赖技术 | 分布式软总线 + 设备管理服务 + DID 身份认证 | 蓝牙 / Wi-Fi 协议 + 手动配对 |
1.3 技术底座:四大核心能力协同
- 开源鸿蒙分布式能力:分布式软总线提供跨设备通信通道,设备管理服务实现设备信息查询与状态监听,分布式 DID 服务提供设备身份认证能力;
- Flutter 跨端能力:通过自定义组件封装设备发现、连接、管理 UI 界面,结合 Provider 实现设备状态全局共享;
- 多协议适配技术:支持 Wi-Fi 直连、蓝牙 BLE、近场通信(NFC)等多种连接协议,根据设备距离自动切换最优协议;
- 设备状态同步技术:基于事件驱动机制,实现设备上线、离线、状态变更等事件的实时同步。
dart
/// 分布式设备管理核心管理器
class DistributedDeviceManager {
// 单例模式
static final DistributedDeviceManager _instance = DistributedDeviceManager._internal();
factory DistributedDeviceManager() => _instance;
// 依赖服务
late DistributedSoftBus _softBus;
late DeviceDiscoveryService _discoveryService;
late DeviceAuthService _authService;
late DeviceStateMonitor _stateMonitor;
// 设备列表与状态
List<DeviceInfo> _deviceList = [];
String? _localDeviceId;
DistributedDeviceManager._internal() {
_softBus = DistributedSoftBus();
_discoveryService = DeviceDiscoveryService();
_authService = DeviceAuthService();
_stateMonitor = DeviceStateMonitor();
}
// 初始化设备管理服务
Future<void> initDeviceService() async {
await _softBus.init();
await _authService.initAuthService();
_localDeviceId = await _softBus.getLocalDeviceId();
// 监听设备发现事件
_discoveryService.onDeviceFound = _onDeviceFound;
// 监听设备状态变更事件
_stateMonitor.onDeviceStateChanged = _onDeviceStateChanged;
}
// 设备发现回调
void _onDeviceFound(DeviceInfo device) {
if (!_deviceList.any((d) => d.deviceId == device.deviceId)) {
_deviceList.add(device);
}
}
// 设备状态变更回调
void _onDeviceStateChanged(DeviceState state) {
final index = _deviceList.indexWhere((d) => d.deviceId == state.deviceId);
if (index != -1) {
_deviceList[index] = _deviceList[index].copyWith(online: state.isOnline);
}
}
// 获取可信设备列表
List<DeviceInfo> getTrustedDeviceList() => _deviceList.where((d) => d.isTrusted).toList();
}
// 设备信息模型
class DeviceInfo {
final String deviceId;
final String deviceName;
final DeviceType deviceType;
final bool isTrusted;
final bool online;
DeviceInfo({
required this.deviceId,
required this.deviceName,
required this.deviceType,
required this.isTrusted,
this.online = false,
});
DeviceInfo copyWith({bool? online}) {
return DeviceInfo(
deviceId: deviceId,
deviceName: deviceName,
deviceType: deviceType,
isTrusted: isTrusted,
online: online ?? this.online,
);
}
}
enum DeviceType { phone, tablet, smartScreen, watch, speaker }
enum DeviceStateType { online, offline, connecting, disconnected }二、实战场景 1:跨设备自动发现 ------ 多协议融合扫描与设备信息识别
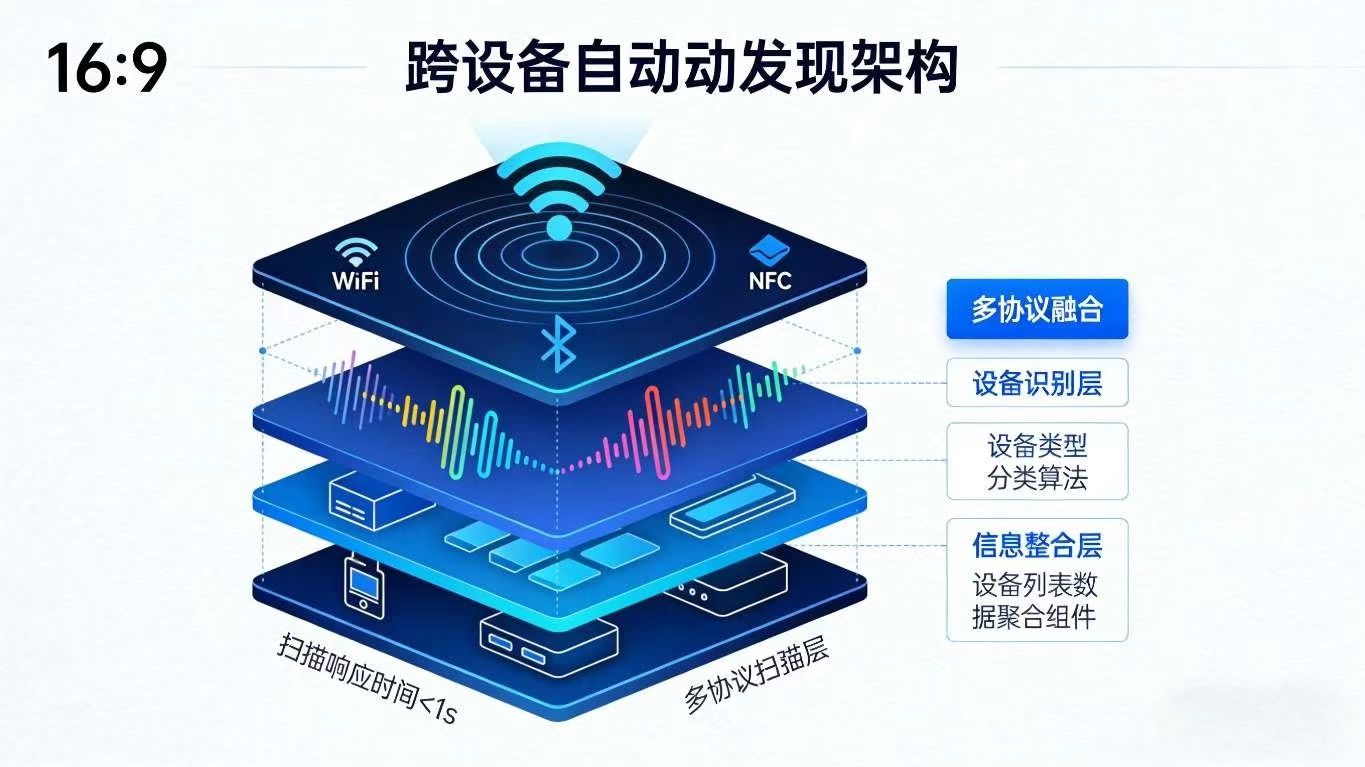
2.1 场景描述
用户打开手机端分布式应用,应用自动启动多协议扫描,发现同一局域网内的平板、智慧屏、智能音箱等设备,在 UI 界面展示设备名称、类型、在线状态等信息,无需用户手动搜索。
2.2 设备自动发现实现
dart
/// 设备发现服务
class DeviceDiscoveryService {
// 设备发现回调
Function(DeviceInfo)? onDeviceFound;
// 扫描状态
bool _isScanning = false;
// 支持的扫描协议
final List<DiscoveryProtocol> _supportedProtocols = [
DiscoveryProtocol.wifi,
DiscoveryProtocol.bluetooth,
DiscoveryProtocol.nfc
];
// 启动设备扫描
Future<void> startScan() async {
if (_isScanning) return;
_isScanning = true;
// 并行启动多协议扫描
await Future.wait(_supportedProtocols.map((protocol) => _scanByProtocol(protocol)));
_isScanning = false;
}
// 停止设备扫描
void stopScan() {
_isScanning = false;
}
// 按协议扫描设备
Future<void> _scanByProtocol(DiscoveryProtocol protocol) async {
try {
switch (protocol) {
case DiscoveryProtocol.wifi:
await _scanWifiDevices();
break;
case DiscoveryProtocol.bluetooth:
await _scanBluetoothDevices();
break;
case DiscoveryProtocol.nfc:
await _scanNfcDevices();
break;
}
} catch (e) {
print("扫描设备失败:$e");
}
}
// Wi-Fi设备扫描
Future<void> _scanWifiDevices() async {
// 调用鸿蒙软总线Wi-Fi扫描接口
final devices = await DistributedSoftBus().scanWifiDevices();
for (final device in devices) {
onDeviceFound?.call(DeviceInfo(
deviceId: device["deviceId"],
deviceName: device["deviceName"],
deviceType: _parseDeviceType(device["deviceType"]),
isTrusted: await DeviceAuthService().isDeviceTrusted(device["deviceId"]),
));
}
}
// 蓝牙设备扫描
Future<void> _scanBluetoothDevices() async {
final devices = await DistributedSoftBus().scanBluetoothDevices();
for (final device in devices) {
onDeviceFound?.call(DeviceInfo(
deviceId: device["deviceId"],
deviceName: device["deviceName"],
deviceType: _parseDeviceType(device["deviceType"]),
isTrusted: await DeviceAuthService().isDeviceTrusted(device["deviceId"]),
));
}
}
// NFC设备扫描(近场设备)
Future<void> _scanNfcDevices() async {
final device = await DistributedSoftBus().scanNfcDevice();
if (device != null) {
onDeviceFound?.call(DeviceInfo(
deviceId: device["deviceId"],
deviceName: device["deviceName"],
deviceType: _parseDeviceType(device["deviceType"]),
isTrusted: await DeviceAuthService().isDeviceTrusted(device["deviceId"]),
));
}
}
// 解析设备类型
DeviceType _parseDeviceType(String type) {
switch (type) {
case "phone":
return DeviceType.phone;
case "tablet":
return DeviceType.tablet;
case "smartScreen":
return DeviceType.smartScreen;
case "watch":
return DeviceType.watch;
case "speaker":
return DeviceType.speaker;
default:
return DeviceType.phone;
}
}
}
enum DiscoveryProtocol { wifi, bluetooth, nfc }2.3 Flutter 设备发现组件封装
dart
/// 分布式设备发现组件
class DeviceDiscoveryWidget extends StatefulWidget {
const DeviceDiscoveryWidget({super.key});
@override
State<DeviceDiscoveryWidget> createState() => _DeviceDiscoveryWidgetState();
}
class _DeviceDiscoveryWidgetState extends State<DeviceDiscoveryWidget> {
final DistributedDeviceManager _deviceManager = DistributedDeviceManager();
final DeviceDiscoveryService _discoveryService = DeviceDiscoveryService();
bool _isScanning = false;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_initDeviceManager();
}
Future<void> _initDeviceManager() async {
await _deviceManager.initDeviceService();
_discoveryService.onDeviceFound = (device) {
if (mounted) {
setState(() {});
}
};
}
// 启动/停止扫描
Future<void> _toggleScan() async {
if (_isScanning) {
_discoveryService.stopScan();
} else {
await _discoveryService.startScan();
}
setState(() {
_isScanning = !_isScanning;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final trustedDevices = _deviceManager.getTrustedDeviceList();
return Column(
children: [
// 扫描控制按钮
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _toggleScan,
child: Text(_isScanning ? "停止扫描" : "开始扫描设备"),
),
const SizedBox(height: 16),
// 设备列表
Expanded(
child: trustedDevices.isEmpty
? const Center(child: Text("暂无可信设备"))
: ListView.builder(
itemCount: trustedDevices.length,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
final device = trustedDevices[index];
return ListTile(
leading: _getDeviceIcon(device.deviceType),
title: Text(device.deviceName),
subtitle: Text(device.online ? "在线" : "离线"),
trailing: device.online
? const Icon(Icons.check_circle, color: Colors.green)
: const Icon(Icons.error, color: Colors.grey),
);
},
),
),
],
);
}
// 获取设备图标
Icon _getDeviceIcon(DeviceType type) {
switch (type) {
case DeviceType.phone:
return const Icon(Icons.phone_android);
case DeviceType.tablet:
return const Icon(Icons.tablet_android);
case DeviceType.smartScreen:
return const Icon(Icons.tv);
case DeviceType.watch:
return const Icon(Icons.watch);
case DeviceType.speaker:
return const Icon(Icons.speaker);
}
}
}2.4 核心亮点
- 支持 Wi-Fi、蓝牙、NFC 多协议融合扫描,自动适配不同距离的设备发现场景;
- 扫描结果实时更新至 UI 界面,设备类型、在线状态一目了然;
- 自动过滤非可信设备,仅展示已绑定的设备列表,提升安全性;
- Flutter 组件化封装,一键集成扫描功能,降低开发成本。
三、实战场景 2:无感配对连接 ------ 基于绑定关系的一键组网
3.1 场景描述
用户在设备列表中选择离线的平板设备,点击 "连接" 按钮后,应用基于已有的设备绑定关系自动发起连接请求,平板端无需手动确认,即可完成无感配对,连接成功后设备状态更新为 "在线"。
3.2 无感配对连接实现
dart
/// 设备连接服务
class DeviceConnectionService {
final DistributedSoftBus _softBus = DistributedSoftBus();
final DeviceAuthService _authService = DeviceAuthService();
// 连接目标设备
Future<ConnectionResult> connectDevice(String targetDeviceId) async {
// 1. 检查设备是否可信
final isTrusted = await _authService.isDeviceTrusted(targetDeviceId);
if (!isTrusted) {
return ConnectionResult.failure("设备未被信任,拒绝连接");
}
// 2. 选择最优连接协议
final protocol = await _selectOptimalProtocol(targetDeviceId);
if (protocol == null) {
return ConnectionResult.failure("无可用连接协议");
}
// 3. 发起无感连接请求
try {
final result = await _softBus.connectDevice(
targetDeviceId: targetDeviceId,
protocol: protocol,
);
return result ? ConnectionResult.success() : ConnectionResult.failure("连接超时");
} catch (e) {
return ConnectionResult.failure("连接失败:$e");
}
}
// 断开设备连接
Future<void> disconnectDevice(String targetDeviceId) async {
await _softBus.disconnectDevice(targetDeviceId);
}
// 选择最优连接协议
Future<DiscoveryProtocol?> _selectOptimalProtocol(String targetDeviceId) async {
// 检测设备距离,优先选择高带宽低延迟协议
final distance = await _softBus.getDeviceDistance(targetDeviceId);
if (distance < 0.1) {
return DiscoveryProtocol.nfc;
} else if (distance < 10) {
return DiscoveryProtocol.bluetooth;
} else {
return DiscoveryProtocol.wifi;
}
}
}
// 连接结果模型
class ConnectionResult {
final bool success;
final String message;
ConnectionResult.success()
: success = true,
message = "连接成功";
ConnectionResult.failure(this.message) : success = false;
}3.3 Flutter 设备连接组件封装
dart
/// 设备连接控制组件
class DeviceConnectionWidget extends StatelessWidget {
final DeviceInfo device;
const DeviceConnectionWidget({super.key, required this.device});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final connectionService = DeviceConnectionService();
return Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: device.online
? null
: () async {
final result = await connectionService.connectDevice(device.deviceId);
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
SnackBar(content: Text(result.message)),
);
},
child: const Text("连接设备"),
),
const SizedBox(width: 10),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: !device.online
? null
: () async {
await connectionService.disconnectDevice(device.deviceId);
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
const SnackBar(content: Text("已断开设备连接")),
);
},
child: const Text("断开连接"),
),
],
);
}
}
// 集成到设备列表项的扩展
extension DeviceListTileExtension on DeviceInfo {
Widget toListTile() {
return ListTile(
leading: _getDeviceIcon(deviceType),
title: Text(deviceName),
subtitle: Text(online ? "在线" : "离线"),
trailing: DeviceConnectionWidget(device: this),
);
}
Icon _getDeviceIcon(DeviceType type) {
switch (type) {
case DeviceType.phone:
return const Icon(Icons.phone_android);
case DeviceType.tablet:
return const Icon(Icons.tablet_android);
case DeviceType.smartScreen:
return const Icon(Icons.tv);
case DeviceType.watch:
return const Icon(Icons.watch);
case DeviceType.speaker:
return const Icon(Icons.speaker);
}
}
}3.4 核心亮点
- 基于设备距离自动选择最优连接协议,NFC 近场极速连接、Wi-Fi 远距离稳定连接;
- 仅允许可信设备连接,连接过程无需手动确认,实现真正的无感组网;
- 连接结果实时反馈,成功 / 失败原因清晰展示;
- 支持一键断开连接,设备状态同步更新。
四、实战场景 3:动态设备管理 ------ 实时状态监控与事件通知
4.1 场景描述
用户将智慧屏设备断电,手机端应用实时接收到设备离线事件,设备列表中智慧屏的状态从 "在线" 变为 "离线",并弹出通知提示;当智慧屏重新通电后,应用自动发现并更新其状态为 "在线"。
4.2 设备状态监控实现
dart
/// 设备状态监控服务
class DeviceStateMonitor {
// 状态变更回调
Function(DeviceState)? onDeviceStateChanged;
// 监控定时器
Timer? _monitorTimer;
// 启动设备状态监控
void startMonitor(List<String> deviceIds) {
_monitorTimer?.cancel();
// 每5秒检查一次设备状态
_monitorTimer = Timer.periodic(const Duration(seconds: 5), (timer) async {
for (final deviceId in deviceIds) {
final isOnline = await DistributedSoftBus().checkDeviceOnline(deviceId);
onDeviceStateChanged?.call(DeviceState(
deviceId: deviceId,
isOnline: isOnline,
timestamp: DateTime.now().millisecondsSinceEpoch,
));
}
});
}
// 停止设备状态监控
void stopMonitor() {
_monitorTimer?.cancel();
}
}
// 设备状态模型
class DeviceState {
final String deviceId;
final bool isOnline;
final int timestamp;
DeviceState({
required this.deviceId,
required this.isOnline,
required this.timestamp,
});
}
/// 设备状态通知组件
class DeviceStateNotificationWidget extends StatelessWidget {
final List<DeviceInfo> deviceList;
const DeviceStateNotificationWidget({super.key, required this.deviceList});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final stateMonitor = DeviceStateMonitor();
stateMonitor.onDeviceStateChanged = (state) {
final device = deviceList.firstWhere((d) => d.deviceId == state.deviceId);
ScaffoldMessenger.of(context).showSnackBar(
SnackBar(
content: Text("${device.deviceName} 已${state.isOnline ? "上线" : "离线"}"),
duration: const Duration(seconds: 2),
),
);
};
// 启动状态监控
WidgetsBinding.instance.addPostFrameCallback((_) {
stateMonitor.startMonitor(deviceList.map((d) => d.deviceId).toList());
});
return const SizedBox.shrink();
}
}4.3 核心亮点
- 定时监控设备在线状态,状态变更实时触发通知;
- 支持批量设备监控,适配多设备协同场景;
- 通知提示简洁明了,用户及时掌握设备状态变化;
- 组件化实现,无需侵入业务逻辑,即插即用。
五、实战场景 4:可信设备认证 ------ 基于 DID 的设备身份校验
5.1 场景描述
陌生设备尝试接入用户的分布式网络时,应用自动触发身份认证流程,通过分布式 DID 服务校验设备身份,发现该设备未在可信列表中,直接拒绝接入请求,并记录异常接入日志。
5.2 设备身份认证实现
dart
/// 设备身份认证服务
class DeviceAuthService {
late DidAuthService _didAuthService;
late Box _trustedDeviceBox;
// 初始化认证服务
Future<void> initAuthService() async {
_didAuthService = DidAuthService();
await _didAuthService.initDidIdentity();
_trustedDeviceBox = await Hive.openBox("trusted_devices");
}
// 检查设备是否可信
Future<bool> isDeviceTrusted(String deviceId) async {
return _trustedDeviceBox.containsKey(deviceId);
}
// 添加可信设备
Future<void> addTrustedDevice(DeviceInfo device) async {
// 1. 获取设备DID身份
final deviceDid = await _getDeviceDid(device.deviceId);
// 2. 验证设备DID合法性
final isValid = await _didAuthService.verifyDidIdentity(deviceDid);
if (isValid) {
await _trustedDeviceBox.put(device.deviceId, device.toJson());
} else {
throw Exception("设备DID身份非法,无法添加为可信设备");
}
}
// 移除可信设备
Future<void> removeTrustedDevice(String deviceId) async {
await _trustedDeviceBox.delete(deviceId);
}
// 获取设备DID身份
Future<String> _getDeviceDid(String deviceId) async {
// 调用鸿蒙分布式DID服务获取设备身份
return await DistributedSoftBus().getDeviceDid(deviceId);
}
}
/// 可信设备管理组件
class TrustedDeviceManagerWidget extends StatefulWidget {
const TrustedDeviceManagerWidget({super.key});
@override
State<TrustedDeviceManagerWidget> createState() => _TrustedDeviceManagerWidgetState();
}
class _TrustedDeviceManagerWidgetState extends State<TrustedDeviceManagerWidget> {
final DeviceAuthService _authService = DeviceAuthService();
List<DeviceInfo> _trustedDevices = [];
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_loadTrustedDevices();
}
Future<void> _loadTrustedDevices() async {
await _authService.initAuthService();
final box = await Hive.openBox("trusted_devices");
setState(() {
_trustedDevices = box.values
.map((json) => DeviceInfo(
deviceId: json["deviceId"],
deviceName: json["deviceName"],
deviceType: _parseDeviceType(json["deviceType"]),
isTrusted: true,
))
.toList();
});
}
DeviceType _parseDeviceType(String type) {
switch (type) {
case "phone":
return DeviceType.phone;
case "tablet":
return DeviceType.tablet;
case "smartScreen":
return DeviceType.smartScreen;
case "watch":
return DeviceType.watch;
case "speaker":
return DeviceType.speaker;
default:
return DeviceType.phone;
}
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text("可信设备管理")),
body: _trustedDevices.isEmpty
? const Center(child: Text("暂无可信设备"))
: ListView.builder(
itemCount: _trustedDevices.length,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
final device = _trustedDevices[index];
return ListTile(
title: Text(device.deviceName),
subtitle: Text(device.deviceType.toString().split(".").last),
trailing: IconButton(
icon: const Icon(Icons.delete, color: Colors.red),
onPressed: () async {
await _authService.removeTrustedDevice(device.deviceId);
_loadTrustedDevices();
},
),
);
},
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () => _showAddDeviceDialog(context),
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
// 显示添加设备对话框
Future<void> _showAddDeviceDialog(BuildContext context) async {
// 实现添加设备逻辑,此处省略
}
}5.3 核心亮点
- 基于分布式 DID 实现设备身份认证,确保接入设备的合法性;
- 支持可信设备的添加 / 移除,灵活管理设备组网权限;
- 非法设备接入自动拒绝,保障分布式网络安全;
- 可视化管理界面,设备信任关系一目了然。
六、关键技术挑战与解决方案
6.1 技术挑战 1:多协议扫描冲突与资源占用
- 问题:同时启动 Wi-Fi、蓝牙、NFC 扫描会导致设备资源占用过高,甚至出现扫描冲突;
- 解决方案:1. 采用分时扫描策略,按协议优先级依次启动扫描;2. 扫描过程中动态调整扫描频率,降低资源消耗;3. 扫描完成后自动关闭闲置协议,释放系统资源。
6.2 技术挑战 2:设备连接不稳定与重连机制
- 问题:设备距离变化或网络波动可能导致连接断开,影响协同体验;
- 解决方案:1. 实现自动重连机制,连接断开后定时尝试重新连接;2. 支持连接优先级设置,核心设备优先重连;3. 网络波动时自动切换连接协议,保障连接稳定性。
6.3 技术挑战 3:陌生设备恶意接入风险
- 问题:陌生设备可能伪造身份尝试接入分布式网络,带来安全隐患;
- 解决方案:1. 双重身份认证,结合 DID 身份校验与设备绑定关系;2. 异常接入行为日志记录,支持安全溯源;3. 接入请求超时限制,防止恶意攻击。
6.4 技术挑战 4:跨平台设备类型识别兼容性
- 问题:不同品牌、型号的设备类型标识不统一,导致识别错误;
- 解决方案:1. 基于设备特征库实现设备类型智能识别;2. 支持自定义设备类型映射,适配特殊设备;3. 提供手动修改设备类型的入口,提升灵活性。
七、常见问题(FAQ)
Q1:分布式设备发现是否需要接入互联网?
A1:不需要。基于开源鸿蒙分布式软总线的设备发现能力,支持局域网内设备的点对点发现与连接,无需依赖互联网,满足离线组网需求。
Q2:可信设备列表是存储在本地还是云端?
A2:默认存储在本地设备的安全存储区,保障设备信息不泄露;若需多设备共享可信列表,可结合开源鸿蒙分布式数据服务实现列表同步。
Q3:支持多少台设备同时组网?
A3:理论上支持无限制设备组网,实际数量取决于主设备的性能与网络带宽;在智能家居场景中,建议组网设备不超过 20 台,以保障连接稳定性。
Q4:设备连接的延迟是多少?
A4:在局域网环境下,无感连接的延迟通常低于 500ms;采用 NFC 协议连接时,延迟可控制在 100ms 以内,实现极速配对。
八、结语
分布式设备发现与连接是开源鸿蒙全场景生态的基石,也是实现多设备协同的必经之路。本文提出的 "自动发现、无感连接、动态管理、可信认证" 四大核心方案,基于开源鸿蒙的分布式软总线与设备管理能力,结合 Flutter 的跨端开发优势,构建了一套完整的分布式设备协同管理体系。
相比于传统设备连接方案,本方案的核心优势在于 **"无感" 与 "安全"**------ 自动扫描发现设备,一键无感配对连接,实时监控设备状态,仅允许可信设备接入,极大降低了用户的操作门槛,提升了分布式组网的安全性与稳定性。在智能家居、智慧办公、车机互联等场景中,该方案能够有效支撑多设备协同的基础能力,为上层应用开发提供可靠保障。
未来,随着开源鸿蒙生态的持续完善,分布式设备连接技术将向 **"零配置组网" 与 "跨地域协同"** 方向演进 ------ 设备通电后自动加入网络,无需任何手动操作;结合 5G / 边缘计算技术,实现跨地域设备的低延迟协同。同时,AI 技术的融入将实现设备连接的智能调度,根据用户场景自动优化设备连接策略。
对于开发者而言,掌握分布式设备发现与连接技术,是构建全场景分布式应用的第一步。后续我们还将探讨 "分布式设备能力虚拟化""跨设备服务调用" 等进阶主题,敬请关注!
欢迎大家加入[开源鸿蒙跨平台开发者社区](https://openharmonycrossplatform.csdn.net),一起共建开源鸿蒙跨平台生态。