url
写url时需要注意的点:
1 url(r'^index/', views.index), 路径的前置导航斜杠(对应根路径那个),不需要写,django自动加上
2 http://127.0.0.1:8000/index 当我们访问django的url路径时,如果请求路径最后没有写/,那么django会发一个重定向的响应,告诉浏览器,加上/再来访问我
# settigns.py配置文件中修改:
# APPEND_SLASH = True # 默认为True, 当值为True时,django需要请求路径后面加上斜杠,如果请求没有加,那么响应301重定向,让浏览器街上斜杠重新请求
# 值为False,就关闭了django的这个功能
# APPEND_SLASH = False
url(r'^index/$', views.index), #/index/ /index
url(r'^index/xx/xx/', views.index2), #/index/ /index
# 注意: 路径写正则时,要注意最好精确匹配,尾部加上$,或者写正则时,尽量不要路径差不多
url(r'^$', views.home), #匹配根路径的写法 url分组
无名分组:
url(r'^books/(\d+)/(\d+)/', views.books) # 无名分组,位置参数,注意参数位置固定
视图函数写法:
def books(request, y, m):
print(y, m) # 2019 匹配出来的都是字符串
return HttpResponse('%s-%s所有书籍都在这儿,你随意看' % (y, m))
有名分组
url(r'^books/(?P<year>\d+)/(?P<month>\d+)/', views.books2),
# def books2(request, year): 函数参数必须和有名分组的名称相同
# def books2(request, year): 而且不在乎参数位置
def books2(request, month, year):
print(year, month) # 2019 匹配出来的都是字符串
return HttpResponse('%s--%s所有书籍都在这儿,你随意看' % (year,month ))
视图部分
request的常用属性
def login(request):
print(request) #<WSGIRequest: GET '/login/?a=1&b=2'> WSGIRequest类的实例化对象
print(request.method)
print(request.POST)
print(request.GET) # request.GET.get('a') == 1
print(request.path) #当前请求路径
print(request.get_full_path()) #当前请求路径包含查询参数
print(request.META) #所有请求头的信息 {''HTTP_USER_AGENT':'asdfasdfasdf',....}
# request.META 字典类型数据,所有的请求头的键都加上了一个HTTP_键名称
return HttpResponse('ok')response方法
301 redirect: 301 代表永久性重定向
302 redirect: 302 代表临时重定向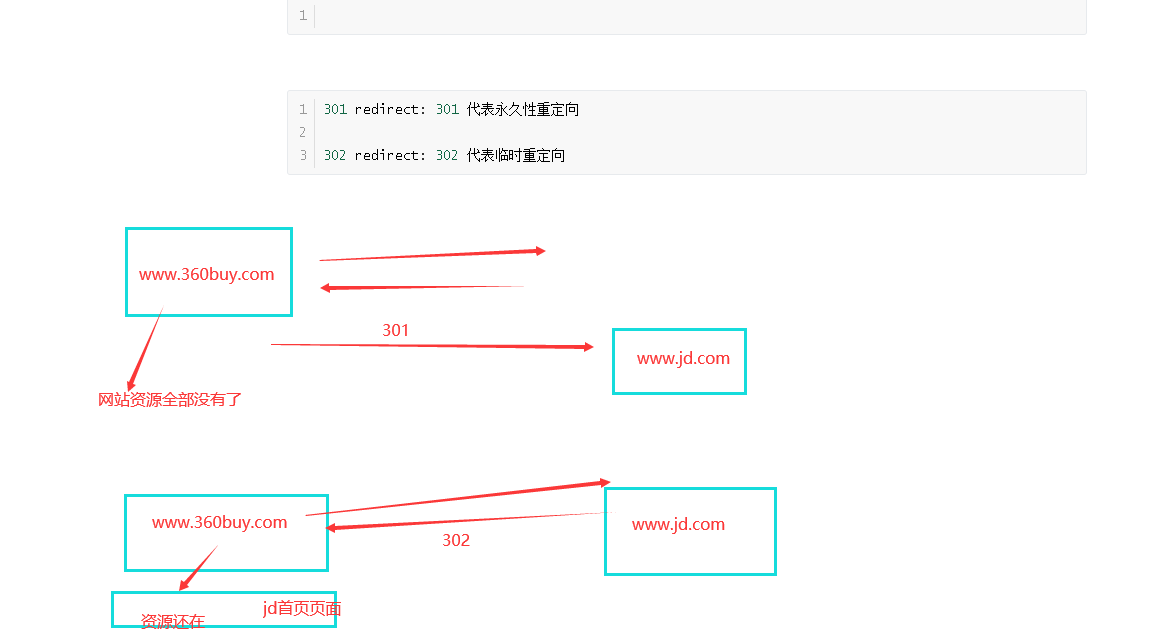
redirect响应
示例:
def login(request):
print(request) #<WSGIRequest: GET '/login/?a=1&b=2'> WSGIRequest类的实例化对象
print(request.method)
print(request.POST)
print(request.GET) # request.GET.get('a') == 1
print(request.path) #当前请求路径
print(request.get_full_path()) #当前请求路径包含查询参数
print(request.META) #所有请求头的信息 {''HTTP_USER_AGENT':'asdfasdfasdf',....}
# request.META 字典类型数据,所有的请求头的键都加上了一个HTTP_键名称
# return HttpResponse('ok')
if request.method == 'GET':
return render(request, 'login.html')
else:
uname = request.POST.get('username')
if uname == 'shiyuan':
return redirect('/home/') #redirect的参数为一个路径
# return render(request, 'home.html') #redirect的参数为一个路径
def home(request):
book = '金瓶梅'
return render(request,'home.html' , {'book': book})三个响应方法:
render 响应页面 默认响应状态码为200
HttpResponse 响应字符串 默认响应状态码为200
redirect 重定向 默认响应状态码是302设置响应头和状态码
def index(request):
re = HttpResponse('xxx')
# re = render('xxx')
# ret = redirect('/home/')
re['name'] = 'gaodaao' # 添加响应头键值对 #HttpResponse setattr
re.status_code = 404 # 修改状态码
return reCBV和FBV
FBV(function base views) 就是在视图里使用函数处理请求。
之前都是FBV模式写的代码,所以就不写例子了。
CBV(class base views) 就是在视图里使用类处理请求。
写视图逻辑的两种方式
urls.py文件的写法
urlpatterns = [
...
url(r'^book/', views.BookView.as_view()),
]视图部分写法
from django.views import View
class BookView(View):
# 通过反射获取到请求方法对应的类中的方法来执行
def get(self,request):
return HttpResponse('ok')
# 需要处理什么请求方法,就写对应名称的方法原码部分
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# Try to dispatch to the right method; if a method doesn't exist,
# defer to the error handler. Also defer to the error handler if the
# request method isn't on the approved list.
if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names: #get
# ['get', 'post', 'put', 'patch', 'delete', 'head', 'options', 'trace']
handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(), self.http_method_not_allowed)
else:
handler = self.http_method_not_allowed
return handler(request, *args, **kwargs) # HttpResponse('ok')CBV模式urls参数
url(r'^articles/(\d+)/', views.ArticalView.as_view()),class ArticalView(View):
# 和FBV模式相同,有名分组是关键字传参,无名分组是位置传参
def get(self,request, year):
print(year)
return HttpResponse('articals')dispatch方法的使用和装饰器的使用
from django.utils.decorators import method_decorator
# 方式 3
# @method_decorator(func,name='post')
# @method_decorator(func,name='get')
class ArticalView(View):
# def get(self,request, year):
# print(year)
# return HttpResponse('articals')
# 重写dispatch方法来进行拓展
# @method_decorator(func) # 方式2
# def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
#
# print('111111')
# ret = super(ArticalView, self).dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
#
# print('222222')
# return ret
# @method_decorator(func) # CBV方法加装饰器的方式1
def get(self,request, year):
print(year)
return render(request, 'articals.html')
# @method_decorator(func)
def post(self,request, year):
print(request.POST)
return HttpResponse('ok')模板渲染
{{变量}}
def index(request):
name = '赵万里'
age = 18
hobby = ['打游戏', '快乐风男', '嫖']
d1 = {'a':'b', 'c': 'd'}
class A:
def __init__(self):
self.username = '万里'
def my_hobby(self):
return '张宇'
a = A()
dd = {
'name': name,
"age": age,
"hobby": hobby,
"d1": d1,
"a": a,
}
# 'asdfasdfasdf{{hobby.0}}' -- hobby[0]
# 模板渲染完成之后, 才返回给浏览器, 浏览器再进行页面渲染, 生成效果
return render(request, 'index.html', dd)过滤器
在原有数据的基础上进行一些额外的加工处理来使用
语法 无参数过滤的用法{{ 变量|过滤器名称 }} 有参数过滤器用法{{变量|过滤器名称:'参数'}}
示例1: <h2>{{ hobby|length }}</h2>
示例2: <h2>{{ xx|default:'啥也不是' }}</h2>django自带的过滤器
length
返回值的长度,作用于字符串和列表。
default
如果一个变量是false或者为空,使用给定的默认值。 否则,使用变量的值。
filesizeformat
将值格式化为一个 "人类可读的" 文件尺寸 (例如 '13 KB', '4.1 MB', '102 bytes', 等等)。例如:
<h3>{{ file_size|filesizeformat }}</h3>slice
切片
ss = 'wanli ai zhangyu'
<h3>{{ ss|slice:'0:5' }}</h3>date
格式化,如果 value=datetime.datetime.now()
{{ value|date:"Y-m-d H:i:s"}}safe
xss攻击. 跨站脚本攻击
a_tag = '<a href="http://www.baidu.com">百度<a/>'
<h2>{{ a_tag|safe }}</h2>truncatechars 截断字符
truncatewords 截断单词
<h2>{{ aa|truncatechars:'8' }}</h2> <!-- 截断字符,注意8包含了三个点 -->
<h2>{{ aa|truncatewords:'2' }}</h2> <!-- 以空格做个截断符号,截断单词,2不包含那三个点 -->cut
移除value中所有的与给出的变量相同的字符串
<h2>{{ aa|cut:' ' }}</h2>join
字符串拼接
hobby = ['打游戏', '快乐风男', '嫖', 'look']
<h2>{{ hobby|join:'+' }}</h2>