本文记录使用 HMAC-SHA256算法对MCU的12字节UID加密得到8字节激活码的实现方式;
执行方式:
-
上位机Android APP端或QT程序端通过 HMAC-SHA256算法通过密钥生成激活码
-
下位机MCU端使用 HMAC-SHA256算法通过相同密钥Key生成激活码
示例代码:
- java端
java
import javax.crypto.Mac;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
public class test7 {
public static byte[] generateActivationCode(byte[] key, byte[] data) throws Exception {
Mac hmac = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
SecretKeySpec secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key, "HmacSHA256");
hmac.init(secretKey);
byte[] fullHash = hmac.doFinal(data);
// 截取前8字节作为激活码
byte[] activationCode = new byte[8];
System.arraycopy(fullHash, 0, activationCode, 0, 8);
return activationCode;
}
public static String bytesToHex(byte[] bytes) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (byte b : bytes) {
sb.append(String.format("%02x", b));
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static byte[] hexStringToByteArray(String hex) {
int len = hex.length();
byte[] data = new byte[len / 2];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i += 2) {
data[i / 2] = (byte) ((Character.digit(hex.charAt(i), 16) << 4)
+ Character.digit(hex.charAt(i+1), 16));
}
return data;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
/** 密钥(需要确保与下位机一致) */
String keyStr = "719562681012"; //719562681012
/** 加密数据: 这里为MCU的UID */
String dataStr = "410059001450303448383620";
System.out.println("Java Version Test:");
System.out.println("Key: " + keyStr);
System.out.println("Data: " + dataStr);
byte[] key = keyStr.getBytes();
byte[] data = hexStringToByteArray(dataStr);
byte[] activationCode = generateActivationCode(key, data);
String hexCode = bytesToHex(activationCode);
System.out.println("Activation Code (8 bytes): " + hexCode);
System.out.println("Full HMAC-SHA256: " + bytesToHex(generateFullHmac(key, data)));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static byte[] generateFullHmac(byte[] key, byte[] data) throws Exception {
Mac hmac = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
SecretKeySpec secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(key, "HmacSHA256");
hmac.init(secretKey);
return hmac.doFinal(data);
}
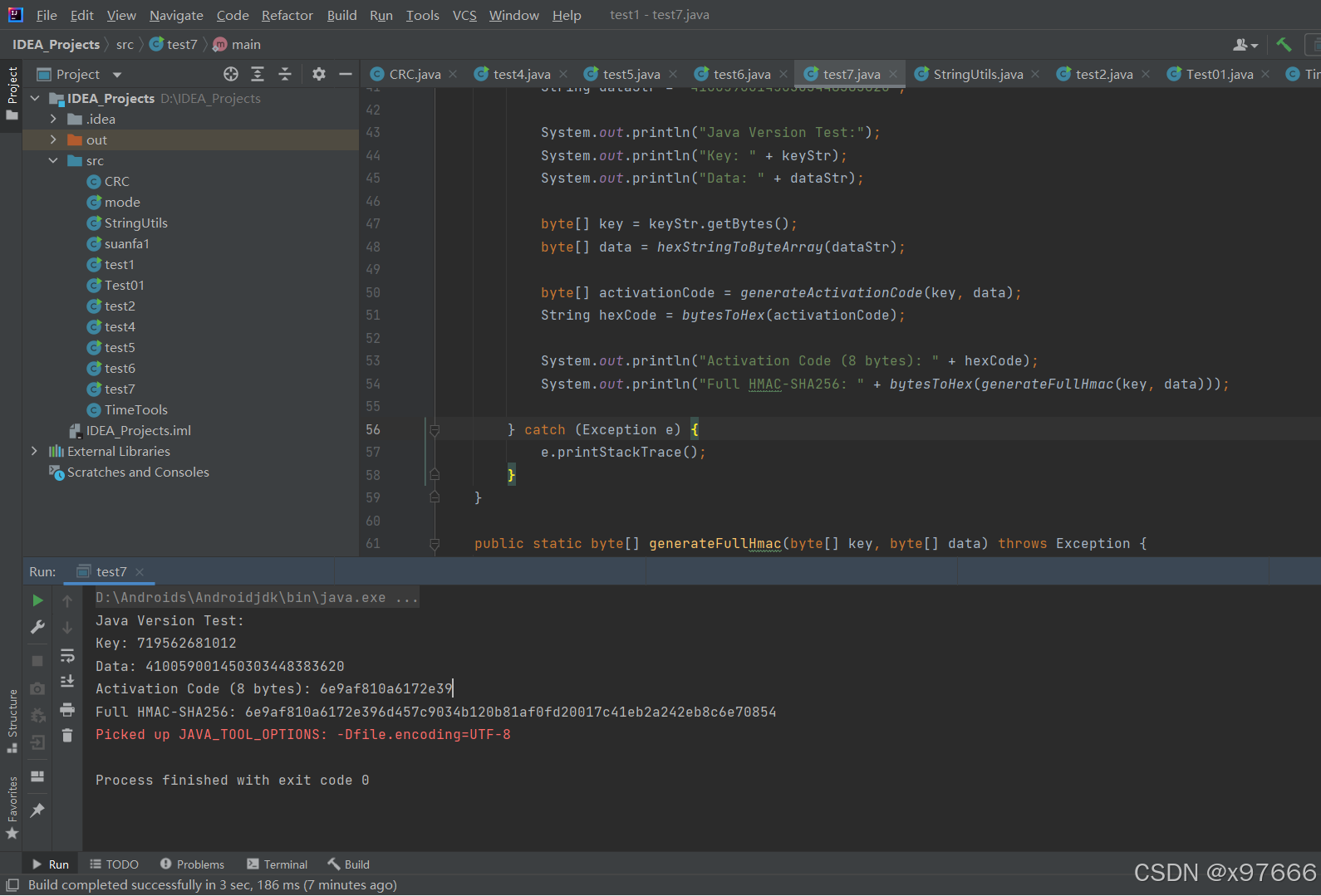
}使用IntelliJ IDEA 运行结果如下:
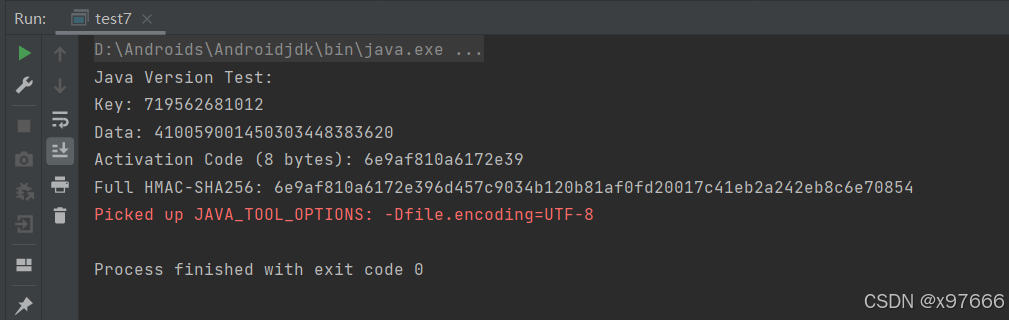
加密出来的激活码: 6e9af810a6172e39(8字节)
bash
Java Version Test:
Key: 719562681012
Data: 410059001450303448383620
Activation Code (8 bytes): 6e9af810a6172e39
Full HMAC-SHA256: 6e9af810a6172e396d457c9034b120b81af0fd20017c41eb2a242eb8c6e70854C语言版本(下位机MCU端):
- Crypto_utils.c文件
cpp
#include "Crypto_utils.h"
#include <string.h>
// SHA256常量
static const uint32_t k[64] = {
0x428a2f98, 0x71374491, 0xb5c0fbcf, 0xe9b5dba5,
0x3956c25b, 0x59f111f1, 0x923f82a4, 0xab1c5ed5,
0xd807aa98, 0x12835b01, 0x243185be, 0x550c7dc3,
0x72be5d74, 0x80deb1fe, 0x9bdc06a7, 0xc19bf174,
0xe49b69c1, 0xefbe4786, 0x0fc19dc6, 0x240ca1cc,
0x2de92c6f, 0x4a7484aa, 0x5cb0a9dc, 0x76f988da,
0x983e5152, 0xa831c66d, 0xb00327c8, 0xbf597fc7,
0xc6e00bf3, 0xd5a79147, 0x06ca6351, 0x14292967,
0x27b70a85, 0x2e1b2138, 0x4d2c6dfc, 0x53380d13,
0x650a7354, 0x766a0abb, 0x81c2c92e, 0x92722c85,
0xa2bfe8a1, 0xa81a664b, 0xc24b8b70, 0xc76c51a3,
0xd192e819, 0xd6990624, 0xf40e3585, 0x106aa070,
0x19a4c116, 0x1e376c08, 0x2748774c, 0x34b0bcb5,
0x391c0cb3, 0x4ed8aa4a, 0x5b9cca4f, 0x682e6ff3,
0x748f82ee, 0x78a5636f, 0x84c87814, 0x8cc70208,
0x90befffa, 0xa4506ceb, 0xbef9a3f7, 0xc67178f2
};
// 右旋转函数
#define ROTRIGHT(word, bits) (((word) >> (bits)) | ((word) << (32 - (bits))))
// SHA256基础函数
#define CH(x, y, z) (((x) & (y)) ^ (~(x) & (z)))
#define MAJ(x, y, z) (((x) & (y)) ^ ((x) & (z)) ^ ((y) & (z)))
#define EP0(x) (ROTRIGHT(x, 2) ^ ROTRIGHT(x, 13) ^ ROTRIGHT(x, 22))
#define EP1(x) (ROTRIGHT(x, 6) ^ ROTRIGHT(x, 11) ^ ROTRIGHT(x, 25))
#define SIG0(x) (ROTRIGHT(x, 7) ^ ROTRIGHT(x, 18) ^ ((x) >> 3))
#define SIG1(x) (ROTRIGHT(x, 17) ^ ROTRIGHT(x, 19) ^ ((x) >> 10))
void sha256_transform(sha256_ctx_t *ctx, const uint8_t data[]) {
uint32_t a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, j, t1, t2, m[64];
// 将数据转换为32位字
for (i = 0, j = 0; i < 16; ++i, j += 4) {
m[i] = (data[j] << 24) | (data[j + 1] << 16) | (data[j + 2] << 8) | data[j + 3];
}
for (; i < 64; ++i) {
m[i] = SIG1(m[i - 2]) + m[i - 7] + SIG0(m[i - 15]) + m[i - 16];
}
a = ctx->state[0];
b = ctx->state[1];
c = ctx->state[2];
d = ctx->state[3];
e = ctx->state[4];
f = ctx->state[5];
g = ctx->state[6];
h = ctx->state[7];
for (i = 0; i < 64; ++i) {
t1 = h + EP1(e) + CH(e, f, g) + k[i] + m[i];
t2 = EP0(a) + MAJ(a, b, c);
h = g;
g = f;
f = e;
e = d + t1;
d = c;
c = b;
b = a;
a = t1 + t2;
}
ctx->state[0] += a;
ctx->state[1] += b;
ctx->state[2] += c;
ctx->state[3] += d;
ctx->state[4] += e;
ctx->state[5] += f;
ctx->state[6] += g;
ctx->state[7] += h;
}
void sha256_init(sha256_ctx_t *ctx) {
ctx->datalen = 0;
ctx->bitlen = 0;
ctx->state[0] = 0x6a09e667;
ctx->state[1] = 0xbb67ae85;
ctx->state[2] = 0x3c6ef372;
ctx->state[3] = 0xa54ff53a;
ctx->state[4] = 0x510e527f;
ctx->state[5] = 0x9b05688c;
ctx->state[6] = 0x1f83d9ab;
ctx->state[7] = 0x5be0cd19;
}
void sha256_update(sha256_ctx_t *ctx, const uint8_t data[], size_t len) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
ctx->data[ctx->datalen] = data[i];
ctx->datalen++;
if (ctx->datalen == 64) {
sha256_transform(ctx, ctx->data);
ctx->bitlen += 512;
ctx->datalen = 0;
}
}
}
void sha256_final(sha256_ctx_t *ctx, uint8_t hash[]) {
size_t i = ctx->datalen;
// 填充
if (ctx->datalen < 56) {
ctx->data[i++] = 0x80;
while (i < 56) {
ctx->data[i++] = 0x00;
}
} else {
ctx->data[i++] = 0x80;
while (i < 64) {
ctx->data[i++] = 0x00;
}
sha256_transform(ctx, ctx->data);
memset(ctx->data, 0, 56);
}
// 添加长度
ctx->bitlen += ctx->datalen * 8;
ctx->data[63] = ctx->bitlen;
ctx->data[62] = ctx->bitlen >> 8;
ctx->data[61] = ctx->bitlen >> 16;
ctx->data[60] = ctx->bitlen >> 24;
ctx->data[59] = ctx->bitlen >> 32;
ctx->data[58] = ctx->bitlen >> 40;
ctx->data[57] = ctx->bitlen >> 48;
ctx->data[56] = ctx->bitlen >> 56;
sha256_transform(ctx, ctx->data);
// 生成哈希值
for (i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
hash[i] = (ctx->state[0] >> (24 - i * 8)) & 0x000000ff;
hash[i + 4] = (ctx->state[1] >> (24 - i * 8)) & 0x000000ff;
hash[i + 8] = (ctx->state[2] >> (24 - i * 8)) & 0x000000ff;
hash[i + 12] = (ctx->state[3] >> (24 - i * 8)) & 0x000000ff;
hash[i + 16] = (ctx->state[4] >> (24 - i * 8)) & 0x000000ff;
hash[i + 20] = (ctx->state[5] >> (24 - i * 8)) & 0x000000ff;
hash[i + 24] = (ctx->state[6] >> (24 - i * 8)) & 0x000000ff;
hash[i + 28] = (ctx->state[7] >> (24 - i * 8)) & 0x000000ff;
}
}
// HMAC-SHA256实现
void hmac_sha256_init(hmac_sha256_ctx_t *ctx, const uint8_t *key, size_t key_len) {
uint8_t key_buffer[SHA256_BLOCK_SIZE] = {0};
// 如果密钥长度超过块大小,先对密钥进行哈希
if (key_len > SHA256_BLOCK_SIZE) {
sha256_ctx_t sha_ctx;
sha256_init(&sha_ctx);
sha256_update(&sha_ctx, key, key_len);
sha256_final(&sha_ctx, key_buffer);
} else {
memcpy(key_buffer, key, key_len);
}
// 生成内填充密钥和外填充密钥
uint8_t i_key_pad[SHA256_BLOCK_SIZE];
uint8_t o_key_pad[SHA256_BLOCK_SIZE];
for (int i = 0; i < SHA256_BLOCK_SIZE; i++) {
i_key_pad[i] = key_buffer[i] ^ 0x36;
o_key_pad[i] = key_buffer[i] ^ 0x5c;
}
// 初始化内部SHA256上下文
sha256_init(&ctx->ctx);
sha256_update(&ctx->ctx, i_key_pad, SHA256_BLOCK_SIZE);
memcpy(ctx->key, o_key_pad, SHA256_BLOCK_SIZE);
}
void hmac_sha256_update(hmac_sha256_ctx_t *ctx, const uint8_t *data, size_t data_len) {
sha256_update(&ctx->ctx, data, data_len);
}
void hmac_sha256_final(hmac_sha256_ctx_t *ctx, uint8_t *digest) {
uint8_t inner_hash[SHA256_DIGEST_SIZE];
// 完成内部哈希
sha256_final(&ctx->ctx, inner_hash);
// 计算外部哈希
sha256_ctx_t outer_ctx;
sha256_init(&outer_ctx);
sha256_update(&outer_ctx, ctx->key, SHA256_BLOCK_SIZE);
sha256_update(&outer_ctx, inner_hash, SHA256_DIGEST_SIZE);
sha256_final(&outer_ctx, digest);
}
void hmac_sha256(const uint8_t *key, size_t key_len,
const uint8_t *data, size_t data_len,
uint8_t *digest) {
hmac_sha256_ctx_t ctx;
hmac_sha256_init(&ctx, key, key_len);
hmac_sha256_update(&ctx, data, data_len);
hmac_sha256_final(&ctx, digest);
}
void hex_to_string(const uint8_t *hash, size_t len, char *output) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < len; i++) {
sprintf(output + (i * 2), "%02x", hash[i]);
}
output[len * 2] = '\0';
}- Crypto_utils.h文件
cpp
#ifndef __CRYPTO_UTILS_H__
#define __CRYPTO_UTILS_H__
#include "main.h"
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#define SHA256_BLOCK_SIZE 64
#define SHA256_DIGEST_SIZE 32
// SHA256上下文结构
typedef struct {
uint8_t data[64];
uint32_t datalen;
uint64_t bitlen;
uint32_t state[8];
} sha256_ctx_t;
// HMAC-SHA256上下文结构
typedef struct {
sha256_ctx_t ctx;
uint8_t key[SHA256_BLOCK_SIZE];
} hmac_sha256_ctx_t;
// SHA256函数声明
void sha256_init(sha256_ctx_t *ctx);
void sha256_update(sha256_ctx_t *ctx, const uint8_t data[], size_t len);
void sha256_final(sha256_ctx_t *ctx, uint8_t hash[]);
// HMAC-SHA256函数声明
void hmac_sha256_init(hmac_sha256_ctx_t *ctx, const uint8_t *key, size_t key_len);
void hmac_sha256_update(hmac_sha256_ctx_t *ctx, const uint8_t *data, size_t data_len);
void hmac_sha256_final(hmac_sha256_ctx_t *ctx, uint8_t *digest);
void hmac_sha256(const uint8_t *key, size_t key_len,
const uint8_t *data, size_t data_len,
uint8_t *digest);
// 工具函数
void hex_to_string(const uint8_t *hash, size_t len, char *output);
#endif下位机端添加.c和.h文件后在main文件中添加下述函数
cpp
// 将十六进制字符串转换为字节数组
void hex_to_bytes(const char* hex, uint8_t* bytes, size_t* out_len) {
size_t hex_len = strlen(hex);
*out_len = hex_len / 2;
for (size_t i = 0; i < hex_len; i += 2) {
sscanf(hex + i, "%2hhx", &bytes[i / 2]);
}
}main函数中验证代码为:
cpp
char* key_str = "719562681012";/* 密钥 */
char* data_hex = "410059001450303448383620";/* 数据UID */
printf("C Version Test:\r\n");
printf("Key: %s\r\n", key_str);
printf("Data: %s\r\n", data_hex);
// 准备密钥和数据
uint8_t key[32];
uint8_t data[32];
size_t key_len = strlen(key_str);
size_t data_len;
memcpy(key, key_str, key_len);
hex_to_bytes(data_hex, data, &data_len);
// 计算HMAC-SHA256
uint8_t digest[32];
hmac_sha256(key, key_len, data, data_len, digest);
// 输出完整哈希和前8字节激活码
printf("Full HMAC-SHA256: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {
printf("%02x", digest[i]);
}
printf("\r\n");
printf("Activation Code (8 bytes): ");
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
printf("%02x", digest[i]);
}
printf("\r\n");C语言端输出结果为:
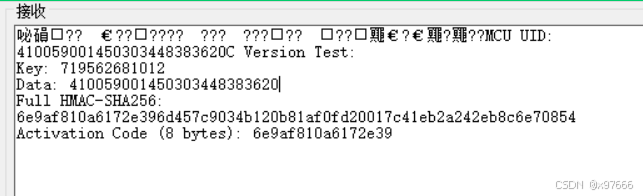
bash
Version Test:
Key: 719562681012
Data: 410059001450303448383620
Full HMAC-SHA256: 6e9af810a6172e396d457c9034b120b81af0fd20017c41eb2a242eb8c6e70854
Activation Code (8 bytes): 6e9af810a6172e39可以看到 c语言端和java端的输出结果是一致的,都是"6e9af810a6172e39",只需要修改key和数据即可使用。
使用图片: