一、简介
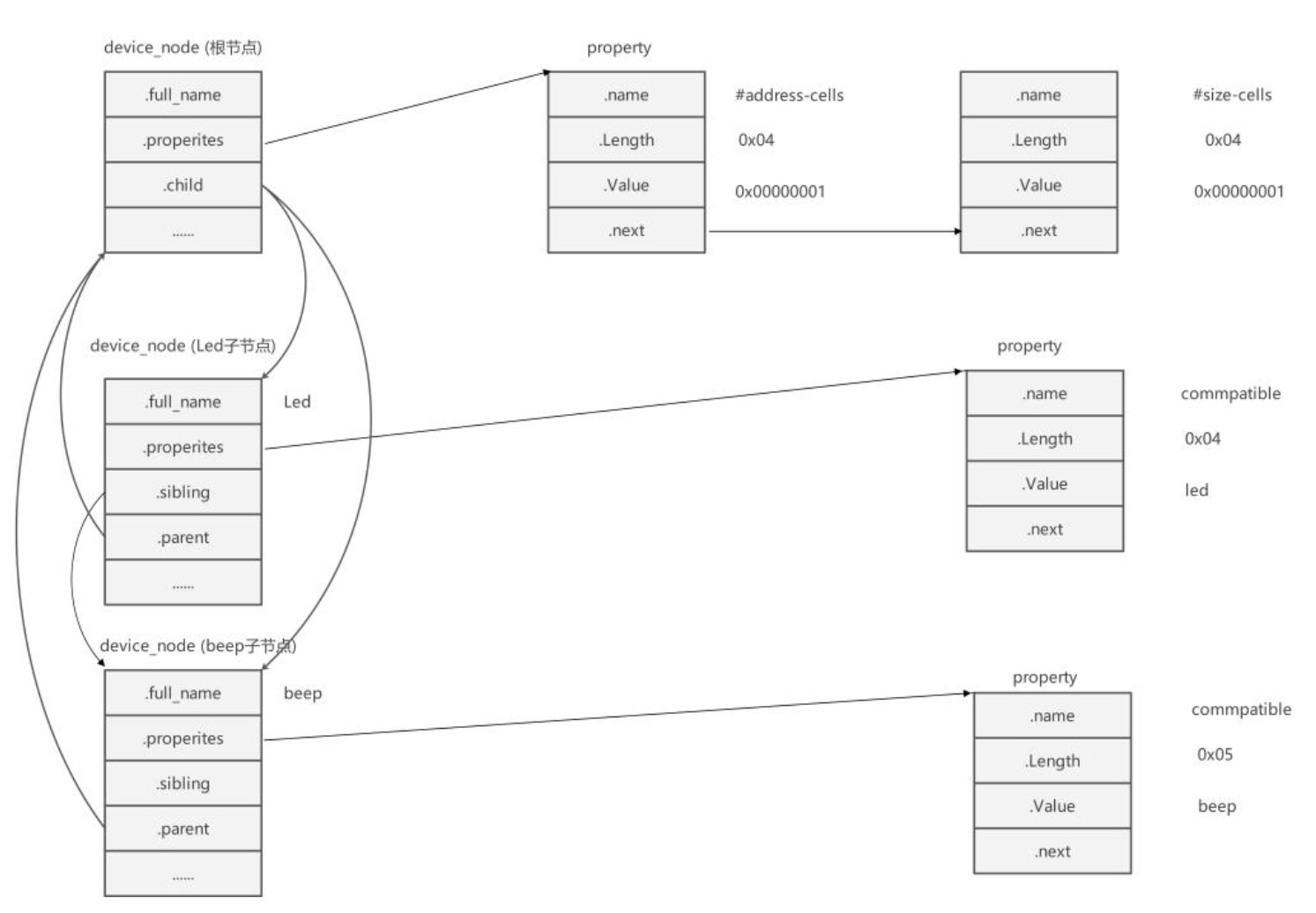
设备树都是以节点的形式挂到设备树上的,因此想要获取这个设备的其他属性信息,必须先获取这个设备的节点
根节点的compatible属性与直子节点中的compatible属性是不一样的,compatible属性用于匹配不同开发板厂商的
二、相关函数与结构体
2.1 查找节点函数
device_node结构体
#include<linux/of.h>
cppstruct device_node { const char *name; //设备节点的名称 const char *type; //设备节点的类型 phandle phandle; //设备节点的句柄 const char *full_name; //设备节点的完整名称 struct fwnode_handle fwnode; //设备节点的固件节点句柄 struct property *properties; //设备节点的属性列表 struct property *deadprops; //已删除的属性列表 struct device_node *parent; //设备节点的父节点 struct device_node *child; //设备节点的子节点 struct device_node *sibling; //设备节点的同级节点 #if defined(CONFIG_OF_KOBJ) struct kobject kobj; //内核对象(用于 sysfs) #endif unsigned long _flags; //设备节点的标志位 void *data; //与设备节点相关的数据指针 #if defined(CONFIG_SPARC) const char *path_component_name; //设备节点的路径组件名称 unsigned int unique_id; //设备节点的唯一标识 struct of_irq_controller *irq_trans; //设备节点的中断控制器 #endif };可以通过 device_node 结构体中节点的名字、 父节点、 子节点和同级节点, 以代码方式构建出与 dts 文件中一致的设备节点关系。其中 properties 字段是指向设备节点属性的指针。 设备节点的属性包含了与设备节点相关联的配置和参数信息
propert结构体
cppstruct property { char *name; //属性的名称 int length; //属性值的长度(字节数) void *value; //属性值 struct property *next; //指向节点的下一个属性 #if defined(CONFIG_OF_DYNAMIC) || defined(CONFIG_SPARC) unsigned long _flags; //属性的标志位 #endif #if defined(CONFIG_OF_PROMTREE) unsigned int unique_id; //属性的唯一标识 #endif #if defined(CONFIG_OF_KOBJ) struct bin_attribute attr; /内核对象二进制属性 #endif };
头文件 #include<linux/of.h>
函数原型 struct device_node *of_find_node_by_path(const char *path)
函数作用 通过路径查找指定节点
参数 path: 指定节点在设备树中的路径
返回值成功:返回 device_node 类型的结构体指针,它保存着设备节点的信息
失败:失败则返回 NULL
头文件 #include<linux/of.h>
函数原型 struct device_node *of_find_node_by_name(struct device_node *from,const,char *name);
函数作用 根据节点名字寻找节点
参数from: 指定从哪个节点开始查找,它本身并不在查找行列中,只查找它后面的节点,如果设置为 NULL 表示从根节点开始查找
name: 要寻找的节点
返回值成功:返回 device_node 类型的结构体指针,它保存着设备节点的信息
失败:失败则返回 NULL
头文件 #include<linux/of.h>
函数原型 struct device_node *of_find_node_by_type(struct device_node *from,const,char *type)
函数作用 根据节点类型寻找节点
参数from: 指定从哪个节点开始查找,它本身并不在查找行列中,只查找它后面的节点,如果设置为 NULL 表示从根节点开始查找
type: 要查找节点的类型,这个类型就是 device_node-> type。
返回值成功:返回 device_node 类型的结构体指针,它保存着设备节点的信息
失败:失败则返回 NULL
头文件 #include<linux/of.h>
函数原型 struct device_node *of_find_compatible_node(struct device_node *from,const␣,char *type, const char *compatible)
函数作用 根据节点类型和 compatible 属性寻找节点
参数from: 指定从哪个节点开始查找,它本身并不在查找行列中,只查找它后面的节点,如果设置为 NULL 表示从根节点开始查找
type: 要查找节点的类型,这个类型就是 device_node-> type。
compatible: 要查找节点的 compatible 属性
返回值成功:返回 device_node 类型的结构体指针,它保存着设备节点的信息
失败:失败则返回 NULL
头文件 #include<linux/of.h>
函数原型static inline struct device_node *of_find_matching_node_and_match(struct,device_node *from, const struct of_device_id *matches, const struct of_device_id **match)
函数作用 根据节点类型和 compatible 属性寻找节点
参数from: 指定从哪个节点开始查找,它本身并不在查找行列中,只查找它后面的节点,如果设置为 NULL 表示从根节点开始查找
matches: 源匹配表,查找与该匹配表想匹配的设备节点
of_device_id:
返回值成功:返回 device_node 类型的结构体指针,它保存着设备节点的信息
失败:失败则返回 NULL
cppstruct of_device_id { char name[32]; //节点中属性为 name 的值 char type[32]; //节点中属性为 device_type 的值 char compatible[128]; //节点的名字,在 device_node 结构体后面放一个字符串, full_name 指向它 const void *data; //链表,连接该节点的所有属性 };
头文件 #include<linux/of.h>
函数原型struct device_node *of_get_parent(const struct device_node *node)
struct device_node *of_get_next_child(const struct device_node *node,,struct device_node *prev)
函数作用 寻找父节点,寻找子节点
参数node: 指定 节点)要查找父/子节点。
prev: 前一个子节点,寻找的是 prev 节点之后的节点。这是一个迭代寻找过程,例如寻找第二个子节点,这里就要填第一个子节点。参数为 NULL 表示寻找第一个子节点
返回值成功:返回 device_node 类型的结构体指针,它保存着设备节点的信息
失败:失败则返回 NULL
2.2 提取属性值函数
通过一组 of 函数从设备节点结构体 (device_node) 中获取想要的设备节点属性信息。
头文件 #include<linux/of.h>
函数原型 struct property *of_find_property(const struct device_node *np,const char*name,int *lenp)
函数作用 查找节点属性
参数np: 指定要获取那个设备节点的属性信息
name: 属性名
lenp: 获取得到的属性值的大小,这个指针作为输出参数,这个参数"带回"的值是实际获取得到的属性大小
返回值成功:返回 property 结构体,节点属性结构体
失败:失败则返回 NULL
头文件 #include<linux/of.h>
函数原型 int of_property_read_u8_array(const struct device_node *np, const char*propname, u8 *out_values, size_t sz)int of_property_read_u16_array(const struct device_node *np, const char*propname, u16 *out_values, size_t sz)
int of_property_read_u32_array(const struct device_node *np, const char*propname, u32 *out_values, size_t sz)
int of_property_read_u64_array(const struct device_node *np, const char*propname, u64 *out_values, size_t sz)
函数作用 读取整形属性函数
参数np: 指定要读取那个设备节点结构体,也就是说读取那个设备节点的数据。
propname: 指定要获取设备节点的哪个属性。
out_values: 这是一个输出参数,是函数的"返回值",保存读取得到的数据
sz: 读取的数组元素数量
返回值成功:返回 0
失败:失败则返回错误码
头文件 #include<linux/of.h>
函数原型 int of_property_read_string(const struct device_node *np,const char*propname,const char **out_string)
函数作用 读取字符串属性函数
参数np: 指定要获取那个设备节点的属性信息
propname: 属性名
out_string: 获取得到字符串指针,这是一个"输出"参数,带回一个字符串指针。也就是
字符串属性值的首地址
返回值成功:0;失败:错误码
头文件 #include<linux/of.h>
函数原型 int of_property_read_string_index(const struct device_node *np,const char*propname, int index,const char **out_string)
函数作用 读取字符串属性函数
参数np: 指定要获取那个设备节点的属性信息
propname: 属性名
index:它用于指定读取属性值中第几个字符串, index 从零开始计数
out_string: 获取得到字符串指针,这是一个"输出"参数,带回一个字符串指针。也就是
字符串属性值的首地址
返回值成功:0;失败:错误码
2.3 代码
设备树代码:
cpp
my_test:DQtest{
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <1>;
compatible="test";
reg=<0xFDD60004 0x4 0xFDD6000C 0x4>;
status = "okay";
};驱动代码:
cpp
#include<linux/init.h>
#include<linux/module.h>
#include<linux/of.h>
int size;
const char *str1,*str2;
int arry[64]={0};
struct device_node*led_device_node;
struct property *led_node_property;
static int led_device_tree_init(void)
{
int ret1,ret2,ret3;
/****按路径查找设备*******/
led_device_node=of_find_node_by_path("/DQtest");
if(led_device_node==NULL)
{
printk("of_find_node_by_path failed\n");
return -1;
}
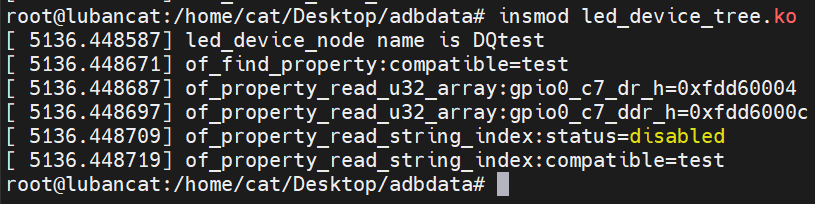
printk("led_device_node name is %s\n",led_device_node->name);
/***************获取节点属性************/
led_node_property=of_find_property(led_device_node,"compatible",&size);
if(led_node_property==NULL)
{
printk("of_find_property failed\n");
return -2;
}
printk("of_find_property:%s=%s\n",led_node_property->name,(char*)led_node_property->value);
/***************获取reg内容*************/
ret1=of_property_read_u32_array(led_device_node,"reg",arry,4);
if(ret1!=0)
{
printk("of_property_read_u32_array failed\n");
return -3;
}
printk("of_property_read_u32_array:gpio0_c7_dr_h=%#x\n",arry[0]);
printk("of_property_read_u32_array:gpio0_c7_ddr_h=%#x\n",arry[2]);
/*************************获取status的值***********************/
ret2=of_property_read_string_index(led_device_node,"status",0,&str1);
if(ret2!=0)
{
printk("of_property_read_string_index failed\n");
return -4;
}
printk("of_property_read_string_index:status=%s\n",str1);
ret3=of_property_read_string_index(led_device_node,"compatible",0,&str2);
if(ret3!=0)
{
printk("of_property_read_string_index failed\n");
return -5;
}
printk("of_property_read_string_index:compatible=%s\n",str2);
return 0;
}
static void led_device_tree_exit(void)
{
printk("led_device_tree_exit\n");
}
module_init(led_device_tree_init);
module_exit(led_device_tree_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
cppof_find_property(led_device_node,"compatible",&size); of_property_read_string_index(led_device_node,"compatible",0,&str2);这两个函数可以达到相同的效果
执行结果
2.4 与设备树匹配
注意:status为"disabled"意味着设备树节点被禁用,内核不会为其创建platform_device。
cpp
#include<linux/init.h>
#include<linux/module.h>
#include<linux/platform_device.h>
#include<linux/of.h>
/*************************匹配成功执行led_probe函数*********************/
static int led_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
printk("hello led_probe\n");
return 0;
}
static int led_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
printk("hello remove\n");
return 0;
}
//定义一个platform_device_id结构体
struct platform_device_id led_device_id =
{
.name="xxx" //用于匹配虚拟总线名字
};
//定义结构体数组,用于配置设备树节点中compatible名字
struct of_device_id led_device_tree[]=
{
{.compatible="test"},
{}
};
/*定义一个plaitform_driver结构体用于注册platform_driver驱动*/
struct platform_driver led_driver=
{
.probe=led_probe, //匹配成功执行led_probe函数
.remove=led_remove, //注销platform_driver执行led_remove函数
.driver=
{
.name="led_test", //总线名,与platform_device结构体中的name进行匹配//用于匹配虚拟总线名字
.owner=THIS_MODULE, //模块所属
.of_match_table=led_device_tree //用于配置设备树节点中compatible名字,匹配优先级最高
},
.id_table=&led_device_id //该结构体中有name,则优先与与platform_device结构体中的name进行匹配
};
static int platform_driver_init(void)
{
int ret1;
printk("hello platform_driver_init\n");
ret1=platform_driver_register(&led_driver);//注册驱动
if(ret1!=0)
{
printk("platform_driver_register failed\n");
return ret1;
}
printk("platform_driver_register succeed\n");
return 0;
}
static void platform_driver_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&led_driver);//注销驱动
printk("byebye platform_driver_exit\n");
}
module_init(platform_driver_init);
module_exit(platform_driver_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");对于代码中,
优先级:
优先:.of_match_table中的name与设备树节点中的compatible匹配,该匹配是与设备树匹配
其次 .id_table中的name与platform_device结构体中的name进行匹配,该匹配是虚拟总线匹配
最后才是.driver.name与platform_device结构体中的name进行匹配,该匹配是虚拟总线匹配
三、设备树驱动
3.1 映射相关函数
在设备树的设备节点中大多会包含一些内存相关的属性,比如常用的 reg 属性。通常情况下,得到寄存器地址之后还要通过 ioremap 函数将物理地址转化为虚拟地址。现在内核提供了 of 函数,自动完成物理地址到虚拟地址的转换
头文件: #include<linux/of_address.h>
函数原型: void __iomem *of_iomap(struct device_node *np, int index)
函数作用 内存映射
参数np: 指定要获取那个设备节点的属性信息
index: 通常情况下 reg 属性包含多段, index 用于指定映射那一段,标号从 0 开始;是对设备树中的reg中的地址进行索引,而不是长度
返回值成功,得到转换得到的地址。失败返回 NULL
函数原型: int of_address_to_resource(struct device_node *dev, int index, struct resource *r)
函数作用 内存映射
参数np: 指定要获取那个设备节点的属性信息
index: 通常情况下 reg 属性包含多段, index 用于指定映射那一段,标号从 0 开始
r: 这是一个 resource 结构体,是"输出参数"用于返回得到的地址信息
返回值成功返回 0,失败返回错误状态码
resource 结构体
cppstruct resource { resource_size_t start; //start: 起始地址 resource_size_t end; //end: 结束地址 const char *name; //name: 属性名字 unsigned long flags; unsigned long desc; struct resource *parent, *sibling, *child; };
**代码:**匹配成功以后,设备信息就会从设备树节点转换成platform_device结构体,会执行probe函数,可以通过probe函数直接获得设备信息,也可以通过of函数获得
cpp
#include<linux/init.h>
#include<linux/module.h>
#include<linux/platform_device.h>
#include<linux/of.h>
#include<linux/of_address.h>
struct device_node*led_device_node;
unsigned int *gpio0_c7_dr_h; //数据寄存器
unsigned int *gpio0_c7_ddr_h; //数据方向寄存器
/*************************匹配成功执行led_probe函数*********************/
static int led_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int ret1;
int arry[4];
printk("hello led_probe\n");
//printk("node name is %s\n",pdev->dev.of_node->name);//直接获取节点资源,也可以通过of函数获取相关资源
/***第二种方法,获取节点*****/
/*led_device_node=of_find_node_by_path("/DQtest");//通过路径获取节点
if(led_device_node==NULL)
{
printk("of_find_node_by_path failed\n");
return -1;
}
printk("led_device_node name is %s\n",led_device_node->name);*/
/***************获取reg内容*************/
ret1=of_property_read_u32_array(pdev->dev.of_node,"reg",arry,4);//与ret1=of_property_read_u32_array(led_device_node,"reg",arry,4);等效
if(ret1!=0)
{
printk("of_property_read_u32_array failed\n");
return -2;
}
printk("of_property_read_u32_array:gpio0_c7_dr_h=%#x\n",arry[0]);
printk("of_property_read_u32_array:gpio0_c7_ddr_h=%#x\n",arry[2]);
/************************************************************************/
/*拿到reg里面的地址,可以注册杂项设备,可以地址映射*/
/********地址映射*******/
gpio0_c7_dr_h=of_iomap(pdev->dev.of_node, 0);//与gpio0_c7_dr_h=of_iomap(led_device_node, 0);等效
gpio0_c7_ddr_h=of_iomap(pdev->dev.of_node, 1);//与gpio0_c7_ddr_h=of_iomap(led_device_node, 2);等效
if(gpio0_c7_dr_h==NULL || gpio0_c7_ddr_h==NULL)
{
printk("of_iomap failed\n");
return -3;
}
printk("of_iomap:gpio0_c7_dr_h=%#x\n",*gpio0_c7_dr_h);
printk("of_iomap:gpio0_c7_ddr_h=%#x\n",*gpio0_c7_ddr_h);
return 0;
}
static int led_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
printk("hello remove\n");
return 0;
}
//定义一个platform_device_id结构体
struct platform_device_id led_device_id =
{
.name="xxx" //用于匹配虚拟总线名字
};
//定义结构体数组,用于配置设备树节点中compatible名字
struct of_device_id led_device_tree[]=
{
{.compatible="test"},
{}
};
/*定义一个plaitform_driver结构体用于注册platform_driver驱动*/
struct platform_driver led_driver=
{
.probe=led_probe, //匹配成功执行led_probe函数
.remove=led_remove, //注销platform_driver执行led_remove函数
.driver=
{
.name="led_test", //总线名,与platform_device结构体中的name进行匹配//用于匹配虚拟总线名字
.owner=THIS_MODULE, //模块所属
.of_match_table=led_device_tree //用于配置设备树节点中compatible名字,匹配优先级最高
},
.id_table=&led_device_id //该结构体中有name,则优先与与platform_device结构体中的name进行匹配
};
static int platform_driver_init(void)
{
int ret1;
printk("hello platform_driver_init\n");
ret1=platform_driver_register(&led_driver);//注册驱动
if(ret1!=0)
{
printk("platform_driver_register failed\n");
return ret1;
}
printk("platform_driver_register succeed\n");
return 0;
}
static void platform_driver_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&led_driver);//注销驱动
printk("byebye platform_driver_exit\n");
}
module_init(platform_driver_init);
module_exit(platform_driver_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");