前言
在现代 Java 开发中,Spring 框架因其灵活性和强大的功能而广受欢迎。在 Spring 的生态系统中,Bean 的创建和管理是核心概念之一。为了提供更大的灵活性,Spring 提供了一些扩展点,使开发者能够在 Bean 的生命周期中进行干预。这些扩展点主要包括 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 和 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 是一种后处理器,它允许开发者在 Spring 容器的标准初始化过程之后,对 BeanFactory 进行修改。通过实现该接口,您可以动态调整 Bean 的定义、修改属性、条件注册 Bean 等,从而实现更复杂的配置。
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 则是另一个更高级的后处理器,它不仅可以修改 BeanFactory,还可以直接操作 BeanDefinition 注册表。这使得开发者能够更自由地添加、删除或修改 BeanDefinition。这两个后处理器提供的灵活性,极大地增强了 Spring 的可扩展性和配置能力。
在接下来的内容中,我们将深入探讨这两个后处理器的工作原理、使用场景以及如何实现它们,以便更好地理解和利用 Spring 的强大功能。
Spring的后处理器
Spring的后处理器是Spring对外开发的重要扩展点,允许我们介入到Bean的整个实例化流程中来,以达到动态注册BeanDefinition,动态修改BeanDefinition,以及动态修改Bean的作用。Spring主要有两种后处理器:
- BeanFactoryPostProcessor:Bean工厂后处理器,在BeanDefinitionMap填充完毕,Bean实例化之前执行;
- BeanPostProcessor:Bean后处理器,一般在Bean实例化之后,填充到单例池singletonObjects之前执行。
Bean工厂后处理器-BeanFactoryPostProcessor
BeanFactoryPostProcessor是一个接口规范,实现了该接口的类只要交由Spring容器管理的话,那么Spring就会回调该接口的方法,用于对BeanDefinition注册和修改的功能。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor定义如下:
java
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory);
}
java
package com.itheima.processor;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("beanDefinitionMap填充完毕后回调该方法");
}
}
xml
<bean class="com.itheima.processor.MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor"></bean>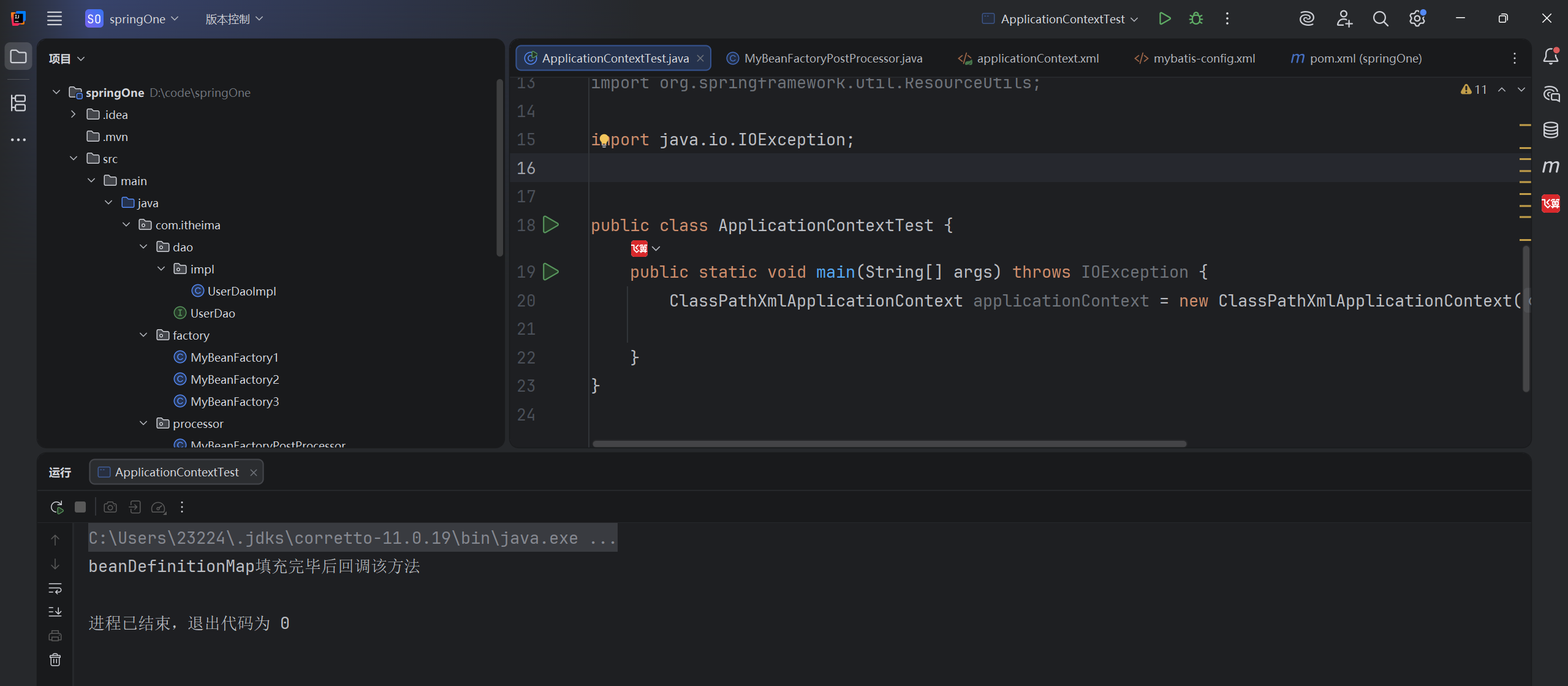
java
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("beanDefinitionMap填充完毕后回调该方法");
//修改某个BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("userService");
beanDefinition.setBeanClassName("com.itheima.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl");
}
}
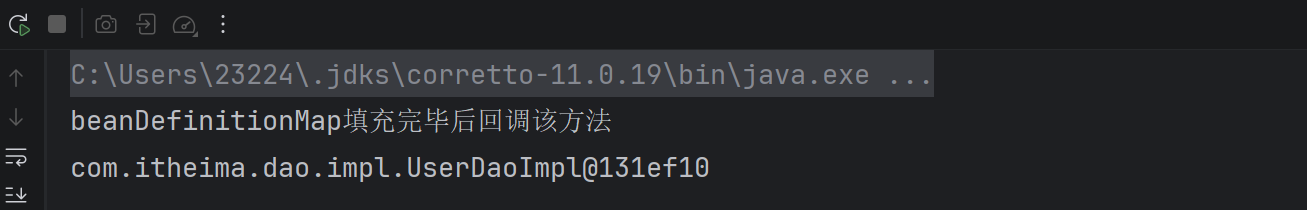
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml");
Object userService = applicationContext.getBean("userService");
System.out.println(userService);
}
创建接口Person和对应实现类PersonImpl
java
package com.itheima.processor;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition;
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("beanDefinitionMap填充完毕后回调该方法");
//动态注册某个BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClassName("com.itheima.dao.impl.PersonDaoImpl");
//强转成DefaultListableBeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory defaultListableBeanFactory = (DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory;
defaultListableBeanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("personDao", beanDefinition);
}
}动态注册 Bean 定义:
创建一个 RootBeanDefinition 实例,这个实例描述了要注册的 Bean 的信息。
使用 setBeanClassName 方法设置 Bean 的实现类为 PersonDaoImpl。
强转为 DefaultListableBeanFactory:由于 beanFactory 是接口类型,我们需要将其强制转换为 DefaultListableBeanFactory 以使用其中的方法。
注册 Bean 定义:通过 registerBeanDefinition 方法将新的 Bean 定义注册到 Spring 容器中,使用 "personDao" 作为 Bean 的名称。
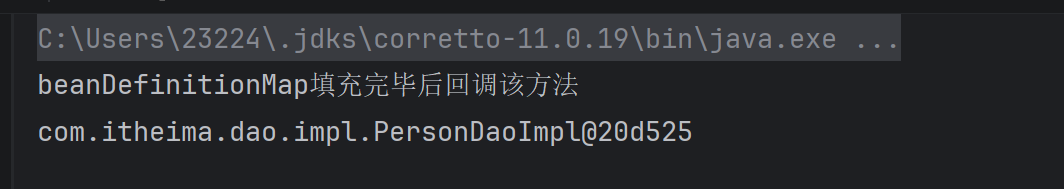
测试代码:
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml");
PersonDao bean = applicationContext.getBean(PersonDao.class);
System.out.println(bean);
}运行结果:
Spring提供了-个 BeanFactoryPostProcessort的子接口 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor专门用于注册BeanDefinition操作
java
package com.itheima.processor;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition;
public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry) throws BeansException {
//注册BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClassName("com.itheima.dao.impl.PersonDaoImpl");
beanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinition("personDao", beanDefinition);
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
}
}
xml
<bean class="com.itheima.processor.MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor"></bean>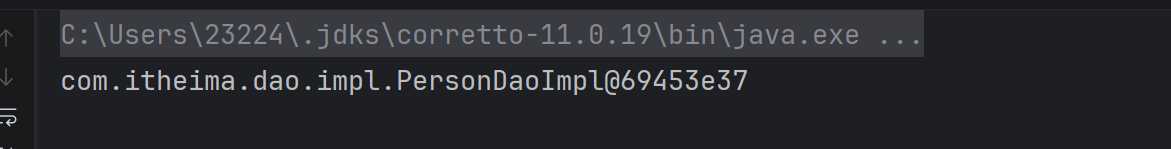
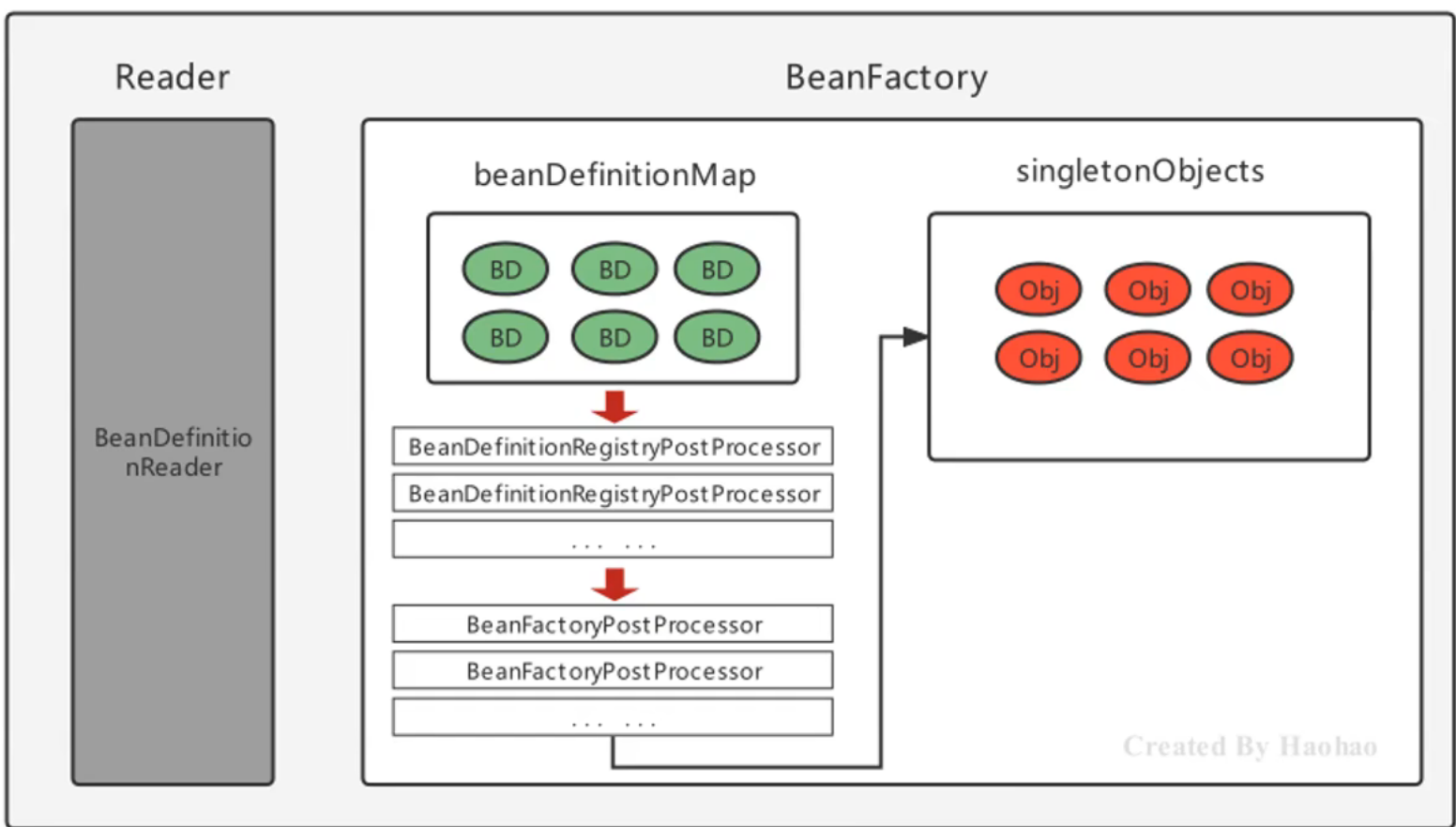
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 在SpringBean的实例化过程中的体现
使用Spring的BeanFactoryPostProcessor扩展点完成自定义注解扫描
- 自定义@MyComponent注解,使用在类上;
- 使用资料中提供好的包扫描器工具BaseClassScanUtils完成指定包的类扫描;
- 自定义BeanFactoryPostProcessor完成注解@MyComponent的解析,解析后最终被Spring管理。
java
package com.itheima.anno;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyComponent {
String value();
}- @Target(ElementType.TYPE):这个元注解指示 MyComponent 注解可以应用于类型(即类、接口或枚举)。它定义了注解的使用范围。
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME):此元注解指定 MyComponent 注解将在运行时保留,因此可以通过反射读取。常见的保留策略还有 SOURCE 和 CLASS,分别表示注解仅在源代码中存在和在编译后类文件中存在,但不在运行时可用。
- String value();:这是 MyComponent 注解的一个属性,表示注解的值。使用注解时,必须提供这个属性的值。这样设计可以让您为标记的类提供额外的信息。
java
package com.itheima.beans;
import com.itheima.anno.MyComponent;
@MyComponent("otherBean")
public class OtherBean {
}工具类BaseClassScanUtils扫描指定的包及其子包下的所有类,收集使用@MyComponent的类
java
package com.itheima.utils;
import com.itheima.anno.MyComponent;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.CachingMetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReader;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class BaseClassScanUtils {
//设置资源规则
private static final String RESOURCE_PATTERN = "/**/*.class";
public static Map<String, Class> scanMyComponentAnnotation(String basePackage) {
//创建容器存储使用了指定注解的Bean字节码对象
Map<String, Class> annotationClassMap = new HashMap<String, Class>();
//spring工具类,可以获取指定路径下的全部类
ResourcePatternResolver resourcePatternResolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
try {
String pattern = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX +
ClassUtils.convertClassNameToResourcePath(basePackage) + RESOURCE_PATTERN;
Resource[] resources = resourcePatternResolver.getResources(pattern);
//MetadataReader 的工厂类
MetadataReaderFactory refractory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory(resourcePatternResolver);
for (Resource resource : resources) {
//用于读取类信息
MetadataReader reader = refractory.getMetadataReader(resource);
//扫描到的class
String classname = reader.getClassMetadata().getClassName();
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(classname);
//判断是否属于指定的注解类型
if(clazz.isAnnotationPresent(MyComponent.class)){
//获得注解对象
MyComponent annotation = clazz.getAnnotation(MyComponent.class);
//获得属value属性值
String beanName = annotation.value();
//判断是否为""
if(beanName!=null&&!beanName.equals("")){
//存储到Map中去
annotationClassMap.put(beanName,clazz);
continue;
}
//如果没有为"",那就把当前类的类名作为beanName
annotationClassMap.put(clazz.getSimpleName(),clazz);
}
}
} catch (Exception exception) {
}
return annotationClassMap;
}
java
package com.itheima.processor;
import com.itheima.anno.MyComponent;
import com.itheima.utils.BaseClassScanUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition;
import java.util.Map;
public class MyComponentBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry) throws BeansException {
//通过扫描工具扫描指定的包及其子包下的所有类,收集使用@MyComponent的类
Map<String, Class> myComponentAnnotationMap = BaseClassScanUtils.scanMyComponentAnnotation("com.itheima");
//遍历map,组装BeanDefinition
myComponentAnnotationMap.forEach((beanName, clazz) -> {
//获得beanClassName
String beanClassName = clazz.getName();//com.itheima.beans.OtherBean
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClassName(beanClassName);
//注册
beanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
});
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
}
}
java
<bean class = "com.itheima.processor.MyComponentBeanFactoryPostProcessor"></bean>测试代码:
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml");
OtherBean bean = applicationContext.getBean(OtherBean.class);
System.out.println(bean);
}运行结果:
总结
通过对这两个后处理器的理解与运用,开发者可以更深入地掌握 Spring 框架的内在机制,充分发挥其强大的功能,提升开发效率与软件质量。希望本文能为您在 Spring 的学习与实践中提供帮助,让您在日后的项目中游刃有余!