ORM
-
MVC或者MVC框架中包括一个重要的部分,就是ORM,它实现了数据模型与数据库的解耦,即数据模型的设计不需要依赖于特定的数据库,通过简单的配置就可以轻松更换数据库,这极大的减轻了开发人员的工作量,不需要面对因数据库变更而导致的无效劳动
-
ORM是"对象-关系-映射"的简称。(Object Relational Mapping,简称ORM)(将来会学一个sqlalchemy,是和他很像的,但是django的orm没有独立出来让别人去使用,虽然功能比sqlalchemy更强大,但是别人用不了)
-
类对象--->sql--->pymysql--->mysql服务端--->磁盘,orm其实就是将类对象的语法翻译成sql语句的一个引擎,明白orm是什么了,剩下的就是怎么使用orm,怎么来写类对象关系语句。
M:model,数据库相关操作
pycharm配置连接数据库
第一步
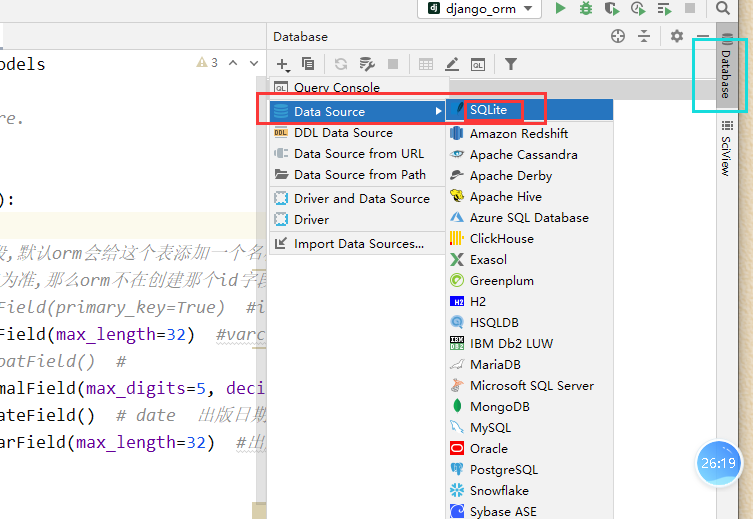
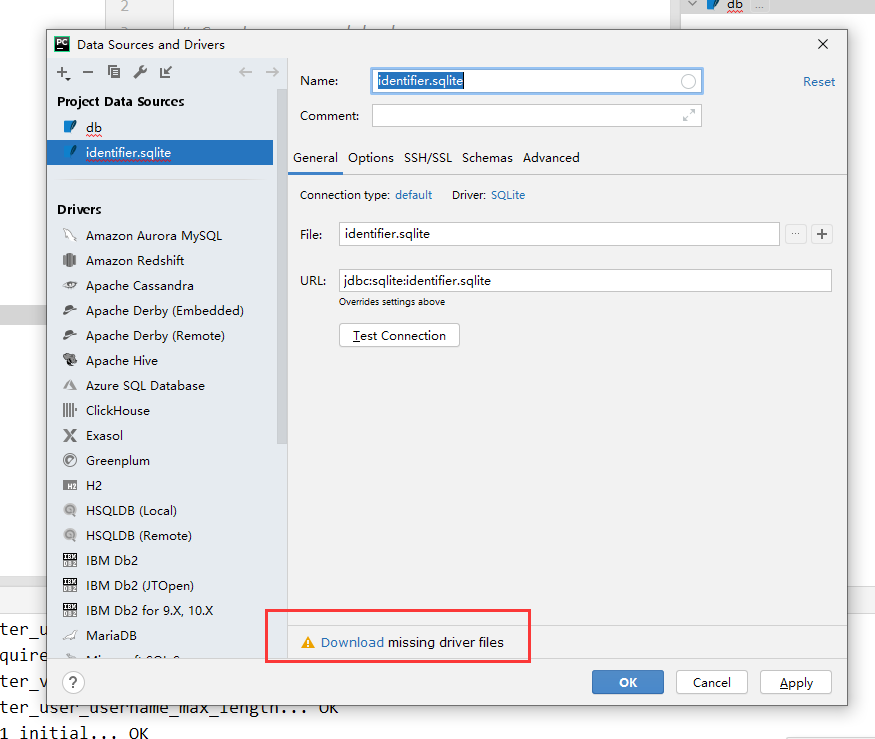
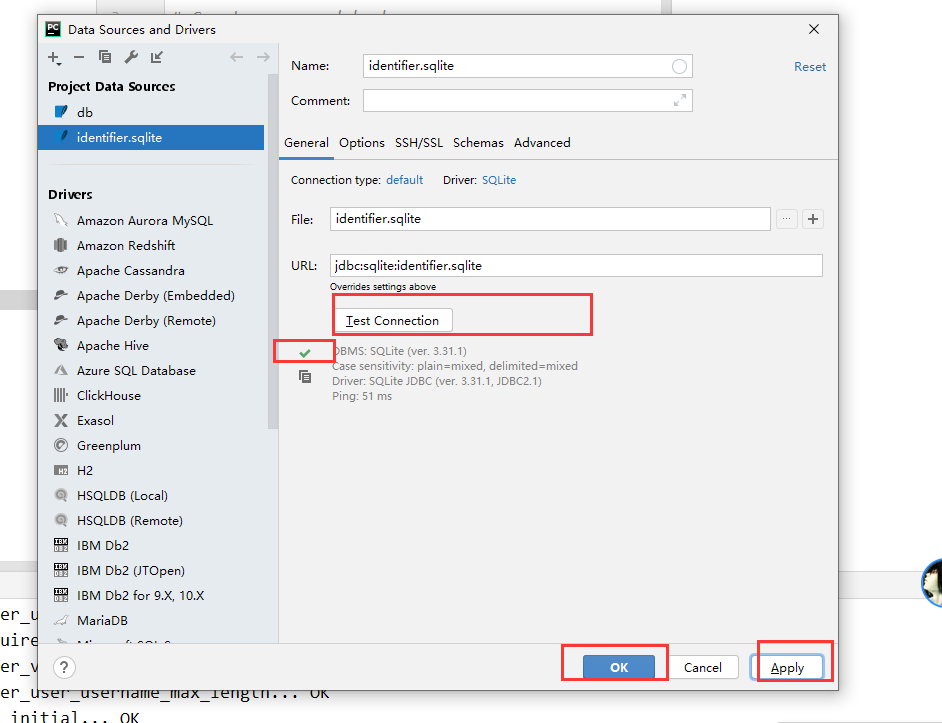
创建模型类
在应用文件夹的models.py文件中写上如下内容
# 属性对应的字段,默认都是不能为空的,也就是加了not null约束
class Book(models.Model):
# 如果没有指定主键字段,默认orm会给这个表添加一个名称为id的主键自增字段
# 如果制定了,以指定的为准,那么orm不在创建那个id字段了
# nid = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) #int primary_key auto_increment,
title = models.CharField(max_length=32) #varchar 书籍名称
# price = models.FloatField() #
price = models.DecimalField(max_digits=5, decimal_places=2) # 999.99 价格
pub_date = models.DateField() # date 出版日期
publish = models.CharField(max_length=32) #出版社名称
# xx = models.CharField(max_length=18, null=True, blank=True) # null=True,blank=True允许该字段数据为空
# xx = models.CharField(max_length=18, default='xxx') # null=True,blank=True允许该字段数据为空
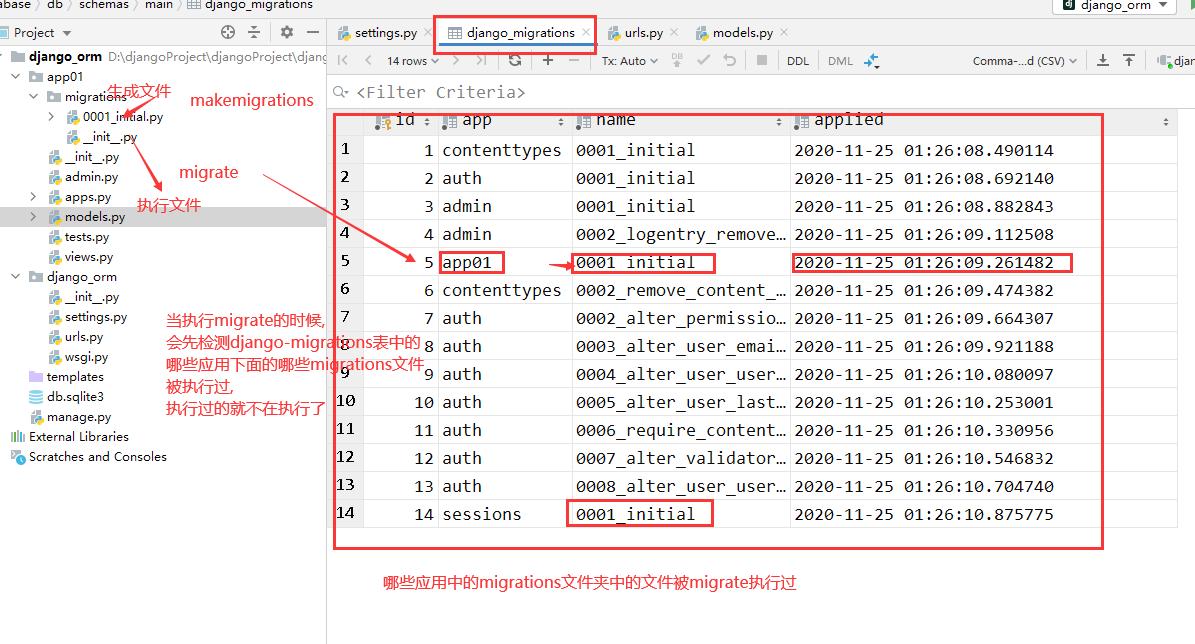
Book生成的表名称为 应用名称_模型类名小写数据库同步(迁移)指令
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate指令的执行流程:
pycharm简单使用
django配置连接msyql
1 创建数据库
create database orm01 charset=utf8mb4;2 settings.py配置文件中写上如下内容
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql',
'NAME': 'orm01',
'HOST':'127.0.0.1',
'PORT':3306,
'USER':'root',
'PASSWORD':'', #有密码的填密码
}
}3 安装pymysql
pip install pymsyql4 在项目主目录下的__init__.py文件中写上如下内容
import pymysql
pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()5 执行数据库同步指令
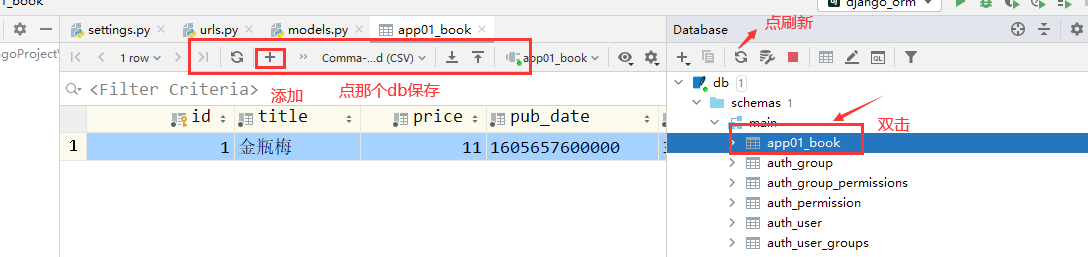
python manage.py migrate只要换了新的数据库,migrate会重新执行migrations文件
查看orm的field对应MySQL的什么字段类型在下面看
C:\python36\Lib\site-packages\django\db\backends\mysql\base.py对应关系
_data_types = {
'AutoField': 'integer AUTO_INCREMENT',
'BigAutoField': 'bigint AUTO_INCREMENT',
'BinaryField': 'longblob',
'BooleanField': 'bool',
'CharField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)',
'CommaSeparatedIntegerField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)',
'DateField': 'date',
'DateTimeField': 'datetime',
'DecimalField': 'numeric(%(max_digits)s, %(decimal_places)s)',
'DurationField': 'bigint',
'FileField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)',
'FilePathField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)',
'FloatField': 'double precision',
'IntegerField': 'integer',
'BigIntegerField': 'bigint',
'IPAddressField': 'char(15)',
'GenericIPAddressField': 'char(39)',
'NullBooleanField': 'bool',
'OneToOneField': 'integer',
'PositiveIntegerField': 'integer UNSIGNED',
'PositiveSmallIntegerField': 'smallint UNSIGNED',
'SlugField': 'varchar(%(max_length)s)',
'SmallIntegerField': 'smallint',
'TextField': 'longtext',
'TimeField': 'time',
'UUIDField': 'char(32)',
}记录的增删改查
增加
# 添加数据记录 方式1
new_book = models.Book(
# id=2,
title='金瓶梅',
price=9.9,
# pub_date=datetime.datetime.now(), #添加时间日期类型数据时可以是时间日期类型的数据,也可以是字符串数据
pub_date='2022-02-02',
publish='32期红浪漫出版社'
# 有默认值的或者可以为空的或者主键字段,都可以不用传值
)
new_book.save()
# 添加方式2 create方法,create方法的返回值为 新添加的数据的模型类对象
new_book = models.Book.objects.create(
title='金瓶梅4',
price=19.9,
# pub_date=datetime.datetime.now(),
pub_date='2022-04-02',
publish='32期红浪漫出版社'
)
print(new_book.title) #通过模型类对象,直接获取属性对应的值
print(new_book.price)批量添加
obj_list = []
for i in range(10):
book_obj = models.Book(
title=f'少年阿宾{i}',
price=10 + i,
pub_date=f'2022-04-1{i}',
publish='32期红浪漫出版社'
)
obj_list.append(book_obj)
models.Book.objects.bulk_create(obj_list) #bulk_create 批量添加查询
book_objs = models.Book.objects.all() #queryset 类似于列表
book_objs = models.Book.objects.filter(id=3) #条件查询 结果为queryset类型数据
models.Book.objects.filter() # filter没有加条件,和all一样的效果
models.Book.objects.filter(id=100) #查不到数据,不会保存,返回空干的queryset类型数据
book_objs = models.Book.objects.get(id=3) # 条件查找 结果为: 模型类对象
models.Book.objects.get() 也是查所有
但是get方法的查询结果有要求,有且只能有一条
models.Book.objects.get(id=100) # 查询不到结果会报错 Book matching query does not exist.
# 查询结果多于一条也会报错 删除
models.Book.objects.filter(id=3).delete() queryset类型数据可以调用delete方法删除查询结果数据
models.Book.objects.get(id=4).delete() 模型类对象也可以调用delete方法删除数据改
# 修改方式1 通过queryset类型数据修改
models.Book.objects.filter(id=5).update(
price=20,
title='xxxx'
)
models.Book.objects.get(id=5).update( #报错:模型类对象不能调用update方法
price=30,
)
# 修改方式2 通过模型类对象来修改
ret = models.Book.objects.get(id=5)
ret.price = 30
ret.title = '少年阿宾00'
ret.save()两个参数解释
DatetimeField、DateField、TimeField这个三个时间字段,都可以设置如下属性
(7)auto_now_add
配置auto_now_add=True,创建数据记录的时候会把当前时间添加到数据库。
(8)auto_now
配置上auto_now=True,每次更新数据记录的时候会更新该字段,标识这条记录最后一次的修改时间。看示例
# models.userinfo.objects.filter(id=1).update( #update不能触发自动更新时间的auto_now参数的作用,
# # 如果用update方法来更新记录,并保存更新记录的时间,需要我们手动给该字段传入当前时间
# name='xxoo',
# b1=datetime.datetime.now()
#
# )
# 这种save方式能够触发auto_now参数自动更新修改时间的动作
ret = models.userinfo.objects.get(id=2)
ret.name='xxoo2'
ret.save() django默认用的utc时间来操作时间数据,
如果需要改为本地时区来存储时间,那么需要修改django的配置文件
在settings.py文件中修改如下内容
# USE_TZ = True
USE_TZ = False基于双下划线的模糊查询
# 查询书名以少年开头的哪些书
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(title__startswith='少年') #以什么开头
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(title__endswith='梅') #以什么结尾
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(title__startswith='p') #区分大小写
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(title__istartswith='p') #不区分大小写
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(title__contains='th') #包含
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(title__icontains='th') #包含 不区分大小写
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(price__gt=15) 大于
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(price__gte=15) 大于等于
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(price__lt=15) 小于
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(price__lte=15) 小于等于
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(price=15 or price=18 or price=30)
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(price__in=[15,18,30]) 价格等于15或者等于18或者等于30的书籍
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(price__range=[15, 20]) #价格大于等于15并且小于等于20, between and
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(id=10, price=15) #逗号连接的查询条件就是and的关系
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(pub_date__year='2020') #2020年的所有书籍
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(pub_date__year='2020',pub_date__month='11') #2020年11月份的所有书籍
# obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(pub_date__year='2020',pub_date__month='11',pub_date__day='25') #2020年11月5号的所有书籍
obj_list = models.Book.objects.filter(pub_date='2020-11-25') #2020年11月5号的所有书籍
print(obj_list)