1. RAII
-
RAII (Resource Acquisition Is Initialization)是一种利用对象生命周期 来控制程序资源(如内存、文件句柄、网络连接、互斥量等等)的简单技术。
-
在对象构造时获取资源 ,接着控制对资源的访问使之在对象的生命周期内始终保持有效,最后在对象析构的时候释放资源。借此,我们实际上把管理一份资源的责任托管给了一个对象。这种做法有两大好处。
-
不需要显式地释放资源。
-
对象所需的资源在其生命期内始终保持有效。
-
-
智能指针 是 RAII 在 C++ 中的具体实现,专门用于管理动态内存,提供更高级的功能(如所有权转移、引用计数等)。
-
关系:智能指针是 RAII 的一种应用,而 RAII 是更广泛的设计思想。
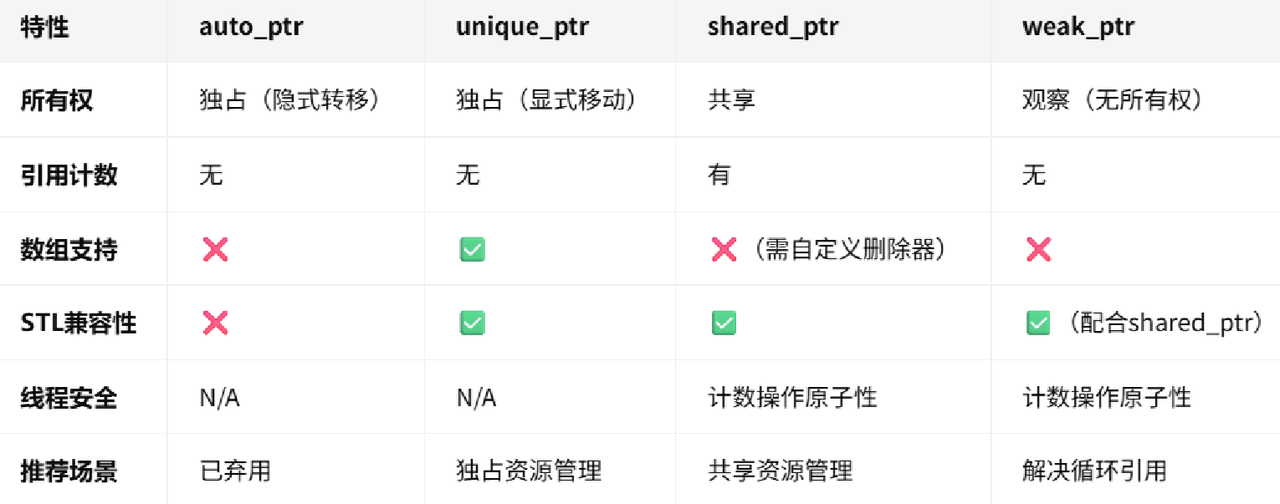
2. 发展历史
-
C++98 auto_ptr 管理权转移 ->不好的设计会出现对象悬空。
-
boost scoped_ptr 防拷贝->简单粗暴,对不需要拷贝的场景非常好。
-
boost shared_ptr 引用计数 ,最后一个释放对象资源->复杂一些,但是支持拷贝,非常完美->问题:循环引用。
-
C++11 unique_ptr 防拷贝->简单粗暴,对不需要拷贝的场景非常好。
-
C++11 shared_ptr 引用计数 ,最后一个释放对象资源->复杂一些,但是支持拷贝,非常完美->问题:循环引用。
-
C++11 weak_ptr 弱引用计数 ->仅观察对象,不影响对象生命周期->解决了循环引用( 如双向链表**)**。
3. auto_ptr
cpp
// C++98
// 管理权转移,最后一个拷贝对象管理资源,被拷贝对象都被置空
// 很多公司都明确规定了,不要用这个
template<class T>
class auto_ptr
{
public:
// RAII
auto_ptr(T* ptr)
:_ptr(ptr)
{}
~auto_ptr()
{
if (_ptr)
{
cout << "delete->" << _ptr << endl;
delete _ptr;
_ptr = nullptr;
}
}
// ap2(ap1)
auto_ptr(auto_ptr<T>& ap)
:_ptr(ap._ptr)
{
ap._ptr = nullptr;
}
T& operator*()
{
return *_ptr;
}
T* operator->()
{
return _ptr;
}
private:
T* _ptr;
};4. unique_ptr
cpp
template<class T>
class unique_ptr
{
public:
// RAII
unique_ptr(T* ptr)
:_ptr(ptr)
{}
~unique_ptr()
{
cout << "delete->" << _ptr << endl;
delete _ptr;
}
T& operator*()
{
return *_ptr;
}
T* operator->()
{
return _ptr;
}
// C++11
unique_ptr(const unique_ptr<T>& up) = delete;
unique_ptr<T>& operator=(const unique_ptr<T>& up) = delete;
private:
// C++98
// 1、只声明不实现
// 2、限定为私有
//unique_ptr(const unique_ptr<T>& up);
//unique_ptr<T>& operator=(const unique_ptr<T>& up);
private:
T* _ptr;
};5. shared_ptr
cpp
template<class T>
class shared_ptr
{
public:
// RAII
shared_ptr(T* ptr = nullptr)
:_ptr(ptr)
, _pcount(new int(1))
{}
template<class D>
shared_ptr(T* ptr, D del)
: _ptr(ptr)
, _pcount(new int(1))
, _del(del)
{}
// function<void(T*)> _del;
void release()
{
if (--(*_pcount) == 0)
{
//cout << "delete->" << _ptr << endl;
//delete _ptr;
_del(_ptr);
delete _pcount;
}
}
~shared_ptr()
{
release();
}
shared_ptr(const shared_ptr<T>& sp)
:_ptr(sp._ptr)
, _pcount(sp._pcount)
{
++(*_pcount);
}
// sp1 = sp3
shared_ptr<T>& operator=(const shared_ptr<T>& sp)
{
if (_ptr != sp._ptr)
{
release();
_ptr = sp._ptr;
_pcount = sp._pcount;
++(*_pcount);
}
return *this;
}
T& operator*()
{
return *_ptr;
}
T* operator->()
{
return _ptr;
}
int use_count() const
{
return *_pcount;
}
T* get() const
{
return _ptr;
}
private:
T* _ptr;
int* _pcount;
function<void(T*)> _del = [](T* ptr) {delete ptr; };
};6. weak_ptr
cpp
template<class T>
class weak_ptr
{
public:
weak_ptr()
:_ptr(nullptr)
{}
weak_ptr(const shared_ptr<T>& sp)
:_ptr(sp.get())
{}
weak_ptr<T>& operator=(const shared_ptr<T>& sp)
{
_ptr = sp.get();
return *this;
}
T& operator*()
{
return *_ptr;
}
T* operator->()
{
return _ptr;
}
private:
T* _ptr;
};7. 对比