目录
[rsync 服务常用配置项](#rsync 服务常用配置项)
[实现rsync daemon服务](#实现rsync daemon服务)
[3、inotify+rsync 实现数据实时同步](#3、inotify+rsync 实现数据实时同步)
[4、sersync 实现数据实时同步](#4、sersync 实现数据实时同步)
一、存储介绍
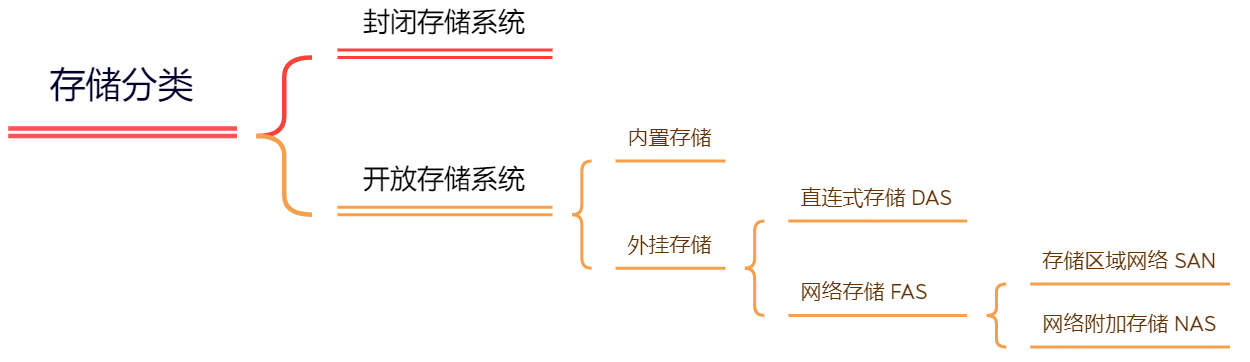
1、常见存储类型
⚪直连式存储:Direct-Attached Storage (DAS)
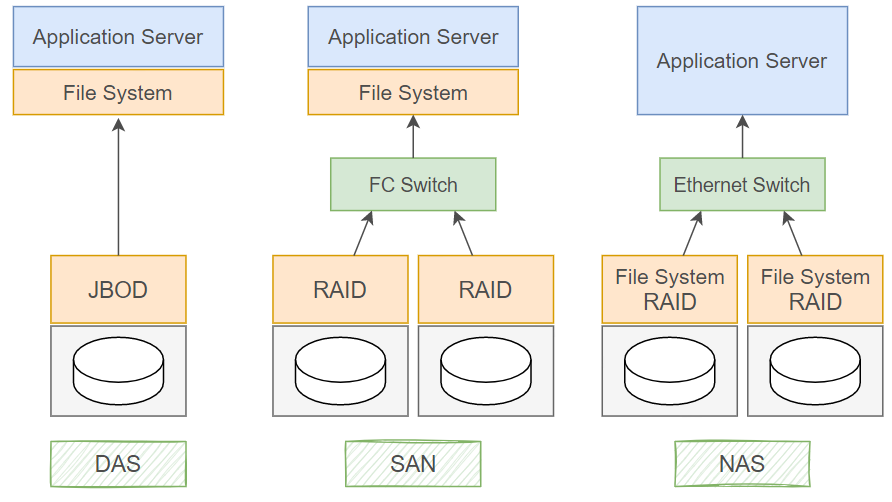
直连式存储(DAS)就像给服务器"直接装硬盘"------存储设备通过物理接口(如SCSI、SAS、FC)与服务器主板或扩展卡绑定,被识别为本地块设备(类似电脑里的C盘、D盘),数据传输不经过网络,因此速度极快、延迟极低。但它最大的局限是"独占性":一台DAS通常只能被一台服务器使用,其他服务器无法直接访问,导致存储资源无法共享,扩展时需频繁更换或增加设备,管理成本也会随服务器数量增加而上升。DAS适合对性能要求高、存储需求集中的单服务器场景(如小型数据库、虚拟机),但在需要多服务器协作或数据共享的环境中(如企业集群、云计算),其封闭性会成为明显短板。
⚪存储区域网络:Storage Area Network (SAN)
存储区域网络(SAN)如同为服务器打造的"高速专用数据公路"------它通过光纤通道(FC)或高速以太网(iSCSI)将多台服务器与独立存储设备(如磁盘阵列、磁带库)连接成专用网络,数据以块级形式传输(类似直接操作本地硬盘)。SAN的核心优势是"共享与高性能":存储资源从服务器中剥离,形成可被多服务器并发访问的集中池,既避免了DAS的"孤岛"问题,又通过专用网络保障了低延迟、高带宽的数据传输,适合对I/O性能要求严苛的场景(如大型数据库、虚拟化集群)。但SAN的部署成本较高(需专用硬件和网络配置),且技术复杂度大于DAS,通常用于企业级核心业务环境。
⚪网络附加存储:Network-Attached Storage (NAS)
网络附加存储(NAS)像是一个"带网络功能的共享文件夹"------它是一台独立设备(内置硬盘和简化操作系统),通过标准网络协议(如NFS、SMB/CIFS)接入局域网,为多台设备(电脑、手机、平板等)提供文件级数据共享服务。NAS的精髓在于"便捷与普适":用户无需关心底层存储细节,只需像访问本地文件夹一样通过网络存取文件,且支持跨平台兼容(Windows、macOS、Linux均可使用)。它部署简单(插网线即用)、管理直观(通常配备Web界面或APP),成本也远低于SAN,但文件级传输的性能和并发能力弱于SAN的块级传输,更适合中小企业的文件共享、多媒体存储或家庭数据中心等轻量级场景。
| 分类 | DAS | NAS | SAN |
|---|---|---|---|
| 传输类型 | SCSI、FC | IP(NFS/SMB/CIFS) | IP、FC、SAS |
| 数据类型 | 数据块(Block-level) | 文件(File-level) | 数据块(Block-level) |
| 典型应用 | 任何需要直接访问存储的场景(如单服务器应用) | 文件服务器(存储非结构化数据,如文档、图片、视频) | 数据库服务器、虚拟化集群、高性能计算(需低延迟块级存储) |
| 优点 | 1. 磁盘与服务器物理直连,访问速度快 2. 结构简单,管理直接 | 1. 不占用服务器资源,独立运行 2. 支持多操作系统跨平台访问 3. 扩展容易,即插即用 4. 安装简单,成本低 | 1. 高扩展性(支持海量存储) 2. 高可用性(冗余设计) 3. 数据集中管理,便于备份恢复 4. 性能接近本地存储 |
| 缺点 | 1. 连接距离短(通常限于机房内) 2. 数据分散,共享困难 3. 存储利用率低 4. 扩展性有限(依赖服务器接口) | 1. 不适合块级应用(如数据库) 2. 大文件传输占用网络带宽 3. 性能受限于以太网速度 | 1. 成本高(专用硬件+网络) 2. 安装和升级复杂(需专业配置) 3. 技术门槛较高 |
| 应用场景 | 数据量不大、对速度要求高的中小企业(如单服务器数据库、本地应用) | 文件共享、多媒体存储、远程访问(如家庭NAS、中小企业文件服务器) | 大型企业核心业务(如银行交易系统、电商数据库、云计算资源池) |
2、常见存储方式
⚪块存储
块存储(Block Storage Service)设备不能被操作系统直接访问,需要创建分区或逻辑卷,再创建文件系统 (EXT3, EXT4, NTFS 等),然后再经过挂载,才能使用。对于主机而言,其并不能识别出存储设备是真正的物理设备还是二次划分的逻辑设备(RAID等),块存储不仅仅是直接使用物理设备,间接使用物理设备的也叫块设备。比如虚拟机上创建的虚拟磁盘。
块存储大多数时候是本地存储,读写速度很快,但不利于扩展,数据不能被共享。
⚪文件存储
文件存储(File Storage Service)可以分为本地文件存储和网络文件存储。文件存储最明显的特征是支持POSIX的文件访问接口,例如 open、read、write、seek、close 等 (这几个是常用的文件操作API接口 ),与块存储不同,主机不需要再对文件存储进行格式化和创建文件系统,文件管理功能已由文件存储自行管理。
文件存储的特点是便于扩展和共享,但读写速度较慢。
⚪对象存储
对象存储(Object Storage Service)也叫基于对象的存储,是一种解决和处理离散单元的方法,可提供基于分布式系统之上的对象形式的数据存储服务。对象存储和我们经常接触到的块和文件系统等存储形态不同,它提供 RESTful API数据读写接口及丰富的 SDK 接口,并且常以网络服务的形式提供数据的访问。
对象存储不支持随机读写,只能进行全读和全写操作(无法直接在存储上进行数据更改,只能以文件为单位进行获取和删除),如果要修改数据,需要先在本地编辑完成后整文件上传。
⚪分布式存储
在海量数据和文件的场景下,单一服务器所能连接的物理介质有限,能提供的存储空间和IO性能也是有限的,所以可以通过多台服务器协同工作,每台服务器连接若干物理介质,再配合分布式存储系统和虚拟化技术,将底层多个物理硬件设备组合成一个统一的存储服务。一个分布式存储系统,可以同时提供块存储,文件存储和对象存储这三种存储方式。
二、NFS服务
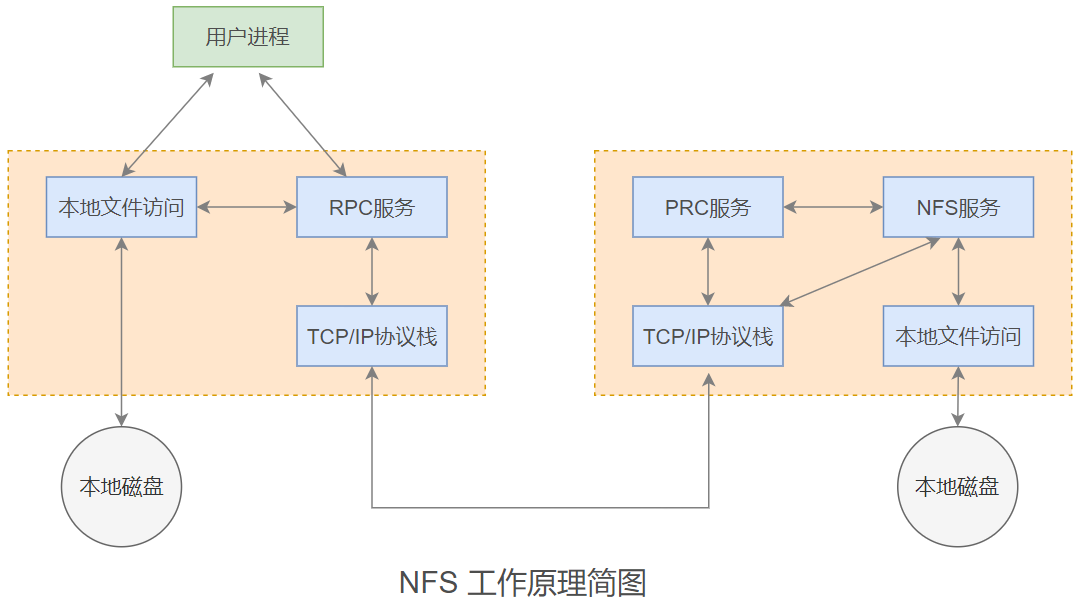
1、NFS工作原理
NFS(Network File System)即网络文件系统,是一种基于TCP/IP协议的分布式文件系统协议,它允许网络中的计算机通过挂载的方式将远程服务器上的共享目录映射到本地文件系统中,从而使用户能够像访问本地文件一样透明地读写远程服务器上的文件,无需关心数据的实际物理位置,主要适用于Linux/Unix系统间的文件共享,也可通过兼容层支持跨平台访问。
NFS的工作原理基于客户端-服务器架构,通过远程过程调用(RPC)机制实现通信:服务器端启动NFS服务后,会向RPC(端口111)注册自身端口信息;客户端发起访问请求时,首先通过RPC获取服务器NFS服务的实际端口,随后直接与该端口建立连接;文件操作请求(如读取、写入)被封装为RPC请求发送至服务器,服务器执行后返回结果,整个过程对用户透明,且文件通常以8KB大小的块为单位传输,支持异步写入以提升性能。
RPC(Remote Procedure Call,远程过程调用)是一种计算机通信协议,用于在不同计算机或进程间调用服务,RPC允许一个程序(客户端)调用另一个程序(服务器)上的过程或函数,而无需了解底层网络细节,客户端发起一个远程过程调用请求,包含要调用的函数名、参数等信息。服务器接收到请求后,执行相应的函数,并将结果返回给客户端。
2、NFS安装和配置
#rocky安装,包含服务端、客户端
yum install nfs-utils
#ubuntu安装
apt install nfs-kernel-server #服务端
apt install nfs-common #客户端
#服务端依赖包,注册中心,nfs 服务中有大量的组件,部份组件端口并不固定,需要依赖rpcbind发布端口
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# dpkg -l rpcbind
Desired=Unknown/Install/Remove/Purge/Hold
| Status=Not/Inst/Conf-files/Unpacked/halF-conf/Half-inst/trig-aWait/Trig-pend
|/ Err?=(none)/Reinst-required (Status,Err: uppercase=bad)
||/ Name Version Architecture Description
+++-==============-=============-============-=====================================================
ii rpcbind 1.2.6-2build1 amd64 converts RPC program numbers into universal addresses
#查看服务端口
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ss -tunlp | grep rpc
udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0:55260 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.statd",pid=16114,fd=8))
udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0:56357 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16122,fd=4))
udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0:51266 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16122,fd=12))
udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpcbind",pid=15492,fd=5),("systemd",pid=1,fd=82))
udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0:40499 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16122,fd=8))
udp UNCONN 0 0 127.0.0.1:602 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.statd",pid=16114,fd=5))
udp UNCONN 0 0 [::]:111 [::]:* users:(("rpcbind",pid=15492,fd=7),("systemd",pid=1,fd=85))
udp UNCONN 0 0 [::]:46225 [::]:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16122,fd=6))
udp UNCONN 0 0 [::]:44193 [::]:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16122,fd=14))
udp UNCONN 0 0 [::]:45547 [::]:* users:(("rpc.statd",pid=16114,fd=10))
udp UNCONN 0 0 [::]:55862 [::]:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16122,fd=10))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:57313 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16122,fd=13))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:51571 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.statd",pid=16114,fd=9))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:47373 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16122,fd=9))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpcbind",pid=15492,fd=4),("systemd",pid=1,fd=61))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:58393 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16122,fd=5))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 [::]:46811 [::]:* users:(("rpc.statd",pid=16114,fd=11))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 [::]:35459 [::]:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16122,fd=15))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 [::]:37163 [::]:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16122,fd=11))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 [::]:58833 [::]:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16122,fd=7))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 [::]:111 [::]:* users:(("rpcbind",pid=15492,fd=6),("systemd",pid=1,fd=84))
#重启服务
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# systemctl restart nfs-server.service
#端口发生变化
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ss -tunlp | grep rpc
udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0:55260 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.statd",pid=16114,fd=8))
udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpcbind",pid=15492,fd=5),("systemd",pid=1,fd=82))
udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0:53422 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16579,fd=12))
udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0:43367 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16579,fd=4))
udp UNCONN 0 0 0.0.0.0:39411 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16579,fd=8))
udp UNCONN 0 0 127.0.0.1:602 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.statd",pid=16114,fd=5))
udp UNCONN 0 0 [::]:111 [::]:* users:(("rpcbind",pid=15492,fd=7),("systemd",pid=1,fd=85))
udp UNCONN 0 0 [::]:35033 [::]:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16579,fd=6))
udp UNCONN 0 0 [::]:36146 [::]:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16579,fd=10))
udp UNCONN 0 0 [::]:50603 [::]:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16579,fd=14))
udp UNCONN 0 0 [::]:45547 [::]:* users:(("rpc.statd",pid=16114,fd=10))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:34573 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16579,fd=9))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:46071 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16579,fd=13))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:51571 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.statd",pid=16114,fd=9))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpcbind",pid=15492,fd=4),("systemd",pid=1,fd=61))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:46113 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16579,fd=5))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 [::]:46811 [::]:* users:(("rpc.statd",pid=16114,fd=11))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 [::]:55677 [::]:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16579,fd=15))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 [::]:111 [::]:* users:(("rpcbind",pid=15492,fd=6),("systemd",pid=1,fd=84))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 [::]:50273 [::]:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16579,fd=7))
tcp LISTEN 0 4096 [::]:46151 [::]:* users:(("rpc.mountd",pid=16579,fd=11))
#由于服务端监听的端口会发生变化,所以需要依赖rpcbind对客户端提供注册服务,rpcbind端口不会发生变化NFS服务本身并不固定在某个特定的端口上运行,而是动态地选择可用的端口。客户端在发起NFS请求时,需要知道服务器上NFS服务监听的端口号。
rpcbind服务用于管理RPC服务的端口映射,允许NFS服务在启动时注册其提供的RPC程序号、版本号以及所使用的端口号。客户端通过查询rpcbind服务,可以获取到NFS服务当前监听的端口号,从而建立连接。
#查看服务端使用的端口
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rpcinfo -p
program vers proto port service
100000 4 tcp 111 portmapper #rpcbind,早期叫portmapper
100000 3 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 2 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 4 udp 111 portmapper
100000 3 udp 111 portmapper
100000 2 udp 111 portmapper
100024 1 udp 55260 status
100024 1 tcp 51571 status
100005 1 udp 43367 mountd
100005 1 tcp 46113 mountd
100005 2 udp 39411 mountd
100005 2 tcp 34573 mountd
100005 3 udp 53422 mountd
100005 3 tcp 46071 mountd
100003 3 tcp 2049 nfs
100003 4 tcp 2049 nfs
100227 3 tcp 2049
100021 1 udp 50889 nlockmgr
100021 3 udp 50889 nlockmgr
100021 4 udp 50889 nlockmgr
100021 1 tcp 33585 nlockmgr
100021 3 tcp 33585 nlockmgr
100021 4 tcp 33585 nlockmgr服务端主要进程
/usr/sbin/rpc.mountd #挂载和卸载nfs文件系统,包括权限管理
/usr/sbin/rpc.nfsd #主要的nfs进程,管理客户端是否可登录
/usr/sbin/rpc.statd #非必要,检查文件一致性,可修复文件日志目录
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# tree /var/lib/nfs
/var/lib/nfs
├── etab
├── export-lock
├── nfsdcld
│ └── main.sqlite
├── rmtab
├── sm
├── sm.bak
├── state
└── v4recovery
4 directories, 5 files配置文件
/etc/exports
/etc/exports.d/*.exports
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# cat /etc/exports
# /etc/exports: the access control list for filesystems which may be exported
# to NFS clients. See exports(5).
#
# Example for NFSv2 and NFSv3:
# /srv/homes hostname1(rw,sync,no_subtree_check) hostname2(ro,sync,no_subtree_check)
#
# Example for NFSv4:
# /srv/nfs4 gss/krb5i(rw,sync,fsid=0,crossmnt,no_subtree_check)
# /srv/nfs4/homes gss/krb5i(rw,sync,no_subtree_check)
#
#共享规则说明:
#每一行都是一个共享配置,包含两列
#NFS服务器上要被共享的目录路径 可以共享此目录的客户端主机(配置项...) 可以共享此目录的客户端主机(配置项...)
#/PATH client-1(opt1,opt2,...) client-2(opt1,opt2,...) [client-3]
# 以 # 开头的是注释行
#客户端主机写法:
# anonymous,* 表示不限制,即任何主机都能访问
# 单个主机可以写具体的IPV4,IPV6,FQDN,主机名
# 网段 10.0.0.0/24 10.0.0.0/225.225.225.0 这两种格式都行
# 主机名,主机名可以用 通配符 表示多台主机
# 网域或主机组 @group_name
# gss/krb5i 这种写法来限制对使用rpcsec_gss安全性的客户端的访问
#配置项写法
# 默认 (ro,sync,root_squash,no_all_squash)
#主要选项
# ro 只读访问:客户端只能读取共享目录中的内容,无法进行写入或修改操作。
# rw 读写访问:客户端可以自由地读取和修改共享目录中的文件。
# root_squash 将远程客户端上的root用户映射为NFS服务器上的匿名用户(UID=65534),增强系统安全性。
# no_root_squash 保持远程客户端上的root用户身份,直接映射为NFS服务器上的root用户,可能带来安全隐患。
# all_squash 将所有远程客户端用户映射为NFS服务器上的匿名用户(UID=65534),此选项会覆盖no_root_squash设置。
# anonuid 指定匿名用户的用户ID(UID),用于自定义映射后的用户身份。
# anongid 指定匿名用户的组ID(GID),与anonuid配合使用,确定匿名用户的组归属。
# sync 同步写入:确保数据在客户端请求后立即写入NFS服务器的磁盘,保证数据一致性,但性能较低。
# async 异步写入:数据先缓存在NFS服务器内存中,稍后再写入磁盘,提高性能,但可能增加数据丢失风险。
# insecure 允许NFS服务通过非保留端口(1024以上)进行通讯,降低安全性要求,便于某些客户端访问。
# subtree_check 启用子树检查:在访问共享子目录时,NFS服务器会检查其父目录的权限,确保访问的合法性。
# no_subtree_check 禁用子树检查:提高性能,特别是在频繁访问共享子目录时,但可能降低安全性。
# wdelay 写入延迟:当多个客户端同时写入时,NFS服务器会等待一段时间,将多个写入操作合并,减少磁盘I/O次数。
# no_wdelay 无写入延迟:客户端的写入请求会立即被处理,不进行合并,适用于对实时性要求较高的场景。
# hide 隐藏共享:不共享NFS服务器上的特定子目录(在NFSv4中此选项无效)。
# no_hide 显示共享:共享NFS服务器上的所有子目录(在NFSv4中此选项无效,且通常不需要显式设置)。
# secure 要求NFS服务通过保留端口(1024以下)进行通讯,增强安全性。
# insecure 允许NFS服务通过非保留端口(1024以上)通讯 3、NFS常用工具
rpcinfo
rpcinfo 可以访问指定的 RPC 服务器,显示其响应信息,从而查询出在该服务器上注册的RPC服务。如果不指定主机,则默认是当前主机。
#格式
rpcinfo [-opt...] [host]
#常用选项
-p [host] #查看注册在指定主机上的rpcbind V2 版本的 RPC 服务
-m|-s [host] #查看rpcbind的RPC服务,-s 简短格式显示
#显示已注册到本机的所有RPC服务
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# rpcinfo
program version netid address service owner
100000 4 tcp6 ::.0.111 portmapper superuser
100000 3 tcp6 ::.0.111 portmapper superuser
100000 4 udp6 ::.0.111 portmapper superuser
100000 3 udp6 ::.0.111 portmapper superuser
100000 4 tcp 0.0.0.0.0.111 portmapper superuser
100000 3 tcp 0.0.0.0.0.111 portmapper superuser
100000 2 tcp 0.0.0.0.0.111 portmapper superuser
100000 4 udp 0.0.0.0.0.111 portmapper superuser
100000 3 udp 0.0.0.0.0.111 portmapper superuser
100000 2 udp 0.0.0.0.0.111 portmapper superuser
100000 4 local /run/rpcbind.sock portmapper superuser
100000 3 local /run/rpcbind.sock portmapper superuser
#显示已注册到本机的rpcbind V2 版本的 RPC 服务
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# rpcinfo -p
program vers proto port service
100000 4 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 3 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 2 tcp 111 portmapper
100000 4 udp 111 portmapper
100000 3 udp 111 portmapper
100000 2 udp 111 portmapper
#简短格式
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# rpcinfo -s
program version(s) netid(s) service owner
100000 2,3,4 local,udp,tcp,udp6,tcp6 portmapper superuser
#指定主机
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# rpcinfo -s 10.0.0.150
program version(s) netid(s) service owner
100000 2,3,4 local,udp,tcp,udp6,tcp6 portmapper superuser
100024 1 tcp6,udp6,tcp,udp status 116
100005 3,2,1 tcp6,udp6,tcp,udp mountd superuser
100003 4,3 tcp6,tcp nfs superuser
100227 3 tcp6,tcp - superuser
100021 4,3,1 tcp6,udp6,tcp,udp nlockmgr superuserexportfs
exportfs 命令用于管理本机 NFS 文件系统,默认配置文件是 /etc/exports。
cpp
exportfs [-adfhioruvs] [host:/path]
#常用选项
-a #全部挂载或者全部卸载
-r #重新挂载
-u #卸载
-v #显示本机共享mount.nfs
客户端 NFS 服务挂载命令,将远程NFS 服务器上共享出来的目录挂载到本机,可以直接写成 mount。
showmount
用于查看NFS服务器上的共享目录信息。
-e:显示NFS服务器上所有输出的共享目录
-a:显示已经与客户端连接上的目录信息4、NFS共享实现
统一客户端主机用户和权限的方法:
⚪保证客户端主机使用相同的用户(相同的用户ID)对共享目录进行读写。
⚪在NFS 服务器上统一映射。
⚪使用 LDAP 服务进行集中的帐号管理。
#server-150
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# apt install nfs-kernel-server
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# mkdir -pv /data/dir{a,b}
mkdir: created directory '/data'
mkdir: created directory '/data/dira'
mkdir: created directory '/data/dirb'
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# cp /etc/fstab /data/dira
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# vim /etc/exports
/data/dira *
#重新读取配置文件
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# exportfs -r
#查看共享规则
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# exportfs -v
/data/dira <world>(sync,wdelay,hide,no_subtree_check,sec=sys,ro,secure,root_squash,no_all_squash)
#client-152
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# showmount
clnt_create: RPC: Program not registered
#查看服务端NFS共享规则
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# showmount -e 10.0.0.150
Export list for 10.0.0.150:
/data/dira *
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# mkdir -p /data/dir{1,2}
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ls /data/dir1
#将服务端共享目录挂载本地
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# mount 10.0.0.150:/data/dira /data/dir1
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ls /data/dir1
fstab
#server
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# cp /etc/issue /data/dira
#client
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ll /data/dir1
total 16
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 18:08 ./
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Dec 13 18:04 ../
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 657 Dec 13 17:57 fstab
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 26 Dec 13 18:08 issue
#client2-153
[root@rocky8-153 ~]#mkdir -p /data/dira{1,2}
[root@rocky8-153 ~]#ls /data/dira{1,2}
/data/dira1:
/data/dira2:
[root@rocky8-153 ~]#mount 10.0.0.150:/data/dira /data/dira1
[root@rocky8-153 ~]#ll /data/dira1
total 8
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 657 Dec 13 17:57 fstab
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 26 Dec 13 18:08 issue
#client-1,2
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# touch /data/dir1/test
touch: cannot touch '/data/dir1/test': Read-only file system
[root@rocky8-153 ~]#touch /data/dira1/test
touch: cannot touch '/data/dira1/test': Read-only file system
#在NFS共享规则中设置 可读 不可写,因此无法创建
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# cat /etc/exports
/data/dira *
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# exportfs -v
/data/dira <world>(sync,wdelay,hide,no_subtree_check,sec=sys,ro,secure,root_squash,no_all_squash)
#server
#修改共享规则
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# vim /etc/exports
/data/dira * 10.0.0.152(rw) 10.0.0.153
#重新读取
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# exportfs -r
#查看
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# exportfs -v
/data/dira 10.0.0.152(sync,wdelay,hide,no_subtree_check,sec=sys,rw,secure,root_squash,no_all_squash)
/data/dira 10.0.0.153(sync,wdelay,hide,no_subtree_check,sec=sys,ro,secure,root_squash,no_all_squash)
#client-1
#仍无法创建,但是提示发生变化,没有权限
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# touch /data/dir1/test
touch: cannot touch '/data/dir1/test': Permission denied
#client-2
[root@rocky8-153 ~]#touch /data/dira1/test
touch: cannot touch '/data/dira1/test': Read-only file system
#补充
#网段写法
/data/dira 10.0.0.0/24(rw)
#永久挂载,客户端主机,写文件/etc/fstab
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# vim /etc/fstab
10.0.0.152:/data/dira /data/dir1 nfs defaults,_netdev 0 0
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# reboot
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ls /data/dir1
fstab issue
#client-3
root@ubuntu-158:~# showmount -e 10.0.0.150
Export list for 10.0.0.150:
/data/dira 10.0.0.153,10.0.0.152
root@ubuntu-158:~# mkdir -p /data/dir{1,2}
#没有写共享规则,无法挂载
root@ubuntu-158:~# mount 10.0.0.150:/data/dira /data/dir1
Created symlink '/run/systemd/system/remote-fs.target.wants/rpc-statd.service' → '/usr/lib/systemd/system/rpc-statd.service'.
mount.nfs: access denied by server while mounting 10.0.0.150:/data/dira
#server
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# mkdir /data/www
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# vim /etc/exports
/data/dira 10.0.0.152(rw) 10.0.0.153
/data/www *
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# exportfs -r
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# exportfs -v
/data/dira 10.0.0.152(sync,wdelay,hide,no_subtree_check,sec=sys,rw,secure,root_squash,no_all_squash)
/data/dira 10.0.0.153(sync,wdelay,hide,no_subtree_check,sec=sys,ro,secure,root_squash,no_all_squash)
/data/www <world>(sync,wdelay,hide,no_subtree_check,sec=sys,ro,secure,root_squash,no_all_squash)
#client-1
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# apt install nginx
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# vim /etc/fstab
#10.0.0.150:/data/dira /data/dir1 nfs defaults,_netdev 0 0 #注释
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# showmount -e 10.0.0.150
Export list for 10.0.0.150:
/data/www *
/data/dira 10.0.0.153,10.0.0.152
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ls /var/www/html/
index.nginx-debian.html
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# mount 10.0.0.150:/data/www /var/www/html/
#server
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# echo "hello world" > /data/www/index.html
#client-1
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ls /var/www/html
index.html
#此时页面内容发生变化
#client-3
[root@rocky8-159 ~]$yum install -y httpd
[root@rocky8-159 ~]$systemctl start httpd
[root@rocky8-159 ~]$mount 10.0.0.150:/data/www /var/www/html/
[root@rocky8-159 ~]$ls /var/www/html/
index.html
#client-1,3
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# echo "this page from 152" >> /var/www/html/index.html
-bash: /var/www/html/index.html: Read-only file system
[root@rocky8-159 ~]$echo "this page from 159" >> /var/www/html/index.html
-bash: /var/www/html/index.html: Read-only file system
#更改共享规则
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# vim /etc/exports
/data/dira 10.0.0.152(rw) 10.0.0.153
/data/www *(rw)
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# exportfs -r
#还是不能写,提示跟之前一样
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# echo "this page from 152" >> /var/www/html/index.html
-bash: /var/www/html/index.html: Permission denied
[root@rocky8-159 ~]$echo "this page from 159" >> /var/www/html/index.html
-bash: /var/www/html/index.html: Permission denied
#在NFS服务端查看,属主属组对该目录有写权限
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ll /data/www -d
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:35 /data/www/
#客户端查看,属主属组对该目录也有写权限,但是客户机上的 root ,并不是 NFS 服务端的 root,所以
还是没权限写,仅是名字相同
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ll /var/www/html -d
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:35 /var/www/html/
#在NFS端将权限打满
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# chmod -R 777 /data/www/
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ll /data/www -d
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:35 /data/www/
#在客户机上查看
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ll /var/www/html -d
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:35 /var/www/html/
#可以写入,刷新页面查看
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# echo "this page from 152" >> /var/www/html/index.html
[root@rocky8-159 ~]$echo "this page from 159" >> /var/www/html/index.html
#client-1,3
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# touch /var/www/html/test.html
[root@rocky8-159 ~]$touch /var/www/html/test2.html
#查看
#客户端创建的文件属主属组变成nobody,nogroup
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ll /var/www/html/
total 12
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:59 ./
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:32 ../
-rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 50 Dec 13 19:57 index.html*
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 19:59 test2.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 19:59 test.html
[root@rocky8-159 ~]$ll /var/www/html/
total 4
-rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 50 Dec 13 19:57 index.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nobody 0 Dec 13 19:59 test2.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nobody 0 Dec 13 19:59 test.html
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# id nobody
uid=65534(nobody) gid=65534(nogroup) groups=65534(nogroup)
[root@rocky8-159 ~]$id nobody
uid=65534(nobody) gid=65534(nobody) groups=65534(nobody)
#服务端查看
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ll /data/www/
total 12
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:59 ./
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:20 ../
-rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 50 Dec 13 19:57 index.html*
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 19:59 test2.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 19:59 test.html
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# id nobody
uid=65534(nobody) gid=65534(nogroup) groups=65534(nogroup)
#客户端 root 用户会被映射成 id 为 65534 的用户,则 root 用户创建的文件属主ID 为 65534
#在NFS 服务器上修改规则,添加 no_root_squash
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# vim /etc/exports
/data/dira 10.0.0.152(rw) 10.0.0.153
/data/www *(rw,no_root_squash)
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# exportfs -r
#client-1
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# touch /var/www/html/test-1.html
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ll /var/www/html/
total 12
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 20:08 ./
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:32 ../
-rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 50 Dec 13 19:57 index.html*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 13 20:08 test-1.html #客户端属主属组不再是nobody,nogroup,而是服务端root用户
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 19:59 test2.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 19:59 test.html
[root@rocky8-159 ~]$ll /var/www/html/
total 4
-rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 50 Dec 13 19:57 index.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 13 20:08 test-1.html #同上
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nobody 0 Dec 13 19:59 test2.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nobody 0 Dec 13 19:59 test.html
#普通用户不映射
#client-1
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# useradd -u 1234 -s /bin/bash -m -d /home/timoo timoo
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# id timoo
uid=1234(timoo) gid=1234(timoo) groups=1234(timoo)
#
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# su - timoo
timoo@ubuntu2204-152:~$ touch /var/www/html/tomii.html
timoo@ubuntu2204-152:~$ ll /var/www/html/
total 12
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 20:12 ./
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:32 ../
-rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 50 Dec 13 19:57 index.html*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 13 20:08 test-1.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 19:59 test2.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 19:59 test.html
-rw-rw-r-- 1 timoo timoo 0 Dec 13 20:12 tomii.html
#查看server,client-3
#找不到对应的用户,直接显示UID
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ll /data/www/
total 12
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 20:12 ./
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:20 ../
-rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 50 Dec 13 19:57 index.html*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 13 20:08 test-1.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 19:59 test2.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 19:59 test.html
-rw-rw-r-- 1 1234 1234 0 Dec 13 20:12 tomii.html
[root@rocky8-159 ~]$ll /var/www/html/
total 4
-rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 50 Dec 13 19:57 index.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 13 20:08 test-1.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nobody 0 Dec 13 19:59 test2.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nobody 0 Dec 13 19:59 test.html
-rw-rw-r-- 1 1234 1234 0 Dec 13 20:12 tomii.html
#在服务端以相同UID创建用户再次查看
root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# useradd -u 1234 -s /bin/bash -m -d /home/hhao1 hhao1
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# id hhao1
uid=1234(hhao1) gid=1234(hhao1) groups=1234(hhao1)
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ll /data/www/
total 12
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 20:12 ./
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:20 ../
-rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 50 Dec 13 19:57 index.html*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 13 20:08 test-1.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 19:59 test2.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 19:59 test.html
-rw-rw-r-- 1 hhao1 hhao1 0 Dec 13 20:12 tomii.html
#client-3
[root@rocky8-159 ~]$ll /var/www/html/
total 4
-rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 50 Dec 13 19:57 index.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 13 20:08 test-1.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nobody 0 Dec 13 19:59 test2.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nobody 0 Dec 13 19:59 test.html
-rw-rw-r-- 1 1234 1234 0 Dec 13 20:12 tomii.html
#再次修改规则,all_squash 项会覆盖 no_root_squash
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# vim /etc/exports
/data/dira 10.0.0.152(rw) 10.0.0.153
/data/www *(rw,no_root_squash,all_squash)
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# exportfs -r
#client-1
timoo@ubuntu2204-152:~$ touch /var/www/html/tomii-2.html
timoo@ubuntu2204-152:~$ ll /var/www/html/
total 12
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 20:21 ./
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:32 ../
-rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 50 Dec 13 19:57 index.html*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 13 20:08 test-1.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 19:59 test2.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 19:59 test.html
-rw-rw-r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 20:21 tomii-2.html
-rw-rw-r-- 1 timoo timoo 0 Dec 13 20:12 tomii.html
#server
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ll /data/www/
total 12
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 20:21 ./
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:20 ../
-rwxrwxrwx 1 root root 50 Dec 13 19:57 index.html*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 13 20:08 test-1.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 19:59 test2.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 19:59 test.html
-rw-rw-r-- 1 nobody nogroup 0 Dec 13 20:21 tomii-2.html
-rw-rw-r-- 1 hhao1 hhao1 0 Dec 13 20:12 tomii.html
#统一用户映射
#server
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# groupadd -g 12345 www
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# useradd -u 12345 -g 12345 -s /sbin/nologin www
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# vim /etc/exports
/data/dira 10.0.0.152(rw) 10.0.0.153
/data/www *(rw,no_root_squash,all_squash,anongid=12345,anonuid=12345)
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# exportfs -r
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rm -rf /data/www/*
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# echo "NFS server" > /data/www/index.html
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ll /data/www/
total 12
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 20:27 ./
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:20 ../
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 11 Dec 13 20:27 index.html
#client-1,3
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ll /var/www/html/
total 12
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 20:27 ./
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:32 ../
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 11 Dec 13 20:27 index.html
#client-1
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# touch /var/www/html/test-1.html
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ll /var/www/html/
total 12
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 20:29 ./
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:32 ../
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 11 Dec 13 20:27 index.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 12345 12345 0 Dec 13 20:29 test-1.html
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# su - timoo
timoo@ubuntu2204-152:~$ touch /var/www/html/tomii.html
timoo@ubuntu2204-152:~$ ll /var/www/html/
total 12
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 20:30 ./
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:32 ../
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 11 Dec 13 20:27 index.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 12345 12345 0 Dec 13 20:29 test-1.html
-rw-rw-r-- 1 12345 12345 0 Dec 13 20:30 tomii.html
#client-3
[root@rocky8-159 ~]$touch /var/www/html/test-2.html
#server
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ll /data/www/
total 12
drwxrwxrwx 2 root root 4096 Dec 13 20:31 ./
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Dec 13 19:20 ../
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 11 Dec 13 20:27 index.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 www www 0 Dec 13 20:29 test-1.html
-rw-r--r-- 1 www www 0 Dec 13 20:31 test-2.html
-rw-rw-r-- 1 www www 0 Dec 13 20:30 tomii.html三、数据实时同步
在生产环境中,某些场景下,要将数据或文件进行实时同步,保证数据更新后其它节点能立即获得最新的数据。
数据同步的方式
⚪PULL:拉,使用定时任务的方式配合同步命令或脚本等,从指定服务器上将数据同步到本地,一般是周期性定时同步。
⚪PUSH:推,如果当前机器上的数据或文件发生更新了,立即推送到指定的节点上,可以做到实时同步。
1、inotify服务
inotify 是一个内核用于通知用户空间程序文件系统变化的机制,在监听到文件系统发生变化后,会向相应的应用程序发送事件,如文件增加,修改,删除等事件发生后可以立即让用户空间知道。
#inotify 是内核中的功能,在2.6.13版本的内核开始都默认存在
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# grep -i inotify /boot/config-5.15.0-164-generic
CONFIG_INOTIFY_USER=y
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# grep -i inotify /boot/config-5.15.0-163-generic
CONFIG_INOTIFY_USER=y
[root@rocky8-153 ~]#grep -i inotify /boot/config-4.18.0-553.77.1.el8_10.x86_64
CONFIG_INOTIFY_USER=y
[root@rocky8-153 ~]#grep -i inotify /boot/config-4.18.0-553.el8_10.x86_64
CONFIG_INOTIFY_USER=y
#内核参数
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ls -l /proc/sys/fs/inotify
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 13 20:45 max_queued_events
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 13 20:45 max_user_instances
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Dec 13 20:45 max_user_watches
#inotify 事件队列最大长度,如值太小会出现 Event Queue Overflow 错误,默认 16384, 生产环境建议调大,比如 327679
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events 16384
#每个用户创建inotify实例最大值,默认值 128
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_instances 128
#每个inotify实例可以监视的文件的总数量
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches
14165
#一个用户可以最多开128个inotify实例,每个实例最多可以监控14165个文件
#内核参数如果需要修改,可以配置文件
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# cat /etc/sysctl.conf
fs.inotify.max_queued_events=66666
fs.inotify.max_user_instances=256
fs.inotify.max_user_watches=100000
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# sysctl -p
fs.inotify.max_queued_events = 66666
fs.inotify.max_user_instances = 256
fs.inotify.max_user_watches = 100000
#安装软件
inotify 是内核中的功能模块,只能通过调用API接口的形式使用其功能,可以通过相关软件来对其进行操作,能实现内核中 inotify 调用的软件主要有以下几个:inotify-tools,sersync,lrsyncd
#centos系列中该软件来自于 epel 源
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# apt install inotify-tools
#主要工具
/usr/bin/fsnotifywait #fsnotify监控工具,fsnotify 是 inotify 的新版本
/usr/bin/fsnotifywatch #fsnotify统计工具
/usr/bin/inotifywait #实时监控指定目录的所有事件,在被监控的文件或目录上等待特定事件发生(open,close,write..)
/usr/bin/inotifywatch #收集被监控的文件系统使用的统计数据,指文件系统事件发生的次数统计
inotifywait [options] file1 [file2] [file3] [...]
# 常用选项
-h|--help # 显示帮助信息
@<file> # 排除指定文件(不监控该文件)
--exclude <pattern> # 不监控匹配正则的文件/目录(区分大小写)
--excludei <pattern> # 不监控匹配正则的文件/目录(不区分大小写)
--include <pattern> # 仅监控匹配正则的文件/目录(区分大小写)
--includei <pattern> # 仅监控匹配正则的文件/目录(不区分大小写)
-m|--monitor # 持续监听(默认执行一次后退出)
-d|--daemon # 以守护进程运行(需配合-o指定输出文件)
-P|--no-dereference # 不跟随软链接(监控链接本身而非目标)
-r|--recursive # 递归监控目录及其子目录
--fromfile <file> # 从文件读取要监控的文件/目录列表
-o|--outfile <file> # 将事件输出到指定文件
-s|--syslog # 将错误日志输出到syslog
-q|--quiet # 简洁输出(仅显示事件信息)
-qq # 完全禁用输出
--format <fmt> # 自定义输出格式(见下方可用字段)
--no-newline # 输出不换行(需配合--format使用)
--timefmt <fmt> # 自定义时间格式(见下方可用字段)
-c|--csv # 以CSV格式输出事件
-t|--timeout <seconds> # 设置超时时间(0表示永不超时)
-e|--event <event1> [...] # 仅监听指定事件(默认监听所有事件)
# --format 可用字段
%T # 时间(格式由--timefmt指定)
%w # 触发事件的目录路径(相当于dirname)
%f # 触发事件的文件名(相当于basename,目录事件为空)
%e # 发生的事件名称(多个事件用逗号分隔)
%Xe # 发生的事件名称(多个事件用X分隔)
# --timefmt 可用字段
%Y # 年份(包含世纪,如2023)
%y # 年份(不含世纪,如23)
%m # 月份(01-12)
%d # 日期(01-31)
%H # 小时(00-23,24小时制)
%M # 分钟(00-59)
%S # 秒(00-60)
# -e 可指定的事件类型
access # 文件被读取
modify # 文件内容被修改
attrib # 文件属性变化(权限、时间戳等)
close_write # 以写入模式打开的文件被关闭
close_nowrite # 以只读模式打开的文件被关闭
close # 文件关闭事件(覆盖前两项)
open # 文件被打开
moved_to # 文件/目录被移动到监控目录
moved_from # 文件/目录从监控目录移出
move # 文件/目录在监控目录内移动
move_self # 监控的文件/目录本身被移动
create # 创建新文件/目录
delete # 删除文件/目录
delete_self # 监控的文件/目录本身被删除
unmount # 监控的目录被卸载
#只监控一个事件
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# tree /data
/data
├── dira
│ ├── fstab
│ └── issue
└── dirb
2 directories, 2 files
#开始监控
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# inotifywait /data
Setting up watches.
Watches established.
#终端2执行
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ls /data/
dira dirb
#提示 open 事件并退出
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# inotifywait /data
Setting up watches.
Watches established.
/data/ OPEN,ISDIR
#持续监控
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# inotifywait -m /data
Setting up watches.
Watches established.
#终端2
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ls /data
dira dirb
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ls /data/dira
fstab issue
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# touch /data/test.txt
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rm -rf /data/test.txt
#查看监控,一条命令可能有多个事件
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# inotifywait -m /data
Setting up watches.
Watches established.
/data/ OPEN,ISDIR
/data/ ACCESS,ISDIR
/data/ ACCESS,ISDIR
/data/ CLOSE_NOWRITE,CLOSE,ISDIR
/data/ OPEN,ISDIR dira
/data/ ACCESS,ISDIR dira
/data/ ACCESS,ISDIR dira
/data/ CLOSE_NOWRITE,CLOSE,ISDIR dira
/data/ CREATE test.txt
/data/ OPEN test.txt
/data/ ATTRIB test.txt
/data/ CLOSE_WRITE,CLOSE test.txt
/data/ DELETE test.txt
#递归监控
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# tree /data/
/data/
├── dira
│ ├── fstab
│ └── issue
└── dirb
2 directories, 2 files
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# inotifywait -m /data
Setting up watches.
Watches established.
#终端2
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# touch /data/dirb/test.txt
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# mkdir /data/dirb/dirc
#无法监控到刚才的操作
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# inotifywait -m /data
Setting up watches.
Watches established.
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rm -rf /data/dirb/test.txt
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rm -rf /data/dirb/dirc
#递归持续监控
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# inotifywait -m -r /data
Setting up watches. Beware: since -r was given, this may take a while!
Watches established.
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# touch /data/dirb/test.txt
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# mkdir /data/dirb/dirc
#递归持续监控
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# inotifywait -m -r /data
Setting up watches. Beware: since -r was given, this may take a while!
Watches established.
/data/dirb/ CREATE test.txt
/data/dirb/ OPEN test.txt
/data/dirb/ ATTRIB test.txt
/data/dirb/ CLOSE_WRITE,CLOSE test.txt
/data/dirb/ CREATE,ISDIR dirc
/data/dirb/ OPEN,ISDIR dirc
/data/dirb/ ACCESS,ISDIR dirc
/data/dirb/ CLOSE_NOWRITE,CLOSE,ISDIR dirc
#将结果输出到文件
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# inotifywait -m -r /data -o inotify.txt
Setting up watches. Beware: since -r was given, this may take a while!
Watches established.
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ls /data/dira
fstab issue
#不会显示
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# inotifywait -m -r /data -o inotify.txt
Setting up watches. Beware: since -r was given, this may take a while!
Watches established.
#查看输出到文件
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# cat inotify.txt
/data/ OPEN,ISDIR dira
/data/dira/ OPEN,ISDIR
/data/ ACCESS,ISDIR dira
/data/dira/ ACCESS,ISDIR
/data/ ACCESS,ISDIR dira
/data/dira/ ACCESS,ISDIR
/data/ CLOSE_NOWRITE,CLOSE,ISDIR dira
/data/dira/ CLOSE_NOWRITE,CLOSE,ISDIR
#追加,但不覆盖
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rm -rf /data/dirb/test.txt
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rm -rf /data/dirb/dirc
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# cat inotify.txt
/data/ OPEN,ISDIR dira
/data/dira/ OPEN,ISDIR
/data/ ACCESS,ISDIR dira
/data/dira/ ACCESS,ISDIR
/data/ ACCESS,ISDIR dira
/data/dira/ ACCESS,ISDIR
/data/ CLOSE_NOWRITE,CLOSE,ISDIR dira
/data/dira/ CLOSE_NOWRITE,CLOSE,ISDIR
/data/dirb/ DELETE test.txt
/data/dirb/ OPEN,ISDIR dirc
/data/dirb/dirc/ OPEN,ISDIR
/data/dirb/ ACCESS,ISDIR dirc
/data/dirb/dirc/ ACCESS,ISDIR
/data/dirb/ ACCESS,ISDIR dirc
/data/dirb/dirc/ ACCESS,ISDIR
/data/dirb/ CLOSE_NOWRITE,CLOSE,ISDIR dirc
/data/dirb/dirc/ CLOSE_NOWRITE,CLOSE,ISDIR
/data/dirb/dirc/ DELETE_SELF
/data/dirb/ DELETE,ISDIR dirc
#从文件中读取要监控的内容
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# echo "/data" > a.txt
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# inotifywait -mr --fromfile a.txt
Setting up watches. Beware: since -r was given, this may take a while!
Watches established.
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ls /data
dira dirb
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# inotifywait -mr --fromfile a.txt
Setting up watches. Beware: since -r was given, this may take a while!
Watches established.
/data/ OPEN,ISDIR
/data/ ACCESS,ISDIR
/data/ ACCESS,ISDIR
/data/ CLOSE_NOWRITE,CLOSE,ISDIR
#后台守护执行,并指定输出格式
inotifywait -drq /data -o inotify.log --timefmt "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" --format "%T %w %f event: %e"
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ls /data/dira
fstab issue
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# cat inotify.log
2025-12-13 22:05:17 /data/ dira event: OPEN,ISDIR
2025-12-13 22:05:17 /data/dira/ event: OPEN,ISDIR
2025-12-13 22:05:17 /data/ dira event: ACCESS,ISDIR
2025-12-13 22:05:17 /data/dira/ event: ACCESS,ISDIR
2025-12-13 22:05:17 /data/ dira event: ACCESS,ISDIR
2025-12-13 22:05:17 /data/dira/ event: ACCESS,ISDIR
2025-12-13 22:05:17 /data/ dira event: CLOSE_NOWRITE,CLOSE,ISDIR
2025-12-13 22:05:17 /data/dira/ event: CLOSE_NOWRITE,CLOSE,ISDIR
#指定输出格式,且只记录特定事件
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# inotifywait -mrq /data/ --timefmt "%F %H:%M:%S" --format "%T %w%f event:%;e" -e create,delete,moved_to,close_write,attrib
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# touch /data/dirb/test.log
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rm -rf /data/dirb/test.log
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# inotifywait -mrq /data/ --timefmt "%F %H:%M:%S" --format "%T %w%f event:%;e" -e create,delete,moved_to,close_write,attrib
2025-12-13 22:08:51 /data/dirb/test.log event:CREATE
2025-12-13 22:08:51 /data/dirb/test.log event:ATTRIB
2025-12-13 22:08:51 /data/dirb/test.log event:CLOSE_WRITE;CLOSE
2025-12-13 22:08:59 /data/dirb/test.log event:DELETE2、rsync服务
rsync 常用于做为 linux系统下的数据镜像备份工具,实现远程同步,支持本地复制,或者与其他SSH、rsync主机同步数据,支持增量备份,配合任务计划,rsync能实现定时或间隔同步,配合 inotify 或sersync,可以实现触发式的实时数据同步。
#安装
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# apt install rsync
# Local
rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... DEST # 本地文件同步
# Access via remote shell
rsync [OPTION]... [USER@]HOST:SRC [DEST] # PULL 拉,将远程主机上的文件拉到本地
rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... [USER@]HOST:DEST # PUSH 推,将本地文件推送到远程主机上
# Access via rsync daemon:
rsync [OPTION]... [USER@]HOST::SRC [DEST] # PULL 拉,将远程主机上的文件拉到本地
rsync [OPTION]... rsync://[USER@]HOST[:PORT]/SRC [DEST] # PULL 拉,将远程主机上的文件拉到本地
rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... [USER@]HOST::DEST # PUSH 推,将本地文件推送到远程主机上
rsync [OPTION]... SRC [SRC]... rsync://[USER@]HOST[:PORT]/DEST # PUSH 推,将本地文件推送到远程主机上
#前两者的本质是通过本地或远程shell,而第3种方式则是让远程主机上运行 rsyncd 服务,使其监听在一个端口上,等待客户端的连接,此种方式使用的 rsync 的专有协议。
#常用选项
#基础操作
--verbose|-v # 显示详细过程(最多 -vvvv)
--quiet|-q # 不输出错误信息
--archive|-a # 归档模式(保留文件属性,等价于 -rlptgoD)
--recursive|-r # 递归传输目录
--backup|-b # 目标文件存在时先备份(默认后缀 ~)
--backup-dir=DIR # 指定备份目录
--suffix=SUFFIX # 自定义备份后缀(如 --suffix=.bak)
--update|-u # 仅更新源文件比目标文件新的内容(接收端判断)
#链接处理
--links|-l # 传输软链接本身(不是传输其指向的文件)
--copy-links|-L # 跟随软链接,传输实际文件/目录
--copy-unsafe-links # 跟随非安全软链接(可能跳出传输目录)
--safe-links # 忽略非安全软链接(默认行为)
#权限与属性
--perms|-p # 保留文件权限(不包括特殊权限)
--owner|-o # 保留所有者(需 root 权限)
--group|-g # 保留所属组(需 root 权限)
--times|-t # 保留修改时间(mtime)
--acls # 保留 ACL 权限
--xattrs # 保留扩展属性
--chmod=MODE # 强制修改文件权限(如 --chmod=u=rw,g=r,o=)
#文件筛选
--exclude=PATTERN # 排除匹配的文件(如 --exclude='*.tmp')
--exclude-from=FILE # 从文件读取排除规则
--include=PATTERN # 强制包含匹配的文件
--include-from=FILE # 从文件读取包含规则
--min-size=SIZE # 最小传输文件大小(如 --min-size=1M)
--max-size=SIZE # 最大传输文件大小(如 --max-size=1G)
--max-delete=NUM # 最多删除 NUM 个目标文件
#删除与同步
--delete # 删除目标端多余文件(保持严格同步)
--delete-before # 传输前删除目标端多余文件
--delete-during # 传输中删除目标端多余文件(默认)
--delete-delay # 传输完成后删除目标端多余文件
--delete-excluded # 删除目标端被排除的文件
--ignore-existing # 仅传输目标端不存在的文件
--existing # 仅更新目标端已存在的文件
--force # 强制删除非空目录
#传输优化
--compress|-z # 压缩传输数据(节省带宽)
--compress-level=NUM # 设置压缩级别(1-9,默认 6)
--skip-compress=LIST # 跳过压缩的文件类型(如 --skip-compress=gz/zip)
--whole-file|-W # 全量传输(不计算差异,适合大文件或高带宽)
--partial # 保留部分传输的文件(断点续传)
--partial-dir=DIR # 指定部分传输文件的临时目录
--progress # 显示传输进度条
--stats # 显示传输统计信息
--human-readable|-h # 以易读格式显示大小(如 KB/MB/GB)
#网络与安全
--rsh=COMMAND|-e # 指定远程 shell(默认 ssh)
--port=PORT # 指定远程端口(默认 22)
--bwlimit=RATE # 限制带宽(KB/s,如 --bwlimit=100)
--ipv4|-4 # 强制使用 IPv4
--ipv6|-6 # 强制使用 IPv6
--contimeout=SECS # 设置连接超时(秒)
--timeout=SECS # 设置 I/O 超时(秒)
--ignore-errors # 忽略 I/O 错误继续传输
--password-file=FILE # 从文件读取密码(用于 rsync daemon 模式)
#守护进程模式
--daemon # 以守护进程模式运行
--address=IP # 绑定到指定 IP
--config=FILE # 指定配置文件(默认 /etc/rsyncd.conf)
--module=NAME # 同步指定模块(需配置 rsyncd.conf)
--no-motd # 隐藏守护进程欢迎信息
#其他
--dry-run|-n # 测试模式(不实际传输,配合 -vvv 查看细节)
--version|-V # 显示版本信息
--help|-h # 显示帮助信息rsync 服务常用配置项
#查看配置示例
cat /usr/share/doc/rsync/examples/rsyncd.conf
# GLOBAL OPTIONS #全局配置部份
motd file=/etc/motd #motd 文件路径
log file=/var/log/rsyncd #日志文件
pid file=/var/run/rsyncd.pid #PID 文件
syslog facility=daemon #rsyslog 日志服务中的日志归类
socket options= #socket 选项,具体见 man setsockopt
[ftp] #客户端显示的名称
comment = public archive #客户端列出该共享目录时的说明信息
path = /var/www/pub #服务端具体目录
use chroot = yes #更改映射目录的根目录
max connections=10 #最大连接数,同时有多少客户端可以连接
lock file = /var/lock/rsyncd #锁文件
read only = yes #默认客户端只读访问
list = yes #客户端是否可以列出服务端内容
uid = nobody #默认将客户端上传的文件属主映射成 nobody
gid = nogroup #默认将客户端上传的文件属组映射成 nobody
exclude = #指定排除项,在此处指定的内容在客户端无法显示
exclude from = #从指定文件中读取排除项
include = #指定显示项,配合 exclude,exclude from 使用
include from = #同上
auth users = #客户端用户名,启用此项表示禁用匿名连接
secrets file = /etc/rsyncd.secrets #客户端用户名和密码对应文件
strict modes = yes #严格检查权限,此选项用于 windows 系统上的 rsync
hosts allow = #客户端白名单
hosts deny = #客户端黑名单
ignore errors = no #不忽略错误
ignore nonreadable = yes #
transfer logging = no #是否开启传输日志
log format = %t: host %h (%a) %o %f (%l bytes). Total %b bytes. #默认日志格式
timeout = 600 #超时时长
refuse options = checksum dry-run #服务端拒绝客户端执行的命令列表
dont compress = *.gz *.tgz *.zip *.z *.rpm *.deb *.iso *.bz2 *.tbz #不压缩指定文件
#查看配置帮助
man rsyncd.conf实现rsync daemon服务
#150 - client
#152 - server bak
#server
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# systemctl status rsync.service
○ rsync.service - fast remote file copy program daemon
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/rsync.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
Docs: man:rsync(1)
man:rsyncd.conf(5)
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# systemctl enable --now rsync.service
Synchronizing state of rsync.service with SysV service script with /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install.
Executing: /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable rsync
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/rsync.service → /lib/systemd/system/rsync.service.
#启动失败
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# systemctl status rsync.service
○ rsync.service - fast remote file copy program daemon
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/rsync.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
Condition: start condition failed at Sun 2025-12-14 13:47:27 CST; 17s ago
└─ ConditionPathExists=/etc/rsyncd.conf was not met #缺少配置文件
Docs: man:rsync(1)
man:rsyncd.conf(5)
Dec 14 13:47:27 ubuntu2204-152 systemd[1]: Condition check resulted in fast remote file copy program daemon being skipped.
#创建空配置文件
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# touch /etc/rsyncd.conf
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# systemctl enable --now rsync.service
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# systemctl status rsync.service
● rsync.service - fast remote file copy program daemon
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/rsync.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sun 2025-12-14 13:48:53 CST; 1s ago
Docs: man:rsync(1)
man:rsyncd.conf(5)
Main PID: 16726 (rsync)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 2177)
Memory: 1.3M
CPU: 24ms
CGroup: /system.slice/rsync.service
└─16726 /usr/bin/rsync --daemon --no-detach
Dec 14 13:48:53 ubuntu2204-152 systemd[1]: Started fast remote file copy program daemon.
Dec 14 13:48:54 ubuntu2204-152 rsyncd[16726]: rsyncd version 3.2.7 starting, listening on port 873
#监听873端口
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ss -tunlp | grep rsync
tcp LISTEN 0 5 0.0.0.0:873 0.0.0.0:* users:(("rsync",pid=16726,fd=4))
tcp LISTEN 0 5 [::]:873 [::]:* users:(("rsync",pid=16726,fd=5))
#client连接服务端
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rsync rsync://10.0.0.152
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# echo $?
0
#server
#修改服务端配置,指定共享目录
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# tree /data
/data
├── dir1
└── dir2
2 directories, 0 files
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# vim /etc/rsyncd.conf
[dir1]
path=/data/dir1
read only=no
#重启服务
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# systemctl restart rsync.service
#client
#客户端再次测试,可以看到内容
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rsync rsync://10.0.0.152
dir1
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rsync 10.0.0.152:: #写法2,:: 表示走rsync协议
dir1
#传输文件到远程失败,此处的 root 是指rsync服务的用户,当前服务端并没有配置此信息,默认会被映射成 nobody
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rsync /etc/fstab root@10.0.0.152::dir1
rsync: [receiver] mkstemp "/.fstab.hcbLdR" (in dir1) failed: Permission denied (13)
rsync error: some files/attrs were not transferred (see previous errors) (code 23) at main.c(1338) [sender=3.2.7]
#server
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# apt install acl
#配置权限
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# setfacl -m u:nobody:rwx /data/dir1
#客户端再次测试,上传成功,现在使用的是匿名连接
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rsync /etc/fstab root@10.0.0.152::dir1
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ls /data/dir1
fstab
#客户端服务端都不存在的用户
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rsync /etc/issue xxx@10.0.0.152::dir1
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ll /data/dir1
total 16
drwxrwxr-x+ 2 root root 4096 Dec 14 14:36 ./
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Dec 13 18:04 ../
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 657 Dec 14 14:35 fstab
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 26 Dec 14 14:36 issue
#指定映射账号,指定日志文件,指定远程连接用户名和密码,禁用匿名连接
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# vim /etc/rsyncd.conf
uid=root
gid=root
max connections=0
log file=/var/log/rsyncd.log
pid file=/var/run/rsyncd.pid
lock file=/var/run/rsyncd.lock
[dir1]
path=/data/dir1
comment=rsync di1
read only=no
auth users=rsyncer
secrets file=/etc/rsyncd.pwd
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# cat /etc/rsyncd.pwd
rsyncer:12345
#重启服务
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# systemctl restart rsync.service
#客户端再次测试,匿名非匿名都报错
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rsync 10.0.0.152::dir1
Password:
@ERROR: auth failed on module dir1
rsync error: error starting client-server protocol (code 5) at main.c(1863) [Receiver=3.2.7]
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rsync rsyncer@10.0.0.152::dir1
Password:
@ERROR: auth failed on module dir1
rsync error: error starting client-server protocol (code 5) at main.c(1863) [Receiver=3.2.7]
#查看服务端日志,密码文件不能被所有人可读
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# cat /var/log/rsyncd.log
...
2025/12/14 14:50:13 [17194] secrets file must not be other-accessible (see strict modes option)
2025/12/14 14:50:13 [17194] auth failed on module dir1 from UNKNOWN (10.0.0.150) for rsyncer: ignoring secrets file
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ll /etc/rsync*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 230 Dec 14 14:44 /etc/rsyncd.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6 Dec 14 14:45 /etc/rsyncd.pwd
#修改密码文件权限
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsyncd.pwd
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ll /etc/rsync*
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 230 Dec 14 14:44 /etc/rsyncd.conf
-rw------- 1 root root 6 Dec 14 14:45 /etc/rsyncd.pwd
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rsync 10.0.0.152::dir1
Password:
@ERROR: auth failed on module dir1
rsync error: error starting client-server protocol (code 5) at main.c(1863) [Receiver=3.2.7]
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rsync rsyncer@10.0.0.152::dir1
Password:
drwxrwxr-x 4,096 2025/12/14 14:36:02 .
-rw-r--r-- 657 2025/12/14 14:35:49 fstab
-rw-r--r-- 26 2025/12/14 14:36:02 issue
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rsync /etc/hosts rsyncer@10.0.0.152::dir1
Password:
#服务端查看,新文件属主属组发生了变化
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# ll /data/dir1
total 20
drwxrwxr-x+ 2 root root 4096 Dec 14 14:57 ./
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 Dec 13 18:04 ../
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 657 Dec 14 14:35 fstab
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 220 Dec 14 14:57 hosts
-rw-r--r-- 1 nobody nogroup 26 Dec 14 14:36 issue
#client
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# tree /data/
/data/
├── dira
│ ├── fstab
│ ├── hhaosocool
│ └── issue
└── dirb
2 directories, 3 files
#server
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# tree /data/dir1/
/data/dir1/
├── fstab
├── hosts
└── issue
0 directories, 3 files
#client
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# echo "12345"> /etc/rsyncd-client.pwd
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsyncd-client.pwd
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rsync -avz --delete --password-file=/etc/rsyncd-client.pwd /data/ rsyncer@10.0.0.152::dir1
sending incremental file list
deleting issue
deleting hosts
deleting fstab
./
dira/
dira/fstab
dira/hhaosocool
dira/issue
dirb/
sent 780 bytes received 115 bytes 1,790.00 bytes/sec
total size is 683 speedup is 0.76
#再次查看服务端,与客户端保持一致
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# tree /data/dir1/
/data/dir1/
├── dira
│ ├── fstab
│ ├── hhaosocool
│ └── issue
└── dirb
2 directories, 3 files3、inotify+rsync 实现数据实时同步
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# cat rsync.sh
#!/bin/bash
SRC='/data/'
DEST='rsyncer@10.0.0.152::dir1'
# 检查并安装依赖
dpkg -V inotify-tools &>/dev/null || apt install inotify-tools -y
dpkg -V rsync &>/dev/null || apt install rsync -y
# 不间断监控目录事件并触发 rsync 同步
inotifywait -mrq \
--exclude=".*\.swp" \
--timefmt '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S' \
--format '%T %w %f' \
-e create,delete,moved_to,close_write,attrib ${SRC} | while read DATE TIME DIR FILE; do
FILEPATH=${DIR}${FILE}
rsync -az --delete --password-file=./data_rsync.pwd "${SRC}" "${DEST}" && \
echo "At ${TIME} on ${DATE}, file ${FILEPATH} was backed up via rsync" >> ./data_rsync.log
done
#执行脚本前置操作
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# echo "12345" > data_rsync.pwd
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# vim rsync.sh
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# chmod 600 data_rsync.pwd
#不然会出现如下情况
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# bash ./rsync.sh
rsync: [sender] could not open password file ./www_rsync.pwd: No such file or directory (2)
rsync error: syntax or usage error (code 1) at authenticate.c(189) [sender=3.2.7]
#客户端
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# tree /data/
/data/
├── dira
│ ├── fstab
│ ├── hhaosocool
│ └── issue
└── dirb
2 directories, 3 files
#服务端
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# tree /data/
/data/
├── dir1
│ └── test
├── dir2
└── dir3
├── fstab
└── issue
3 directories, 3 files
#测试
#客户端
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# bash rsync.sh
#终端2
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# touch /data/dirb/test.txt
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# mkdir /data/dira/source
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# rm -rf /data/dira/hhaosocool
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# tree /data/
/data/
├── dira
│ ├── fstab
│ ├── issue
│ └── source
└── dirb
└── test.txt
3 directories, 3 files
#查看服务端
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# tree /data/
/data/
├── dir1
│ ├── dira
│ │ ├── fstab
│ │ ├── issue
│ │ └── source
│ └── dirb
│ └── test.txt
├── dir2
└── dir3
├── fstab
└── issue
6 directories, 5 files
#查看客户端日志,由于某些行为会触发多个事件,导致多次调用脚本,效率不高
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# cat data_rsync.log
At 15:35:30 on 2025-12-14, file /data/dirb/test.txt was backed up via rsync
At 15:35:30 on 2025-12-14, file /data/dirb/test.txt was backed up via rsync
At 15:35:30 on 2025-12-14, file /data/dirb/test.txt was backed up via rsync
At 15:36:02 on 2025-12-14, file /data/dira/source was backed up via rsync
At 15:36:23 on 2025-12-14, file /data/dira/hhaosocool was backed up via rsync4、sersync 实现数据实时同步
#下载
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# wget https://storage.googleapis.com/google-code-archive-downloads/v2/code.google.com/sersync/sersync2.5.4_64bit_binary_stable_final.tar.gz
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# tar -zxvf sersync2.5.4_64bit_binary_stable_final.tar.gz
GNU-Linux-x86/
GNU-Linux-x86/sersync2
GNU-Linux-x86/confxml.xml
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# mv GNU-Linux-x86/ /usr/local/sersync
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ls /usr/local/sersync/
confxml.xml sersync2配置说明
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<head version="2.5">
<!-- 主机配置:监控服务器的IP和端口(默认8008用于HTTP监控) -->
<host hostip="localhost" port="8008"></host>
<!-- 调试模式:是否开启调试日志(false表示关闭) -->
<debug start="false"/>
<!-- 文件系统类型:是否为XFS文件系统(false表示非XFS) -->
<fileSystem xfs="false"/>
<!-- 文件过滤规则:排除指定文件或目录(不触发同步) -->
<filter start="false">
<exclude expression="(.*)\.svn"></exclude> <!-- 排除.svn目录 -->
<exclude expression="(.*)\.gz"></exclude> <!-- 排除.gz压缩文件 -->
<exclude expression="^info/*"></exclude> <!-- 排除info目录及其内容 -->
<exclude expression="^static/*"></exclude> <!-- 排除static目录及其内容 -->
</filter>
<!-- inotify监控事件配置:控制哪些文件操作触发同步 -->
<inotify>
<delete start="true"/> <!-- 监控文件删除事件 -->
<createFolder start="true"/> <!-- 监控目录创建事件 -->
<createFile start="false"/> <!-- 不监控文件创建事件(避免频繁触发) -->
<closeWrite start="true"/> <!-- 监控文件写入完成事件(如保存文件) -->
<moveFrom start="true"/> <!-- 监控文件移动出目录事件 -->
<moveTo start="true"/> <!-- 监控文件移动入目录事件 -->
<attrib start="false"/> <!-- 不监控文件属性变更(如权限修改) -->
<modify start="false"/> <!-- 不监控文件内容修改事件(避免重复同步) -->
</inotify>
<!-- sersync核心配置 -->
<sersync>
<!-- 本地监控路径及远程同步目标 -->
<localpath watch="/opt/tongbu"> <!-- 监控本地目录/opt/tongbu -->
<remote ip="127.0.0.1" name="tongbu1"/> <!-- 同步到本地的rsync模块tongbu1 -->
<!-- 可添加多个远程目标(注释示例) -->
<!--<remote ip="192.168.8.39" name="tongbu"/>-->
<!--<remote ip="192.168.8.40" name="tongbu"/>-->
</localpath>
<!-- rsync参数配置 -->
<rsync>
<commonParams params="-artuz"/> <!-- 常用参数:-a归档 -r递归 -t保留时间 -u更新 -z压缩 -->
<auth start="false" users="root" passwordfile="/etc/rsync.pas"/> <!-- 是否启用rsync认证 -->
<userDefinedPort start="false" port="874"/> <!-- 自定义rsync端口(默认873) -->
<timeout start="false" time="100"/> <!-- 超时时间(秒) -->
<ssh start="false"/> <!-- 是否使用SSH加密传输 -->
</rsync>
<!-- 失败重试日志:记录同步失败的文件,定期重试 -->
<failLog path="/tmp/rsync_fail_log.sh" timeToExecute="60"/> <!-- 每60分钟执行一次重试 -->
<!-- 定时全量同步配置(默认关闭) -->
<crontab start="false" schedule="600"> <!-- 每600分钟(10小时)执行一次 -->
<crontabfilter start="false"> <!-- 过滤规则(示例) -->
<exclude expression="*.php"/> <!-- 排除.php文件 -->
<exclude expression="info/*"/> <!-- 排除info目录 -->
</crontabfilter>
</crontab>
<!-- 插件配置(默认关闭) -->
<plugin start="false" name="command"/> <!-- 命令插件:同步后执行自定义命令 -->
</sersync>
<!-- 命令插件:同步后执行脚本(需配合plugin的start="true"启用) -->
<plugin name="command">
<param prefix="/bin/sh" suffix="" ignoreError="true"/> <!-- 执行脚本的前缀(如/bin/sh) -->
<filter start="false"> <!-- 过滤触发脚本的文件类型 -->
<include expression="(.*)\.php"/> <!-- 仅对.php文件触发 -->
<include expression="(.*)\.sh"/> <!-- 仅对.sh文件触发 -->
</filter>
</plugin>
<!-- Socket插件:实时通知其他服务器(如缓存服务器) -->
<plugin name="socket">
<localpath watch="/opt/tongbu"> <!-- 监控路径 -->
<deshost ip="192.168.138.20" port="8009"/> <!-- 通知目标IP和端口 -->
</localpath>
</plugin>
<!-- CDN刷新插件:同步后自动刷新CDN缓存 -->
<plugin name="refreshCDN">
<localpath watch="/data0/htdocs/cms.xoyo.com/site/"> <!-- 监控路径 -->
<cdninfo domainname="ccms.chinacache.com" port="80" username="xxxx" passwd="xxxx"/> <!-- CDN认证信息 -->
<sendurl base="http://pic.xoyo.com/cms"/> <!-- CDN基础URL -->
<regexurl regex="false" match="cms.xoyo.com/site([/a-zA-Z0-9]*).xoyo.com/images"/> <!-- URL匹配规则 -->
</localpath>
</plugin>
</head>命令用法和参数
[root@ubuntu2204-150 sersync]# ./sersync2 -h
set the system param
execute:echo 50000000 > /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches
execute:echo 327679 > /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events
parse the command param
_______________________________________________________
参数-d:启用守护进程模式
参数-r:在监控前,将监控目录与远程主机用rsync命令推送一遍
c参数-n: 指定开启守护线程的数量,默认为10个
参数-o:指定配置文件,默认使用confxml.xml文件
参数-m:单独启用其他模块,使用 -m refreshCDN 开启刷新CDN模块
参数-m:单独启用其他模块,使用 -m socket 开启socket模块
参数-m:单独启用其他模块,使用 -m http 开启http模块
不加-m参数,则默认执行同步程序
________________________________________________________________
#客户端
[root@ubuntu2204-150 sersync]# tree /data/
/data/
└── dira
├── fstab
└── issue
1 directory, 2 files
#服务端
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# tree /data/
/data/
└── dir1
└── hhaosocool
1 directory, 1 file
#client
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# touch /data/dira/test.txt
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# mkdir /data/dira/dirb
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# tree /data/
/data/
└── dira
├── dirb
├── fstab
├── issue
└── test.txt
2 directories, 3 files
#启动服务
[root@ubuntu2204-150 sersync]# ./sersync2 -dro ./confxml.xml
#服务端
[root@ubuntu2204-152 ~]# tree /data/dir1/
/data/dir1/
├── dirb
├── fstab
├── issue
└── test.txt
1 directory, 3 files
#
<sersync>
<localpath watch="/data/dira">
<remote ip="10.0.0.152" name="dir1"/>
</localpath>
<rsync>
<commonParams params="-artuz"/>
<auth start="true" users="rsyncer" passwordfile="/etc/rsyncd-client.pwd"/> #此处pwd 是要实时同步的client 采用非交互式的pwd 而不是服务端的
<userDefinedPort start="false" port="874"/><!-- port=874 -->
<timeout start="false" time="100"/><!-- timeout=100 -->
<ssh start="false"/>
</rsync>
[root@ubuntu2204-150 ~]# ps aux |grep sersync
root 3341 0.0 0.0 92340 1328 ? Ssl 17:25 0:00 ./sersync2 -dro ./confxml.xml
root 3359 0.0 0.1 6480 2324 pts/1 S+ 17:28 0:00 grep --color=auto sersync| 对比项 | inotify+rsync | sersync |
|---|---|---|
| 监控机制 | 监控目录事件,但需遍历整个目录对比差异 | 直接记录变化文件/子目录,无需全目录遍历 |
| 同步效率 | 低(文件量大时遍历耗时,网络开销大) | 高(仅同步变化内容,多线程并行处理) |
| 资源占用 | CPU/I/O负载高(频繁遍历) | 低(精准同步减少无效操作) |
| 实时性 | 延迟较高(依赖遍历速度) | 实时性强(变化立即触发同步) |
| 错误处理 | 无内置重试机制,需手动脚本处理 | 自动重试失败文件(默认10小时重试一次) |
| 定时同步 | 需额外配置crontab | 内置定时任务(无需外部工具) |
| 过滤临时文件 | 需手动配置脚本过滤(如.swp) |
内置过滤规则(减少无效同步) |
| 扩展性 | 依赖脚本,灵活性高但维护复杂 | 支持Socket/HTTP插件,二次开发方便 |
| 配置复杂度 | 高(需编写监控脚本+rsync参数调优) | 低(XML配置文件,开箱即用) |
| 适用场景 | 小规模数据、低频同步、需精细控制 | 大规模数据、高频实时同步、高可靠性需求 |