FastAPI是一个基于Python的高性能Web框架,用于快速构建API接口服务。FastAPI带有原生的异步支持,具备极高的性能。
1.框架基础使用
1.1 创建FastAPI项目
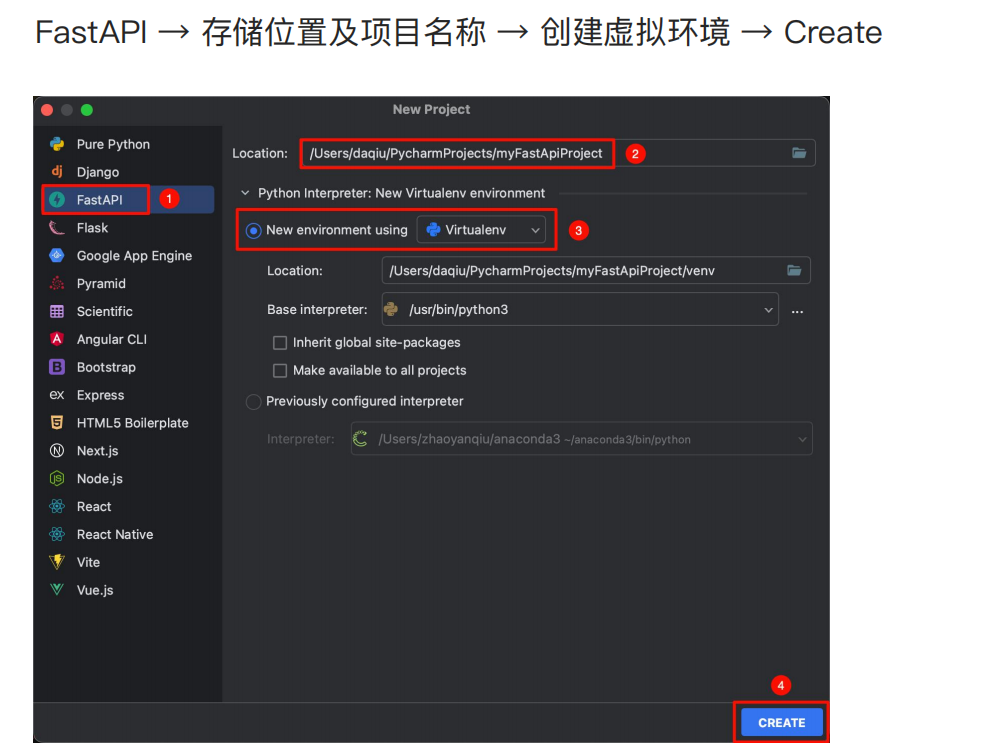
创建虚拟环境是为了隔离项目运行环境,避免依赖冲突,保持全局环境的干净与稳定。
项目运行:
方式一:run项目
方式二:运行指令:uvicorn 模块名:app(应用实例名) --reload ( --reload:更改代码后自动重启服务器)
访问交互式文档:
1.2 路由
路由就是URL地址与处理函数之间的映射关系,它决定了用户访问某个特定网址时,服务器应执行哪个后端接口来返回响应结果。
FastAPI的路由定义基于Python的装饰器模式:

实例:
python
from fastapi import FastAPI
# 创建 FastAPI 实例
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/lgh")
async def get_lgh():
return {"data":"你好 吕贵浩"}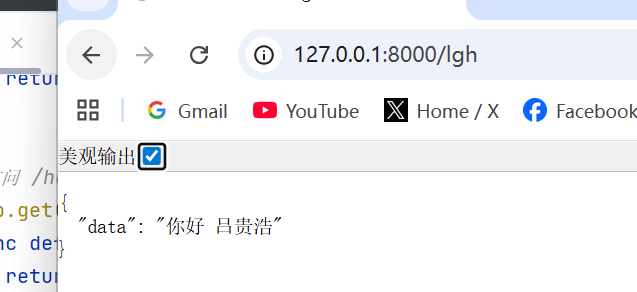
1.3 参数
参数就是客户端发送请求时附带的额外信息和指令,参数的作用就是让同一个接口能根据不同的输入,返回不同的输出,实现动态交互。同一段接口逻辑,根据参数不同返回不同的数据。

1.3.1 路径参数
FastAPI允许为参数声明额外的信息和校验,通过导入FastAPI的Path函数实现。
python
from fastapi import FastAPI, Path
app = FastAPI()
# 需求:查找书籍的详情,路径参数 id,取值范围 1-100
@app.get("/book/{id}")
async def get_book(id: int = Path(..., gt=0, lt=101,
description="书籍id,取值范围1-100")):
return {"id": id, "title": f"这是第{id}本书"}
# 需求:查找书籍的作者,路径参数 name,长度范围 2-10
@app.get("/author/{name}")
async def get_name(name: str = Path(..., min_length=2, max_length=10)):
return {"msg": f"这是{name}的信息"}1.3.2 查询参数
声明的参数不是路径参数时,路径操作函数会将该参数自动解释为查询参数。是同Query函数实现查询参数补充操作。
python
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
# 需求 查询新闻 → 分页,skip: 跳过的记录数, limit:返回的记录数 10
@app.get("/news/news_list")
async def get_news_list(
skip: int = Query(0, description="跳过的记录数", lt=100),
limit: int = Query(10, description="返回的记录数")
):
return {"skip": skip, "limit": limit}1.3.3 请求体参数
创建类型并设计接口,借助Field添加类型注解。
python
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
app = FastAPI()
# 注册: 用户名和密码 → str
class User(BaseModel):
username: str = Field(default="张三", min_length=2,
max_length=10, description="用户名,长度要求2-10个字")
password: str = Field(min_length=3, max_length=20)
@app.post("/register")
async def register(user: User):
return user1.4 请求与响应
1.4.1 响应类型
默认情况下,FastAPI 会自动将路径操作函数返回的 Python 对象(字典、列表、Pydantic 模型等),经由 jsonable_encoder 转换为 JSON 兼容格式,并包装为 JSONResponse 返回。这省去了手动序列化的步骤,让开发者能更专注于业务逻辑。如果需要返回非 JSON 数据(如 HTML、文件流),FastAPI 提供了丰富的响应类型来返回不同数据。

1.4.2 相应类型设置方式

HTML格式:
python
from fastapi import FastAPI
from fastapi.responses import HTMLResponse
app = FastAPI()
# 接口 → 响应 HTML 代码
@app.get("/html", response_class=HTMLResponse)
async def get_html():
return "<h1>这是一级标题</h1>"文件格式:
python
from fastapi import FastAPI
from fastapi.responses import FileResponse
app = FastAPI()
# 接口: 返回一张图片内容
@app.get("/file")
async def get_file():
path = "./files/1.jpeg"
return FileResponse(path)自定义响应数据格式:
python
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
# 需求:新闻接口 → 响应数据格式 id、title、content
class News(BaseModel):
id: int
title: str
content: str
@app.get("/news/{id}", response_model=News)
async def get_news(id: int):
return {
"id": id,
"title": f"这是第{id}本书",
"content": "这是一本好书"
}response_model是路径操作装饰器(如@app.get或@app.post)的关键参数,它通过一个Pydantic模型来严格定义和约束API端点的输出格式。这一机制在提供自动数据验证和序列化的同时,更是保障数据安全性的第一道防线。
1.5 异常处理
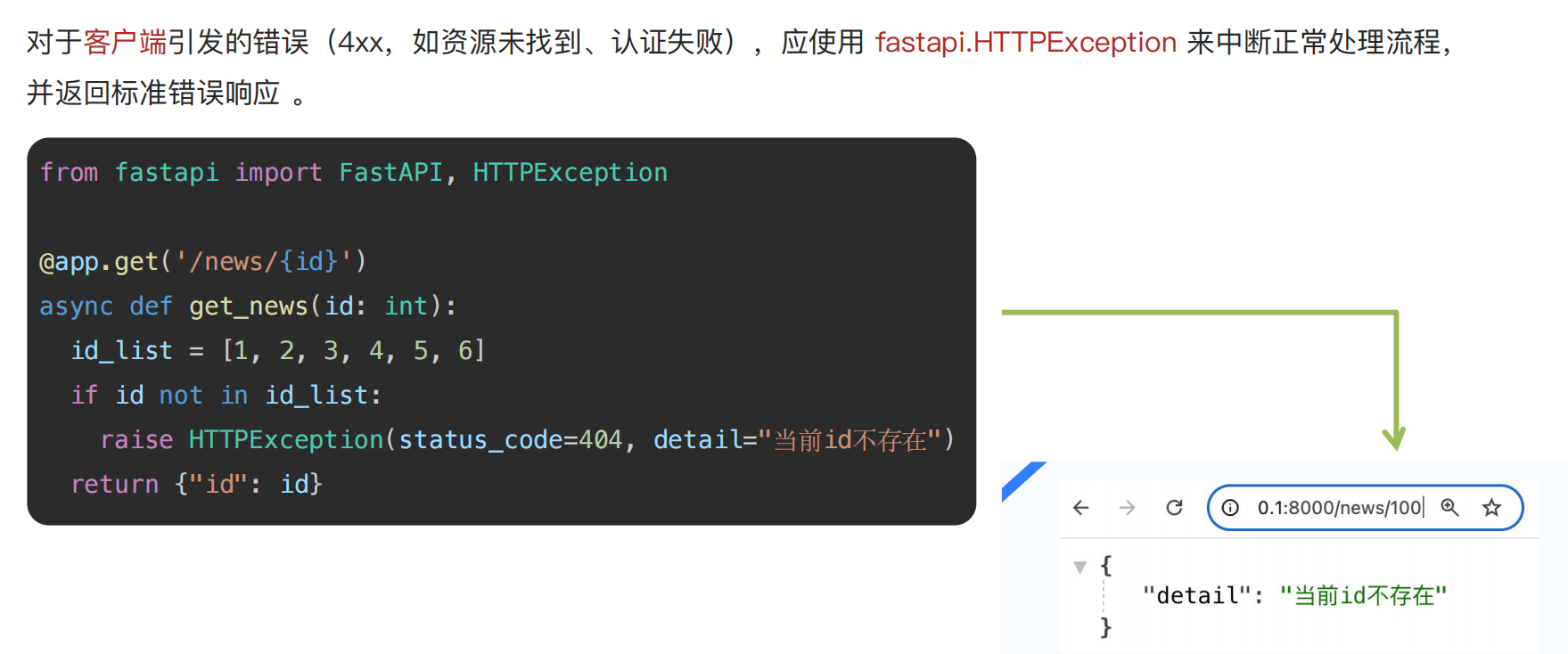
2.引入中间件与依赖注入
2.1 中间件
中间件(Middleware)是一个在每次请求进入 FastAPI 应用时都会被执行的函数。它在请求到达实际的路径操作(路由处理函数)之前运行,并且在响应返回给客户端之前再运行一次。
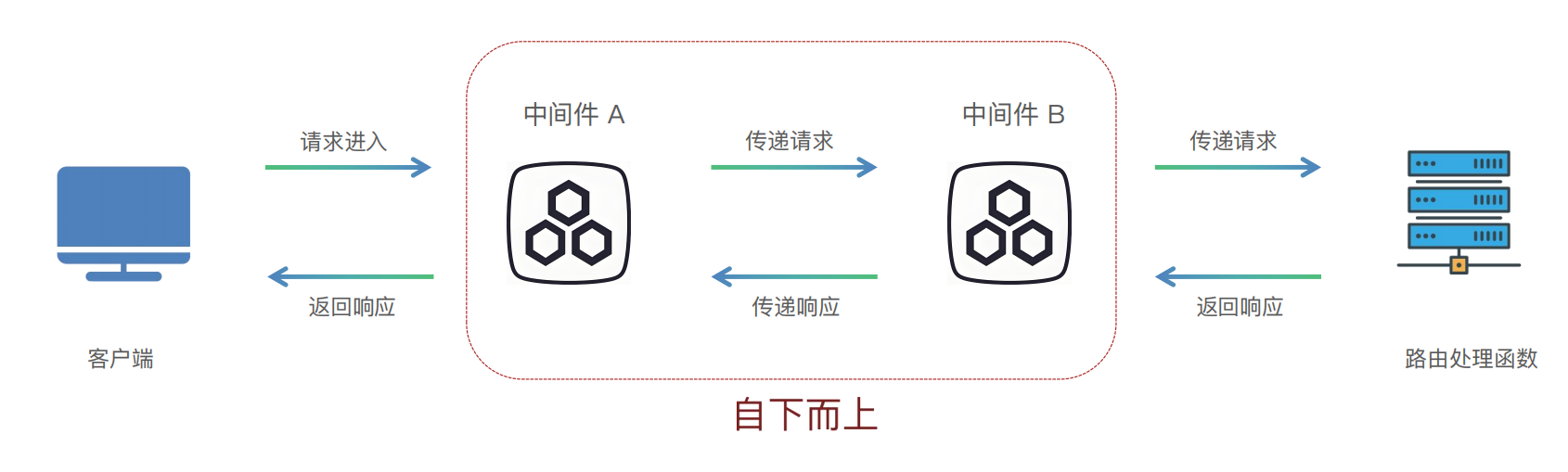
中间件:函数顶部使用装饰器@app.middleware("http"),多个中间件的执行顺序是自下而上。
python
@app.middleware("http")
async def middleware2(request, call_next):
print("中间件2 start")
response = await call_next(request)
print("中间件2 end")
return response
@app.middleware("http")
async def middleware1(request, call_next):
print("中间件1 start")
response = await call_next(request)
print("中间件1 end")
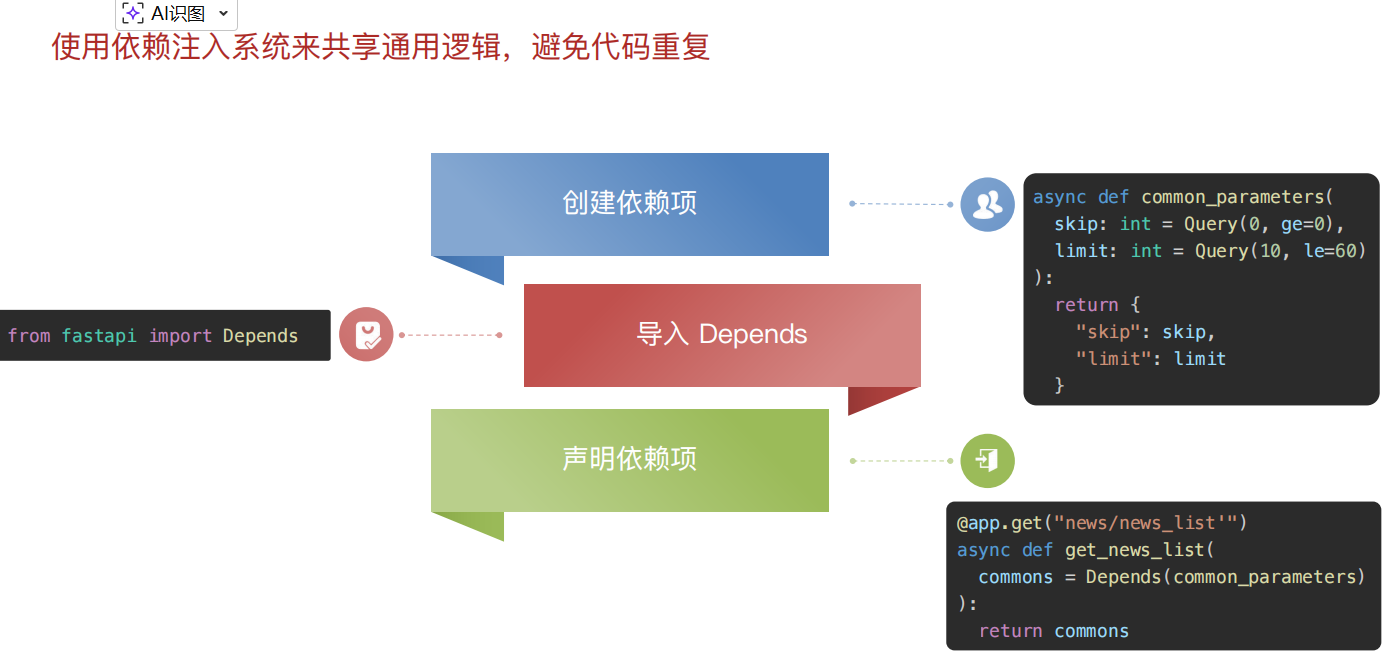
return response2.2 依赖注入
使用依赖注入系统来共享通用逻辑,减少代码重复
python
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query, Depends # 2. 导入 Depends
app = FastAPI()
# 分页参数逻辑共用: 新闻列表和用户列表
# 1. 依赖项
async def common_parameters(
skip: int = Query(0, ge=0),
limit: int = Query(10, le=60)
):
return {"skip": skip, "limit": limit}
# 3. 声明依赖项 → 依赖注入
@app.get("/news/news_list")
async def get_news_list(commons=Depends(common_parameters)):
return commons
@app.get("/user/user_list")
async def get_user_list(commons=Depends(common_parameters)):
return commons
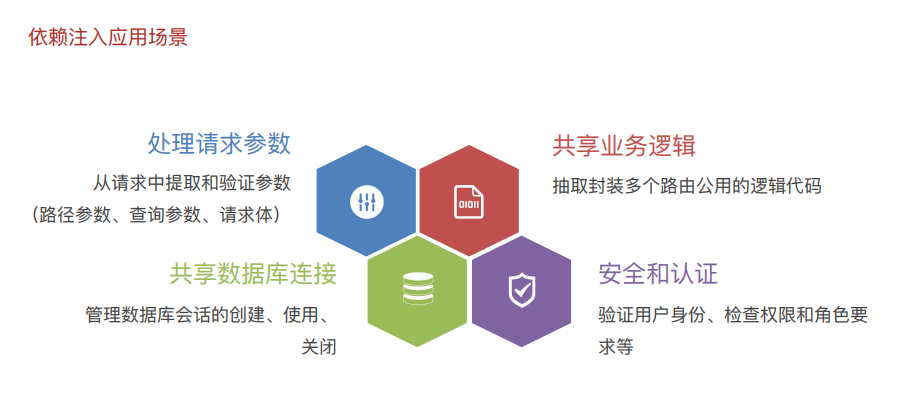
3.ORM
ORM(Object-RelationalMapping,对象关系映射)是一种编程技术,用于在面向对象编程语言和关系型数据库之间建立映射。它允许开发者通过操作对象的方式与数据库进行交互,而无需直接编写复杂的 SQL 语句。
优势:减少重复的 SQL 代码代码更简洁易读自动处理数据库连接和事务自动防止 SQL 注入攻击。
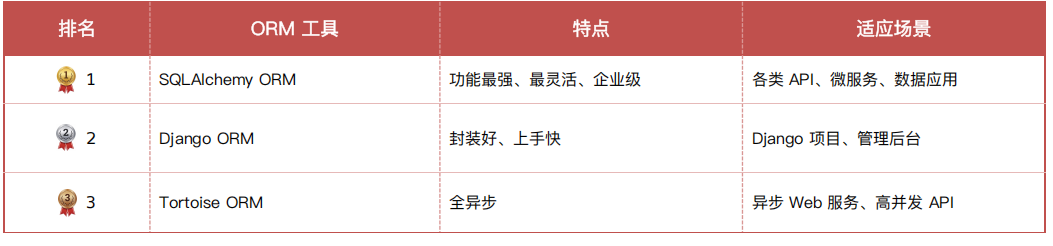
ORM使用流程:

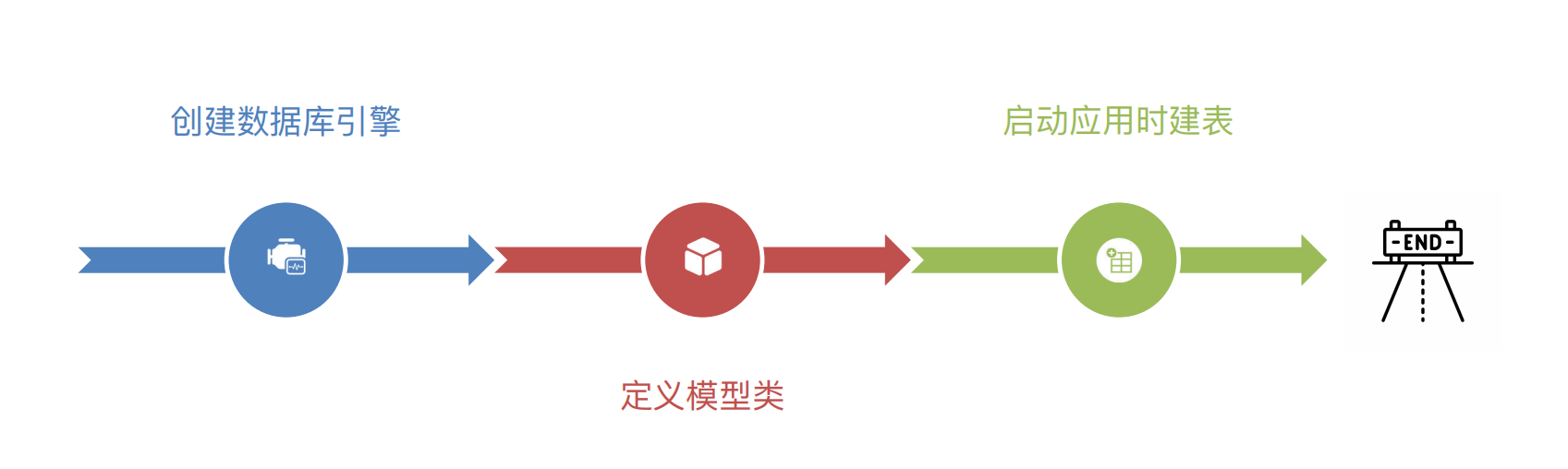
3.1 建表
python
from datetime import datetime
from fastapi import FastAPI, Depends
from sqlalchemy import DateTime, func, String, Float, select
from sqlalchemy.ext.asyncio import create_async_engine, async_sessionmaker, AsyncSession
from sqlalchemy.orm import DeclarativeBase, Mapped, mapped_column
app = FastAPI()
# 1. 创建异步引擎
ASYNC_DATABASE_URL = "mysql+aiomysql://root:xxx@localhost:3306/fast_api?charset=utf8"
async_engine = create_async_engine(
ASYNC_DATABASE_URL,
echo=True, # 可选,输出 SQL 日志
pool_size=10, # 设置连接池活跃的连接数
max_overflow=20 # 允许额外的连接数
)
# 2. 定义模型类: 基类 + 表对应的模型类
# 基类:创建时间、更新时间;书籍表:id、书名、作者、价格、出版社
class Base(DeclarativeBase):
create_time: Mapped[datetime] = mapped_column(DateTime, insert_default=func.now(), default=func.now, comment="创建时间")
update_time: Mapped[datetime] = mapped_column(DateTime, insert_default=func.now(), default=func.now, onupdate=func.now(), comment="修改时间")
class Book(Base):
__tablename__ = "book"
id: Mapped[int] = mapped_column(primary_key=True, comment="书籍id")
bookname: Mapped[str] = mapped_column(String(255), comment="书名")
author: Mapped[str] = mapped_column(String(255), comment="作者")
price: Mapped[float] = mapped_column(Float, comment="价格")
publisher: Mapped[str] = mapped_column(String(255), comment="出版社")
# 3. 建表:定义函数建表 → FastAPI 启动的时候调用建表的函数
async def create_tables():
# 获取异步引擎,创建事务 - 建表
async with async_engine.begin() as conn:
await conn.run_sync(Base.metadata.create_all) # Base 模型类的元数据创建
@app.on_event("startup")
async def startup_event():
await create_tables()
@app.get("/")
async def root():
return {"message": "Hello World"}3.2 在路由匹配中使用ORM
核心:创建依赖项,使用Depends注入到处理函数。
python
# 创建异步会话工厂
# 需求:查询功能的接口,查询图书 → 依赖注入:创建依赖项获取数据库会话 + Depends 注入路由处理函数
AsyncSessionLocal = async_sessionmaker(
bind=async_engine, # 绑定数据库引擎
class_=AsyncSession, # 指定会话类
expire_on_commit=False # 提交后会话不过期,不会重新查询数据库
)
# 依赖项
async def get_database():
async with AsyncSessionLocal() as session:
try:
yield session # 返回数据库会话给路由处理函数
await session.commit() # 提交事务
except Exception:
await session.rollback() # 有异常,回滚
raise
finally:
await session.close() # 关闭会话
@app.get("/book/books")
async def get_book_list(db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_database)):
# 查询
result = await db.execute(select(Book))
book = result.scalars().all()
return book3.3 数据库操作

3.3.1 查询
查询数据:
python
@app.get("/book/books")
async def get_book_list(db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_database)):
# result = await db.execute(select(Book)) # 查询 → 返回一个 ORM 对象
# book = result.scalars().all() # 获取所有
# book = result.scalars().first() # 获取第一个
book = await db.get(Book, 5) # 获取单条数据 → 根据主键
return book查询条件:
python
# 需求:路径参数 书籍id
@app.get("/book/get_book/{book_id}")
async def get_book_list(book_id: int, db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_database)):
result = await db.execute(select(Book).where(Book.id == book_id))
book = result.scalar_one_or_none()
return book
# 需求:条件 价格大于等于200
@app.get("/book/search_book")
async def get_search_book(db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_database)):
result = await db.execute(select(Book).where(Book.price >= 200))
books = result.scalars().all()
return books
python
@app.get("/book/search_book")
async def get_search_book(db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_database)):
# 需求: 作者以 曹 开头 % _
# like() 模糊查询: % 任意个字符;_ 一个单个字符
# result = await db.execute(select(Book).where(Book.author.like("曹_")))
# & | ~ 与非
# result = await db.execute(select(Book).where((Book.author.like("曹%")) | (Book.price > 100)))
# in_() 包含
# 需求:书籍id列表,数据库里面的 id 如果在 书籍id列表里面 就返回
id_list = [1, 3, 5, 7]
result = await db.execute(select(Book).where(Book.id.in_(id_list)))
book = result.scalars().all()
return book聚合查询:
python
@app.get("/book/count")
async def get_count(db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_database)):
# 聚合查询 select( func.方法名(模型类.属性) )
# result = await db.execute(select(func.count(Book.id)))
# result = await db.execute(select(func.max(Book.price)))
# result = await db.execute(select(func.sum(Book.price)))
result = await db.execute(select(func.avg(Book.price)))
num = result.scalar() # 用来提取一个数值 → 标量值
return num分页查询:
python
@app.get("/book/get_book_list")
async def get_book_list(
page: int = 1,
page_size: int = 3,
db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_database)
):
# (页码 - 1) * 每页数量
skip = (page - 1) * page_size
# offset 跳过的记录数 ; limit 每页的记录数
stmt = select(Book).offset(skip).limit(page_size)
result = await db.execute(stmt)
books = result.scalars().all()
return books查询总结:


3.3.2 新增数据
python
# 需求:用户输入图书信息(id、书名、作者、价格、出版社) → 新增
# 用户输入 → 参数 → 请求体
class BookBase(BaseModel):
id: int
bookname: str
author: str
price: float
publisher: str
@app.post("/book/add_book")
async def add_book(book: BookBase, db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_database)):
# ORM对象 → add → commit
book_obj = Book(**book.__dict__)
db.add(book_obj)
await db.commit()
return book3.3.3 修改数据
python
@app.put("/book/update_book/{book_id}")
async def update_book(book_id: int, data: BookUpdate, db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_database)):
# 1. 查找图书
db_book = await db.get(Book, book_id)
# 如果未找到 抛出异常
if db_book is None:
raise HTTPException(
status_code=404,
detail="查无此书"
)
# 2. 找到了则修改:重新赋值
db_book.bookname = data.bookname
db_book.author = data.author
db_book.price = data.price
db_book.publisher = data.publisher
# 3. 提交到数据库
await db.commit()
return db_book3.3.4 删除数据
python
@app.delete("/book/delete_book/{book_id}")
async def delete_book(book_id: int, db: AsyncSession = Depends(get_database)):
# 先查再删 提交
db_book = await db.get(Book, book_id)
if db_book is None:
raise HTTPException(
status_code=404,
detail="查无此书"
)
await db.delete(db_book)
await db.commit()
return {"msg": "删除图书成功"}