一、sql是什么?
结构化查询语句。RDBMS中的通用的语句。比如:mysql、oracle、PG、mysql 等。
符合sql标准。
二、sql 常用种类
DDL 数据定义语言 create drop alter truncate。
查看方式 help data definition
DML 数据操作语言 insert delete update select
查看方式 help data manipulation
DCL 数据控制语言
查看方式 help account management
三、sql_mode
保证数据存储和应用的时候保证有效性。
比如说。
1、日期,常识中不能出现0年0月0日。2、除数不能为0。3、only_full_group_by
四、字符集
utf8(5.7必须改)最大可以存三字节的字符。 一个中文是3字节
utf8mb4(8.0默认是这个) 最大可以存4字节的字符。一个 emoji 表情4字节。五 校对规则(排序规则) collate
默认大小写不敏感(不区分大小写)
utf8mb4_0900_as_cs
六、数据类型
1、字符类型。
char (N) #定长字符串类型,不管存多少值预留空间。最多255字节。
varchar(65535) #变长的字符串类型,按需分配存储空间。额外分配1-2个字符存储字符长度。
enum
**设置字符长度时要注意。索引最大前缀3072字节。如果表是utf8的需要1024。所以varchar(1024)是最好在这个之内。如果是utf8mb4的则在768个字节以内。
#早期5.6支持索引最大前缀768字节。
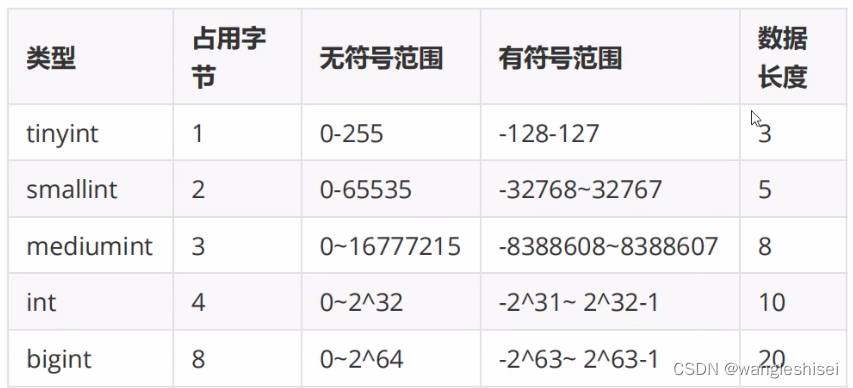
2、数字类型
tinyint #整数,占用字节0-255
int #整数,0-2的23次方-1
bigint #整数,0-2的64次方-1
#主机id,自增列最好用bigint
decimal #decima(6,2)表示总长度为6,小数位数占二位的数值。
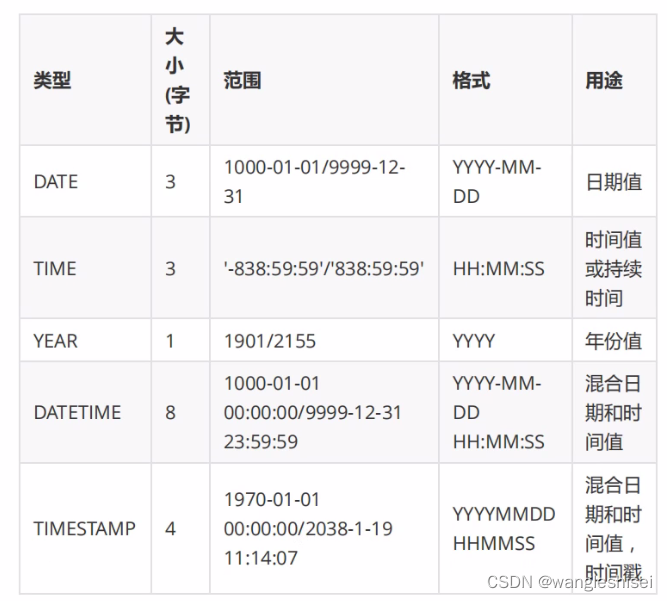
3、时间类型
4、json类型
直接添加 json
insert into test values('{"country":"CHN","region":"bj"}');
六、表约束和表属性。
PK ( primary key ) : 主键约束,非空且唯一,每个表只能有一个。
UK (unique): 唯一键约束,唯一的。
NN ( not ) : 非空,不能为空
auto_increment : 自增长。
default : 默认值。
comment :注释信息
unsigned :对于数字列设置无符号。
参考命令
create table c1(id bigint not null auto_increment primary key comment'id',name varchar(10) not null comment'姓名',sn int not null unique comment'sn');七、库定义。
创建表之后要建默认字符集。
生产环境建议配置文件客户端和服务端都添加+ character-set-server=utf8 #默认创建表为utf8.
set global character_set_server='utf8';
八、表定义
命令
create table #创建表
alter table #修改表
truncate #清空表
desc #查看表列信息
show create table; #查看建表语句。
添加索引
alter table test add index idx_name(name);
修改列属性。
alter table test modify sname varchar(200) not null comment'姓名';
添加列
alter table test add column cs varchar(10);
克隆表结构
create table abb like test;- 表明要有规范。不能大写字母,不能数字,不能和内置字符冲突,尽量表名开头cs_test.
- 显示设置engine charset collate
- 数据类型:选择合适的、简短的、足够的。
- 显示设置主键。如果自增id。使用bigint unsigned
- 每个列设置NN。可以适配 default(默认值)
- 每个列加注释 comment
修改表定义
创建表
create table test(id bigint not null auto_increment primary key comment'(id 列)');
添加列(建议用这条命令,不要用在某一列后面添加的命令。#加列 8.0之后就可以直接加了。8.0之前可以使用pt-osc,或者建议使用 这个 gh-ots)
alter table test add name varchar(150) not null comment'(姓名)';8.0之后直接在库上进行如下操作风险较小。
加列。 add column
加索引。 add index
数值从小变大varchar(10)---->varchar(30)。
8.0其他要避开业务繁忙期。或者使用pt-osc,gh-ost
删除列 alter table test drop a;
表数据操作
1、插入
insert into t1(id,name) values
(1,cheng),
(2,shuai),
(3,shuai);
2、删除
delete from t1 where id>1 and id <10;
#建议替换为伪删除。添加一行 为状态列。
特性:
delete 删除数据不会立即释放空间,HWM(水位)不会下降。
truncate ---> 删除空间数据会释放,表结构会保留。HWM(水位) 会下降。
drop --->表定义和数据都被清空,磁盘空间会释放。
3、修改
update t1 set name=cheng,time=10 where id=3;4、查找
select查询变量。
select @@server_id;
调用函数
select now();
select 配合其他字句应用。
语法
select *
from
where
group by
having
order by
limit;

查询语句 where条件
条件查询格式
1、like查询
select * from t1 where name like 'ch%';
#like 不要用'%%' 不走索引。
2、数字查询>
select * from t1 where id = 5;
可以使用 < > <= >= # != 不建议使用(不走索引)。
3、并且 或者
select * from t1 where id>5 and name like 'c%';
select * from t1 where id>5 or name like 'c%';
如果俩查询条件一样可以拆解为
select * from t1 where id name ('cc','bb');
和(优化语句)
select * from t1 where id='1'
union all
select * from t1 where id>'2';查询某个数据库里面所有的表信息。
select table_schema,table_name,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='world' group by table_schema,table_name;聚合函数
count() #查看行数
max()
min()
avg()
sum() #加和
group_concat() #两列合并成一列显示
having #不建议使用 后判断
select sum(id) from test group by cs having sum(id) > 3;group by 分组
select sum(id) from test group by cs having sum(id)> 1;order by 排序
倒序
select sum(id) from test group by cs having sum(id)> 1 order by sum(id) desc;
顺序
select sum(id) from test group by cs having sum(id)> 1 order by sum(id);limit
limit 5,6; 跳过5行显示后6行。
注意:limit 1000000,200 前面偏移量大。100w行影响性能太大。手动基于主键查出来在limit。jion 多表关联。
笛卡尔乘积。多表连接需要用到
for i in 9
for i in 9传统连接(很早的运维可能有这个习惯)
select * from a,b where a.id=b.aid;现在使用
内连接
select * from a inner jion b on a.id=b.aid;
左外连接(a 代表左边)
select * from a left jion b on a.id=b.aid;
功能:
1、左表所有数据+右表满足条件的数据。
2、left jion 可以强制左表为驱动表。(一般小表放在驱动表)
3、select * from a left jion b on a.id=b.aid where is null;