关注我,学习c++不迷路:
专栏如下:
后续会更新更多有趣的小知识,关注我带你遨游知识世界

期待你的关注。
文章目录
- [1. 前言:](#1. 前言:)
- [2. 重新设计结构:](#2. 重新设计结构:)
-
- [2-1 节点设计:](#2-1 节点设计:)
- [2-2 迭代器设计:](#2-2 迭代器设计:)
- [3. 完善迭代器:](#3. 完善迭代器:)
-
- [3-1 operator``++``:](#3-1 operator
++:) - [3-2 operator``--``](#3-2 operator
--)
- [3-1 operator``++``:](#3-1 operator
- [4. 主干设计Tree部分:](#4. 主干设计Tree部分:)
-
- [4-1 新加部分:](#4-1 新加部分:)
- 4-2改变部分:
- [6. 开始封装map和set:](#6. 开始封装map和set:)
-
- 6-1set:
- [6-2 map:](#6-2 map:)
- [7. 总结:](#7. 总结:)
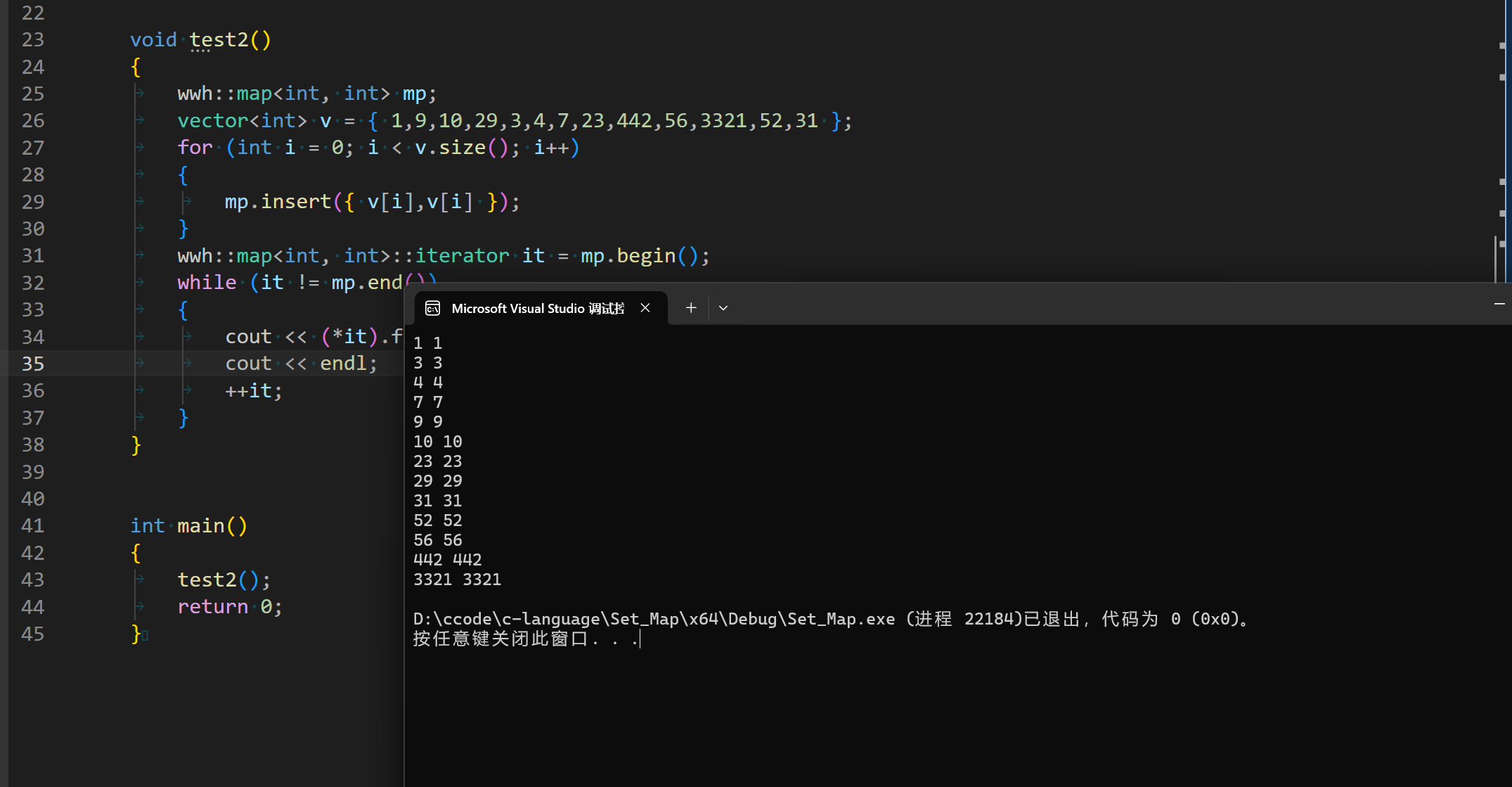
1. 前言:
我们之前已经学习了如何设计并且写出红黑树,这次我们需要利用这些来封装出一个红黑树。
在我们的红黑树中是没有实现迭代器,在这里面我们需要实现,同时我们还需要设计使红黑树同时能满足set和map,其中set是一个key,而map是key和val,我们需要怎么设计才能满足这个条件呢?
不妨来看看SGI中的STL是怎么设计的:
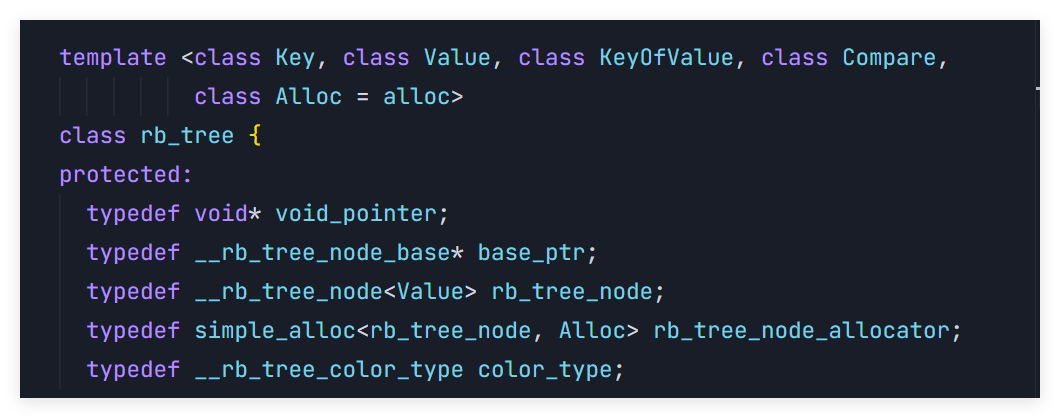
在这里面,我们的模板不再简单的是:
源码中传入传入了类型key和val以及两个仿函数。这两个函数一个是用于不同类型的比较。另一个则是来满足set和map的不同。
- Key :键类型
- Value :值类型
- KeyOfValue :从Value中提取Key的函数对象
- Compare :键值比较函数对象
- Alloc :内存分配器。
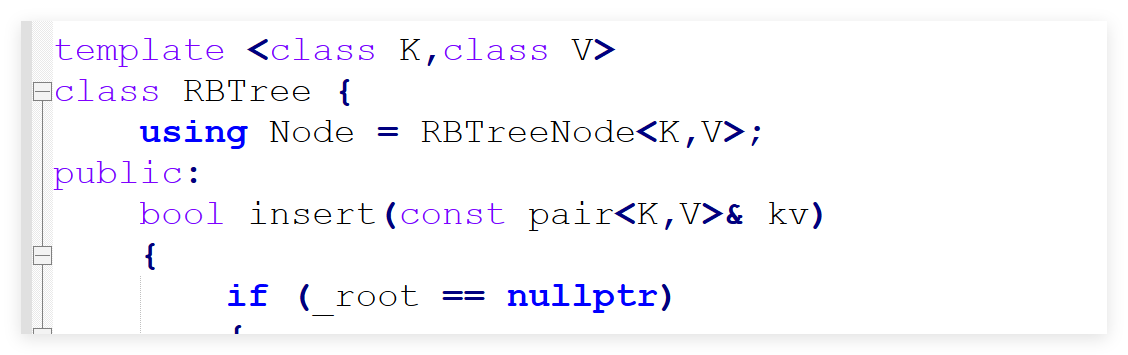
在stl_set.h中设计成这样:
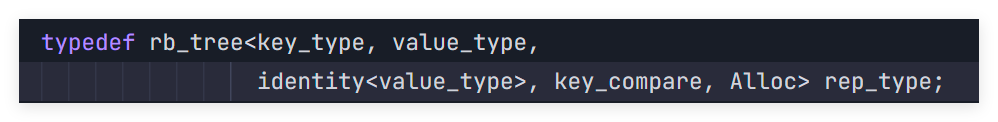

我们发现,key既是key_type也是value_type。这样就也满足了占位,但是如果是map,传入了pair,如何取到pair的first,这个就要讲到后面的KeyOfValue。
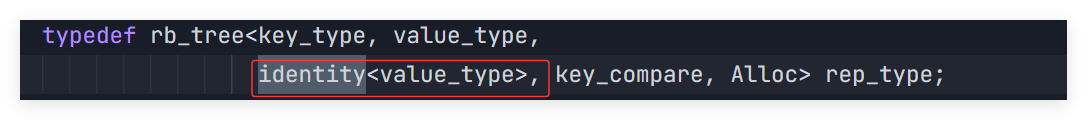
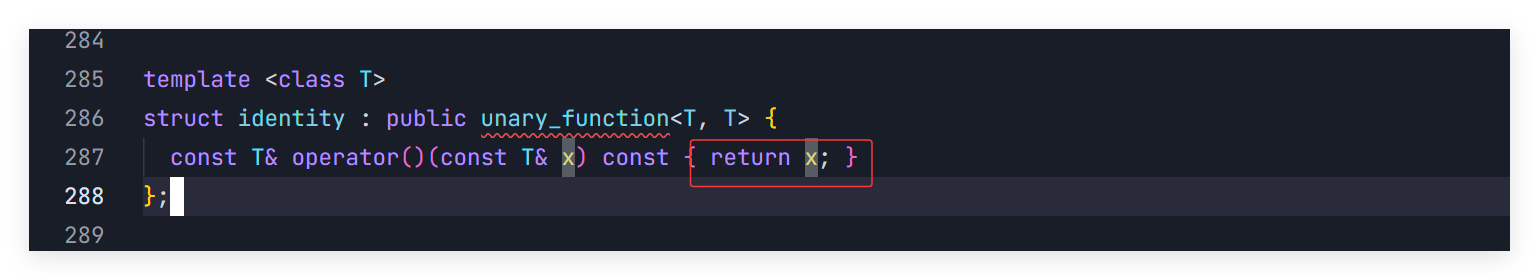
这里就讲述了是怎么面对不同的数据类型来做不同的做取值的,这里可能讲的不清楚,但是没事。后面我们还会详细的讲讲。
2. 重新设计结构:
2-1 节点设计:
我们为了与stl保持高度一致,我们也采取差不多的设计,那么我们原本的节点也需要改变:我们节点只有一个类型就是T,无论传入的是key,还是pair<K,V>;都只给一个名字叫T:
cpp
enum Color {
BLACK,
RED,
};
template<class T>
class RBTreeNode {
public:
RBTreeNode(const T& date)
:_date(date)
,_parent(nullptr)
,_left(nullptr)
,_right(nullptr)
{ }
T _date;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
Color _col;
};这样一个节点就好了,后续只需连接或者插入就可以满足红黑树,同时为了满足迭代器,还要传入的参数,也要改变:
cpp
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree {
using Node = RBTreeNode<T>;
public:
using Iterator = RBTreeIterator<T, const T&, T*>;
using constIterator = RBTreeIterator<T, const T&,T*>;
Node* _root = nullptr;
};里面也对外公开了迭代器,同时模板也不再是简单的<K,V>结构了,这里是key和T结构。T可以是后面传入的key,也可以是pair<K,V>。
2-2 迭代器设计:
在stl中,迭代器传入了三个参数,这些都是为了迭代器后续的实现完成的,这些操作使得迭代器可以像指针一样使用,同时提供了类型安全和容器无关的统一接口。
- Value参数
- 作用 :表示迭代器指向的元素类型
- 用途 :定义了迭代器所操作的值的类型
- 示例 :在红黑树中,Value可能是 int 、 pair<const int, string> 等
-
- Ref参数
- 作用 :表示迭代器解引用后返回的引用类型
- 用途 :控制迭代器返回的是可修改引用还是只读引用
- 示例 :
- 对于普通迭代器: Ref = Value& (可修改引用)
- 对于常量迭代器: Ref = const Value& (只读引用)
- Ptr参数
- 作用 :表示迭代器通过 -> 操作符返回的指针类型
- 用途 :控制迭代器返回的指针类型
- 示例 :
- 对于普通迭代器: Ptr = Value* (可修改指针)
- 对于常量迭代器: Ptr = const Value* (只读指针)
那么遵循这种结构,我们也可以来尝试实现这种结构吧:
//开始封装迭代器,里面是节点。
cpp
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
class RBTreeIterator {
using Node = RBTreeNode<T>;
using Self = RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr>;
private:
Node* _node;
Node* _root;
};这里还要_root是后面需要使用的。
3. 完善迭代器:
在我们设计的迭代器还少了很多主要功能比如++和- -,我来尝试实现:
3-1 operator++:
我们可以看看节点是如何进入下一个节点的,在红黑树中,我们是按照左中右来遍历的,那么我们可以总结出:
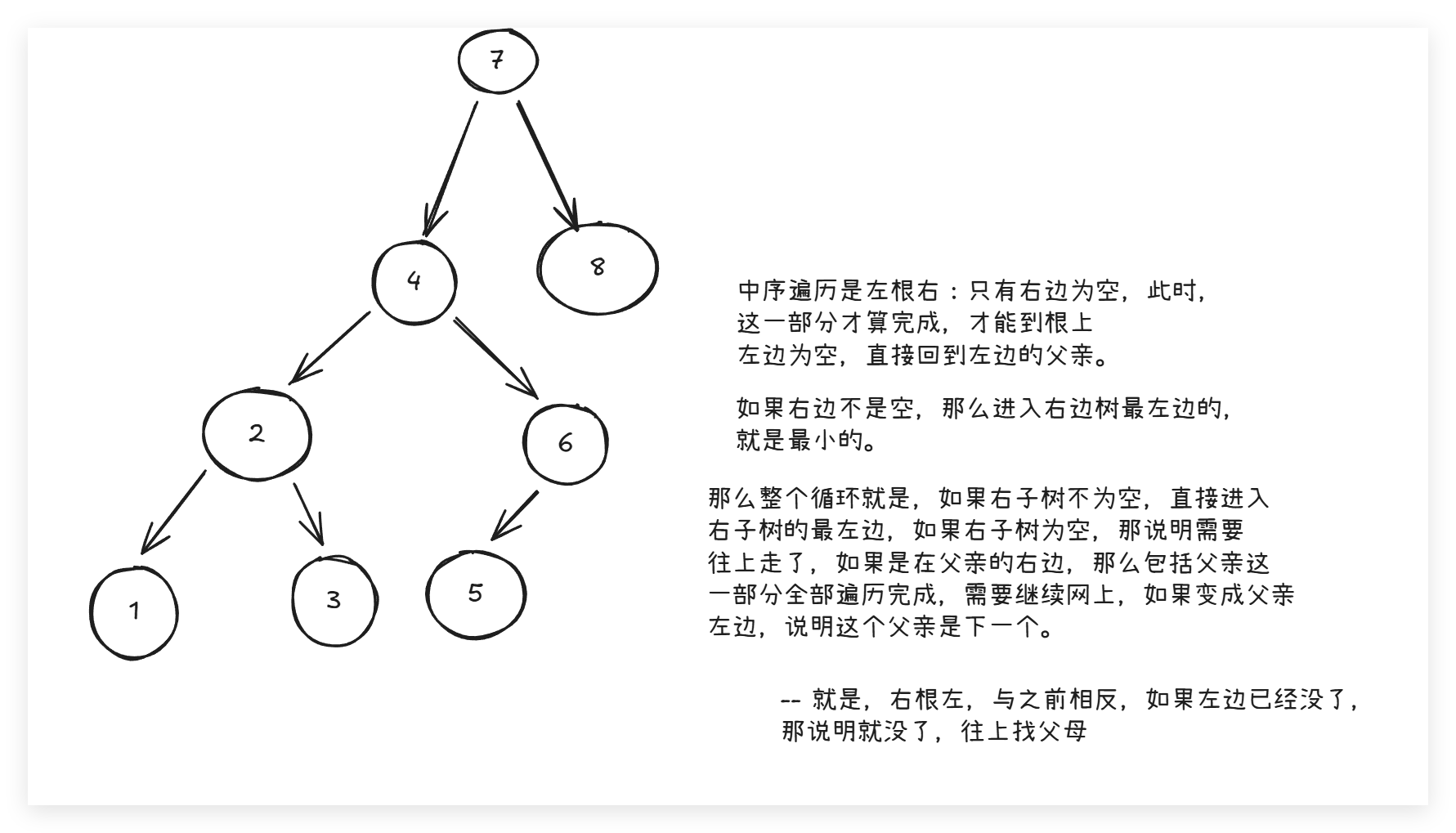
那么我们就有:
cpp
Self operator++()
{
if (_node->_right)
{
//如果右边不是空的,说明下一个节点就是右子树最小的即最左边的
Node* min = _node->_right;
while (min->_left)
{
min = min->_left;
}
_node = min;
}
else {
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}这就是加加的逻辑。完成++。
3-2 operator--
--的逻辑与这个大致相似,但是不同的是:如何从空节点回到最后也是end()节点呢?
这里就用到了_root.利用这个找到这个end节点就是最右边的节点:
cpp
Self operator--()
{
if (_node == nullptr)
{
Node* rootMax = _root;
while (rootMax && rootMax->_right)
{
rootMax = rootMax->_right;
}
_node = rootMax;
}
if (_node->_left)
{
Node* max = _node->_left;
while (max->_left)
{
max = max->_right;
}
_node = max;
}
else {
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = _node->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}但是我们在运行时很快就发现了这个错误:
错误 1:operator-- 的逻辑穿透(致命)
现象:当迭代器为 end() 时,你找到了最大节点 rootMax,但没有返回。代码会继续向下执行,导致逻辑混乱。
修正:处理完 end() 情况后,必须立即 return *this;。
cpp
Self operator--()
{
if (_node == nullptr)
{
Node* rootMax = _root;
while (rootMax && rootMax->_right)
{
rootMax = rootMax->_right;
}
_node = rootMax;
return *this;
}
if (_node->_left)
{
Node* max = _node->_left;
while (max->_right)
{
max = max->_right;
}
_node = max;
}
else {
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = _node->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}这样就完成了大致的逻辑。
4. 主干设计Tree部分:
4-1 新加部分:
在之前的部分,我么便可以尝试提供迭代器的接口,分别是:begin和end。
- 在这里begin就是最小的,那么就是左子树最左边的,同时防止数为空导致空指针解引用。
- end则比较简单,只需传入空即可。
- 需要给出两部分迭代器,一个常性迭代器,一个正常的
cpp
Iterator begin()
{
Node* cur = _root;
if (_root == nullptr)
return end(); // 空树时直接返回 end()
while (cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return Iterator(cur,_root);
}
constIterator begin()const
{
Node* cur = _root;
if (_root == nullptr)
return end();
while (cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return constIterator(cur, _root);
}
Iterator end()
{
return Iterator(nullptr, _root);
}
constIterator end() const
{
return Iterator(nullptr, _root);
}4-2改变部分:
这里大部分逻辑不变,但是由于前面的变量发生改变,所以发生改变:
cpp
pair<Iterator,bool> insert(const T& date)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(date);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return { Iterator(_root,_root),true };
}
KeyOfT kot;
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(date) > kot(cur->_date))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(date) < kot(cur->_date))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
return {Iterator(cur,_root),false};
}
cur = new Node(date);
if (kot(date) < kot(parent->_date))
parent->_left = cur;
else
parent->_right = cur;
Node* NewNode = cur;
cur->_col = RED;//默认插入为红色,如果插入黑色不满足红黑树
cur->_parent = parent;
//开始分类讨论:
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* Gparent = parent->_parent;
//如果父亲不是空并且父亲为红色就进入循环:
if (Gparent->_left == parent)
{
// G
// p u
Node* uncle = Gparent->_right;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED )
{
//开始变色:
uncle->_col = BLACK;
parent->_col = BLACK;
Gparent->_col = RED;//注意事项
cur = Gparent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else {
//这里uncle不可能是黑色的,如果parent是红色的,那么uncle如果存在,就必须是红色的
// G
//p
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
// G
// p
//c
RotateR(Gparent);
parent->_col = BLACK;
Gparent->_col = RED;
}
else if (cur == parent->_right)
{
// G
// p
// c
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(Gparent);
Gparent->_col = RED;
cur->_col = BLACK;//cur做了Gpa
}
//这里需不要break?之前需要更新是因为Gpanet的parent可能也是红色
break;
}
}
else {
// G
//u P
Node* uncle = Gparent->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//开始变色:
uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;
Gparent->_col = RED;
cur = Gparent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else {
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
// G
// p
// c
RotateL(Gparent);
parent->_col = BLACK;
Gparent->_col = RED;
}
else {
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(Gparent);
cur->_col = BLACK;
Gparent->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;//无论如何都要让_root变成黑色
return {Iterator(NewNode,_root),true};
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
Node* Pparent = parent->_parent;
//第一步:处理subLR
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
//第二部处理:parent
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
//第三部处理Pparent和 subL
subL->_parent = Pparent;
if (Pparent == nullptr)
_root = subL;
else {
if (parent == Pparent->_left)
Pparent->_left = subL;
else
Pparent->_right = subL;
}
}
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
Node* Pparent = parent->_parent;
//1.处理:subRL
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
//2.处理:parent
parent->_parent = subR;
subR->_left = parent;
//3.处理Pparent和subR;
subR->_parent = Pparent;
if (Pparent == nullptr)
_root = subR;
else {
if (parent == Pparent->_left)
Pparent->_left = subR;
else
Pparent->_right = subR;
}
}
void Inorder()
{
_Inorder(_root);
}
Node* Find(const T& date)
{
KeyOfT kot;
if (_root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(date) > kot(cur->_date))
cur = cur->_right;
else if (kot(date) < kot(cur->_date))
cur = cur->_left;
else
return cur;
}
return nullptr;
}
bool IsRBTree()
{
//可以直接判断,就直接在这里写:
if (_root == nullptr)
return true;
if (_root->_col == RED)
return false;
int RefNum = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
RefNum++;
cur = cur->_left;
}
return _Check(_root, 0, RefNum);
}
size_t Size()
{
return _Size(_root);
}
size_t Height()
{
return _Height(_root);
}
private:
void _Inorder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_Inorder(root->_left);
cout << root->_date << endl;
_Inorder(root->_right);
}
bool _Check(Node* root, int BH, int RN)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
if (BH != RN)
{
cout << "存在黑色结点的数量不相等的路径" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;//控制递归返回条件。
}
if (root->_col == BLACK)
BH++;
if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED)
{
//如果是根节点,是不会找他的父节点,就不会空指针的解引用
cout << "存在两个红色节点" << endl;
return false;
}
return _Check(root->_left, BH, RN) && _Check(root->_right, BH, RN);
}
size_t _Size(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
//没遍历一个都会加1.
return _Size(root->_left) + _Size(root->_right) + 1;
}
//size_t _Height(Node* root)
//{
// if (root == nullptr)
// return 0;
// size_t LH = _Height(root->_left);
// size_t RH = _Height(root->_right);
// return 1 + max(LH, RH);
//}
size_t _Height(Node* root)
{
queue<Node*> q;
q.push(root);
size_t height = 0;
while (!q.empty())
{
height++;
//如果不为空
size_t size = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
Node* node = q.front();
if(node->_left)
q.push(node->_left);
if(node->_right)
q.push(node->_right);
q.pop();
}
}
return height;
}
Node* _root = nullptr;
};6. 开始封装map和set:
6-1set:
终于写到这里了,我们在这里开始封装:
先写setofKey,取出类型里面的key,在这里我们就有:
cpp
template<class K>
class set {
struct SetOfT {
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
//如果是set ,那么就放回set的关键词key
}
};- RBTree<K, const K, SetOfT> 的第三个模板参数通常表示"如何从节点存储的值取出用于比较的键"。对 map 会是取 pair.first,对 set 就是"值自身"。
- SetOfT::operator()(const K& key) 做的就是恒等映射------接收一个 K 的引用并返回同一个 K 的 const 引用,避免不必要的拷贝。
- 返回 const K& 的前提是调用方把一个有效的 K 实例(通常是节点内存储的值)以引用传入,返回的引用仍然有效。千万不要返回指向局部临时对象的引用
同时开始封装各种接口:
cpp
public:
using iterator = RBTree<K, const K, SetOfT>::Iterator;
using const_iterator = RBTree<K, const K, SetOfT>::constIterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _t.insert(key);
}
size_t height()
{
return _t.Height();
}
void Inorder()
{
_t.Inorder();
}
private:
RBTree<K, const K, SetOfT> _t;
};
}
cpp
#pragma once
#include"RBTree.h"
namespace wwh{
template<class K>
class set {
struct SetOfT {
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
//如果是set ,那么就放回set的关键词key
}
};
public:
using iterator = RBTree<K, const K, SetOfT>::Iterator;
using const_iterator = RBTree<K, const K, SetOfT>::constIterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _t.insert(key);
}
size_t height()
{
return _t.Height();
}
void Inorder()
{
_t.Inorder();
}
private:
RBTree<K, const K, SetOfT> _t;
};
}6-2 map:
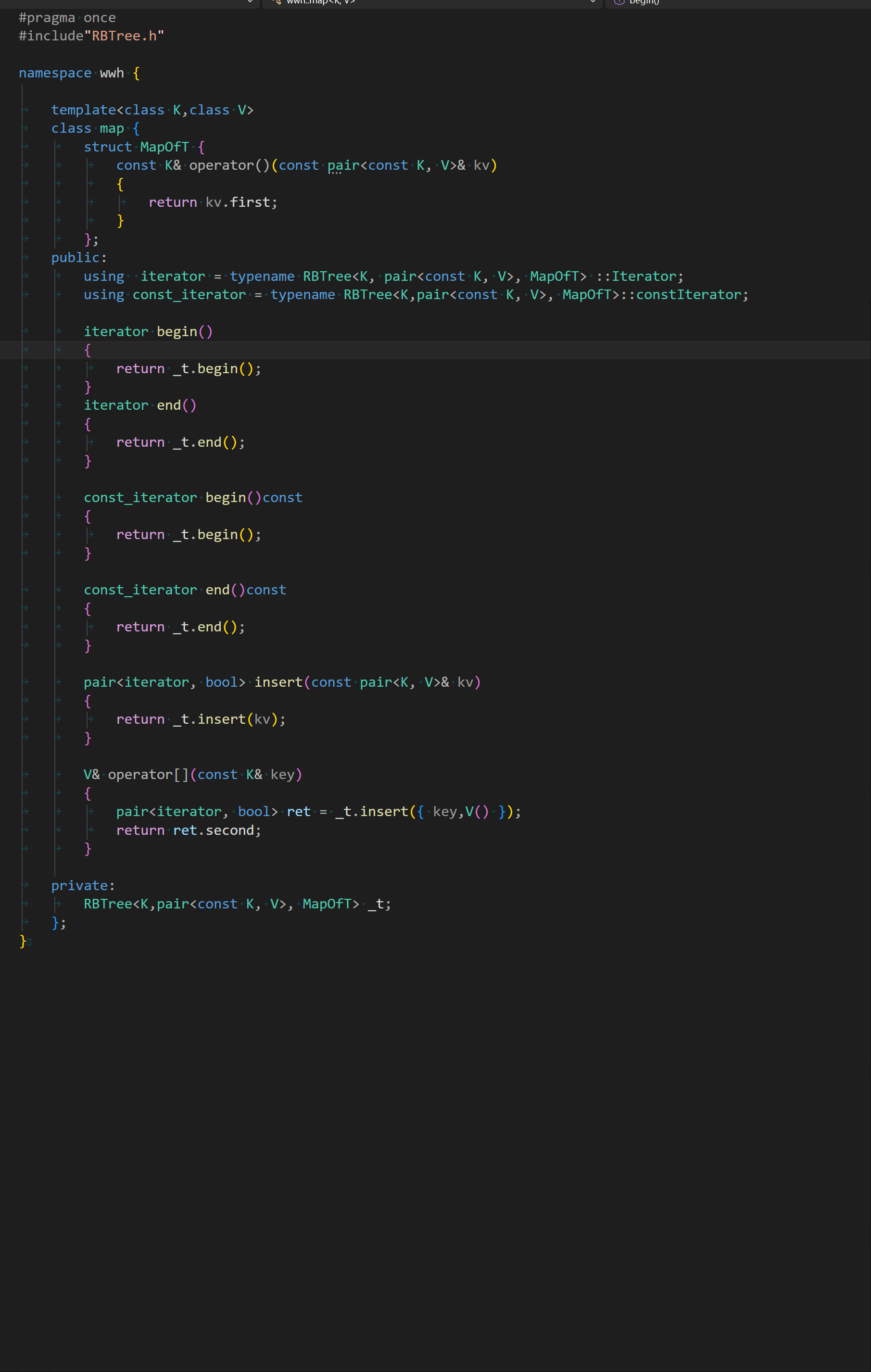
与set相似,我们这里也准备了mapofkey:
cpp
template<class K,class V>
class map {
struct MapOfT {
const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};后面完成封装:
cpp
#pragma once
#include"RBTree.h"
namespace wwh {
template<class K,class V>
class map {
struct MapOfT {
const K& operator()(const pair<const K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
using iterator = typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapOfT> ::Iterator;
using const_iterator = typename RBTree<K,pair<const K, V>, MapOfT>::constIterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.insert(kv);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.insert({ key,V() });
return ret.second;
}
private:
RBTree<K,pair<const K, V>, MapOfT> _t;
};
}7. 总结:
最好我们来测试一下: