写在开头的话
今天让我们学习一下如何实现一个简单的本地搜索引擎
知识点:
(1)索引构建(2)搜索功能(3)用户界面
如何实现一个简单的本地搜索引擎
实现一个简单的本地搜索引擎可以通过以下步骤完成:
- 索引构建:从文本文件中读取内容,并为每个单词创建一个倒排索引。
- 搜索功能:基于倒排索引来搜索给定关键词,并返回匹配的文件或文本位置。
- 用户界面:提供简单的命令行界面,允许用户输入查询并获得结果。
索引构建
在信息检索系统中,倒排索引和正排索引是两种基本的索引结构,用于提高搜索效率。下面是对这两种索引结构的介绍以及示例。
正排索引(Forward Index)
定义
正排索引是将文档的内容与其标识符(如文档 ID)直接关联的索引结构。对于每个文档,正排索引存储该文档的所有内容。
特点
- 适合于需要快速访问文档内容的场景。
- 主要用于数据的存储和展示,而非检索。
示例
假设有以下三个文档:
- 文档 1:
"Hello world" - 文档 2:
"Hello from the other side" - 文档 3:
"Welcome to the world"
正排索引示例如下:
| 文档 ID | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 1 | Hello world |
| 2 | Hello from the other side |
| 3 | Welcome to the world |
倒排索引(Inverted Index)
定义
倒排索引是将单词(或词项)映射到包含该单词的文档的索引结构。对于每个单词,倒排索引存储一个包含该单词的文档列表。
特点
- 适合于快速检索包含特定单词的文档。
- 主要用于搜索引擎和信息检索系统。
示例
使用上述文档数据构建倒排索引:
- 文档 1 :
"Hello world" - 文档 2 :
"Hello from the other side" - 文档 3 :
"Welcome to the world"
倒排索引示例如下:
| 单词 | 文档 ID 列表 |
|---|---|
| Hello | [1, 2] |
| world | [1, 3] |
| from | [2] |
| the | [2, 3] |
| other | [2] |
| side | [2] |
| Welcome | [3] |
| to | [3] |
构建倒排索引的详细过程
- 文档处理:读取每个文档,将其内容分词(即将文档内容分解为单独的词项)。
- 词项标准化:对词项进行标准化(如小写化、去除标点符号)。
- 构建索引:遍历每个词项,将其映射到包含该词项的文档 ID 列表中。
Java示例代码
java
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class InvertedIndex {
private Map<String, Set<Integer>> index = new HashMap<>();
// Index a single document
public void indexDocument(int docId, String content) {
String[] words = content.split("\\s+");
for (String word : words) {
word = word.toLowerCase().replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z0-9]", "");
index.computeIfAbsent(word, k -> new HashSet<>()).add(docId);
}
}
// Print the inverted index
public void printIndex() {
index.forEach((word, docs) ->
System.out.println("Word: " + word + " -> Documents: " + docs));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
InvertedIndex invertedIndex = new InvertedIndex();
// Indexing sample documents
invertedIndex.indexDocument(1, "Hello world");
invertedIndex.indexDocument(2, "Hello from the other side");
invertedIndex.indexDocument(3, "Welcome to the world");
// Print the inverted index
invertedIndex.printIndex();
}
}- 正排索引:直接存储文档内容,适用于需要访问文档内容的场景。
- 倒排索引:存储单词到文档 ID 的映射,适用于快速检索包含特定单词的文档。
运行结果
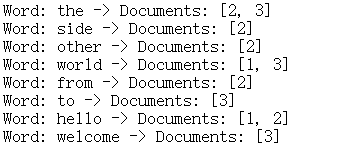
搜索功能
简单介绍
搜索功能是现代信息检索系统的核心,它的设计目标是从大量数据中迅速找到相关的信息。实现高效的搜索功能通常涉及几个关键步骤和技术。
详细介绍关键步骤
1. 数据预处理
在搜索之前,数据需要经过预处理以便高效检索。这包括:
- 分词(Tokenization):将文本分解为单独的单词或词组。这对自然语言处理特别重要。
- 去除停用词(Stop Words Removal):去除常见但信息量少的词,例如"的","和"等。
- 词干提取(Stemming)和词形还原(Lemmatization):将单词还原为其词根形式,以统一不同形式的词,例如"running"和"runner"都还原为"run"。
2. 构建索引
索引是提高检索效率的关键结构。常见的索引类型包括:
- 倒排索引(Inverted Index):记录每个词项及其出现的文档。适用于文本数据检索。
- 正排索引(Forward Index):记录每个文档的内容。适用于文档内容的快速访问。
倒排索引示例:
假设我们有以下文档:
doc1: "Hello world"doc2: "Hello from the other side"doc3: "Welcome to the world"
倒排索引如下:
| 单词 | 文档 ID 列表 |
|---|---|
| Hello | [1, 2] |
| world | [1, 3] |
| from | [2] |
| the | [2, 3] |
| other | [2] |
| side | [2] |
| Welcome | [3] |
| to | [3] |
3. 查询处理
查询处理包括:
- 解析查询:将用户输入的查询字符串转换为结构化的查询,例如分词和去停用词。
- 查询执行:根据索引查找包含查询词的文档。对于倒排索引,通常通过交集操作来找到同时包含多个查询词的文档。
查询示例:
查询 "Hello world" 可以在倒排索引中找到文档 1 和 2。
4. 排序
搜索结果需要按照相关性排序。常见的排序方法包括:
- TF-IDF(Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency):衡量一个词对文档的相对重要性。
- BM25:一种改进的 TF-IDF 模型,考虑文档长度和词频的饱和效应。
- PageRank:用于网页搜索,基于链接分析网页的重要性。
5. 结果呈现
搜索结果需要以用户友好的方式展示,包括:
- 结果列表:显示文档标题、摘要和链接。
- 高亮显示:突出显示匹配的关键词。
- 分页:对搜索结果进行分页处理,以便用户可以逐页查看。
Java示例代码
下面是一个简单的 Java 示例,展示了如何使用倒排索引进行基本的搜索功能。
java
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class SimpleSearchEngine {
private Map<String, Set<Integer>> invertedIndex = new HashMap<>();
// Index a document
public void indexDocument(int docId, String content) {
String[] words = content.split("\\s+");
for (String word : words) {
word = word.toLowerCase().replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z0-9]", "");
invertedIndex.computeIfAbsent(word, k -> new HashSet<>()).add(docId);
}
}
// Search for a query
public Set<Integer> search(String query) {
String[] words = query.split("\\s+");
Set<Integer> result = new HashSet<>();
for (String word : words) {
word = word.toLowerCase().replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z0-9]", "");
Set<Integer> docIds = invertedIndex.getOrDefault(word, new HashSet<>());
if (result.isEmpty()) {
result.addAll(docIds);
} else {
result.retainAll(docIds);
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleSearchEngine searchEngine = new SimpleSearchEngine();
// Indexing sample documents
searchEngine.indexDocument(1, "Hello world");
searchEngine.indexDocument(2, "Hello from the other side");
searchEngine.indexDocument(3, "Welcome to the world");
// Searching
Set<Integer> result = searchEngine.search("Hello world");
System.out.println("Documents containing 'Hello world': " + result);
}
}运行结果
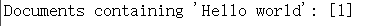
用户界面
Java示例代码
以下是一个完整的 Java 示例代码,展示了如何实现一个简单的本地搜索引擎,包括倒排索引的构建和查询功能。该示例将包含文档的索引、搜索和结果展示。
java
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class SimpleSearchEngine {
private Map<String, Set<Integer>> invertedIndex = new HashMap<>();
// Index a document
public void indexDocument(int docId, String content) {
String[] words = content.split("\\s+");
for (String word : words) {
word = word.toLowerCase().replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z0-9]", "");
invertedIndex.computeIfAbsent(word, k -> new HashSet<>()).add(docId);
}
}
// Search for a query
public Set<Integer> search(String query) {
String[] words = query.split("\\s+");
Set<Integer> result = new HashSet<>();
for (String word : words) {
word = word.toLowerCase().replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z0-9]", "");
Set<Integer> docIds = invertedIndex.getOrDefault(word, new HashSet<>());
if (result.isEmpty()) {
result.addAll(docIds);
} else {
result.retainAll(docIds);
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleSearchEngine searchEngine = new SimpleSearchEngine();
// Indexing sample documents
searchEngine.indexDocument(1, "Hello world");
searchEngine.indexDocument(2, "Hello from the other side");
searchEngine.indexDocument(3, "Welcome to the world");
// Testing the search functionality
System.out.println("Indexing complete.");
// Search for different queries
System.out.println("Searching for 'Hello world':");
Set<Integer> result1 = searchEngine.search("Hello world");
System.out.println("Documents containing 'Hello world': " + result1);
System.out.println("Searching for 'world':");
Set<Integer> result2 = searchEngine.search("world");
System.out.println("Documents containing 'world': " + result2);
System.out.println("Searching for 'Hello':");
Set<Integer> result3 = searchEngine.search("Hello");
System.out.println("Documents containing 'Hello': " + result3);
System.out.println("Searching for 'Welcome':");
Set<Integer> result4 = searchEngine.search("Welcome");
System.out.println("Documents containing 'Welcome': " + result4);
}
}代码说明
-
倒排索引构建:
indexDocument(int docId, String content):接收文档 ID 和内容,将内容分词并更新倒排索引。每个单词(去除标点和小写化)映射到包含该单词的文档 ID 集合。
-
搜索功能:
search(String query):接收查询字符串,分词后查找包含所有查询词的文档。使用集合交集操作找到符合所有查询词的文档。
-
测试:
main方法中,示例代码展示了如何索引文档并进行不同查询的测试,输出包含特定单词的文档 ID 集合。
运行结果

简单总结
本地搜索引擎示例通过倒排索引实现基本的搜索功能。它包括文档的索引和查询两部分。通过将文档内容分词,并将每个词映射到包含它的文档 ID 集合中,构建了倒排索引。在查询时,系统根据查询词找到包含所有词的文档 ID 集合。测试结果验证了索引和查询的正确性,并展示了搜索引擎的基本功能。