课程目标
- 掌握while循环的语法和使用场景
- 理解do-while循环的特点和适用情况
- 学会在不同场景下选择合适的循环结构
- 掌握循环嵌套的复杂应用
- 能够解决复杂的模式输出和计算问题
- 理解循环控制语句break和continue的用法
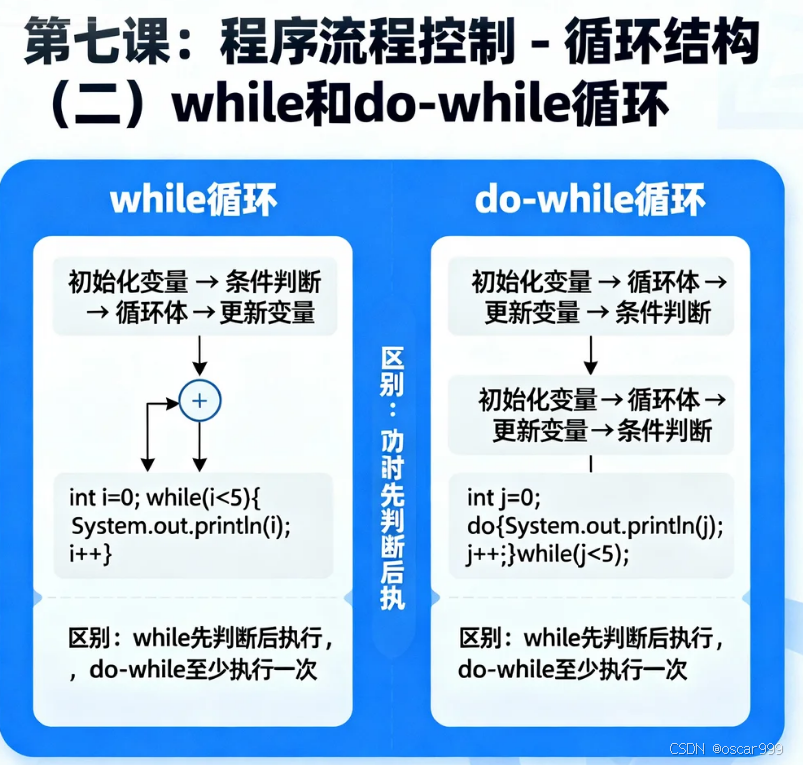
第一部分:while循环(50分钟)
1.1 while循环的基本概念
while循环的特点:
- 先判断条件,再执行循环体
- 适合循环次数不确定的情况
- 条件为真时继续循环,为假时退出
语法:
cpp
while (条件) {
// 循环体
}执行流程图:
plain
开始
↓
检查条件
↓
条件为假 → 结束循环
↓条件为真
执行循环体
↓
检查条件 → ...1.2 基本的while循环示例
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int count = 1; // 初始化计数器
// 输出1到5的数字
while (count <= 5) {
cout << "当前数字: " << count << endl;
count++; // 更新计数器
}
cout << "循环结束!" << endl;
return 0;
}1.3 while循环与for循环的对比
相同功能的两种实现:
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 使用for循环输出1-5
cout << "for循环: ";
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 使用while循环输出1-5
cout << "while循环: ";
int j = 1; // 初始化
while (j <= 5) { // 条件
cout << j << " ";
j++; // 更新
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}1.4 while循环的适用场景
场景1:用户输入验证
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int score;
// 要求用户输入有效的成绩(0-100)
cout << "请输入成绩(0-100): ";
cin >> score;
// 如果输入无效,要求重新输入
while (score < 0 || score > 100) {
cout << "输入无效!请重新输入成绩(0-100): ";
cin >> score;
}
cout << "输入的成绩是: " << score << endl;
return 0;
}场景2:游戏循环
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int playerHealth = 100;
int monsterHealth = 80;
int playerAttack, monsterAttack;
cout << "=== 勇士斗恶龙 ===" << endl;
// 游戏主循环
while (playerHealth > 0 && monsterHealth > 0) {
cout << "\n你的生命值: " << playerHealth;
cout << " | 恶龙生命值: " << monsterHealth << endl;
// 玩家攻击
cout << "请输入你的攻击力(1-20): ";
cin >> playerAttack;
monsterHealth -= playerAttack;
cout << "你对恶龙造成了 " << playerAttack << " 点伤害!" << endl;
// 如果恶龙还活着,进行反击
if (monsterHealth > 0) {
monsterAttack = 10 + rand() % 11; // 10-20的随机伤害
playerHealth -= monsterAttack;
cout << "恶龙对你造成了 " << monsterAttack << " 点伤害!" << endl;
}
}
// 判断游戏结果
if (playerHealth > 0) {
cout << "\n恭喜!你击败了恶龙!" << endl;
} else {
cout << "\n很遗憾,你被恶龙击败了..." << endl;
}
return 0;
}场景3:数据统计
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int number;
int sum = 0, count = 0;
double average;
cout << "请输入一系列整数,输入0结束:" << endl;
// 读取第一个数字
cout << "请输入第1个数字: ";
cin >> number;
// 循环读取直到输入0
while (number != 0) {
sum += number;
count++;
cout << "请输入第" << count + 1 << "个数字: ";
cin >> number;
}
// 计算结果
if (count > 0) {
average = static_cast<double>(sum) / count;
cout << "\n=== 统计结果 ===" << endl;
cout << "数字个数: " << count << endl;
cout << "总和: " << sum << endl;
cout << "平均值: " << average << endl;
} else {
cout << "没有输入有效数字!" << endl;
}
return 0;
}第二部分:do-while循环(40分钟)
2.1 do-while循环的特点
do-while循环的特点:
- 先执行循环体,再判断条件
- 循环体至少执行一次
- 适合需要至少执行一次的情况
语法:
cpp
do {
// 循环体
} while (条件);执行流程图:
plain
开始
↓
执行循环体
↓
检查条件
↓
条件为真 → 执行循环体
↓条件为假
结束循环2.2 do-while循环示例
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int number;
// 使用do-while确保至少执行一次
do {
cout << "请输入一个正整数: ";
cin >> number;
if (number <= 0) {
cout << "输入无效!请重新输入。" << endl;
}
} while (number <= 0); // 条件不满足时继续循环
cout << "你输入的正整数是: " << number << endl;
return 0;
}2.3 do-while的典型应用:菜单系统
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int choice;
do {
// 显示菜单
cout << "\n=== 学生管理系统 ===" << endl;
cout << "1. 添加学生" << endl;
cout << "2. 删除学生" << endl;
cout << "3. 查询学生" << endl;
cout << "4. 显示所有学生" << endl;
cout << "0. 退出系统" << endl;
cout << "请选择操作: ";
cin >> choice;
// 根据选择执行相应操作
switch (choice) {
case 1:
cout << "执行添加学生功能..." << endl;
break;
case 2:
cout << "执行删除学生功能..." << endl;
break;
case 3:
cout << "执行查询学生功能..." << endl;
break;
case 4:
cout << "执行显示所有学生功能..." << endl;
break;
case 0:
cout << "感谢使用,再见!" << endl;
break;
default:
cout << "无效选择,请重新输入!" << endl;
}
} while (choice != 0); // 选择0时退出
return 0;
}2.4 while vs do-while 对比
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int number = 10;
cout << "while循环测试:" << endl;
// 先判断条件,条件为false,不执行循环体
while (number < 5) {
cout << "这个不会执行" << endl;
number++;
}
cout << "while循环后number = " << number << endl;
cout << "\ndo-while循环测试:" << endl;
// 先执行循环体,再判断条件
do {
cout << "这个会执行一次" << endl;
number++;
} while (number < 5);
cout << "do-while循环后number = " << number << endl;
return 0;
}第三部分:循环控制语句(40分钟)
3.1 break语句
break的作用: 立即退出当前循环
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 查找第一个能被7整除的数
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
if (i % 7 == 0) {
cout << "找到第一个能被7整除的数: " << i << endl;
break; // 找到后立即退出循环
}
cout << "检查: " << i << endl;
}
return 0;
}3.2 continue语句
continue的作用: 跳过本次循环的剩余代码,直接进入下一次循环
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 输出1-10的奇数
cout << "1-10的奇数: ";
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
continue; // 如果是偶数,跳过输出
}
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}3.3 break和continue的综合应用
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int number;
cout << "请输入数字(输入负数退出):" << endl;
while (true) { // 无限循环
cout << "请输入一个数字: ";
cin >> number;
// 输入负数时退出
if (number < 0) {
cout << "输入负数,程序结束!" << endl;
break;
}
// 跳过0
if (number == 0) {
cout << "0被跳过" << endl;
continue;
}
// 处理正数
cout << "你输入的是正数: " << number << endl;
cout << "它的平方是: " << number * number << endl;
}
return 0;
}第四部分:循环嵌套进阶(50分钟)
4.1 多重循环的概念
循环嵌套: 在一个循环内部包含另一个循环
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 外层循环控制行
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
cout << "外层循环 i = " << i << endl;
// 内层循环控制列
for (int j = 1; j <= 2; j++) {
cout << " 内层循环 j = " << j << endl;
}
cout << "外层循环结束" << endl;
cout << "---" << endl;
}
return 0;
}4.2 复杂图案输出
打印菱形:
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cout << "请输入菱形大小(奇数): ";
cin >> n;
// 上半部分
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i += 2) {
// 打印空格
for (int j = 1; j <= (n - i) / 2; j++) {
cout << " ";
}
// 打印星号
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
cout << "*";
}
cout << endl;
}
// 下半部分
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 1; i -= 2) {
// 打印空格
for (int j = 1; j <= (n - i) / 2; j++) {
cout << " ";
}
// 打印星号
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
cout << "*";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}4.3 数学表格生成
乘法表增强版:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int size;
cout << "请输入乘法表大小: ";
cin >> size;
// 打印表头
cout << " ";
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
cout << setw(4) << i;
}
cout << endl;
// 打印分隔线
cout << " ";
for (int i = 1; i <= size * 4; i++) {
cout << "-";
}
cout << endl;
// 打印乘法表
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
cout << setw(2) << i << " |";
for (int j = 1; j <= size; j++) {
cout << setw(4) << i * j;
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}4.4 组合数学问题
组合计数:
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int count = 0;
cout << "所有的三位数组合(各位数字不同):" << endl;
// 百位数字从1-9
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
// 十位数字从0-9,但不能与百位相同
for (int j = 0; j <= 9; j++) {
if (j == i) continue; // 跳过相同的数字
// 个位数字从0-9,不能与前两位相同
for (int k = 0; k <= 9; k++) {
if (k == i || k == j) continue; // 跳过相同的数字
int number = i * 100 + j * 10 + k;
cout << number << " ";
count++;
// 每10个数字换行
if (count % 10 == 0) {
cout << endl;
}
}
}
}
cout << "\n总共有 " << count << " 个满足条件的三位数" << endl;
return 0;
}第五部分:综合应用示例(50分钟)
5.1 猜数字游戏
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
int main() {
srand(time(0)); // 设置随机数种子
int secretNumber = rand() % 100 + 1; // 1-100的随机数
int guess, attempts = 0;
const int maxAttempts = 7;
cout << "=== 猜数字游戏 ===" << endl;
cout << "我想了一个1-100之间的数字,你有" << maxAttempts << "次机会猜中它!" << endl;
while (attempts < maxAttempts) {
attempts++;
cout << "\n第" << attempts << "次尝试,请输入你的猜测: ";
cin >> guess;
if (guess == secretNumber) {
cout << "恭喜!你猜对了!" << endl;
cout << "你用了 " << attempts << " 次猜中了数字 " << secretNumber << endl;
break;
} else if (guess < secretNumber) {
cout << "太小了!" << endl;
} else {
cout << "太大了!" << endl;
}
// 提示剩余次数
cout << "还剩 " << maxAttempts - attempts << " 次机会" << endl;
// 最后一次机会的提示
if (attempts == maxAttempts - 1) {
// 给一个范围提示
int lower = max(1, secretNumber - 10);
int upper = min(100, secretNumber + 10);
cout << "提示:数字在 " << lower << " 到 " << upper << " 之间" << endl;
}
}
if (attempts == maxAttempts && guess != secretNumber) {
cout << "\n很遗憾,你没有猜中。正确的数字是: " << secretNumber << endl;
}
return 0;
}5.2 素数筛选器
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int limit;
cout << "请输入上限(找出该范围内的所有素数): ";
cin >> limit;
if (limit < 2) {
cout << "没有素数!" << endl;
return 0;
}
cout << "2到" << limit << "之间的素数:" << endl;
int count = 0;
int perLine = 10; // 每行显示10个素数
// 检查每个数字是否为素数
for (int number = 2; number <= limit; number++) {
bool isPrime = true;
// 检查从2到number-1是否有因数
for (int i = 2; i * i <= number; i++) { // 优化:检查到平方根即可
if (number % i == 0) {
isPrime = false;
break;
}
}
// 如果是素数,输出
if (isPrime) {
cout << setw(6) << number;
count++;
// 每行显示perLine个素数后换行
if (count % perLine == 0) {
cout << endl;
}
}
}
cout << "\n\n总共找到 " << count << " 个素数" << endl;
return 0;
}5.3 数字金字塔进阶
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int rows;
cout << "请输入金字塔行数: ";
cin >> rows;
// 数字金字塔
for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++) {
// 打印前导空格
for (int j = 1; j <= rows - i; j++) {
cout << " ";
}
// 打印左半部分(递增)
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
cout << j << " ";
}
// 打印右半部分(递减)
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 1; j--) {
cout << j << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << "\n字符金字塔:\n";
// 字符金字塔
for (int i = 1; i <= rows; i++) {
// 打印前导空格
for (int j = 1; j <= rows - i; j++) {
cout << " ";
}
// 打印字符
char currentChar = 'A';
for (int j = 1; j <= 2 * i - 1; j++) {
cout << currentChar;
if (j < i) {
currentChar++;
} else {
currentChar--;
}
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}5.4 分数统计系统
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int studentCount;
int subjectCount;
cout << "请输入学生人数: ";
cin >> studentCount;
cout << "请输入科目数量: ";
cin >> subjectCount;
// 输入每个学生的每科成绩
for (int student = 1; student <= studentCount; student++) {
cout << "\n=== 第" << student << "个学生 ===" << endl;
double totalScore = 0;
double highestScore = 0;
double lowestScore = 100;
for (int subject = 1; subject <= subjectCount; subject++) {
double score;
cout << "请输入第" << subject << "科成绩: ";
cin >> score;
totalScore += score;
if (score > highestScore) {
highestScore = score;
}
if (score < lowestScore) {
lowestScore = score;
}
}
double averageScore = totalScore / subjectCount;
// 输出学生成绩统计
cout << fixed << setprecision(2);
cout << "总分: " << totalScore << endl;
cout << "平均分: " << averageScore << endl;
cout << "最高分: " << highestScore << endl;
cout << "最低分: " << lowestScore << endl;
// 成绩评价
if (averageScore >= 90) {
cout << "评价: 优秀" << endl;
} else if (averageScore >= 80) {
cout << "评价: 良好" << endl;
} else if (averageScore >= 70) {
cout << "评价: 中等" << endl;
} else if (averageScore >= 60) {
cout << "评价: 及格" << endl;
} else {
cout << "评价: 不及格" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}第六部分:循环结构选择指南(20分钟)
6.1 如何选择合适的循环结构
| 循环类型 | 适用场景 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| for循环 | 循环次数已知 | 初始化、条件、更新都在一行 |
| while循环 | 循环次数未知,先判断后执行 | 适合输入验证、条件控制 |
| do-while循环 | 循环次数未知,至少执行一次 | 适合菜单系统、用户交互 |
6.2 循环选择示例
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int choice;
// 场景1:已知次数 - 使用for循环
cout << "场景1:输出1-10的平方" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
cout << i << "² = " << i * i << endl;
}
// 场景2:未知次数,先判断 - 使用while循环
cout << "\n场景2:输入验证" << endl;
int age;
cout << "请输入年龄: ";
cin >> age;
while (age < 0 || age > 150) {
cout << "年龄无效!请重新输入: ";
cin >> age;
}
// 场景3:至少执行一次 - 使用do-while循环
cout << "\n场景3:菜单系统" << endl;
do {
cout << "1. 开始游戏" << endl;
cout << "2. 设置" << endl;
cout << "3. 退出" << endl;
cout << "请选择: ";
cin >> choice;
// 处理选择...
} while (choice != 3);
return 0;
}练习与作业
基础练习(必做)
练习1:数字反转
输入一个正整数,使用循环将其数字反转。
例如:输入12345,输出54321
练习2:最大公约数(GCD)
使用欧几里得算法计算两个数的最大公约数。
算法:gcd(a,b) = gcd(b, a mod b),直到b为0
练习3:简单计算器循环版
改进之前的计算器,使其可以连续进行计算,直到用户选择退出。
挑战练习(选做)
挑战1:帕斯卡三角形
输出指定行数的帕斯卡三角形(杨辉三角)。
plain
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1挑战2:数字黑洞
实现数字黑洞6174的验证:
- 任选一个四位数(数字不能全相同)
- 数字按降序排列和升序排列,得到最大数和最小数
- 用大数减小数,得到新的四位数
- 重复上述步骤,最多7步,必然会得到6174
挑战3:生命游戏
实现康威生命游戏的简单版本,在控制台显示细胞演化过程。
实验任务
任务1:循环性能比较
对同一个问题分别用for、while、do-while实现,比较代码的可读性和适用性。
任务2:嵌套循环深度测试
测试多层嵌套循环的性能和可读性,找出合理的嵌套深度。
任务3:循环优化实验
对素数判断算法进行优化,比较优化前后的性能差异。
学习总结
今天学到了:
- ✅ while循环:先判断后执行,适合次数不确定的循环
- ✅ do-while循环:先执行后判断,至少执行一次
- ✅ 循环控制语句:break(退出循环)和continue(跳过本次)
- ✅ 循环嵌套进阶:复杂图案和数学问题的解决
- ✅ 循环结构选择:根据不同场景选择合适的循环类型
关键技能:
- 循环设计:根据问题特点选择合适的循环结构
- 条件控制:编写有效的循环条件和退出条件
- 嵌套应用:使用多重循环解决复杂问题
- 算法思维:将数学问题转化为循环解决方案
下一课预告:
下一节课我们将进行阶段性复习与测评,综合运用前面学过的所有知识,通过小测验和编程闯关游戏来巩固学习成果!