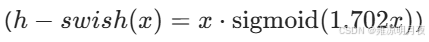轻量化网络的概述
共性目标:
**工业标准:**准,便宜,快,稳
**准确率:**残差基本上解决了ACC准确率的问题
**便宜:**模型小,运行速度快,占用内存也要少【轻量化】
实现轻量化模型的手段:
1.模型层数少。
2.多用1x1和3x3卷积,空间可分离,分组卷积,深度可分离卷积 + 1x1卷积 (我们用DW卷积深度可分离卷积)
3.残差
4.牺牲精度,获取速度。
总之一句话:在保证精度的前提下,通过降低计算量和参数量,适配移动端 / 嵌入式设备
MobileNet
MobileNet 是谷歌提出的移动端专用轻量级网络,三个版本迭代核心是在轻量化基础上持续提升精度和速度。
1.MobileNet V1:
核心创新 ------ 深度可分离卷积
普通卷积:同时完成通道融合和空间特征提取,计算量巨大。
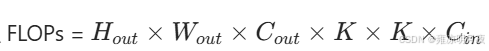
K是卷积核的大小,C_in/C_out是输入输出的通道数。
深度可分离卷积: MobileNet V1就是将其拆分为两步卷积:

代码实现:
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class DepthwiseSeparableConv(nn.Module):
"""深度可分离卷积模块(MobileNet V1核心)"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1):
super().__init__()
# 1. 深度卷积:groups=in_channels,保证每个通道独立卷积
self.depthwise = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=in_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
groups=in_channels # 分组卷积的极致:每组1个通道
)
# 2. 逐点卷积:1x1卷积融合通道
self.pointwise = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels=in_channels,
out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0
)
# 标配BN+ReLU
self.bn_dw = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels)
self.bn_pw = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
def forward(self, x):
# DW -> BN -> ReLU -> PW -> BN -> ReLU
x = self.relu(self.bn_dw(self.depthwise(x)))
x = self.relu(self.bn_pw(self.pointwise(x)))
return x
# 测试模块
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.randn(2, 64, 32, 32) # batch_size=2, 通道=64, 特征图=32x32
conv_dw_pw = DepthwiseSeparableConv(64, 128)
out = conv_dw_pw(x)
print(f"输入shape: {x.shape}, 输出shape: {out.shape}") # 输出应为 [2, 128, 32, 32]局限性
- 深度卷积的卷积核数量少,提取特征能力弱,精度略低于标准卷积网络
- 没有残差连接,网络深度受限
2.MobileNet V2⭐:
核心创新 ------逆残差 + 线性瓶颈
- 逆残差(Inverted Residual)
- 传统残差(ResNet):降维→卷积→升维(通道先减后增)
- 逆残差:升维→卷积→降维(通道先增后减)
- 原因:轻量级网络通道数少,先升维可以增加特征多样性,提升卷积的表达能力
- 线性瓶颈(Linear Bottleneck)
- 传统卷积后用ReLU6(ReLU 的变种,限制输出最大为 6,适配移动端量化)
- 但 ReLU 在低维空间会破坏特征(信息丢失),因此在逐点卷积降维后用线性激活代替 ReLU
代码实现:
python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project :Pytorch
@File :MobileNet V2.py
@IDE :PyCharm
@Author :wjj
@Date :2025/12/28 13:49
@Description:MobileNet V2
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class InvertedResidual(nn.Module):
"""MobileNet V2 逆残差块"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride,expend_ratio=6):
super(InvertedResidual, self).__init__()
self.stride = stride
self.expend_ratio = expend_ratio
#使用 assert 确保 stride 只能是 1 或 2,保证特征图不变/下采样
#避免更大步幅导致特征信息丢失过多
assert stride in [1, 2], "stride must be 1 or 2"
#升维后的隐藏通道数
hidden_dim = in_channels * expend_ratio
"""
残差连接生效条件(两个条件必须同时满足)
1.stride == 1:特征图的宽、高尺寸不变(步幅 2 会导致尺寸减半,无法直接逐元素相加)。
2.in_channels == out_channels:输入与输出的通道数一致(通道数不同无法直接逐元素相加).
"""
self.use_res_connect = self.stride == 1 and in_channels == out_channels # 是否用残差连接
#升维
self.pw1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, hidden_dim, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim)
self.relu6 = nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
#深度卷积
self.dw = nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, kernel_size=3, stride=1, groups=hidden_dim, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim)
#逐点卷积 降维+线性瓶颈
self.pw2 = nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, out_channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.pw1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu6(out)
out = self.dw(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu6(out)
out = self.pw2(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.use_res_connect:
out = out + x
return out
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.randn(2, 32, 64, 64)
block = InvertedResidual(32, 16, stride=1, expend_ratio=6)
out = block(x)
print(f"输入shape: {x.shape}, 输出shape: {out.shape}") # stride=1时shape不变3.MobileNet V3:
核心创新:NAS 搜索 + SE 注意力 + h3. 改进
- NAS 搜索:用强化学习搜索最优的网络结构和参数(如 expand_ratio、stride)
- 嵌入 SE 注意力:在逆残差块中加入轻量级通道注意力(SE 模块),提升精度
- 改进激活函数 :用 h-swish 代替 ReLU6,精度更高且量化友好
4.尾部结构优化:去除冗余的卷积层,用全局平均池化(GAP)直接接全连接层
代码实例:
python
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Project :Pytorch
@File :MobileNet V3.py
@IDE :PyCharm
@Author :wjj
@Date :2025/12/28 14:12
@Description:SE 模块 + h-swish
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class SEModule(nn.Module):
"""轻量级通道注意力:SE模块(适配MobileNet V3)"""
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=4):
super(SEModule, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(channel, channel // reduction, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(channel // reduction, channel, bias=False),
nn.Hardsigmoid(inplace=True) # 量化友好,代替sigmoid
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c)
y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
return x * y
class h_swish(nn.Module):
"""h-swish激活函数"""
def forward(self, x):
# 移除F.hardsigmoid的inplace=True,解决兼容性问题
return x * F.hardsigmoid(x)
class InvertedResidualV3(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,in_channels, out_channels, stride, expand_ratio, use_se=True):
super(InvertedResidualV3, self).__init__()
# 倒残差先升维度再卷积再降维度
hidden_dim = in_channels * expand_ratio
self.use_res_connect = stride == 1 and in_channels == out_channels
self.use_se = use_se # 保留布尔标记,不被覆盖
# 1×1 逐点卷积(PW1,升维):stride固定为1,仅负责通道扩充
self.pw1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, hidden_dim, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim)
self.act = h_swish()
# 3x3深度卷积(DW,空间特征提取):stride使用外部传入值,负责空间尺寸变换
self.dw = nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, 3, stride, 1, groups=hidden_dim, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(hidden_dim)
# SE模块实例化为self.se,保留self.use_se布尔标记
if self.use_se:
self.se = SEModule(hidden_dim) # 加入SE注意力
# 1×1 逐点卷积(PW2,降维 / 线性瓶颈):stride固定为1,仅负责通道压缩
self.pw2 = nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.act(self.bn1(self.pw1(x)))
out = self.act(self.bn2(self.dw(out)))
# 调用实例化的self.se模块
if self.use_se:
out = self.se(out)
out = self.bn3(self.pw2(out))
if self.use_res_connect:
out = out + x
return out
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.randn(2, 32, 64, 64)
block = InvertedResidualV3(32, 16, stride=1, expand_ratio=6, use_se=True)
out = block(x)
print(f"输入shape: {x.shape}, 输出shape: {out.shape}")4.V1 vs V2 vs V3
| 版本 | 核心创新 | 计算量 | 精度 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1 | 深度可分离卷积 | 最小 | 最低 | 极致轻量化场景(如单片机) |
| V2 | 逆残差 + 线性瓶颈 | 中等 | 中等 | 移动端通用场景(如手机 APP) |
| V3 | NAS+SE 注意力 + h-swish | 略高于 V1 | 最高 | 对精度有要求的移动端场景(如实时检测) |
ShuffleNet
ShuffleNet 是旷视提出的轻量级网络,核心思路是分组卷积 + 通道洗牌,解决分组卷积的通道隔离问题。
1.ShuffleNet V1:
核心创新 ------ 分组卷积 + 通道洗牌
背景:
分组卷积(Group Conv)可以降低计算量,但会导致通道间信息隔离(不同组的通道互不交流),降低精度。
核心改进:
- 分组逐点卷积:将 1x1卷积分组,进一步降低计算量
- 通道洗牌(Channel Shuffle):打乱分组后的通道顺序,实现跨组信息交流
通道洗牌原理:
- 输入:g 个组,每组 c 个通道 → 总通道数 gc
- 步骤 1:将通道维度 reshape 为 (g, c)
- 步骤 2:转置为 (c, g)
- 步骤 3:flatten 为 gc 个通道 → 完成洗牌
代码实现:
python
def channel_shuffle(x, groups):
"""通道洗牌函数"""
b, c, h, w = x.size()
assert c % groups == 0, "通道数必须能被组数整除"
return x.view(b, groups, c//groups, h, w).permute(0, 2, 1, 3, 4).reshape(b, c, h, w)
class ShuffleBlockV1(nn.Module):
"""ShuffleNet V1 残差块"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride, groups=3):
super().__init__()
self.stride = stride
mid_channels = out_channels // 4 # 瓶颈层通道数
self.groups = groups
if stride == 2:
# 步幅为2时,用深度卷积下采样+拼接代替残差连接
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, 3, stride, 1, groups=in_channels, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, mid_channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
in_channels = mid_channels
else:
self.branch1 = nn.Identity() # 步幅为1时,分支1直接传递
# 分支2:分组卷积+通道洗牌
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, mid_channels, 1, 1, 0, groups=groups, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, mid_channels, 3, stride, 1, groups=mid_channels, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels),
nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, mid_channels, 1, 1, 0, groups=groups, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
out1 = self.branch1(x)
out2 = self.branch2(x if self.stride == 1 else out1)
out = torch.cat([out1, out2], dim=1) # 拼接
out = channel_shuffle(out, self.groups) # 通道洗牌
return out
# 测试
if __name__ == "__main__":
x = torch.randn(2, 24, 64, 64)
block = ShuffleBlockV1(24, 48, stride=2, groups=3)
out = block(x)
print(f"输入shape: {x.shape}, 输出shape: {out.shape}")2.ShuffleNet V2⭐:
核心创新 ------4 个高效设计原则
- 同等通道数:输入输出通道数相等时,分组卷积计算量最小
- 减少分组数:分组数过多会增加内存访问开销
- 减少碎片化:避免过多的小分支(如 GoogLeNet 的 Inception),降低并行计算难度
- 降低元素级操作:减少 ReLU、Add 等逐元素操作的数量
代码实践:
python
class ShuffleBlockV2(nn.Module):
"""ShuffleNet V2 残差块:通道拆分代替分组卷积"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride):
super().__init__()
self.stride = stride
assert stride in [1, 2]
mid_channels = out_channels // 2
if stride == 2:
# 步幅2:两路都卷积+拼接
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, 3, stride, 1, groups=in_channels, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, mid_channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, mid_channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, mid_channels, 3, stride, 1, groups=mid_channels, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels),
nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, mid_channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
else:
# 步幅1:通道拆分为两路,一路直接传递
assert in_channels == out_channels
self.branch1 = nn.Identity()
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, mid_channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, mid_channels, 3, stride, 1, groups=mid_channels, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels),
nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, mid_channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
def forward(self, x):
if self.stride == 1:
x1, x2 = x.chunk(2, dim=1) # 通道拆分
out = torch.cat([x1, self.branch2(x2)], dim=1)
else:
out = torch.cat([self.branch1(x), self.branch2(x)], dim=1)
out = channel_shuffle(out, 2) # 固定分组数2
return out| 版本 | 核心创新 | 计算效率 | 精度 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1 | 分组卷积 + 通道洗牌 | 高 | 中等 | 分组数可调,灵活度高 |
| V2 | 4 条高效原则 + 通道拆分 | 更高 | 更高 | 实际推理速度快,移动端首选 |