一、先明确 SDPA 的核心原理
SDPA 是 Transformer 注意力机制的核心,公式如下:
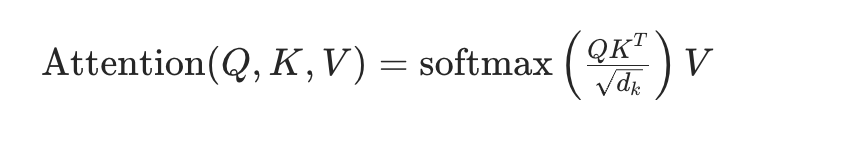
关键要素:
- 缩放(Scaled):除以(\sqrt{d_k})((d_k)是每个 head 的维度),避免(QK^T)数值过大导致 softmax 饱和;
- 点积(Dot-Product):Q 和 K 的转置做点积,计算注意力分数;
- 掩码(Mask):支持 padding 掩码 / 因果掩码,过滤无效 token 或未来 token;
- Softmax:将注意力分数归一化为概率分布;
- 加权求和:用归一化的分数对 V 加权,得到上下文感知的输出。
二、手动实现 SDPA(理解核心逻辑)
以下是纯 PyTorch 手动实现的 SDPA,包含缩放、注意力掩码、因果掩码核心逻辑,注释详细且适配新手理解:
python
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
def scaled_dot_product_attention_manual(
q: torch.Tensor,
k: torch.Tensor,
v: torch.Tensor,
attn_mask: torch.Tensor = None, # padding掩码:[batch_size, seq_len_q, seq_len_k]
is_causal: bool = False, # 是否启用因果掩码(下三角)
dropout_p: float = 0.0 # dropout概率
) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
手动实现SDPA,参数与PyTorch原生API对齐
参数说明:
- q: [batch_size, num_heads, seq_len_q, head_dim] 查询向量
- k: [batch_size, num_heads, seq_len_k, head_dim] 键向量
- v: [batch_size, num_heads, seq_len_k, head_dim] 值向量
- attn_mask: 注意力掩码(0=有效,-inf=无效),None则无掩码
- is_causal: 是否启用因果掩码(仅看前文)
- dropout_p: dropout概率,0则不使用
"""
# 1. 获取head_dim,计算缩放因子
head_dim = q.size(-1)
scale = torch.sqrt(torch.tensor(head_dim, dtype=torch.float32))
# 2. 计算QK^T(点积)并缩放
# Q: [bs, n_head, len_q, d_k] → K^T: [bs, n_head, d_k, len_k] → attn_scores: [bs, n_head, len_q, len_k]
attn_scores = torch.matmul(q, k.transpose(-2, -1)) / scale
# 3. 应用因果掩码(如果启用)
if is_causal:
# 生成下三角因果掩码:len_q × len_k,未来位置设为-∞
causal_mask = torch.tril(torch.ones(q.size(-2), k.size(-2), dtype=torch.bool)).to(q.device)
attn_scores = attn_scores.masked_fill(~causal_mask, float('-inf'))
# 4. 应用注意力掩码(padding掩码/自定义掩码)
if attn_mask is not None:
# 适配掩码维度:如果是2D([bs, len_k]),扩展为4D([bs, 1, 1, len_k])
if attn_mask.dim() == 2:
attn_mask = attn_mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2) # [bs, 1, 1, len_k]
attn_scores = attn_scores + attn_mask # 无效位置(-inf)叠加
# 5. Softmax归一化,得到注意力权重
attn_weights = F.softmax(attn_scores, dim=-1)
# 6. 应用dropout(可选)
if dropout_p > 0.0:
attn_weights = F.dropout(attn_weights, p=dropout_p)
# 7. 加权求和V,得到最终注意力输出
attn_output = torch.matmul(attn_weights, v) # [bs, n_head, len_q, d_k]
return attn_output手动实现的测试示例(模拟 Qwen3 单 head 场景)
python
# 模拟Qwen3-7B的单head输入:batch_size=1,num_heads=1,seq_len=5,head_dim=128
bs, n_head, seq_len, head_dim = 1, 1, 5, 128
q = torch.randn(bs, n_head, seq_len, head_dim).to("cuda")
k = torch.randn(bs, n_head, seq_len, head_dim).to("cuda")
v = torch.randn(bs, n_head, seq_len, head_dim).to("cuda")
# 测试1:启用因果掩码(模拟自回归生成)
output_causal = scaled_dot_product_attention_manual(q, k, v, is_causal=True)
print("因果掩码输出形状:", output_causal.shape) # torch.Size([1, 1, 5, 128])
# 测试2:添加padding掩码(模拟批量输入)
padding_mask = torch.tensor([[1,1,1,0,0]]).to("cuda") # 后2个token是padding
padding_mask = padding_mask.masked_fill(padding_mask == 0, float('-inf')) # 0→-inf
output_padding = scaled_dot_product_attention_manual(q, k, v, attn_mask=padding_mask)
print("Padding掩码输出形状:", output_padding.shape) # torch.Size([1, 1, 5, 128])mask作用
mask主要是屏蔽掉attention矩阵无效的权重,
- 比如说padding值(attention_mask得来)
- 防止前面的字符看到后面字符的值(casual_mask矩阵得来)
