编写满足当前需求的程序只是第一步。编写你和你的同事,可以随着新需求轻松演进、适配的程序,才是真正的目标。
引入一些重要的面向对象和设计模式实践,来构建易于测试,维护和重用的高质量软件。
1.策略模式
含义:存在一系列的算法,将所有继承自同样接口的算法抽取到独立类中,并且这些算法可以相互替代。
可以参考这里的介绍:C++ 策略模式讲解和代码示例
适用场景:
- 完成同一任务的算法有着多种变体,希望在运行时进行切换时。将算法抽离出来成为独立的不同的算法类对象。
- 当存在有多个只是在某个行为时,略有不同时。可以将这些不同抽离到单独的类层次中,作为独立的发展方向。并且可以减少冗余的代码。
- 当发现某一任务的处理算法与业务逻辑关联不强时,可以将算法与业务逻辑隔离解耦。让业务逻辑通过简单接口调用算法即可。
实现方法:
1.策略类:定义一个抽象策略接口类;然后基于这个接口类实现具体的算法类。
2.调用端:保存一个抽象接口类的基类指针或者引用;实现一个设置,切换具体算法类对象的函数;在使用时,通过基类指针或者引用,通过调用通用接口来执行具体算法;
2.代码实践
使用策略设计模式,将图像处理算法封装到一个类中。这个模式可以轻易的进行算法替换,或者将一系列算法链式组合,构建一个更复杂的处理算法。这个模式通过一个直观的接口,以及隐藏算法的复杂性,简化了算法的部署使用。
一旦一个算法使用策略模式将自己封装到类中,使用时只需创建一个类实例对象即可。通常,在程序初始化时,创建该实例对象。构造时初始化算法的各种参数,以便立即投入使用。使用对应方法,可以读取和修改算法参数。
如有GUI,可用控件更加直观地进行参数的展示和修改。
从如何部署使用一个颜色检测算法类开始:
设计一个算法:
从给定图片中,查找指定颜色值,将结果以二值图像进行输出,符合的像素以255 白色表示,不符合则输出 0 黑色。该算法还接收一个 误差 参数,在误差范围内的也认为是符合的像素值。
代码:
明白意思即可,两个具体处理的算法类其实还是有很多重复代码的。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <chrono>
using std::string;
// 算法策略抽象基类
class Strategy
{
public:
virtual ~Strategy() = default;
virtual cv::Mat process(const cv::Mat &image) = 0;
};
class ImageProcessor
{
std::unique_ptr<Strategy> _strategy;
public:
explicit ImageProcessor(std::unique_ptr<Strategy> &&strategy = {}): _strategy(std::move(strategy))
{
}
void setStrategy(std::unique_ptr<Strategy> &&strategy)
{
_strategy = std::move(strategy);
}
void processLogic(string filePath)
{
// 读取输入图像
cv::Mat input_image1 = cv::imread(filePath);
// 检查输入图像
if (input_image1.empty())
{
std::cerr << "Error: Could not open or find input image" << std::endl;
return;
}
cv::namedWindow("input_image1", cv::WINDOW_NORMAL);
cv::imshow("input_image1", input_image1);
cv::waitKey(0);
cv::Mat result = _strategy->process(input_image1);
cv::namedWindow("result", cv::WINDOW_NORMAL);
cv::imshow("result", result);
cv::waitKey(0);
}
};
class ColorDetector:public Strategy
{
int _tolerance;
cv::Vec3b m_target_color;
cv::Mat _result;
int getDistanceToTargetColor(const cv::Vec3b &color)
{
// std::cout << "color: " << color << std::endl;
// std::cout << "color: " << abs(m_target_color[0] - color[0]) << std::endl;
// std::cout << "color: " << abs(m_target_color[1] - color[1]) << std::endl;
// std::cout << "color: " << abs(m_target_color[2] - color[2]) << std::endl;
//return abs(m_target_color[0] - color[0]) + abs(m_target_color[1] - color[1]) + abs(m_target_color[2] - color[2]);
//标准平方差距离公式:(R1-R2)^2+(G1-G2)^2+(B1-B2)^2
//return sqrt(pow(m_target_color[0] - color[0], 2) + pow(m_target_color[1] - color[1], 2) + pow(m_target_color[2] - color[2], 2));
//Euclidean norm of a vector 向量的欧几里德范数
//return static_cast<int>(cv::norm(m_target_color - color));//错误写法,因为所有的矩阵和矢量计算操作符,都有saturate_cast转换,会将结果值转换为合法值。
return static_cast<int>(cv::norm(cv::Vec3i(m_target_color[0]-color[0]
, m_target_color[1]-color[1]
, m_target_color[2]-color[2])));
}
public:
ColorDetector(): _tolerance(50),m_target_color(cv::Vec3b(0,0,0))
{
}
cv::Mat process(const cv::Mat &image)
{
std::cout << "ColorDetector" << std::endl;
//_result在图片的大小和类型不同时才会重新分配。
_result.create(image.size(), CV_8UC1);
//只是对彩色图像的处理
cv::Mat_<cv::Vec3b>::const_iterator it = image.begin<cv::Vec3b>();
cv::Mat_<cv::Vec3b>::const_iterator it_end = image.end<cv::Vec3b>();
cv::Mat_<uchar>::iterator it_out = _result.begin<uchar>();
for ( ; it != it_end; it++)
{
if(getDistanceToTargetColor(*it) <= _tolerance)//颜色匹配
{
//std
*it_out = 255;
}
else//不匹配
{
*it_out = 0;
}
it_out++;
}
return _result;
}
cv::Mat operator()(const cv::Mat &image)
{
return process(image);
}
//BGR 顺序
void setTargetColor(uchar blue, uchar green, uchar red)
{
m_target_color = cv::Vec3b(blue, green, red);
}
void setTargetColor(const cv::Vec3b &color)
{
m_target_color = color;
}
cv::Vec3b targetColor()
{
return m_target_color;
}
void setTolerance(int tolerance)
{
if (tolerance < 0)
{
tolerance = 0;
std::cout << "tolerance can not be less than 0" << std::endl;
}
_tolerance = tolerance;
}
int tolerance()
{
return _tolerance;
}
};
class AnotherAlgorithm:public Strategy
{
int _tolerance;
cv::Vec3b m_target_color;
public:
AnotherAlgorithm(): _tolerance(50),m_target_color(cv::Vec3b(0,0,0)) {}
cv::Mat process(const cv::Mat &image) override
{
std::cout << "AnotherAlgorithm" << std::endl;
cv::Mat result;
//result.create(image.size(), image.type());
std::cout << "result.create " << std::endl;
// 计算绝对差值
cv::Mat target_color_mat = cv::Mat(image.size(), image.type(), m_target_color);
cv::absdiff(image, target_color_mat, result);
std::cout << "absdiff " << std::endl;
// 拆分为三个通道
std::vector<cv::Mat> channels;
cv::split(result, channels);
std::cout << "split " << std::endl;
// 求和
result = channels[0] + channels[1] + channels[2];
std::cout << "result " << std::endl;
// 二值化
cv::threshold(result, result, _tolerance, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY_INV);
std::cout << "threshold " << std::endl;
return result;
}
cv::Mat operator()(const cv::Mat &image)
{
return process(image);
}
//BGR 顺序
void setTargetColor(uchar blue, uchar green, uchar red)
{
m_target_color = cv::Vec3b(blue, green, red);
}
void setTargetColor(const cv::Vec3b &color)
{
m_target_color = color;
}
cv::Vec3b targetColor()
{
return m_target_color;
}
void setTolerance(int tolerance)
{
if (tolerance < 0)
{
tolerance = 0;
std::cout << "tolerance can not be less than 0" << std::endl;
}
_tolerance = tolerance;
}
int tolerance()
{
return _tolerance;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
// 检查命令行参数
if (argc != 3)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <input_image1> <output_image>" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
ImageProcessor processor;
//创建颜色检测器
std::unique_ptr<ColorDetector> algorithm1 = std::make_unique<ColorDetector>();
algorithm1->setTargetColor(cv::Vec3b(230, 190, 130));
processor.setStrategy(std::move(algorithm1));
processor.processLogic(argv[1]);
//创建另一个算法
std::unique_ptr<AnotherAlgorithm> algorithm2 = std::make_unique<AnotherAlgorithm>();
algorithm2->setTargetColor(cv::Vec3b(230, 190, 130));
processor.setStrategy(std::move(algorithm2));
processor.processLogic(argv[1]);
return 0;
}执行结果:
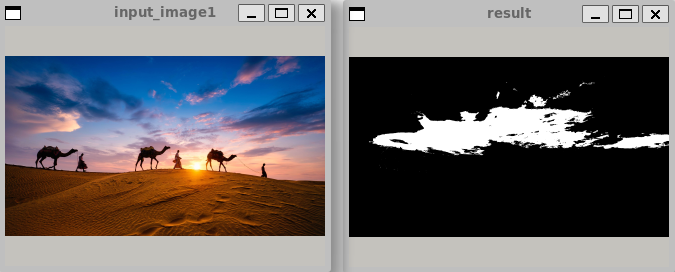
3.其它拓展
3.1 比较两个像素向量的距离
所谓距离,就是对差距的衡量,笼统理解就是两个向量的差值的和。但是也有有多种别的定义方式。
笼统的差值的和的实现方式:
cpp
int distance(const cv::Vec3i &color, const cv::Vec3i &target)
{
return abs(color[0] - target[0]) + abs(color[1] - target[1]) + abs(color[2] - target[2]);
}向量的欧几里德范数 作为对距离的衡量:
欧几里德范数 ,也称为欧氏距离或欧几里得度量,是数学中用于衡量向量空间中两点间直线距离的标准方法。
cpp
int distance(const cv::Vec3i &color, const cv::Vec3i &target)
{
return static_cast<int>(cv::norm(cv::Vec3i(target[0]-color[0]
, target[1]-color[1]
, target[2]-color[2])));
}- cv::Vec3i: 表示一个三通道的整数向量。 因为每个通道的计算结果都是整数
- cv::norm: 求两个向量的欧几里德范数。
你可能想起之前的计算方法,直接使用矩阵相减:
cpp
return static_cast<int>(cv:norm<uchar,3>(color - target))); //错误方法这是有问题的计算方法,因为所有的这些四则运算操作方法,都有一个 saturate_cast() 方法,用于对计算结果进行合法取值。因此,所有差值小于0 的结果,都会隐式的被赋值为0.
这是不对的。正确版本如下:
cpp
cv::Vec3b dist;
cv::absdiff(color, target, dist);
return cv::sum(dist)[0];但是使用这个方法,效率太低。
3.2 使用 OpenCV 的函数
除了上诉使用 迭代器循环遍历来实现计算。也可以直接使用一系列的OpenCV的函数来实现。
使用既有的方法可以快速实现功能,并减少BUG。而且这些方法通常是高效的。但是使用既有代码,可能会产生更多的中间步骤,这可能导致着更多的内存消耗。
使用OpenCV的函数重新实现处理:
cpp
cv::Mat process(const cv::Mat &image)
{
cv::Mat result;
// 计算绝对差值
cv::absdiff(image, m_target_color, result);
// 拆分为三个通道
std::vector<cv::Mat> channels;
cv::split(result, channels);
// 求和
result = channels[0] + channels[1] + channels[2];
// 二值化
cv::threshold(result, result, _tolerance, 255, cv::THRESH_BINARY_INV);
return result;
}- cv::absdiff : 接收一个image 或者 Scalar 参数来,比较得出绝对差值。当参数为image类型时,需要有相同的大小(分辨率,通道数)。当参数为Scalar 类型时,原始图像的每个像素依次与其进行计算。
- cv::split: 将图片的每个通道分离开来。用于后需求和。
- 求和+ : 要注意,矩阵的算术运算都运用了 saturate 进行了合理取值。最大值不会超过 255
- cv::threshold: 创建二值图像,通过比较每个像素和 threshold (阈值,第三个参数) ,在 cv::THRESH_BINARY 模式下,对于大于 阈值和0 的像素,填充指定的 最大值(第四个参数)。在这里,指定的是 cv::THRESH_BINART_INV 模式,意味着,小于等于 阈值的像素值,将会被填充指定的最大值。 类似的,cv::THRESH_TOZERO 和 cv::THRESH_TOZERO_INV , 对于 大于 或者小于等于指定阈值的像素值,保持值不变。
3.3 函数对象
通过类的 operator() 重载,可以实现函数对象。 可以像使用函数一样,使用对应类的实例对象。实例对象的名称,就像函数名一样。
cv::Mat operator()(const cv::Mat &image)
{
return process(image);
}