深入理解创建型、结构型、行为型设计模式,掌握软件设计的核心分类逻辑。
文章目录
-
- [🌟 引言:一次代码重构的顿悟时刻](#🌟 引言:一次代码重构的顿悟时刻)
- [一、设计模式分类全景图 🗺️](#一、设计模式分类全景图 🗺️)
- [二、创建型模式(5种):对象的"诞生艺术" 👶](#二、创建型模式(5种):对象的“诞生艺术” 👶)
-
- [2.1 核心思想与作用](#2.1 核心思想与作用)
- [2.2 五种创建型模式详解](#2.2 五种创建型模式详解)
- [2.3 代码示例对比](#2.3 代码示例对比)
- [2.4 创建型模式选择指南](#2.4 创建型模式选择指南)
- [三、结构型模式(7种):对象/类的"组合艺术" 🧩](#三、结构型模式(7种):对象/类的“组合艺术” 🧩)
-
- [3.1 核心思想与作用](#3.1 核心思想与作用)
- [3.2 七种结构型模式详解](#3.2 七种结构型模式详解)
- [3.3 代码示例对比](#3.3 代码示例对比)
- [3.4 结构型模式选择指南](#3.4 结构型模式选择指南)
- [四、行为型模式(11种):对象间的"协作艺术" 💃](#四、行为型模式(11种):对象间的“协作艺术” 💃)
-
- [4.1 核心思想与作用](#4.1 核心思想与作用)
- [4.2 十一种行为型模式详解](#4.2 十一种行为型模式详解)
- [4.3 代码示例对比](#4.3 代码示例对比)
- [4.4 行为型模式选择指南](#4.4 行为型模式选择指南)
- [五、三大类模式对比与关联 🔗](#五、三大类模式对比与关联 🔗)
-
- [5.1 核心区别总结](#5.1 核心区别总结)
- [5.2 关联与组合使用](#5.2 关联与组合使用)
- [5.3 学习路径建议](#5.3 学习路径建议)
- [六、实际应用场景与选择指南 🎯](#六、实际应用场景与选择指南 🎯)
-
- [6.1 不同场景的模式选择](#6.1 不同场景的模式选择)
- [6.2 行业最佳实践](#6.2 行业最佳实践)
- [6.3 避免常见误区](#6.3 避免常见误区)
- [七、总结与展望 📚](#七、总结与展望 📚)
-
- [7.1 核心要点总结](#7.1 核心要点总结)
- [7.2 未来发展趋势](#7.2 未来发展趋势)
- [参考资料 📖](#参考资料 📖)
🌟 引言:一次代码重构的顿悟时刻
记得我第一次参与大型项目重构时,面对数千行杂乱无章的代码感到无从下手。直到团队架构师指着屏幕说:"这里要用工厂模式解耦,那里可以用策略模式替换if-else... " 那一刻我突然明白,设计模式不仅是技术,更是组织和思考代码的方式。
今天我们就来系统解析GoF(四人帮)提出的23种设计模式是如何分为三大类 的,这不仅是面试常考点,更是写出优雅代码的必备知识框架。
一、设计模式分类全景图 🗺️
首先,让我们通过一个全景图快速了解23种设计模式的分类体系:
GoF 23种设计模式 创建型模式 5种 结构型模式 7种 行为型模式 11种 工厂方法 Factory Method 抽象工厂 Abstract Factory 建造者 Builder 原型 Prototype 单例 Singleton 适配器 Adapter 桥接 Bridge 组合 Composite 装饰器 Decorator 外观 Facade 享元 Flyweight 代理 Proxy 责任链 Chain of Responsibility 命令 Command 解释器 Interpreter 迭代器 Iterator 中介者 Mediator 备忘录 Memento 观察者 Observer 状态 State 策略 Strategy 模板方法 Template Method 访问者 Visitor
核心分类逻辑 :这三种分类不是随意的,而是基于设计模式要解决的核心问题来划分的:
| 分类 | 核心问题 | 类比 | 关键特征 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 创建型 | 如何创建对象? | "生孩子"的艺术 | 关注对象的实例化过程 |
| 结构型 | 如何组合对象/类? | "搭积木"的艺术 | 关注类与对象的组合方式 |
| 行为型 | 对象如何交互协作? | "跳交谊舞"的艺术 | 关注对象间的通信和职责分配 |
下面我们深入探讨每一类设计模式。
二、创建型模式(5种):对象的"诞生艺术" 👶
2.1 核心思想与作用
创建型模式的核心是将对象的创建与使用分离。想象一下你去餐厅吃饭:你只需点菜(使用),而不需要关心菜是怎么做出来的(创建)。
主要解决以下问题:
- 隐藏创建逻辑:客户端不依赖具体类的创建细节
- 提高灵活性:可以轻松切换不同的对象创建方式
- 复用创建过程:相同的创建逻辑可以在多处使用
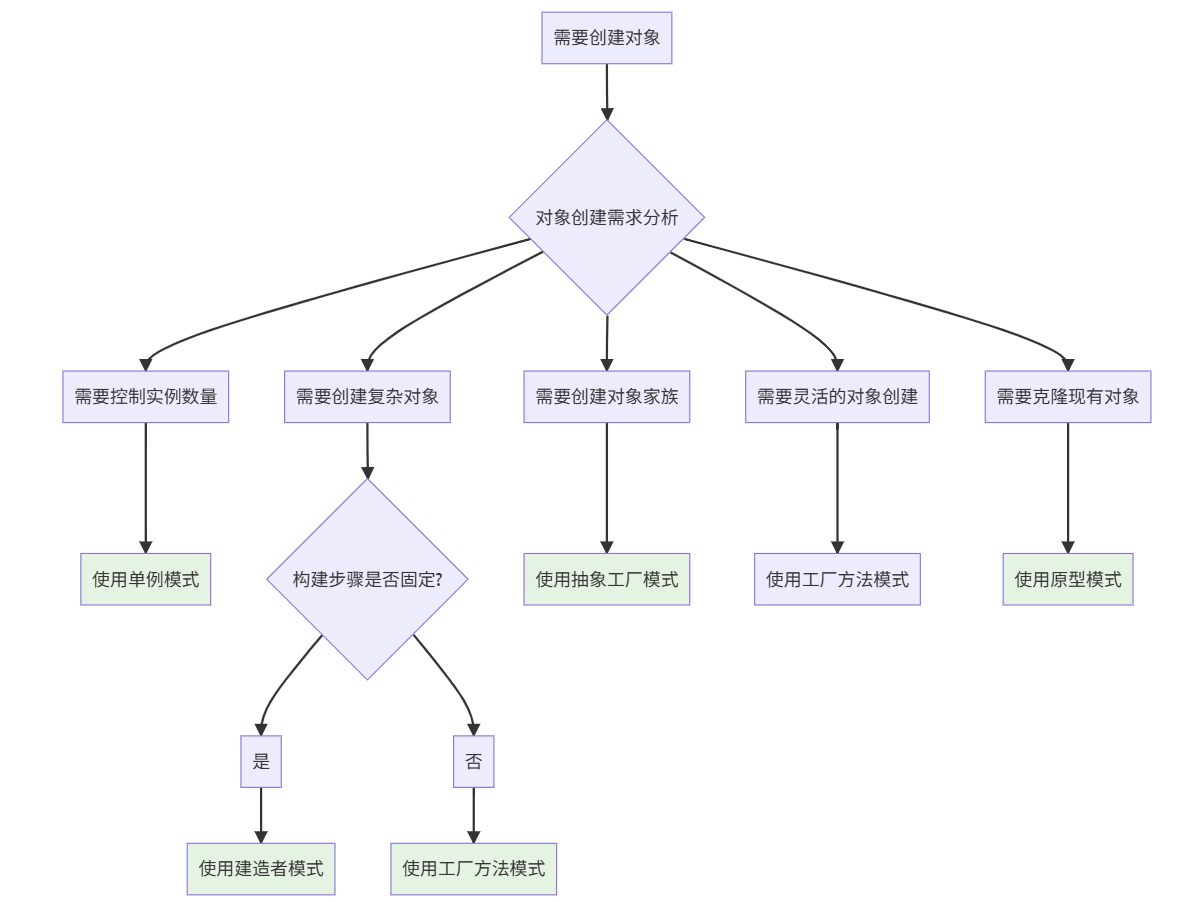
2.2 五种创建型模式详解
| 模式 | 要解决的问题 | 典型场景 | 一句话理解 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 工厂方法 | 不指定具体类创建对象 | 文档编辑器创建不同类型的文档 | "我需要一个产品,但不知道具体是哪个工厂生产的" |
| 抽象工厂 | 创建相关对象家族 | 跨平台UI组件(Windows/Mac按钮、文本框) | "我需要一套配套的产品(如现代风格家具)" |
| 建造者 | 创建复杂对象(分步骤) | 创建一份包含头、体、尾的复杂HTML文档 | "我需要一步步构造一个复杂对象" |
| 原型 | 通过复制创建对象 | 游戏中的怪物复制,细胞分裂 | "我想克隆一个现有对象" |
| 单例 | 确保类只有一个实例 | 数据库连接池,配置管理器 | "这个类只能有一个'皇帝'" |
2.3 代码示例对比
java
// 示例:不同创建型模式解决同一问题(创建数据库连接)
// 1. 简单创建(无模式) - 问题:直接依赖具体类
Connection conn = new MySQLConnection(); // 紧耦合
// 2. 工厂方法模式
public interface ConnectionFactory {
Connection createConnection();
}
public class MySQLFactory implements ConnectionFactory {
public Connection createConnection() {
return new MySQLConnection();
}
}
// 使用
ConnectionFactory factory = new MySQLFactory();
Connection conn = factory.createConnection();
// 3. 抽象工厂模式 - 创建相关对象家族
public interface DatabaseFactory {
Connection createConnection();
Statement createStatement();
ResultSet createResultSet();
}
public class MySQLFactory implements DatabaseFactory {
public Connection createConnection() { return new MySQLConnection(); }
public Statement createStatement() { return new MySQLStatement(); }
public ResultSet createResultSet() { return new MySQLResultSet(); }
}
// 4. 建造者模式 - 构建复杂连接对象
public class ConnectionBuilder {
private String url;
private String username;
private int timeout;
private boolean ssl;
public ConnectionBuilder setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; return this; }
public ConnectionBuilder setUsername(String username) { /*...*/ return this; }
public ConnectionBuilder setTimeout(int timeout) { /*...*/ return this; }
public ConnectionBuilder setSsl(boolean ssl) { /*...*/ return this; }
public Connection build() {
// 复杂的构建逻辑
return new ComplexConnection(url, username, timeout, ssl);
}
}
// 使用
Connection conn = new ConnectionBuilder()
.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db")
.setUsername("root")
.setTimeout(5000)
.setSsl(true)
.build();
// 5. 原型模式 - 克隆现有连接
public abstract class ConnectionPrototype implements Cloneable {
public abstract ConnectionPrototype clone();
}
public class MySQLConnection extends ConnectionPrototype {
private String config;
@Override
public MySQLConnection clone() {
return new MySQLConnection(this.config); // 克隆自己
}
}
// 使用
MySQLConnection original = new MySQLConnection("config1");
MySQLConnection cloned = original.clone(); // 克隆对象
// 6. 单例模式 - 确保唯一连接管理器
public class ConnectionManager {
private static ConnectionManager instance;
private ConnectionManager() {} // 私有构造
public static synchronized ConnectionManager getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new ConnectionManager();
}
return instance;
}
}
// 使用
ConnectionManager manager = ConnectionManager.getInstance();2.4 创建型模式选择指南
三、结构型模式(7种):对象/类的"组合艺术" 🧩
3.1 核心思想与作用
结构型模式关注如何将类或对象组合成更大、更复杂的结构,同时保持结构的灵活性和高效性。
主要解决以下问题:
- 接口不兼容:如何让不兼容的接口一起工作
- 功能扩展:如何动态地为对象添加新功能
- 结构优化:如何优化大量小对象的资源使用
- 访问控制:如何控制对对象的访问
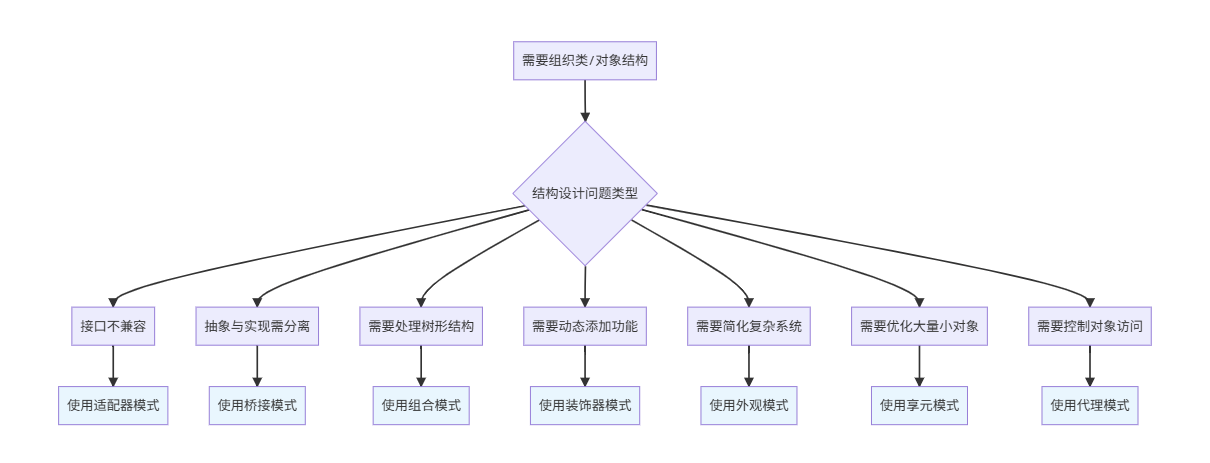
3.2 七种结构型模式详解
| 模式 | 要解决的问题 | 典型场景 | 一句话理解 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 适配器 | 接口不兼容 | 电源插头转换器,老系统集成 | "把一个接口转换成客户端期望的另一个接口" |
| 桥接 | 抽象与实现分离 | 不同形状(圆/方)与不同颜色(红/蓝)的组合 | "将抽象部分与实现部分分离,使它们可以独立变化" |
| 组合 | 部分-整体层次结构 | 文件系统(文件/文件夹),组织架构 | "用树形结构表示'部分-整体'层次" |
| 装饰器 | 动态添加功能 | Java I/O流,给咖啡加糖/加奶 | "动态地给对象添加额外的职责" |
| 外观 | 简化复杂子系统 | 客服总机,一键启动电脑 | "为复杂子系统提供一个简单的统一接口" |
| 享元 | 高效共享大量细粒度对象 | 文本编辑器中的字符对象,棋类游戏的棋子 | "共享大量细粒度对象以节省内存" |
| 代理 | 控制对象访问 | 明星经纪人,VPN代理服务器 | "为其他对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问" |
3.3 代码示例对比
java
// 示例:不同结构型模式解决图形处理问题
// 1. 适配器模式 - 让不兼容的接口一起工作
// 旧接口:只能绘制基本形状
public interface LegacyShape {
void drawBasic();
}
// 新接口:支持高级绘制
public interface ModernShape {
void draw();
void resize();
void rotate();
}
// 适配器:让旧接口适配新接口
public class ShapeAdapter implements ModernShape {
private LegacyShape legacyShape;
public ShapeAdapter(LegacyShape shape) {
this.legacyShape = shape;
}
@Override
public void draw() {
legacyShape.drawBasic(); // 适配调用
}
@Override
public void resize() {
System.out.println("Resizing...");
}
@Override
public void rotate() {
System.out.println("Rotating...");
}
}
// 2. 桥接模式 - 分离抽象与实现
// 实现部分接口
public interface Color {
String applyColor();
}
public class RedColor implements Color {
@Override
public String applyColor() { return "红色"; }
}
public class BlueColor implements Color {
@Override
public String applyColor() { return "蓝色"; }
}
// 抽象部分
public abstract class Shape {
protected Color color; // 桥接的关键:持有实现部分
public Shape(Color color) {
this.color = color;
}
public abstract void draw();
}
public class Circle extends Shape {
public Circle(Color color) {
super(color);
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("绘制" + color.applyColor() + "的圆形");
}
}
// 使用:可以独立变化形状和颜色
Shape redCircle = new Circle(new RedColor());
Shape blueCircle = new Circle(new BlueColor());
// 3. 装饰器模式 - 动态添加功能
public interface Coffee {
double getCost();
String getDescription();
}
public class SimpleCoffee implements Coffee {
@Override
public double getCost() { return 5.0; }
@Override
public String getDescription() { return "普通咖啡"; }
}
// 装饰器基类
public abstract class CoffeeDecorator implements Coffee {
protected Coffee decoratedCoffee;
public CoffeeDecorator(Coffee coffee) {
this.decoratedCoffee = coffee;
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return decoratedCoffee.getCost();
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return decoratedCoffee.getDescription();
}
}
// 具体装饰器
public class MilkDecorator extends CoffeeDecorator {
public MilkDecorator(Coffee coffee) {
super(coffee);
}
@Override
public double getCost() {
return super.getCost() + 2.0;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return super.getDescription() + ",加牛奶";
}
}
// 使用:动态组合功能
Coffee myCoffee = new SimpleCoffee();
myCoffee = new MilkDecorator(myCoffee);
myCoffee = new SugarDecorator(myCoffee);
System.out.println(myCoffee.getDescription() + " 价格:" + myCoffee.getCost());
// 4. 组合模式 - 处理树形结构
public abstract class FileSystemComponent {
protected String name;
public FileSystemComponent(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public abstract void display(int depth);
public abstract void add(FileSystemComponent component);
public abstract void remove(FileSystemComponent component);
}
// 叶子节点:文件
public class File extends FileSystemComponent {
public File(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void display(int depth) {
System.out.println("-".repeat(depth) + " 文件:" + name);
}
@Override
public void add(FileSystemComponent component) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("文件不能添加子组件");
}
@Override
public void remove(FileSystemComponent component) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("文件不能移除子组件");
}
}
// 容器节点:文件夹
public class Folder extends FileSystemComponent {
private List<FileSystemComponent> children = new ArrayList<>();
public Folder(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void display(int depth) {
System.out.println("-".repeat(depth) + " 文件夹:" + name);
for (FileSystemComponent child : children) {
child.display(depth + 2);
}
}
@Override
public void add(FileSystemComponent component) {
children.add(component);
}
@Override
public void remove(FileSystemComponent component) {
children.remove(component);
}
}
// 5. 外观模式 - 简化复杂子系统
public class ComputerFacade {
private CPU cpu;
private Memory memory;
private HardDrive hardDrive;
public ComputerFacade() {
this.cpu = new CPU();
this.memory = new Memory();
this.hardDrive = new HardDrive();
}
// 简化启动过程
public void startComputer() {
System.out.println("正在启动计算机...");
cpu.freeze();
memory.load(0, hardDrive.read(0, 1024));
cpu.jump(0);
cpu.execute();
System.out.println("计算机启动完成!");
}
}
// 6. 享元模式 - 共享细粒度对象
public class CharacterFlyweight {
private char symbol;
private String font;
private int size;
public CharacterFlyweight(char symbol, String font, int size) {
this.symbol = symbol;
this.font = font;
this.size = size;
}
public void display(int x, int y) {
System.out.println("显示字符 '" + symbol + "' 在位置(" + x + "," + y + ")");
}
}
// 享元工厂
public class CharacterFactory {
private Map<String, CharacterFlyweight> pool = new HashMap<>();
public CharacterFlyweight getCharacter(char symbol, String font, int size) {
String key = symbol + "-" + font + "-" + size;
if (!pool.containsKey(key)) {
pool.put(key, new CharacterFlyweight(symbol, font, size));
}
return pool.get(key);
}
}
// 7. 代理模式 - 控制访问
public interface Image {
void display();
}
public class RealImage implements Image {
private String filename;
public RealImage(String filename) {
this.filename = filename;
loadFromDisk(); // 昂贵的初始化操作
}
private void loadFromDisk() {
System.out.println("从磁盘加载图片:" + filename);
}
@Override
public void display() {
System.out.println("显示图片:" + filename);
}
}
// 代理:延迟加载
public class ImageProxy implements Image {
private String filename;
private RealImage realImage;
public ImageProxy(String filename) {
this.filename = filename;
}
@Override
public void display() {
if (realImage == null) {
realImage = new RealImage(filename); // 延迟初始化
}
realImage.display();
}
}3.4 结构型模式选择指南
四、行为型模式(11种):对象间的"协作艺术" 💃
4.1 核心思想与作用
行为型模式关注对象之间的职责分配和通信方式,定义对象间如何交互以及如何完成复杂的任务。
主要解决以下问题:
- 职责分配:如何合理分配对象间的职责
- 通信机制:对象之间如何通信而不产生紧耦合
- 算法封装:如何封装算法使其可互换
- 状态管理:如何管理对象的状态变化
4.2 十一种行为型模式详解
| 模式 | 要解决的问题 | 典型场景 | 一句话理解 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 责任链 | 请求发送者与接收者解耦 | 审批流程,异常处理链 | "把请求沿链条传递,直到有对象处理它" |
| 命令 | 将请求封装为对象 | 撤销/重做功能,任务队列 | "把请求封装成对象,以便参数化客户端" |
| 解释器 | 定义语言的文法表示 | 正则表达式,SQL解析 | "定义语言的文法,并解释该语言中的句子" |
| 迭代器 | 顺序访问集合元素 | Java集合的Iterator | "提供一种方法顺序访问聚合对象的元素" |
| 中介者 | 对象间交互集中管理 | 聊天室,机场控制塔 | "用一个中介对象封装一系列对象交互" |
| 备忘录 | 保存和恢复对象状态 | 游戏存档,事务回滚 | "在不破坏封装的前提下捕获对象状态" |
| 观察者 | 对象间一对多依赖 | 事件监听,消息订阅 | "对象状态改变时通知所有依赖它的对象" |
| 状态 | 对象状态改变时行为改变 | 红绿灯,工作流状态 | "允许对象在内部状态改变时改变行为" |
| 策略 | 算法族封装,可互换 | 支付方式选择,排序算法选择 | "定义一系列算法,使它们可以互相替换" |
| 模板方法 | 定义算法骨架,步骤延迟 | 冲泡饮料流程,银行业务流程 | "定义算法骨架,某些步骤延迟到子类" |
| 访问者 | 在不修改类的情况下添加操作 | 编译器语法树访问,报表生成 | "在不修改类结构的前提下定义新操作" |
4.3 代码示例对比
java
// 示例:不同行为型模式解决电商订单处理问题
// 1. 责任链模式 - 处理审批流程
public abstract class OrderHandler {
protected OrderHandler nextHandler;
public void setNextHandler(OrderHandler handler) {
this.nextHandler = handler;
}
public abstract void handle(Order order);
}
public class ValidationHandler extends OrderHandler {
@Override
public void handle(Order order) {
if (order.isValid()) {
System.out.println("订单验证通过");
if (nextHandler != null) {
nextHandler.handle(order);
}
} else {
System.out.println("订单验证失败");
}
}
}
public class PaymentHandler extends OrderHandler {
@Override
public void handle(Order order) {
if (order.processPayment()) {
System.out.println("支付处理成功");
if (nextHandler != null) {
nextHandler.handle(order);
}
} else {
System.out.println("支付处理失败");
}
}
}
public class ShippingHandler extends OrderHandler {
@Override
public void handle(Order order) {
if (order.prepareShipping()) {
System.out.println("发货准备完成");
if (nextHandler != null) {
nextHandler.handle(order);
}
} else {
System.out.println("发货准备失败");
}
}
}
// 构建责任链
OrderHandler chain = new ValidationHandler();
chain.setNextHandler(new PaymentHandler());
chain.setNextHandler(new ShippingHandler());
// 处理订单
chain.handle(order);
// 2. 观察者模式 - 订单状态通知
public interface OrderObserver {
void update(Order order);
}
public class CustomerNotifier implements OrderObserver {
@Override
public void update(Order order) {
System.out.println("通知客户:订单状态已更新为 " + order.getStatus());
}
}
public class WarehouseNotifier implements OrderObserver {
@Override
public void update(Order order) {
if (order.getStatus() == OrderStatus.PAID) {
System.out.println("通知仓库:准备发货订单 " + order.getId());
}
}
}
public class Order {
private List<OrderObserver> observers = new ArrayList<>();
private OrderStatus status;
public void addObserver(OrderObserver observer) {
observers.add(observer);
}
public void removeObserver(OrderObserver observer) {
observers.remove(observer);
}
public void setStatus(OrderStatus newStatus) {
this.status = newStatus;
notifyObservers();
}
private void notifyObservers() {
for (OrderObserver observer : observers) {
observer.update(this);
}
}
}
// 3. 策略模式 - 支付方式选择
public interface PaymentStrategy {
boolean pay(double amount);
}
public class CreditCardPayment implements PaymentStrategy {
private String cardNumber;
private String expiryDate;
public CreditCardPayment(String cardNumber, String expiryDate) {
this.cardNumber = cardNumber;
this.expiryDate = expiryDate;
}
@Override
public boolean pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("使用信用卡支付 " + amount + " 元");
// 调用信用卡支付API
return true;
}
}
public class PayPalPayment implements PaymentStrategy {
private String email;
public PayPalPayment(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public boolean pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("使用PayPal支付 " + amount + " 元");
// 调用PayPal API
return true;
}
}
public class PaymentContext {
private PaymentStrategy strategy;
public void setPaymentStrategy(PaymentStrategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public boolean executePayment(double amount) {
return strategy.pay(amount);
}
}
// 使用
PaymentContext context = new PaymentContext();
context.setPaymentStrategy(new CreditCardPayment("1234-5678", "12/25"));
context.executePayment(100.0);
// 4. 模板方法模式 - 订单处理流程
public abstract class OrderProcessingTemplate {
// 模板方法:定义算法骨架
public final void processOrder(Order order) {
validateOrder(order);
calculateTotal(order);
applyDiscounts(order);
processPayment(order);
shipOrder(order);
sendNotification(order);
}
// 具体步骤,有些是固定的,有些需要子类实现
protected void validateOrder(Order order) {
System.out.println("验证订单基本信息");
}
protected abstract void calculateTotal(Order order);
protected void applyDiscounts(Order order) {
System.out.println("应用默认折扣");
}
protected abstract void processPayment(Order order);
protected void shipOrder(Order order) {
System.out.println("安排发货");
}
protected void sendNotification(Order order) {
System.out.println("发送订单确认通知");
}
}
// 具体实现
public class OnlineOrderProcessing extends OrderProcessingTemplate {
@Override
protected void calculateTotal(Order order) {
System.out.println("计算在线订单总额(含运费)");
}
@Override
protected void processPayment(Order order) {
System.out.println("处理在线支付");
}
}
public class InStoreOrderProcessing extends OrderProcessingTemplate {
@Override
protected void calculateTotal(Order order) {
System.out.println("计算店内订单总额(不含运费)");
}
@Override
protected void processPayment(Order order) {
System.out.println("处理店内现金/刷卡支付");
}
@Override
protected void shipOrder(Order order) {
System.out.println("店内取货,无需发货");
}
}
// 5. 状态模式 - 订单状态管理
public interface OrderState {
void handle(OrderContext context);
}
public class NewOrderState implements OrderState {
@Override
public void handle(OrderContext context) {
System.out.println("处理新订单:验证、确认库存");
context.setState(new ProcessingOrderState());
}
}
public class ProcessingOrderState implements OrderState {
@Override
public void handle(OrderContext context) {
System.out.println("处理中:准备发货");
context.setState(new ShippedOrderState());
}
}
public class ShippedOrderState implements OrderState {
@Override
public void handle(OrderContext context) {
System.out.println("已发货:等待确认收货");
context.setState(new DeliveredOrderState());
}
}
public class DeliveredOrderState implements OrderState {
@Override
public void handle(OrderContext context) {
System.out.println("已送达:订单完成");
context.setState(new CompletedOrderState());
}
}
public class OrderContext {
private OrderState currentState;
public OrderContext() {
this.currentState = new NewOrderState();
}
public void setState(OrderState state) {
this.currentState = state;
}
public void process() {
currentState.handle(this);
}
}
// 使用
OrderContext order = new OrderContext();
order.process(); // 新订单 → 处理中
order.process(); // 处理中 → 已发货
order.process(); // 已发货 → 已送达4.4 行为型模式选择指南
需要管理对象间交互 交互问题类型 需要解耦发送者与接收者 需要将请求封装为对象 需要定义语言文法 需要顺序访问集合 需要集中管理对象交互 需要保存恢复对象状态 需要一对多依赖通知 需要根据状态改变行为 需要封装可互换算法 需要定义算法骨架 需要在不修改类的情况下添加操作 使用责任链模式 使用命令模式 使用解释器模式 使用迭代器模式 使用中介者模式 使用备忘录模式 使用观察者模式 使用状态模式 使用策略模式 使用模板方法模式 使用访问者模式
五、三大类模式对比与关联 🔗
5.1 核心区别总结
关注点 行为型模式(11种) 结构型模式(7种) 创建型模式(5种) 对象创建 类/对象组合 对象交互 责任链 命令 解释器 迭代器 中介者 备忘录 观察者 状态 策略 模板方法 访问者 适配器 桥接 组合 装饰器 外观 享元 代理 工厂方法 抽象工厂 建造者 原型 单例
5.2 关联与组合使用
在实际项目中,设计模式往往组合使用,形成更强大的解决方案:
| 组合示例 | 使用的模式 | 解决的问题 |
|---|---|---|
| MVC架构 | 观察者 + 策略 + 组合 | 用户界面与业务逻辑分离 |
| Spring框架 | 工厂 + 代理 + 模板方法 | 依赖注入与AOP编程 |
| 日志系统 | 责任链 + 装饰器 | 灵活的日志级别和输出目标 |
| 游戏开发 | 状态 + 观察者 + 命令 | 游戏状态管理和用户输入处理 |
java
// 示例:组合使用多个设计模式(电商促销系统)
// 1. 策略模式:不同促销算法
public interface PromotionStrategy {
double applyPromotion(double amount);
}
public class DiscountStrategy implements PromotionStrategy {
private double discountRate;
@Override
public double applyPromotion(double amount) {
return amount * discountRate;
}
}
public class FullReductionStrategy implements PromotionStrategy {
private double threshold;
private double reduction;
@Override
public double applyPromotion(double amount) {
return amount >= threshold ? amount - reduction : amount;
}
}
// 2. 工厂模式:创建促销策略
public class PromotionFactory {
public static PromotionStrategy createStrategy(String type, Map<String, Object> params) {
switch (type) {
case "discount":
return new DiscountStrategy((Double) params.get("rate"));
case "fullReduction":
return new FullReductionStrategy(
(Double) params.get("threshold"),
(Double) params.get("reduction")
);
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("未知促销类型");
}
}
}
// 3. 观察者模式:促销活动通知
public class PromotionSubject {
private List<PromotionObserver> observers = new ArrayList<>();
public void addObserver(PromotionObserver observer) {
observers.add(observer);
}
public void startPromotion(String promotionName) {
System.out.println("开始促销活动:" + promotionName);
notifyObservers(promotionName);
}
private void notifyObservers(String promotionName) {
for (PromotionObserver observer : observers) {
observer.onPromotionStart(promotionName);
}
}
}
// 4. 装饰器模式:叠加促销效果
public abstract class PromotionDecorator implements PromotionStrategy {
protected PromotionStrategy decoratedStrategy;
public PromotionDecorator(PromotionStrategy strategy) {
this.decoratedStrategy = strategy;
}
@Override
public double applyPromotion(double amount) {
return decoratedStrategy.applyPromotion(amount);
}
}
public class PointsPromotionDecorator extends PromotionDecorator {
private int pointsMultiplier;
public PointsPromotionDecorator(PromotionStrategy strategy, int multiplier) {
super(strategy);
this.pointsMultiplier = multiplier;
}
@Override
public double applyPromotion(double amount) {
double discounted = super.applyPromotion(amount);
System.out.println("赠送积分:" + (int)(discounted * pointsMultiplier));
return discounted;
}
}
// 综合使用
public class PromotionSystem {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用工厂创建基础策略
Map<String, Object> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("rate", 0.8);
PromotionStrategy baseStrategy = PromotionFactory.createStrategy("discount", params);
// 使用装饰器添加积分功能
PromotionStrategy finalStrategy = new PointsPromotionDecorator(baseStrategy, 10);
// 计算促销价格
double originalPrice = 100.0;
double finalPrice = finalStrategy.applyPromotion(originalPrice);
System.out.println("原价:" + originalPrice + ",促销价:" + finalPrice);
}
}5.3 学习路径建议
对于初学者,我建议按以下顺序学习:
- 第一阶段(基础掌握):单例、工厂方法、策略、观察者、装饰器
- 第二阶段(进阶理解):建造者、适配器、代理、模板方法、状态
- 第三阶段(高级应用):抽象工厂、组合、责任链、命令、访问者
- 第四阶段(融会贯通):桥接、享元、外观、中介者、备忘录、解释器、迭代器
六、实际应用场景与选择指南 🎯
6.1 不同场景的模式选择
| 应用场景 | 推荐模式 | 理由 |
|---|---|---|
| 对象创建复杂 | 建造者、工厂方法 | 封装复杂创建逻辑 |
| 需要统一接口 | 适配器、外观 | 简化或统一不同接口 |
| 动态添加功能 | 装饰器、代理 | 运行时灵活扩展 |
| 算法可互换 | 策略、状态 | 封装变化点,易于扩展 |
| 一对多依赖 | 观察者、发布-订阅 | 解耦通知关系 |
| 处理树形结构 | 组合、访问者 | 自然表示层次关系 |
| 需要撤销操作 | 命令、备忘录 | 记录状态,支持回滚 |
| 性能优化 | 享元、原型 | 共享对象,减少创建开销 |
6.2 行业最佳实践
| 行业/框架 | 常用模式 | 典型应用 |
|---|---|---|
| Java EE/Spring | 工厂、代理、模板方法 | Bean管理、AOP、事务管理 |
| Android开发 | 观察者、适配器、建造者 | LiveData、RecyclerView.Adapter、AlertDialog.Builder |
| 游戏开发 | 状态、命令、享元 | 游戏状态管理、输入处理、粒子系统 |
| 前端框架 | 观察者、装饰器、策略 | Vue/React响应式、高阶组件、表单验证 |
| 数据库ORM | 工厂、代理、模板方法 | 连接池管理、延迟加载、查询模板 |
6.3 避免常见误区
- 不要为模式而模式:简单问题用简单方法解决
- 理解比记忆重要:理解模式意图,而非死记结构
- 模式可组合变通:根据实际需求调整模式实现
- 考虑团队水平:选择团队熟悉且能维护的模式
- 评估引入成本:复杂模式可能增加理解难度
七、总结与展望 📚
7.1 核心要点总结
通过本文的学习,我们应该掌握:
-
三大分类逻辑:
- 创建型 (5种):解决对象创建问题
- 结构型 (7种):解决类/对象组合问题
- 行为型 (11种):解决对象交互问题
-
分类记忆口诀:
- 创建型:工厂单例造原型,抽象建造一家亲
- 结构型:适配桥接组合装,外观享元代你忙
- 行为型:责任命令解释器,迭代中介备忘录,观察状态策略定,模板访问行为全
-
核心价值 :设计模式提供经过验证的解决方案 ,提高代码的可重用性、可维护性和灵活性。
7.2 未来发展趋势
随着编程范式的发展,设计模式也在不断演进:
- 函数式模式兴起:Monad、Functor、Applicative等函数式编程模式
- 响应式模式普及:观察者模式的现代化身(Reactive Streams)
- 并发模式重要:Promise、Future、Actor等并发处理模式
- 云原生模式:Circuit Breaker、Bulkhead、Sidecar等微服务模式
- 领域驱动设计:DDD中的实体、值对象、聚合根等模式
💡 最后的建议 :设计模式分类只是开始,真正的价值在于理解每种模式的意图和适用场景。建议从实际项目中的痛点出发,思考如何用设计模式解决问题,这才是学习的正确路径。
参考资料 📖
- 设计模式分类 | 菜鸟教程 - 中文分类详解
- Design Patterns by Refactoring.Guru - 交互式学习网站
- Java设计模式:23种设计模式全面解析 - GitHub代码示例
🔍 学习建议:理论学习后,尝试在个人项目中实践1-2种模式,从简单场景开始。同时,多阅读优秀开源项目的源码,分析其中设计模式的应用,这是提升设计能力的有效途径。
标签 : 设计模式 创建型模式 结构型模式 行为型模式 软件设计