- 导入与初始化
bash
from __future__ import unicode_literals, print_function, division # 确保Python 2/3兼容性
from io import open # 解决文件编码问题
import unicodedata # 处理Unicode字符
import string # 字符集操作
import re # 正则表达式
import random # 随机数生成
import torch # PyTorch核心库
import torch.nn as nn # 神经网络模块
from torch import optim # 优化器
import torch.nn.functional as F # 功能函数(如softmax)
# 设置设备(GPU优先,无GPU则用CPU)
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(device) # 输出当前设备(如 cuda:0 或 cpu)- 语言处理类(Lang)
bash
class Lang:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name # 语言名称(如 'eng')
self.word2index = {} # 词 -> 索引(如 "hello" -> 5)
self.word2count = {} # 词 -> 出现次数(用于构建词汇表)
self.index2word = {0: "SOS", 1: "EOS"} # 索引 -> 词(SOS=开始, EOS=结束)
self.n_words = 2 # 词汇表大小(初始包含SOS/EOS)
def addSentence(self, sentence):
# 将句子拆分为单词,逐个添加到词汇表
for word in sentence.split(' '):
self.addWord(word) # 调用addWord处理单个词
def addWord(self, word):
# 如果词不在词汇表中,添加并初始化计数
if word not in self.word2index:
self.word2index[word] = self.n_words
self.word2count[word] = 1
self.index2word[self.n_words] = word
self.n_words += 1
else:
self.word2count[word] += 1 # 已存在词,计数+1- 文本预处理函数
3.1 Unicode转ASCII
bash
def unicodeToAscii(s):
# 将Unicode字符(如 é)转为ASCII(如 e)
# unicodedata.normalize('NFD', s):分解字符(如 é -> e + ̌)
# category(c) != 'Mn':过滤掉非字母符号(如重音符号)
return ''.join(
c for c in unicodedata.normalize('NFD', s)
if unicodedata.category(c) != 'Mn'
)3.2 文本标准化
bash
def normalizeString(s):
# 1. 转小写 + 去前后空格
s = unicodeToAscii(s.lower().strip())
# 2. 用空格分隔标点(如 "Hello!" -> "Hello !")
s = re.sub(r"([.!?])", r" \1", s)
# 3. 移除非字母/标点字符(保留a-zA-Z.!?)
s = re.sub(r"[^a-zA-Z.!?]+", r" ", s)
return s- 数据加载与过滤
4.1 读取语料库
bash
def readLangs(lang1, lang2, reverse=False):
print("Reading lines...")
# 读取文件(如 'eng-fra.txt'),按行分割
lines = open('%s-%s.txt'%(lang1,lang2), encoding='utf-8').read().strip().split('\n')
# 每行按制表符分割成 [源语言, 目标语言]
pairs = [[normalizeString(s) for s in l.split('\t')] for l in lines]
# 创建语言对象(根据是否反转语言顺序)
if reverse:
pairs = [list(reversed(p)) for p in pairs] # 交换源/目标语言
input_lang = Lang(lang2) # 输入语言 = 目标语言
output_lang = Lang(lang1) # 输出语言 = 源语言
else:
input_lang = Lang(lang1) # 输入语言 = 源语言
output_lang = Lang(lang2) # 输出语言 = 目标语言
return input_lang, output_lang, pairs4.2 过滤语料
bash
MAX_LENGTH = 10 # 最大句子长度(超过则丢弃)
eng_prefixes = (
"i am ", "i m ",
"he is", "he s ",
"she is", "she s ",
"you are", "you re ",
"we are", "we re ",
"they are", "they re "
)
def filterPair(p):
# 条件1: 源句长度 < MAX_LENGTH
# 条件2: 目标句长度 < MAX_LENGTH
# 条件3: 目标句以指定前缀开头(如 "i am" -> "je suis")
return len(p[0].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and \
len(p[1].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and p[1].startswith(eng_prefixes)
def filterPairs(pairs):
return [pair for pair in pairs if filterPair(pair)] # 保留符合条件的pair4.3 数据预处理
bash
def prepareData(lang1, lang2, reverse=False):
input_lang, output_lang, pairs = readLangs(lang1, lang2, reverse)
print("Read %s sentence pairs" % len(pairs))
# 应用过滤器
pairs = filterPairs(pairs[:]) # [:] 防止修改原列表
print("Trimmed to %s sentence pairs" % len(pairs))
# 将所有句子添加到语言对象中(构建词汇表)
for pair in pairs:
input_lang.addSentence(pair[0]) # 源句
output_lang.addSentence(pair[1]) # 目标句
print("Counted words:")
print(input_lang.name, input_lang.n_words) # 源语言词汇量
print(output_lang.name, output_lang.n_words) # 目标语言词汇量
return input_lang, output_lang, pairs- 模型架构
5.1 编码器(EncoderRNN)
bash
class EncoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size):
super(EncoderRNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size # 隐藏层维度
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size) # 词嵌入层
self.gru = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size) # GRU单元(输入/输出维度=hidden_size)
def forward(self, input, hidden):
# 1. 词嵌入: [1] -> [1, hidden_size]
embedded = self.embedding(input).view(1, 1, -1) # 重塑为(batch=1, seq_len=1, hidden_size)
# 2. 通过GRU: 输出[1,1,hidden_size], 隐藏状态[1,1,hidden_size]
output, hidden = self.gru(embedded, hidden)
return output, hidden
def initHidden(self):
# 初始化隐藏状态(全0张量)
return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)5.2 注意力解码器(AttnDecoderRNN)
bash
class AttnDecoderRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size, dropout_p=0.1, max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
super(AttnDecoderRNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.output_size = output_size # 目标词汇表大小
self.dropout_p = dropout_p
self.max_length = max_length
# 层定义
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(self.output_size, self.hidden_size) # 目标词嵌入
self.attn = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size * 2, self.max_length) # 注意力权重计算
self.attn_combine = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size * 2, self.hidden_size) # 注意力加权后融合
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(self.dropout_p)
self.gru = nn.GRU(self.hidden_size, self.hidden_size)
self.out = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.output_size) # 输出层
def forward(self, input, hidden, encoder_outputs):
# 1. 词嵌入 + Dropout
embedded = self.embedding(input).view(1, 1, -1)
embedded = self.dropout(embedded)
# 2. 计算注意力权重
# 输入: [hidden_size] (当前隐藏状态) + [hidden_size] (嵌入词) -> [hidden_size*2]
# 通过self.attn -> [max_length] (每个编码器输出的权重)
attn_weights = F.softmax(self.attn(torch.cat((embedded[0], hidden[0]), 1)), dim=1)
# 3. 加权求和(用注意力权重加权编码器输出)
# attn_weights: [1, max_length] -> [1, 1, max_length]
# encoder_outputs: [max_length, hidden_size] -> [1, max_length, hidden_size]
attn_applied = torch.bmm(attn_weights.unsqueeze(0), encoder_outputs.unsqueeze(0)) # [1,1,hidden_size]
# 4. 融合嵌入词 + 注意力输出
output = torch.cat((embedded[0], attn_applied[0]), 1) # [1, hidden_size*2]
output = self.attn_combine(output).unsqueeze(0) # [1,1,hidden_size]
# 5. 通过GRU和输出层
output = F.relu(output)
output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden)
output = F.log_softmax(self.out(output[0]), dim=1) # [output_size]
return output, hidden, attn_weights # 注意力权重用于可视化
def initHidden(self):
return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device)- 数据转换函数
bash
def indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence):
# 将句子转为词汇索引列表(如 "hello world" -> [5, 12])
return [lang.word2index[word] for word in sentence.split(' ')]
def tensorFromSentence(lang, sentence):
# 1. 获取索引列表
indexes = indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence)
# 2. 添加EOS标记(结束符)
indexes.append(EOS_token)
# 3. 转为张量 (seq_len, 1) 用于批次处理
return torch.tensor(indexes, dtype=torch.long, device=device).view(-1, 1)
def tensorsFromPair(pair):
# 将pair转为编码器输入和解码器目标
input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, pair[0])
target_tensor = tensorFromSentence(output_lang, pair[1])
return (input_tensor, target_tensor)- 训练循环
7.1 单轮训练(含教师强制)
bash
teacher_forcing_ratio = 0.5 # 教师强制概率(50%用真实目标,50%用模型预测)
def train(input_tensor, target_tensor, encoder, decoder, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer, criterion, max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
# 1. 初始化编码器隐藏状态
encoder_hidden = encoder.initHidden()
# 2. 清空梯度
encoder_optimizer.zero_grad()
decoder_optimizer.zero_grad()
input_length = input_tensor.size(0) # 源句长度
target_length = target_tensor.size(0) # 目标句长度
# 3. 初始化编码器输出(全0张量)
encoder_outputs = torch.zeros(max_length, encoder.hidden_size, device=device)
loss = 0 # 累计损失
# 4. 编码器前向传播
for ei in range(input_length):
encoder_output, encoder_hidden = encoder(input_tensor[ei], encoder_hidden)
encoder_outputs[ei] = encoder_output[0, 0] # 保存每个时间步的输出
# 5. 解码器初始化
decoder_input = torch.tensor([[SOS_token]], device=device) # SOS作为初始输入
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden # 用编码器最终隐藏状态
# 6. 教师强制决策
use_teacher_forcing = True if random.random() < teacher_forcing_ratio else False
if use_teacher_forcing:
# 教师强制:用真实目标词作为下一轮输入
for di in range(target_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, _ = decoder(
decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs)
loss += criterion(decoder_output, target_tensor[di]) # 计算损失
decoder_input = target_tensor[di] # 下一轮输入 = 真实目标词
else:
# 无教师强制:用模型预测的词作为下一轮输入
for di in range(target_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, _ = decoder(
decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs)
loss += criterion(decoder_output, target_tensor[di])
# 获取预测词的索引(top1)
topv, topi = decoder_output.topk(1)
decoder_input = topi.squeeze().detach() # 丢弃梯度(不参与反向传播)
# 如果预测到EOS,提前结束
if decoder_input.item() == EOS_token:
break
# 7. 反向传播 + 优化
loss.backward()
encoder_optimizer.step()
decoder_optimizer.step()
return loss.item() / target_length # 平均损失7.2 训练迭代主循环
bash
def trainIters(encoder, decoder, n_iters, print_every=1000, plot_every=100, learning_rate=0.01):
start = time.time()
plot_losses = [] # 记录损失用于绘图
print_loss_total = 0
plot_loss_total = 0
# 初始化优化器(SGD)
encoder_optimizer = optim.SGD(encoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
decoder_optimizer = optim.SGD(decoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# 从语料库随机抽取n_iters个样本
training_pairs = [tensorsFromPair(random.choice(pairs)) for _ in range(n_iters)]
criterion = nn.NLLLoss() # 负对数似然损失(适合分类任务)
for iter in range(1, n_iters + 1):
training_pair = training_pairs[iter - 1]
input_tensor, target_tensor = training_pair
# 执行单轮训练
loss = train(input_tensor, target_tensor, encoder, decoder,
encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer, criterion)
# 累计损失
print_loss_total += loss
plot_loss_total += loss
# 每print_every轮打印损失
if iter % print_every == 0:
print_loss_avg = print_loss_total / print_every
print_loss_total = 0
print('%s (%d %d%%) %.4f' % (
timeSince(start, iter / n_iters), # 已用时间
iter, iter / n_iters * 100, # 进度百分比
print_loss_avg # 平均损失
))
# 每plot_every轮记录损失(用于绘图)
if iter % plot_every == 0:
plot_loss_avg = plot_loss_total / plot_every
plot_losses.append(plot_loss_avg)
plot_loss_total = 0
return plot_losses # 返回损失列表- 评估与可视化
8.1 评估函数
bash
def evaluate(encoder, decoder, sentence, max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
with torch.no_grad(): # 禁用梯度计算(评估时不需要)
input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, sentence)
input_length = input_tensor.size()[0]
# 初始化编码器
encoder_hidden = encoder.initHidden()
encoder_outputs = torch.zeros(max_length, encoder.hidden_size, device=device)
# 编码器前向
for ei in range(input_length):
encoder_output, encoder_hidden = encoder(input_tensor[ei], encoder_hidden)
encoder_outputs[ei] += encoder_output[0, 0] # 累加输出
# 解码器初始化
decoder_input = torch.tensor([[SOS_token]], device=device)
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden
decoded_words = [] # 保存预测词
decoder_attentions = torch.zeros(max_length, max_length) # 注意力权重矩阵
# 解码过程
for di in range(max_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder(
decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs)
# 记录注意力权重
decoder_attentions[di] = decoder_attention.data
topv, topi = decoder_output.data.topk(1) # 选最高概率词
# 如果预测到EOS,停止
if topi.item() == EOS_token:
decoded_words.append('<EOS>')
break
else:
decoded_words.append(output_lang.index2word[topi.item()])
decoder_input = topi.squeeze().detach() # 用预测词作为下一轮输入
return decoded_words, decoder_attentions[:di + 1] # 截断到实际长度8.2 随机评估
bash
def evaluateRandomly(encoder, decoder, n=5):
for i in range(n):
pair = random.choice(pairs)
print('>', pair[0]) # 源句
print('=', pair[1]) # 真实目标
output_words, _ = evaluate(encoder, decoder, pair[0])
output_sentence = ' '.join(output_words)
print('<', output_sentence) # 预测结果- 模型训练与评估
bash
# 模型参数
hidden_size = 256
encoder1 = EncoderRNN(input_lang.n_words, hidden_size).to(device)
attn_decoder1 = AttnDecoderRNN(hidden_size, output_lang.n_words, dropout_p=0.1).to(device)
# 训练10000轮
plot_losses = trainIters(encoder1, attn_decoder1, 10000, print_every=5000)
# 随机评估5个样本
evaluateRandomly(encoder1, attn_decoder1)
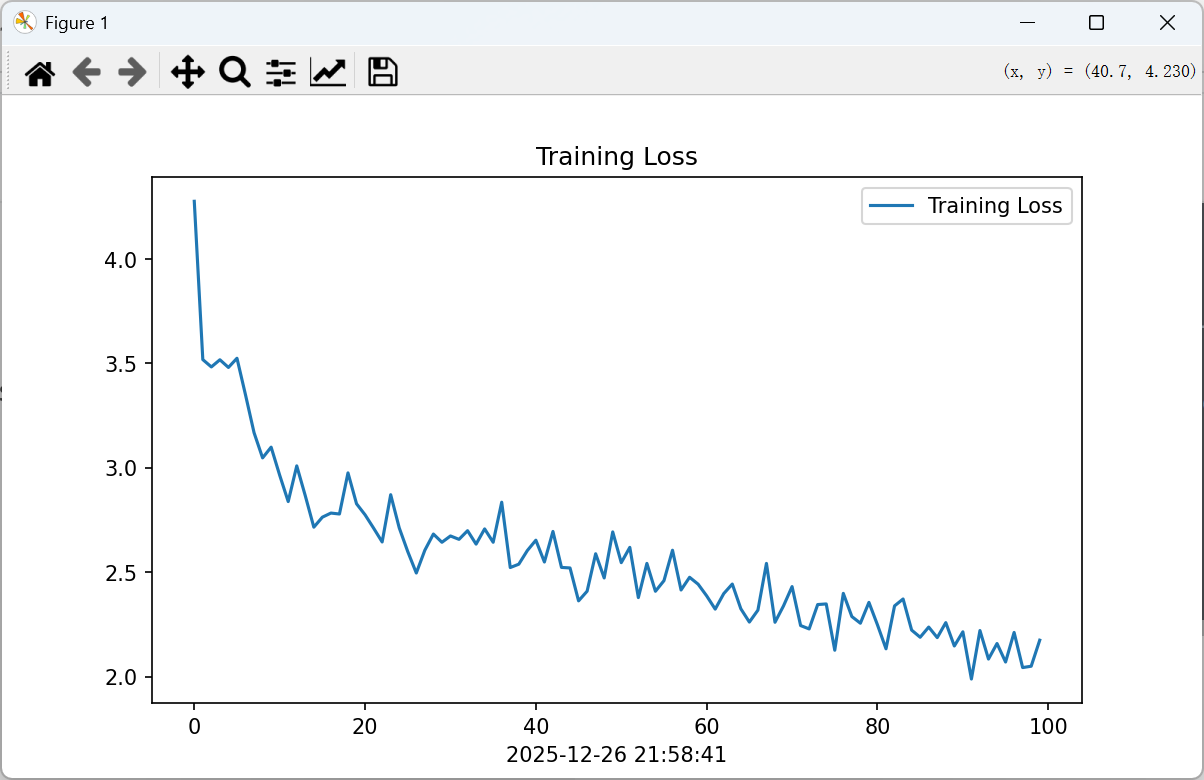
# 保存训练损失图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") # 忽略警告
# 设置中文显示(可选)
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 绘制损失曲线
epochs_range = range(len(plot_losses))
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 3))
plt.plot(epochs_range, plot_losses, label='Training Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.title('Training Loss')
plt.xlabel(datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')) # 当前时间
plt.show()