本文深入剖析MyBatis的SQL执行模块,带你全面理解Executor执行器体系、缓存机制、事务管理和批处理原理。
一、MyBatis整体架构与SQL执行模块
在深入SQL执行模块之前,我们先了解MyBatis的整体架构,以及SQL执行模块在其中的核心地位。
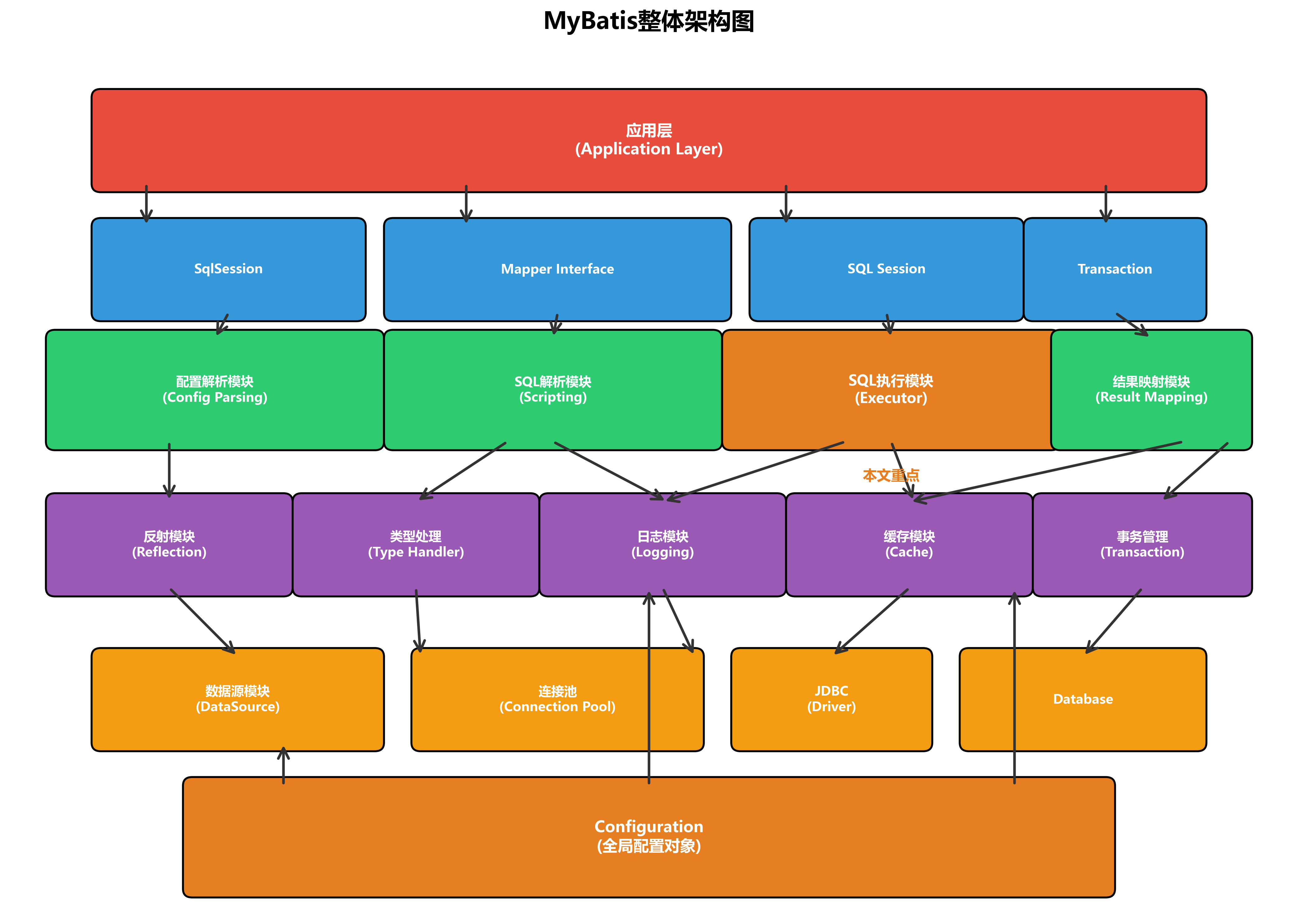
1.1 SQL执行模块的核心职责
SQL执行模块主要承担以下核心职责:
1、SQL执行:根据MappedStatement执行SQL语句,并返回结果
2、缓存管理:管理一级缓存和二级缓存,提高查询性能
3、事务管理:控制数据库事务的提交、回滚和关闭
4、批处理支持:支持批量操作,提升数据修改效率
5、Statement管理:管理JDBC Statement对象的生命周期
6、插件拦截:提供拦截点,支持插件扩展1.2 Executor接口体系
Executor是SQL执行模块的顶层接口,定义了SQL执行的基本方法:
public interface Executor {
// 执行查询(带缓存Key)
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql);
// 执行查询
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler);
// 执行更新(插入、更新、删除)
int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter);
// 刷新批量操作
List<BatchResult> flushStatements();
// 提交事务
void commit(boolean required);
// 回滚事务
void rollback(boolean required);
// 创建CacheKey
CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql);
// 判断是否缓存
boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey cacheKey);
// 清空本地缓存
void clearLocalCache();
// 获取事务
Transaction getTransaction();
// 关闭执行器
void close(boolean forceRollback);
}二、Executor执行器架构
MyBatis提供了多种Executor实现,以适应不同的使用场景。
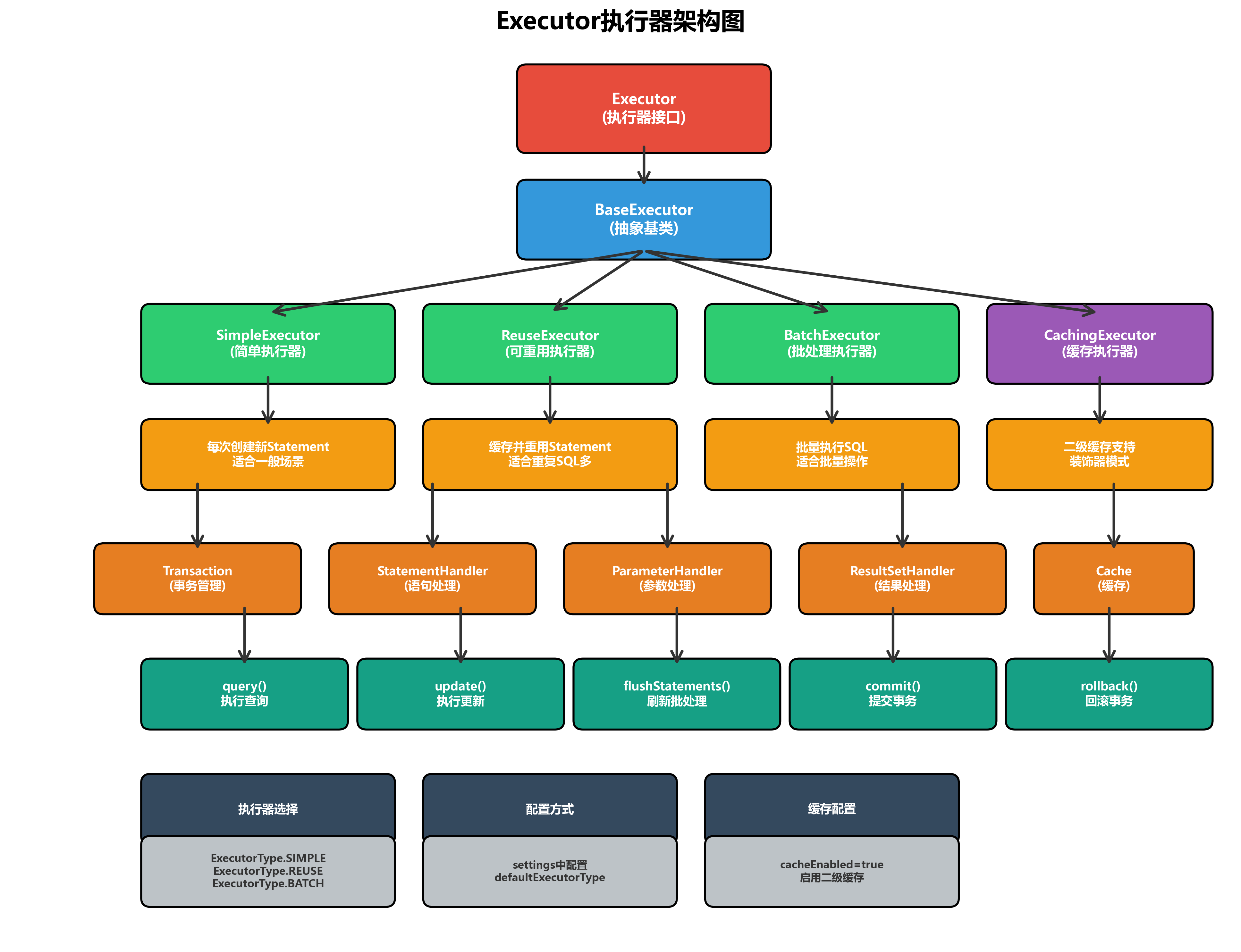
2.1 Executor继承体系
Executor采用了装饰器模式,提供了灵活的功能扩展:
Executor (接口)
├── BaseExecutor (抽象基类)
│ ├── SimpleExecutor (简单执行器)
│ ├── ReuseExecutor (可重用执行器)
│ └── BatchExecutor (批处理执行器)
└── CachingExecutor (缓存执行器)2.2 BaseExecutor抽象基类
BaseExecutor实现了Executor接口的大部分功能,定义了SQL执行的基本流程:
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
protected Transaction transaction;
protected Executor wrapper;
protected ConcurrentLinkedQueue<DeferredLoad<?>> deferredLoads;
protected PerpetualCache localCache; // 一级缓存
protected PerpetualCache localOutputParameterCache;
protected Configuration configuration;
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) {
// 1. 创建BoundSql
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 2. 创建CacheKey
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
// 3. 执行查询
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) {
// 检查本地缓存
List<E> list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
return list;
}
// 执行数据库查询
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
return list;
}
}2.3 SimpleExecutor简单执行器
SimpleExecutor是最基础的执行器实现,每次执行SQL都会创建新的Statement对象:
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
// 1. 创建Configuration对象
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 2. 创建StatementHandler
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter,
rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 3. 创建Statement
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 4. 执行查询
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
// 5. 关闭Statement
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
@Override
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter,
RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.update(stmt);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
}2.4 ReuseExecutor可重用执行器
ReuseExecutor会缓存Statement对象,相同SQL可以重用Statement,减少Statement创建开销:
public class ReuseExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
private final Map<String, Statement> statementMap = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter,
rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
Statement stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog(), boundSql.getSql());
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
}
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog, String sql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 尝试从缓存中获取Statement
stmt = statementMap.get(sql);
if (stmt == null) {
// 缓存未命中,创建新的Statement
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, statementLog);
statementMap.put(sql, stmt);
}
return stmt;
}
}2.5 BatchExecutor批处理执行器
BatchExecutor专门用于批量操作,会将多个SQL语句批量执行:
public class BatchExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
private final List<Statement> statementList = new ArrayList<>();
private final List<BatchResult> batchResultList = new ArrayList<>();
private String currentSql;
private MappedStatement currentStatement;
@Override
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameterObject,
RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
Statement stmt;
// 检查是否需要切换SQL
if (sql.equals(currentSql) && ms.equals(currentStatement)) {
// 相同SQL,复用Statement
int last = statementList.size() - 1;
stmt = statementList.get(last);
} else {
// 不同SQL,创建新Statement
currentSql = sql;
currentStatement = ms;
stmt = prepareStatement(handler);
statementList.add(stmt);
batchResultList.add(new BatchResult(ms, sql, parameterObject));
}
// 添加批处理
handler.parameterize(stmt);
handler.batch(stmt);
return BATCH_UPDATE_RETURN_VALUE;
}
@Override
public List<BatchResult> doFlushStatements(boolean isRollback) throws SQLException {
List<BatchResult> results = new ArrayList<>();
try {
for (int i = 0, n = statementList.size(); i < n; i++) {
Statement stmt = statementList.get(i);
BatchResult batchResult = batchResultList.get(i);
try {
if (!isRollback) {
// 执行批处理
int[] updateCounts = stmt.executeBatch();
batchResult.setUpdateCounts(updateCounts);
}
results.add(batchResult);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new BatchExecutorException("Error updating database. Cause: " + e, e, batchResult);
}
}
return results;
} finally {
// 清空缓存
statementList.clear();
batchResultList.clear();
currentSql = null;
currentStatement = null;
}
}
}2.6 CachingExecutor缓存执行器
CachingExecutor是Executor的装饰器,在底层Executor之上增加了二级缓存功能:
public class CachingExecutor implements Executor {
private final Executor delegate;
private final TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager();
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 1. 获取BoundSql
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 2. 创建CacheKey
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
// 3. 查询缓存
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
// 1. 检查二级缓存
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
// 刷新缓存(如果需要)
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
// 检查缓存是否命中
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list != null) {
return list;
}
}
}
// 2. 缓存未命中,委托给底层Executor执行
List<E> list = delegate.<E>query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
// 3. 将结果放入二级缓存
if (cache != null) {
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list);
}
return list;
}
}三、SQL执行流程
SQL的执行流程是Executor的核心工作流程。
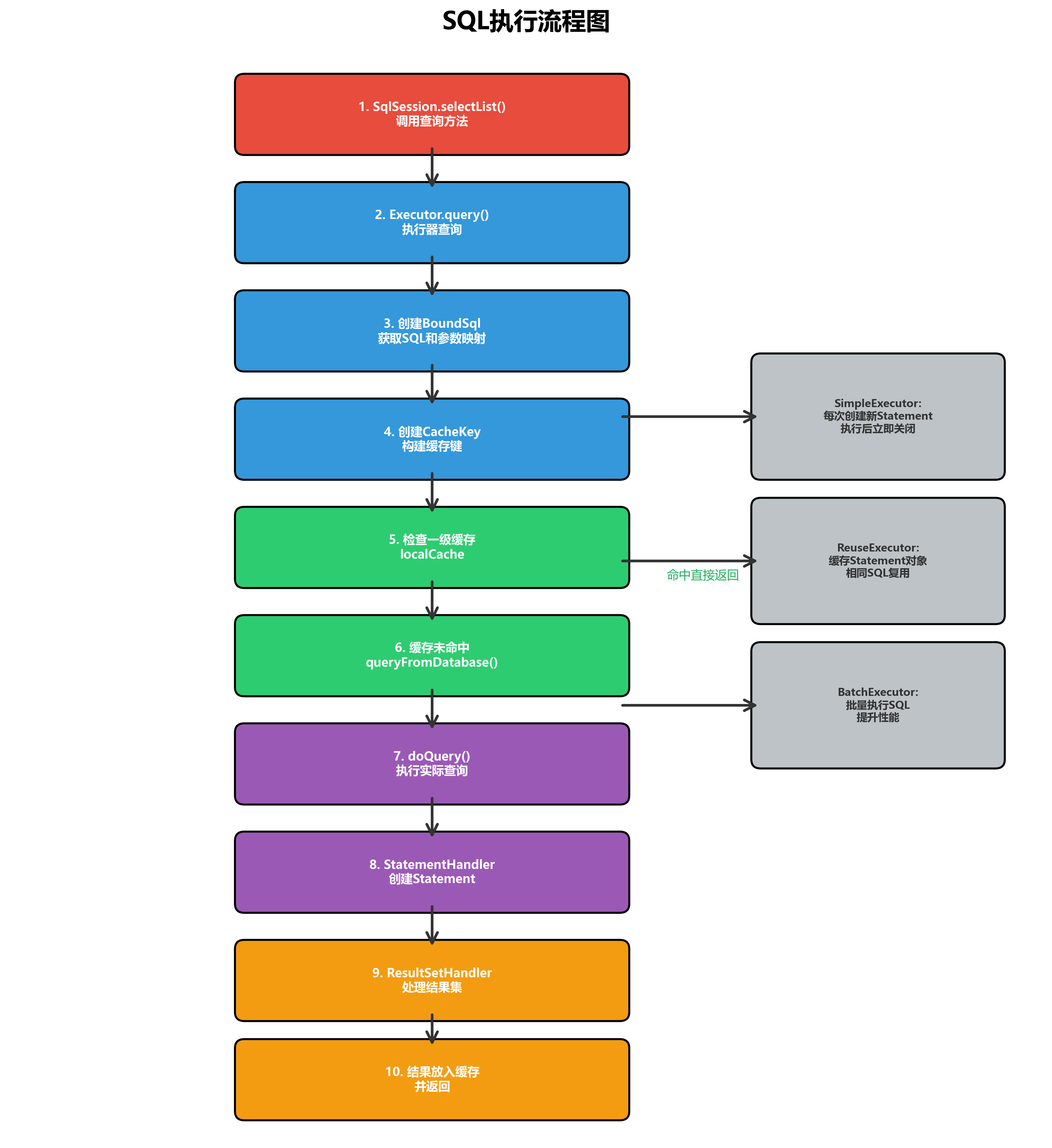
3.1 完整执行流程
以查询操作为例,完整的SQL执行流程如下:
// 1. SqlSession调用Executor
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
// 1.1 获取MappedStatement
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 1.2 调用Executor执行查询
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
// 2. Executor执行查询
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) {
// 2.1 获取BoundSql
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 2.2 创建CacheKey
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
// 2.3 执行查询
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
// 3. 检查一级缓存
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) {
List<E> list;
// 3.1 检查一级缓存
if (resultHandler == null) {
list = (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key);
}
if (list != null) {
return list;
}
// 3.2 缓存未命中,查询数据库
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
return list;
}
// 4. 查询数据库
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) {
List<E> list;
// 4.1 占位缓存,处理循环依赖
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 4.2 执行查询
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
// 4.3 移除占位符
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
// 4.4 将结果放入一级缓存
localCache.putObject(key, list);
// 4.5 处理延迟加载
if (ms.getConfiguration().isLazyLoadingEnabled()) {
if (deferredLoads != null && !deferredLoads.isEmpty()) {
deferredLoads.clear();
}
}
return list;
}
// 5. 执行实际查询
protected abstract <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;3.2 StatementHandler的作用
StatementHandler负责Statement的创建、参数设置和SQL执行:
public interface StatementHandler {
// 准备Statement
Statement prepare(Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout) throws SQLException;
// 参数化Statement
void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException;
// 执行查询
<E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException;
// 执行更新
int update(Statement statement) throws SQLException;
// 批处理
void batch(Statement statement) throws SQLException;
// 获取BoundSql
BoundSql getBoundSql();
}3.3 ResultSetHandler的作用
ResultSetHandler负责将ResultSet映射为Java对象:
public interface ResultSetHandler {
// 处理结果集
<E> List<E> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException;
// 处理游标结果集
<E> Cursor<E> handleCursorResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException;
// 处理输出参数
void handleOutputParameters(CallableStatement cs) throws SQLException;
}四、缓存管理机制
MyBatis提供了两级缓存机制,有效提升查询性能。
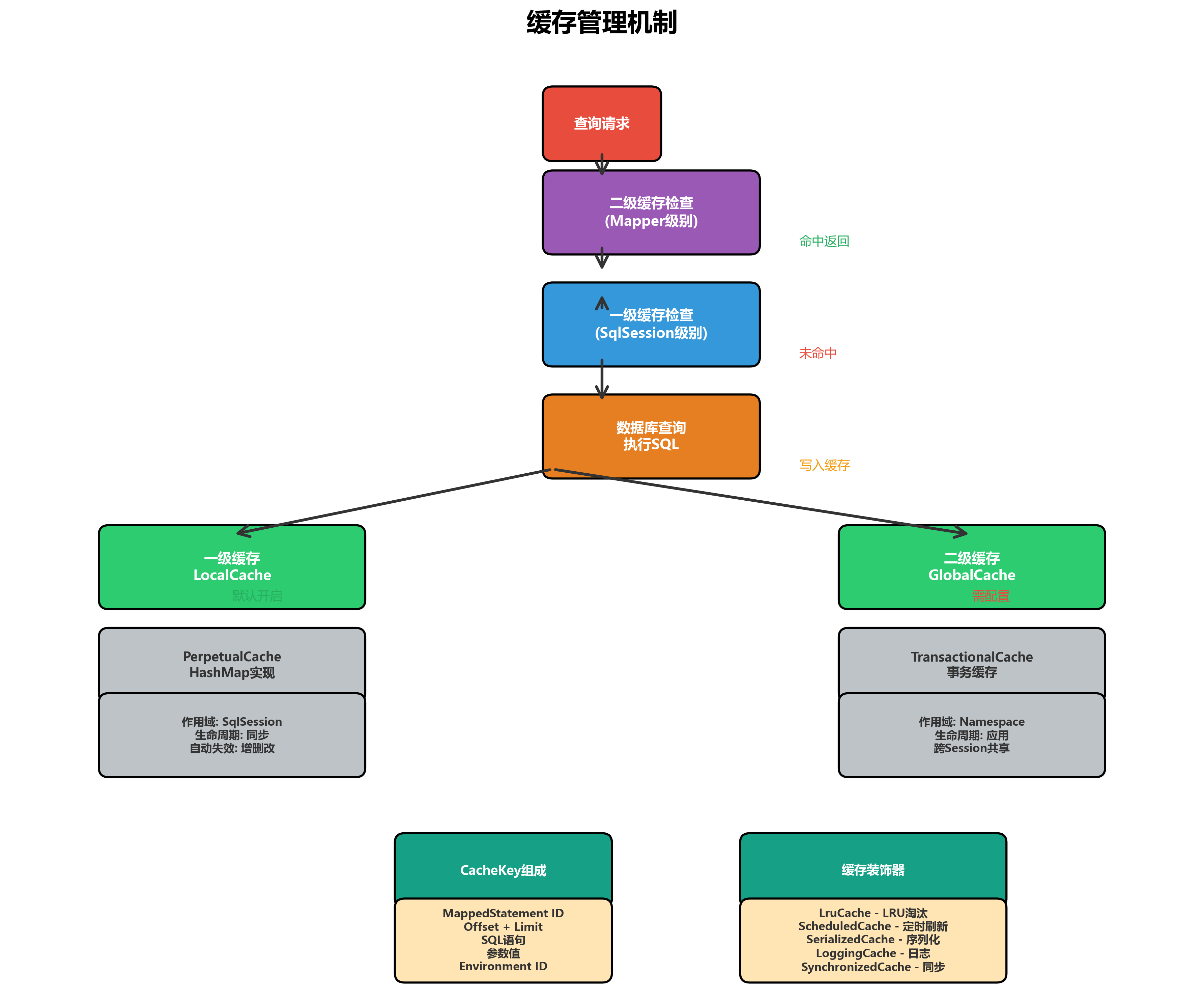
4.1 一级缓存(Local Cache)
一级缓存是SqlSession级别的缓存,默认开启,作用域是当前SqlSession:
public class PerpetualCache implements Cache {
private final String id;
private final Map<Object, Object> cache = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
cache.put(key, value);
}
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
return cache.get(key);
}
@Override
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
return cache.remove(key);
}
@Override
public void clear() {
cache.clear();
}
}一级缓存的特点:
1、作用域:SqlSession级别
2、生命周期:与SqlSession相同,SqlSession关闭时缓存清空
3、缓存Key:由MappedStatement ID、参数SQL、分页参数等组成
4、自动失效:执行增删改操作时,一级缓存会自动清空4.2 二级缓存(Global Cache)
二级缓存是Mapper级别的缓存,需要手动配置,作用域是Namespace:
<!-- 在Mapper XML中配置二级缓存 -->
<cache eviction="LRU" flushInterval="60000" size="1024" readOnly="true"/>二级缓存的特点:
1、作用域:Namespace(Mapper)级别
2、生命周期:应用级别,直到应用关闭
3、跨Session共享:多个SqlSession可以共享
4、配置灵活:可以自定义缓存策略4.3 缓存Key的构建
CacheKey由多个元素组成,确保缓存键的唯一性:
@Override
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey();
// 1. MappedStatement ID
cacheKey.update(ms.getId());
// 2. 分页参数
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit());
// 3. SQL语句
cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql());
// 4. 参数值
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) {
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
Object value;
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
cacheKey.update(value);
}
// 5. Environment ID
if (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) {
cacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId());
}
return cacheKey;
}4.4 缓存装饰器模式
MyBatis使用装饰器模式实现缓存功能的增强:
// 基础缓存
Cache cache = new PerpetualCache("myCache");
// 添加LRU淘汰策略
cache = new LruCache(cache);
// 添加定时刷新
cache = new ScheduledCache(cache);
// 添加序列化支持
cache = new SerializedCache(cache);
// 添加日志记录
cache = new LoggingCache(cache);
// 添加同步支持
cache = new SynchronizedCache(cache);4.5 缓存使用示例
// 一级缓存示例
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 第一次查询,访问数据库
User user1 = mapper.selectById(1L);
// 第二次查询,从一级缓存获取
User user2 = mapper.selectById(1L);
// user1 == user2,同一对象
} finally {
session.close();
}
// 二级缓存示例
SqlSession session1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
SqlSession session2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
UserMapper mapper1 = session1.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
UserMapper mapper2 = session2.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// session1第一次查询,访问数据库
User user1 = mapper1.selectById(1L);
// session1提交,将数据写入二级缓存
session1.commit();
// session2查询,从二级缓存获取
User user2 = mapper2.selectById(1L);
// user1 equals user2(不同对象,但值相等)
} finally {
session1.close();
session2.close();
}五、事务管理
事务管理是数据库操作的重要组成部分,Executor负责事务的创建、提交和回滚。
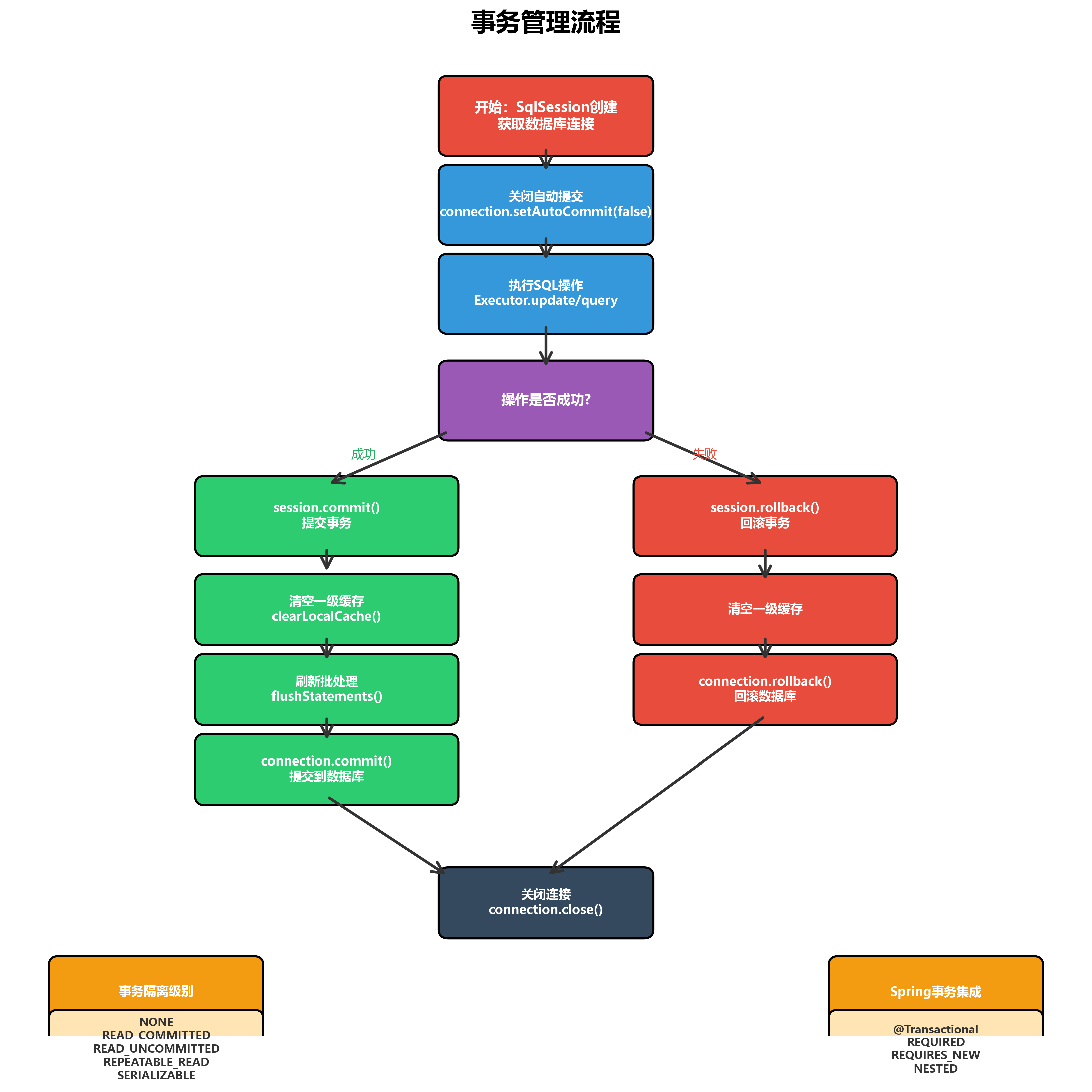
5.1 Transaction接口
Transaction是事务管理的顶层接口:
public interface Transaction {
// 获取数据库连接
Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;
// 提交事务
void commit() throws SQLException;
// 回滚事务
void rollback() throws SQLException;
// 关闭连接
void close() throws SQLException;
// 获取事务超时时间
Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException;
}5.2 事务隔离级别
MyBatis支持标准的事务隔离级别:
public enum IsolationLevel {
NONE(Connection.TRANSACTION_NONE),
READ_COMMITTED(Connection.TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED),
READ_UNCOMMITTED(Connection.TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED),
REPEATABLE_READ(Connection.TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ),
SERIALIZABLE(Connection.TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE);
}配置示例:
<settings>
<setting name="defaultTransactionIsolationLevel" value="READ_COMMITTED"/>
</settings>5.3 事务管理流程
Executor的事务管理流程:
// 提交事务
@Override
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Cannot commit, transaction is already closed");
}
// 1. 清空本地缓存
clearLocalCache();
// 2. 刷新批量操作
List<BatchResult> batchResults = flushStatements(true);
// 3. 提交事务
if (required) {
transaction.commit();
}
return batchResults;
}
// 回滚事务
@Override
public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Cannot rollback, transaction is already closed");
}
try {
// 1. 清空本地缓存
clearLocalCache();
// 2. 刷新批量操作
flushStatements(true);
// 3. 回滚事务
if (required) {
transaction.rollback();
}
} finally {
if (required) {
// 4. 关闭事务
transaction.close();
}
}
}5.4 自动提交与手动提交
// 自动提交模式
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
try {
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
mapper.insert(user);
// 无需手动提交,自动提交
} finally {
session.close();
}
// 手动提交模式(默认)
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
mapper.insert(user);
// 需要手动提交
session.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 异常时回滚
session.rollback();
throw e;
} finally {
session.close();
}5.5 Spring事务集成
在Spring环境中,通常使用Spring的事务管理:
@Service
@Transactional
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
public void updateUser(User user) {
// Spring管理事务,无需手动提交
userMapper.update(user);
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void transfer(Long fromId, Long toId, BigDecimal amount) {
// 转账操作:同一事务
userMapper.decrease(fromId, amount);
userMapper.increase(toId, amount);
}
}六、批处理机制
批处理可以显著提升批量操作的性能。
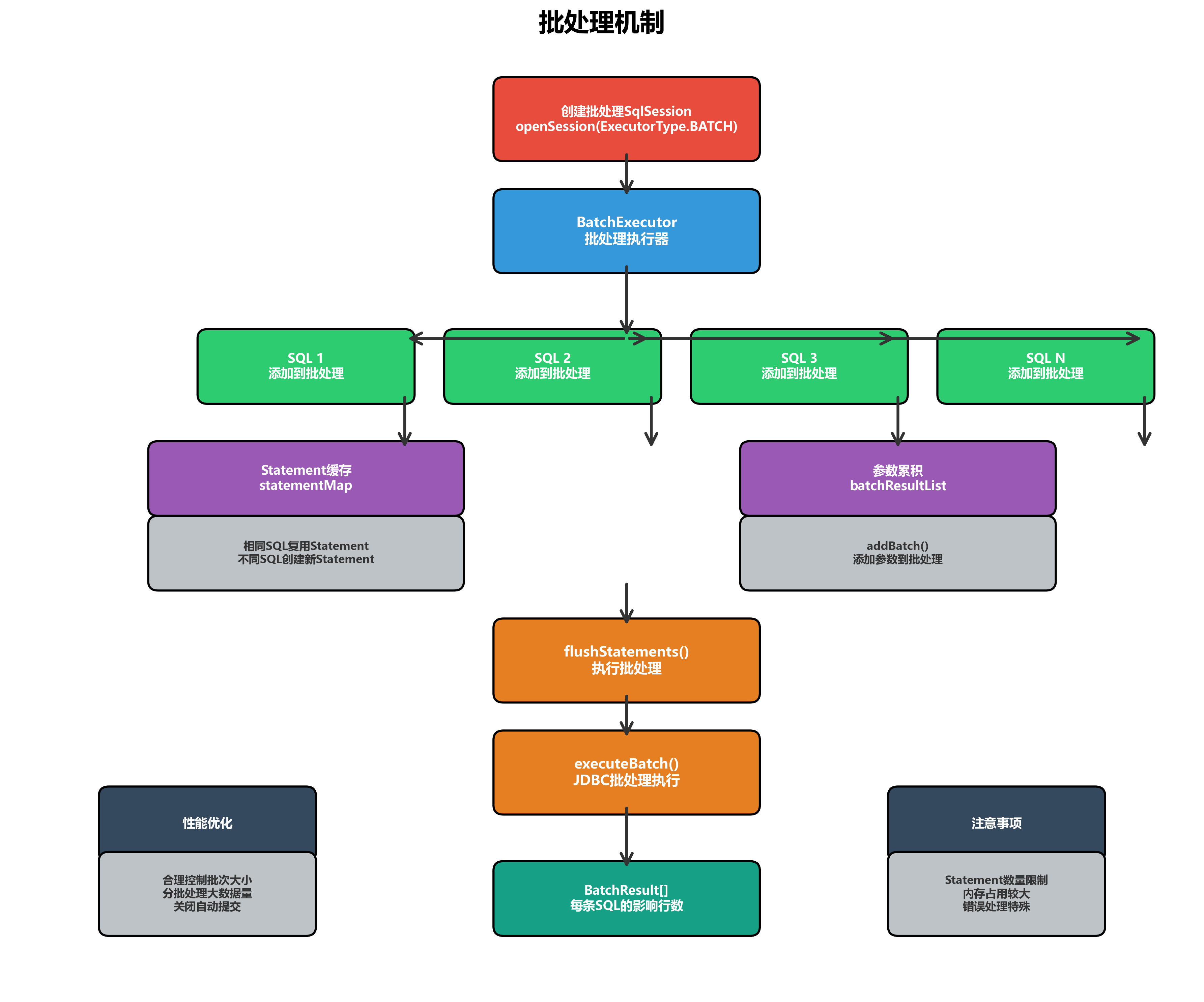
6.1 批处理配置
使用批处理需要指定ExecutorType:
// 创建批处理SqlSession
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.BATCH);
try {
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 批量插入
for (User user : userList) {
mapper.insert(user);
}
// 刷新并执行批处理
session.flushStatements();
// 提交事务
session.commit();
} finally {
session.close();
}6.2 批处理原理
BatchExecutor的工作原理:
1、SQL缓存:相同SQL复用Statement
2、参数累积:多次调用addBatch()
3、批量执行:调用executeBatch()
4、结果返回:返回每条SQL的执行结果
@Override
public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject) throws SQLException {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameterObject,
RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
Statement stmt;
// 检查是否可以复用Statement
if (sql.equals(currentSql) && ms.equals(currentStatement)) {
stmt = statementList.get(statementList.size() - 1);
} else {
stmt = prepareStatement(handler);
statementList.add(stmt);
batchResultList.add(new BatchResult(ms, sql, parameterObject));
currentSql = sql;
currentStatement = ms;
}
// 参数化并添加到批处理
handler.parameterize(stmt);
handler.batch(stmt);
return BATCH_UPDATE_RETURN_VALUE;
}6.3 批处理性能优化
批处理的性能优化建议:
1、合理控制批次大小:避免一次性提交过多SQL
2、使用BatchExecutor:批量操作时使用批处理执行器
3、关闭自动提交:手动控制事务提交
4、合理使用flushStatements:控制批处理执行时机
// 分批处理示例
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.BATCH);
try {
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
int batchSize = 1000;
List<List<User>> batches = Lists.partition(userList, batchSize);
for (List<User> batch : batches) {
for (User user : batch) {
mapper.insert(user);
}
// 每批次刷新一次
session.flushStatements();
session.clearCache();
}
session.commit();
} finally {
session.close();
}6.4 批处理返回结果
批处理返回的是每条SQL影响的行数:
List<BatchResult> results = session.flushStatements();
for (BatchResult result : results) {
int[] updateCounts = result.getUpdateCounts();
for (int count : updateCounts) {
System.out.println("影响行数: " + count);
}
}6.5 批处理注意事项
1.Statement限制:数据库对PreparedStatement数量有限制
2.内存占用:大量SQL会占用较多内存
3.错误处理:批处理中某条SQL失败,需要特别处理
4.日志输出:批处理日志可能较多,建议适当调整日志级别七、最佳实践
7.1 Executor选择建议
| 场景 | 推荐Executor | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 一般查询 | SIMPLE | 默认选择,每次创建新Statement |
| 重复查询多 | REUSE | 复用Statement,减少创建开销 |
| 批量操作 | BATCH | 显著提升批量操作性能 |
| 启用二级缓存 | CACHING | 在其他Executor基础上增加缓存 |
7.2 性能优化建议
1、合理使用缓存:根据业务特点选择缓存级别
2、批量操作优化:大量数据修改使用BatchExecutor
3、及时清理缓存:避免缓存数据过期
4、控制事务范围:事务尽量小,减少锁竞争
5、使用连接池:避免频繁创建连接7.3 常见问题解决
问题1:一级缓存未生效
// 问题代码
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user1 = mapper.selectById(1L);
User user2 = mapper.selectById(1L);
// user1 != user2,缓存未生效
// 原因:两次查询不在同一SqlSession
// 解决:确保在同一个SqlSession中查询问题2:二级缓存脏数据
<!-- 解决方案:设置刷新间隔 -->
<cache eviction="LRU" flushInterval="60000" size="1024" readOnly="false"/>问题3:批处理内存溢出
// 解决方案:分批处理
int batchSize = 1000;
for (int i = 0; i < totalSize; i += batchSize) {
List<User> batch = userList.subList(i, Math.min(i + batchSize, totalSize));
processBatch(session, batch);
session.flushStatements();
session.clearCache();
}八、总结
MyBatis的SQL执行模块是整个框架的核心执行引擎,通过精心设计的Executor体系,实现了高效的SQL执行、灵活的缓存管理、可靠的事务控制和强大的批处理能力。