基础知识
用户空间和内核空间
进程的寻址空间(内存地址)被划分为两部分:内核空间和用户空间。
寻址空间是CPU相关的,一个32位的CPU最大的寻址空间是232。每一个地址对应一个字节的内存,也就是最大的寻址空间为4GB,其中对应的虚拟内存地址的低地址 0 - 3GB为用户空间,高地址为 3GB - 4GB内核空间。
- 用户空间只能执行受限的命令(R3),而且不能直接调用系统资源。
- 内核空间可以执行特权命令(R0),调用一切系统资源。
I/O读写
Linux为了提高I/O效率,会在用户空间和内核空间都加入缓冲区。
- 写数据时,需要把用户缓冲数据拷贝到内核缓冲区,然后写入设备
- 读数据时,需要从设备读取数据到内核缓冲区,然后拷贝到用户缓冲区。
也就是需要等待数据,以及数据需要再不同空间的buffer中需要拷贝。
Linux I/O模型
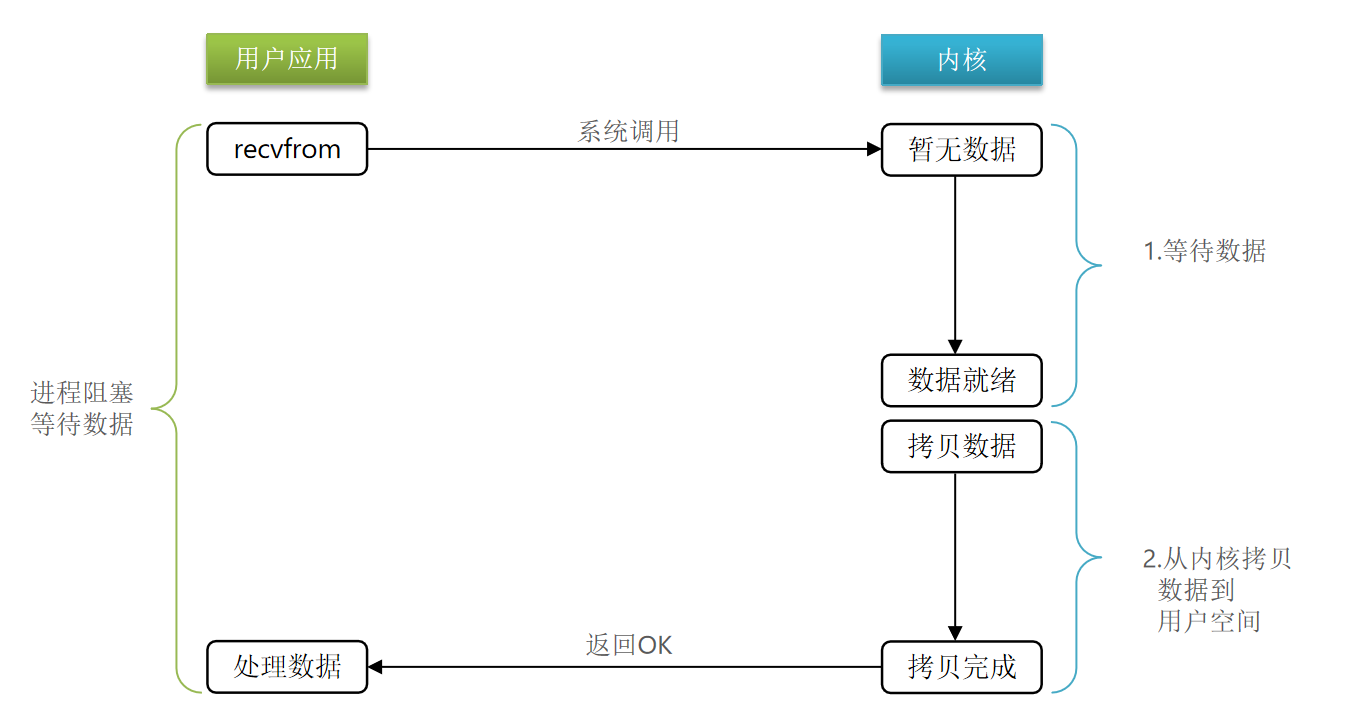
阻塞I/O
Blocking IO在两阶段都需要进行阻塞等待。
阶段一(用户向内核请求数据数据未到达):
-
用户进程尝试读取数据(比如网卡数据)
-
此时数据尚未到达,内核需要等待数据
-
此时用户进程也处于阻塞状态
阶段二(数据从内核缓冲区拷贝到用户缓冲区):
-
数据到达并拷贝到内核缓冲区,代表已就绪
-
将内核数据拷贝到用户缓冲区
-
拷贝过程中,用户进程依然阻塞等待
-
拷贝完成,用户进程解除阻塞,处理数据
非阻塞I/O
在阶段一为忙等,阶段二为阻塞等待。
阶段一:
-
用户进程尝试读取数据(比如网卡数据)
-
此时数据尚未到达,内核需要等待数据
-
返回异常给用户进程
-
用户进程拿到error后,再次尝试读取
-
循环往复,直到数据就绪
阶段二:
-
将内核数据拷贝到用户缓冲区
-
拷贝过程中,用户进程依然阻塞等待
-
拷贝完成,用户进程解除阻塞,处理数据
非阻塞I/O并没有提升读取数据的性能。
I/O多路复用
单个线程监听多个FD,获取FD的状态。
在请求数据时,对于阻塞I/O,调用recvfrom时,若没有数据,阻塞I/O会使CPU阻塞,非阻塞I/O使CPU空转。
单线程只能依次处理I/O。
增加效率的办法:
多线程
事件通知机制,当数据准备好时,才通知线程去处理当前I/O。
用户进程如何知道内核中数据是否就绪?
文件描述符:Linux一切皆文件
IO多路复用:是利用单个线程来同时监听多个FD,并在某个FD可读、可写时得到通知,从而避免无效的等待,充分利用CPU资源。
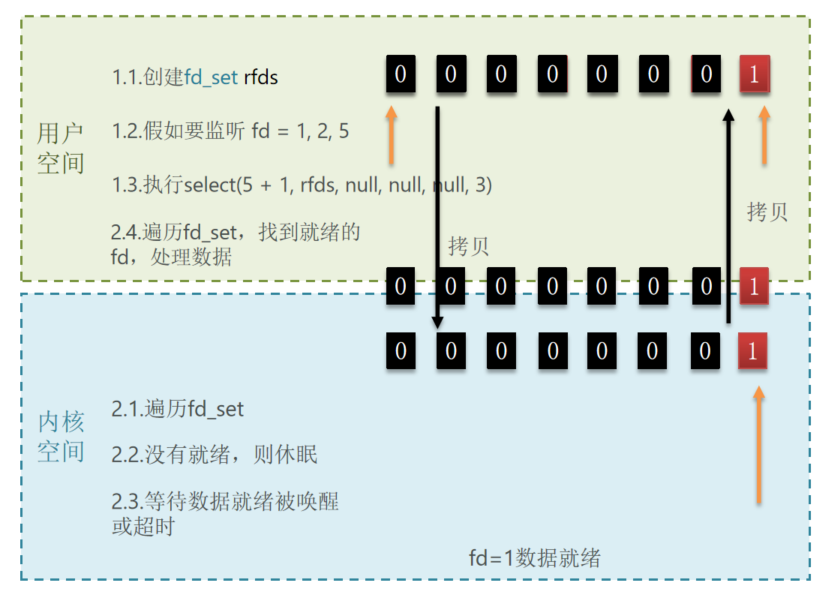
阶段一:
用户进程调用select,指定要监听的FD集合
内核监听FD对应的多个socket
任意一个或多个socket数据就绪则返回readable
此过程中用户进程阻塞
阶段二:
用户进程找到就绪的socket
依次调用recvfrom读取数据
内核将数据拷贝到用户空间
用户进程处理数据
三种多路复用实现:
select
c
// 定义类型别名 __fd_mask,本质是 long int
typedef long int __fd_mask;
/* fd_set 记录要监听的fd集合,及其对应状态 */
typedef struct {
// fds_bits是long类型数组,长度为 1024/32 = 32
// 共1024个bit位,每个bit位代表一个fd,0代表未就绪,1代表就绪
__fd_mask fds_bits[__FD_SETSIZE / __NFDBITS];
// ...
} fd_set;
// select函数,用于监听fd_set,也就是多个fd的集合
int select(
int nfds, // 要监视的fd_set的最大fd + 1
fd_set *readfds, // 要监听读事件的fd集合
fd_set *writefds,// 要监听写事件的fd集合
fd_set *exceptfds, // // 要监听异常事件的fd集合
// 超时时间,null-用不超时;0-不阻塞等待;大于0-固定等待时间
struct timeval *timeout
);select限制为1024个FD,也就是使用位图做标记
会有两次数据拷贝,并且要得知具体是哪个FD就绪,需要遍历。
poll
IO流程:
① 创建polfd数组,向其中添加关注的fd信息,数组大小自定义。
② 调用poll函数,将pollfd数组拷贝到内核空间,转为链表存储。
③ 内核遍历fd,判断是否就绪。
④ 数据就绪或者超时后,拷贝polfds数组到用户空间,返回就绪fd数量n
⑤ 用户进程判断n是否大于0
⑥ 大于0则遍历polfd数组,找到就绪的fd。
c
// pollfd 中的事件类型
#define POLLIN //可读事件
#define POLLOUT //可写事件
#define POLLERR //错误事件
#define POLLNVAL //fd未打开
// pollfd结构
struct pollfd {
int fd; /* 要监听的fd */
short int events; /* 要监听的事件类型:读、写、异常 */
short int revents;/* 实际发生的事件类型 */
};
// poll函数
int poll(
struct pollfd *fds, // pollfd数组,可以自定义大小
nfds_t nfds, // 数组元素个数
int timeout // 超时时间
);自身优缺点:
与select对比:
select模式中的fd_set大小固定为1024,而pollfd在内核中采用链表,理论上无上限
监听FD越多,每次遍历消耗时间也越久,性能反而会下降
epoll
epoll是对select和poll的改进,其提供了三个函数:
三个函数代表三步,分别为创建,添加/修改FD,检查就绪列表。
c
struct eventpoll {
//...
struct rb_root rbr; // 一颗红黑树,记录要监听的FD
struct list_head rdlist;// 一个链表,记录就绪的FD
//...
};
// 1.创建一个epoll实例,内部是event poll,返回对应的句柄epfd
int epoll_create(int size);
// 2.将一个FD添加到epoll的红黑树中,并设置ep_poll_callback
// callback触发时,就把对应的FD加入到rdlist这个就绪列表中
int epoll_ctl(
int epfd, // epoll实例的句柄
int op, // 要执行的操作,包括:ADD(增)、MOD(改)、DEL(删)
int fd, // 要监听的FD
struct epoll_event *event // 要监听的事件类型:读、写、异常等
);
// 3.检查rdlist列表是否为空,不为空则返回就绪的FD的数量
int epoll_wait(
int epfd, // epoll实例的句柄
struct epoll_event *events, // 空event数组,用于接收就绪的FD
int maxevents, // events数组的最大长度
int timeout // 超时时间,-1永不超时;0不阻塞;大于0为阻塞时间
);FD是一个无符号整数,使用红黑数进行记录;ep_poll_callback是一个回调函数,其作用就是监听fd,并把对应的FD添加到rdlist当中。
图中的红色代表就绪FD。
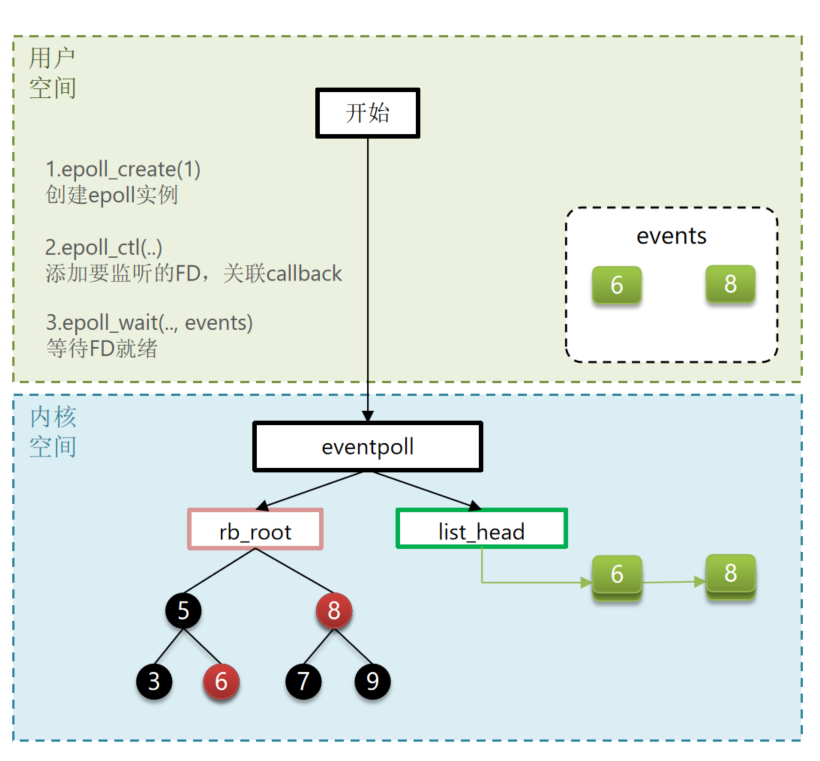
注意:在epoll中只是将就绪的FD传输到用户空间,而与select或poll模式拷贝整个监听数组或链表不同。
Epoll不仅仅是传输效率高的一种实现,并且其还支持多种触发模式:
水平触发和边缘触发:类似与数字电路中的电平触发与边沿触发。
使用两种触发的逻辑是不同的:
水平触发
水平触发可以不必一次性读完全部数据,因为下一次还会有事件再通知读取。
c
// 相对简单,不用担心数据遗漏
while (true) {
int nfds = epoll_wait(epfd, events, MAX_EVENTS, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < nfds; i++) {
if (events[i].events & EPOLLIN) {
// 读取数据,可以不一次读完
// 下次epoll_wait还会通知
char buf[1024];
int n = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
// 即使没读完,下次还会通知
}
}
}边缘触发
但是边缘触发就必须在事件通知后将所有数据全部读取完毕才可以。
c
// 必须一次处理完所有数据
while (true) {
int nfds = epoll_wait(epfd, events, MAX_EVENTS, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < nfds; i++) {
if (events[i].events & EPOLLIN) {
// 必须循环读取,直到读完所有数据
while (true) {
char buf[1024];
int n = read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
if (n <= 0) {
if (errno == EAGAIN || errno == EWOULDBLOCK) {
// 数据已读完
break;
}
// 错误处理
close(fd);
break;
}
// 处理数据
process_data(buf, n);
}
}
}
}I/O多路复用-事件通知机制
当FD中有数据可读时,调用epoll_wait就可以得到通知,但是事件通知的模式有两种:
LT:当FD有数据可读时,会重复通知多次,直到数据处理完成吗,是Epoll的默认模式:
ET:当FD有数据可读时,只会通知一次,不管数据是否处理完成。
当FD就绪时,ET和LT 模式 List_head中的链表处理方式不同:ET会直接断开就绪的FD链表,然后从内核空间拷贝到用户空间,所以相当于只会通知一次。但是LT不同,其拷贝后,会再添加到List_head链表中。
LT和ET的区别:
ET模式下:如果要读取数据,不可以在while循环中采取阻塞模式去读取,因为如果读取不到数据,其会一直阻塞。
LT模式下:多线程读取数据容易造成重复消费,也就是惊群现象。
总结:
ET模式避免了LT模式可能出现的惊群现象;
ET模式最好结合非阻塞I/O读取FD数据,相比LT会复杂一些。
基于epoll模式的Web服务
红黑树:记录监听的FD
链表:记录就绪FD
注册FD
注册ep_poll_callback当FD就绪时,将就绪FD记录到List_head链表中
判断list_head是否为空
是
否
epollin
是FD请求连接
否
epollerr
服务端
epoll_create
rb_root
list_head
创建ServerSocket得到FD:ssfd
epoll_ctl:注册并监听ssfd
epoll_wait:等待FD就绪
是否有FD就绪
判断事件类型
是否ssfd可读
accept接收客户端Socket得到对应FD
读取请求数据
写出响应
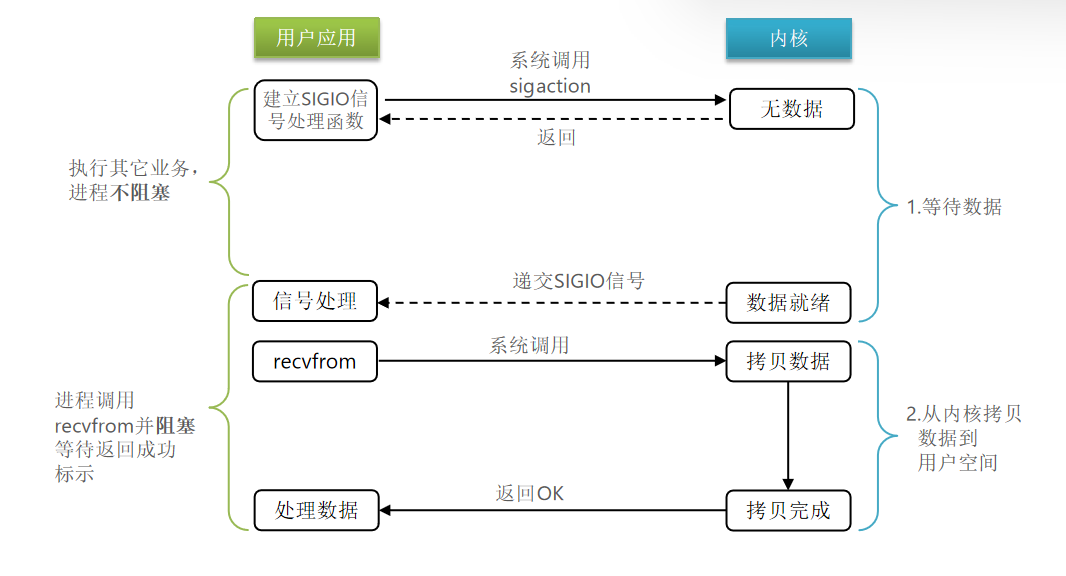
信号驱动I/O
与内核机建立SIGIO的信号关联并设置回调,当内核有FD就绪时,会发出SIGIO信号通知用户,期间用户应用可以执行其他任务,无需阻塞等待。
异步I/O
同步和异步
I/O操作是同步还是异步,关键看数据在内核空间与用户空间拷贝过程(数据读写的I/O操作),也就是阶段二是同步的还是异步的:
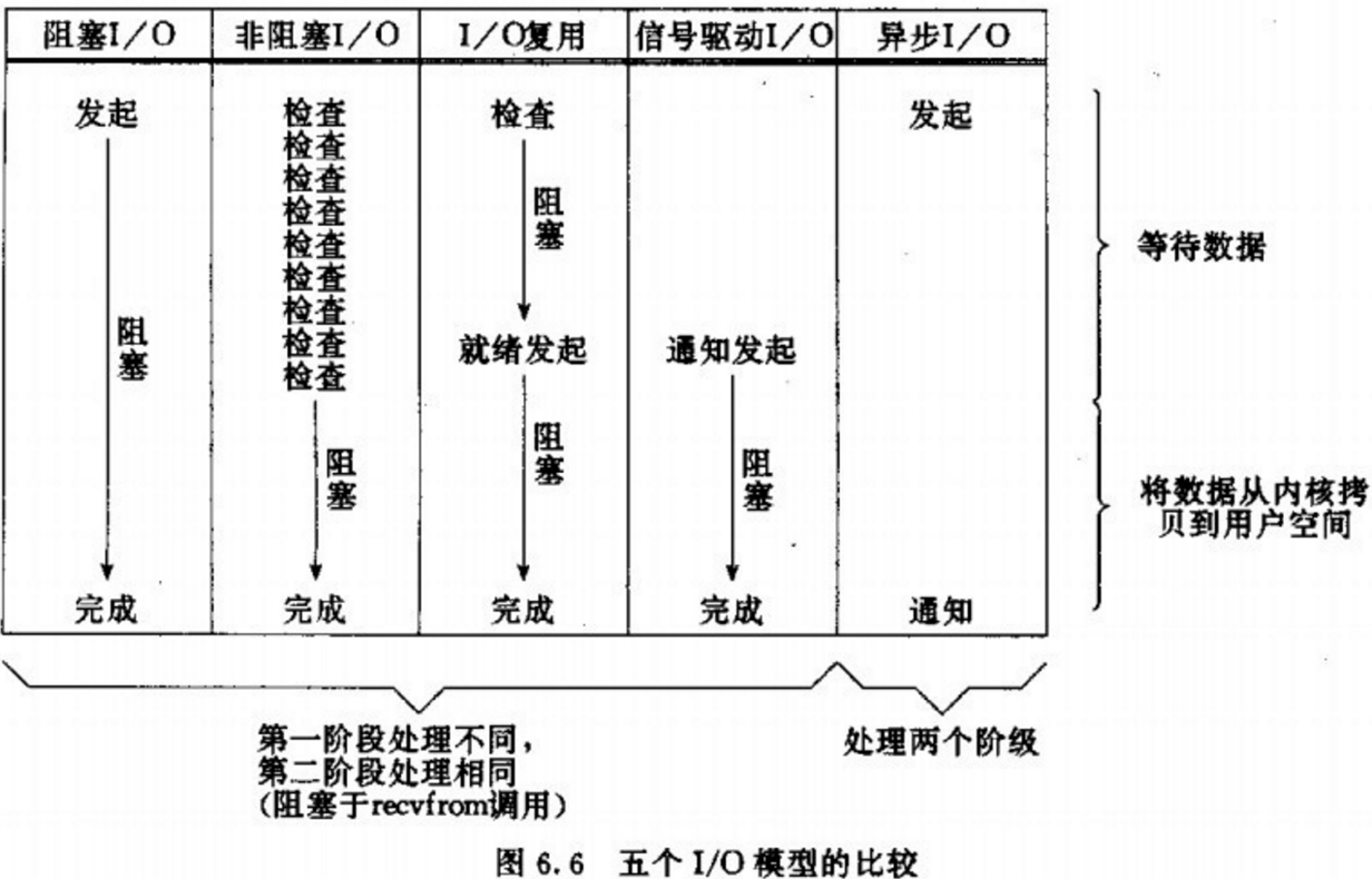
Redis网络模型
单线程还是多线程?
Redis中的核心业务部分(命令处理)是单线程,整个Redis是多线程。
Redis中的重要节点:
Redis V4.0:引入多线程异步处理一些耗时较长的任务,比如删除命令unlink。
Redis V6.0:核心网络模型中引入多线程,进一步提高对于多核CPU的利用率。
为什么Redis选择单线程?
除去持久化不谈,Redis是纯内存操作,执行速度非常快,其性能瓶颈是网络延迟而不是执行速度,因此多线程并不会带来巨大的性能提升。
多线程会导致过多的上下文切换,带来了不必要的开销
引入多线程会面临线程安全问题,必然要引入线程锁这种安全手段,实现复杂程度增高,而且性能大打折扣。
6.0之前单线程网络模型
Redis通过I/O多路复用来提升网络性能,并且支持各种不同的多路复用实现,并且将这些实现进行封装,提供了高性能事件库API库AE:
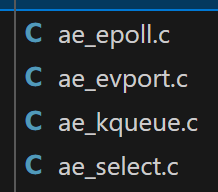
这里可以看出Redis支持各种系统的I/O多路复用技术,evport是Solaris(sun公司的Unix系统),kqueue是BSD家族操作系统(比如MacOS)
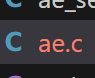
其中的ae.c文件中会判断当前系统的支持,从而选择对应的I/O多路复用。
c
#ifdef HAVE_EVPORT
#include "ae_evport.c"
#else
#ifdef HAVE_EPOLL
#include "ae_epoll.c"
#else
#ifdef HAVE_KQUEUE
#include "ae_kqueue.c"
#else
#include "ae_select.c"
#endif
#endif
#endif不管是那种类型的I/O多路复用,其实对于实现上的函数接口是类似的,与之前的epoll非常类似。也就是创建、注册、等待就绪等多个函数,可以看之前的epoll的流程框图来理解对应的流程。

Redis启动流程
从server.c开始执行:
核心方法①:initServer(); //初始化服务
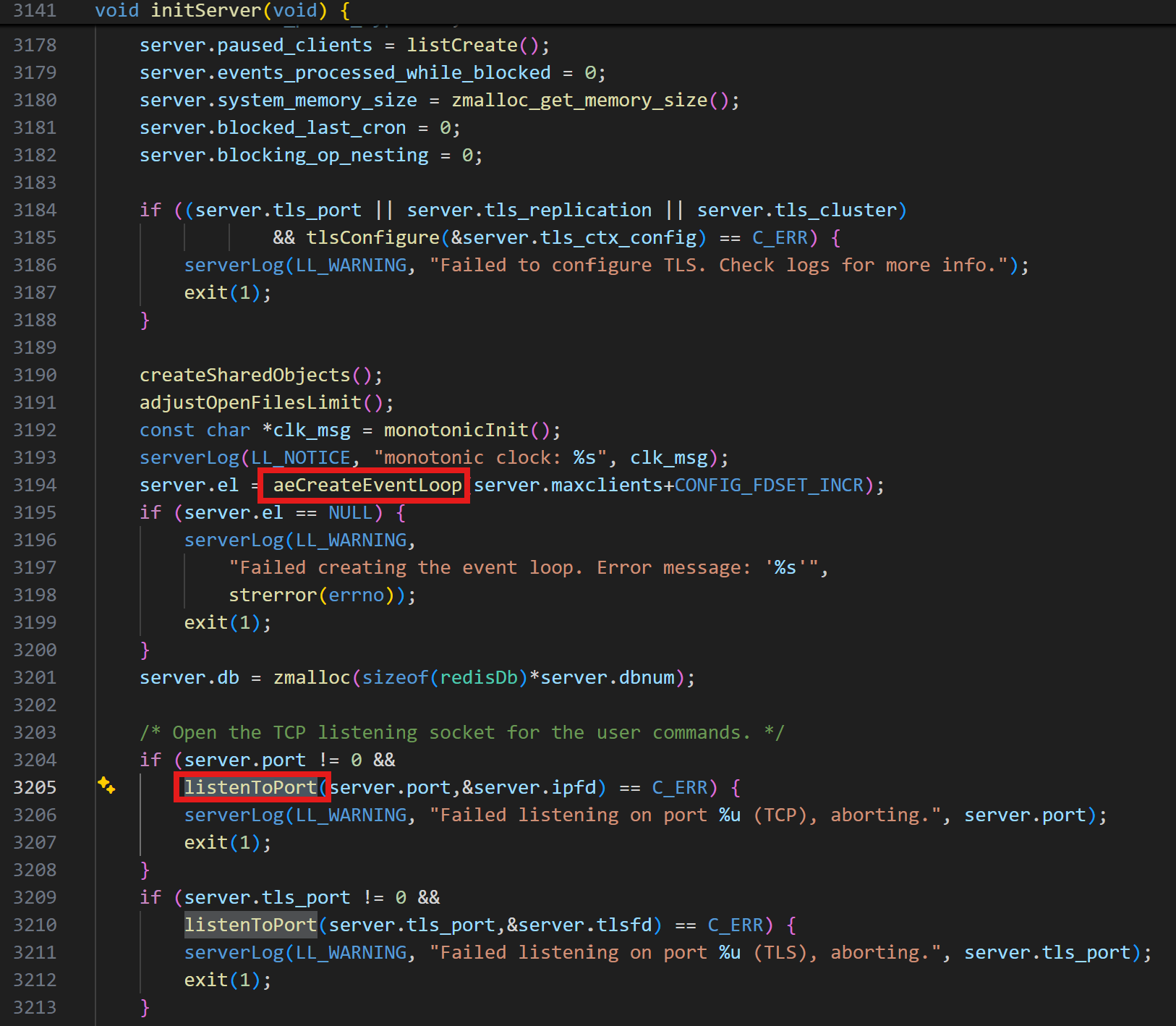
其中aeCreateEventLoop,其中会调用aeApiCreate,类似epoll_create
源码如下:
c
aeEventLoop *aeCreateEventLoop(int setsize) {
aeEventLoop *eventLoop;
int i;
monotonicInit(); /* just in case the calling app didn't initialize */
if ((eventLoop = zmalloc(sizeof(*eventLoop))) == NULL) goto err;
eventLoop->events = zmalloc(sizeof(aeFileEvent)*setsize);
eventLoop->fired = zmalloc(sizeof(aeFiredEvent)*setsize);
if (eventLoop->events == NULL || eventLoop->fired == NULL) goto err;
eventLoop->setsize = setsize;
eventLoop->timeEventHead = NULL;
eventLoop->timeEventNextId = 0;
eventLoop->stop = 0;
eventLoop->maxfd = -1;
eventLoop->beforesleep = NULL;
eventLoop->aftersleep = NULL;
eventLoop->flags = 0;
if (aeApiCreate(eventLoop) == -1) goto err;
/* Events with mask == AE_NONE are not set. So let's initialize the
* vector with it. */
for (i = 0; i < setsize; i++)
eventLoop->events[i].mask = AE_NONE;
return eventLoop;
err:
if (eventLoop) {
zfree(eventLoop->events);
zfree(eventLoop->fired);
zfree(eventLoop);
}
return NULL;
}其中listenToPort是监听TCP端口,并且去创建 ServerSocket ,并得到FD。
所以此函数就是获取FD,那么获取到FD之后就是需要量FD注册到I/O多路复用器中,去监听当前的FD是否就绪。
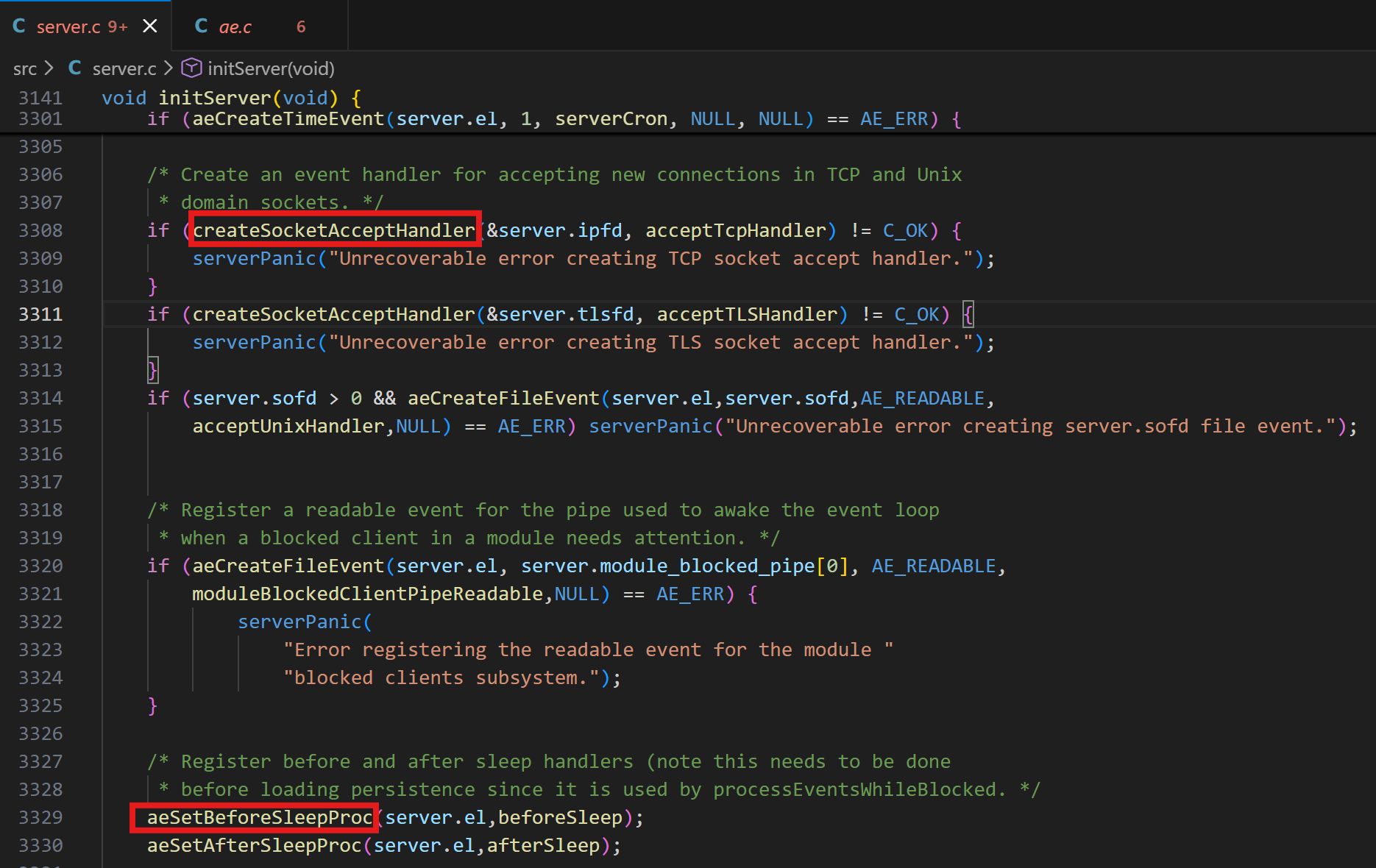
所以后续就是 createSocketAcceptHandler ,注册连接处理器,内部会调用
aeCreateFileEvent,监听Socket的FD读事件,并绑定读处理器ReadQueryFromClient。
c
/* Create an event handler for accepting new connections in TCP or TLS domain sockets.
* This works atomically for all socket fds */
int createSocketAcceptHandler(socketFds *sfd, aeFileProc *accept_handler) {
int j;
for (j = 0; j < sfd->count; j++) {
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, sfd->fd[j], AE_READABLE, accept_handler,NULL) == AE_ERR) {
/* Rollback */
for (j = j-1; j >= 0; j--) aeDeleteFileEvent(server.el, sfd->fd[j], AE_READABLE);
return C_ERR;
}
}
return C_OK;
}这里的accept_handler的入参是一个 acceptTcpHandler:
c
void acceptTcpHandler(aeEventLoop *el, int fd, void *privdata, int mask) {
int cport, cfd, max = MAX_ACCEPTS_PER_CALL;
char cip[NET_IP_STR_LEN];
UNUSED(el);
UNUSED(mask);
UNUSED(privdata);
while(max--) {
cfd = anetTcpAccept(server.neterr, fd, cip, sizeof(cip), &cport);
if (cfd == ANET_ERR) {
if (errno != EWOULDBLOCK)
serverLog(LL_WARNING,
"Accepting client connection: %s", server.neterr);
return;
}
anetCloexec(cfd);
serverLog(LL_VERBOSE,"Accepted %s:%d", cip, cport);
acceptCommonHandler(connCreateAcceptedSocket(cfd),0,cip);
}
}在 anetTcpAccept 中:
c
int anetTcpAccept(char *err, int s, char *ip, size_t ip_len, int *port) {
int fd;
struct sockaddr_storage sa;
socklen_t salen = sizeof(sa);
if ((fd = anetGenericAccept(err,s,(struct sockaddr*)&sa,&salen)) == -1)
return ANET_ERR;
if (sa.ss_family == AF_INET) {
struct sockaddr_in *s = (struct sockaddr_in *)&sa;
if (ip) inet_ntop(AF_INET,(void*)&(s->sin_addr),ip,ip_len);
if (port) *port = ntohs(s->sin_port);
} else {
struct sockaddr_in6 *s = (struct sockaddr_in6 *)&sa;
if (ip) inet_ntop(AF_INET6,(void*)&(s->sin6_addr),ip,ip_len);
if (port) *port = ntohs(s->sin6_port);
}
return fd;
}
c
static int anetGenericAccept(char *err, int s, struct sockaddr *sa, socklen_t *len) {
int fd;
while(1) {
fd = accept(s,sa,len);
if (fd == -1) {
if (errno == EINTR)
continue;
else {
anetSetError(err, "accept: %s", strerror(errno));
return ANET_ERR;
}
}
break;
}
return fd;
}可以看到这部分的主要事情,是接收Socket连接,获取FD。
在获取到FD之后,建立connection,关联FD
也就是在 acceptCommonHandler(connCreateAcceptedSocket(cfd),0,cip);
c
connection *connCreateAcceptedSocket(int fd) {
connection *conn = connCreateSocket();
conn->fd = fd;
conn->state = CONN_STATE_ACCEPTING;
return conn;
}//暂不确定,暂时只看到下面源码,并未理清调用关系
之后内部调用 aeApiAddEvent(fd,READABLE) //暂时不能确认
监听Socket的FD读事件,并绑定读处理器readQueryFromClient
connSetReadHandler(conn, readQueryFromClient);
c
networking.c
void protectClient(client *c) {
c->flags |= CLIENT_PROTECTED;
if (c->conn) {
connSetReadHandler(c->conn,NULL);
connSetWriteHandler(c->conn,NULL);
}
}
/* This will undo the client protection done by protectClient() */
void unprotectClient(client *c) {
if (c->flags & CLIENT_PROTECTED) {
c->flags &= ~CLIENT_PROTECTED;
if (c->conn) {
connSetReadHandler(c->conn,readQueryFromClient);
if (clientHasPendingReplies(c)) clientInstallWriteHandler(c);
}
}
}后续就是 aeSetBeforeSleepProc(server.el,beforeSleep);
aeSetAfterSleepProc(server.el,afterSleep);
因为后续等待FD就绪的过程中,线程会处于休眠状态,那么线程在休眠状态之前和之后的一些处理工作,可以放入到aeSetBeforeSleepProc和aeSetAfterSleepProc。也就是前后处理器。
所以回顾一下:在 initServer() 中做的工作主要是:
aeCreateEventLoop相当于epoll_create
listenToPort 相当于创建FD
createSocketAcceptHandler 相当于 epoll_ctl 并将就绪后的处理函数传入
aeSetBeforeSleepProc/aeSetAfterSleepProc 线程休眠前后置处理器
核心方法②:aeMain(server.el); //开始监听事件循环
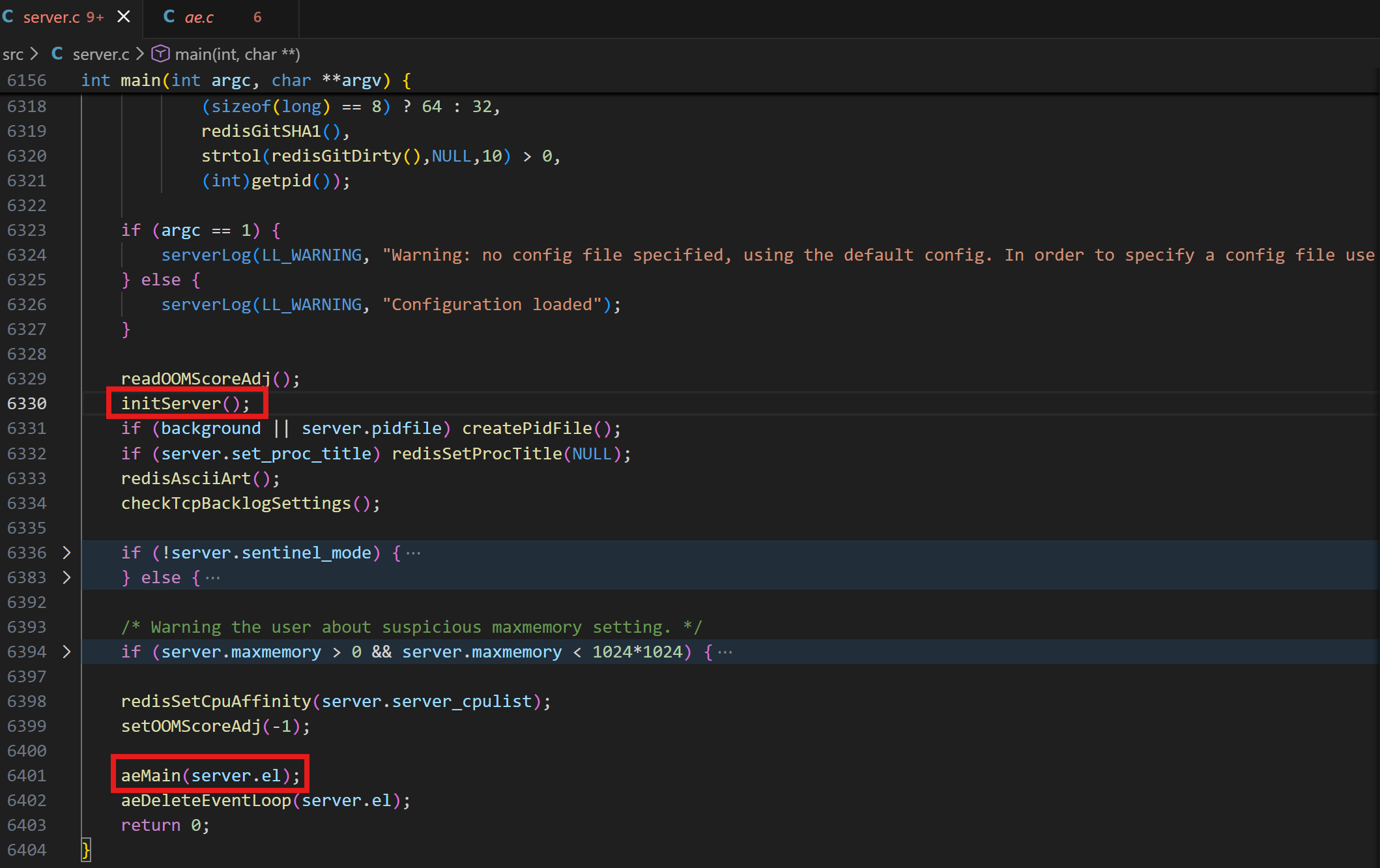
源码如下:
c
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
eventLoop->stop = 0;
while (!eventLoop->stop) {
aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS|
AE_CALL_BEFORE_SLEEP|
AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP);
}
}上面代码就是一个标准的循环监听的标准写法,可以来继续看一下aeProcessEvents函数中的内容。
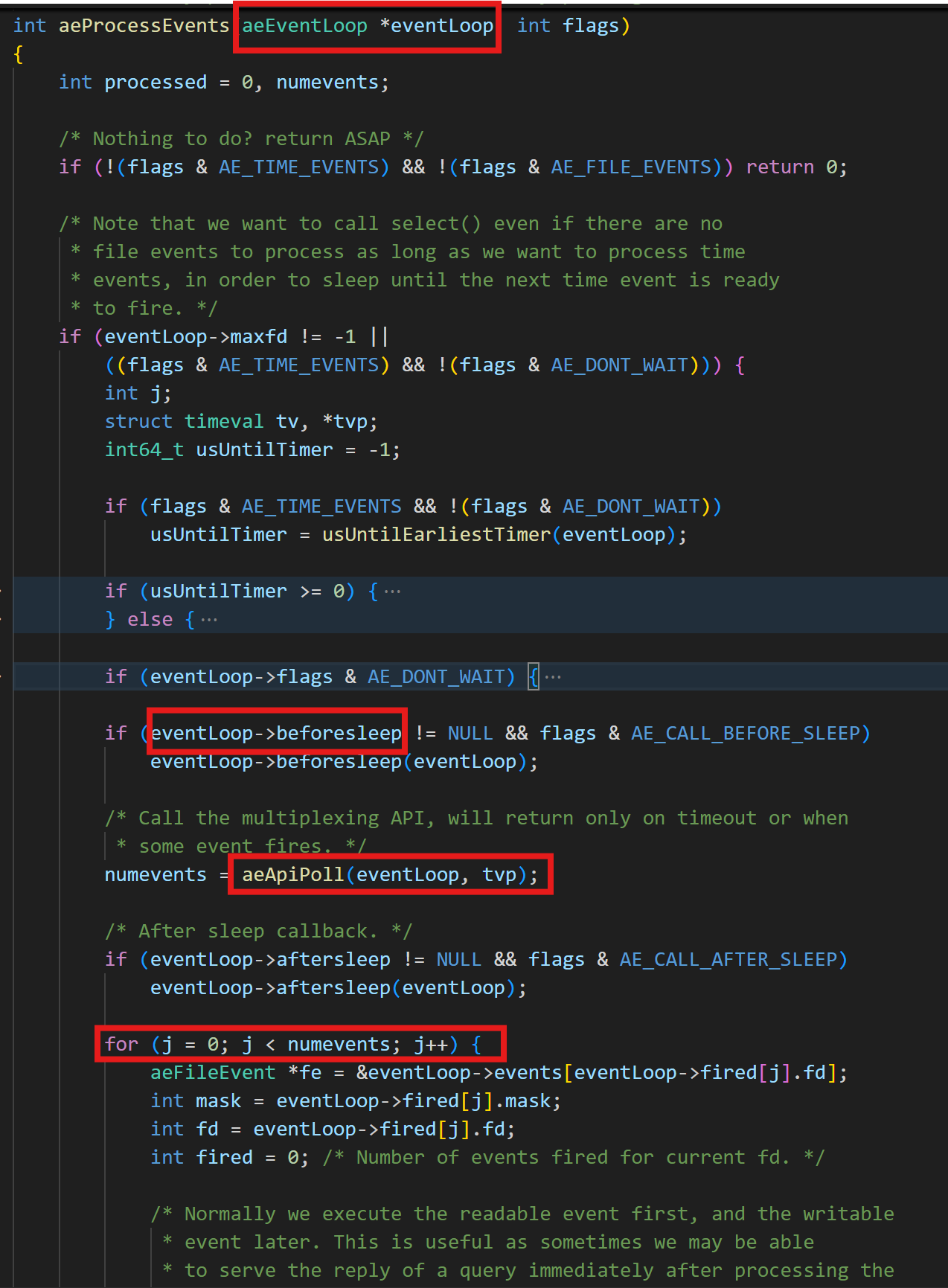
其中 eventloop 是 Redis 管理 epoll 的具体运行时框架;其中aeProcessEventsw围绕eventloop 事件循环 做了一系列工作,aeApiPoll 等待注册的FD就绪,相当于 epoll_wait。在其运行之前会调用beforeSleep以及在其运行之后对调用afterSleep。之后就是使用for循环来遍历就绪的FD并调用对应的FD处理器。
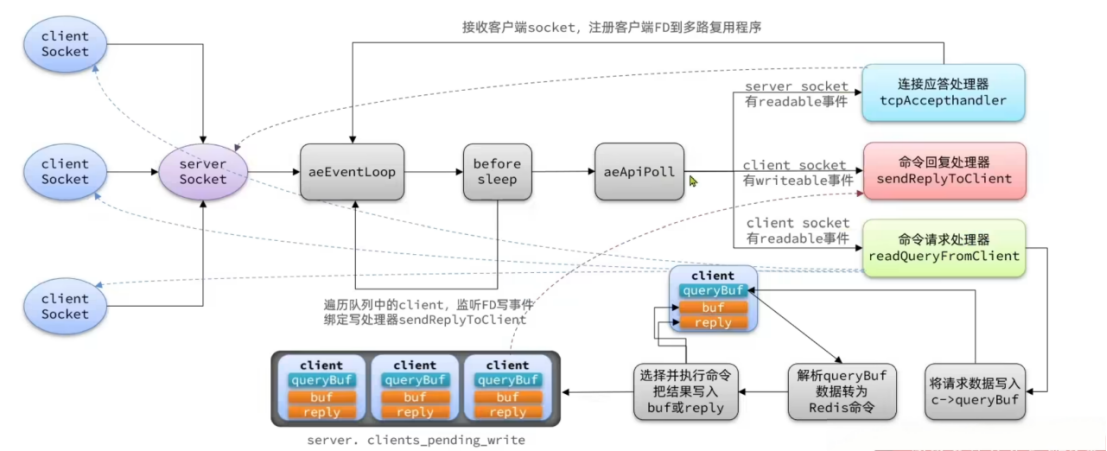
Redis 整体网络模型
整体模型如下:
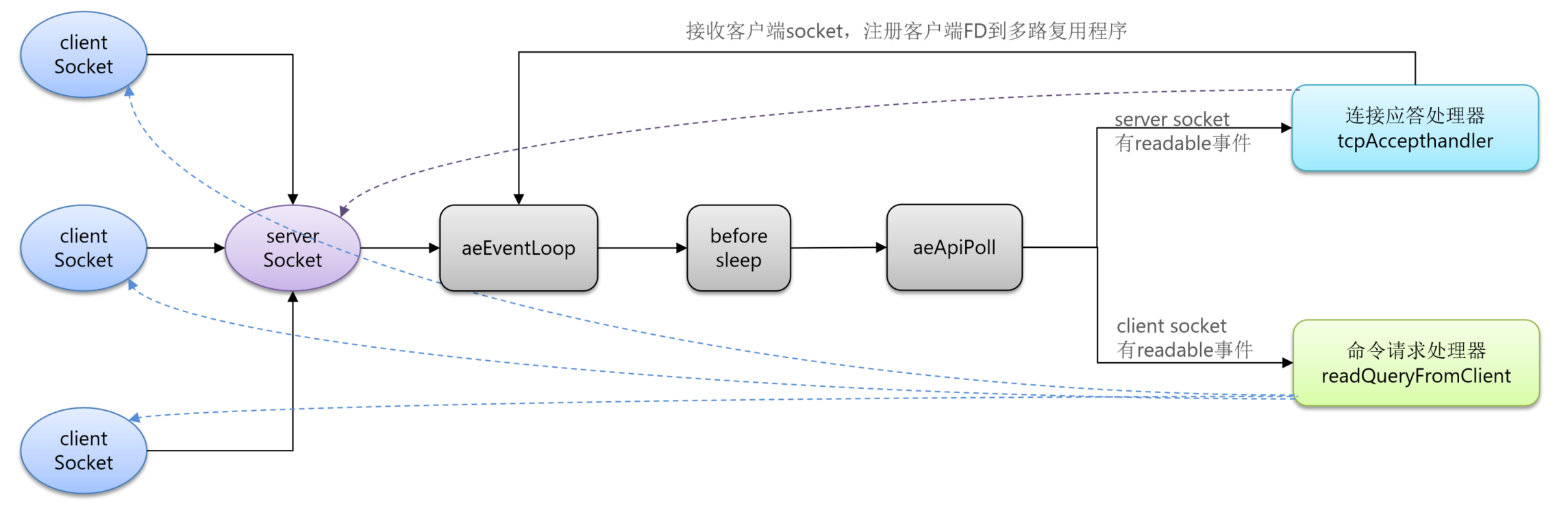
接下来看命令请求处理器的源码:
readQueryFromClient
c
networking.c
void readQueryFromClient(connection *conn) {
client *c = connGetPrivateData(conn);
int nread, readlen;
size_t qblen;
/* Check if we want to read from the client later when exiting from
* the event loop. This is the case if threaded I/O is enabled. */
if (postponeClientRead(c)) return;
/* Update total number of reads on server */
atomicIncr(server.stat_total_reads_processed, 1);
readlen = PROTO_IOBUF_LEN;
/* If this is a multi bulk request, and we are processing a bulk reply
* that is large enough, try to maximize the probability that the query
* buffer contains exactly the SDS string representing the object, even
* at the risk of requiring more read(2) calls. This way the function
* processMultiBulkBuffer() can avoid copying buffers to create the
* Redis Object representing the argument. */
if (c->reqtype == PROTO_REQ_MULTIBULK && c->multibulklen && c->bulklen != -1
&& c->bulklen >= PROTO_MBULK_BIG_ARG)
{
ssize_t remaining = (size_t)(c->bulklen+2)-sdslen(c->querybuf);
/* Note that the 'remaining' variable may be zero in some edge case,
* for example once we resume a blocked client after CLIENT PAUSE. */
if (remaining > 0 && remaining < readlen) readlen = remaining;
}
qblen = sdslen(c->querybuf);
if (c->querybuf_peak < qblen) c->querybuf_peak = qblen;
c->querybuf = sdsMakeRoomFor(c->querybuf, readlen);
nread = connRead(c->conn, c->querybuf+qblen, readlen);
if (nread == -1) {
if (connGetState(conn) == CONN_STATE_CONNECTED) {
return;
} else {
serverLog(LL_VERBOSE, "Reading from client: %s",connGetLastError(c->conn));
freeClientAsync(c);
return;
}
} else if (nread == 0) {
serverLog(LL_VERBOSE, "Client closed connection");
freeClientAsync(c);
return;
} else if (c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) {
/* Append the query buffer to the pending (not applied) buffer
* of the master. We'll use this buffer later in order to have a
* copy of the string applied by the last command executed. */
c->pending_querybuf = sdscatlen(c->pending_querybuf,
c->querybuf+qblen,nread);
}
sdsIncrLen(c->querybuf,nread);
c->lastinteraction = server.unixtime;
if (c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) c->read_reploff += nread;
atomicIncr(server.stat_net_input_bytes, nread);
if (sdslen(c->querybuf) > server.client_max_querybuf_len) {
sds ci = catClientInfoString(sdsempty(),c), bytes = sdsempty();
bytes = sdscatrepr(bytes,c->querybuf,64);
serverLog(LL_WARNING,"Closing client that reached max query buffer length: %s (qbuf initial bytes: %s)", ci, bytes);
sdsfree(ci);
sdsfree(bytes);
freeClientAsync(c);
return;
}
/* There is more data in the client input buffer, continue parsing it
* in case to check if there is a full command to execute. */
processInputBuffer(c);
}从客户端读取数据,并将数据放入到缓冲区之后做解析,解析完成后的字符串转化为Redis命令存入到 Client *c的argv中,之后处理Client *c的argv中存储的命令。
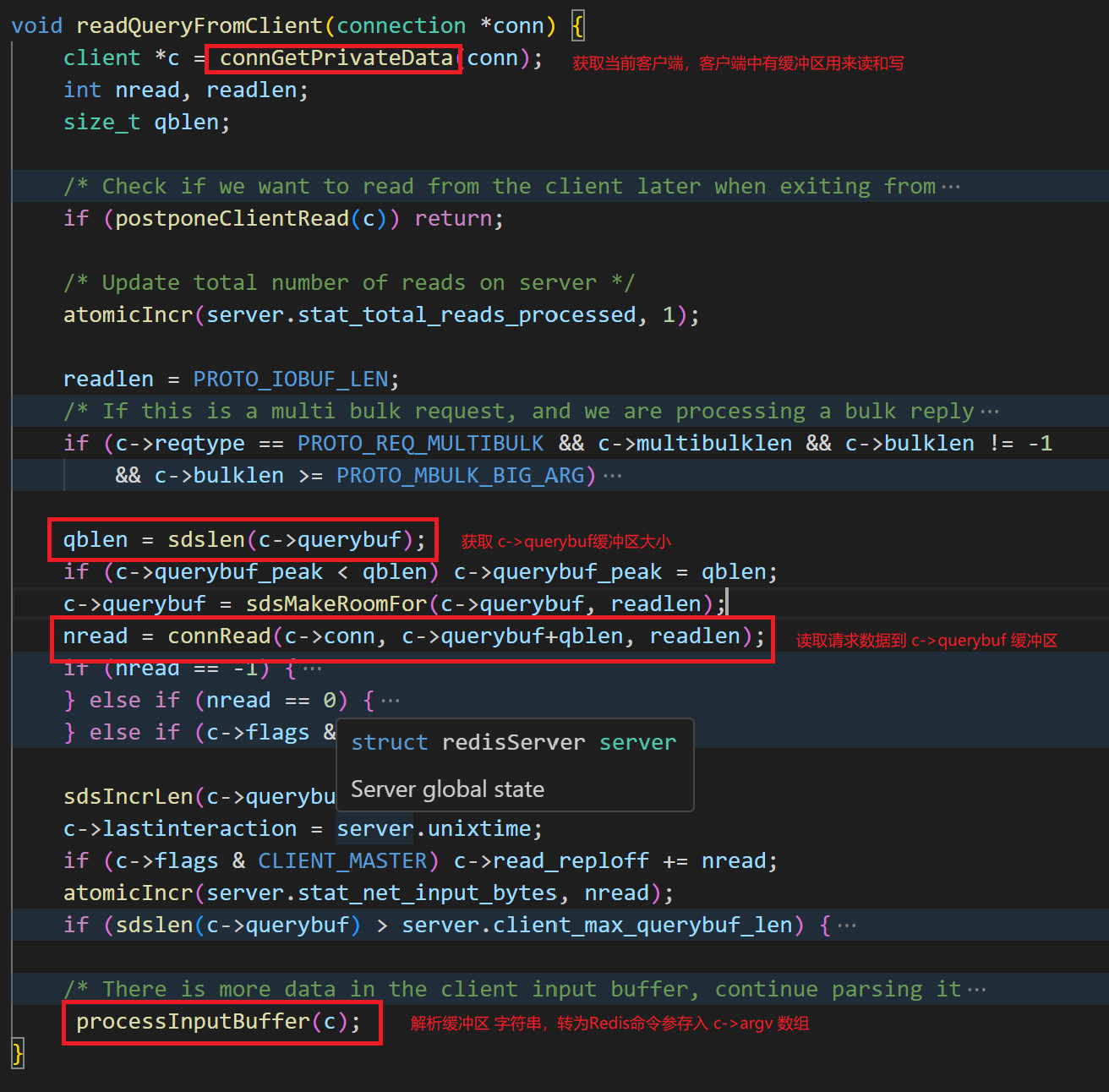
下面是ProcessInputBuffer的源码:
c
/* This function is called every time, in the client structure 'c', there is
* more query buffer to process, because we read more data from the socket
* or because a client was blocked and later reactivated, so there could be
* pending query buffer, already representing a full command, to process. */
void processInputBuffer(client *c) {
/* Keep processing while there is something in the input buffer */
while(c->qb_pos < sdslen(c->querybuf)) {
/* Immediately abort if the client is in the middle of something. */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_BLOCKED) break;
/* Don't process more buffers from clients that have already pending
* commands to execute in c->argv. */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_PENDING_COMMAND) break;
/* Don't process input from the master while there is a busy script
* condition on the slave. We want just to accumulate the replication
* stream (instead of replying -BUSY like we do with other clients) and
* later resume the processing. */
if (server.lua_timedout && c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) break;
/* CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY closes the connection once the reply is
* written to the client. Make sure to not let the reply grow after
* this flag has been set (i.e. don't process more commands).
*
* The same applies for clients we want to terminate ASAP. */
if (c->flags & (CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY|CLIENT_CLOSE_ASAP)) break;
/* Determine request type when unknown. */
if (!c->reqtype) {
if (c->querybuf[c->qb_pos] == '*') {
c->reqtype = PROTO_REQ_MULTIBULK;
} else {
c->reqtype = PROTO_REQ_INLINE;
}
}
if (c->reqtype == PROTO_REQ_INLINE) {
if (processInlineBuffer(c) != C_OK) break;
/* If the Gopher mode and we got zero or one argument, process
* the request in Gopher mode. To avoid data race, Redis won't
* support Gopher if enable io threads to read queries. */
if (server.gopher_enabled && !server.io_threads_do_reads &&
((c->argc == 1 && ((char*)(c->argv[0]->ptr))[0] == '/') ||
c->argc == 0))
{
processGopherRequest(c);
resetClient(c);
c->flags |= CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY;
break;
}
} else if (c->reqtype == PROTO_REQ_MULTIBULK) {
if (processMultibulkBuffer(c) != C_OK) break;
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown request type");
}
/* Multibulk processing could see a <= 0 length. */
if (c->argc == 0) {
resetClient(c);
} else {
/* If we are in the context of an I/O thread, we can't really
* execute the command here. All we can do is to flag the client
* as one that needs to process the command. */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_PENDING_READ) {
c->flags |= CLIENT_PENDING_COMMAND;
break;
}
/* We are finally ready to execute the command. */
if (processCommandAndResetClient(c) == C_ERR) {
/* If the client is no longer valid, we avoid exiting this
* loop and trimming the client buffer later. So we return
* ASAP in that case. */
return;
}
}
}
/* Trim to pos */
if (c->qb_pos) {
sdsrange(c->querybuf,c->qb_pos,-1);
c->qb_pos = 0;
}
}当前函数的作用就是做一些判断,并且处理命令并重置客户端。
下面就是processCommandAndResetClient函数:其中最主要的是
processCommand函数,用来处理c -> argv 中的命令。
c
networking.c
/* This function calls processCommand(), but also performs a few sub tasks
* for the client that are useful in that context:
*
* 1. It sets the current client to the client 'c'.
* 2. calls commandProcessed() if the command was handled.
*
* The function returns C_ERR in case the client was freed as a side effect
* of processing the command, otherwise C_OK is returned. */
int processCommandAndResetClient(client *c) {
int deadclient = 0;
client *old_client = server.current_client;
server.current_client = c;
if (processCommand(c) == C_OK) {
commandProcessed(c);
}
if (server.current_client == NULL) deadclient = 1;
/*
* Restore the old client, this is needed because when a script
* times out, we will get into this code from processEventsWhileBlocked.
* Which will cause to set the server.current_client. If not restored
* we will return 1 to our caller which will falsely indicate the client
* is dead and will stop reading from its buffer.
*/
server.current_client = old_client;
/* performEvictions may flush slave output buffers. This may
* result in a slave, that may be the active client, to be
* freed. */
return deadclient ? C_ERR : C_OK;
}接下来是processCommand函数的源码:
主要是处理c->argv中的命令。
c
networking.c
/* If this function gets called we already read a whole
* command, arguments are in the client argv/argc fields.
* processCommand() execute the command or prepare the
* server for a bulk read from the client.
*
* If C_OK is returned the client is still alive and valid and
* other operations can be performed by the caller. Otherwise
* if C_ERR is returned the client was destroyed (i.e. after QUIT). */
int processCommand(client *c) {
if (!server.lua_timedout) {
/* Both EXEC and EVAL call call() directly so there should be
* no way in_exec or in_eval or propagate_in_transaction is 1.
* That is unless lua_timedout, in which case client may run
* some commands. */
serverAssert(!server.propagate_in_transaction);
serverAssert(!server.in_exec);
serverAssert(!server.in_eval);
}
moduleCallCommandFilters(c);
/* The QUIT command is handled separately. Normal command procs will
* go through checking for replication and QUIT will cause trouble
* when FORCE_REPLICATION is enabled and would be implemented in
* a regular command proc. */
if (!strcasecmp(c->argv[0]->ptr,"quit")) {
addReply(c,shared.ok);
c->flags |= CLIENT_CLOSE_AFTER_REPLY;
return C_ERR;
}
/* Now lookup the command and check ASAP about trivial error conditions
* such as wrong arity, bad command name and so forth. */
c->cmd = c->lastcmd = lookupCommand(c->argv[0]->ptr);
if (!c->cmd) {
sds args = sdsempty();
int i;
for (i=1; i < c->argc && sdslen(args) < 128; i++)
args = sdscatprintf(args, "`%.*s`, ", 128-(int)sdslen(args), (char*)c->argv[i]->ptr);
rejectCommandFormat(c,"unknown command `%s`, with args beginning with: %s",
(char*)c->argv[0]->ptr, args);
sdsfree(args);
return C_OK;
} else if ((c->cmd->arity > 0 && c->cmd->arity != c->argc) ||
(c->argc < -c->cmd->arity)) {
rejectCommandFormat(c,"wrong number of arguments for '%s' command",
c->cmd->name);
return C_OK;
}
int is_read_command = (c->cmd->flags & CMD_READONLY) ||
(c->cmd->proc == execCommand && (c->mstate.cmd_flags & CMD_READONLY));
int is_write_command = (c->cmd->flags & CMD_WRITE) ||
(c->cmd->proc == execCommand && (c->mstate.cmd_flags & CMD_WRITE));
int is_denyoom_command = (c->cmd->flags & CMD_DENYOOM) ||
(c->cmd->proc == execCommand && (c->mstate.cmd_flags & CMD_DENYOOM));
int is_denystale_command = !(c->cmd->flags & CMD_STALE) ||
(c->cmd->proc == execCommand && (c->mstate.cmd_inv_flags & CMD_STALE));
int is_denyloading_command = !(c->cmd->flags & CMD_LOADING) ||
(c->cmd->proc == execCommand && (c->mstate.cmd_inv_flags & CMD_LOADING));
int is_may_replicate_command = (c->cmd->flags & (CMD_WRITE | CMD_MAY_REPLICATE)) ||
(c->cmd->proc == execCommand && (c->mstate.cmd_flags & (CMD_WRITE | CMD_MAY_REPLICATE)));
if (authRequired(c)) {
/* AUTH and HELLO and no auth commands are valid even in
* non-authenticated state. */
if (!(c->cmd->flags & CMD_NO_AUTH)) {
rejectCommand(c,shared.noautherr);
return C_OK;
}
}
/* Check if the user can run this command according to the current
* ACLs. */
int acl_errpos;
int acl_retval = ACLCheckAllPerm(c,&acl_errpos);
if (acl_retval != ACL_OK) {
addACLLogEntry(c,acl_retval,acl_errpos,NULL);
switch (acl_retval) {
case ACL_DENIED_CMD:
rejectCommandFormat(c,
"-NOPERM this user has no permissions to run "
"the '%s' command or its subcommand", c->cmd->name);
break;
case ACL_DENIED_KEY:
rejectCommandFormat(c,
"-NOPERM this user has no permissions to access "
"one of the keys used as arguments");
break;
case ACL_DENIED_CHANNEL:
rejectCommandFormat(c,
"-NOPERM this user has no permissions to access "
"one of the channels used as arguments");
break;
default:
rejectCommandFormat(c, "no permission");
break;
}
return C_OK;
}
/* If cluster is enabled perform the cluster redirection here.
* However we don't perform the redirection if:
* 1) The sender of this command is our master.
* 2) The command has no key arguments. */
if (server.cluster_enabled &&
!(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) &&
!(c->flags & CLIENT_LUA &&
server.lua_caller->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) &&
!(!cmdHasMovableKeys(c->cmd) && c->cmd->firstkey == 0 &&
c->cmd->proc != execCommand))
{
int hashslot;
int error_code;
clusterNode *n = getNodeByQuery(c,c->cmd,c->argv,c->argc,
&hashslot,&error_code);
if (n == NULL || n != server.cluster->myself) {
if (c->cmd->proc == execCommand) {
discardTransaction(c);
} else {
flagTransaction(c);
}
clusterRedirectClient(c,n,hashslot,error_code);
c->cmd->rejected_calls++;
return C_OK;
}
}
/* Handle the maxmemory directive.
*
* Note that we do not want to reclaim memory if we are here re-entering
* the event loop since there is a busy Lua script running in timeout
* condition, to avoid mixing the propagation of scripts with the
* propagation of DELs due to eviction. */
if (server.maxmemory && !server.lua_timedout) {
int out_of_memory = (performEvictions() == EVICT_FAIL);
/* performEvictions may flush slave output buffers. This may result
* in a slave, that may be the active client, to be freed. */
if (server.current_client == NULL) return C_ERR;
int reject_cmd_on_oom = is_denyoom_command;
/* If client is in MULTI/EXEC context, queuing may consume an unlimited
* amount of memory, so we want to stop that.
* However, we never want to reject DISCARD, or even EXEC (unless it
* contains denied commands, in which case is_denyoom_command is already
* set. */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_MULTI &&
c->cmd->proc != execCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != discardCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != resetCommand) {
reject_cmd_on_oom = 1;
}
if (out_of_memory && reject_cmd_on_oom) {
rejectCommand(c, shared.oomerr);
return C_OK;
}
/* Save out_of_memory result at script start, otherwise if we check OOM
* until first write within script, memory used by lua stack and
* arguments might interfere. */
if (c->cmd->proc == evalCommand || c->cmd->proc == evalShaCommand) {
server.lua_oom = out_of_memory;
}
}
/* Make sure to use a reasonable amount of memory for client side
* caching metadata. */
if (server.tracking_clients) trackingLimitUsedSlots();
/* Don't accept write commands if there are problems persisting on disk
* and if this is a master instance. */
int deny_write_type = writeCommandsDeniedByDiskError();
if (deny_write_type != DISK_ERROR_TYPE_NONE &&
server.masterhost == NULL &&
(is_write_command ||c->cmd->proc == pingCommand))
{
if (deny_write_type == DISK_ERROR_TYPE_RDB)
rejectCommand(c, shared.bgsaveerr);
else
rejectCommandFormat(c,
"-MISCONF Errors writing to the AOF file: %s",
strerror(server.aof_last_write_errno));
return C_OK;
}
/* Don't accept write commands if there are not enough good slaves and
* user configured the min-slaves-to-write option. */
if (server.masterhost == NULL &&
server.repl_min_slaves_to_write &&
server.repl_min_slaves_max_lag &&
is_write_command &&
server.repl_good_slaves_count < server.repl_min_slaves_to_write)
{
rejectCommand(c, shared.noreplicaserr);
return C_OK;
}
/* Don't accept write commands if this is a read only slave. But
* accept write commands if this is our master. */
if (server.masterhost && server.repl_slave_ro &&
!(c->flags & CLIENT_MASTER) &&
is_write_command)
{
rejectCommand(c, shared.roslaveerr);
return C_OK;
}
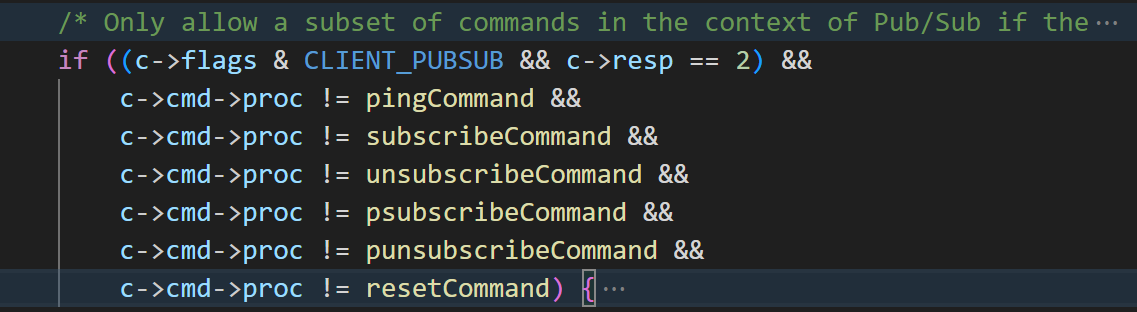
/* Only allow a subset of commands in the context of Pub/Sub if the
* connection is in RESP2 mode. With RESP3 there are no limits. */
if ((c->flags & CLIENT_PUBSUB && c->resp == 2) &&
c->cmd->proc != pingCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != subscribeCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != unsubscribeCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != psubscribeCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != punsubscribeCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != resetCommand) {
rejectCommandFormat(c,
"Can't execute '%s': only (P)SUBSCRIBE / "
"(P)UNSUBSCRIBE / PING / QUIT / RESET are allowed in this context",
c->cmd->name);
return C_OK;
}
/* Only allow commands with flag "t", such as INFO, SLAVEOF and so on,
* when slave-serve-stale-data is no and we are a slave with a broken
* link with master. */
if (server.masterhost && server.repl_state != REPL_STATE_CONNECTED &&
server.repl_serve_stale_data == 0 &&
is_denystale_command)
{
rejectCommand(c, shared.masterdownerr);
return C_OK;
}
/* Loading DB? Return an error if the command has not the
* CMD_LOADING flag. */
if (server.loading && is_denyloading_command) {
rejectCommand(c, shared.loadingerr);
return C_OK;
}
/* Lua script too slow? Only allow a limited number of commands.
* Note that we need to allow the transactions commands, otherwise clients
* sending a transaction with pipelining without error checking, may have
* the MULTI plus a few initial commands refused, then the timeout
* condition resolves, and the bottom-half of the transaction gets
* executed, see Github PR #7022. */
if (server.lua_timedout &&
c->cmd->proc != authCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != helloCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != replconfCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != multiCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != discardCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != watchCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != unwatchCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != resetCommand &&
!(c->cmd->proc == shutdownCommand &&
c->argc == 2 &&
tolower(((char*)c->argv[1]->ptr)[0]) == 'n') &&
!(c->cmd->proc == scriptCommand &&
c->argc == 2 &&
tolower(((char*)c->argv[1]->ptr)[0]) == 'k'))
{
rejectCommand(c, shared.slowscripterr);
return C_OK;
}
/* Prevent a replica from sending commands that access the keyspace.
* The main objective here is to prevent abuse of client pause check
* from which replicas are exempt. */
if ((c->flags & CLIENT_SLAVE) && (is_may_replicate_command || is_write_command || is_read_command)) {
rejectCommandFormat(c, "Replica can't interract with the keyspace");
return C_OK;
}
/* If the server is paused, block the client until
* the pause has ended. Replicas are never paused. */
if (!(c->flags & CLIENT_SLAVE) &&
((server.client_pause_type == CLIENT_PAUSE_ALL) ||
(server.client_pause_type == CLIENT_PAUSE_WRITE && is_may_replicate_command)))
{
c->bpop.timeout = 0;
blockClient(c,BLOCKED_PAUSE);
return C_OK;
}
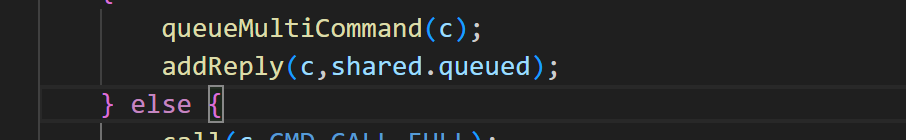
/* Exec the command */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_MULTI &&
c->cmd->proc != execCommand && c->cmd->proc != discardCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != multiCommand && c->cmd->proc != watchCommand &&
c->cmd->proc != resetCommand)
{
queueMultiCommand(c);
addReply(c,shared.queued);
} else {
call(c,CMD_CALL_FULL);
c->woff = server.master_repl_offset;
if (listLength(server.ready_keys))
handleClientsBlockedOnKeys();
}
return C_OK;
}核心代码代码有:
根据命令名称寻找命令对应的command:
之后执行command,得到响应结果。
上文中的proc定义如下:
c
typedef void redisCommandProc(client *c);
typedef int redisGetKeysProc(struct redisCommand *cmd, robj **argv, int argc, getKeysResult *result);
struct redisCommand {
char *name;
redisCommandProc *proc;
int arity;
char *sflags; /* Flags as string representation, one char per flag. */
uint64_t flags; /* The actual flags, obtained from the 'sflags' field. */
/* Use a function to determine keys arguments in a command line.
* Used for Redis Cluster redirect. */
redisGetKeysProc *getkeys_proc;
/* What keys should be loaded in background when calling this command? */
int firstkey; /* The first argument that's a key (0 = no keys) */
int lastkey; /* The last argument that's a key */
int keystep; /* The step between first and last key */
long long microseconds, calls, rejected_calls, failed_calls;
int id; /* Command ID. This is a progressive ID starting from 0 that
is assigned at runtime, and is used in order to check
ACLs. A connection is able to execute a given command if
the user associated to the connection has this command
bit set in the bitmap of allowed commands. */
};最后把执行结果写出, 比如如果ping命令,就会返回pong给Client。
接下来是addReply的源码:
尝试把结果写回到 c-buf 客户端写缓冲区;
c
/* -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Higher level functions to queue data on the client output buffer.
* The following functions are the ones that commands implementations will call.
* -------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/* Add the object 'obj' string representation to the client output buffer. */
void addReply(client *c, robj *obj) {
if (prepareClientToWrite(c) != C_OK) return;
if (sdsEncodedObject(obj)) {
if (_addReplyToBuffer(c,obj->ptr,sdslen(obj->ptr)) != C_OK)
_addReplyProtoToList(c,obj->ptr,sdslen(obj->ptr));
} else if (obj->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INT) {
/* For integer encoded strings we just convert it into a string
* using our optimized function, and attach the resulting string
* to the output buffer. */
char buf[32];
size_t len = ll2string(buf,sizeof(buf),(long)obj->ptr);
if (_addReplyToBuffer(c,buf,len) != C_OK)
_addReplyProtoToList(c,buf,len);
} else {
serverPanic("Wrong obj->encoding in addReply()");
}
}如果 c-buf 写不下,就写到 c->reply,这里的是一个链表; _addReplyProtoToList
之后将客户端添加到server.clients_pending_write这个队列中,等待被写出。
此时在aeEventLoop代码以及全部执行完成,但是我们会发现一个问题,也就是缓冲区未成功写入的数据仍旧在队列中,并未写入。那么这一部分的功能已经不是当前模块的功能了,Redis将其放置在了beforeSleep中。
下面是beforeSleep的源码:
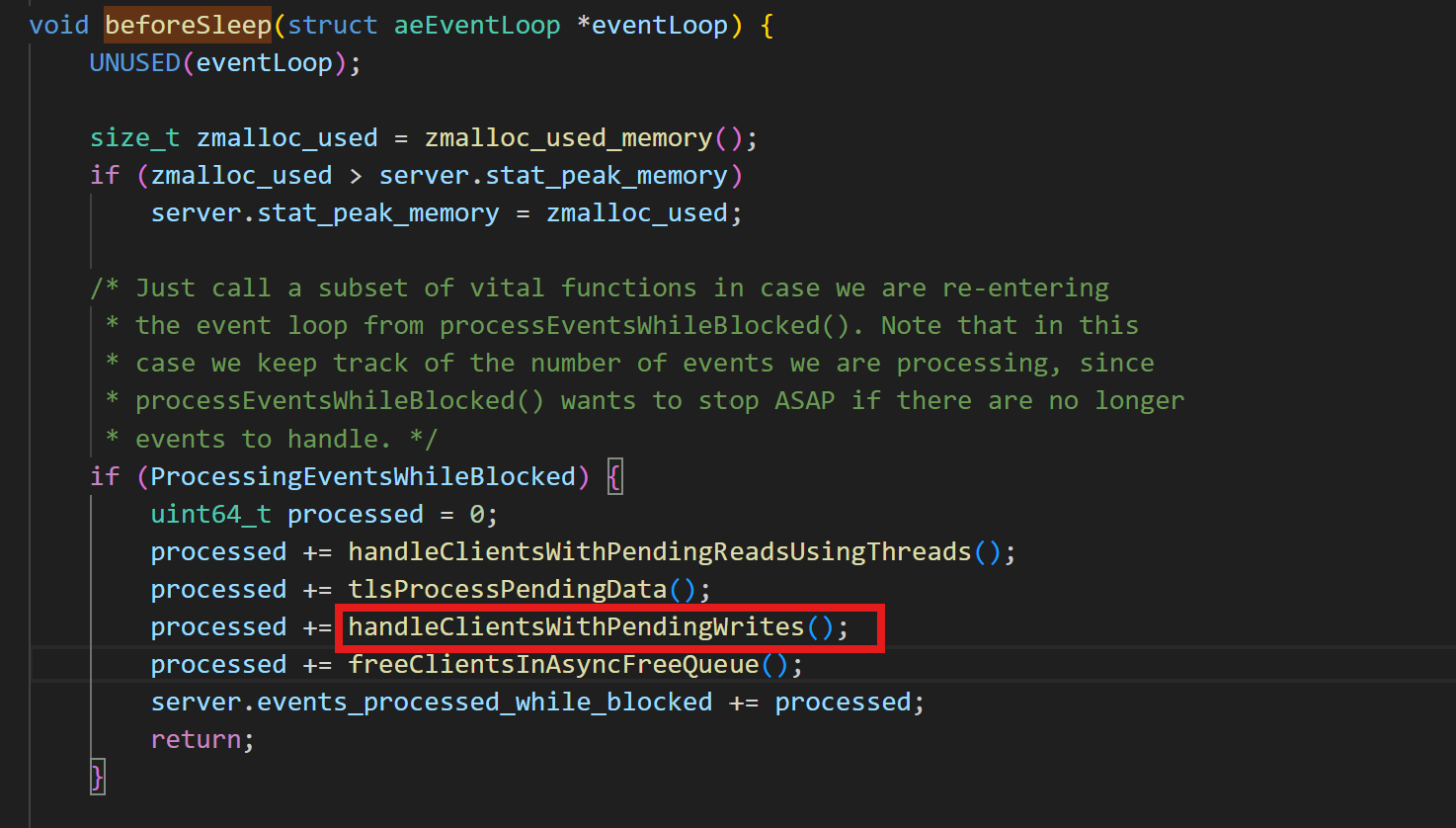
在函数:handleClientsWithPendingWrites()中:
源码如下:也就是使用迭代器取出对应的队列中的数据,并将数据写出。其中内部调用aeApiAddEvent(fd,WRITABLE),监听Socket的FD的读事件
并且绑定写处理器,sendReplyToClient,把响应写到客户端Socket
c
int handleClientsWithPendingWrites(void) {
listIter li;
listNode *ln;
int processed = listLength(server.clients_pending_write);
listRewind(server.clients_pending_write,&li);
while((ln = listNext(&li))) {
client *c = listNodeValue(ln);
c->flags &= ~CLIENT_PENDING_WRITE;
listDelNode(server.clients_pending_write,ln);
/* If a client is protected, don't do anything,
* that may trigger write error or recreate handler. */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_PROTECTED) continue;
/* Don't write to clients that are going to be closed anyway. */
if (c->flags & CLIENT_CLOSE_ASAP) continue;
/* Try to write buffers to the client socket. */
if (writeToClient(c,0) == C_ERR) continue;
/* If after the synchronous writes above we still have data to
* output to the client, we need to install the writable handler. */
if (clientHasPendingReplies(c)) {
int ae_barrier = 0;
/* For the fsync=always policy, we want that a given FD is never
* served for reading and writing in the same event loop iteration,
* so that in the middle of receiving the query, and serving it
* to the client, we'll call beforeSleep() that will do the
* actual fsync of AOF to disk. the write barrier ensures that. */
if (server.aof_state == AOF_ON &&
server.aof_fsync == AOF_FSYNC_ALWAYS)
{
ae_barrier = 1;
}
if (connSetWriteHandlerWithBarrier(c->conn, sendReplyToClient, ae_barrier) == C_ERR) {
freeClientAsync(c);
}
}
}
return processed;
}所以总体的流程如下:
6.0之后多线程改进单线程模型
之前单线程的瓶颈点:
命令处理:
需要空客户端连接中读取Socket,读出对应的字符串并将解析为Redis中的命令。这里是读Socket ,那么就是受到网络I/O的影响。
添加多线程的部分:
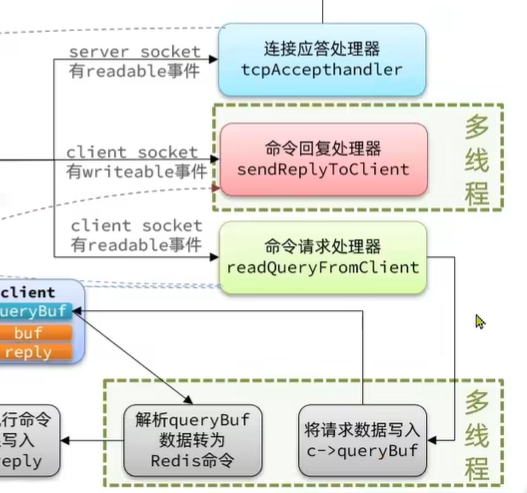
减少因为网络I/O而造成的性能下降,虽然并未改善单条命令的处理时间,但是整体的吞吐量却得到了明显的提升。
通信协议
RESP协议
Redis是一种CS架构的软件。RESP协议为 Redis Serialization Protocol。
1.2版本中引入RESP协议。2.0版本中RESP2为Redis通信标准。6.0版本后,RESP2升级为RESP3,增加了更多的数据类型并且支持了客户端缓存。
RESP中通过首字节的字符来区分不同的数据类型,常用的数据类型包括了5种:
- 单行字符串:"+",后面跟上单行字符串,以CRLF("\r\n")结尾。
- 错误:"-",与单行字符串类似,只是字符串是异常信息。
- 数值:":",后面跟上数字格式的字符串,以CRLF结尾。
- 多行字符串:"",表示二进制安全的字符串,最大支持512MB;记录长度以及具体的字符串,这样就可以了。例如:5\r\nhello\r\n。特殊情况:大小为0表示空字符串,大小-1表示不存在。
- 数组:"*",后面跟上数组元素个数,跟上元素,元素数据类型不限。发请求一般就是一个数组。
模拟Redis客户端
java
import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
static Socket s;
static PrintWriter writer;
static BufferedReader reader;
public static void main(String[] args) {
String host = "";
int port = 6379;
try {
//建立连接
s = new Socket(host, port);
//获取输入流和输出流
writer = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(s.getOutputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//发送请求
sendRequest();
//解析响应
handleResponse();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private static Object handleResponse() {
//五种情况:读取首字节
try {
int prefix = reader.read();
switch (prefix) {
case '+' :
return reader.readLine();
case '-' :
throw new RuntimeException(reader.readLine());
case ':' :
return Long.parseLong(reader.readLine());
case '$' :
int len = Integer.parseInt(reader.readLine());
if (len == -1) {
return null;
}
if (len == 0) {
return "";
}
return reader.readLine();
case '*' :
return readBulkString();
default:
throw new RuntimeException("错误的数据格式!");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private static Object readBulkString() throws IOException {
//获取数组大小
int len = Integer.parseInt(reader.readLine());
if (len <= 0) {
return null;
}
//定义一个集合接受元素
List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>(len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
list.add(handleResponse());
}
//遍历,依次读取
}
private static void sendRequest(String ... args) {
writer.println("*" + args.length);
for (String arg : args) {
writer.println("$"+ arg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8).length);
writer.println(arg);
}
writer.flush();
}
}