一 LSTM:长短期记忆网络LSTM
long short-term memory.是一种时间循环神经网络,存在长期依赖问题而专门设计出来的,所有的RNN都具有一种重复神经网络模块的链接形式。
RNN的问题:存在梯度爆炸和消失的问题。
梯度小时:RNN梯度小时是因为激活函数tanh函数导数载0到1之间,反向传播时更新前面时刻的参数时,当参数w初始化为小于1的数,则多个tanh函数 * w相乘,讲导致求的偏导极小,小于1的数连乘,从而导致梯度消失。
梯度爆炸:当参数初始化为足够大,使得tanh函数的倒数乘以w大于1,则将导致偏导极大大于1的数连乘,从而导致梯度爆炸。
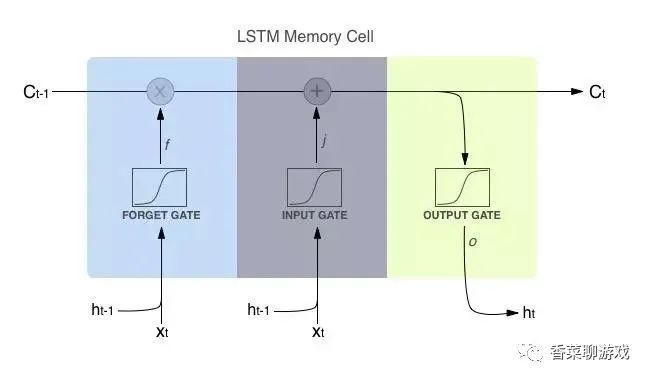
f(t) = sigmod(weight(f)[Ht-1, Xt] + Bf)
这是一个线形函数
I(t) = sigmod(weight(i)[Ht-1, Xt] + Bi)
这是另一个神经元
Ct = tanh(Wc*[Ht-1, Xt] + Bc)
Ot = sigmod(Wo [Ht-1, Xt] + Bo)
Ht = Ot * tanh(Ct)
二 代码实现
import` `torch`
`import` `torch.nn` `as` `nn`
`import` `torch.nn.functinal`
`import` `numpy` `as` `np`
`import` `pandas` `as` `pd`
`import` `matplotlib.pyplot` `as` `plt`
`#导入数据`
`#load` `the` `dataset`
`fight_data` `=` `pd.read_csv('flights.csv', usecols=[1], engine='python')`
`dataset` `=` `fight_dta.values`
`dataset` `=` `dataset.astype('float32')`
`print(flight_data.head())`
`print(flight_data.shape)`
`#绘制每月乘客的出行频率`
`fig_size = plt.rcParams['figure.figsize']`
`fig_size[0] = 15`
`fig_size[1] = 5`
`plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = fig_size`
`plt.title('Month vs Passenger')`
`plt.ylabel('Total Passengers')`
`plt.xlabel('Months')`
`plt.grid(True)`
`plt.autoscale(axis='x',tight=True)`
`plt.plot(flight_data['passengers'])`
`plt.show()`
`数据预处理`
`flight_data.columns` `#显示数据集中,列的数据类型`
`all_data` `=` `flight_data['passenger'].values.astype(flaot)` `#将passenger列的数据类型改为float`
`#划分测试集和训练集`
`test_data_size` `= 12`
`train_data` `= all_data[:-test_data_size]` `#除了最后12个数据,其他全取`
`test_data` `= all_data[-test_data_size:]#取最后12个数据`
`print(len(train_data))`
`print(len(test_data))`
`#最大最小缩放器进行归一化,减小误差`
`from` `skleearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler`
`scaler` `= MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(-1, -1))`
`train_dta_normalized =` `scaler.fit_transform(train_data.reshape(-1, 1))`
`#查看归一化之后的前5条数据和后5条数据`
`print(train_data_normalized[:5])`
`print(train_data_normalized[-5:])`
`#将数据集转换为tensor,` `因为Pytorch模型使用Tensor进行训练的,并将训练数据转换为输入序列和相应的标签`
`train_data_normalized` `= torch.FloatTensor(train_data_normalized).view(-1)`
`#view相当于numpy中的resize,` `参数代表数组不同维的维度`
`#参数为-1表示,这个维的维度由机器自行推断,如果没有-1,那么view中的所有参数就要和tensor中的元素总个数一致`
`#定义create_inout_sequences函数,接受原始输入数据,并返回一个元组列表`
`def create_inout_sequence(input_dta, tw):`
`inout_seq=[]`
`L` `=` `len(input_data)`
`for i` `in` `range(L-tw):`
`train_seq =` `input_data[i:i+tw]`
`train_label` `= input_data[i+tw:i+tw+1]#预测time_step之后的第一个数值`
`inout_seq.append((train_seq, train_label))` `#inout_seq内的数据不断更新,但是总量只有tw` `+ 1个`
`return` `inout_seq`
`train_window` `=` `12#设置训练输入的序列长度为12,类似于time_step` `= 12`
`train_inout_seq = create_inout_sequences(train_data_normalized, train_window)`
`print(train_inout_seq[:5])#产看数据集改造结果`
`notice:`
`crate_inout_sequences` `返回的元组列表由一个个序列组成`
`每一个序列有13个数据,分别是设置的12个数据,` `train_window` `+第13个数据label`
`第一个序列由前12个数据组成,第13个数据是第一个序列的标签`
`同样,第二个序列从第二个数据开始,到第13个数据结束,而第14个数据是第二个序列的标签,以此类推`
`创建LSTM模型`
`参数说明`
`1` `input_size` `对应的计特征数量,案例中为1,即passengers乘客数量`
`2` `output_size` `预测变量的个数,计数据标签的个数`
`3` `hidden_lay_size` `隐藏层的特征数,也就是隐藏层的神经元个数`
`class` `LSTM(nn.Module):` `#注意Module首字母需要大写`
`def` `__init__(self, input_size=1, hidden_layer_size=100, output_size=1):`
`super().__init__()`
`self.hidden_layer_size =` `hidden_layer_size`
`#创建LSTM层和linear层,` `LSTM层提取特征,linear层用作最后的预测`
`##LSTM算法接受三个输入,先前的隐藏状态,先前的单元状态和当前输入`
`self.lstm` `=` `nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_layer_size)`
`self.linear` `= nn.Linear(hidden_layer_size, output_size)` `//定义全连接层,输入是隐藏层,输出是1`
`#初始化隐含状态及细胞状态C,hidden_cell变量包含先前的隐藏状态和单元状态`
`self.hiddne_cell` `= (torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_layer_size),`
`torch.zeros(1, ,1, self.hidden_layer_size))`
`def` `forward(self, input_seq):`
`lstm_out,` `self.hidden_cell =` `self.lstm(input_seq.view(len(input_seq), 1, -1), self.hidden_cell)`
`#lstm的输出是当前时间步的隐藏状态Ht和单元状态Ct以及输出lstm_out`
`#按照lstm的格式修改input_seq的形状,作为linear层的输入`
`predictions` `= self.linear(lstm_out,.view(len(input_seq), -1))`
`return predictions[-1]` `#返回predictions的最后一个元素`
`forward方法;LSTM层的输入与输出:out,` `(Ht,Ct)` `=` `lstm(input, (H0, C0))其中`
`一` `输入格式:lstm(input, (H0, C0))`
`1 input为(seq_len, batchm input_size)格式的tensor, seq_len即为time_step`
`2 H0为num------layers*` `num_directions, batch,` `hidden_size格式的tensor,隐藏状态的初始状态`
`3` `C0为` `seq_len, batch, input_size` `格式的tensor,` `细胞初始状态`
`二` `输出格式,` `output, (Ht, Ct)`
`1 output为(seq_len, batch, num_directions * hidden_size)格式为tensor, 包含上输出特征H_t(源于LSTM每个t的最后一层)`
`2` `ht为(num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size格式的tensor)`
`3 Ct为(num_layers * num_directions, batch, hidden_size)格式为tensor`
`#创建LSTM类的对象,定义损失函数和优化器`
`model` `= LSTM()`
`loss_functions` `=` `nn.MSELoss()`
`optimizer` `= torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)` `#简历优化器实例`
`print(model)`
`#模型训练`
`batch-size是指1次迭代使用的样本数据量`
`epoch时把所有训练数据完整过一遍,就是训练几遍`
`由于默认情况下权重是在Pytorch神经网络中随机初始化的,因此可能获得不同的值`
`epochs` `= 300`
`for i in` `range(epochs):`
`for` `seq, labels` `in train_inout_seq:`
`#清楚网络先前的梯度值`
`optimizer.zero_grad()` `#训练模型时需要使模型处于训练模式,调用model.train(),` `缺省情况下,梯度是累加的,需要手动吧梯度初始化或者清零,调用`
`optimizer.zero_grad()`
`#初始化隐藏层数据`
`model.hidden_cell = (torch.zeros(1, 1, model_hidden_layer_size),`
`torch.zeros(1, 1, model.hidden_layer_size))`
`#实例化模型`
`y_pred = model(seq)`
`#计算损失,反向传播梯度以及更新模型参数`
`signle_loss` `= loss_function(y_pred, labels)#训练过程中,正向传播生成网络的输出,计算输出和实际值之间的损失值`
`single_loss.backward()` `#调用loss.backward(自动生成梯度`
`optimizer.step()` `#使用optimizer.step()执行优化器,把梯度传播回每个网络`
`#n查看模型训练的结果`
`if i%25 == 1:`
` print(f'epoch:{i:3} loss:{single_loss.item():10.8f}')`
`print(f'epoch:{i:3} loss:{single_loss.item():10.10f}')`
`#预测`
`test_input中包含12个数据`
`在for循环中,12个数据用于对测试机第一个数据进行预测,然后将预测值附加到test_inputs列表中`
`在第二次迭代中,最后12个数据再次用作输入,并进行新的预测,然后,将第二次预测的新值再次添加到列表中`
`由于测试集中有12个元素,因此该循环将执行12次`
`循环结束后,test_inputs列表将包含24个数据,其中最后12个数据将是测试集的预测值`
`fut_pred` `= 1`
`2test_inputs = train_data_normalized[-train_window:].tolist()` `#首先打印出数据列表的最后12个值`
`print(test_inputs)`
`#更改模型为测试或者验证模式`
`model.val()` `把tranning属性设置为false,` `使模型处于测试或者验证状态`
`for i in` `range(fut_pred):`
`seq` `= torch.FloatTensor(test_inputs[-train_window:])`
`with` `torch.no_grad():`
`model.hidden = (torch.zeros(1, 1, model.hidden_layer_size),`
`torch.zeros(1, 1, model.hidden_layer_size))`
`test_inputs.append(model(seq).item())`
`#打印最后的12个预测值`
`#由于对训练集数据进行了标准化,因此预测数据也是标准化了的`
`#需要将归一化的预测值转换为实际的预测值。通过inverse_transform实现`
`actual_predictions = scaler.inverse_transform(np.array(test_inputs[train_window:]).reshape(-1, 1))`
`print(actual_predictions)`
`"""`
`根据实际值,绘制预测值`
`"""`
`x = np.arange(132, 132+fut_pred, 1)`
`plt.title('Month vs Passenger with all data')`
`plt.ylabel('Total Passengers')`
`plt.xlabel('Months')`
`plt.grid(True)`
`plt.autoscale(axis='x', tight=True)`
`plt.plot(flight_data['passengers'])`
`plt.plot(x, actual_predictions)`
`plt.show()`
`#绘制最近12个月的实际和预测乘客数量,以更大的尺度观测数据`
`plt.title('Month vs Passenger last pred data')`
`plt.ylabel('Total Passengers')`
`plt.xlabel('Months')`
`plt.grid(True)`
`plt.autoscale(axis='x', tight=True)`
`plt.plot(flight_data['passengers'][-train_window:])`
`plt.plot(x, actual_predictions)`
`plt.show()`
`