目录
[两数之和 梦的开始](#两数之和 梦的开始)
生命游戏
思路1:开一个相同的二维数组储存答案
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
void gameOfLife(vector<vector<int>> &board)
{
vector<vector<int>> ret = board;
int dx[8] = {-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1};
int dy[8] = {-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1};
int n = board.size(), m = board[0].size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
int count = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m)
{
if (board[x][y] == 1)
count++;
}
}
if ((board[i][j] == 1 && (count == 2 || count == 3)) || (board[i][j] == 0 && count == 3))
ret[i][j] = 1;
else
ret[i][j] = 0;
}
}
board = ret;
}
};思路2:使用(从右往左)第二个 bit 进行标记,就不用额外开辟空间
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
void gameOfLife(vector<vector<int>> &board)
{
int dx[8] = {-1, -1, -1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1};
int dy[8] = {-1, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 1};
int n = board.size(), m = board[0].size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
int count = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if (x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m)
{
// if((board[x][y]&1)==1) count++;
count += board[x][y] & 1;
}
}
if (((board[i][j] & 1) == 1 && (count == 2 || count == 3)) || ((board[i][j] & 1) == 0 && count == 3))
{
board[i][j] |= 2;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
board[i][j] >>= 1;
// if((board[i][j]&2)==2) board[i][j]=1;
// else board[i][j]=0;
}
}
}
};赎金信
解法:哈希
统计 ransomNote 中的每个种类字符个数是否大于 magazine
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
bool canConstruct(string ransomNote, string magazine)
{
int hashr[26] = {0}, hashm[26] = {0};
for (auto &ch : ransomNote)
hashr[ch - 'a']++;
for (auto &ch : magazine)
hashm[ch - 'a']++;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
{
if (hashr[i] > hashm[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
};同构字符串
思路1:各自映射
当以 s 为参照物时,看看 t 中的字符映射到 s字符时是否是 1对1 的关系;反过来(s 映射到 t )也是如此,两中情况都成立才说明是同字符串
cpp
class Solution {
public:
bool IsMapping(const string& s1, const string& s2)
{
unordered_map<char,char> hash;
for(int i=0;i<s1.size();i++)
{
char ch1 = s1[i], ch2 = s2[i];
if(!hash.contains(ch1))
{
// 建立映射
hash[ch1] = ch2;
}
else
{
// 是不是之前建立的映射
if(hash[ch1] != ch2)
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool isIsomorphic(string s, string t) {
// 映射对应关系都互换
return IsMapping(s,t) && IsMapping(t,s);
}
};思路2:翻译
把字符串的映射情况统一"翻译"成数字,使用 count 为1进行记录,比如:abb 和 egg:a -> e 第一次出来,该位置为1,count++...最后 b -> g 出现过了所有还是2;翻译结果 122 和 122,比较翻译结果是否一致即可
注:收集结果要以一个特殊字符比如" "分隔开,不然即可出现
"abcdefghijkaa" -> 123456789101111
"abcdefghijaak" -> 123456789101111
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
string IsMapping(const string &s)
{
unordered_map<char, int> hash;
string ret;
int count = 1;
for (auto &ch : s)
{
if (!hash.contains(ch))
{
hash[ch] = count;
count++;
}
// 可能第一个和第十一个字符映射重复
// "abcdefghijkaa" "abcdefghijaak"
ret += to_string(hash[ch]) + " ";
}
return ret;
}
bool isIsomorphic(string s, string t)
{
// 翻译出来是否相等
cout << IsMapping(s) << ' ' << IsMapping(t) << endl;
return IsMapping(s) == IsMapping(t);
}
};优化:使用两个哈希表来优化,遍历一遍,如何字符串保存的结果不同直接返回 false
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
bool isIsomorphic(string s, string t)
{
unordered_map<char, int> hashs, hasht;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
char s1 = s[i], t1 = t[i];
// 使用下标来记录
if (!hashs.contains(s1))
hashs[s1] = i + 1;
if (!hasht.contains(t1))
hasht[t1] = i + 1;
if (hashs[s1] != hasht[t1])
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};负二进制转换
解法:模拟
二进制:使用 %2 除2的思路,对于负二进制,我们同样可以用这个做法。但是由于是负数,我们在取余的时候,可能会出现负数。但是二进制是没有负数的,因此我们要将余数为负数修正为余数为正数,即 -1 修正为 1,对应的商就应该增加 1进行抵消
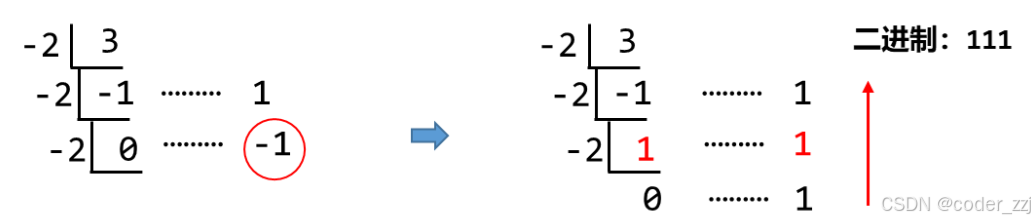
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
string baseNeg2(int n)
{
if (n == 0)
return "0";
string ret;
int mod = 0;
while (n)
{
mod = n % (-2);
n /= (-2);
// 取模为-1时特殊判断
if (mod == -1)
{
mod += 2;
n++;
}
// 倒着存
ret = to_string(mod) + ret;
}
return ret;
}
};十进制转任意进制
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
string decToBit(int n, int bit)
{
string s = to_string(n), ret;
while (s != "0")
{
string tmp;
// 字符串除法
int mod = 0, sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
sum = mod * 10 + (s[i] - '0');
tmp += to_string(sum / bit);
mod = sum % bit;
}
// 每次取低位,如果是大于10进制的要使用哈希表对应字符,比如16进制的10->'A'
ret = to_string(mod) + ret;
// 去前导0,比如: 145 -> 072 -> 72
while (tmp.size() > 1 && tmp.front() == '0')
tmp.erase(tmp.begin());
s = tmp;
}
return ret;
}
};单词规律
上题的加强版,处理字符变成字符串即可,使用思路2的翻译法来完成
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
bool wordPattern(string pattern, string s)
{
unordered_map<string, int> hashs;
stringstream ss(s);
string tmp, ret1;
int count = 1;
while (ss >> tmp)
{
if (!hashs.contains(tmp))
{
hashs[tmp] = count;
count++;
}
ret1 += to_string(hashs[tmp]);
}
unordered_map<char, int> hashp;
string ret2;
count = 1;
for (auto &ch : pattern)
{
if (!hashp.contains(ch))
{
hashp[ch] = count;
count++;
}
ret2 += to_string(hashp[ch]);
}
return ret1 == ret2;
}
};有效的字母异位词
解法:哈希
统计字符个数是否相等
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
bool isAnagram(string s, string t)
{
int hash1[26] = {0}, hash2[26] = {0};
for (auto &ch : s)
hash1[ch - 'a']++;
for (auto &ch : t)
hash2[ch - 'a']++;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
{
if (hash1[i] != hash2[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
};字母异位词分组
解法:哈希表
用哈希表分组,把排序后的字符串当作哈希表的 key,排序前的字符串加到对应的列表中(哈希表的 value)
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
vector<vector<string>> groupAnagrams(vector<string> &strs)
{
unordered_map<string, vector<string>> hash;
for (auto &str : strs)
{
string tmp = str;
sort(str.begin(), str.end());
hash[str].push_back(tmp);
}
vector<vector<string>> ret;
for (auto &[a, b] : hash)
ret.push_back(b);
return ret;
}
};两数之和 梦的开始
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int> &nums, int target)
{
unordered_map<int, int> hash;
vector<int> ret(2);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
{
if (hash.contains(target - nums[i]))
{
ret[0] = i, ret[1] = hash[target - nums[i]];
}
hash.insert({nums[i], i});
}
return ret;
}
};快乐数
解法1:哈希表
使用哈希表储存每一个计算结果
为1就是快乐数
计算结果不为1并且与前面的计算结果重复了就返回false
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
bool isHappy(int n)
{
unordered_set<int> hash;
while (true)
{
int tmp = n, sum = 0;
while (tmp)
{
sum += pow(tmp % 10, 2);
tmp /= 10;
}
cout << sum << endl;
if (sum == 1)
return true;
if (hash.contains(sum))
break;
hash.insert(sum);
n = sum;
}
return false;
}
};解法2:快慢指针
无论是快乐数还是不是,在某个时间段都能相等,在相等时判断是不是等于1即可,此时就不用开空间储存计算结果了
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
int happyVal(int n)
{
int sum = 0;
while (n)
{
sum += pow(n % 10, 2);
n /= 10;
}
return sum;
}
bool isHappy(int n)
{
int slow = n, fast = n;
while (true)
{
slow = happyVal(slow);
fast = happyVal(fast);
fast = happyVal(fast);
if (slow == fast)
{
if (slow == 1)
return true;
else
break;
}
}
return false;
}
};最长连续序列
解法:哈希
题目要求时间复杂度 O(N),先使用哈希表进hash行储存
主要思路:对每个数x进行遍历,看看x+1,x+2...有多少个,取最大值
优化1:不使用 nums 进行遍历,而使用 hash 进行遍历,因为里面是去重后的结果
优化2:遇到 x-1 在 hash 了,直接进行下一个数的遍历
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int longestConsecutive(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_set<int> hash;
for(auto& num:nums) hash.insert(num);
int ret = 0;
// 哈希表进行遍历
for(auto& x:hash)
{
// 前面遍历过了
if(hash.contains(x-1)) continue;
int y = x + 1;
while(hash.contains(y))
y++;
ret = max(ret, y - x);
}
return ret;
}
};汇总区间
解法:模拟
两次简单循环找连续自然数区间
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
vector<string> summaryRanges(vector<int> &nums)
{
vector<string> ret;
int n = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n;)
{
string s = to_string(nums[i]);
int j = i;
while (j + 1 < n && (long long)nums[j + 1] - nums[j] == 1)
j++;
if (nums[i] != nums[j])
s += "->" + to_string(nums[j]);
ret.push_back(s);
i = j + 1;
}
return ret;
}
};合并区间
解法:模拟
先按照左端点(第一个数)排序,保障接下来模拟区间不会断开;
每次按照第i组数的第二个数与第i+1组数的第一个数进行比较,大于等于往下找,因为不知道谁比较大,往下找之前要先取二者最大值
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
vector<vector<int>> merge(vector<vector<int>> &intervals)
{
sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end());
vector<vector<int>> ret;
int n = intervals.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n;)
{
vector<int> v(2);
int j = i, max_val = intervals[j][1];
while (j + 1 < n && max_val >= intervals[j + 1][0])
{
max_val = max(max_val, intervals[j + 1][1]);
j++;
}
v[0] = intervals[i][0], v[1] = max_val;
ret.push_back(v);
i = j + 1;
}
return ret;
}
};插入区间
分为不重叠和重叠的情况进行判断
cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> insert(vector<vector<int>>& intervals, vector<int>& newInterval) {
if(intervals.empty()) return {newInterval};
vector<vector<int>> ret;
int n=intervals.size(),i=0;
while(i<n && intervals[i][1] < newInterval[0]) ret.push_back(intervals[i++]);
// {[1,2]} [3,4] 的话如果 min_val=INT_MAX max_val=INT_MIN 就错了
int j=i,min_val=newInterval[0],max_val=newInterval[1];
while(i<n && intervals[i][0] <= newInterval[1])
{
min_val = min(min_val,min(intervals[i][0],newInterval[0]));
max_val = max(max_val,max(intervals[i][1],newInterval[1]));
i++;
}
ret.push_back({min_val,max_val});
for(int k=i;k<n;k++) ret.push_back(intervals[k]);
return ret;
}
};有效的括号
解法:栈
使用栈进行模拟,分情况进行判断
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
bool isValid(string s)
{
stack<char> st;
for (auto &ch : s)
{
if (st.empty() || ch == '(' || ch == '[' || ch == '{')
st.push(ch);
else if (st.size() > 0)
{
if (ch == ')' && st.top() == '(')
st.pop();
else if (ch == ']' && st.top() == '[')
st.pop();
else if (ch == '}' && st.top() == '{')
st.pop();
else
return false;
}
else
return false;
}
return st.size() == 0;
}
};简化路径
解法:栈模拟
先把 path 用 / 分割,得到一个字符串列表
遍历字符串列表的同时,用栈维护遍历过的字符串:
- 如果当前字符串是空串或者 .,什么也不做(跳过)。
- 如果当前字符串不是 ..,那么把字符串入栈。
- 否则弹出栈顶字符串(前提是栈不为空),模拟返回上一级目录。
使用 "/" 将字符串列表的字符串进行拼接
cpp
class Solution
{
public:
string simplifyPath(string path)
{
auto split_view = path | std::views::split('/');
// C++23 直接转换
auto dirs = std::ranges::to<std::vector<std::string>>(split_view);
stack<string> st;
for (auto &dir : dirs)
{
if (dir == "" || dir == ".")
continue;
else if (dir != "..")
st.push(dir);
else
{
if (!st.empty())
st.pop();
}
}
string ret;
while (!st.empty())
{
ret = st.top() + '/' + ret;
st.pop();
}
while (ret.size() && ret.back() == '/')
ret.pop_back();
ret = '/' + ret;
return ret;
}
};
class Solution
{
public:
string simplifyPath(string path)
{
stringstream ss(path);
string tmp;
vector<string> dirs;
while (getline(ss, tmp, '/'))
{
if (tmp == "" || tmp == ".")
continue;
else if (tmp != "..")
dirs.push_back(tmp);
else
{
if (dirs.size())
dirs.pop_back();
}
}
string ret;
for (auto &dir : dirs)
ret = ret + '/' + dir;
return ret.empty() ? "/" : ret;
}
};以上便是全部内容,有问题欢迎在评论区指正,感谢观看!