前言
本章分析Kafka的数据复制。
- 回顾Controller选举和Topic创建;
- Leader选举;
- 数据复制;
- 高水位 和 ISR;
注:
- 基于Kafka2.6,无KRaft;
- 往期回顾:juejin.cn/column/7523... ;
一、Controller
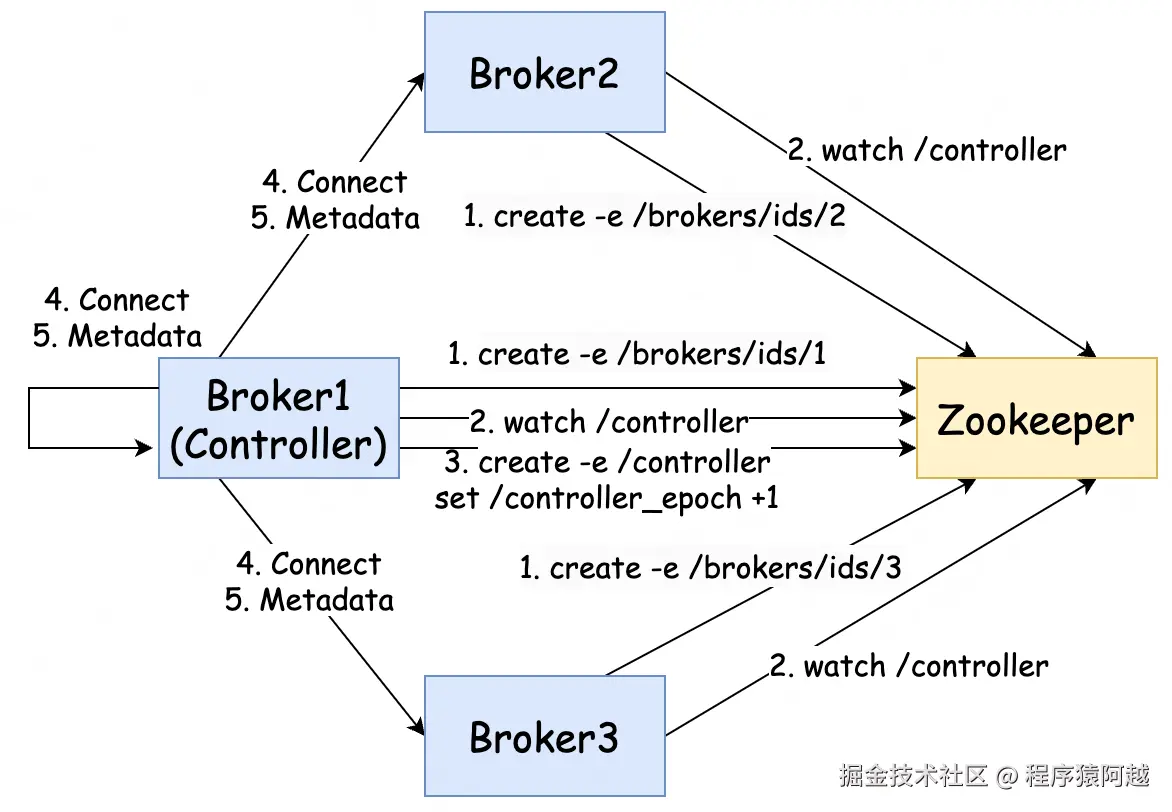
Controller:Broker集群中的特殊角色,负责管理Topic和Broker。
ControllerEventThread#doWork,controller-event-thread单线程处理各类事件,如Topic变更、Broker变更。
Controller选举:
- KafkaZkClient#registerBroker:Broker注册/brokers/ids/{brokerId}临时ZNode。
ruby
# /brokers/ids/{brokerId}
{"listener_security_protocol_map":{"PLAINTEXT":"PLAINTEXT"},
"endpoints":["PLAINTEXT://localhost:9092"],
"jmx_port":-1,"port":9092,
"host":"localhost","version":4,"timestamp":"1766887228838"}- KafkaController#processStartup:Broker watch /controller节点,如果不存在尝试创建/controller临时ZNode,并更新controller任期 = /controller_epoch + 1,成为Controller。
通过ZK的MultiOp(打包create -e /controller和set /controller_epoch)+ ZNode Version乐观更新实现。
bash
# /controller
数据={"version":1,"brokerid":1(成为controller的brokerId),"timestamp":"xxx"}
# /controller_epoch
数据=1(任期)- KafkaController#onControllerFailover:Broker成为Controller后处理
-
监听ZNode,包括:/brokers/ids Broker变更、/brokers/topics Topic变更;
-
组装内存ControllerContext,包括:
- /brokers/ids:broker信息;
- /brokers/topics:topic信息;
- /brokers/topics/{topic}:topic分区分配;
- /brokers/topics/{topic}/partitions/{partitionId}/state:topic分区状态LeaderAndIsr;
- 与所有broker建立连接(包括自己);
-
发送UpdateMetadataRequest给所有存活broker,包含broker和topic分区信息,broker将数据缓存到MetadataCache;
二、Topic分区Leader选举
2-1、创建Topic初始状态
回顾Topic创建,分区Leader如何产生,简化流程如下。
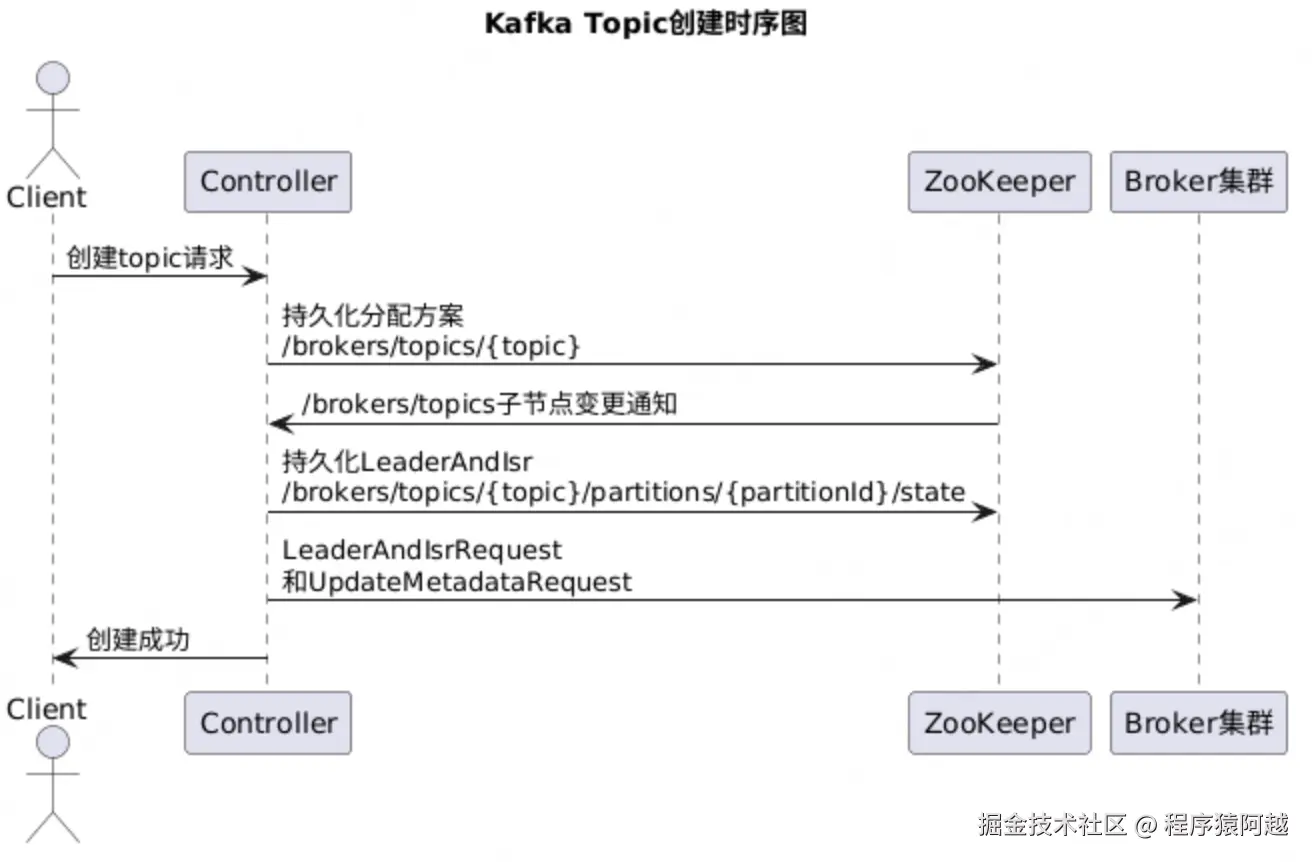
有两个状态需要Controller在创建Topic时定义:
- AdminUtils#assignReplicasToBrokers:分区分配方案 ,根据请求分区数 和副本数 ,将副本均匀分布在不同Broker节点上,通过 /brokers/topics/{topic} 持久化。
json
# 这个topic只有一个分区,每个分区有两个副本
# p0分区的两个副本在brokerId=111和222上
{"version":2,"partitions":{"0":[222,111]}}- ZkPartitionStateMachine#initializeLeaderAndIsrForPartitions:LeaderAndIsr分区状态 ,isr列表=当时在线的broker ,leader=isr列表第一个副本 ,通过 /brokers/topics/{topic}/partitions/{partitionId}/state持久化。
json
# p0分区的isr列表为222和111,当前leader副本是222
{"controller_epoch":1,"leader":222,"version":1,"leader_epoch":0,"isr":[222,111]}完成Topic创建后,Controller通过LeaderAndIsrRequest 把分区状态下发给分区相关Broker,Broker根据自己是leader还是follower做出反应。
2-2、Leader选举主流程
ZkPartitionStateMachine#doElectLeaderForPartitions:Controller处理Leader选举
- 查询/brokers/topics/{topic}/partitions/{partitionId}/state得到当前LeaderAndIsr;
- 根据策略选主;
- 更新/brokers/topics/{topic}/partitions/{partitionId}/state;
- 发送LeaderAndIsr请求给相关Broker;
scala
private def doElectLeaderForPartitions(
partitions: Seq[TopicPartition],
partitionLeaderElectionStrategy: PartitionLeaderElectionStrategy
): (Map[TopicPartition, Either[Exception, LeaderAndIsr]], Seq[TopicPartition]) = {
// 1. 查询/brokers/topics/{topic}/partitions/{partitionId}/state
val getDataResponses = zkClient.getTopicPartitionStatesRaw(partitions)
val validLeaderAndIsrs = mutable.Buffer.empty[(TopicPartition, LeaderAndIsr)]
getDataResponses.foreach { getDataResponse =>
val partition = getDataResponse.ctx.get.asInstanceOf[TopicPartition]
if (getDataResponse.resultCode == Code.OK) {
TopicPartitionStateZNode.decode(getDataResponse.data, getDataResponse.stat) match {
case Some(leaderIsrAndControllerEpoch) =>
validLeaderAndIsrs += partition -> leaderIsrAndControllerEpoch.leaderAndIsr
}
}
if (validLeaderAndIsrs.isEmpty) {
return (failedElections.toMap, Seq.empty)
}
// 2. 根据策略选主
val (partitionsWithoutLeaders, partitionsWithLeaders) = partitionLeaderElectionStrategy match {
case OfflinePartitionLeaderElectionStrategy(allowUnclean) =>
// ...
case ReassignPartitionLeaderElectionStrategy =>
// ...
case PreferredReplicaPartitionLeaderElectionStrategy =>
// ...
case ControlledShutdownPartitionLeaderElectionStrategy =>
// ...
}
// partition -> replicas
val recipientsPerPartition = partitionsWithLeaders.map(result => result.topicPartition -> result.liveReplicas).toMap
// partition -> leaderAndIsr
val adjustedLeaderAndIsrs = partitionsWithLeaders.map(result => result.topicPartition -> result.leaderAndIsr.get).toMap
// 3. 更新/brokers/topics/topicA/partitions/0/state
val UpdateLeaderAndIsrResult(finishedUpdates, updatesToRetry) = zkClient.updateLeaderAndIsr(
adjustedLeaderAndIsrs, controllerContext.epoch, controllerContext.epochZkVersion)
// 4. LeaderAndIsr请求
finishedUpdates.foreach { case (partition, result) =>
result.foreach { leaderAndIsr =>
val replicaAssignment = controllerContext.partitionFullReplicaAssignment(partition)
val leaderIsrAndControllerEpoch = LeaderIsrAndControllerEpoch(leaderAndIsr, controllerContext.epoch)
// 更新controllerContext内存
controllerContext.partitionLeadershipInfo.put(partition, leaderIsrAndControllerEpoch)
controllerBrokerRequestBatch.addLeaderAndIsrRequestForBrokers(recipientsPerPartition(partition), partition,
leaderIsrAndControllerEpoch, replicaAssignment, isNew = false)
}
}
(finishedUpdates ++ failedElections, updatesToRetry)
}2-3、Leader选举策略
Leader选举有4种策略,对应多种场景。
scala
sealed trait PartitionLeaderElectionStrategy
// case1 zk发现分区leader broker非正常下线
// case2 ElectLeadersRequest(忽略) admin api手动触发 allowUnclean=true
final case class OfflinePartitionLeaderElectionStrategy(allowUnclean: Boolean) extends PartitionLeaderElectionStrategy
// case3 AlterPartitionReassignmentsRequest: 分区重分配
final case object ReassignPartitionLeaderElectionStrategy extends PartitionLeaderElectionStrategy
// case4 controller定时:leader自动rebalance;
// case5 ElectLeadersRequest (忽略)admin api手动触发
final case object PreferredReplicaPartitionLeaderElectionStrategy extends PartitionLeaderElectionStrategy
// case6 ControlledShutdownRequest:Broker正常下线
final case object ControlledShutdownPartitionLeaderElectionStrategy extends PartitionLeaderElectionStrategy2-3-1、Broker异常下线
场景一:controller通过watch /brokers/ids发现broker下线(BrokerChangeHandler),且该broker是某分区leader。
ZkPartitionStateMachine#collectUncleanLeaderElectionState:获取分区-LeaderAndIsr-是否允许unlean选举。
如果topic配置(或全局)unclean.leader.election.enable=true(默认false),可以从非ISR副本中选Leader。
scala
private def collectUncleanLeaderElectionState(
leaderAndIsrs: Seq[(TopicPartition, LeaderAndIsr)],
allowUnclean: Boolean
): Seq[(TopicPartition, Option[LeaderAndIsr], Boolean)] = {
// isr中无存活副本的分区(1) | isr中有存活副本的分区(2)
val (partitionsWithNoLiveInSyncReplicas, partitionsWithLiveInSyncReplicas) = leaderAndIsrs.partition {
case (partition, leaderAndIsr) =>
val liveInSyncReplicas = leaderAndIsr.isr.filter(controllerContext.isReplicaOnline(_, partition))
liveInSyncReplicas.isEmpty
}
// 针对(1)中的分区,unclean.leader.election.enable=true的topic可以unclean选举
val electionForPartitionWithoutLiveReplicas = if (allowUnclean) {
// ... ElectLeadersRequest忽略
} else {
// unclean.leader.election.enable=true的topic可以unclean选举
val (logConfigs, failed) = zkClient.getLogConfigs(
partitionsWithNoLiveInSyncReplicas.iterator.map { case (partition, _) => partition.topic }.toSet,
config.originals()
)
partitionsWithNoLiveInSyncReplicas.map { case (partition, leaderAndIsr) =>
(
partition,
Option(leaderAndIsr),
logConfigs(partition.topic).uncleanLeaderElectionEnable.booleanValue()
)
}
}
electionForPartitionWithoutLiveReplicas ++
partitionsWithLiveInSyncReplicas.map { case (partition, leaderAndIsr) =>
(partition, Option(leaderAndIsr), false)
}
}PartitionLeaderElectionAlgorithms#offlinePartitionLeaderElection:
- 优先ISR中的存活副本选择;2. 如果允许unclean,从非ISR的存活副本中选择;
scala
def offlinePartitionLeaderElection(assignment: Seq[Int],
isr: Seq[Int],
liveReplicas: Set[Int],
uncleanLeaderElectionEnabled: Boolean,
controllerContext: ControllerContext): Option[Int] = {
// 1. 优先从 isr中的存活副本 选leader
assignment.find(id => liveReplicas.contains(id) && isr.contains(id)).orElse {
if (uncleanLeaderElectionEnabled) {
// 2. unclean开启 允许从 非isr中的存活副本 选leader
val leaderOpt = assignment.find(liveReplicas.contains)
if (leaderOpt.isDefined)
controllerContext.stats.uncleanLeaderElectionRate.mark()
leaderOpt
} else {
None
}
}
}Election#leaderForOffline:根据leader选举结果设置isr列表,正常选举-isr剔除下线broker,unlean选举-只包含leader。
scala
private def leaderForOffline(partition: TopicPartition,
leaderAndIsrOpt: Option[LeaderAndIsr],
uncleanLeaderElectionEnabled: Boolean,
controllerContext: ControllerContext): ElectionResult = {
val assignment = controllerContext.partitionReplicaAssignment(partition)
val liveReplicas = assignment.filter(replica => controllerContext.isReplicaOnline(replica, partition))
leaderAndIsrOpt match {
case Some(leaderAndIsr) =>
val isr = leaderAndIsr.isr
// 选leader
val leaderOpt = PartitionLeaderElectionAlgorithms.offlinePartitionLeaderElection(
assignment, isr, liveReplicas.toSet, uncleanLeaderElectionEnabled, controllerContext)
val newLeaderAndIsrOpt = leaderOpt.map { leader =>
// leader在isr里,正常选举,isr剔除下线broker
val newIsr = if (isr.contains(leader)) isr.filter(replica => controllerContext.isReplicaOnline(replica, partition))
// leader不在isr里,unlean选举,isr只包含leader
else List(leader)
leaderAndIsr.newLeaderAndIsr(leader, newIsr)
}
ElectionResult(partition, newLeaderAndIsrOpt, liveReplicas)
case None =>
ElectionResult(partition, None, liveReplicas)
}
}2-3-2、分区重分配
场景二:通过AlterPartitionReassignmentsRequest(admin api)分区重分配触发,由于新的副本分配方案中不包含老leader,进而触发leader选举。
Election#leaderForReassign:reassign场景下的leader选举,从reassign目标副本集中选择isr中的存活副本,isr保持不变。
scala
private def leaderForReassign(partition: TopicPartition,
leaderAndIsr: LeaderAndIsr,
controllerContext: ControllerContext): ElectionResult = {
// reassign的目标副本集
val targetReplicas = controllerContext.partitionFullReplicaAssignment(partition).targetReplicas
val liveReplicas = targetReplicas.filter(replica => controllerContext.isReplicaOnline(replica, partition))
val isr = leaderAndIsr.isr
// reassign目标副本集 选择 isr中的存活副本
val leaderOpt = PartitionLeaderElectionAlgorithms.reassignPartitionLeaderElection(targetReplicas, isr, liveReplicas.toSet)
// isr保持不变 --- isr会在下一步stopRemovedReplicasOfReassignedPartition删除
val newLeaderAndIsrOpt = leaderOpt.map(leader => leaderAndIsr.newLeader(leader))
ElectionResult(partition, newLeaderAndIsrOpt, targetReplicas)
}
// PartitionLeaderElectionAlgorithms
def reassignPartitionLeaderElection(reassignment: Seq[Int], isr: Seq[Int], liveReplicas: Set[Int]): Option[Int] = {
reassignment.find(id => liveReplicas.contains(id) && isr.contains(id))
}2-3-3、Leader自动Rebalance
场景三:Controller定时检测Leader角色是否均匀分布在Broker集群里,如果不均匀则触发Rebalance,转移分区Leader。
AdminUtils#assignReplicasToBrokers:创建Topic时,Controller会使用以下策略将分区副本均匀分布在不同Broker节点上,每个分区的第一个副本(replica)成为leader。preferred副本 就是 分区分配的第一个副本。

从/kafka/brokers/topics/{topic}上看,比如0分区的preferred副本是brokerId=222。
json
{"partitions":{"0":[222,111],"1":[111,333],"2":[333,222]}}leader自动rebalance默认配置:
- auto.leader.rebalance.enable=true,leader自动rebalance;
- leader.imbalance.check.interval.seconds=300,每5分钟检测一次;
- leader.imbalance.per.broker.percentage=10,不平衡比率超过10%,触发分区leader rebalance;
KafkaController#checkAndTriggerAutoLeaderRebalance:自动rebalance检测如下,主要在于如何触发10%。
比如:brokerId=333在10个partition里排在第一位(preferred副本)。
case1-10个partition里有2个partition,brokerId=333不是leader,imbalanceRatio=20%,针对这两个partition要执行rebalance;
case2-如果只有1个partition,brokerId=333不是leader,由于imbalanceRatio=10%,未超过阈值,则不会rebalance。
scala
private def checkAndTriggerAutoLeaderRebalance(): Unit = {
// preferred副本(每个分区的第一个副本) -> topic partition -> 副本
val preferredReplicasForTopicsByBrokers: Map[Int, Map[TopicPartition, Seq[Int]]] =
controllerContext.allPartitions.filterNot {
tp => topicDeletionManager.isTopicQueuedUpForDeletion(tp.topic)
}.map { tp =>
(tp, controllerContext.partitionReplicaAssignment(tp) )
}.toMap.groupBy { case (_, assignedReplicas) => assignedReplicas.head }
preferredReplicasForTopicsByBrokers.foreach { case (leaderBroker, topicPartitionsForBroker) =>
val topicsNotInPreferredReplica = topicPartitionsForBroker.filter { case (topicPartition, _) =>
val leadershipInfo = controllerContext.partitionLeadershipInfo.get(topicPartition)
leadershipInfo.exists(_.leaderAndIsr.leader != leaderBroker)
}
val imbalanceRatio = topicsNotInPreferredReplica.size.toDouble / topicPartitionsForBroker.size
// 对于当前broker 非preferred分区 / 非preferred+preferred分区 > 10 %
if (imbalanceRatio > (config.leaderImbalancePerBrokerPercentage.toDouble / 100)) {
// 循环非preferred分区,broker在这个分区的isr里且存活,这个分区才会重新选举
val candidatePartitions = topicsNotInPreferredReplica.keys.filter(tp =>
controllerContext.partitionsBeingReassigned.isEmpty &&
!topicDeletionManager.isTopicQueuedUpForDeletion(tp.topic) &&
controllerContext.allTopics.contains(tp.topic) &&
canPreferredReplicaBeLeader(tp)
)
onReplicaElection(candidatePartitions.toSet, ElectionType.PREFERRED, AutoTriggered)
}
}
}Election#leaderForPreferredReplica:选举策略就是从assignment分区分配中取第一个副本(preferred)。
scala
private def leaderForPreferredReplica(partition: TopicPartition,
leaderAndIsr: LeaderAndIsr,
controllerContext: ControllerContext): ElectionResult = {
// 分区当前分配情况,如:brokerId=[1, 2]
val assignment = controllerContext.partitionReplicaAssignment(partition)
val liveReplicas = assignment.filter(replica => controllerContext.isReplicaOnline(replica, partition))
val isr = leaderAndIsr.isr
// preferred策略,选assignment中第一个副本,要求它在isr中且存活
val leaderOpt = PartitionLeaderElectionAlgorithms.preferredReplicaPartitionLeaderElection(assignment, isr, liveReplicas.toSet)
// isr不变
val newLeaderAndIsrOpt = leaderOpt.map(leader => leaderAndIsr.newLeader(leader))
ElectionResult(partition, newLeaderAndIsrOpt, assignment)
}
// PartitionLeaderElectionAlgorithms
def preferredReplicaPartitionLeaderElection(assignment: Seq[Int], isr: Seq[Int], liveReplicas: Set[Int]): Option[Int] = {
assignment.headOption.filter(id => liveReplicas.contains(id) && isr.contains(id))
}2-3-4、Broker正常下线
场景四:Broker正常下线。
KafkaServer#shutdown:Broker正常下线会向Controller发送ControlledShutdownRequest。
KafkaController#doControlledShutdown:Controller发现该Broker是某些分区的leader,触发leader选举。
scala
private def doControlledShutdown(id: Int, brokerEpoch: Long): Set[TopicPartition] = {
// ...
val (partitionsLedByBroker, partitionsFollowedByBroker) = partitionsToActOn.partition { partition =>
controllerContext.partitionLeadershipInfo(partition).leaderAndIsr.leader == id
}
// 对于自己是leader的分区,重新选举,发送LeaderAndIsr
partitionStateMachine.handleStateChanges(partitionsLedByBroker.toSeq, OnlinePartition, Some(ControlledShutdownPartitionLeaderElectionStrategy))
// ...
// 对于自己是follower的分区,将自己从isr中移除,发送LeaderAndIsr
replicaStateMachine.handleStateChanges(partitionsFollowedByBroker.map(partition =>
PartitionAndReplica(partition, id)).toSeq, OfflineReplica)
// ...
}Election#leaderForControlledShutdown:leader选择存活isr中的一个,排除下线broker。
scala
private def leaderForControlledShutdown(partition: TopicPartition,
leaderAndIsr: LeaderAndIsr,
shuttingDownBrokerIds: Set[Int],
controllerContext: ControllerContext): ElectionResult = {
val assignment = controllerContext.partitionReplicaAssignment(partition)
val liveOrShuttingDownReplicas = assignment.filter(replica =>
controllerContext.isReplicaOnline(replica, partition, includeShuttingDownBrokers = true))
val isr = leaderAndIsr.isr
// leader = 从 (存活isr - 下线broker) 中选一个
val leaderOpt = PartitionLeaderElectionAlgorithms.controlledShutdownPartitionLeaderElection(assignment, isr,
liveOrShuttingDownReplicas.toSet, shuttingDownBrokerIds)
// isr = isr - 下线broker
val newIsr = isr.filter(replica => !shuttingDownBrokerIds.contains(replica))
val newLeaderAndIsrOpt = leaderOpt.map(leader => leaderAndIsr.newLeaderAndIsr(leader, newIsr))
ElectionResult(partition, newLeaderAndIsrOpt, liveOrShuttingDownReplicas)
}
// PartitionLeaderElectionAlgorithms
def controlledShutdownPartitionLeaderElection(assignment: Seq[Int],
isr: Seq[Int], liveReplicas: Set[Int],
shuttingDownBrokers: Set[Int]): Option[Int] = {
assignment.find(id => liveReplicas.contains(id)
&& isr.contains(id) && !shuttingDownBrokers.contains(id))
}三、Broker处理LeaderAndIsrRequest
当Leader或ISR变更,Controller会下发LeaderAndIsrRequest。
java
public class LeaderAndIsrRequestData implements ApiMessage {
// controller的brokerId
private int controllerId;
// controller任期
private int controllerEpoch;
// controller看到当前broker的epoch
private long brokerEpoch;
// 分区状态
private List<LeaderAndIsrTopicState> topicStates;
// 相关的存活的leader brokers
private List<LeaderAndIsrLiveLeader> liveLeaders;
}
static public class LeaderAndIsrTopicState implements Message {
private String topicName;
private List<LeaderAndIsrPartitionState> partitionStates;
}
static public class LeaderAndIsrPartitionState implements Message {
private String topicName;
// 分区
private int partitionIndex;
private int controllerEpoch;
// 分区leader的brokerId
private int leader;
// leader epoch
private int leaderEpoch;
// isr列表
private List<Integer> isr;
// 副本列表
private List<Integer> replicas;
// ...
}ReplicaManager#becomeLeaderOrFollower:Broker处理LeaderAndIsrRequest。
- 请求合法性校验,如controller任期等;
- 分区成为leader执行makeLeaders,反之执行makeFollowers;
- 开启highwatermark-checkpoint线程,将内存高水位刷盘到replication-offset-checkpoint文件;
- onLeadershipChange,如果是系统topic,consumer_offsets-加载消费进度到内存,transaction_state-加载事务状态到内存;
scala
def becomeLeaderOrFollower(correlationId: Int,
leaderAndIsrRequest: LeaderAndIsrRequest,
onLeadershipChange: (Iterable[Partition], Iterable[Partition]) => Unit): LeaderAndIsrResponse = {
replicaStateChangeLock synchronized {
val controllerId = leaderAndIsrRequest.controllerId
// 入参分区状态
val requestPartitionStates = leaderAndIsrRequest.partitionStates.asScala
// 1. 校验controller epoch
if (leaderAndIsrRequest.controllerEpoch < controllerEpoch) {
leaderAndIsrRequest.getErrorResponse(0, Errors.STALE_CONTROLLER_EPOCH.exception)
} else {
val responseMap = new mutable.HashMap[TopicPartition, Errors]
controllerEpoch = leaderAndIsrRequest.controllerEpoch
val partitionStates = new mutable.HashMap[Partition, LeaderAndIsrPartitionState]()
requestPartitionStates.foreach { partitionState =>
// 2. 内存获取或创建partition
val topicPartition = new TopicPartition(partitionState.topicName, partitionState.partitionIndex)
val partitionOpt = getPartition(topicPartition) match {
case HostedPartition.Offline =>
responseMap.put(topicPartition, Errors.KAFKA_STORAGE_ERROR)
None
case HostedPartition.Online(partition) =>
Some(partition)
case HostedPartition.None =>
val partition = Partition(topicPartition, time, this)
allPartitions.putIfNotExists(topicPartition, HostedPartition.Online(partition))
Some(partition)
}
// 3. 校验partition leader的epoch,需要大于当前节点看到的leader的epoch,才能做其他操作
partitionOpt.foreach { partition =>
val currentLeaderEpoch = partition.getLeaderEpoch
val requestLeaderEpoch = partitionState.leaderEpoch
if (requestLeaderEpoch > currentLeaderEpoch) {
if (partitionState.replicas.contains(localBrokerId))
partitionStates.put(partition, partitionState)
else {
responseMap.put(topicPartition, Errors.UNKNOWN_TOPIC_OR_PARTITION)
}
} else if (requestLeaderEpoch < currentLeaderEpoch) {
responseMap.put(topicPartition, Errors.STALE_CONTROLLER_EPOCH)
} else {
responseMap.put(topicPartition, Errors.STALE_CONTROLLER_EPOCH)
}
}
}
// 4. 根据partition状态,成为leader或follower,会创建log数据目录和文件
val partitionsToBeLeader = partitionStates.filter { case (_, partitionState) =>
partitionState.leader == localBrokerId
}
val partitionsToBeFollower = partitionStates.filter { case (k, _) => !partitionsToBeLeader.contains(k) }
val highWatermarkCheckpoints = new LazyOffsetCheckpoints(this.highWatermarkCheckpoints)
val partitionsBecomeLeader = if (partitionsToBeLeader.nonEmpty)
makeLeaders(controllerId, controllerEpoch, partitionsToBeLeader, correlationId, responseMap,
highWatermarkCheckpoints)
else
Set.empty[Partition]
val partitionsBecomeFollower = if (partitionsToBeFollower.nonEmpty)
makeFollowers(controllerId, controllerEpoch, partitionsToBeFollower, correlationId, responseMap,
highWatermarkCheckpoints)
else
Set.empty[Partition]
// 5. 开启highwatermark-checkpoint线程
startHighWatermarkCheckPointThread()
// 6. 如果是协调者系统topic,如consumer_offsets和transaction_state,加载 消费进度 和 事务状态
onLeadershipChange(partitionsBecomeLeader, partitionsBecomeFollower)
val responsePartitions = responseMap.iterator.map { case (tp, error) =>
new LeaderAndIsrPartitionError()
.setTopicName(tp.topic)
.setPartitionIndex(tp.partition)
.setErrorCode(error.code)
}.toBuffer
new LeaderAndIsrResponse(new LeaderAndIsrResponseData()
.setErrorCode(Errors.NONE.code)
.setPartitionErrors(responsePartitions.asJava))
}
}
}3-1、leader
Partition#makeLeader:如果分区成为leader
- 更新assignment和leaderAndIsr到内存;
- 尝试创建Log数据目录和文件;
- leader变更,自己成为新leader,初始化远程副本状态;
- isr变更 ,可能导致高水位变更,高水位升高触发相关延迟任务完成(如produce请求acks=-1);
这里关注1和3,高水位变更后面再看。
scala
def makeLeader(partitionState: LeaderAndIsrPartitionState,
highWatermarkCheckpoints: OffsetCheckpoints): Boolean = {
val (leaderHWIncremented, isNewLeader) = inWriteLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) {
controllerEpoch = partitionState.controllerEpoch
val isr = partitionState.isr.asScala.map(_.toInt).toSet
val addingReplicas = partitionState.addingReplicas.asScala.map(_.toInt)
val removingReplicas = partitionState.removingReplicas.asScala.map(_.toInt)
// 1. 更新assignment和leaderAndIsr到内存
updateAssignmentAndIsr(
assignment = partitionState.replicas.asScala.map(_.toInt),
isr = isr,
addingReplicas = addingReplicas,
removingReplicas = removingReplicas
)
// 2. 尝试创建Log数据文件,高水位=replication-offset-checkpoint中的高水位
createLogIfNotExists(partitionState.isNew, isFutureReplica = false, highWatermarkCheckpoints)
// 内存变量更新...
val leaderLog = localLogOrException
val leaderEpochStartOffset = leaderLog.logEndOffset
leaderEpoch = partitionState.leaderEpoch
leaderEpochStartOffsetOpt = Some(leaderEpochStartOffset)
zkVersion = partitionState.zkVersion
leaderLog.maybeAssignEpochStartOffset(leaderEpoch, leaderEpochStartOffset)
val isNewLeader = !isLeader
val curTimeMs = time.milliseconds
remoteReplicas.foreach { replica =>
val lastCaughtUpTimeMs = if (inSyncReplicaIds.contains(replica.brokerId)) curTimeMs else 0L
replica.resetLastCaughtUpTime(leaderEpochStartOffset, curTimeMs, lastCaughtUpTimeMs)
}
// 记录leader任期的起始offset到leader-epoch-checkpoint
leaderLog.maybeAssignEpochStartOffset(leaderEpoch, leaderEpochStartOffset)
if (isNewLeader) {
// 3. 刚成为leader,初始化其他副本状态
leaderReplicaIdOpt = Some(localBrokerId)
remoteReplicas.foreach { replica =>
replica.updateFetchState(
followerFetchOffsetMetadata = LogOffsetMetadata.UnknownOffsetMetadata,
followerStartOffset = Log.UnknownOffset,
followerFetchTimeMs = 0L,
leaderEndOffset = Log.UnknownOffset)
}
}
// 4. 每次isr变更,重新计算hw,因为isr可能变小,导致hw变大
(maybeIncrementLeaderHW(leaderLog), isNewLeader)
}
// hw增加,尝试完成延迟操作,比如produce请求acks=-1
if (leaderHWIncremented)
tryCompleteDelayedRequests()
isNewLeader
}Partition#updateAssignmentAndIsr:更新分区分配和isr信息到内存。
如当前brokerId=1,assignment=[1,2,3]代表有3个副本,isr=[1,2]代表有2个副本追上当前leader副本,remoteReplicasMap=brokerId in (2,3)的副本信息Replica。
scala
// 其他副本id(brokerId) 和 信息
private val remoteReplicasMap = new Pool[Int, Replica]
// isr集合 包含n个brokerId
var inSyncReplicaIds = Set.empty[Int]
// assignment分配信息 包含n个brokerId
var assignmentState: AssignmentState = SimpleAssignmentState(Seq.empty)
def updateAssignmentAndIsr(assignment: Seq[Int],
isr: Set[Int],
addingReplicas: Seq[Int],
removingReplicas: Seq[Int]): Unit = {
// 更新其他副本map
val newRemoteReplicas = assignment.filter(_ != localBrokerId)
val removedReplicas = remoteReplicasMap.keys.filter(!newRemoteReplicas.contains(_))
newRemoteReplicas.foreach(id => remoteReplicasMap.getAndMaybePut(id, new Replica(id, topicPartition)))
remoteReplicasMap.removeAll(removedReplicas)
if (addingReplicas.nonEmpty || removingReplicas.nonEmpty)
// 分区重分配中间状态
assignmentState = OngoingReassignmentState(addingReplicas, removingReplicas, assignment)
else
// 正常状态,更新assignment分配情况
assignmentState = SimpleAssignmentState(assignment)
// isr集合变更
inSyncReplicaIds = isr
}Leader需要维护Replica副本信息包括:
- logEndOffsetMetadata:LEO,follower写入offset;
- logStartOffset:follower起始offset;
- lastFetchLeaderLogEndOffset:follower最后一次发送FetchRequest时,leader的LEO写入offset进度;
- lastFetchTimeMs:follower最后一次发送FetchRequest的时间戳;
- lastCaughtUpTimeMs :follower追上leader的时间戳,用于判断follower是否会离开isr的关键,后面再看;
scala
class Replica(val brokerId: Int, val topicPartition: TopicPartition) {
private[this] var _logEndOffsetMetadata = LogOffsetMetadata.UnknownOffsetMetadata
private[this] var _logStartOffset = Log.UnknownOffset
private[this] var lastFetchLeaderLogEndOffset = 0L
private[this] var lastFetchTimeMs = 0L
private[this] var _lastCaughtUpTimeMs = 0L
}3-2、follower
ReplicaManager#makeFollowers:
- partition.makeFollower:类似Leader,updateAssignmentAndIsr更新内存数据,创建log数据文件,如果leader发生变更(或leader epoch变更),返回true,进行下一步;
- leader变更,分区加入ReplicaFetcherManager,fetch初始offset=当前分区副本的高水位;
scala
private def makeFollowers(controllerId: Int,
controllerEpoch: Int,
partitionStates: Map[Partition, LeaderAndIsrPartitionState],
correlationId: Int,
responseMap: mutable.Map[TopicPartition, Errors],
highWatermarkCheckpoints: OffsetCheckpoints) : Set[Partition] = {
partitionStates.foreach { case (partition, partitionState) =>
responseMap.put(partition.topicPartition, Errors.NONE)
}
val partitionsToMakeFollower: mutable.Set[Partition] = mutable.Set()
try {
partitionStates.foreach { case (partition, partitionState) =>
val newLeaderBrokerId = partitionState.leader
try {
metadataCache.getAliveBrokers.find(_.id == newLeaderBrokerId) match {
case Some(_) =>
// 1. 对于partition的leader存活的情况下,makeFollower
if (partition.makeFollower(partitionState, highWatermarkCheckpoints))
partitionsToMakeFollower += partition
}
} catch {
responseMap.put(partition.topicPartition, Errors.KAFKA_STORAGE_ERROR)
}
}
// 先从fetcher线程中移除分区
replicaFetcherManager.removeFetcherForPartitions(partitionsToMakeFollower.map(_.topicPartition))
partitionsToMakeFollower.foreach { partition =>
completeDelayedFetchOrProduceRequests(partition.topicPartition)
}
if (isShuttingDown.get()) {
} else {
// 2. 分区加入fetcher
val partitionsToMakeFollowerWithLeaderAndOffset = partitionsToMakeFollower.map { partition =>
val leader = metadataCache.getAliveBrokers.find(_.id == partition.leaderReplicaIdOpt.get).get
.brokerEndPoint(config.interBrokerListenerName)
// follower从HW开始同步
val fetchOffset = partition.localLogOrException.highWatermark
partition.topicPartition -> InitialFetchState(leader, partition.getLeaderEpoch, fetchOffset)
}.toMap
// 分区 -> InitialFetchState(leader/epoch/offset)
replicaFetcherManager.addFetcherForPartitions(partitionsToMakeFollowerWithLeaderAndOffset)
}
} catch {
throw e
}
partitionsToMakeFollower
}AbstractFetcherManager#addFetcherForPartitions:每个分区需要分配到一个固定的Fetcher线程。默认num.replica.fetchers=1,分区对应fetcher线程=hash(partition)%1=0,代表针对一个broker只开启一个fetcher线程,如ReplicaFetcherThread-0-{brokerId}。
scala
// brokerId + fetcherId -> FetcherThread
private[server] val fetcherThreadMap =
new mutable.HashMap[BrokerIdAndFetcherId, T]
def addFetcherForPartitions(partitionAndOffsets: Map[TopicPartition, InitialFetchState]): Unit = {
lock synchronized {
// 1. getFetcherId 分配fetcherId = hash(TopicPartition) % num.replica.fetchers(1) = 0
val partitionsPerFetcher = partitionAndOffsets.groupBy { case (topicPartition, brokerAndInitialFetchOffset) =>
BrokerAndFetcherId(brokerAndInitialFetchOffset.leader, getFetcherId(topicPartition))
}
// ReplicaFetcherThread-$fetcherId-${sourceBroker.id}
def addAndStartFetcherThread(brokerAndFetcherId: BrokerAndFetcherId,
brokerIdAndFetcherId: BrokerIdAndFetcherId): T = {
val fetcherThread = createFetcherThread(brokerAndFetcherId.fetcherId, brokerAndFetcherId.broker)
fetcherThreadMap.put(brokerIdAndFetcherId, fetcherThread)
fetcherThread.start()
fetcherThread
}
for ((brokerAndFetcherId, initialFetchOffsets) <- partitionsPerFetcher) {
// 2. 创建或获取分区对应Fetcher线程 = hash(brokerId + fetcherId)
val brokerIdAndFetcherId = BrokerIdAndFetcherId(brokerAndFetcherId.broker.id, brokerAndFetcherId.fetcherId)
val fetcherThread = fetcherThreadMap.get(brokerIdAndFetcherId) match {
case Some(currentFetcherThread) if currentFetcherThread.sourceBroker == brokerAndFetcherId.broker =>
currentFetcherThread
case Some(f) =>
f.shutdown()
addAndStartFetcherThread(brokerAndFetcherId, brokerIdAndFetcherId)
case None =>
addAndStartFetcherThread(brokerAndFetcherId, brokerIdAndFetcherId)
}
// initialOffsetAndEpochs = 拉取位点高水位 + 当前leader epoch
val initialOffsetAndEpochs = initialFetchOffsets.map { case (tp, brokerAndInitOffset) =>
tp -> OffsetAndEpoch(brokerAndInitOffset.initOffset, brokerAndInitOffset.currentLeaderEpoch)
}
// 3. 分区初始offset加入fetcherThread
addPartitionsToFetcherThread(fetcherThread, initialOffsetAndEpochs)
}
}
}
def addPartitions(initialFetchStates: Map[TopicPartition, OffsetAndEpoch]): Set[TopicPartition] = {
partitionMapLock.lockInterruptibly()
try {
failedPartitions.removeAll(initialFetchStates.keySet)
initialFetchStates.foreach { case (tp, initialFetchState) =>
val currentState = partitionStates.stateValue(tp)
val updatedState = if (currentState != null && currentState.currentLeaderEpoch == initialFetchState.leaderEpoch) {
currentState
} else if (initialFetchState.offset < 0) {
fetchOffsetAndTruncate(tp, initialFetchState.leaderEpoch)
} else {
// 初始状态=Truncating
PartitionFetchState(initialFetchState.offset, None, initialFetchState.leaderEpoch, state = Truncating)
}
partitionStates.updateAndMoveToEnd(tp, updatedState)
}
partitionMapCond.signalAll()
initialFetchStates.keySet
} finally partitionMapLock.unlock()
}FetcherThread维护拉取broker每个分区的Fetch状态,初始状态为Truncating。
scala
abstract class AbstractFetcherThread(...) {
// map结构 key=partition value=PartitionFetchState
private val partitionStates = new PartitionStates[PartitionFetchState]
}
case class PartitionFetchState(
// 拉取offset
fetchOffset: Long,
lag: Option[Long],
// leader epoch
currentLeaderEpoch: Int,
// 拉取异常,延迟时间
delay: Option[DelayedItem],
// 状态
state: ReplicaState)
}
sealed trait ReplicaState
case object Truncating extends ReplicaState
case object Fetching extends ReplicaState四、数据复制
4-1、Follower
Fetcher线程循环执行truncate和fetch,对应Truncating状态和Fetching状态分区。
scala
override def doWork(): Unit = {
maybeTruncate()
maybeFetch()
}4-1-1、truncate
每个分区数据目录下都有一个leader-epoch-checkpoint 文件,用于记录leader任期 对应数据起始offset,用于保证多个分区副本的最终一致性(数据截断)。
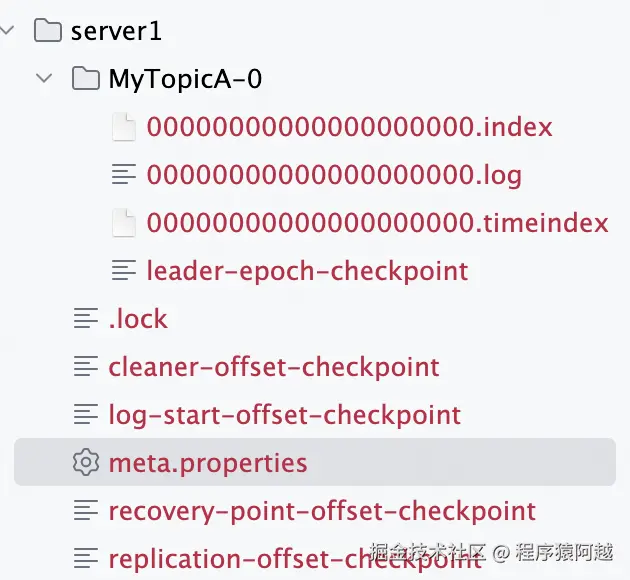
比如下面这个文件:epoch=0,offset=[0,1500);epoch=1,offset=[1500,3200);epoch=2,offset=[3200,?)。
arduino
3 // 条目数量
0 0 // epoch 起始offset
1 1500 // epoch 起始offset
2 3200 // epoch 起始offsetleader-epoch-checkpoint的写入时机:
- leader:处理LeaderAndIsrRequest,写入自己的新任期和当前LEO;
- follower:处理FetchResponse,写入数据时,创建新leader epoch数据记录;
AbstractFetcherThread#maybeTruncate:根据当前分区是否有leader epoch分为两种情况。
- 分区有数据写入,所以存在epoch,需要请求leader获取该epoch的结束offset;
- 分区没数据记录,没有epoch,从高水位截断数据;
scss
private def maybeTruncate(): Unit = {
val (partitionsWithEpochs, partitionsWithoutEpochs) = fetchTruncatingPartitions()
// case1 分区有数据记录,需要通过分区epoch
if (partitionsWithEpochs.nonEmpty) {
truncateToEpochEndOffsets(partitionsWithEpochs)
}
// case2 分区没数据记录,从高水位截断数据
if (partitionsWithoutEpochs.nonEmpty) {
truncateToHighWatermark(partitionsWithoutEpochs)
}
}AbstractFetcherThread#truncateToEpochEndOffsets:
- follower发送OffsetsForLeaderEpochRequest给leader,获取follower当前分区数据的最后一个epoch对应的结束offset;
- leader查询内存中的leader-epoch-checkpoint,返回epoch的结束offset;
- follower如果发现leader返回offset小于自己的offset,执行数据截断maybeTruncateToEpochEndOffsets;
- 分区进入Fetching状态;
第1和第2步在消费者消费中提到过,消费者发现分区leader任期变更,需要发送OffsetsForLeaderEpochRequest获取拉取数据对应leader epoch的最后offset。
scala
private def truncateToEpochEndOffsets(latestEpochsForPartitions: Map[TopicPartition, EpochData]): Unit = {
// 1. 发送OffsetsForLeaderEpochRequest
val endOffsets = fetchEpochEndOffsets(latestEpochsForPartitions)
inLock(partitionMapLock) {
// 校验请求期间 leader epoch没发生变化
val epochEndOffsets = endOffsets.filter { case (tp, _) =>
val curPartitionState = partitionStates.stateValue(tp)
val partitionEpochRequest = latestEpochsForPartitions.getOrElse(tp, {
throw new IllegalStateException()
})
val leaderEpochInRequest = partitionEpochRequest.currentLeaderEpoch.get
curPartitionState != null && leaderEpochInRequest == curPartitionState.currentLeaderEpoch
}
// 2. 执行数据截断
val ResultWithPartitions(fetchOffsets, partitionsWithError) = maybeTruncateToEpochEndOffsets(epochEndOffsets, latestEpochsForPartitions)
// 3-1. partitionsWithError - leaderEpoch发生变更,延迟fetch
handlePartitionsWithErrors(partitionsWithError, "truncateToEpochEndOffsets")
// 3-2. fetchOffsets - 标记分区截断完成,进入Fetching
updateFetchOffsetAndMaybeMarkTruncationComplete(fetchOffsets)
}
}Log#truncateTo:数据截断逻辑如下
scala
private[log] def truncateTo(targetOffset: Long): Boolean = {
maybeHandleIOException() {
if (targetOffset >= logEndOffset) {
// 正常情况,当前数据的leader epoch的结束offset >= LEO当前写入进度
false
} else {
// 异常情况,leader副本比follower副本数据多,比如发生unclean选举
info(s"Truncating to offset $targetOffset")
lock synchronized {
checkIfMemoryMappedBufferClosed()
if (segments.firstEntry.getValue.baseOffset > targetOffset) {
// 如果所有数据都大于目标offset,全量截断
truncateFullyAndStartAt(targetOffset)
} else {
// 删除超过targetOffset的segment
val deletable = logSegments.filter(segment => segment.baseOffset > targetOffset)
removeAndDeleteSegments(deletable, asyncDelete = true)
// 对当前segment截断到targetOffset
activeSegment.truncateTo(targetOffset)
// 更新offset信息,如LEO、HW、recoveryPoint(刷盘进度)...
updateLogEndOffset(targetOffset)
updateLogStartOffset(math.min(targetOffset, this.logStartOffset))
// leader-epoch-checkpoint也需要截断
leaderEpochCache.foreach(_.truncateFromEnd(targetOffset))
loadProducerState(targetOffset, reloadFromCleanShutdown = false)
}
true
}
}
}
}4-1-2、fetch
AbstractFetcherThread#maybeFetch:
- 构造FetchRequest;
- 发送FetchRequest;
- 收到FetchResponse数据,写入分区log;
- 更新Fetch状态,下次拉取offset=写入进度;
scala
private def maybeFetch(): Unit = {
// 1. 构建FetchRequest
val fetchRequestOpt = inLock(partitionMapLock) {
val ResultWithPartitions(fetchRequestOpt, partitionsWithError)
= buildFetch(partitionStates.partitionStateMap.asScala)
fetchRequestOpt
}
// 2. 发送FetchRequest
fetchRequestOpt.foreach { case ReplicaFetch(sessionPartitions, fetchRequest) =>
processFetchRequest(sessionPartitions, fetchRequest)
}
}
// 分区 -> 分区fetch状态
private val partitionStates = new PartitionStates[PartitionFetchState]
protected val partitionMapLock = new ReentrantLock
private val partitionMapCond = partitionMapLock.newCondition()
private def processFetchRequest(sessionPartitions: util.Map[TopicPartition, FetchRequest.PartitionData],
fetchRequest: FetchRequest.Builder): Unit = {
val partitionsWithError = mutable.Set[TopicPartition]()
var responseData: Map[TopicPartition, FetchData] = Map.empty
// 1. 发送FetchRequest,接收FetchResponse
try {
trace(s"Sending fetch request $fetchRequest")
responseData = fetchFromLeader(fetchRequest)
} catch {
case t: Throwable =>
if (isRunning) {
inLock(partitionMapLock) {
partitionsWithError ++= partitionStates.partitionSet.asScala
partitionMapCond.await(fetchBackOffMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
}
}
}
inLock(partitionMapLock) {
responseData.foreach { case (topicPartition, partitionData) =>
Option(partitionStates.stateValue(topicPartition)).foreach { currentFetchState =>
partitionData.error match {
case Errors.NONE =>
// 2. 写数据
val logAppendInfoOpt = processPartitionData(topicPartition, currentFetchState.fetchOffset,
partitionData)
// 3. 设置下次fetch offset
logAppendInfoOpt.foreach { logAppendInfo =>
val validBytes = logAppendInfo.validBytes
val nextOffset = if (validBytes > 0) logAppendInfo.lastOffset + 1 else currentFetchState.fetchOffset
val lag = Math.max(0L, partitionData.highWatermark - nextOffset)
if (validBytes > 0 && partitionStates.contains(topicPartition)) {
val newFetchState = PartitionFetchState(nextOffset, Some(lag), currentFetchState.currentLeaderEpoch, state = Fetching)
partitionStates.updateAndMoveToEnd(topicPartition, newFetchState)
}
}
// 异常加入partitionsWithError...
}
}
}
}
// 4. 异常分区 延迟fetch
if (partitionsWithError.nonEmpty) {
handlePartitionsWithErrors(partitionsWithError, "processFetchRequest")
}
}这里就看1和3。
第一步,构造FetchRequest同正常消费者:
- 有增量Fetch,没有分区变更的情况下,不需要发送所有分区;
- 默认Fetch参数相同:
- replica.fetch.min.bytes=1,如果消息不足1个字节,FetchRequest在server端被挂起;
- replica.fetch.wait.max.ms=500,不足minBytes被挂起时长;
- replica.fetch.max.bytes=1MB,单分区最大拉取字节数;
- replica.fetch.response.max.bytes=10MB,单次Fetch响应最大字节数;
唯一区别是,FetchRequest中的replicaId=follower的brokerId,因为leader需要统计每个副本的同步情况,控制ISR。
ReplicaFetcherThread#processPartitionData:第三步,follower收到FetchResponse。
- 数据写入分区log(同leader写log一致,包括建立索引、leader-epoch-checkpoint,recovery-point刷盘进度);
- 高水位=leader.高水位、logStartOffset=leader.logStartOffset;
scala
override def processPartitionData(topicPartition: TopicPartition,
fetchOffset: Long,
partitionData: FetchData): Option[LogAppendInfo] = {
val partition = replicaMgr.nonOfflinePartition(topicPartition).get
val log = partition.localLogOrException
val records = toMemoryRecords(partitionData.records)
// 写数据
val logAppendInfo = partition.appendRecordsToFollowerOrFutureReplica(records, isFuture = false)
val leaderLogStartOffset = partitionData.logStartOffset
// follower更新hw=leader
val followerHighWatermark = log.updateHighWatermark(partitionData.highWatermark)
// follower更新logStartOffset=leader
log.maybeIncrementLogStartOffset(leaderLogStartOffset, LeaderOffsetIncremented)
logAppendInfo
}
// 写入数据appendRecordsToFollowerOrFutureReplica
// Log#appendAsFollower
def appendAsFollower(records: MemoryRecords): LogAppendInfo = {
append(records,
origin = AppendOrigin.Replication,
interBrokerProtocolVersion = ApiVersion.latestVersion,
// 不需要分配数据记录的offset
assignOffsets = false,
leaderEpoch = -1,
ignoreRecordSize = true)
}4-2、Leader
4-2-1、处理FetchRequest
Leader处理Follower的FetchRequest同处理Consumer一致。
Partition#updateFollowerFetchState:区别是读取log数据结束后,需要更新follower的fetch状态,用于控制高低水位和ISR。
scala
def updateFollowerFetchState(followerId: Int,
followerFetchOffsetMetadata: LogOffsetMetadata,
followerStartOffset: Long,
followerFetchTimeMs: Long,
leaderEndOffset: Long): Boolean = {
getReplica(followerId) match {
case Some(followerReplica) =>
// 低水位 和删除数据有关 忽略
val oldLeaderLW = if (delayedOperations.numDelayedDelete > 0) lowWatermarkIfLeader else -1L
val prevFollowerEndOffset = followerReplica.logEndOffset
// 1. 更新follower副本状态
followerReplica.updateFetchState(
followerFetchOffsetMetadata, // follower本次请求的offset
followerStartOffset, // follower的logStartOffset
followerFetchTimeMs, // 收到fetch请求的时间
leaderEndOffset) // leader当前的写入位置LEO
val newLeaderLW = if (delayedOperations.numDelayedDelete > 0) lowWatermarkIfLeader else -1L
val leaderLWIncremented = newLeaderLW > oldLeaderLW
// 2. 如果follower不在isr中,校验是否需要扩张isr
if (!inSyncReplicaIds.contains(followerId))
maybeExpandIsr(followerReplica, followerFetchTimeMs)
// 3. follower可能已经在isr中,校验是否需要增加HW
val leaderHWIncremented = if (prevFollowerEndOffset != followerReplica.logEndOffset) {
leaderLogIfLocal.exists(leaderLog => maybeIncrementLeaderHW(leaderLog, followerFetchTimeMs))
} else {
false
}
// 高低水位变化,可能完成挂起的请求,比如ProduceRequest acks=-1
if (leaderLWIncremented || leaderHWIncremented)
tryCompleteDelayedRequests()
true
case None =>
false
}
}Replica#updateFetchState:每次follower拉消息,leader需要更新follower副本的同步进度。
fetch offset代表了follower的LEO,同步进度用lastCaughtUpTimeMs上次追上leader的时间表示。
- 如果本次fetch offset ≥ leader的LEO写入位置,代表follower已经完全追上leader,lastCaughtUpTimeMs=本次fetch请求收到时间;
- 如果本次fetch offset ≥ 上次fetch时leader的LEO写入位置,代表follower在上次追上leader,lastCaughtUpTimeMs=上次fetch请求收到时间;
- 否则,lastCaughtUpTimeMs保持不变;
scala
// follower的写入进度LEO
private[this] var _logEndOffsetMetadata = LogOffsetMetadata.UnknownOffsetMetadata
// follower的logStartOffset
private[this] var _logStartOffset = Log.UnknownOffset
// 上次fetch时的leader的LEO
private[this] var lastFetchLeaderLogEndOffset = 0L
// 上次fetch时间
private[this] var lastFetchTimeMs = 0L
// 上次追上leader的时间
private[this] var _lastCaughtUpTimeMs = 0L
def updateFetchState(
// fetch请求offset
followerFetchOffsetMetadata: LogOffsetMetadata,
// fetch请求中的logStartOffset
followerStartOffset: Long,
// leader收到fetch请求时间
followerFetchTimeMs: Long,
// leader收到fetch请求时的LEO写入进度
leaderEndOffset: Long): Unit = {
// 如果fetch offset >= leader写入位置
// lastCaughtUpTimeMs=本次fetch请求时间,代表follower已经完全追上leader
if (followerFetchOffsetMetadata.messageOffset >= leaderEndOffset)
_lastCaughtUpTimeMs = math.max(_lastCaughtUpTimeMs, followerFetchTimeMs)
// 否则,如果本次fetch offset >= 上次fetch时leader的LEO,
// lastCaughtUpTimeMs=上次fetch请求时间,代表follower在上一次fetch时追上leader
else if (followerFetchOffsetMetadata.messageOffset >= lastFetchLeaderLogEndOffset)
_lastCaughtUpTimeMs = math.max(_lastCaughtUpTimeMs, lastFetchTimeMs)
// 记录follower的本次fetch请求情况
_logStartOffset = followerStartOffset
_logEndOffsetMetadata = followerFetchOffsetMetadata
lastFetchLeaderLogEndOffset = leaderEndOffset
lastFetchTimeMs = followerFetchTimeMs
}4-2-2、高水位(HW)变化
高水位的作用:
- 发送消息,acks=-1(all),需要等待HW超过本批消息,才能响应客户端成功;
- 消费消息,默认隔离级别=READ_UNCOMMITTED,只能消费小于HW的消息;
高水位升高的场景:
- ISR变化:ISR收缩到1,只剩Leader,如Follower下线Leader收到LeaderAndIsrRequest;
- 副本LEO变化:Leader收到Follower的Fetch请求,发现Follower的LEO增加;当ISR只有Leader时,Leader收到ProduceRequest,Leader的LEO增加;
Partition#maybeIncrementLeaderHW:计算HW,HW只能单调递增,如果新HW小于老HW,不更新。
- 参与HW计算的副本 = ISR内副本 + 上次追上Leader的LEO的时间在replica.lag.time.max.ms=30s内的副本;
- HW = 这些副本的LEO的最小值;
当isr中只包含leader副本,leader的LEO持续增加导致hw持续增加。如果没有30秒buffer,follower可能永远无法追上hw,导致没有除leader以外的副本能进入isr。
scala
private def maybeIncrementLeaderHW(leaderLog: Log, curTime: Long = time.milliseconds): Boolean = {
inReadLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) {
var newHighWatermark = leaderLog.logEndOffsetMetadata
remoteReplicasMap.values.foreach { replica =>
// 取LEO的最小值
if (replica.logEndOffsetMetadata.messageOffset < newHighWatermark.messageOffset &&
// 副本 = Fetch延迟小于30s(replica.lag.time.max.ms)
// || ISR中的副本
(curTime - replica.lastCaughtUpTimeMs <= replicaLagTimeMaxMs || inSyncReplicaIds.contains(replica.brokerId))) {
newHighWatermark = replica.logEndOffsetMetadata
}
}
// 尝试更新HW,HW只能单调递增,如果新HW小于老HW,不更新
leaderLog.maybeIncrementHighWatermark(newHighWatermark) match {
case Some(oldHighWatermark) =>
true
case None =>
false
}
}
}4-2-3、ISR扩张
ISR(In-Sync Replicas)是与Leader副本同步的副本列表,包含Leader自己。
ISR在保证可用性 和一致性之间取得平衡:
- 发送消息acks=-1,Leader数据写入,需要高水位≥当时的LEO,才响应客户端成功。发送消息无需等待所有副本写入成功,高水位取决于所有isr副本LEO的最小值,保证可用性。此外通过配置min.insync.replicas(默认1),当isr小于该值,返回生产者拒绝写入,保证一致性;
- 默认unclean.leader.election.enable=false,leader下线,新leader副本只能从isr中选取,避免数据丢失;
ISR 扩张触发:Leader收到Follower的Fetch请求。
Partition#maybeExpandIsr:如果follower进入isr,leader更新/brokers/topics/{topic}/partitions/{partitionId}/state,并更新自身内存isr。
scala
private def maybeExpandIsr(followerReplica: Replica, followerFetchTimeMs: Long): Unit = {
// 读锁下 判一次是否需要扩张
val needsIsrUpdate = inReadLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) {
needsExpandIsr(followerReplica)
}
if (needsIsrUpdate) {
// 如果需要 升级写锁 判一次是否需要扩张
inWriteLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) {
if (needsExpandIsr(followerReplica)) {
val newInSyncReplicaIds = inSyncReplicaIds + followerReplica.brokerId
// 更新/brokers/topics/{topic}/partitions/{partitionId}/state和内存
expandIsr(newInSyncReplicaIds)
}
}
}
}Partition#needsExpandIsr:follower进入isr要求:1)follower LEO ≥ leader当前HW 2)follower LEO ≥ 当前leader任期的起始offset。
第二点的原因参考github.com/apache/kafk...和issues.apache.org/jira/browse...。
scala
// isr副本集合 包含n个brokerId
var inSyncReplicaIds = Set.empty[Int]
// 当前leader任期的起始offset
private var leaderEpochStartOffsetOpt: Option[Long] = None
private def needsExpandIsr(followerReplica: Replica): Boolean = {
leaderLogIfLocal.exists { leaderLog =>
val leaderHighwatermark = leaderLog.highWatermark
!inSyncReplicaIds.contains(followerReplica.brokerId)
&& isFollowerInSync(followerReplica, leaderHighwatermark)
}
}
private def isFollowerInSync(followerReplica: Replica, highWatermark: Long): Boolean = {
val followerEndOffset = followerReplica.logEndOffset
followerEndOffset >= highWatermark
&& leaderEpochStartOffsetOpt.exists(followerEndOffset >= _)
}4-2-4、ISR收缩
ReplicaManager#startup:根据最大延迟replica.lag.time.max.ms=30000/2,每15秒跑一次,校验是否需要收缩isr。
scala
private val allPartitions = new Pool[TopicPartition, HostedPartition](
valueFactory = Some(tp => HostedPartition.Online(Partition(tp, time, this)))
)
def startup(): Unit = {
// 定时校验是否需要收缩isr
scheduler.schedule("isr-expiration", maybeShrinkIsr _,
period = config.replicaLagTimeMaxMs / 2,
unit = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
}
private def maybeShrinkIsr(): Unit = {
allPartitions.keys.foreach { topicPartition =>
nonOfflinePartition(topicPartition).foreach(_.maybeShrinkIsr())
}
}Partition#maybeShrinkIsr:处理方式类似isr扩张。
scala
def maybeShrinkIsr(): Unit = {
// 1. 读锁 判断是否需要shrink
val needsIsrUpdate = inReadLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) {
needsShrinkIsr()
}
// 2. 如果需要 上写锁再次判断
val leaderHWIncremented = needsIsrUpdate
&& inWriteLock(leaderIsrUpdateLock) {
leaderLogIfLocal match {
case Some(leaderLog) =>
// 3. 获取踢出isr的副本ids
val outOfSyncReplicaIds = getOutOfSyncReplicas(replicaLagTimeMaxMs)
if (outOfSyncReplicaIds.nonEmpty) {
val newInSyncReplicaIds = inSyncReplicaIds -- outOfSyncReplicaIds
// 4. 更新zk和内存
shrinkIsr(newInSyncReplicaIds)
// 5. isr收缩,可能导致hw增加
maybeIncrementLeaderHW(leaderLog)
} else {
false
}
case None => false
}
}
// 6. 如果hw增加,可能需要完成produceRequest等挂起请求
if (leaderHWIncremented)
tryCompleteDelayedRequests()
}
// 如果有出isr的副本,需要上写锁
private def needsShrinkIsr(): Boolean = {
if (isLeader) {
val outOfSyncReplicaIds = getOutOfSyncReplicas(replicaLagTimeMaxMs)
outOfSyncReplicaIds.nonEmpty
} else {
false
}
}Partition#getOutOfSyncReplicas:follower踢出isr需要满足条件:
1)follower副本的LEO 没到达 leader副本LEO;
2)follower副本上次追上leader的时间(lastCaughtUpTimeMs)超出30s(replica.lag.time.max.ms);
scala
def getOutOfSyncReplicas(maxLagMs: Long): Set[Int] = {
// 需要校验的副本id = isr - leader自己
val candidateReplicaIds = inSyncReplicaIds - localBrokerId
val currentTimeMs = time.milliseconds()
// leader的leo
val leaderEndOffset = localLogOrException.logEndOffset
candidateReplicaIds.filter(replicaId => isFollowerOutOfSync(replicaId, leaderEndOffset, currentTimeMs, maxLagMs))
}
private def isFollowerOutOfSync(replicaId: Int,
leaderEndOffset: Long,
currentTimeMs: Long,
maxLagMs: Long): Boolean = {
val followerReplica = getReplicaOrException(replicaId)
followerReplica.logEndOffset != leaderEndOffset
&& (currentTimeMs - followerReplica.lastCaughtUpTimeMs) > maxLagMs
}总结
leader选举
leader选举由controller角色broker执行,选举流程:
- 查询/brokers/topics/{topic}/partitions/{partitionId}/state得到当前LeaderAndIsr;
- 根据策略选主;
- 更新/brokers/topics/{topic}/partitions/{partitionId}/state;
- 发送LeaderAndIsr请求给相关Broker;
选举场景和算法:
- broker作为分区leader异常下线,controller通过/brokers/ids子节点watch发现。优先从isr存活副本 中选leader,isr = isr - 线下broker;如果开启unclean选举(unclean.leader.election.enable =true),降级从非isr存活副本中选leader,isr = 新leader;
- broker作为分区leader正常下线,发送ControlledShutdownRequest给controller。从isr存活副本-下线broker中选leader,isr = isr - 下线broker。
- admin执行分区重分配,leader副本从assignment中移除。从reassign目标副本中选择isr存活副本作为leader,isr保持不变;
- controller每5分钟(leader.imbalance.check.interval.seconds )执行leader rebalance,如果判定broker不均衡比率查过10%(leader.imbalance.per.broker.percentage ),触发相关分区重新选举。使用preferred策略,选择assignment中的第一个副本作为leader,isr保持不变;
数据复制
controller完成leader选举,下发LeaderAndIsrRequest给相关分区副本broker。
broker识别自身是leader还是follower走不同逻辑,总体上遵循:follower作为消费者从leader拉消息,消费逻辑是将消息写入本地数据文件。
follower注意点:
- 刚加入的分区处于Truncating状态,需要发送OffsetsForLeaderEpochRequest给leader,请求中包含当前分区数据的最后一个leader epoch。leader返回该epoch的最后一个offset。如果follower发现该offset小于自己的LEO,则执行截断,从该offset开始发送fetch请求;
- 确定fetch offset后,进入Fetching状态,发送FetchRequest(包含副本id=自身brokerId)接收FetchResponse写本地数据文件,包括构建索引、HW=leader.HW;
leader注意点:FetchRequest的副本id识别出是follower拉消息,fetch offset代表了follower的LEO,每次拉消息完成后执行:
- 更新副本同步进度,,同步进度用lastCaughtUpTimeMs 上次追上leader的时间表示:
- 如果本次fetch offset ≥ leader的LEO写入位置,代表follower已经完全追上leader,lastCaughtUpTimeMs=本次fetch请求收到时间;
- 如果本次fetch offset ≥ 上次fetch时leader的LEO写入位置,代表follower在上次追上leader,lastCaughtUpTimeMs=上次fetch请求收到时间;
- 否则,lastCaughtUpTimeMs保持不变;
- 尝试扩张ISR;
- 尝试增加高水位;
高水位
高水位的作用:
- 发送消息,acks=-1(all),需要等待HW超过本批消息,才能响应客户端成功;
- 消费消息,默认隔离级别=READ_UNCOMMITTED,只能消费小于HW的消息;
高水位单调递增,升高场景:ISR收缩、副本LEO增加。
高水位 = min(参与计算的副本的LEO),参与计算的副本 = ISR内副本 + 上次追上Leader的LEO的时间(lastCaughtUpTimeMs)在30s(replica.lag.time.max.ms)内的副本。
ISR
ISR(In-Sync Replicas)是与Leader副本同步的副本列表,包含Leader自己,用于在可用性 和一致性之间取得平衡:
- 发送消息acks=-1,通过配置min.insync.replicas(默认1),当isr副本数小于该值,返回生产者拒绝写入,保证一致性;
- 默认配置下,新leader副本只能从isr中选取,避免数据丢失;
ISR 扩张:
- Leader收到Follower的Fetch请求;
- follower进入isr条件:follower LEO ≥ leader的高水位 且 follower LEO ≥ 当前leader任期的起始offset;
- 如果变更,leader更新/brokers/topics/{topic}/partitions/{partitionId}/state和自身内存;
ISR 收缩:
- leader根据最大延迟replica.lag.time.max.ms=30000/2,每15秒跑一次,校验是否需要收缩isr;
- follower踢出isr条件:follower的LEO<leader的LEO 且 follower上次追上leader的时间(lastCaughtUpTimeMs )超出30s(replica.lag.time.max.ms);
- 如果变更,leader更新/brokers/topics/{topic}/partitions/{partitionId}/state和自身内存;
- ISR收缩可能导致高水位增加;