前言
在Java开发中,你是否经常为空指针异常而烦恼?是否觉得传统的异常处理try-catch代码冗长难看?是否羡慕Scala、Kotlin等语言的函数式编程特性?
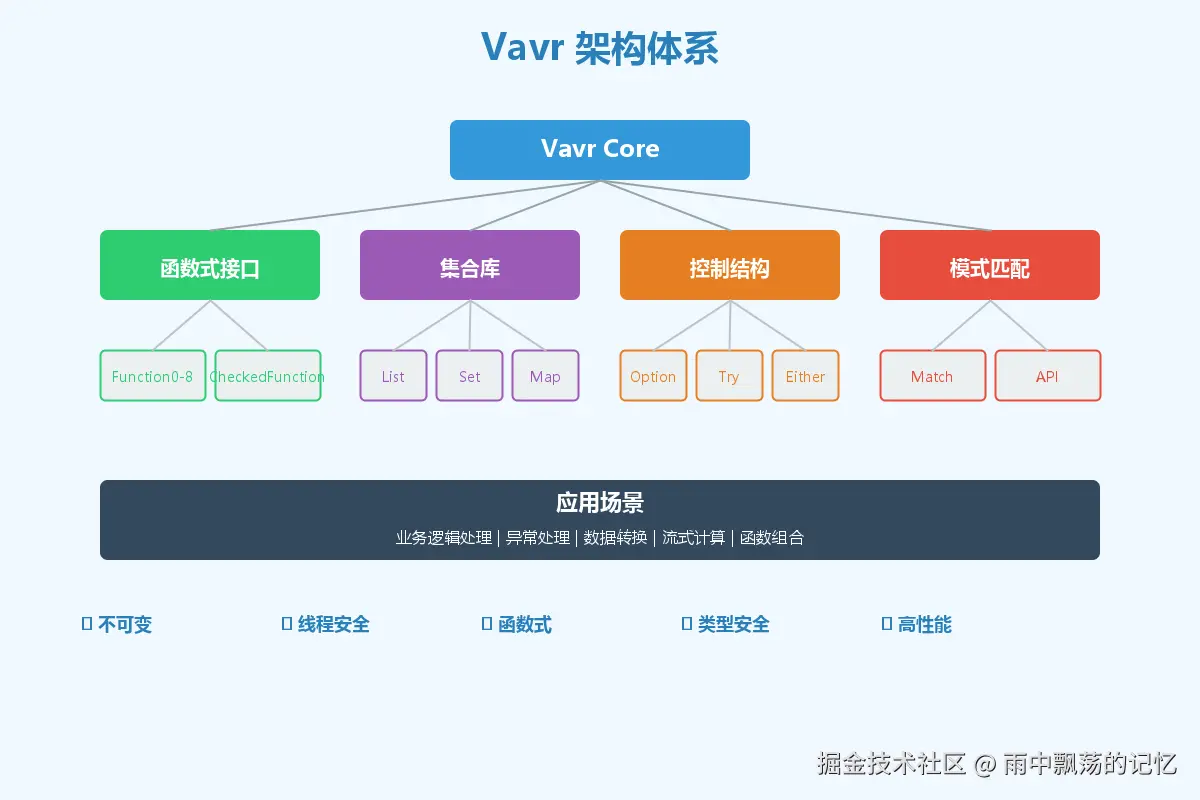
今天,我要向大家介绍一个强大的Java函数式编程库------Vavr(原名Javaslang),它将为你的Java代码带来革命性的改变。
Vavr是一个面向Java 8+的函数式编程库,它提供了持久化的数据结构和函数式控制结构,让Java开发者能够编写更加简洁、安全、优雅的代码。
一、传统Java开发的痛点
空指针异常
Java开发者的噩梦,稍不注意就会导致程序崩溃:
java
// 传统写法:充满if判断
public String getUserCity(User user) {
if (user != null) {
Address address = user.getAddress();
if (address != null) {
City city = address.getCity();
if (city != null) {
return city.getName();
}
}
}
return "Unknown";
}异常处理冗长
try-catch块让代码可读性大打折扣:
typescript
// 传统写法
public String readFile(String path) {
try {
return Files.readString(Path.of(path));
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("读取文件失败", e);
return "默认内容";
}
}集合操作受限
Java标准集合是可变的,容易产生并发问题,且缺少函数式操作。
二、Option:优雅处理空值
2.1 Optio vs Null
Option是Vavr中用于处理可能为空的值的容器类型,彻底告别空指针异常。

2.2 基础用法
rust
/ 创建Option
Option<String> some = Option.of("Hello");
Option<String> none = Option.none();
// 链式调用
Option<Integer> length = some.map(String::length); // Some(5)
// 获取值
String value = some.getOrElse("default"); // "Hello"2.3 实战案例:用户信息查询
kotlin
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
// Vavr方式
public String getUserEmail(Long userId) {
return Option.ofOptional(userRepository.findById(userId))
.map(User::getEmail)
.getOrElse("no-email@example.com");
}
}2.4 配置读取场景
csharp
public class ConfigService {
// Vavr方式:链式调用优雅
public int getTimeout() {
return Option.of(config.get("timeout"))
.flatMap(s -> Try.of(() -> Integer.parseInt(s)).toOption())
.getOrElse(3000);
}
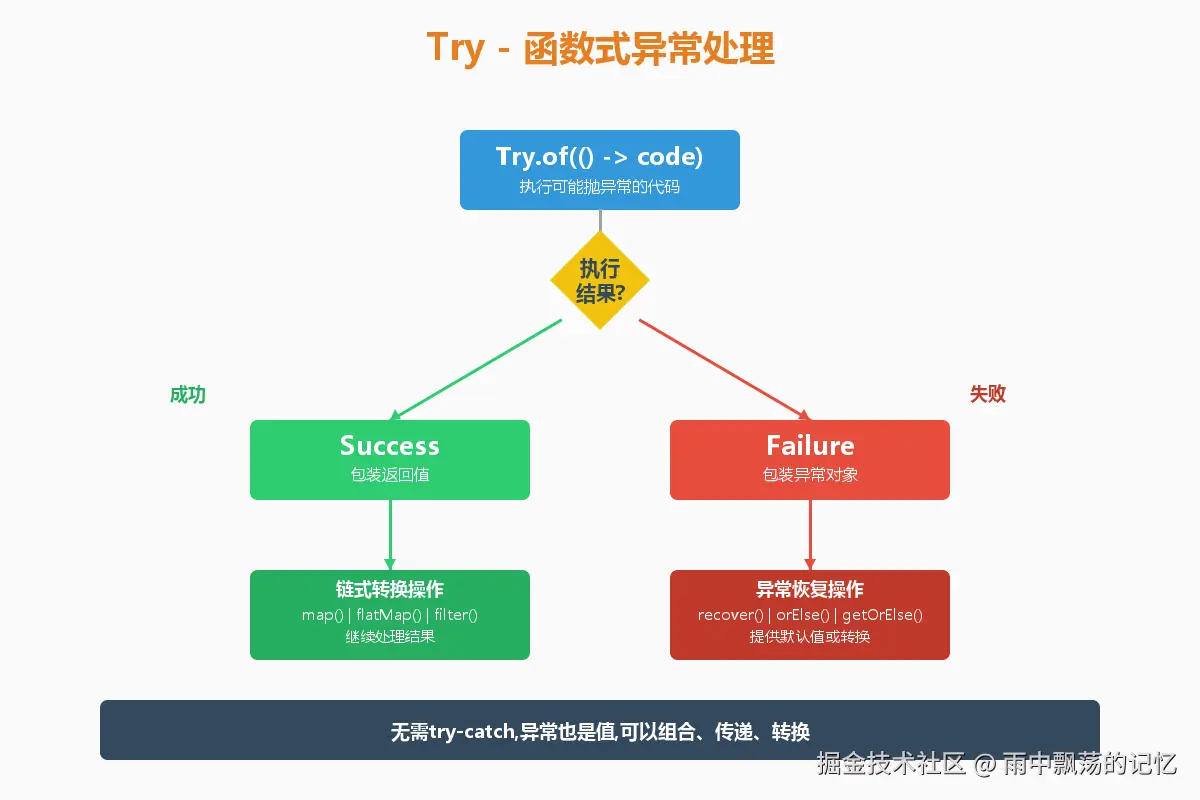
}三、Try:函数式异常处理
3.1 Try的设计理念
Try将异常处理变成了值的传递,而不是控制流的中断。
3.2 HTTP请求处理
kotlin
@Service
public class ExternalApiService {
// Vavr方式:更优雅的异常处理
public Try<UserDTO> fetchUser(Long userId) {
return Try.of(() -> {
String url = "https://api.example.com/users/" + userId;
return restTemplate.getForEntity(url, UserDTO.class).getBody();
});
}
// 链式处理结果
public UserDTO getUserWithFallback(Long userId) {
return fetchUser(userId)
.recover(RestClientException.class, ex -> createDefaultUser())
.recover(TimeoutException.class, ex -> getCachedUser(userId))
.getOrElse(createDefaultUser());
}
}3.3 文件操作场景
kotlin
public class FileService {
// 组合操作:读取文件并解析
public Try<User> loadUserFromFile(String path) {
return readFile(path)
.flatMap(this::parseUser)
.onSuccess(user -> log.info("加载成功: {}", user.getName()))
.onFailure(ex -> log.error("加载失败", ex));
}
// 批量处理
public List<User> loadUsersFromFiles(List<String> paths) {
return paths.stream()
.map(this::loadUserFromFile)
.filter(Try::isSuccess)
.map(Try::get)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
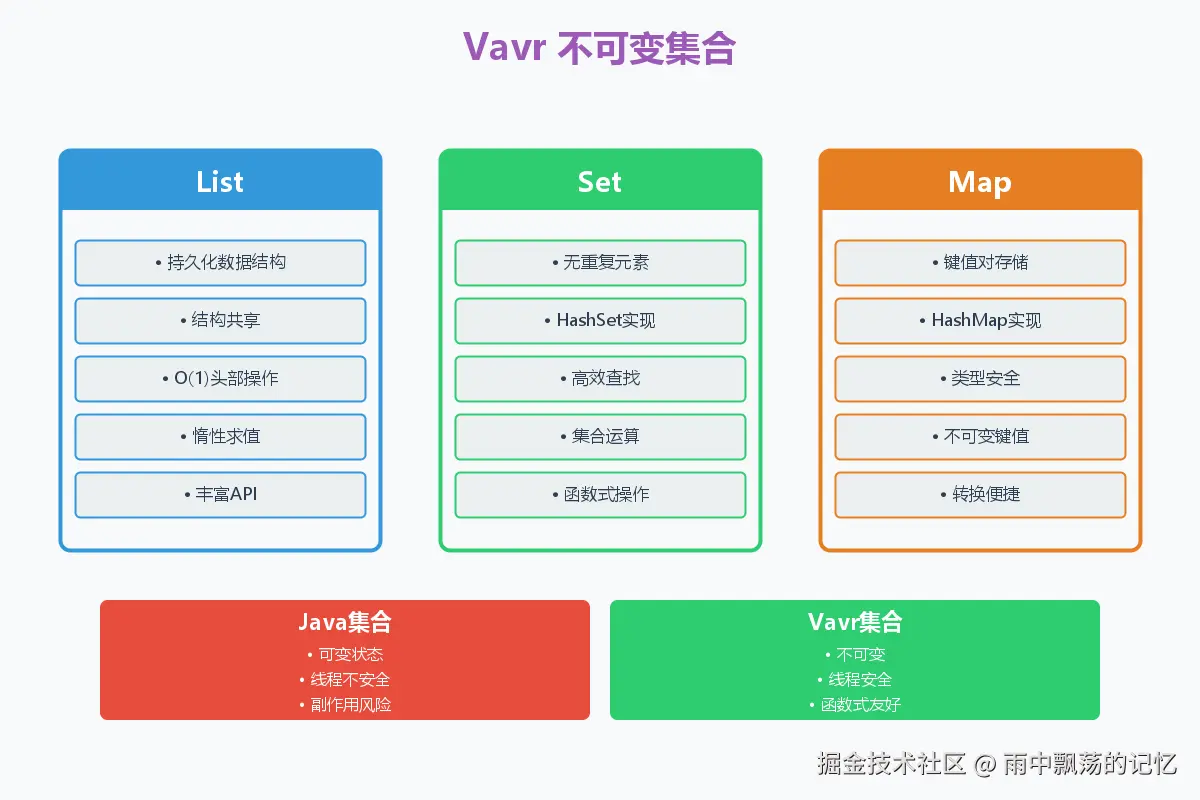
}四、不可变集合:线程安全的函数式集合
4.1 Vavr集合的优势
Vavr提供了完整的不可变集合库,它们都是持久化数据结构,支持结构共享,性能优异。
4.2 数据转换管道
scss
public class DataProcessor {
// Vavr方式:不可变集合
public List<String> processData(List<Integer> numbers) {
return io.vavr.collection.List.ofAll(numbers)
.filter(n -> n > 0)
.map(n -> "正数:" + n)
.toJavaList();
}
// 复杂的数据处理
public List<OrderSummary> processOrders(List<Order> orders) {
return io.vavr.collection.List.ofAll(orders)
.filter(order -> order.getStatus() == OrderStatus.PAID)
.groupBy(Order::getUserId)
.map((userId, userOrders) -> new OrderSummary(
userId,
userOrders.size(),
userOrders.map(Order::getAmount).sum().doubleValue()
))
.toJavaList();
}
}4.3 Map操作
typescript
public class CacheService {
private io.vavr.collection.Map<String, User> userCache =
io.vavr.collection.HashMap.empty();
// 转换值
public Map<String, String> getUserNames() {
return userCache.mapValues(User::getName).toJavaMap();
}
// 过滤
public Map<String, User> getActiveUsers() {
return userCache.filter((id, user) -> user.isActive()).toJavaMap();
}
}五、函数式编程特性
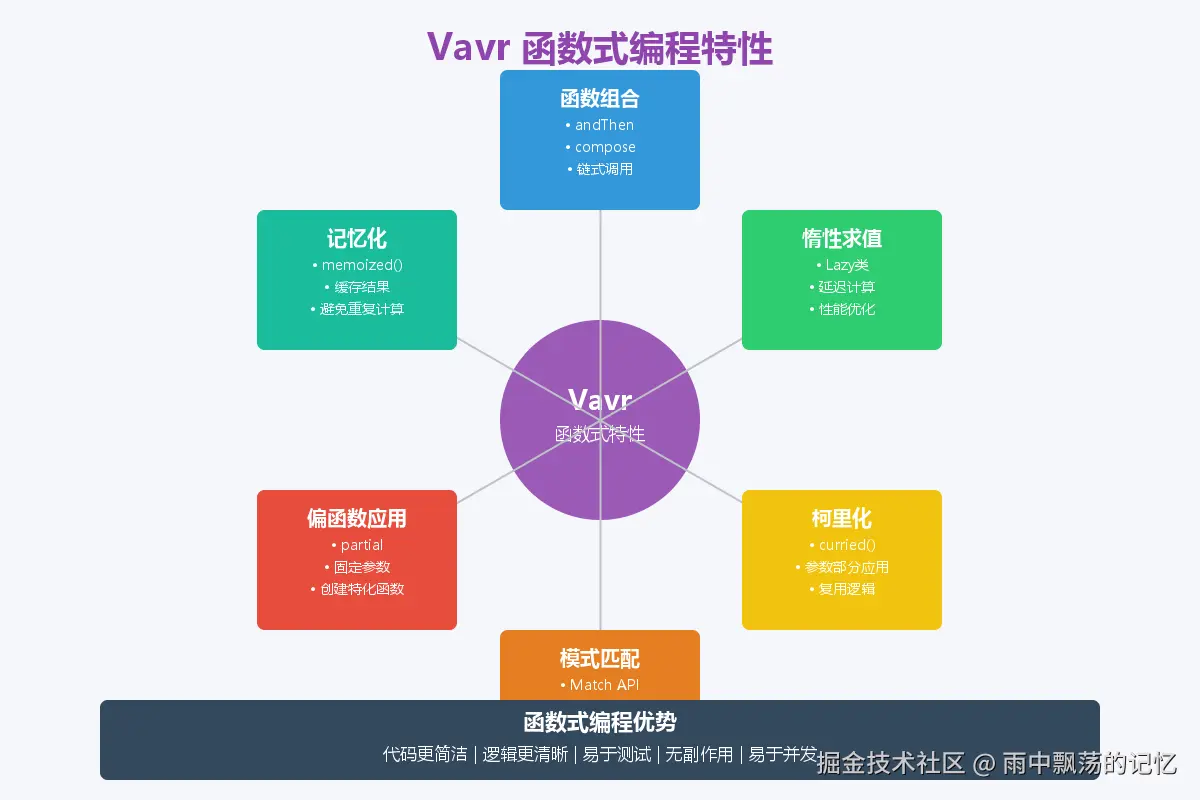
5.1 函数组合
arduino
public class FunctionComposition {
// 定义基础函数
Function1<String, String> trim = String::trim;
Function1<String, String> toUpper = String::toUpperCase;
Function1<String, Integer> length = String::length;
// 组合函数
Function1<String, Integer> processAndGetLength =
trim.andThen(toUpper).andThen(length);
// 结果
int result = processAndGetLength.apply(" hello "); // 5
}5.2 柯里化
arduino
public class CurryingExample {
// 实际应用:日志记录器
Function3<String, String, String, String> logger =
(level, module, message) ->
String.format("[%s][%s] %s", level, module, message);
// 创建专用日志记录器
Function1<String, String> userModuleLogger =
logger.curried().apply("INFO").apply("UserModule");
public void logExample() {
String log1 = userModuleLogger.apply("用户登录成功");
String log2 = userModuleLogger.apply("用户退出登录");
}
}5.3 记忆化
kotlin
public class MemoizationExample {
// 昂贵的计算
Function1<Integer, Long> fibonacci = n -> {
if (n <= 1) return (long) n;
return fibonacci.apply(n - 1) + fibonacci.apply(n - 2);
};
// 记忆化:缓存计算结果
Function1<Integer, Long> memoizedFibonacci = fibonacci.memoized();
// 第一次调用:计算
// 第二次调用:从缓存获取,极快!
}5.4 Lazy惰性求值
arduino
public class LazyExample {
// 惰性计算:只在需要时才执行
Lazy<String> lazyValue = Lazy.of(() -> {
System.out.println("执行昂贵的计算...");
return expensiveComputation();
});
// 实际应用:配置加载
Lazy<Properties> config = Lazy.of(() -> {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.load(new FileInputStream("config.properties"));
return props;
});
public String getConfigValue(String key) {
return config.get().getProperty(key);
}
}六、Pattern Matching:优雅的模式匹配
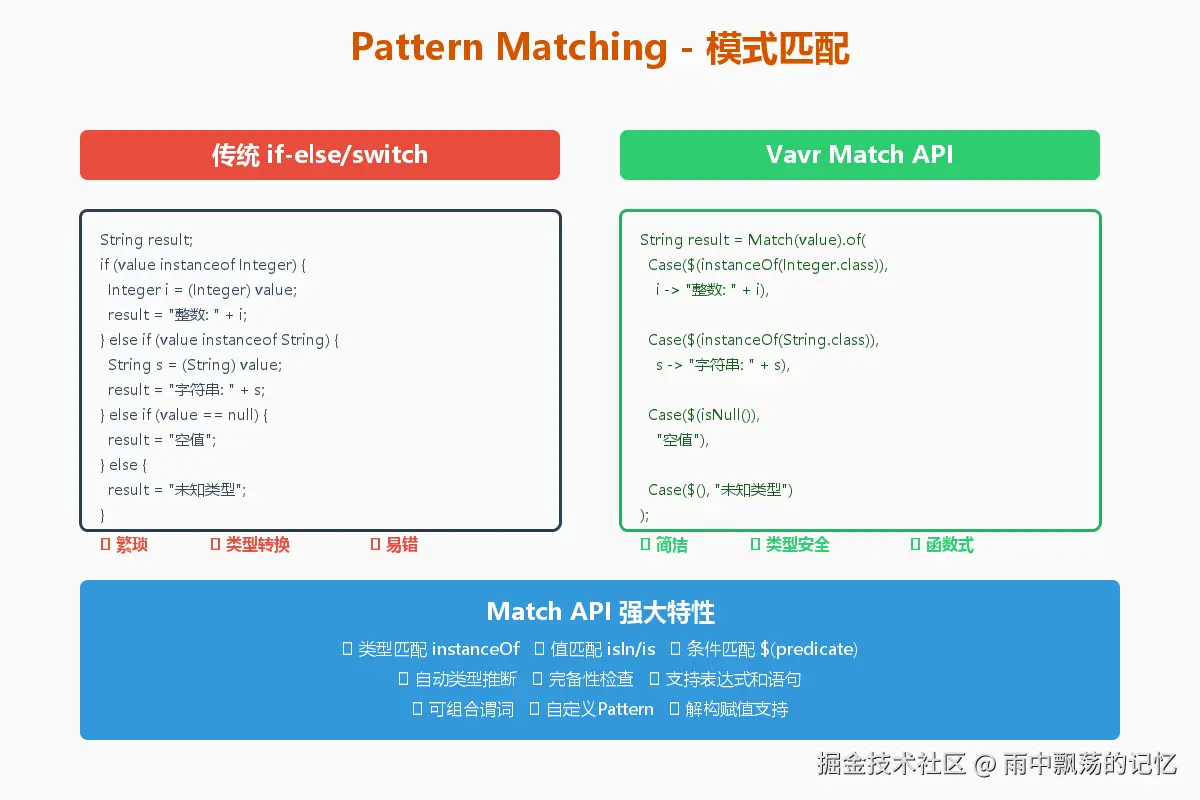
6.1 基础模式匹配
typescript
public class PatternMatchingExample {
// 类型匹配
public String matchType(Object obj) {
return Match(obj).of(
Case($(instanceOf(String.class)), s -> "字符串: " + s),
Case($(instanceOf(Integer.class)), i -> "整数: " + i),
Case($(), o -> "其他类型")
);
}
// 条件匹配
public String classifyAge(int age) {
return Match(age).of(
Case($(n -> n < 0), "无效年龄"),
Case($(n -> n < 18), "未成年"),
Case($(n -> n < 60), "成年"),
Case($(), "老年")
);
}
}6.2 实际应用:HTTP响应处理
less
@RestController
public class ApiController {
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<?> getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
Try<User> userTry = userService.findUserById(id);
return Match(userTry).of(
Case($Success($()), user -> ResponseEntity.ok(user)),
Case($Failure($(instanceOf(UserNotFoundException.class))),
ex -> ResponseEntity.notFound().build()),
Case($Failure($(instanceOf(DatabaseException.class))),
ex -> ResponseEntity.status(503).body("服务暂时不可用")),
Case($Failure($()),
ex -> ResponseEntity.status(500).body("服务器内部错误"))
);
}
}七、Tuple:类型安全的多值容器
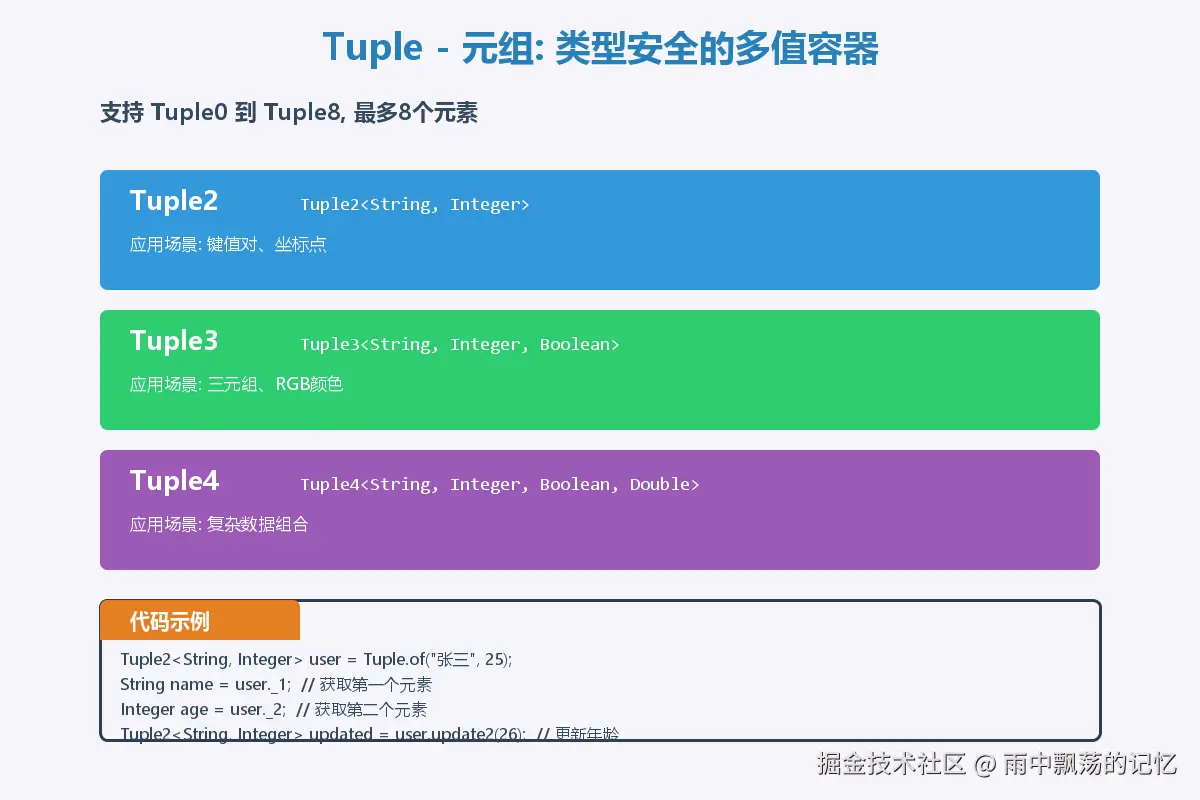
7.1 方法返回多个值
scss
public class StatisticsService {
// 使用Tuple返回多个值
public Tuple3<Double, Integer, Integer> calculate(List<Integer> numbers) {
io.vavr.collection.List<Integer> list =
io.vavr.collection.List.ofAll(numbers);
double avg = list.average().getOrElse(0.0);
int max = list.max().getOrElse(0);
int min = list.min().getOrElse(0);
return Tuple.of(avg, max, min);
}
public void useStatistics() {
Tuple3<Double, Integer, Integer> stats =
calculate(Arrays.asList(1, 5, 3, 9, 2));
System.out.println("平均值: " + stats._1);
System.out.println("最大值: " + stats._2);
System.out.println("最小值: " + stats._3);
}
}7.2 分页结果
arduino
public class PaginationExample {
// 返回数据和总数
public Tuple2<List<Product>, Long> getProductsWithTotal(int page, int size) {
io.vavr.collection.List<Product> allProducts = fetchAllProducts();
long total = allProducts.size();
List<Product> pageData = allProducts
.drop(page * size)
.take(size)
.toJavaList();
return Tuple.of(pageData, total);
}
}八、Either:业务错误处理
8.1 表单验证
less
public class FormValidationService {
public Either<List<String>, UserRegistration> validateRegistration(
String username, String email, String password) {
List<String> errors = new ArrayList<>();
if (username == null || username.length() < 3) {
errors.add("用户名至少3个字符");
}
if (!email.matches("^[A-Za-z0-9+_.-]+@(.+)$")) {
errors.add("邮箱格式不正确");
}
if (password.length() < 8) {
errors.add("密码至少8个字符");
}
return errors.isEmpty()
? Either.right(new UserRegistration(username, email, password))
: Either.left(errors);
}
@PostMapping("/register")
public ResponseEntity<?> register(@RequestBody RegistrationRequest req) {
return validateRegistration(req.getUsername(), req.getEmail(), req.getPassword())
.fold(
errors -> ResponseEntity.badRequest().body(Map.of("errors", errors)),
user -> ResponseEntity.ok(Map.of("message", "注册成功"))
);
}
}九、在Spring Boot中集成
9.1 添加依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vavr</groupId>
<artifactId>vavr</artifactId>
<version>0.10.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vavr</groupId>
<artifactId>vavr-jackson</artifactId>
<version>0.10.4</version>
</dependency>9.2 配置Jackson支持
typescript
@Configuration
public class VavrConfig {
@Bean
public Module vavrModule() {
return new VavrModule();
}
}9.3 Service层最佳实践
kotlin
@Service
public class OrderService {
// 使用Try处理复杂业务流程
@Transactional
public Try<Order> processOrder(OrderRequest request) {
return validateOrder(request)
.flatMap(this::checkInventory)
.flatMap(this::processPayment)
.flatMap(this::createOrder)
.onSuccess(order -> log.info("订单处理成功: {}", order.getId()))
.onFailure(ex -> log.error("订单处理失败", ex));
}
private Try<OrderRequest> validateOrder(OrderRequest request) {
return Try.of(() -> {
if (request.getItems().isEmpty()) {
throw new ValidationException("订单商品不能为空");
}
return request;
});
}
}十、最佳实践
10.1 合理选择数据结构
ini
// 频繁头部操作:使用List
io.vavr.collection.List<Integer> list = io.vavr.collection.List.of(1, 2, 3);
// 随机访问:使用Vector
io.vavr.collection.Vector<Integer> vector = io.vavr.collection.Vector.of(1, 2, 3);
// 键值查找:使用HashMap
io.vavr.collection.Map<String, User> map = io.vavr.collection.HashMap.of(...);10.2 正确使用Try和Option
rust
// 好:使用flatMap避免嵌套
Option<String> email = option.flatMap(user -> Option.of(user.getEmail()));
// 好:只在可能抛异常的地方使用Try
Try<String> fileContent = Try.of(() -> Files.readString(path));10.3 与Java标准库互操作
ini
// Java集合转Vavr
List<String> javaList = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c");
io.vavr.collection.List<String> vavrList =
io.vavr.collection.List.ofAll(javaList);
// Vavr集合转Java
List<String> backToJava = vavrList.toJavaList();总结
Vavr为Java开发者带来了强大的函数式编程能力,让我们能够编写更加优雅、安全、简洁的代码:
vbnet
✅ Option - 告别空指针异常
✅ Try - 函数式异常处理
✅ 不可变集合 - 线程安全且性能优异
✅ 函数式特性 - 组合、柯里化、记忆化✅ 模式匹配 - 优雅的分支处理
✅ Tuple - 类型安全的多值返回✅ Either - 业务错误处理